A Concept of Equivalent Load Scheme for Easy Prediction of Structural Topology When Load Position Changes Randomly
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Design Using a Heuristic Approach to Topology Optimization
2.1. Formulation of the Topology Optimization Problem
2.2. Heuristic Optimization Procedure Based on Cellular Automata
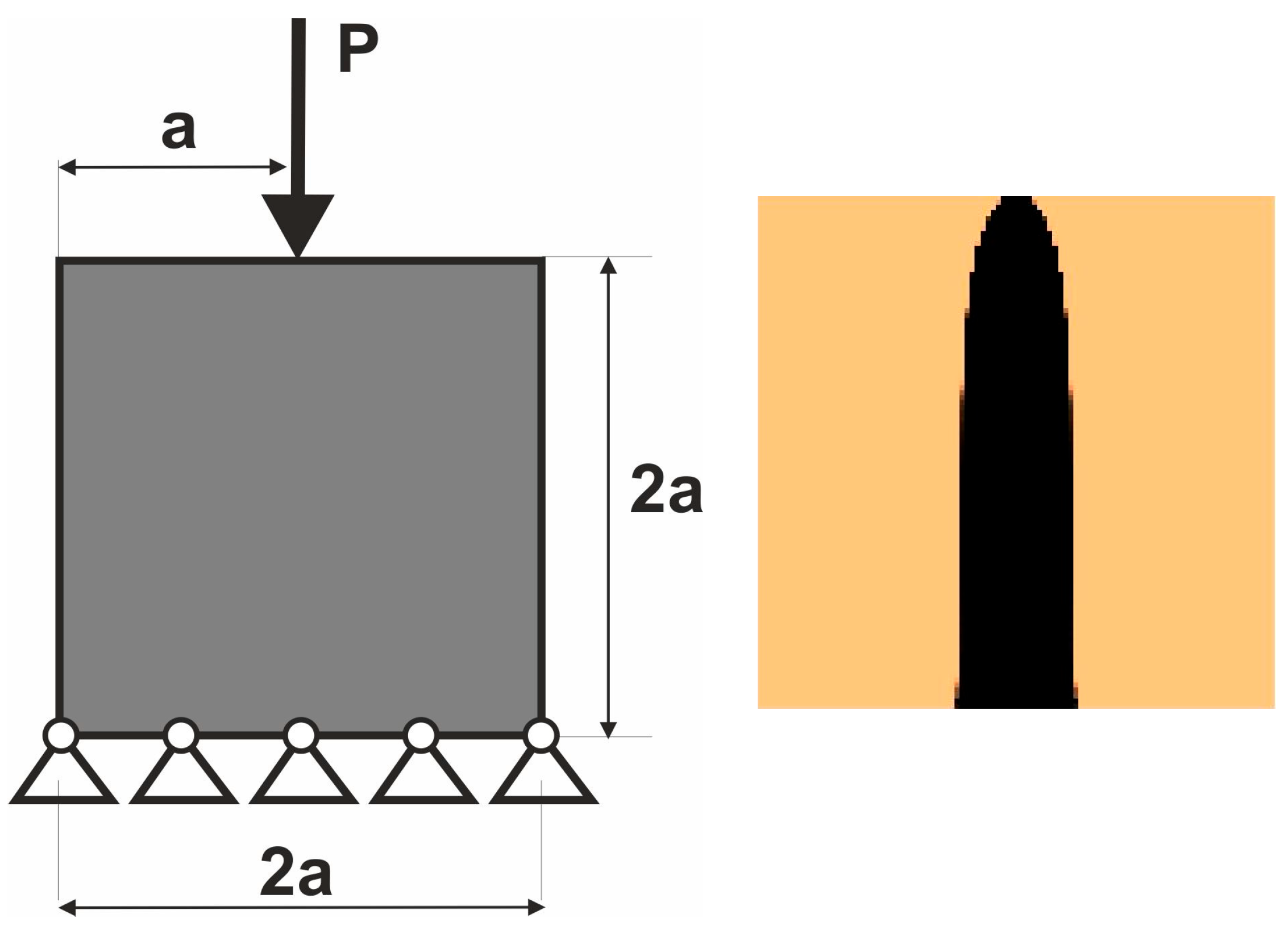
3. Predicting Structural Topology When Load Position Changes Randomly
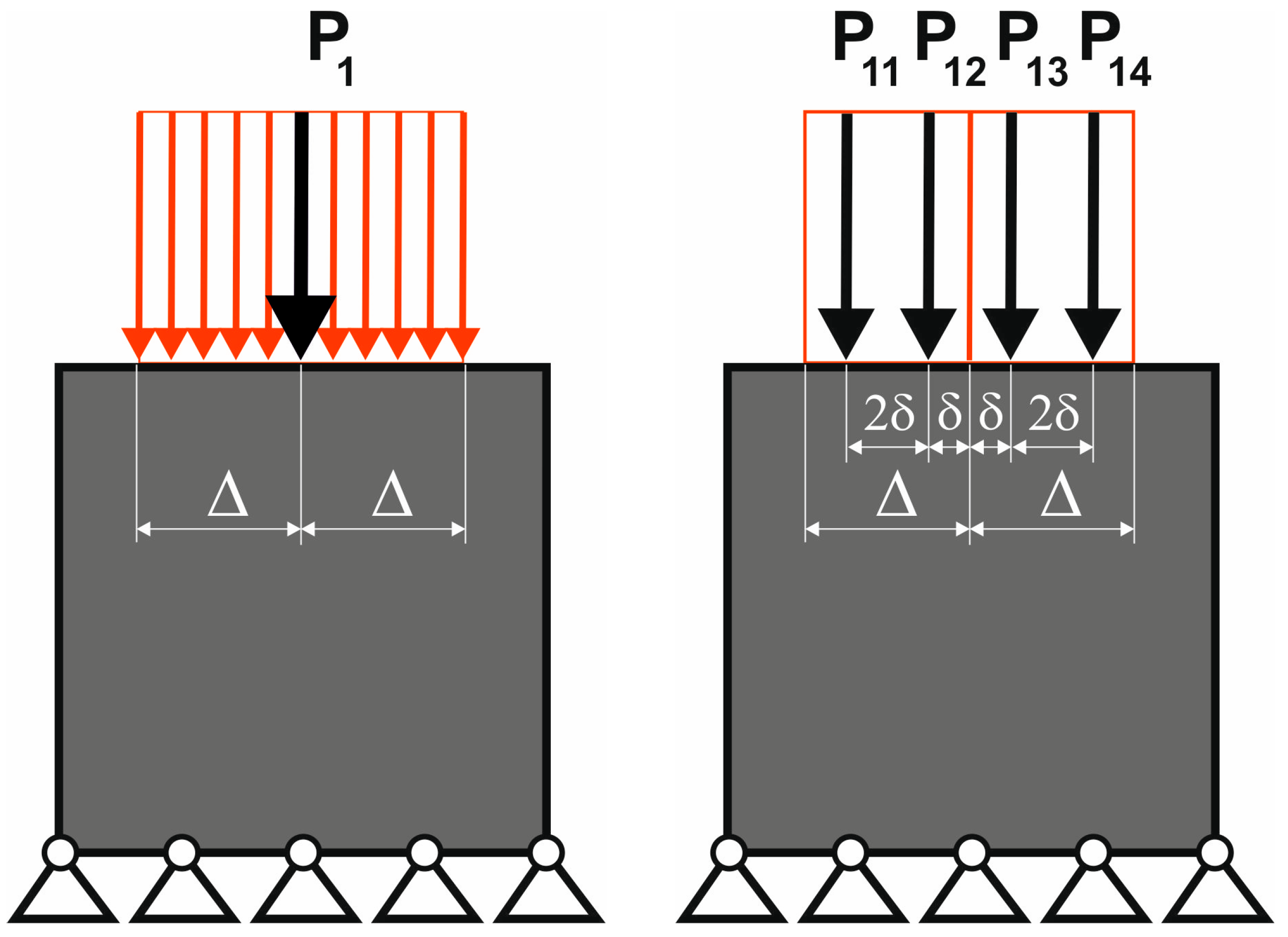
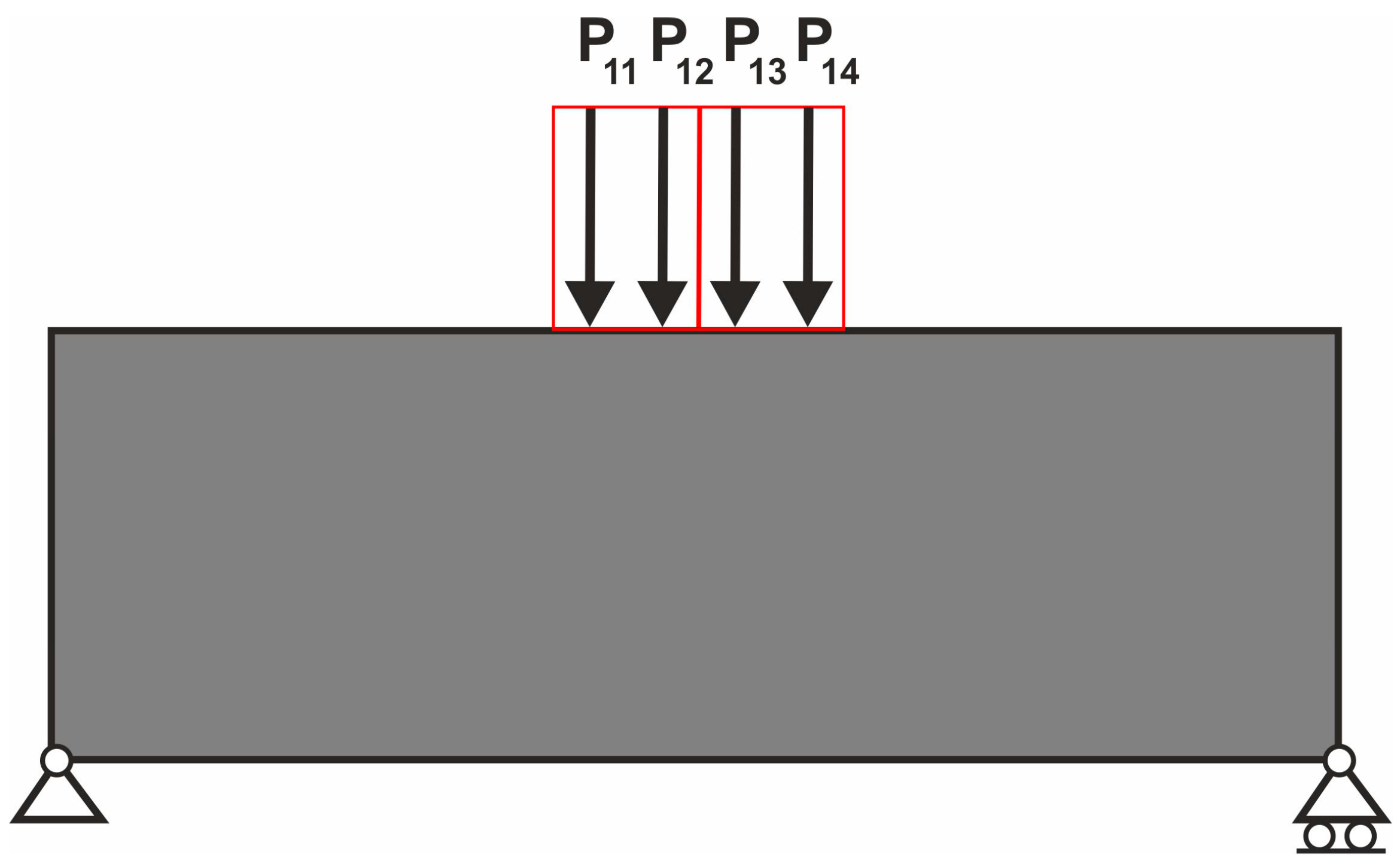
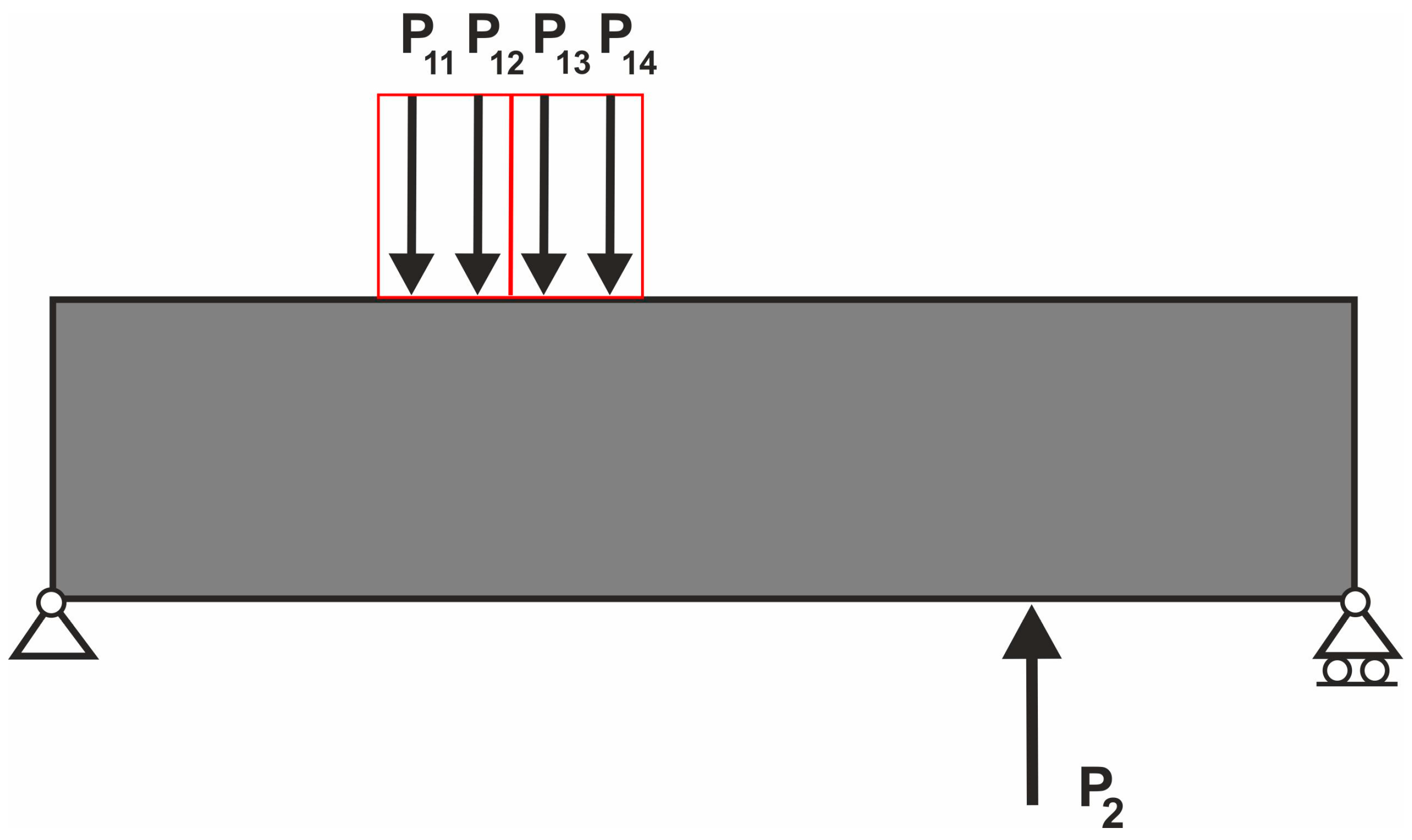
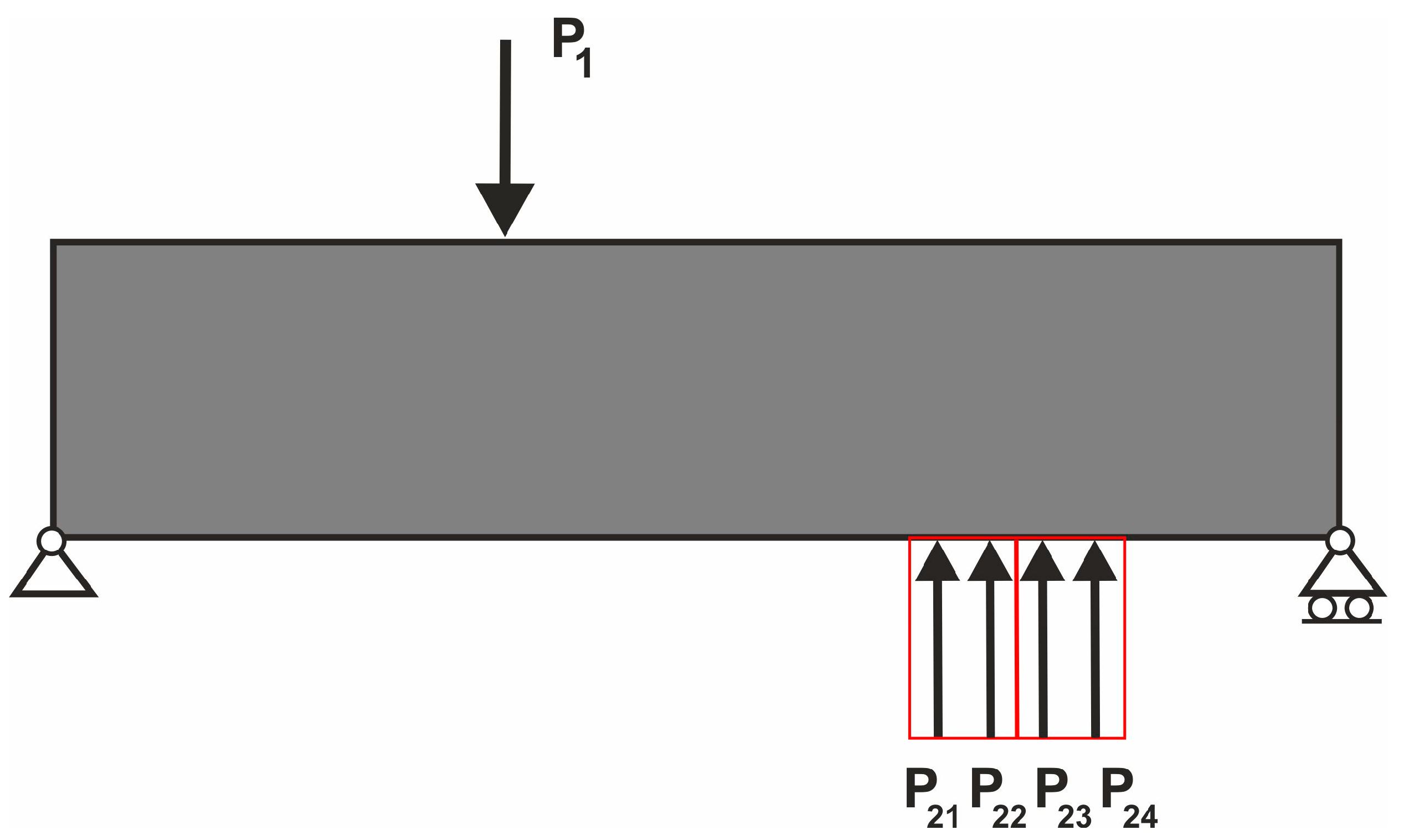
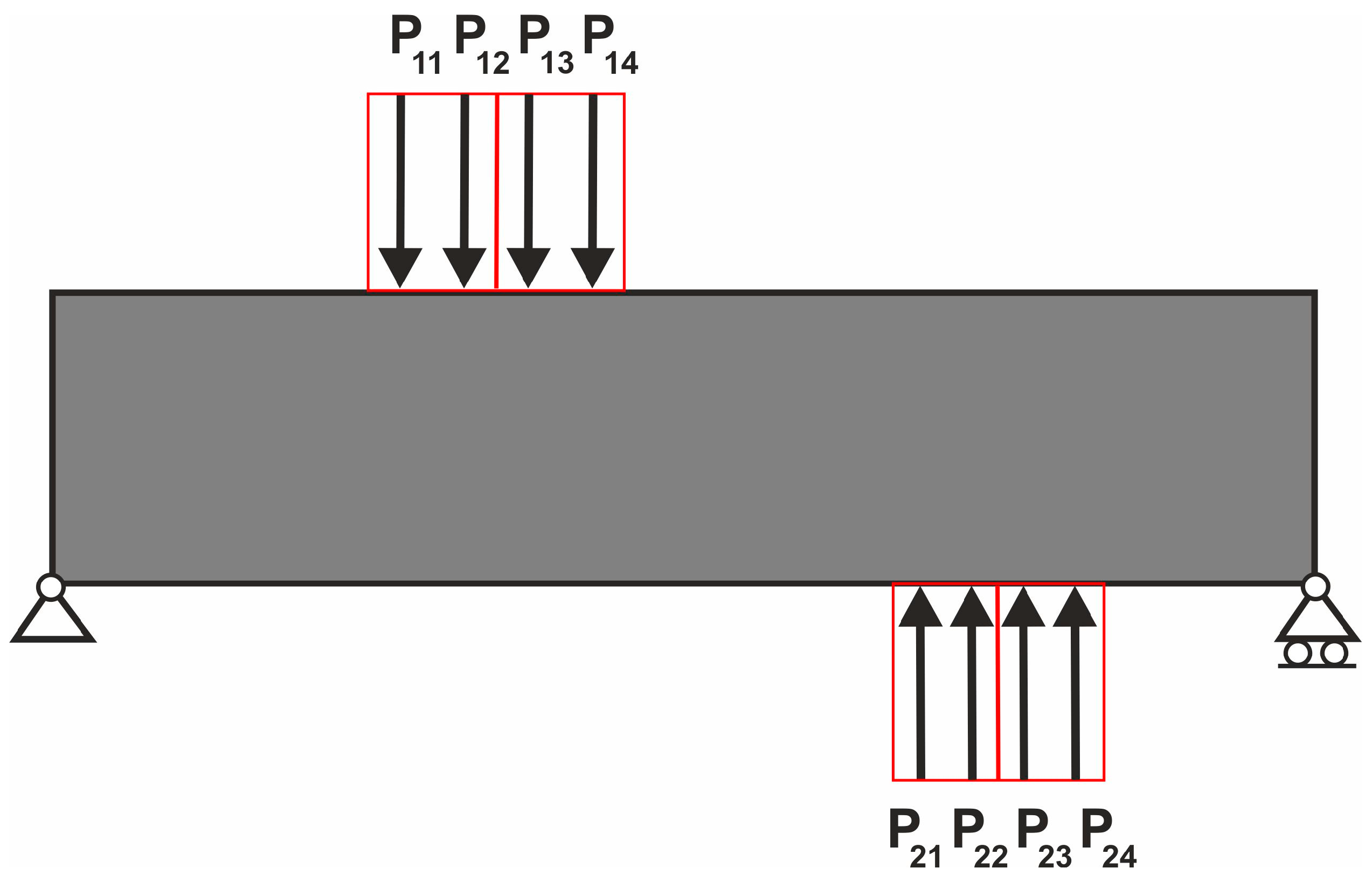
3.1. Loads Applied at Random Positions Simulated by the Multiple Load Case
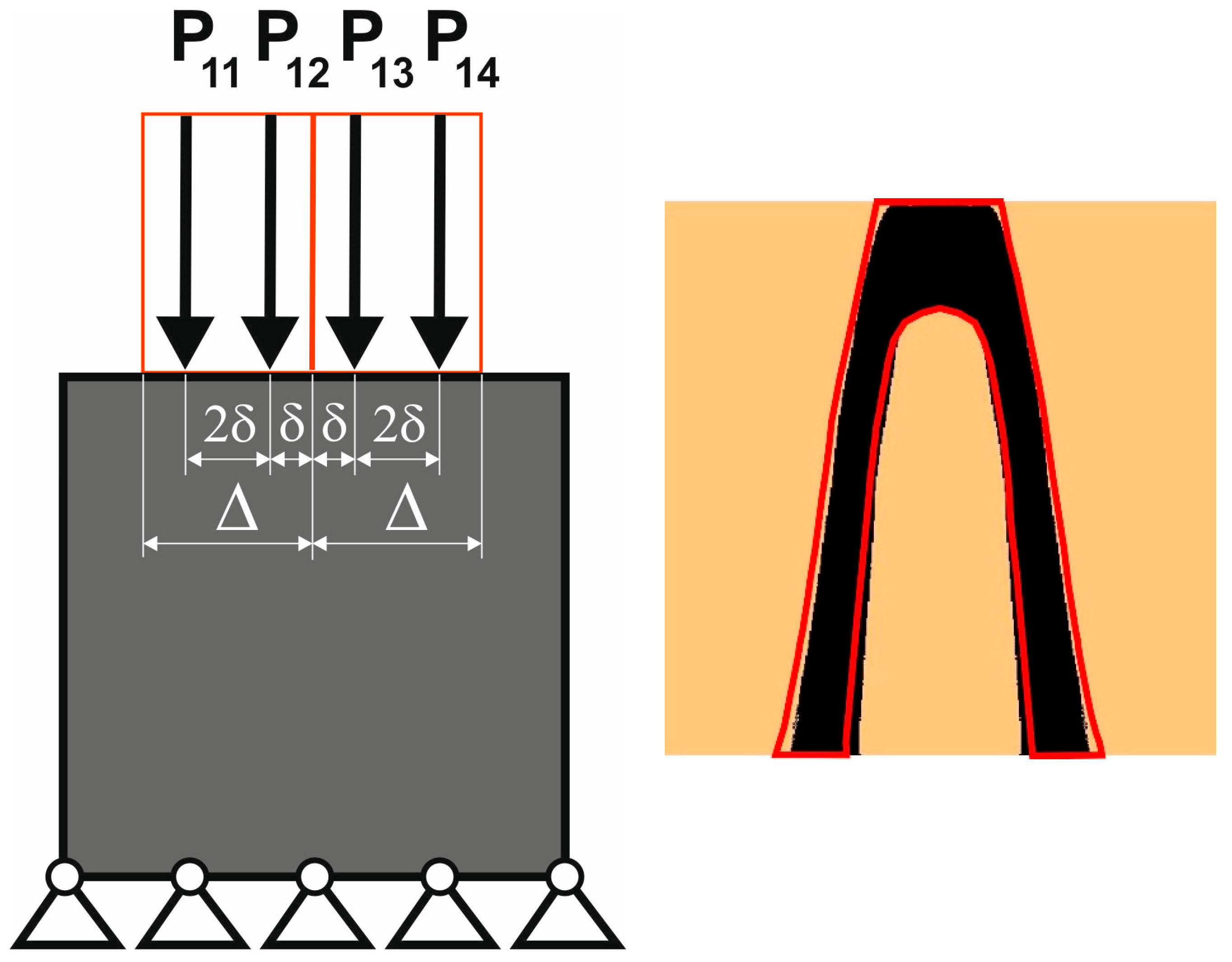
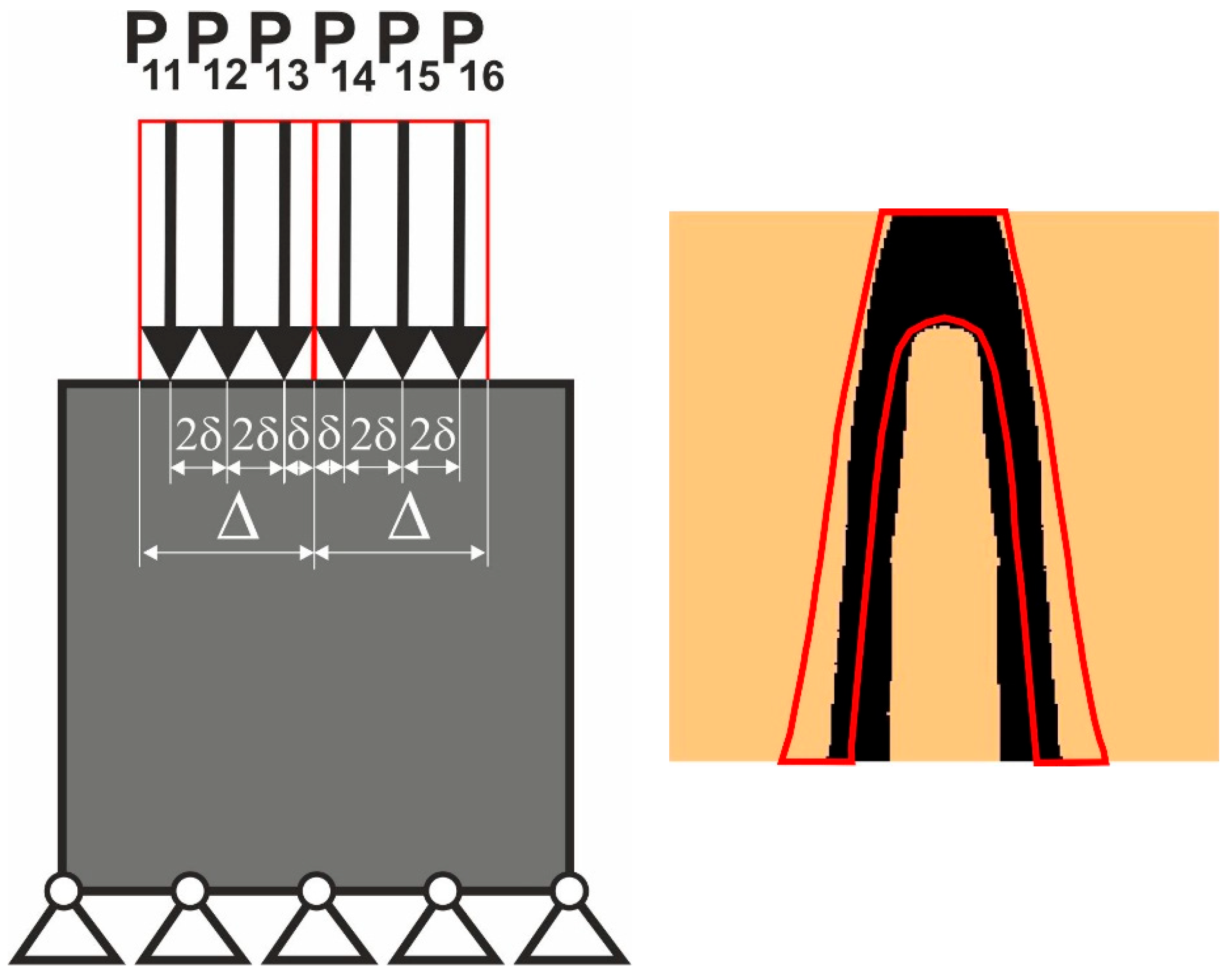
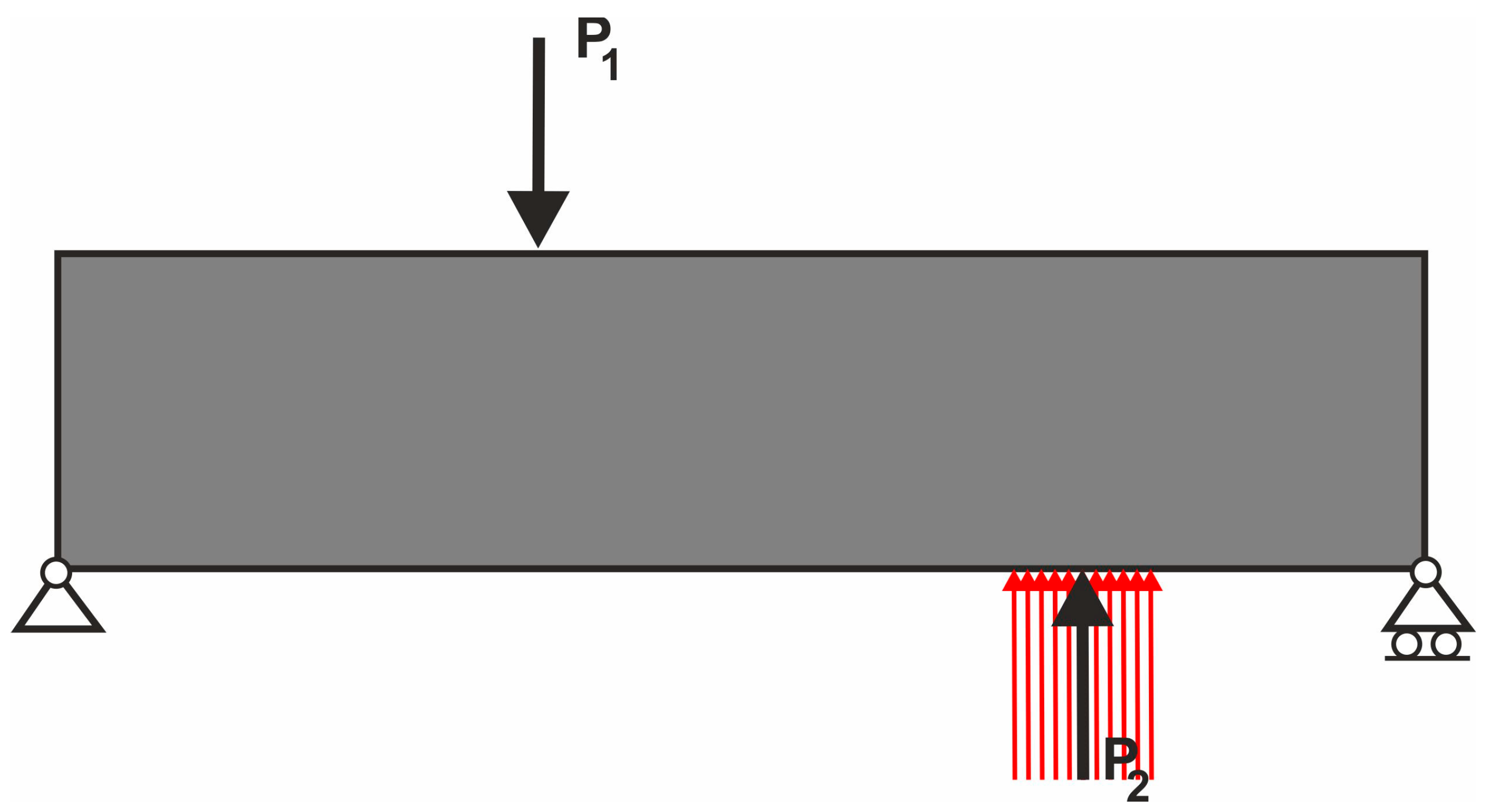
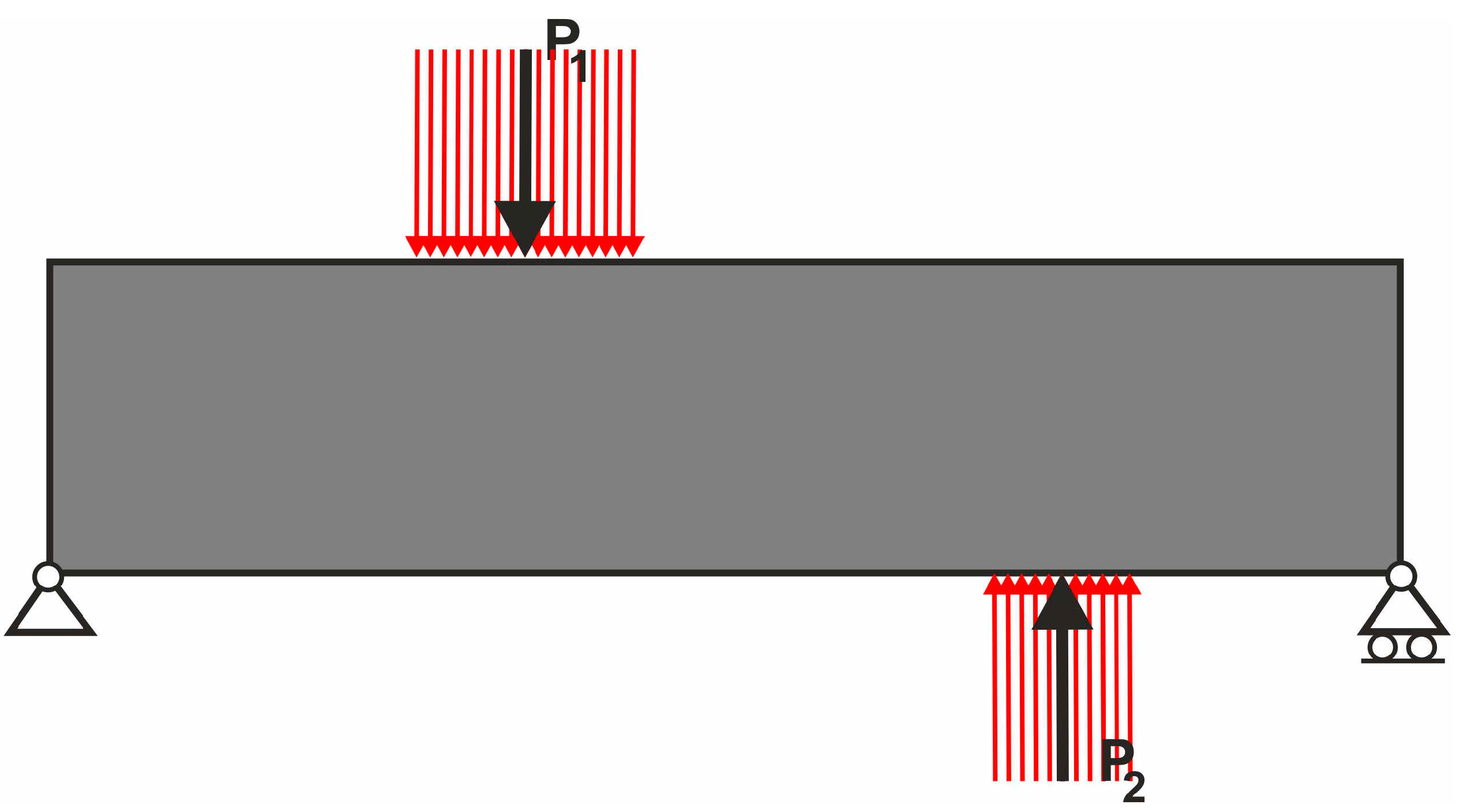
3.2. Equivalent Load Scheme to Represent Loads Applied at Randomly Selected Positions
4. Results
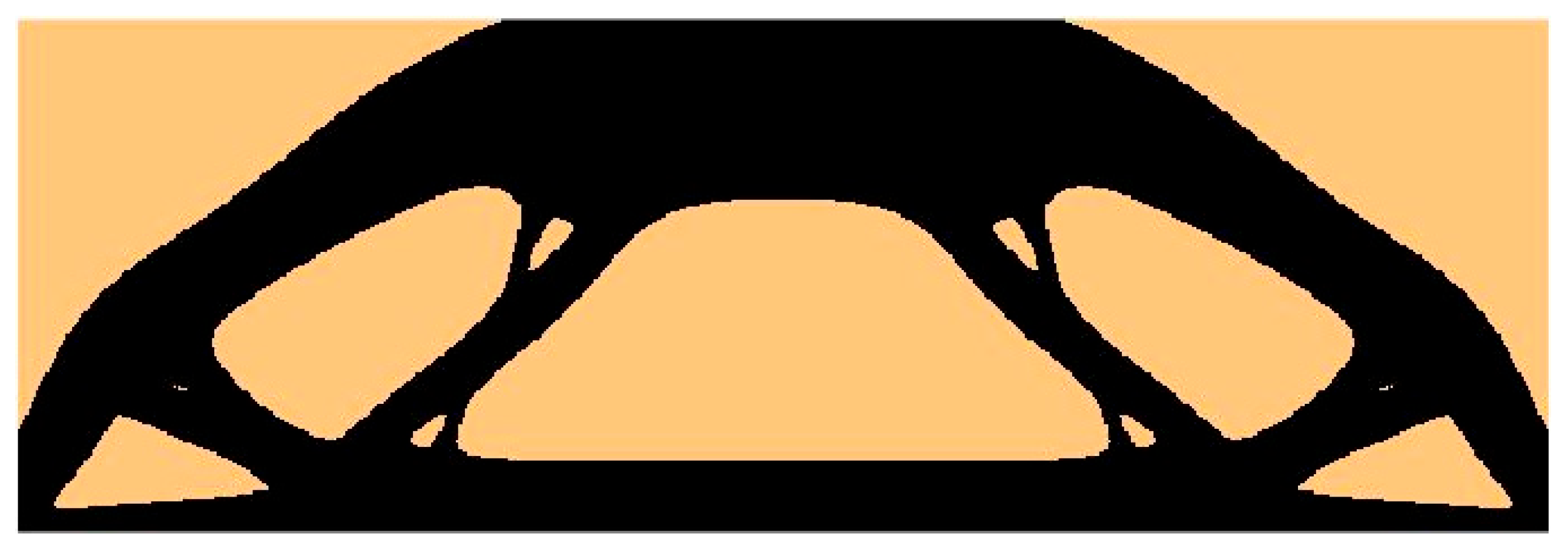
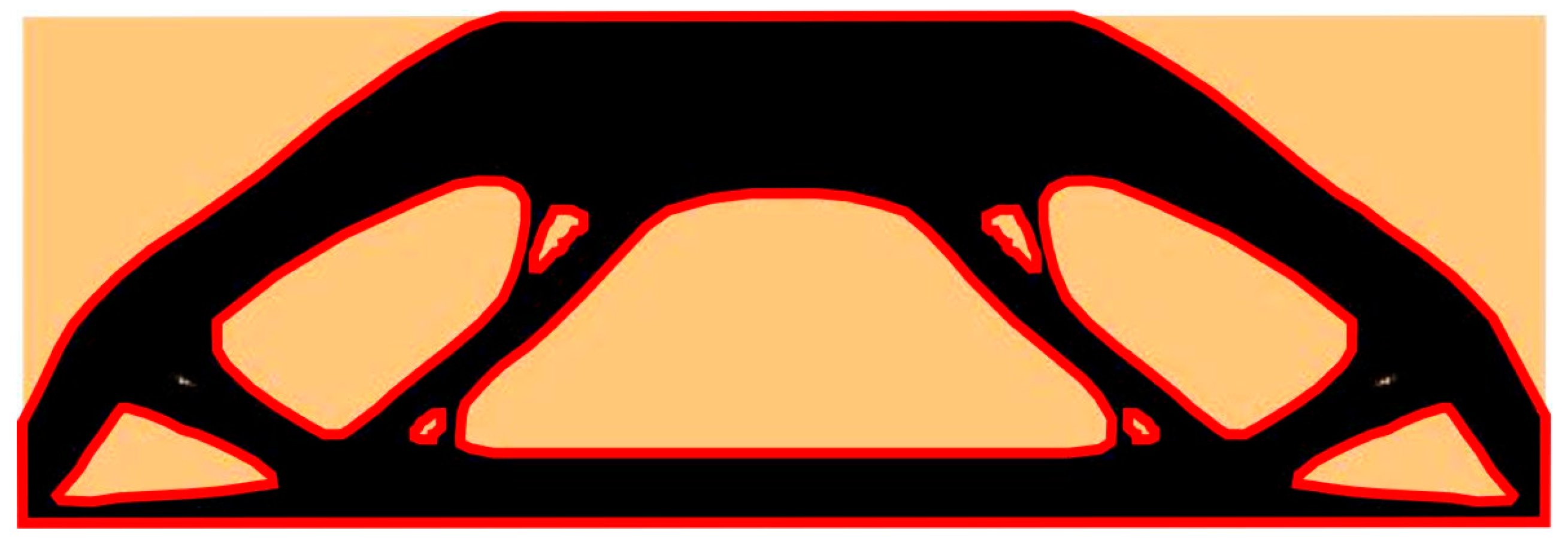
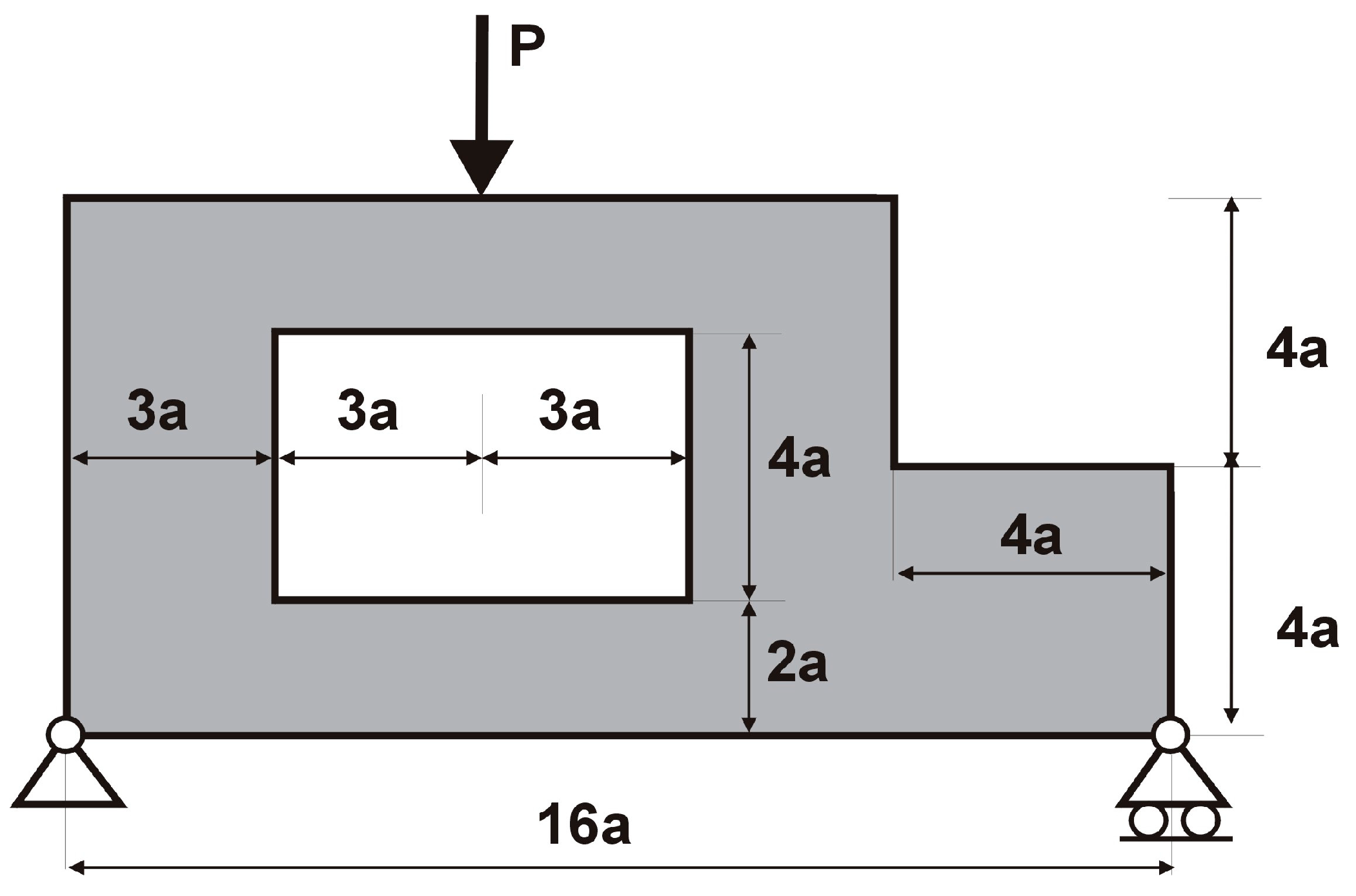
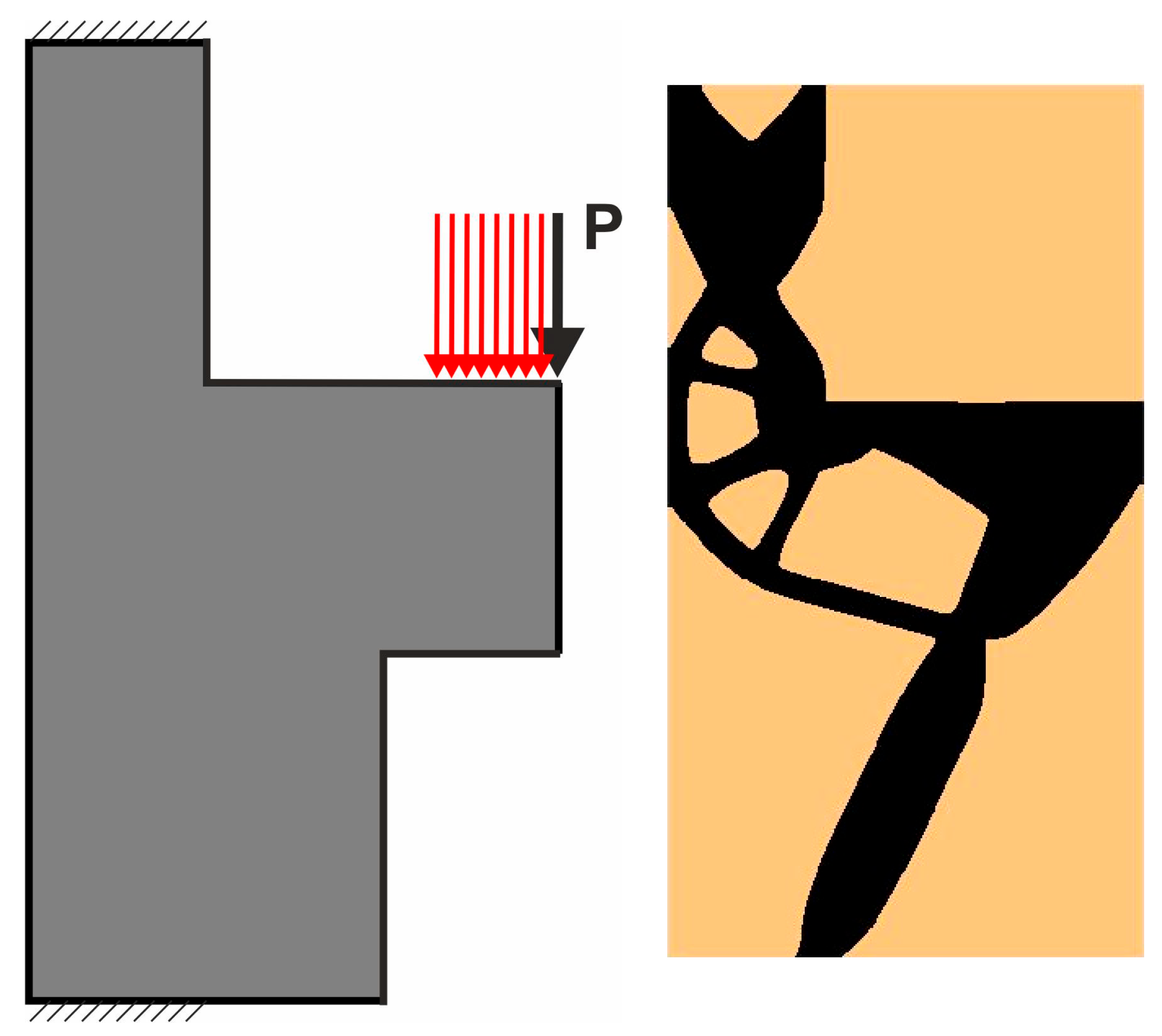
4.1. The Test Structure 1
4.2. The Test Structure 2
4.3. The Test Structure 3
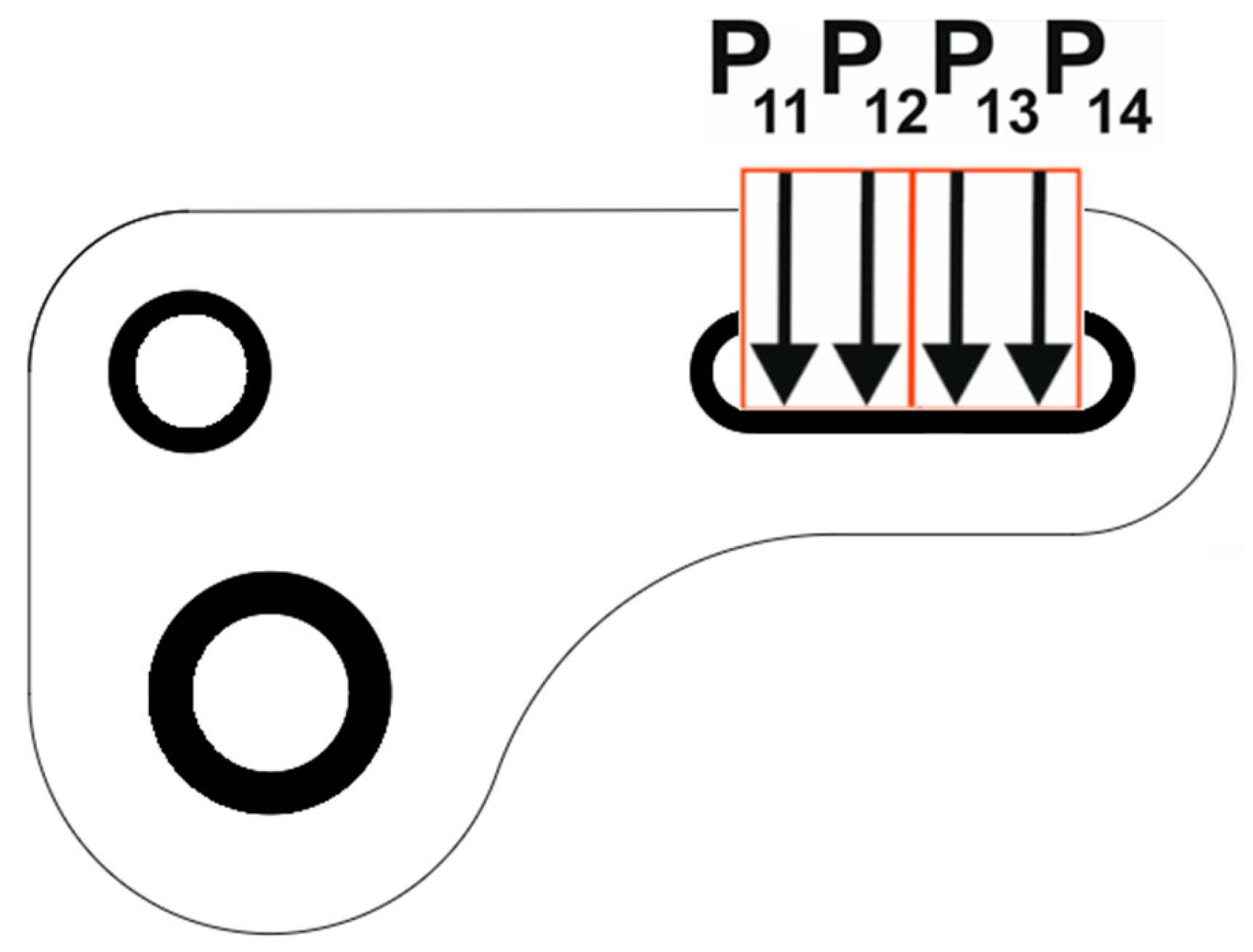
4.4. Test Structure 3 for Two Independently Acting Forces
4.5. Test Structure 4—Asymmetric Range of Random Load Positions
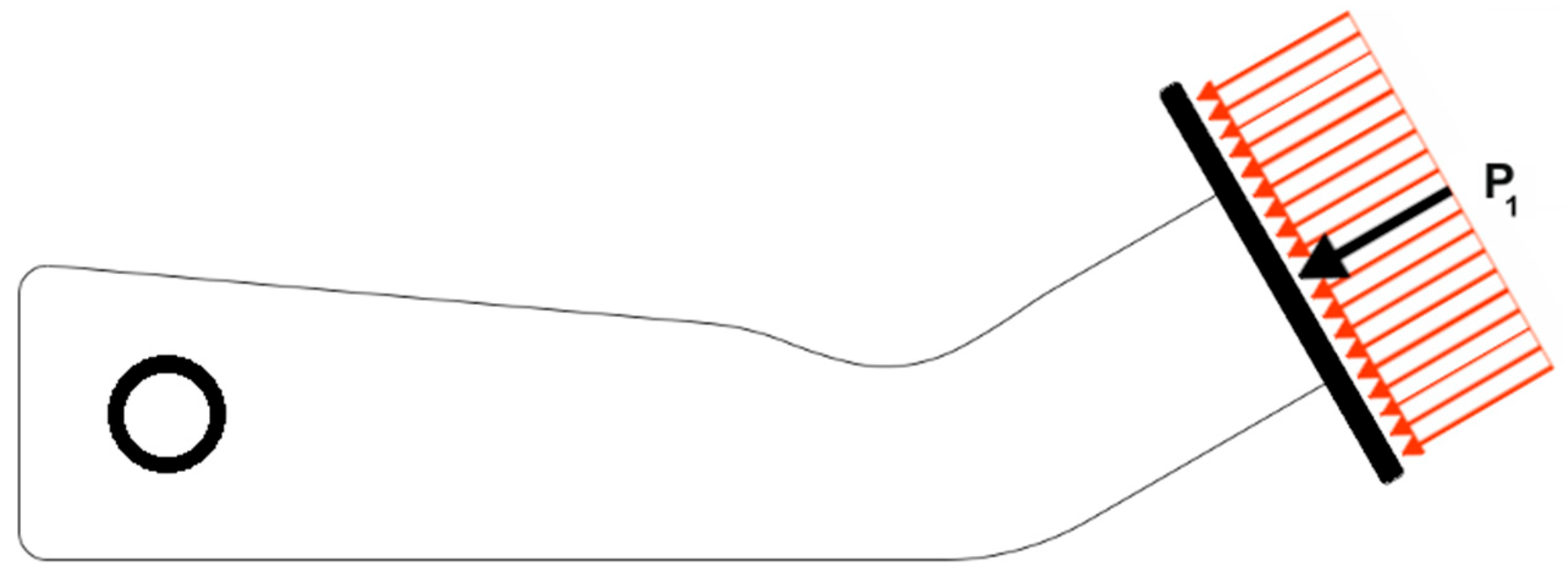
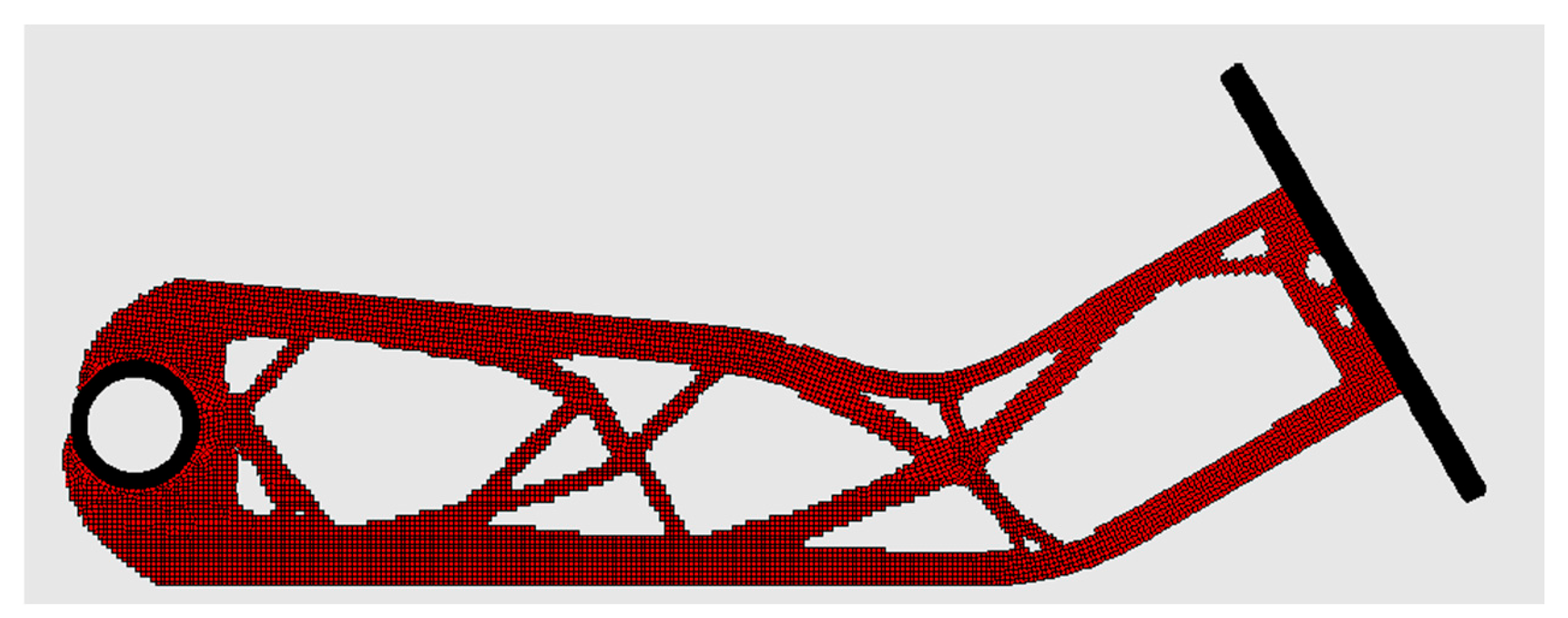
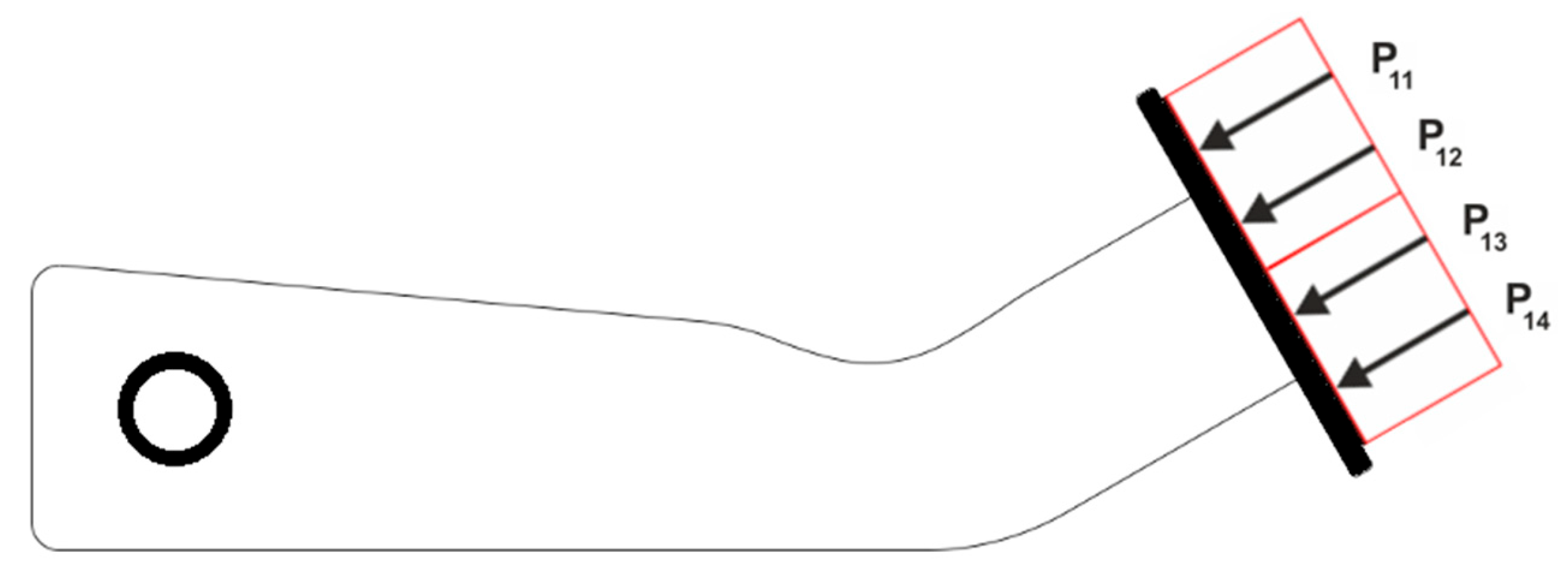
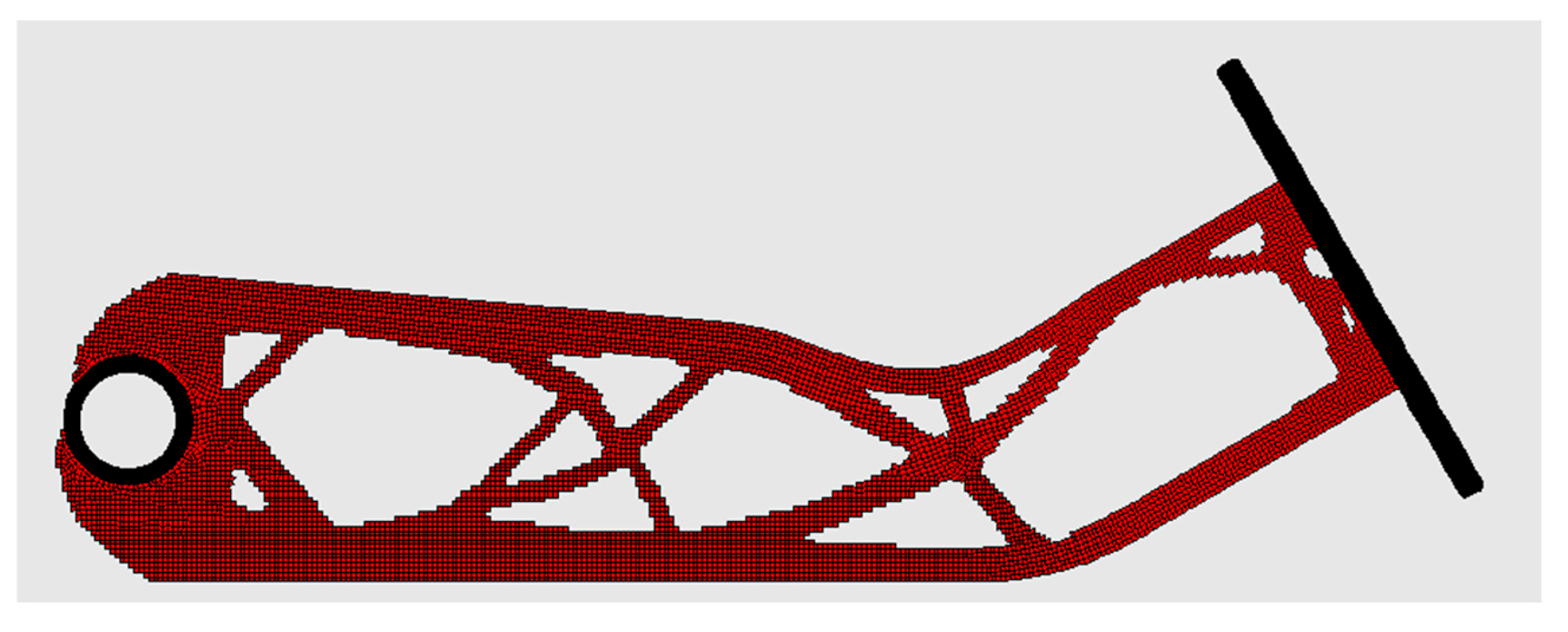
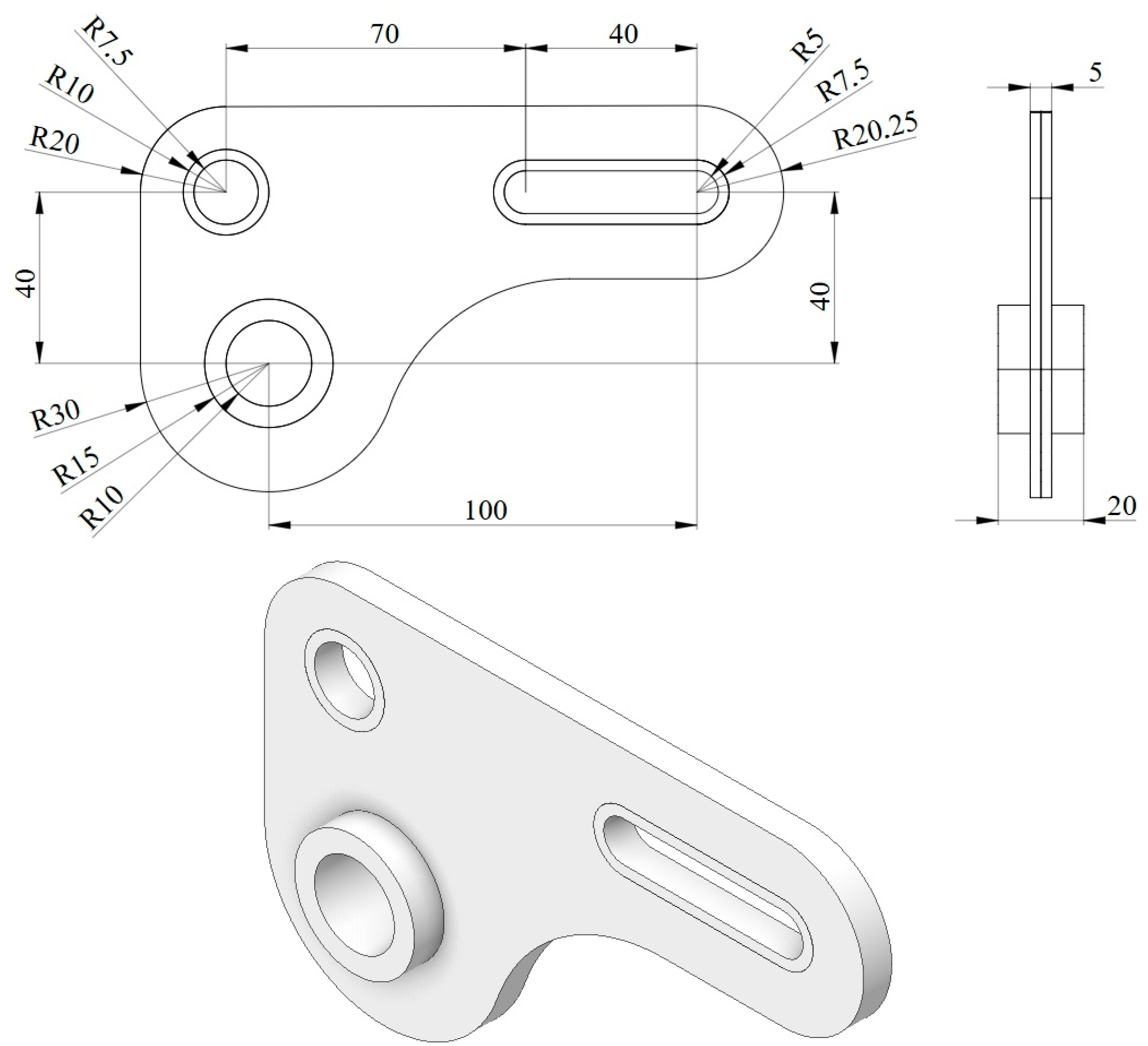
4.6. Engineering Example—Brake Pedal
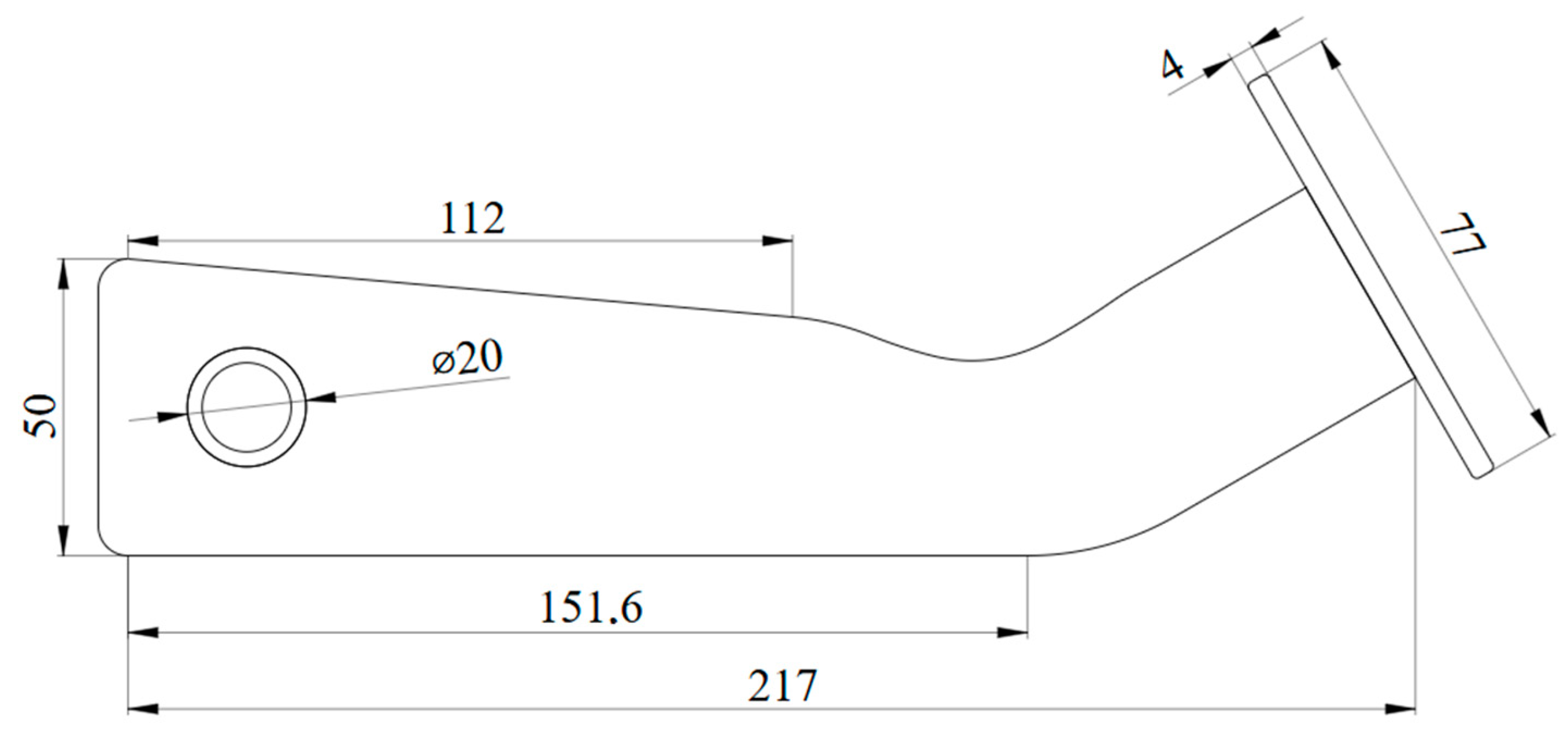
4.7. Engineering Example—Lever Arm
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TO | Topology Optimization |
| CA | Cellular Automata |
| SIMP | Solid Isotropic Material with Penalization |
| ELS | Equivalent Load Scheme |
References
- Bendsoe, M.P.; Sigmund, O. Topology Optimization. Theory, Methods and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaire, G.; Dapogny, C.; Jouve, F. Shape and topology optimization. In Geometric Partial Differential Equations—Part II; Bonito, A., Nochetto, R.H., Eds.; Handbook of Numerical Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 22, pp. 1–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koul, P. A Review of Generative Design Using Machine Learning for Additive Manufacturing. Adv. Mech. Mater. Eng. 2024, 41, 145–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpadulo, E.; Pini, F.; Leali, F. Assessment of Computer-Aided Design Tools for Topology Optimization of Additively Manufactured Automotive Components. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, C.; Gong, P.; Shi, Y.; Yu, Y.; Liu, Z. Topology Optimization Design and Experimental Research of a 3D-Printed Metal Aerospace Bracket Considering Fatigue Performance. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.; Synek, A.; Stauß, T.; Steinnagel, C.; Ehlers, T.; Gembarski, P.C.; Pahr, D.; Lachmayer, R. Development of a density-based topology optimization of homogenized lattice structures for individualized hip endoprostheses and validation using micro-FE. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khadiri, I.E.; Zemzami, M.; Nguyen, N.; Abouelmajd, M.; Hmina, N.; Belhouideg, S. Topology optimization methods for additive manufacturing: A review. Int. J. Simul. Multidiscip. Des. Optim. 