Shortened Acquisition Duration for Brain Tumor 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography on Silicon Photomultiplier Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
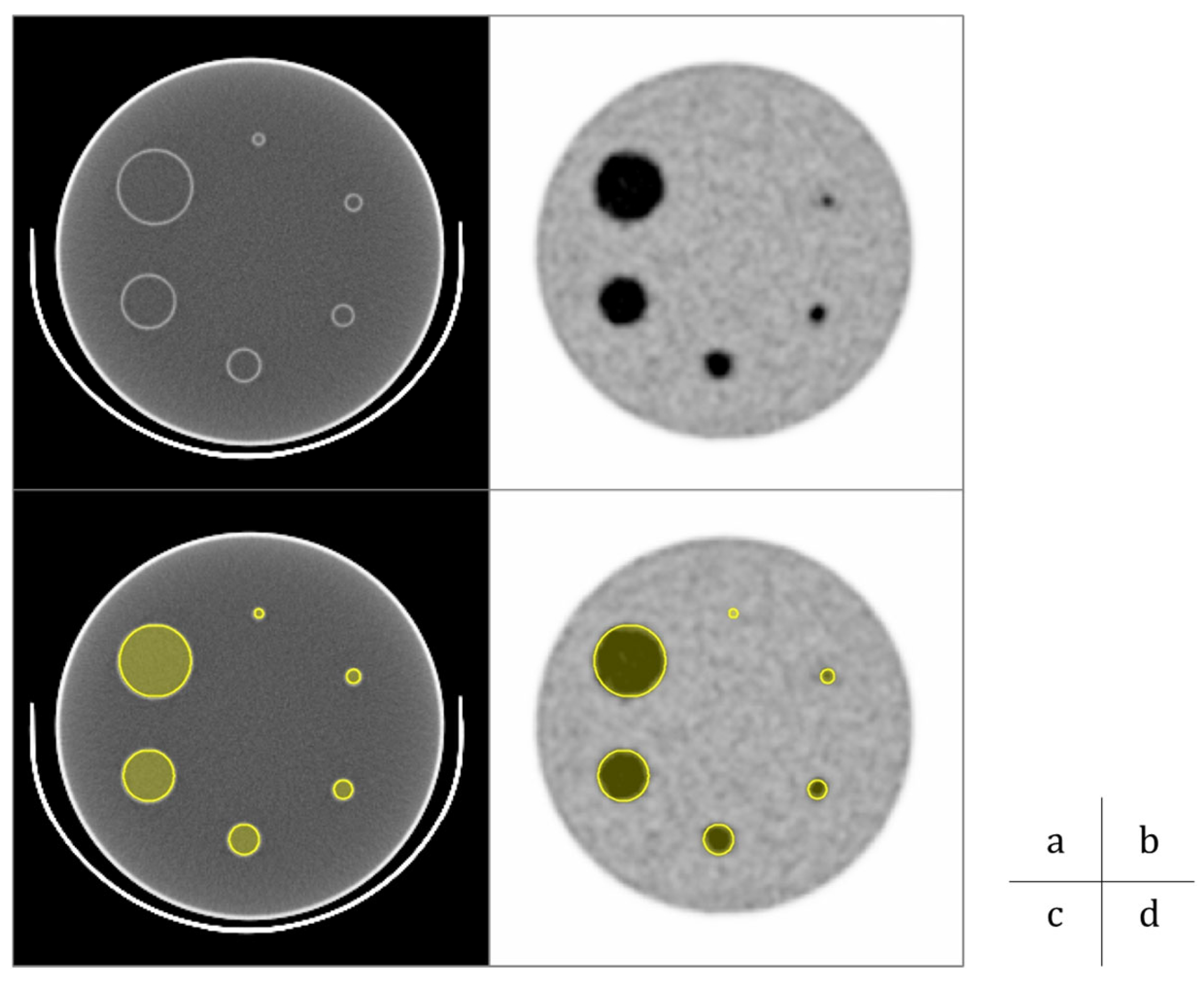
2.1. Phantom Study
- Data Acquisition and Image Reconstruction
- -
- Reconstruction with PSF: Ordered subset expectation maximization algorithm with PSF correction and time-of-flight (TOF) technique using five iterations and five subsets.
- -
- Reconstruction without PSF: Ordered subset expectation maximization algorithm with the TOF technique using three iterations and five subsets.
- Data Analysis
2.2. Clinical Studies
- Data Acquisition and Image Reconstruction
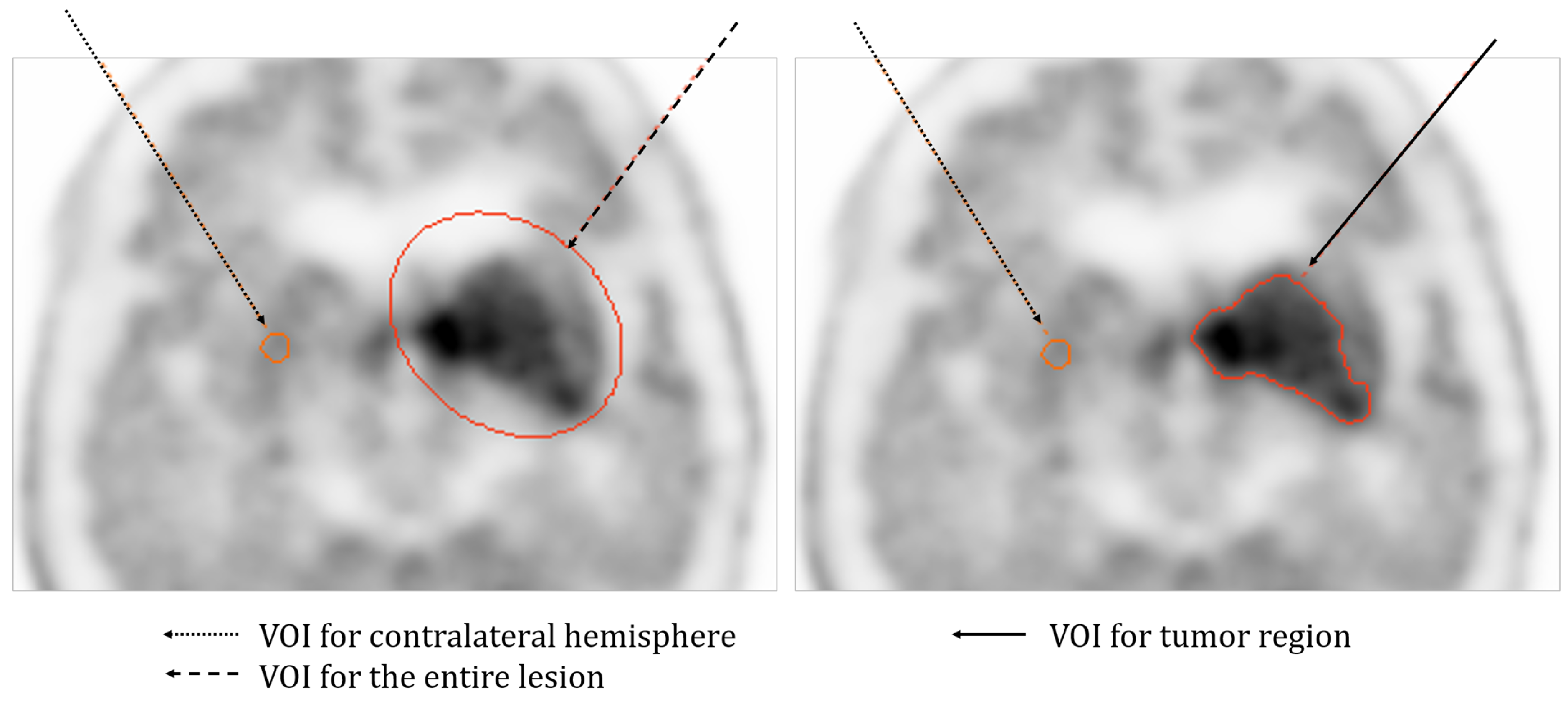
- Data Analysis
- Visual Assessment
- Statistical Analysis
3. Results
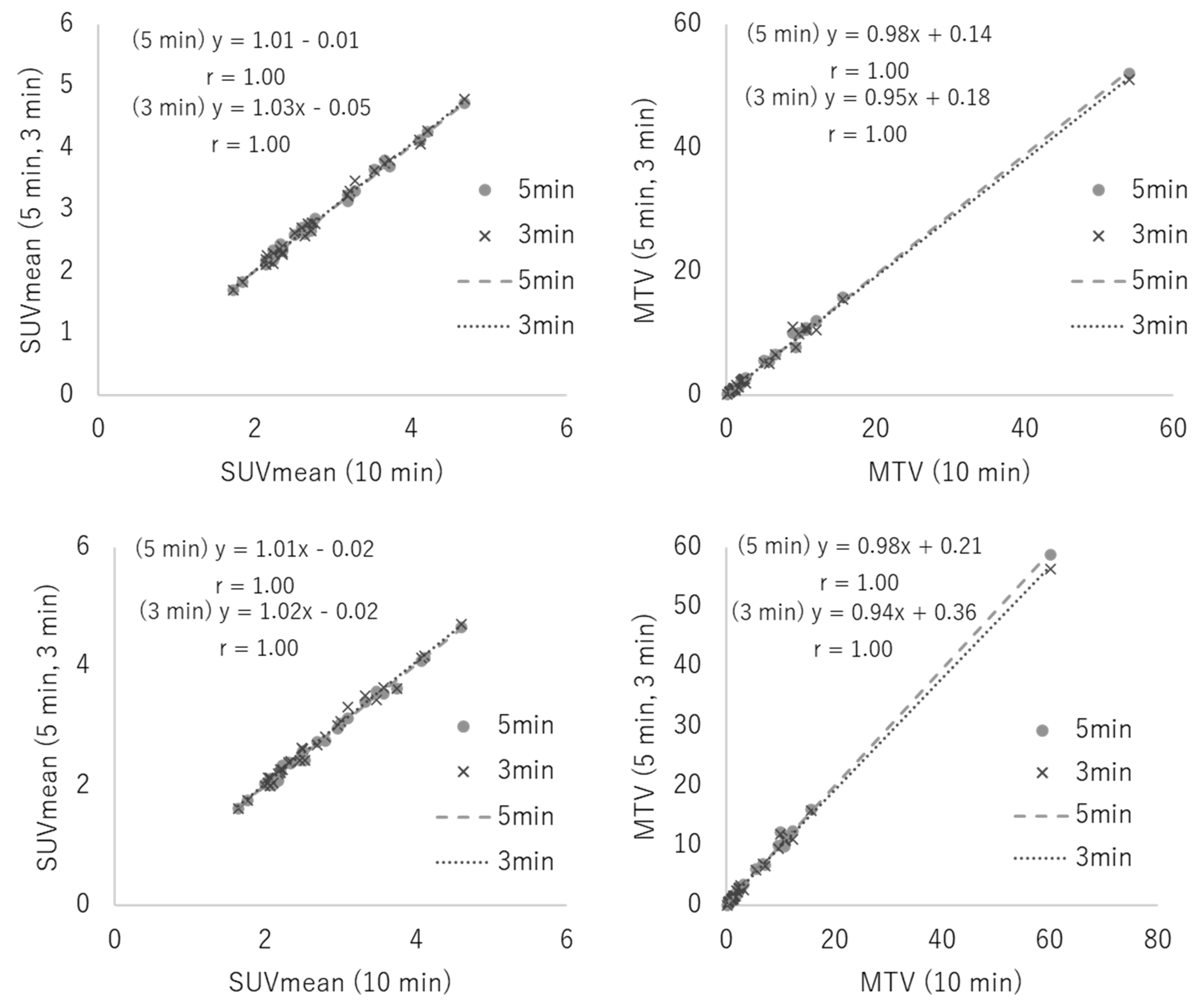
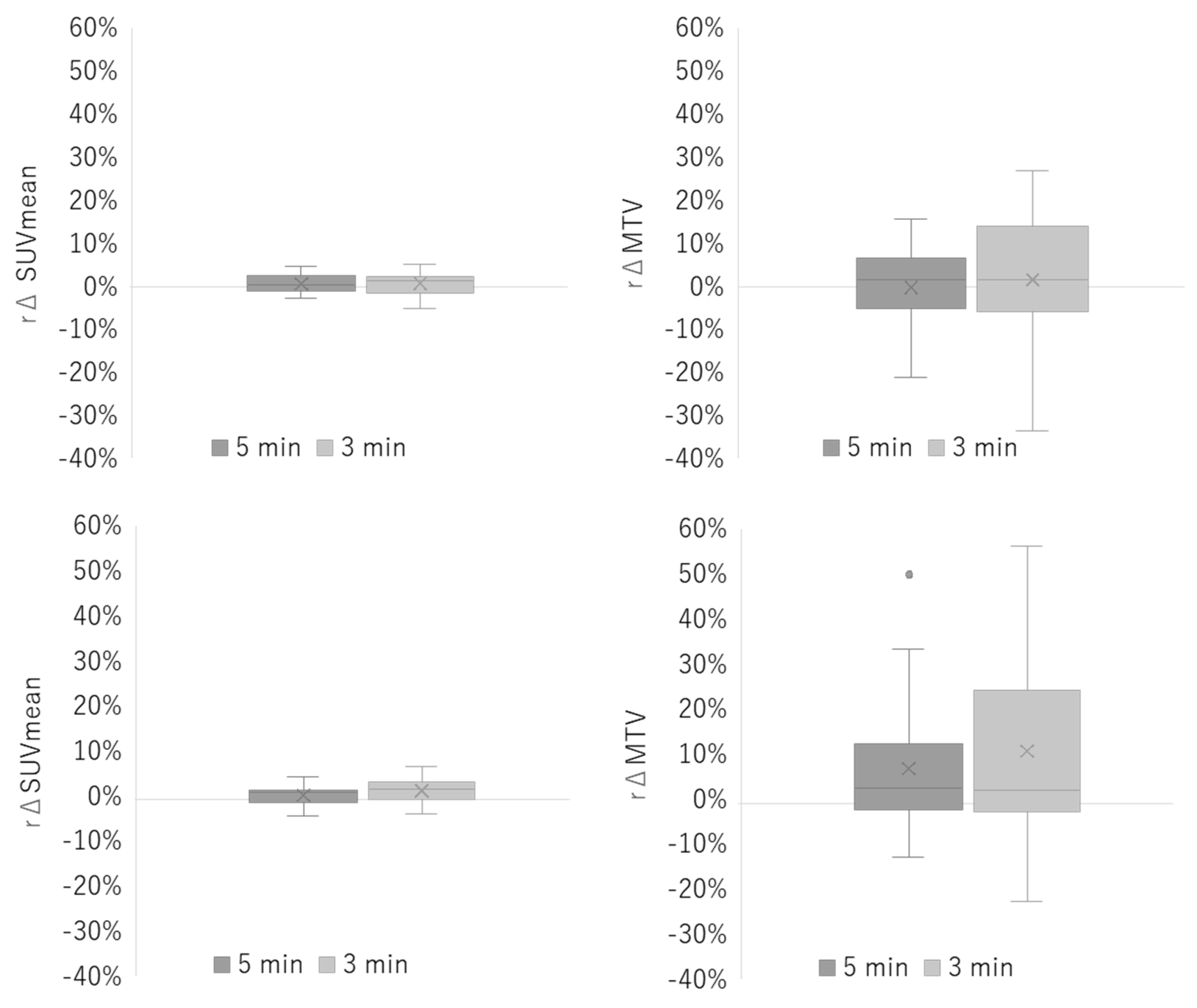
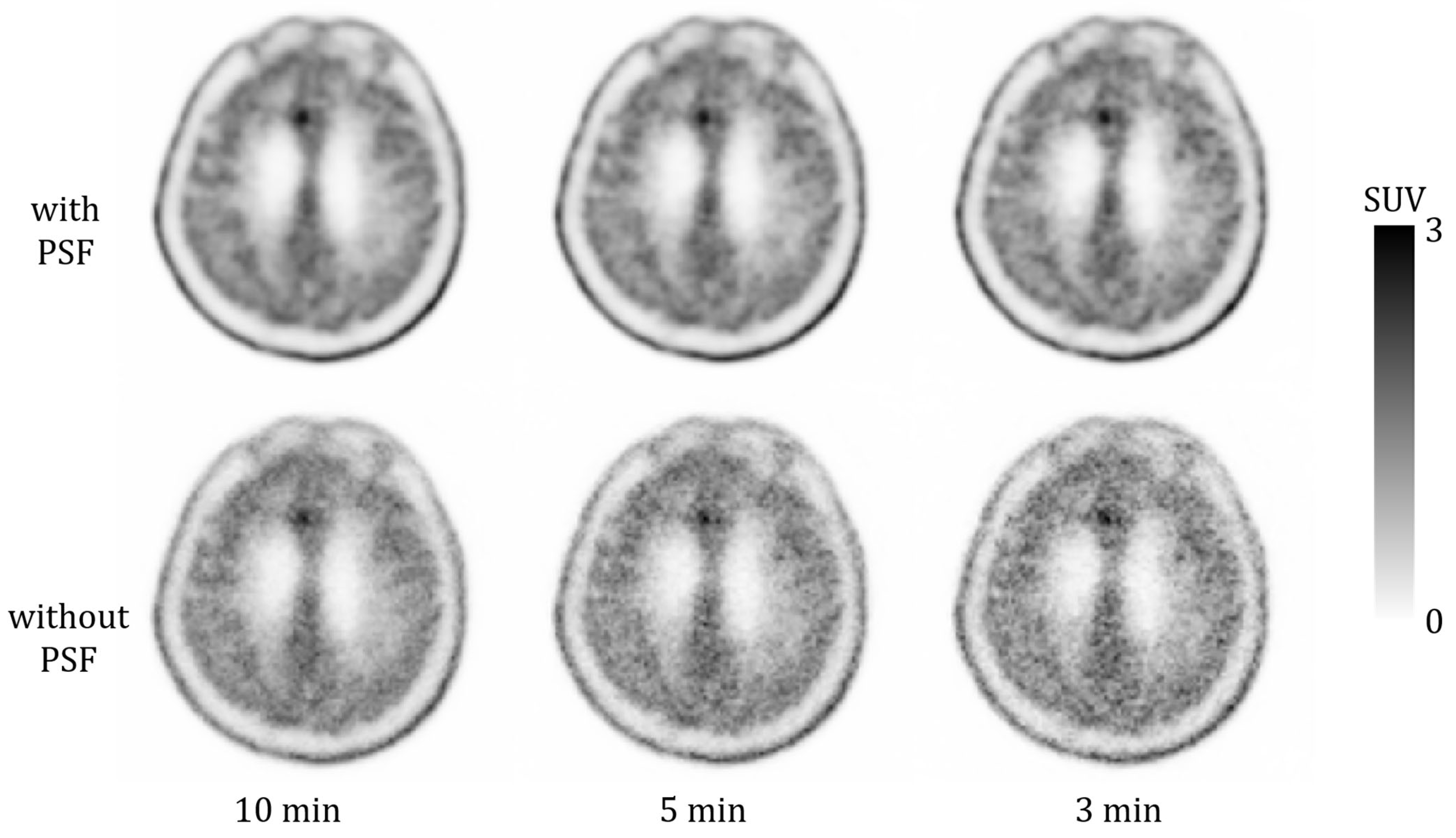
3.1. Phantom Study
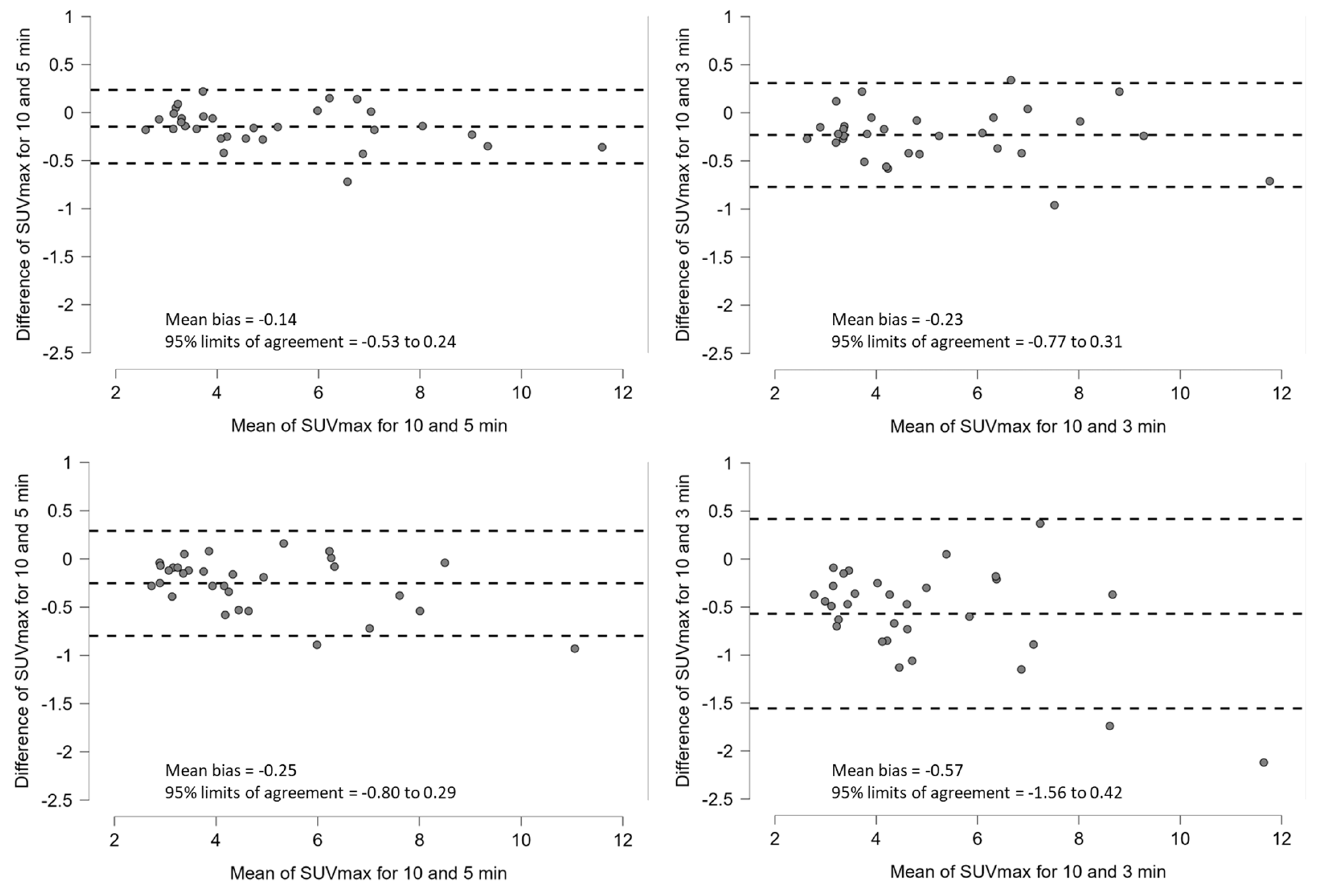
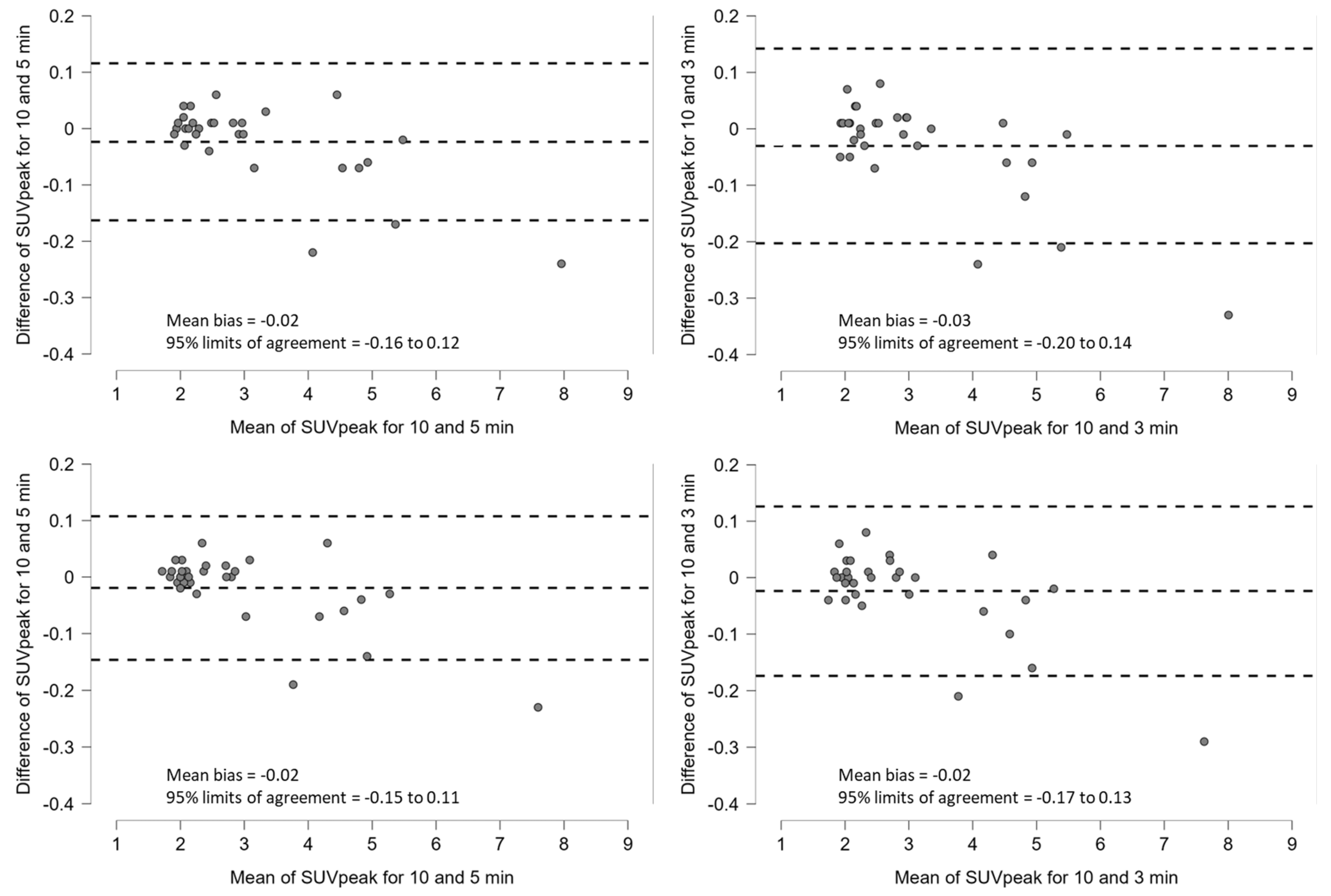
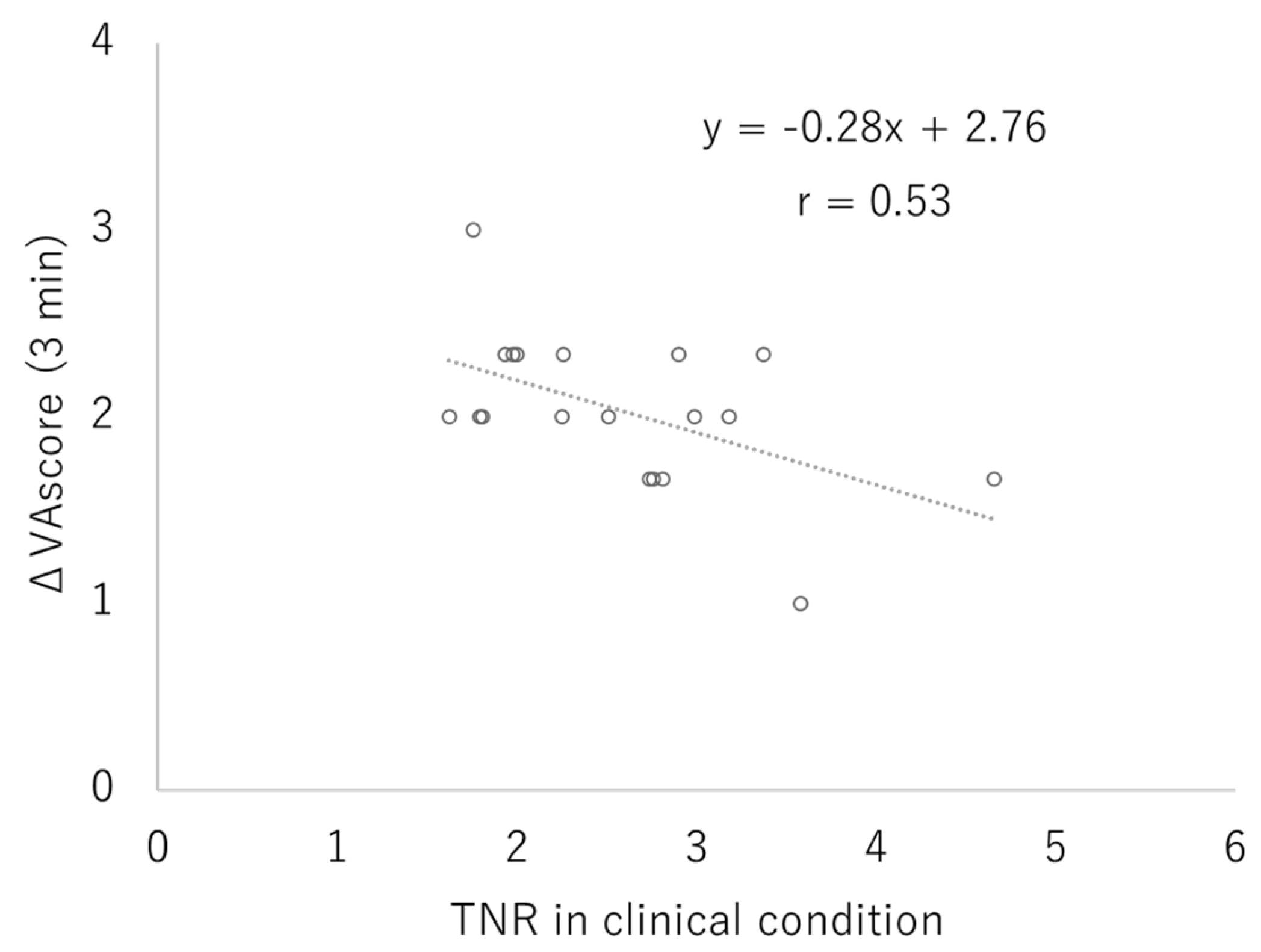
3.2. Clinical Study
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 18F-FDG | 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose |
| PET | Positron Emission Tomography |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| SNR | Signal-to-Noise Ratio |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| SiPM | Silicon Photomultiplier |
| PMT | Photomultiplier Tube |
| JSNM | Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine |
| PSF | Point Spread Function |
| SUV | Standardized Uptake Value |
| SUVmax | Maximum Standardized Uptake Value |
| SUVmean | Mean Standardized Uptake Value |
| SUVpeak | Peak Standardized Uptake Value |
| MTV | Metabolic Tumor Volume |
| VOI | Volume of Interest |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
| TNR | Tumor-to-Normal Ratio |
| OSEM | Ordered Subset Expectation Maximization |
| TOF | Time-of-Flight |
| AMIDE | A Medical Image Data Examiner (software) |
Appendix A
References
- Singhal, T.; Narayanan, T.K.; Jain, V.; Mukherjee, J.; Mantil, J. 11C-L-methionine positron emission tomography in the clinical management of cerebral gliomas. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2008, 10, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J. A meta-analysis on the diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine PET for differentiating brain tumors. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2014, 35, 1058–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.K.