Assessment of 12 Ginsenosides and the Antioxidant Activity of Red Ginseng Sprout Extracts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Sample Preparation
2.2. HPLC-PDA Analysis of Ginsenosides
2.3. Determination of the Total Polyphenol and Flavonoid Content
2.4. DPPH Radical Scavenging Activity
2.5. ABTS Radical Scavenging Activity
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
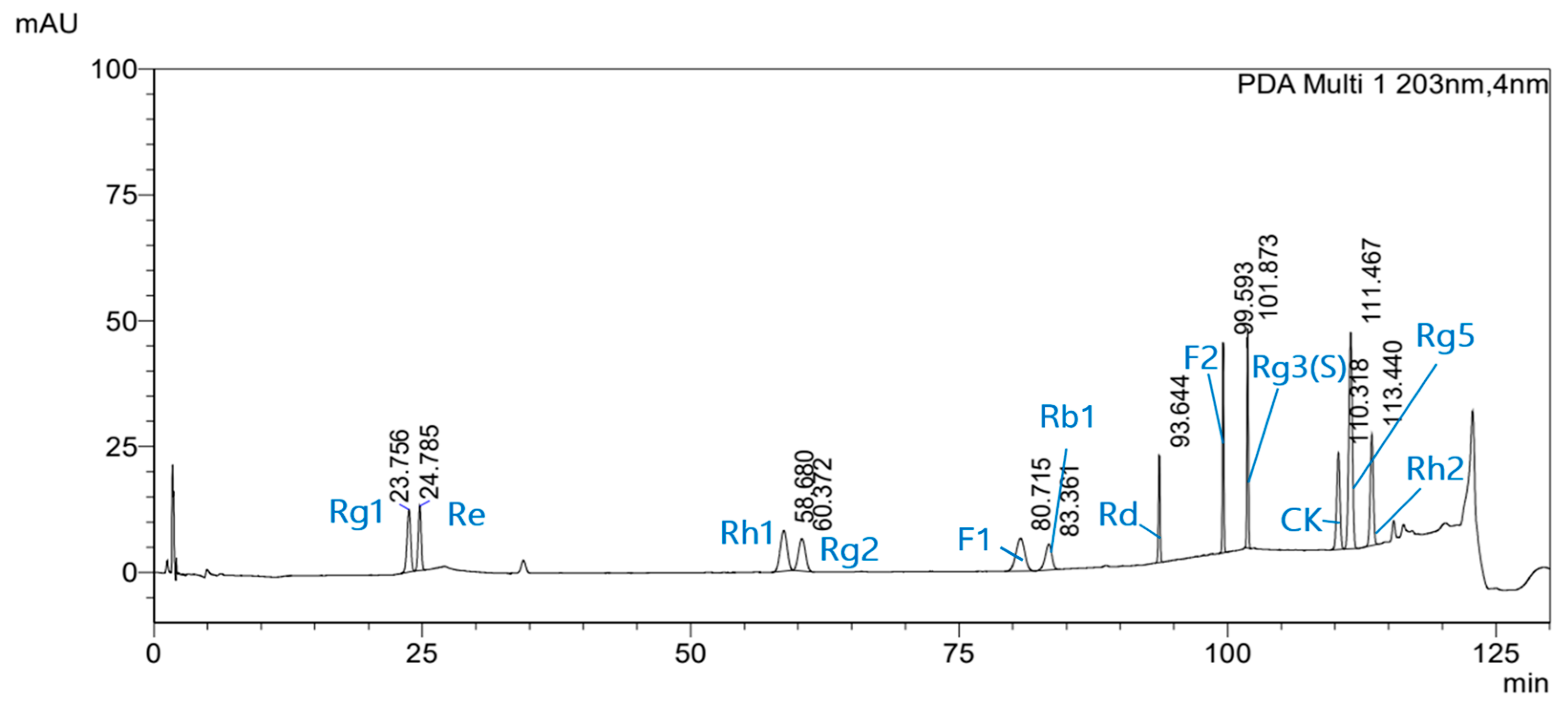
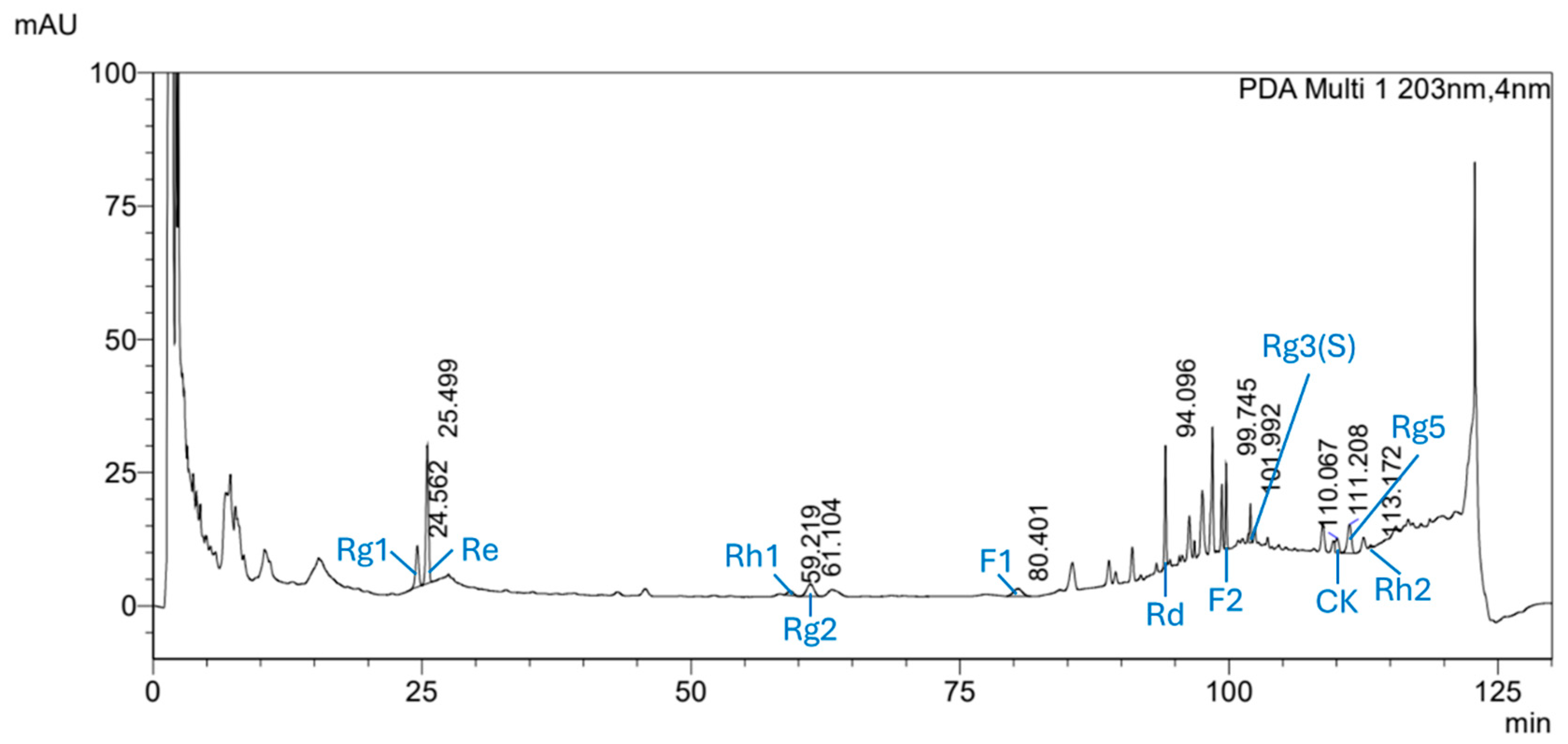
3.1. Qualitative Analysis of Ginsenoside Standards and Mixed Solutions
3.2. Quantitative Analysis of Ginsenosides in RGS Extract
3.3. Total Polyphenol, Flavonoid Content and Antioxidant Activity
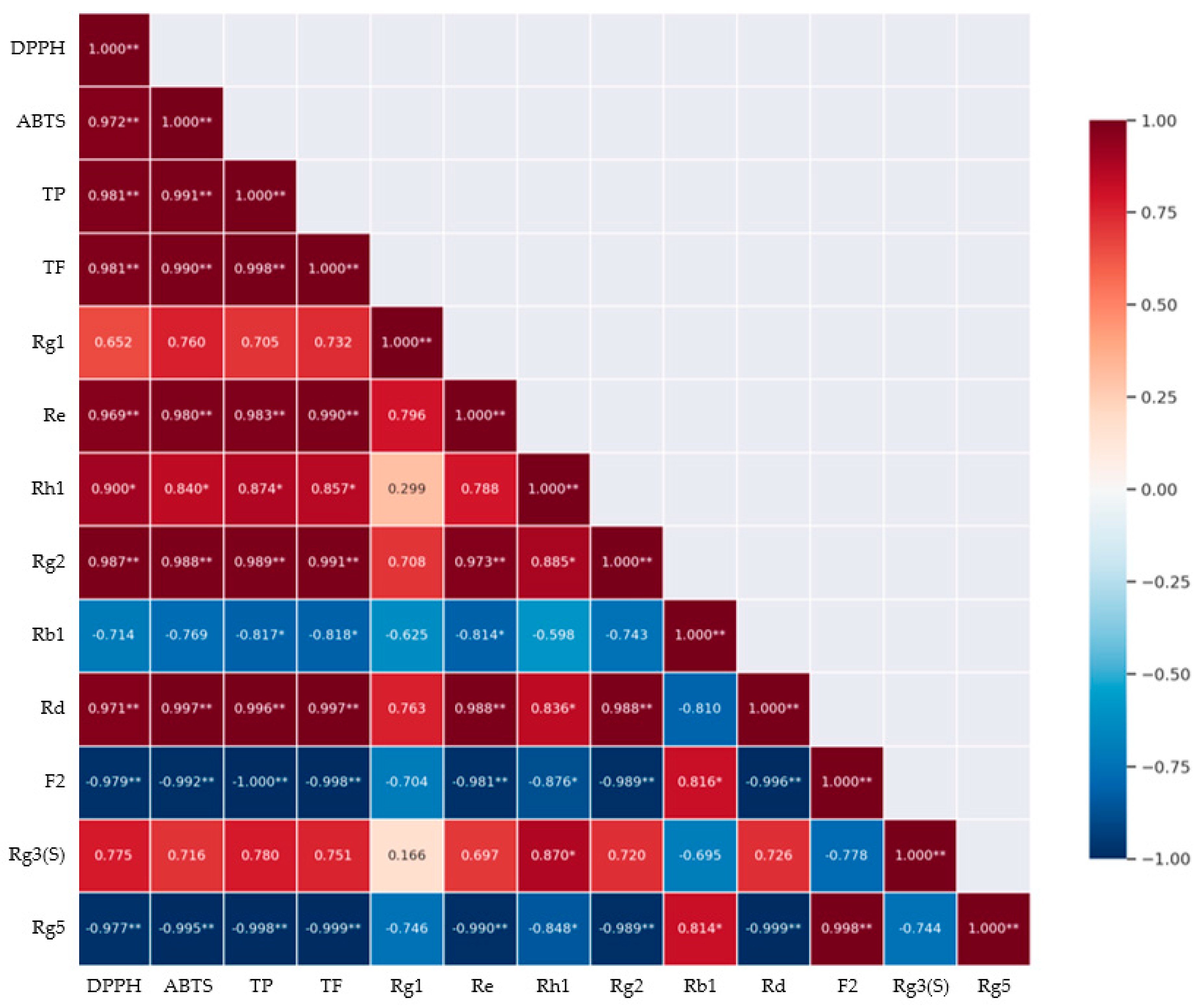
3.4. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.H. Pharmacological and medical applications of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides: A review for use in cardiovascular diseases. J. Ginseng Res. 2018, 42, 264–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, J.; Kim, H.; Park, E.J.; Kim, S.R.; Dusabimana, T.; Jeong, K.; Yun, S.P.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, K.M.; Park, S.W. Fermentation of sprouted ginseng (Panax ginseng) increases flavonoid and phenolic contents to attenuate alcoholic hangover and acute liver injury in mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 49, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baenas, N.; García-Viguera, C.; Moreno, D.A. Elicitation: A tool for enriching the bioactive composition of foods. Molecules 2014, 19, 13541–13563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Luo, J.-G.; Kong, L. Determination of 10 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng of different harvest times based on HPLC fingerprints and principal component analysis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Nguyen, T.K.L.; Oh, M.M. Growth and ginsenosides content of ginseng sprouts according to LED-based light quality changes. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Yan, Y.Z.; Jin, X.; Kim, Y.K.; Uddin, M.R.; Kim, Y.B.; Bae, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, S.W.; Park, S.U. Ginsenoside content in the leaves and roots of Panax ginseng at different ages. Life Sci. 2012, 9, 670–683. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, G.S.; Hyun, D.Y.; Kim, Y.O.; Lee, S.E.; Kwon, H.; Cha, S.W.; Park, C.B.; Kim, Y.B. Investigation of ginsenosides in different parts of Panax ginseng cultured by hydroponics. Korean J. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2010, 28, 216–226. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Gao, X.; Yang, C.; Liang, Z.; Guan, D.; Yuan, T.; Qi, W.; Zhao, D.; Li, X.; Dong, H.; et al. Structural characters and pharmacological activity of protopanaxadiol-type saponins and protopanaxatriol-type saponins from ginseng. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 2024, 9096774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.Z.; Shi, X.J.; Yao, C.L.; Huang, Y.; Hou, J.J.; Han, S.M.; Feng, Z.J.; Wei, W.L.; Wu, W.Y.; Guo, D.A. A novel neutral loss/product ion scan-incorporated integral approach for the untargeted characterization and comparison of the carboxyl-free ginsenosides from Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolius, and Panax notoginseng. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 177, 112813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, X.M.; Huo, Y.; Kang, J.P.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Zhang, H.; Yang, D.U.; Kim, M.; Yang, D.C.; Kang, S.C.; Wang, Y.P. Diversity of ginsenoside profiles produced by various processing technologies. Molecules 2020, 25, 4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, B.K.; Kwon, S.W.; Park, J.H. Chemical diversity of ginseng saponins from Panax ginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 39, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attele, A.S.; Wu, J.A.; Yuan, C.S. Ginseng pharmacology: Multiple constituents and multiple actions. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 1685–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, L.P. Ginsenosides chemistry, biosynthesis, analysis, and potential health effects. In Advances in Food and Nutrition Research; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 55, pp. 1–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.X.; Xiao, P.G. Recent advances on ginseng research in China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1992, 36, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.H. Chemical diversity of Panax ginseng, Panax quinquifolium, and Panax notoginseng. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Ding, L. Investigation of ginsenosides in different parts and ages of Panax ginseng. Food Chem. 2007, 102, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, I.B.; Yu, J.; Suh, S.J.; Jang, I.B.; Kwon, K.B. Growth and ginsenoside content in different parts of ginseng sprouts depending on harvest time. Korean J. Med. Crop Sci. 2018, 26, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, G.; Ahn, N.G.; Bae, B.S.; Han, S.T.; Noh, K.B.; Kim, C.S. New method for simultaneous quantification of 12 ginsenosides in red ginseng powder and extract: In-house method validation. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liu, S.; Zhao, Y. Research progress of HPLC detection and analysis of ginseng rare saponins. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 137, 106960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.Y.; Jen, C.T.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Chen, B.H. A comparative study on analysis of ginsenosides in American ginseng root residue by HPLC-DAD-ESI-MS and UPLC-HRMS-MS/MS. Molecules 2022, 27, 3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Xu, J.; Shi, G.; Xiao, S.; Dai, R.; Wu, S.; Sun, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y. Optimization of flash extraction, separation of ginsenosides, identification by HPLC-FT-ICR-MS and determination of rare ginsenosides in mountain cultivated ginseng. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 44050–44057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sies, H. Oxidative stress: A concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Shim, S.L.; Jang, E.S.; Choi, S.G. Ginsenoside stability and antioxidant activity of Korean red ginseng (Panax ginseng CA meyer) extract as affected by temperature and time. LWT 2024, 200, 116205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.Y.; Cho, D.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, J.H.; Jeong, J.B.; Jeon, S.H.; Lee, J.H.; Ko, E.J.; Cho, K.M.; Lee, J.H. Examining the alterations in metabolite constituents and antioxidant properties in mountain-cultivated ginseng (Panax ginseng CA Meyer) organs during a two-month maturation period. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, B.; Shetty, K. The stimulation of phenolics and antioxidant activity in pea (Pisum sativum) elicited by genetically transformed anise root extract. J. Food Biochem. 2001, 25, 361–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ju, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Phytochemical analysis of Panax species: A review. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Liu, S.; Xing, J.; Pi, Z.; Song, F.; Liu, Z. Trace determination and characterization of ginsenosides in rat plasma through magnetic dispersive solid-phase extraction based on core-shell polydopamine-coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Anal. 2020, 10, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, S.H.; Bae, O.N.; Park, J. Recent methodology in ginseng analysis. J. Ginseng Res. 2012, 36, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Sun, C.; Zheng, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y. Simultaneous determination of nine ginsenosides in functional foods by high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector detection. Food chem. 2010, 123, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.W.; In, G.; Han, S.T.