2023, 14, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiuk, G.; Mrzygłód, M.W. Topology optimization of structures with stress and additive manufacturing constraints. J. Theor. Appl. Mech. 2020, 58, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Yamada, T. Multi-material topology optimization for additive manufacturing considering maximum build volume and assembly process. Eng. Anal. Bound. Elem. 2024, 163, 616–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, D.A.; Jacobs, G.; Zerwas, T.; Delgadillo, A. Integrating Topology Optimization into Model-Based Systems Engineering for Lightweight Structural Design. Forsch. Im Ingenieurwesn 2025, 89, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Yan, L.; Zhu, S. Structural topology optimization in linear and nonlinear elasticity using a discontinuous Galerkin finite element method. Control. Cybern. 2025, 53, 283–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Wang, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, H.; Dong, J.; Yue, W.; Xia, H. Topology Optimization: A Review for Structural Designs Under Statics Problems. Materials 2024, 17, 5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Li, Q.; Liu, S. Dynamic Topology Optimization for Structures Exhibiting Frequency-Dependent Material Properties with Prescribed Frequency Forbidden Band. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2024, 432, 117439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maute, K. Topology Optimization under Uncertainty. In Topology Optimization in Structural and Continuum Mechanics; Rozvany, G.I.N., Lewiński, T., Eds.; CISM International Centre for Mechanical Sciences; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 2014; Volume 549, pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharmanda, G.; Olhoff, N.; Mohamed, A.; Lemaire, M. Reliability-Based Topology Optimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2004, 26, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunning, P.D.; Kim, H.A.; Mullineux, G. Introducing Loading Uncertainty in Topology Optimization. AIAA J. 2011, 49, 760–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shi, Y.; Meng, Z.; Yang, B.; Long, K. Uncertainty-oriented topology optimization of dynamic structures considering hybrid uncertainty of probability and random field. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 256, 110744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashneh, M.; Cucuzza, R.; Aela, P.; Rad, M.M. Reliability-Based Topology Optimization of Imperfect Structures Considering Uncertainty of Load Position. Structures 2024, 69, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresia, J.; Vasconcelos Senhora, F.; Paulino, G.H. Topology Optimization with Continuously Varying Load Magnitude and Direction for Compliance Minimization. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2024, 67, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, T.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, H.; Zhang, D. Robust topology optimization of multi-material structure with load uncertainty based on element-free Galerkin method. Eng. Struct. 2025, 340, 120786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Peng, D.; Hu, W.; Liu, Z.; Tan, J. Collaborative robust topology optimization of FGMs considering hybrid bounded uncertainties based on the distance to ideal solution. Compos. Struct. 2024, 341, 118205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Meng, D.; Alfouneh, M.; Keshtegar, B.; Zhu, S.P. A robust-weighted hybrid nonlinear regression for reliability based topology optimization with multi-source uncertainties. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2025, 447, 118360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, J.; Qin, M.; Huang, Y. A robust multi-material topology optimization method considering load and material uncertainties with univariate interpolation. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 212, 113173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saurabh, S.; Gupta, A.; Chowdhury, R.; Duddu, R. Robust topology optimization for uncertainty in load positions of transient dynamic loading. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 264, 111440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Tian, Z.; Gao, Y.; Faes, M.G.R.; Li, Q. Transient dynamic robust topology optimization methodology for continuum structure under stochastic uncertainties. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 2025, 442, 118019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, D.; Wang, D. An efficient method for concurrent multiscale robust structural topology optimization under loading uncertainties. Comput. Struct. 2025, 318, 107960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong, C.H.; Kye, J.H.; Li, G.S.; Kim, C.H. A non-probabilistic reliability-based topology optimization of continuum structures using evolutionary topology optimization method. J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 2025, 47, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Wang, M.; Chen, J.; Xing, J. Reliability-based topology optimization of geometrically nonlinear structures considering non-probabilistic load parameter and geometric field uncertainties. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2025, 68, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, B.; Liu, M. Fatigue reliability-based topology optimization of compliant mechanisms considering material uncertainties. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2025, 68, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflug, L.; Stingl, M.; Uihlein, A. A Stochastic Method of Moving Asymptotes for Topology Optimization Under Uncertainty. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2025, 126, e70109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, S. A Comprehensive Study on Modern Optimization Techniques for Engineering Applications. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2024, 57, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Neumann, J. Theory of Self-Reproducing Automata; Burks, A.W., Ed.; University of Illinois Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Ulam, S. Random processes and transformations. In Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematics, Cambridge, UK, 30 August–6 September 1950; Volume 2, pp. 85–87. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, N.; Sikdar, B.K.; Deutsch, A.; Canright, G.; Chaudhuri, P.P. A Survey on Cellular Automata. Technical Report, Centre for High Performance Computing, Dresden University of Technology, December 2003. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:10466545 (accessed on 16 November 2025).
- Ghosh, M.; Kumar, R.; Saha, M.; Sikdar, B.K. Cellular Automata and Its Applications. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Automatic Control and Intelligent Systems (I2CACIS), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 20 October 2018; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romitti, G.S.; Liberos, A.; Termenón-Rivas, M.; de Arcaya, J.B.; Serra, D.; Romero, P.; Calvo, D.; Lozano, M.; García-Fernández, I.; Sebastian, R.; et al. Implementation of a Cellular Automaton for Efficient Simulations of Atrial Arrhythmias. Med. Image Anal. 2025, 101, 103484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollier, M.; Zielinski, K.M.C.; Daly, A.J.; Bruno, O.M.; Baetens, J.M. A comprehensive taxonomy of cellular automata. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2025, 140, 108362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, D.C.; Chen, J.H.; Cui, X.Y.; Li, G.Y. Design of Materials Using Hybrid Cellular Automata. Struct. Multidiscip. Optim. 2017, 56, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inou, N.; Shimotai, N.; Uesugi, T. A cellular automaton generating topological structures. In Proceedings of the 2nd European Conference on Smart Structures and Materials, Glasgow, Scotland, 12–14 October 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajs-Zielińska, K.; Bochenek, B. Cellular Automata Approach to Topology Optimization of Graded Multi-Material Structures. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tovar, A.; Patel, N.M.; Niebur, G.L.; Sen, M.; Renaud, J.E. Topology Optimization Using a Hybrid Cellular Automaton Method With Local Control Rules. J. Mech. Des. 2006, 128, 1205–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Chen, H.; Xu, Q.; Feng, F.; Chen, X.; Lv, X.; Lin, X.; Fu, T. Topology Optimization Design of Three-Dimensional Multi-Material and Multi-Body Structure Based on Irregular Cellular Hybrid Cellular Automata Method. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajs-Zielińska, K.; Bochenek, B. Topology algorithm built as an automaton with flexible rules. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2021, 69, e138813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, B.; Tajs-Zielinska, K. Cellular Automaton Mimicking Colliding Bodies for Topology Optimization. Materials 2022, 15, 8057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M.P. Optimal shape design as a material distribution problem. Struct. Optim. 1989, 1, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendsoe, M.P.; Kikuchi, N. Generating optimal topologies in optimal design using a homogenization method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1988, 71, 197–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Rozvany, G. The COC algorithm, Part II: Topological, geometrical and generalized shape optimization. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 1991, 89, 309–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakšić, Z.; Devi, S.; Jakšić, O.; Guha, K. A Comprehensive Review of Bio-Inspired Optimization Algorithms Including Applications in Microelectronics and Nanophotonics. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trojovský, P.; Dehghani, M. A new bio-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems based on walruses behavior. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.E.; Holland, J.H. Genetic algorithms and machine learning. Mach. Learn. 1988, 3, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knypiński, Ł.; Devarapalli, R.; Kamiński, M. Metaheuristic Algorithms in Optimal Design of Engineering Problems. Algorithms 2024, 17, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, B. An easy way for the generation of structural topologies under random loads using cellular automata. Acta Polytech. Hung. 2023, 20, 9–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochenek, B.; Tajs-Zielińska, K. On predicting optimal structural topologies in the presence of random loads. Materials 2025, 18, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajs-Zielińska, K.; Bochenek, B. Heuristic Optimization Rules Applied for the Sustainable Design of Lightweight Engineering Structures Under Loads Subject to Random Changes. Sustainability 2025, 17, 7011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
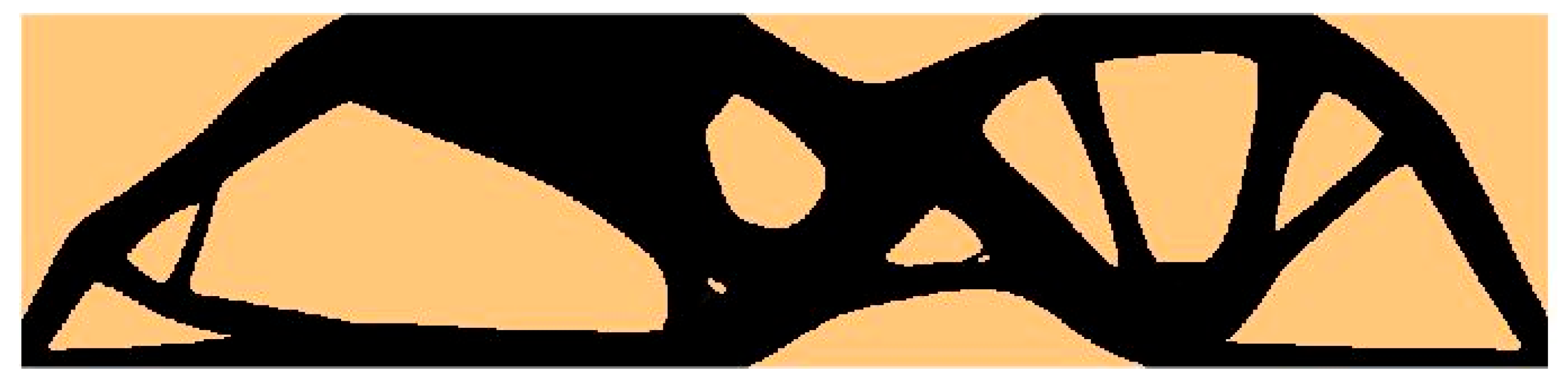
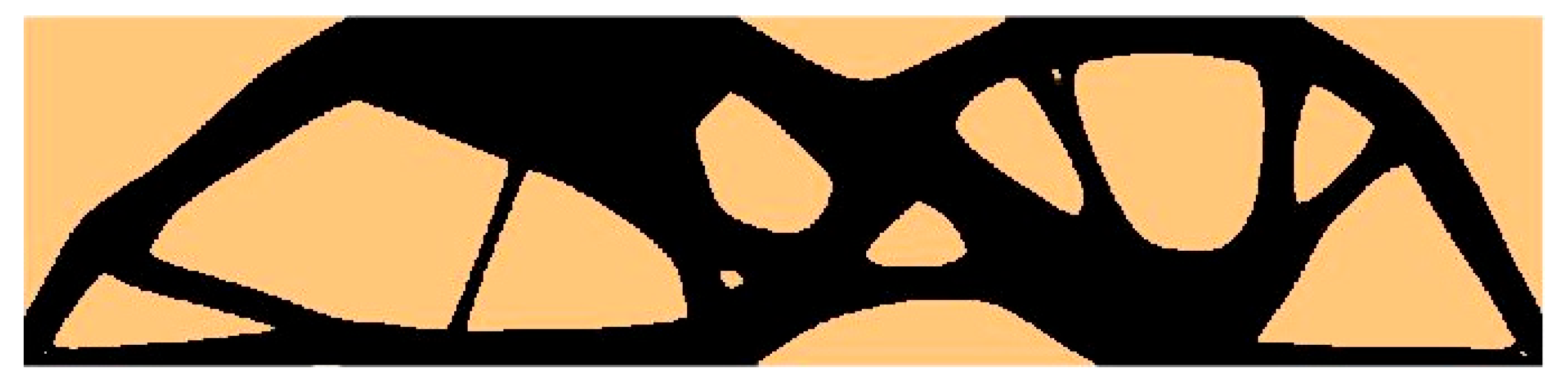
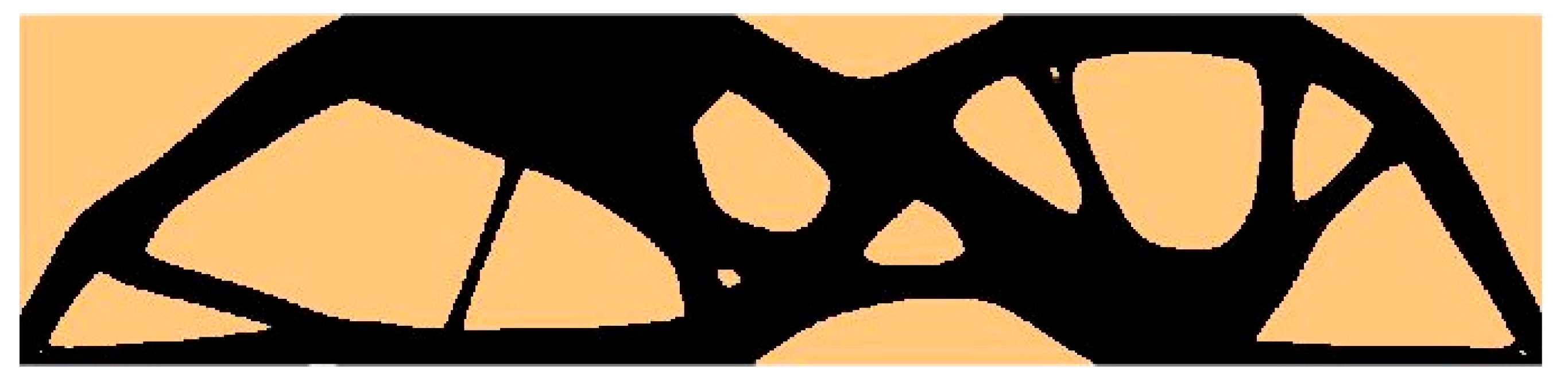







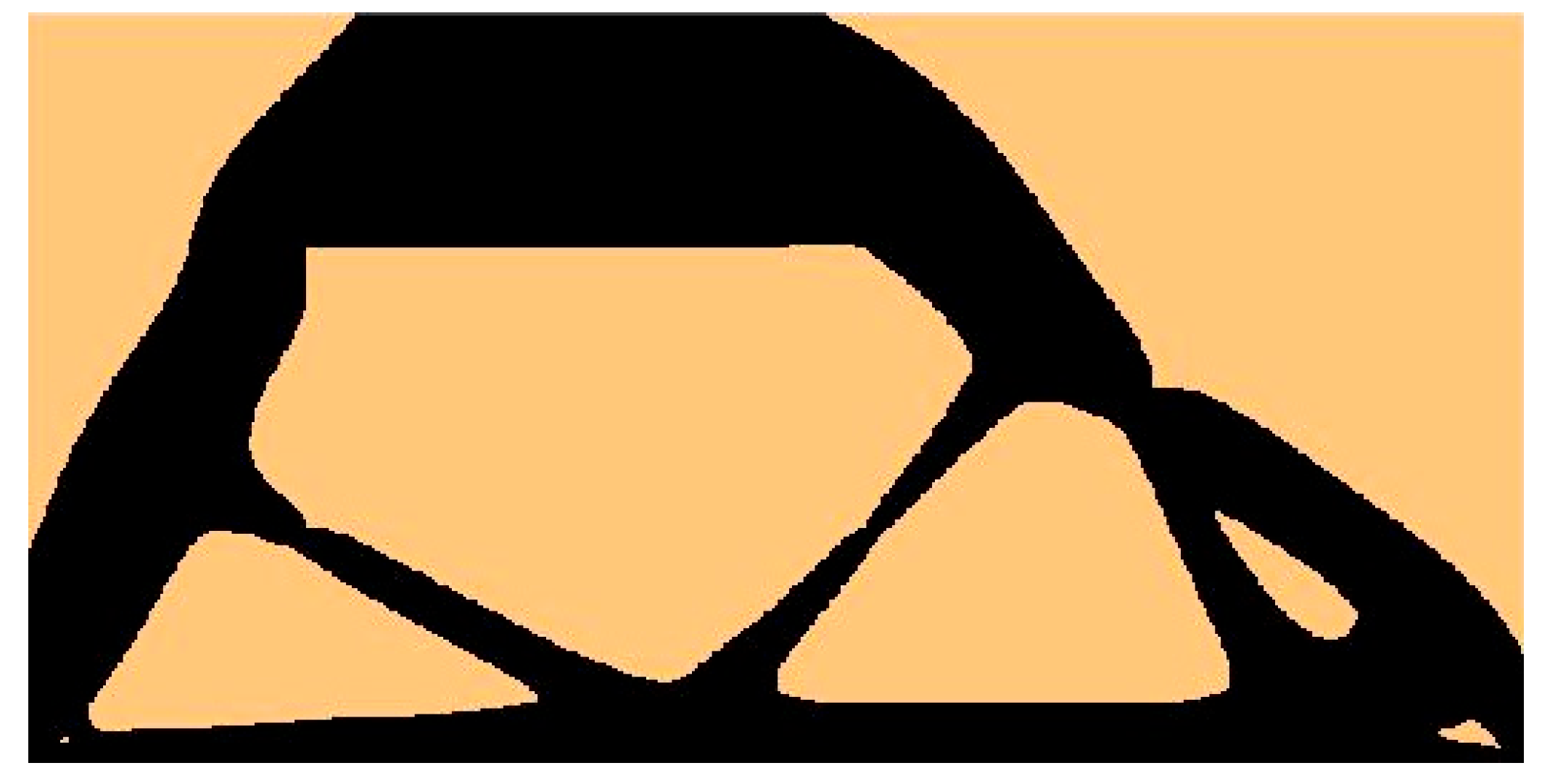
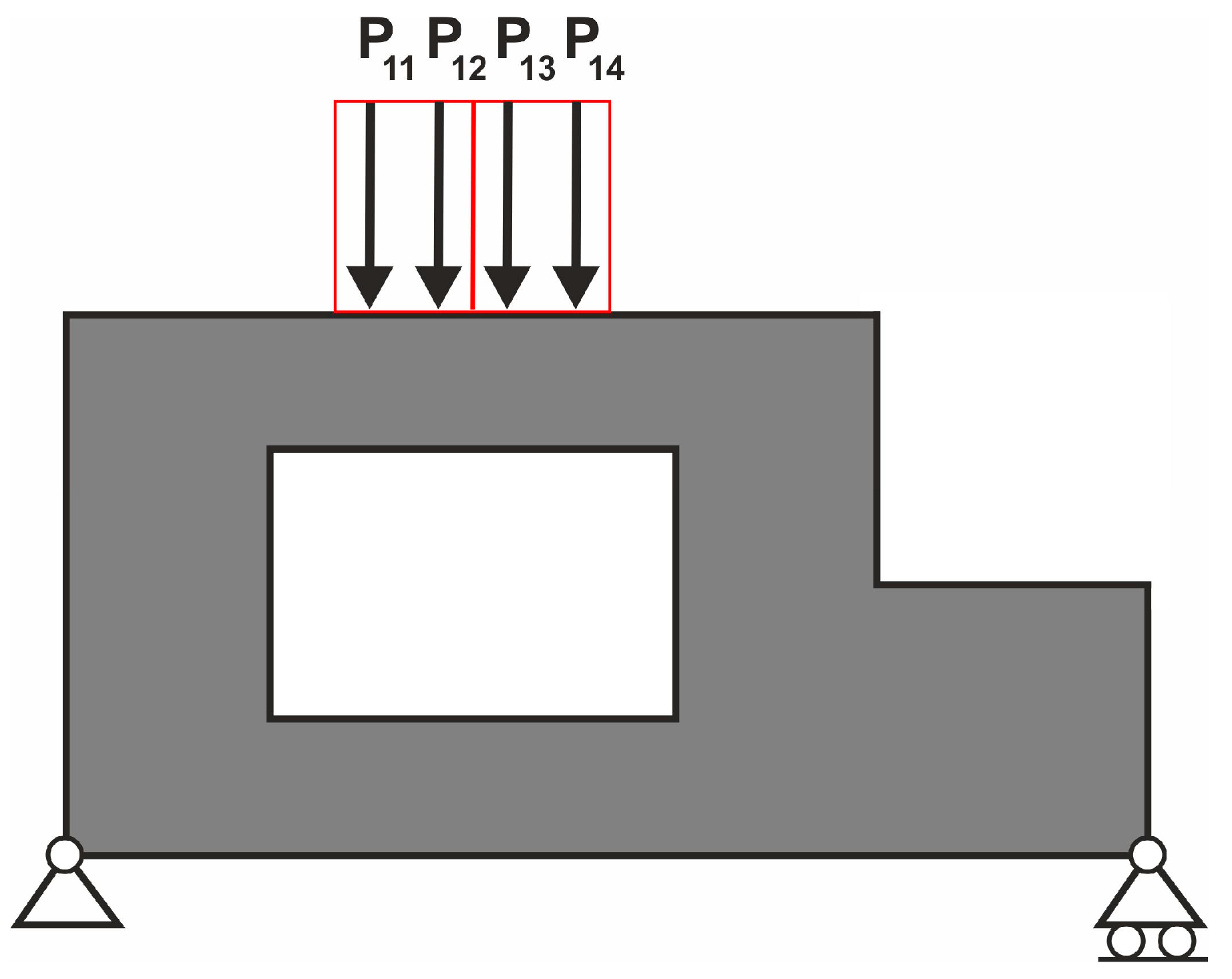
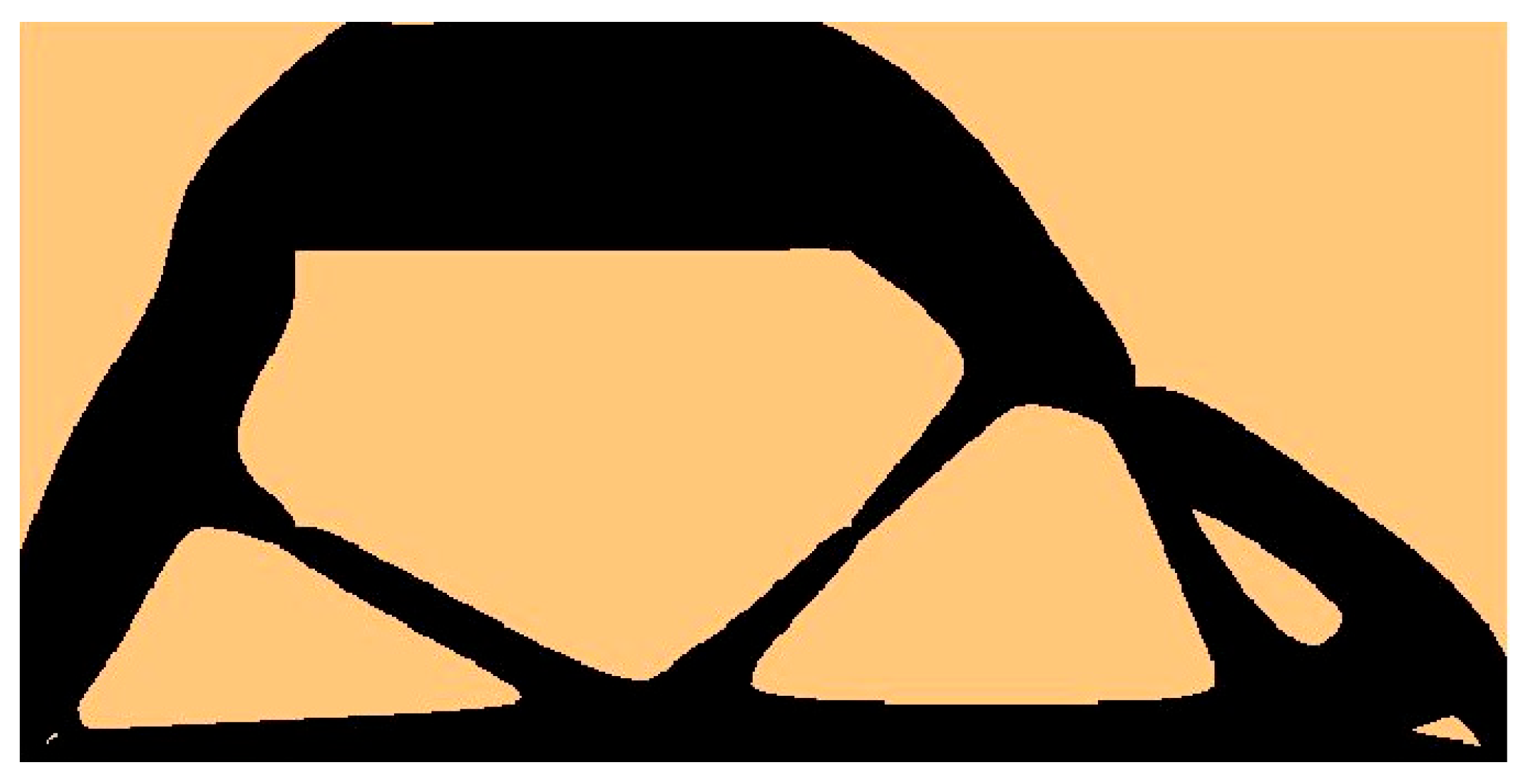
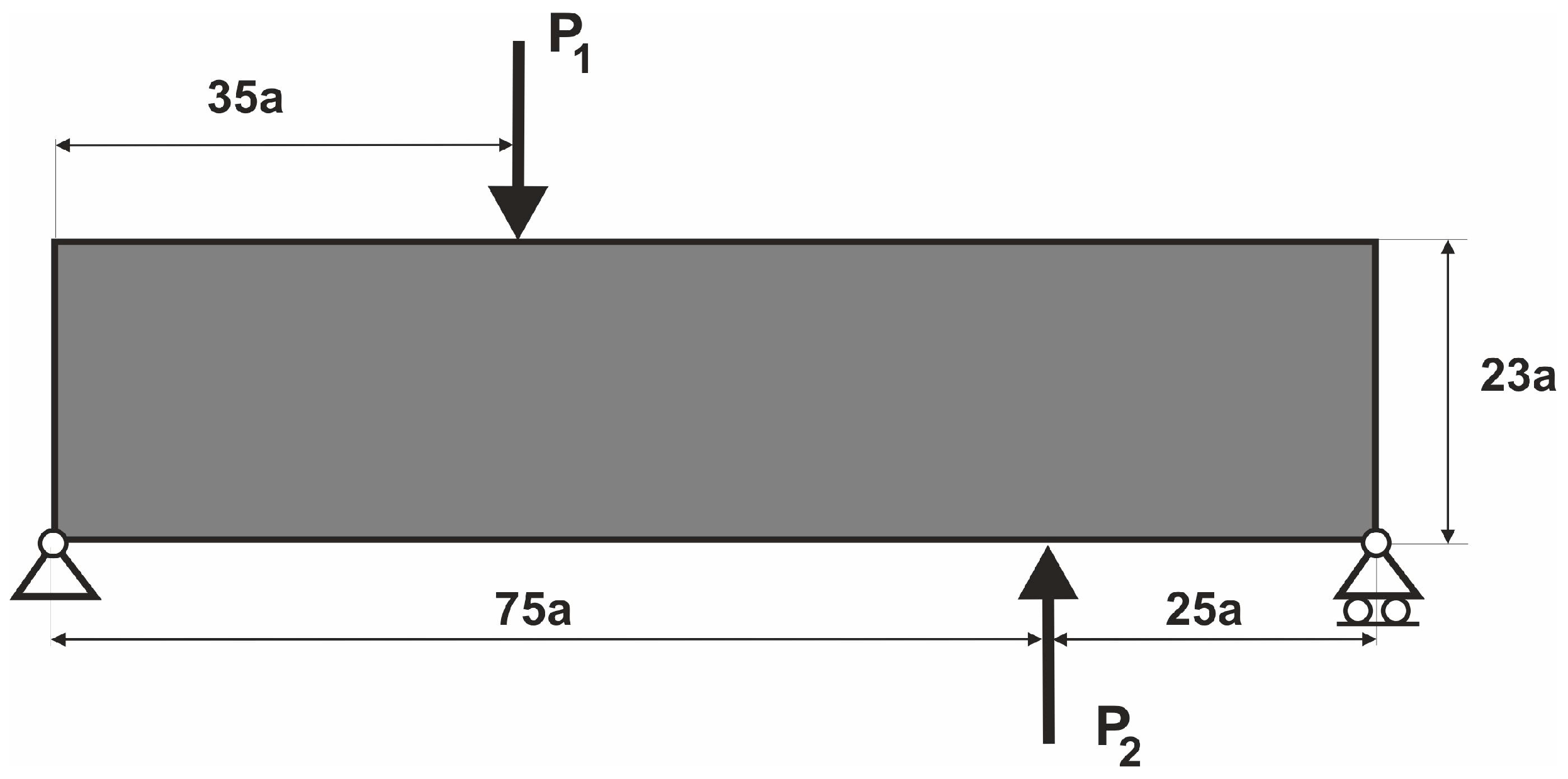





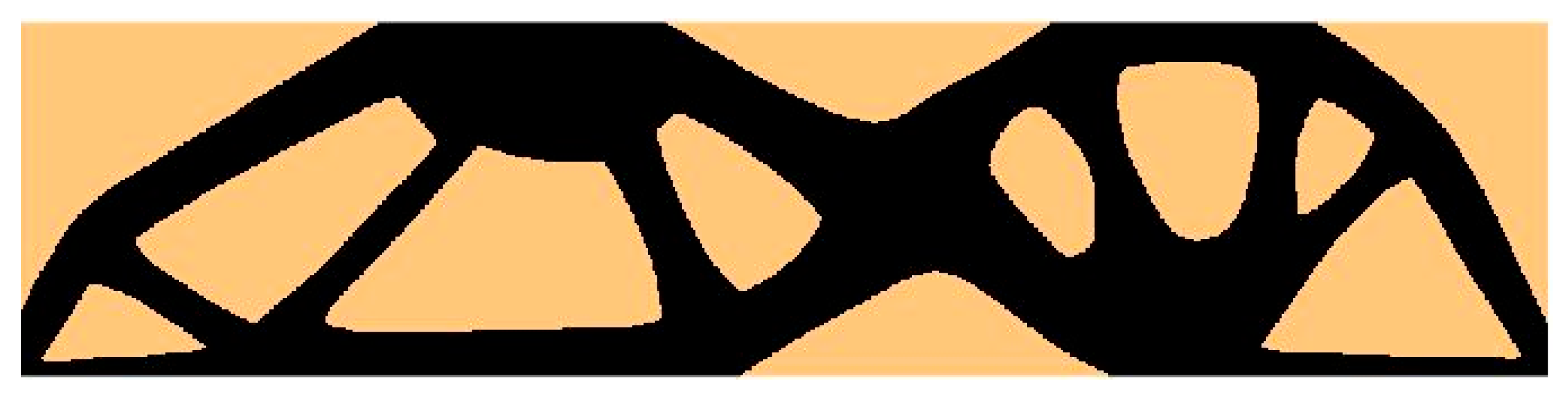







| Structure | Compliance: Multi-Load, Stochastic | Compliance: ELS | Percentage Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Test structure 1 | 26.9596 Nmm | 26.9634 Nmm | 0.01% |
| Test structure 2 | 21.3801 Nmm | 21.3098 Nmm | 0.33% |
| Test structure 3 (P1) | 30.9170 Nmm | 30.7509 Nmm | 0.54% |
| Test structure 3 (P2) | 28.8550 Nmm | 28.7781 Nmm | 0.27% |
| Test structure 3 (P1 + P2) | 31.6918 Nmm | 31.1125 Nmm | 1.83% |
| Test structure 4 | 16.1655 Nmm | 16.0927 Nmm | 0.45% |
| Brake pedal | 13,958.7614 Nmm | 14,004.6986 Nmm | 0.33% |
| Lever arm (3D) | 6.8320 Nmm | 6.6736 Nmm | 2.3% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bochenek, B.; Tajs-Zielińska, K. A Concept of Equivalent Load Scheme for Easy Prediction of Structural Topology When Load Position Changes Randomly. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212294
Bochenek B, Tajs-Zielińska K. A Concept of Equivalent Load Scheme for Easy Prediction of Structural Topology When Load Position Changes Randomly. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212294
Chicago/Turabian StyleBochenek, Bogdan, and Katarzyna Tajs-Zielińska. 2025. "A Concept of Equivalent Load Scheme for Easy Prediction of Structural Topology When Load Position Changes Randomly" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212294
APA StyleBochenek, B., & Tajs-Zielińska, K. (2025). A Concept of Equivalent Load Scheme for Easy Prediction of Structural Topology When Load Position Changes Randomly. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12294. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212294