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, S.K.; Lee, Y.J.; Paek, S.; Yeo, J.S.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, D.S.; Jung, H.W.; Lee, M.C. Usefulness of 11C-methionine PET in the evaluation of brain lesions that are hypo- or isometabolic on 18F-FDG PET. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2002, 29, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirotte, B.; Goldman, S.; Massager, N.; David, P.; Wikler, D.; Vandesteene, A.; Salmon, I.; Brotchi, J.; Levivier, M. Comparison of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine for PET-guided stereotactic brain biopsy of gliomas. J. Nucl. Med. 2004, 45, 1293–1298. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stefano, A.; Leal, A.; Richiusa, S.; Trang, P.; Comelli, A.; Benfante, V.; Cosentino, S.; Sabini, M.G.; Tuttolomondo, A.; Altieri, R.; et al. Robustness of PET radiomics features: Impact of co-registration with MRI. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, N.L.; Weller, M.; Suchorska, B.; Galldiks, N.; Soffietti, R.; Kim, M.M.; la Fougère, C.; Pope, W.; Law, I.; Arbizu, J.; et al. Response Assessment in Neuro-Oncology working group and European Association for Neuro-Oncology recommendations for the clinical use of PET imaging in gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2016, 18, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceyssens, S.; Van Laere, K.; de Groot, T.; Goffin, J.; Bormans, G.; Mortelmans, L. [11C]methionine PET, histopathology, and survival in primary brain tumors and recurrence. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2006, 27, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar]
- Tsuyuguchi, N.; Sunada, I.; Iwai, Y.; Yamanaka, K.; Tanaka, K.; Takami, T.; Otsuka, Y.; Sakamoto, S.; Ohata, K.; Goto, T.; et al. Methionine positron emission tomography of recurrent metastatic brain tumor and radiation necrosis after stereotactic radiosurgery: Is a differential diagnosis possible? J. Neurosurg. 2003, 98, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaerts, C.W.; van Dijken, B.R.; Stormezand, G.N.; van der Weide, H.L.; Wagemakers, M.; Enting, R.H.; van der Hoorn, A. 11C-methyl-L-methionine PET measuring parameters for the diagnosis of tumour progression against radiation-induced changes in brain metastases. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20210275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momose, T.; Nariai, T.; Kawabe, T.; Inaji, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Watanabe, S.; Maehara, T.; Oda, K.; Ishii, K.; Ishiwata, K.; et al. Clinical benefit of 11C methionine PET imaging as a planning modality for radiosurgery of previously irradiated recurrent brain metastases. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 39, 939–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miwa, K.; Shinoda, J.; Yano, H.; Okumura, A.; Iwama, T.; Nakashima, T.; Sakai, N. Discrepancy between lesion distributions on methionine PET and MR images in patients with glioblastoma multiforme: Insight from a PET and MR fusion image study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, K.; Gatterbauer, B.; Becherer, A.; Paul, M.; Kletter, K.; Prayer, D.; Hoeftberger, R.; Hainfellner, J.; Asenbaum, S.; Knosp, E. Surgical target selection in cerebral glioma surgery: Linking methionine (MET) PET image fusion and neuronavigation. Minim. Invasive Neurosurg. 2007, 50, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinto, S.; Caribé, P.; Sebastião Matushita, C.; Bromfman Pianta, D.; Narciso, L.; da Silva, A.M.M. Aiming for [18F]FDG-PET acquisition time reduction in clinical practice for neurological patients. Phys. Med. 2023, 112, 102604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, S.; Ahmed, N.; Gnanasegaran, G.; Musbah, A.; Al Kandari, F.; Van den Wyngaert, T. 18F-NaF PET/CT of obese patients on a lutetium-yttrium oxyorthosilicate PET/CT system: Patient dosimetry, optimization of injected activity, and acquisition time. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2021, 49, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaimoto, Y.; Fukushima, K.; Kanaya, K.; Asanuma, M.; Aoba, K.; Yamamoto, A.; Nakao, R.; Kaneko, K.; Nagao, M.; Chida, K. Optimization of intraventricular radioactive concentration for 13N ammonia PET with time-of-flight scanner: Simplified phantom study with noise equivalent count rate analysis. Ann. Nucl. Cardiol. 2023, 9, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japanese Society of Nuculear Medicine. Standard PET Imaging Protocols and Phantom Test Procedures and Criteria: Executive Summary; Japanese Society of Nuclear Medicine: Tokyo, Japan, 2017; Available online: https://jsnm.org/wp_jsnm/wp-content/themes/theme_jsnm/doc/StandardPETProtocolPhantom20170201.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- van Sluis, J.; de Jong, J.; Schaar, J.; Noordzij, W.; van Snick, P.; Dierckx, R.; Borra, R.; Willemsen, A.; Boellaard, R. Performance characteristics of the digital Biograph Vision PET/CT system. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sluis, J.; Boellaard, R.; Somasundaram, A.; van Snick, P.H.; Borra, R.J.H.