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, K.T.; Cho, B.G.; Han, G.H.; Chang, I.M. Simultaneous determination of 30 ginsenosides in Panax ginseng preparations using ultra performance liquid chromatography. J. Ginseng Res. 2013, 37, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, D.T.; Anh, N.T.K.; Phuong, N.T.T.; Hanh, N.T.H.; Đat, N.T. Simultaneous determination of notoginsenoside R1 and ginsenosides Rg1, Re, Rb1 in dietary supplements by HPLC-DAD. Vietnam. J. Food Control 2021, 4, 160–170. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.; Kim, J.; Yoon, H.I.; Son, J.E. Effect of far-red and UV-B light on the growth and ginsenoside content of ginseng (Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer) sprouts aeroponically grown in plant factories. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2022, 63, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, H.N.; Hong, S.J.; Kang, H.J.; Cho, J.Y.; Kim, D.; Ameer, K.; Kim, Y.M. Enhanced biotransformation of the minor ginsenosides in red ginseng extract by Penicillium decumbens β-glucosidase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2022, 153, 109941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.S.; Yang, K.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, J.E.; Yun, H.N.; Yu, J.W.; Kim, B.S. Antioxidant and immunomodulatory effect of lactic acid bacteria fermented barley sprout hot water extract. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 51, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, M.Y.; Ge, Y.Y.; Geng, F.; He, X.Q.; Xia, Y.; Guo, B.L.; Gan, R.Y. Antioxidant capacity, phytochemical profiles, and phenolic metabolomics of selected edible seeds and their sprouts. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1067597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, A.W. Sprouts and microgreens—Novel food sources for healthy diets. Plants 2022, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, K.H.; Hong, H.D.; Cho, C.W.; Lee, M.Y.; Choi, U.k.; Kim, Y.C. Phenolic acid composition and antioxidative activity of red ginseng prepared by high temperature and high pressure process. Korean J. Food Nutr. 2012, 25, 827–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ko, M.J.; Chung, M.S. Subcritical water extraction of bioactive components from red ginseng (Panax ginseng CA Meyer). J. Supercrit. Fluids 2018, 133, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, G.; La, I.J.; Lee, D.S.; Chae, J.W.; Im, J.H.; Park, S.W.; Fu, X.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, M.H.; Seong, Y.S.; et al. Assessment of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity of barley sprouts. Separations 2025, 12, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randhir, R.; Lin, Y.T.; Shetty, K. Stimulation of phenolics, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities in dark germinated mung bean sprouts in response to peptide and phytochemical elicitors. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeb, A. Concept, mechanism, and applications of phenolic antioxidants in foods. J. Food Biochem. 2020, 44, e13394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldini, M.; Marino, T.; Russo, N.; Toscano, M. Antioxidant properties of phenolic compounds: H-atom versus electron transfer mechanism. J. Phys. Chem. A 2004, 108, 4916–4922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, J.A.; Lee, H.Y.; Kim, S.C.; Cho, D.Y.; Jung, J.G.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, A.R.; Jeong, J.B.; Son, K.H.; Cho, K.M. Changes of nutritional constituents and antioxidant activities by the growth periods of produced ginseng sprouts in plant factory. J. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2022, 65, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Jemli, M.; Kamal, R.; Marmouzi, I.; Zerrouki, A.; Cherrah, Y.; Alaoui, K. Radical-scavenging activity and ferric reducing ability of Juniperus thurifera (L.), J. oxycedrus (L.), J. phoenicea (L.) and Tetraclinis articulata (L.). Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 2016, 6392656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlesier, K.; Harwat, M.; Böhm, V.; Bitsch, R. Assessment of antioxidant activity by using different in vitro methods. Free Radic. Res. 2002, 36, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, W.; Tian, S.; Cao, S. Antioxidant activity and free radical-scavenging capacity of Gynura divaricata leaf extracts at different temperatures. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2011, 7, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, C.L.L.; Yang, A.Y.; Cheng, D.C.; Boyanapalli, S.S.S.; Su, Z.Y.; Khor, T.O.; Gao, S.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.H.; Kong, A.N.T. Pharmacodynamics of ginsenosides: Antioxidant activities, activation of Nrf2, and potential synergistic effects of combinations. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2012, 25, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morshed, M.N.; Ahn, J.C.; Mathiyalagan, R.; Rupa, E.J.; Akter, R.; Karim, M.R.; Jung, D.H.; Yang, D.C.; Jung, S.K. Antioxidant activity of Panax ginseng to regulate ROS in various chronic diseases. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Mu, P.; Chen, C.; Huang, P.; Liu, D. Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion-induced inflammation and oxidative stress via activation of the PI3K/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 19, 3633–3641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Zhang, D.; Yang, D.C. Biosynthesis and biotechnological production of ginsenosides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Ginsenoside | Calibration Curve | R2 | LOD 1 (μg/mL) | LOQ 2 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | y = 1989.9x − 1278.5 | 0.9997 | 1.02 | 3.1 |
| Re | y = 1602.1x + 51.4 | 0.9994 | 1.40 | 4.24 |
| Rh1 | y = 2397.4x − 1117.3 | 0.9996 | 1.63 | 4.95 |
| Rg2 | y = 1956x − 338.6 | 0.9994 | 0.24 | 0.74 |
| Rb1 | y = 2493.6x − 3272.3 | 0.9997 | 3.55 | 10.76 |
| F1 | y = 1513.1x − 1813.0 | 0.9996 | 0.92 | 2.80 |
| Rd | y = 1458.3x + 7.0 | 0.9995 | 0.20 | 0.62 |
| F2 | y = 2312.8x + 225.7 | 0.9996 | 0.43 | 1.31 |
| Rg3(S) | y = 2586.7x + 1528.3 | 0.9995 | 1.69 | 5.11 |
| CK | y = 6625.5x − 4058.9 | 0.9995 | 1.27 | 3.90 |
| Rg5 | y = 2750.0x − 2035.5 | 0.9997 | 0.27 | 0.81 |
| Rh2 | y = 2904.0x + 2154.2 | 0.9997 | 0.71 | 2.16 |
| Sample | Ginsenosides Content (mg/g) | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rg1 | Re | Rh1 | Rg2 | F1 | Rb1 | Rd | F2 | Rg3(S) | CK | Rg5 | Rh2 | Total | |
| Extract (49 brix°) | 3.27 ± 0.02 c | 11.06 ± 0.02 a | 0.55± 0.01 g | 2.48 ± 0.02 d | N.D. 1 | 1.07 ± 0.08 f | 7.14 ± 0.03 b | 1.58 ± 0.00 e | 1.05 ± 0.01 f | TR 2 | 1.54 ± 0.01 e | TR | 31.54 ± 0.22 |
| Sample | Total Polyphenol Content (mg GAE 1/g) | Total Flavonoid Content (mg RE 2/g) |
|---|---|---|
| Extract (49 brix°) | 7.98 ± 0.03 | 4.65 ± 0.02 |
| Compound | DPPH 1 (IC50 2, mg/mL) * | ABTS 3 (IC50, mg/mL) * |
|---|---|---|
| Extract (49 brix°) | 7.88 ± 0.01 a | 24.81 ± 0.05 a |
| Ascorbic acid | 0.03 ± 0.00 b | 0.42 ± 0.01 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oh, G.; Lee, D.-S.; Chae, J.-W.; Park, S.W.; Im, J.-H.; Fu, X.; Lim, J.-S.; Kim, M.-H.; Seong, Y.-S.; Wei, S.; et al. Assessment of 12 Ginsenosides and the Antioxidant Activity of Red Ginseng Sprout Extracts. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312467
Oh G, Lee D-S, Chae J-W, Park SW, Im J-H, Fu X, Lim J-S, Kim M-H, Seong Y-S, Wei S, et al. Assessment of 12 Ginsenosides and the Antioxidant Activity of Red Ginseng Sprout Extracts. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(23):12467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312467
Chicago/Turabian StyleOh, Geon, Do-Sang Lee, Jong-Woo Chae, Seon Woo Park, Ji-Hyun Im, Xiaolu Fu, June-Seok Lim, Min-Hye Kim, Yeon-Seok Seong, Shuai Wei, and et al. 2025. "Assessment of 12 Ginsenosides and the Antioxidant Activity of Red Ginseng Sprout Extracts" Applied Sciences 15, no. 23: 12467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312467
APA StyleOh, G., Lee, D.-S., Chae, J.-W., Park, S. W., Im, J.-H., Fu, X., Lim, J.-S., Kim, M.-H., Seong, Y.-S., Wei, S., Fu, X., La, I.-J., & Lee, O.-H. (2025). Assessment of 12 Ginsenosides and the Antioxidant Activity of Red Ginseng Sprout Extracts. Applied Sciences, 15(23), 12467. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152312467








