Students are subjected to different types of assessments to measure their understanding of a topic. In this study, a weight value is assigned to exam questions according to their difficulty and complexity levels by considering fuzzy rules. After ensuring that these weight values affect the scores students receive, the degree of learning each concept is found. The method used in the study is explained below.
3.1. Preparing Data
A question database is created that shows the weight ratios of the concepts that each question is trying to measure in the question in the range [0, 1].
Table 1 shows a screenshot of the database consisting of programming questions and the weights of the concepts included in the questions.
The fact that the scoring of open-ended questions is based on the opinion of the teacher, or the rater is one of the important factors affecting the quality of written exams. These factors also affect the validity and reliability of the written exam [
28]. In this study, to take precautions against all these factors, the concepts in the programming questions were scored according to their weight ratios, by taking the opinions of two more experts in addition to the researcher, and the final weight levels were determined by taking the average of the scores.
If we assume that there are
m questions in an exam and each question consists of
n concepts, the elements of the
K matrix give the ratio of the concepts contained in the questions according to the prepared database as the following:
where
Qi denotes the
ith question where
and
kij denotes the weight of the concept in the question where
In this study, firstly the exam questions selected by the instructor are scored. It is expressed by the
S matrix:
The product of the ST and K matrices gives the maximum score that can be obtained for each concept if the questions are answered correctly. lj denotes the maximum score that can be obtained if the relevant concept section in the questions is answered correctly.
According to the weights of the concepts included in the exam questions, the full score to be received if the relevant section of each concept is answered correctly is calculated using the following equation:
The student’s answer to each question is scored by the instructor according to the accuracy rate of the sections related to the concepts included in the question. This scoring is done by considering the full scores calculated in the K’ matrix. It is expressed by the
R matrix:
The scores obtained by the student from the sections related to the concepts in each exam question are multiplied by the weight vector. The weight vector is obtained by applying the rules of fuzzy logic to the difficulty and complexity values of each question. The following explains how to obtain the difficulty and complexity attributes that describes with a crisp value for each question.
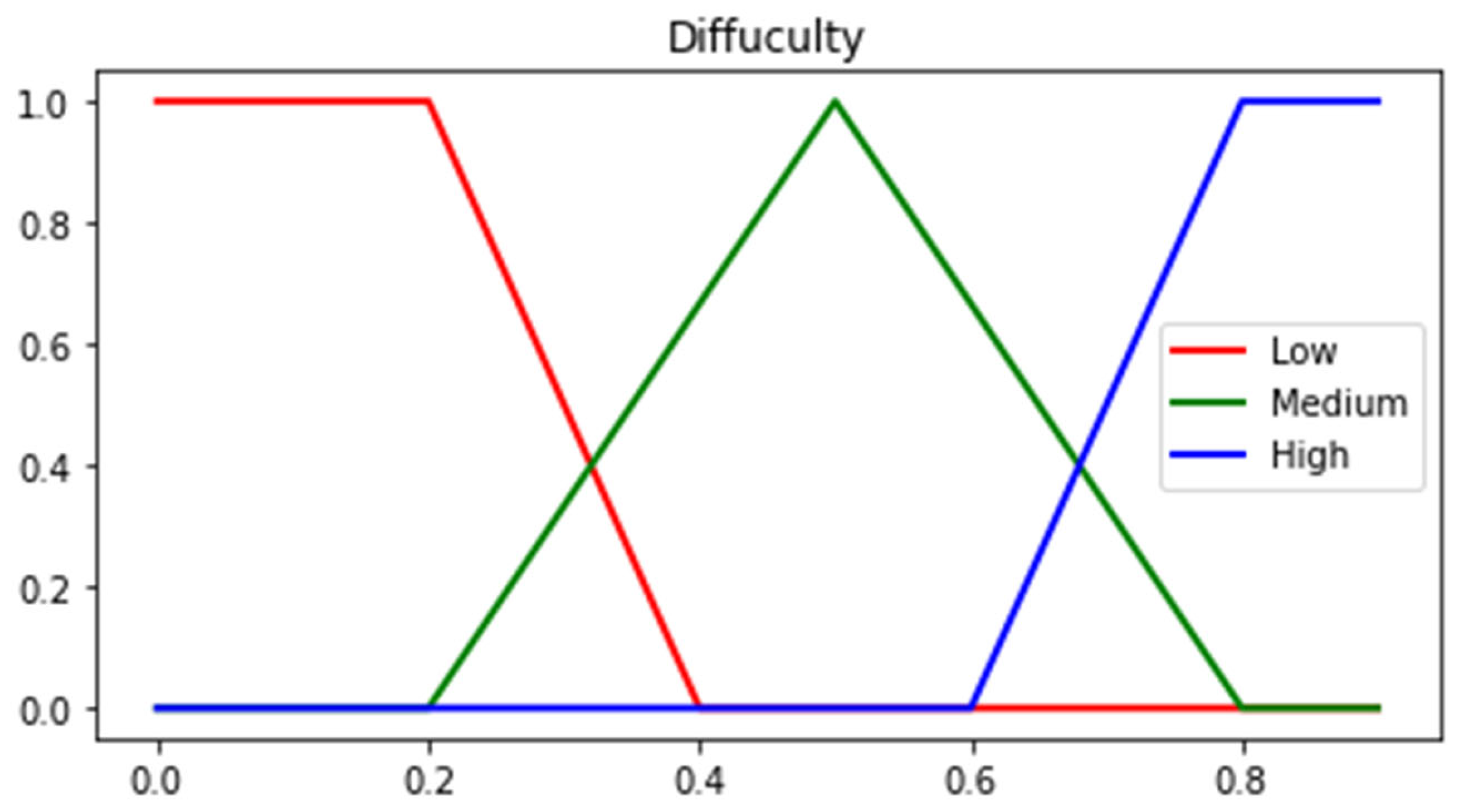
3.2. Difficulty Attribute
It is known that the rate of correct answers to a question indicates the difficulty level of the question. Item difficulty index is calculated as a percentage of the total number of correct responses to items and is calculated using the formula
P = R/T. Here,
P is the item difficulty index,
R is the number of correct answers, and
T is the total number of answers, both correct and incorrect. When a question is considered difficult, its difficulty index value is less than 30% and it is considered easy when the index value is greater than 80%. Based on this, the difficulty level of the question was tried to be determined according to the following equation [
29]:
where
Pi is the item difficulty index;
Ri is the number of correct answers; and
Ti is the total number of answers, both correct and incorrect.