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Stormezand, G.N.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Noordzij, W. Image quality and semiquantitative measurements on the Biograph Vision PET/CT system: Initial experiences and comparison with the Biograph mCT. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlier, T.; Ferrer, L.; Conti, M.; Bodet-Milin, C.; Rousseau, C.; Bercier, Y.; Bendriem, B.; Kraeber-Bodéré, F. From a PMT-based to a SiPM-based PET system: A study to define matched acquisition/reconstruction parameters and NEMA performance of the Biograph Vision 450. EJNMMI Phys. 2020, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sluis, J.; Boellaard, R.; Dierckx, R.A.J.O.; Stormezand, G.N.; Glaudemans, A.W.J.M.; Noordzij, W. Image quality and qctivity optimization in oncologic 18F-FDG PET using the digital Biograph Vision PET/CT System. J. Nucl. Med. 2020, 61, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberts, I.; Sachpekidis, C.; Prenosil, G.; Viscione, M.; Bohn, K.P.; Mingels, C.; Shi, K.; Ashar-Oromieh, A.; Rominger, A. Digital PET/CT allows for shorter acquisition protocols or reduced radiopharmaceutical dose in [18F]-FDG PET/CT. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2021, 35, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, M.; Jentzen, W.; Hofferber, R.; Herrmann, K.; Fendler, W.P.; Rischpler, C.; Umutlu, L.; Conti, M.; Costa, P.F.; Sraieb, M.; et al. Evaluation of 18F-FDG PET/CT images acquired with a reduced scan time duration in lymphoma patients using the digital biograph vision. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inomata, T.; Sato, K.; Ibaraki, M.; Kominami, M.; Kinoshita, F.; Shinohara, Y.; Kato, M.; Kinoshita, T. Evaluation of low-dose whole-body FDG PET with SiPM-based PET/CT Scanner: Visual and semi-quantitative analyses using random sampling from full-dose scan data (in Japanese). Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi 2023, 79, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morimoto, M.; Kudomi, N.; Maeda, Y.; Kobata, T.; Oishi, A.; Matsumoto, K.; Monden, T.; Iwasaki, T.; Mitamura, K.; Norikane, T.; et al. Effect of quantitative values on shortened acquisition duration in brain tumor 11C-methionine PET/CT. EJNMMI Phys. 2021, 8, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekari, M.; Ghafarian, P.; Ahangari, S.; Ay, M.R. Quantification of the impact of TOF and PSF on PET images using the noise-matching concept: Clinical and phantom study. Nucl. Sci. Tech. 2017, 28, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, G.; Ishikawa, K.; Mitsumoto, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Ohya, N.; Baba, S.; Abe, K.; Sasaki, M. Improvement in PET/CT image quality with a combination of point-spread function and time-of-flight in relation to reconstruction parameters. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1716–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.L. Gibbs artifact reduction by nonnegativity constraint. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2011, 39, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, D.L.; Miller, M.I.; Thomas, L.J.; Politte, D.G. Noise and edge artifacts in maximum-likelihood reconstructions for emission tomography. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1987, 6, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasnon, C.; Desmonts, C.; Quak, E.; Gervais, R.; Do, P.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; Aide, N. Harmonizing SUVs in multicentre trials when using different generation PET systems: Prospective validation in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 40, 985–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutsui, Y.; Awamoto, S.; Himuro, K.; Umezu, Y.; Baba, S.; Sasaki, M. Edge artifacts in point spread function-based PET reconstruction in relation to object size and reconstruction parameters. Asia Ocean. J. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2017, 5, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, G.C.; Galla, N.; Ferraro, R.; Kovanlikaya, I. The added prognostic value of metabolic tumor size on FDG-PET at first suspected recurrence of glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neuroimaging 2017, 27, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.R.; Green, S.B.; Shapiro, W.R. The prognostic importance of tumor size in malignant gliomas: A computed tomographic scan study by the Brain Tumor Cooperative Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 1988, 6, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Shen, L.; Huang, X.; Zhang, G. Maximal tumor diameter in the preoperative tumor magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2 image is associated with prognosis of Grade II Glioma. Medicine 2021, 100, e24850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Arita, H.; Okita, Y.; Chiba, Y.; Kagawa, N.; Fujimoto, Y.; Kishima, H.; Kanemura, Y.; Nonaka, M.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of 11C-Methionine PET for nonenhancing gliomas. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninatti, G.; Sollini, M.; Bono, B.; Gozzi, N.; Fedorov, D.; Antunovic, L.; Gelardi, F.; Navarria, P.; Politi, L.S.; Pessina, F.; et al. Preoperative [11C]methionine PET to personalize treatment decisions in patients with lower-grade gliomas. Neuro Oncol. 2022, 24, 1546–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajo, K.; Uda, T.; Kawashima, T.; Terakawa, Y.; Ishibashi, K.; Tsuyuguchi, N.; Tanoue, Y.; Nagahama, A.; Uda, H.; Koh, S.; et al. Maximum 11C-methionine PET uptake as a prognostic imaging biomarker for newly diagnosed and untreated astrocytic glioma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibaraki, M.; Matsubara, K.; Shinohara, Y.; Shidahara, M.; Sato, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kinoshita, T. Brain partial volume correction with point spreading function reconstruction in high-resolution digital PET: Comparison with an MR-based method in FDG imaging. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2022, 36, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibaraki, M.; Shinohara, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Sato, K.; Ohmura, T.; Yamamoto, H.; Kinoshita, T. Arrival time mapping with 15O-gas PET for cerebrovascular steno-occlusive diseases: A comparative study with CT perfusion. EJNMMI Res. 2025, 15, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, Y.; Ibaraki, M.; Matsubara, K.; Sato, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Kinoshita, T. Visualization of small brain nuclei with a high-spatial resolution, clinically available whole-body PET scanner. Ann. Nucl. Med. 2024, 38, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loening, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S. AMIDE: A free software tool for multimodality medical image analysis. Mol. Imaging 2003, 2, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kracht, L.W.; Miletic, H.; Busch, S.; Jacobs, A.H.; Voges, J.; Hoevels, M.; Klein, J.C.; Herholz, K.; Heiss, W.D. Delineation of brain tumor extent with [11C]L-methionine positron emission tomography: Local comparison with stereotactic histopathology. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 7163–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, M.Y.; Paeng, J.C.; Cheon, G.J.; Lee, D.S.; Chung, J.K.; Kim, E.E.; Kang, K.W. Prognostic value of metabolic tumor volume on 11C-Methionine PET in predicting progression-free survival in high-grade glioma. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 49, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonni, I.; Baratto, L.; Park, S.; Hatami, N.; Srinivas, S.; Davidzon, G.; Gambhir, S.S.; Iagaru, A. Initial experience with a SiPM-based PET/CT scanner: Influence of acquisition time on image quality. EJNMMI Phys. 2018, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JASP Team. JASP (Version 0.95.4) [Computer Software]; JASP Team: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024. Available online: https://jasp-stats.org/ (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Uda, T.; Tsuyuguchi, N.; Terakawa, Y.; Takami, T.; Ohata, K. Evaluation of the accumulation of 11C-methionine with standardized uptake value in the normal brain. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodge, M.A.; Chaudhry, M.A.; Wahl, R.L. Noise considerations for PET quantification using maximum and peak standardized uptake value. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 1041–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, G.; Ikari, Y.; Nishida, H.; Nishio, T.; Ohnishi, A.; Maebatake, A.; Sasaki, M.; Senda, M. Influence of statistical fluctuation on reproducibility and accuracy of SUVmax and SUVpeak: A phantom study. J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2015, 43, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, A.; Lacoeuille, F.; Fosse, P.; Vervueren, L.; Cahouet-Vannier, A.; Dabli, D.; Bouchet, F.; Couturier, O. For avid glucose tumors, the SUV peak is the most reliable parameter for [18F]FDG-PET/CT quantification, regardless of acquisition time. EJNMMI Res. 2016, 6, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, M.; Haga, Y.; Sota, M.; Abe, M.; Kaga, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Meguro, T.; Hosoi, Y.; Chida, K. Evaluation of lens doses among medical staff involved in nuclear medicine: Current eye radiation exposure among nuclear-medicine staff. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujisawa, M.; Sota, M.; Haga, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Kataoka, N.; Kato, T.; Kaga, Y.; Abe, M.; Suzuki, M.; Inaba, Y.; et al. Real-time monitoring of occupational radiation exposure in nuclear medicine technologists: An initial study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRP. Radiation dose to patients from radiopharmaceuticals: A compendium of current information related to frequently used substances. ICRP Publ. 2015, 44, 7–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chida, K. What are useful methods to reduce occupational radiation exposure among radiological medical workers, especially for interventional radiology personnel? Radiol. Phys. Technol. 2022, 15, 101–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagehashi, K.; Haga, Y.; Takahira, S.; Tanabe, M.; Nakamura, M.; Sota, M.; Kaga, Y.; Abe, M.; Tada, N.; Chida, K. Evaluation of radiation dose to the lens in interventional cardiology physicians before and after dose limit regulation changes. J. Radiol. Prot. 2024, 44, 031512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chida, K.; Morishima, Y.; Inaba, Y.; Taura, M.; Ebata, A.; Takeda, K.; Shimura, H.; Zuguchi, M. Physician-received scatter radiation with angiography systems used for interventional radiology: Comparison among many X-ray systems. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2012, 149, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
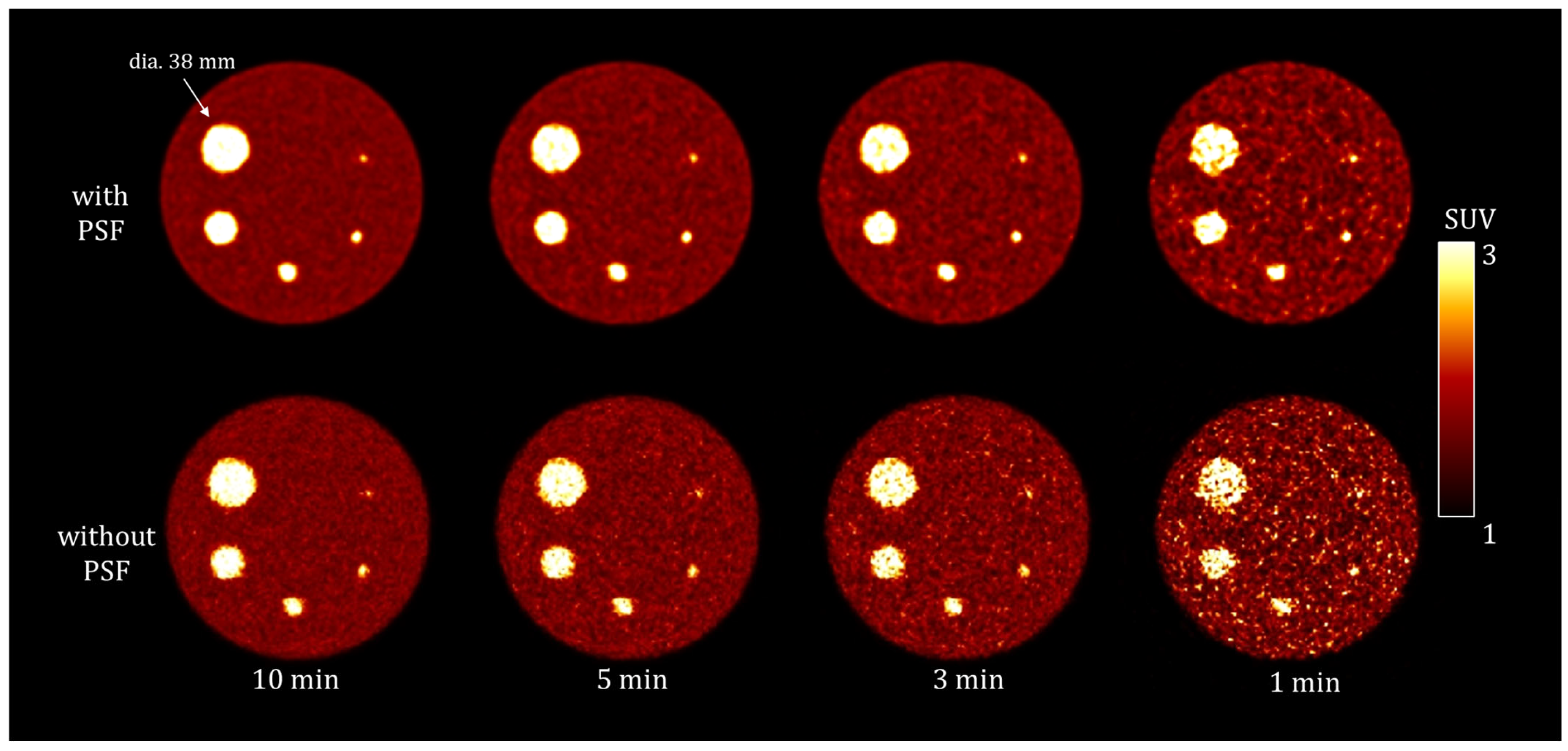
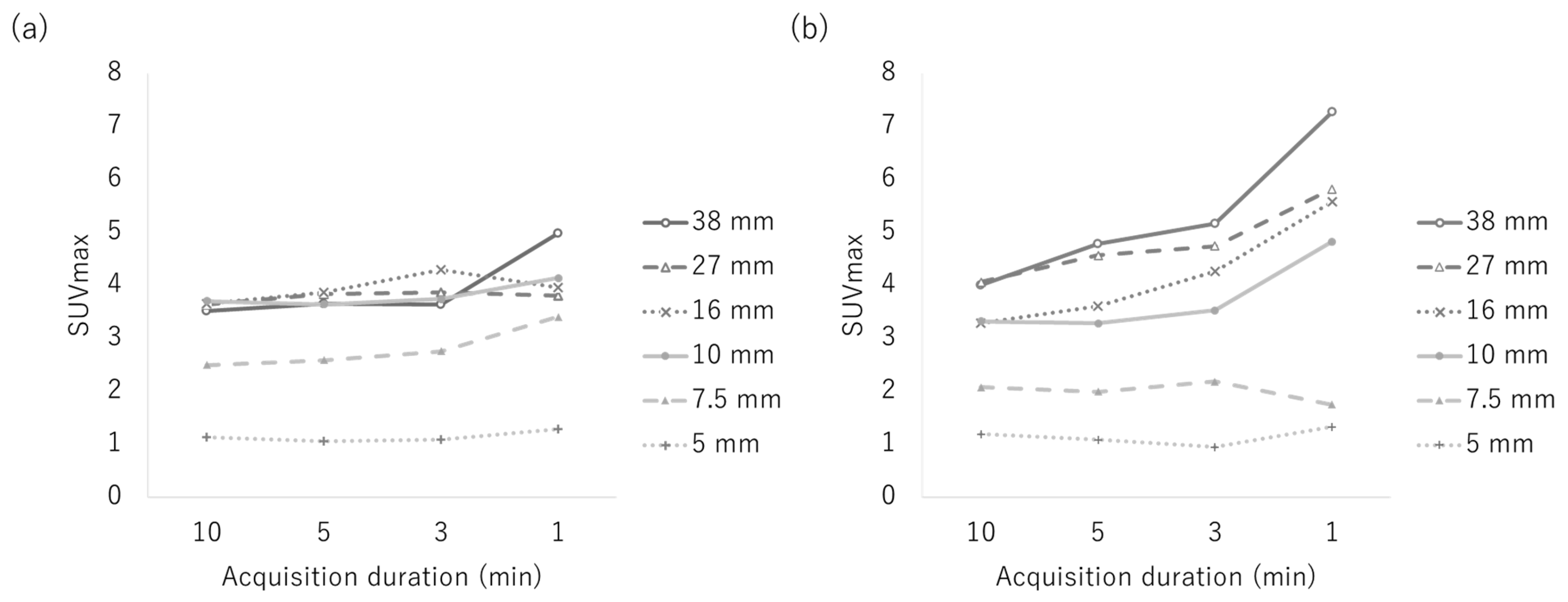
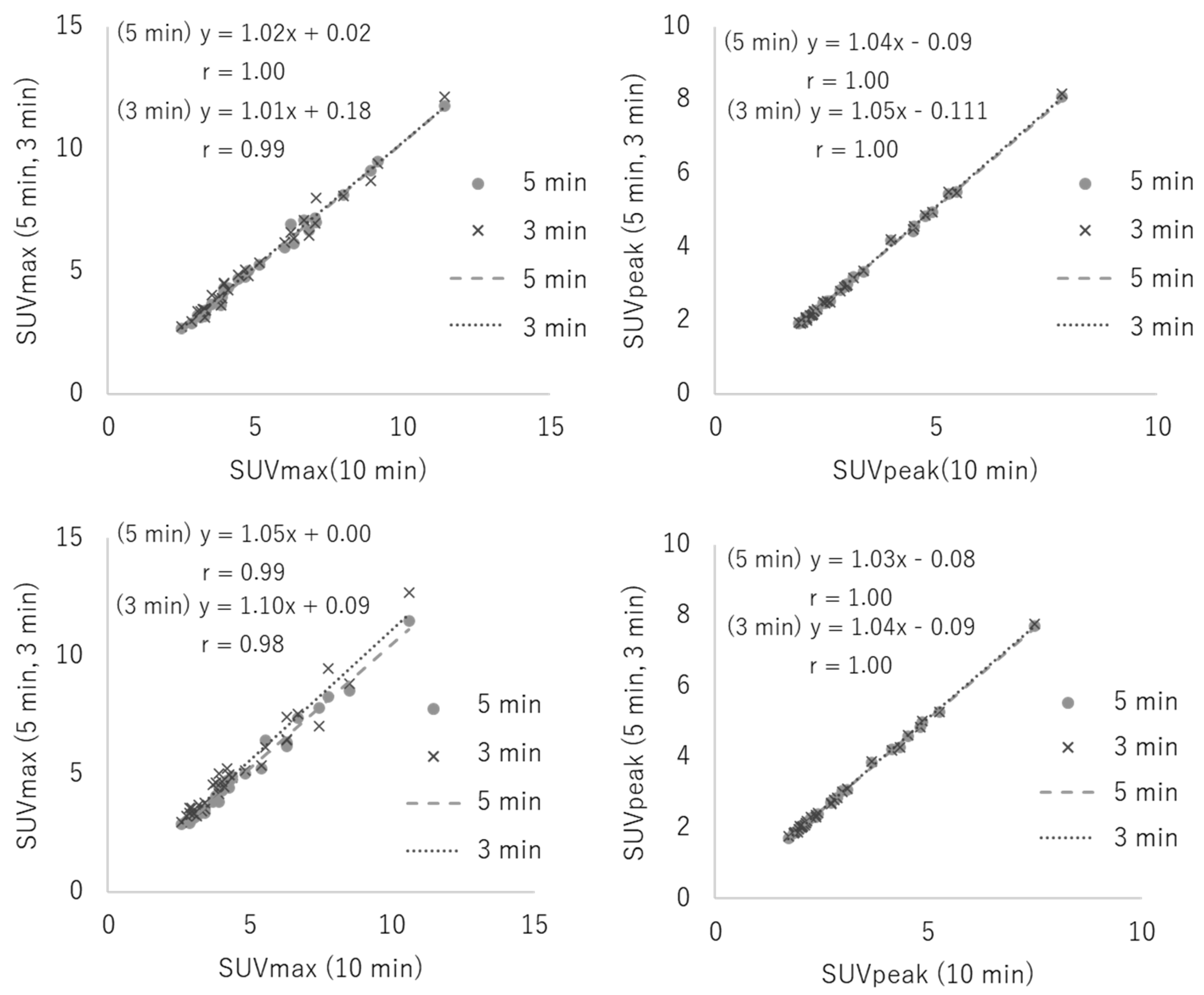
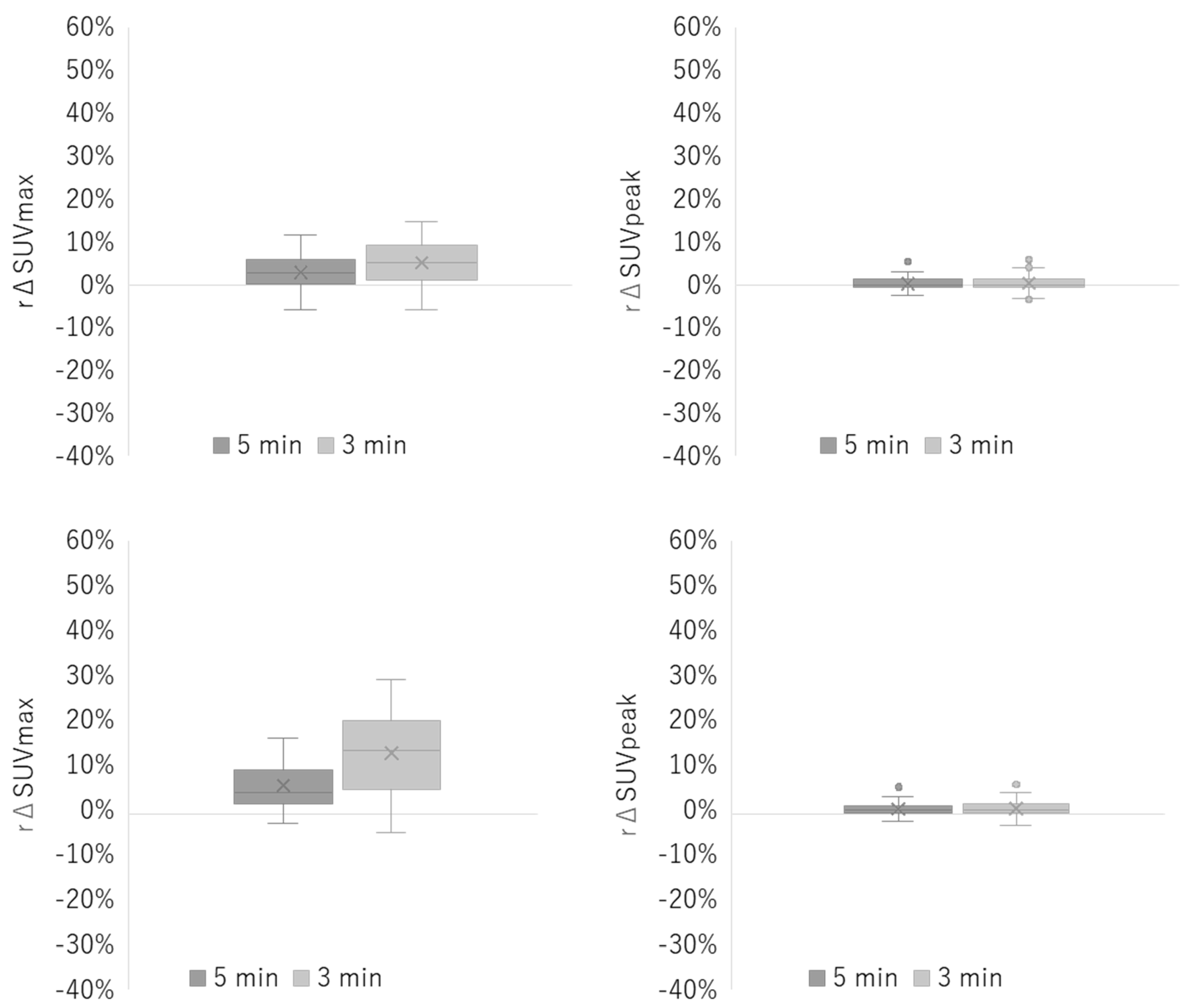
| Reconstruction Condition | Acquisition Duration (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 5 | 3 | |
| with PSF | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| (range) | (reference) | (4–5) | (3–5) |
| without PSF | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| (range) | (2–5) | (1–5) | (1–5) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Inomata, T.; Sato, K.; Ibaraki, M.; Kominami, M.; Shinohara, Y.; Kinoshita, F.; Yamamoto, H.; Kato, M.; Kinoshita, T.; Chida, K. Shortened Acquisition Duration for Brain Tumor 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography on Silicon Photomultiplier Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212292
Inomata T, Sato K, Ibaraki M, Kominami M, Shinohara Y, Kinoshita F, Yamamoto H, Kato M, Kinoshita T, Chida K. Shortened Acquisition Duration for Brain Tumor 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography on Silicon Photomultiplier Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212292
Chicago/Turabian StyleInomata, Takato, Kaoru Sato, Masanobu Ibaraki, Mamoru Kominami, Yuki Shinohara, Fumiko Kinoshita, Hiroyuki Yamamoto, Mamoru Kato, Toshibumi Kinoshita, and Koichi Chida. 2025. "Shortened Acquisition Duration for Brain Tumor 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography on Silicon Photomultiplier Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212292
APA StyleInomata, T., Sato, K., Ibaraki, M., Kominami, M., Shinohara, Y., Kinoshita, F., Yamamoto, H., Kato, M., Kinoshita, T., & Chida, K. (2025). Shortened Acquisition Duration for Brain Tumor 11C-Methionine Positron Emission Tomography on Silicon Photomultiplier Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12292. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212292