In addition, in this study, the level of difficulty of the questions according to the Bloom taxonomy was considered in determining the difficulty level. In 1956, University of Chicago professor Benjamin Bloom classified the development of mental skills from low-level thinking skills to higher-level thinking skills to explain how the learning process develops. Bloom taxonomy shows that learning occurs in stages. Conceptual knowledge must be acquired to put it into practice. Learning to program is a difficult process because it requires cognitive actions such as analysis and synthesis. While writing the codes of a program, basic concepts are brought together to ensure the synthesis step. For the application and analysis steps, dividing the program codes into sections instead of printing them is deemed appropriate for the learners to understand the subject better [
30,
31]. The
Table 2 below summarizes how the stages of learning programming are classified in the context of Bloom taxonomy.
In this study, a database consisting of programming questions was created and the learning stage of each question according to the Bloom taxonomy was determined by taking the opinions of the researcher and experts. The reason we carry out this is to assign a difficulty level according to the learning stage in which the questions are located. These difficulty levels are shown in
Table 3.
The final value of the difficulty level multiplied by the difficulty coefficient values given in
Table 3. Increasing or decreasing the difficulty levels of the questions according to their level of the Bloom taxonomy is formulated as follows:
where
Bi is the Bloom’s taxonomy difficulty coefficient.
Pi is the item difficulty index.
di is the overall difficulty index.
The difficulty vector indicating the question difficulty level of each question is expressed as
D as the following:
3.5. Fuzzy Rules
While writing the fuzzy logic rules, all the fuzzy set connections that can be between the input data and the outputs are considered (
Table 6). The term inclusiveness level is used in this study to mean including all the features and subtleties. It refers to the level of importance achieved by considering all aspects of a question. For the fuzzy logic rules determined during the introduction process, the question difficulty was assigned a value of 0.6 based on expert opinion, and the complexity was assigned a value of 0.4. The difficulty value was determined based on other students’ exam scores and the ratio determined according to Bloom taxonomy. Therefore, the difficulty value was assigned a relatively higher value than the complexity value.
Table 6 includes all the rules that can be written in the logical IF–THEN type that connect the inputs to the output variables.
Fuzzy rules for calculation in case the inclusiveness level of Qi is very low are explained as the following:
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is very low.
The formula that calculates the inclusiveness level of Q
i as very low is shown below:
Fuzzy rules for calculation in case the inclusiveness level of Qi is low are explained as the following:
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is low.
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is low.
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is low.
The formula that calculates the inclusiveness level of Q
i as low is shown below:
Fuzzy rules for calculation in case the inclusiveness level of Qi is sufficient are explained as the following:
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is sufficient.
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is sufficient.
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is sufficient.
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is sufficient.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is sufficient.
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is sufficient.
The formula that calculates the inclusiveness level of Q
i as sufficient is shown below:
Fuzzy rules for calculation in case the inclusiveness level of Qi is satisfactory are explained as the following:
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is satisfactory.
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is satisfactory.
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is satisfactory.
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is satisfactory.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is satisfactory.
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is satisfactory.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is satisfactory.
The formula that calculates the inclusiveness level of Q
i as satisfactory is shown below:
Fuzzy rules for calculation in case the inclusiveness level of Qi is good are explained as the following:
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is good.
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is good.
IF difficulty is low, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is good.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is low THEN question’s inclusiveness level is good.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is good.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is good.
The formula that calculates the inclusiveness level of Q
i as good is shown below:
Fuzzy rules for calculation in case the inclusiveness level of Qi is very good are explained as the following:
IF difficulty is medium, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is very good.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is medium THEN question’s inclusiveness level is very good.
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is very good.
The formula that calculates the inclusiveness level of Q
i as very good is shown below:
Fuzzy rules for calculation in case the inclusiveness level of Qi is excellent are explained the following:
IF difficulty is high, and complexity is high THEN question’s inclusiveness level is excellent.
The formula that calculates the inclusiveness level of Q
i as excellent is shown below: