Abstract
Object detection in remote sensing images is still recognized as a demanding task, largely because of significant scale differences among objects and the complexity of background scenes. Detecting small and medium-sized targets within cluttered environments, in particular, continues to challenge many existing algorithms. To address these issues, this study presents a new model named AERIS-ED (Attention-Enhanced Real-time Intelligence System for Efficient Detection). The framework adopts a C3 (Cross Stage Partial with three convolutions) based backbone and incorporates Efficient Attention (EA) units, but unlike conventional designs, these modules are inserted only at the P3 and P4 levels of the feature pyramid. This focused integration enables richer feature interaction across scales and enhances the recognition of small and medium objects. Comprehensive experiments on the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets highlight the benefits of the proposed approach. On MAR20, the model achieves a mean Average Precision at an Intersection over Union threshold of 0.5 (mAP@0.5) of 95.1% with an inference latency of only 3.8 ms/img. On VEDAI, it secures 83.0% mAP@0.5 while maintaining the same efficiency, thereby confirming its suitability for real-time applications. Overall, the results indicate that AERIS-ED strengthens detection accuracy for small objects without compromising computational speed. These improvements suggest that the architecture is not only promising for multi-scale detection research but also has strong potential in practical remote sensing tasks.
1. Introduction
1.1. Overview
Object detection in remote sensing (RS) imagery remains one of the most challenging problems in modern artificial intelligence and computer vision. The demand for reliable and efficient detection systems is steadily increasing in critical domains such as defense, disaster management, urban planning, and environmental monitoring [1,2]. However, the inherent characteristics of high-resolution imagery including large spatial coverage, scene diversity, variable illumination conditions, and complex background clutter significantly hinder the accurate detection of small and medium scale targets. As widely reported in the literature, small objects consistently exhibit substantially lower detection accuracy compared to larger ones. For instance, evaluations conducted on the Microsoft COCO dataset reveal that the mean accuracy for small objects remains approximately two to three times lower than that of large objects [3]. This performance gap can be attributed to factors such as limited pixel density, the loss of contextual information during sampling, and the tendency of small objects to become easily obscured within cluttered backgrounds.
Detecting small objects is inherently more challenging than detecting larger ones, primarily due to low resolution and the loss of contextual information. The COCO standard is widely employed for evaluating object sizes: small objects (APs) are defined as those with an area smaller than 322 pixels, medium-scale objects (APm) as those between 322 and 962 pixels, and large objects (APl) as those exceeding 962 pixels. This categorization enables a more systematic analysis of performance differences across scales.
In recent years, deep learning-based detectors such as YOLO, Faster R-CNN, and RetinaNet have been widely adopted in both general object detection and remote sensing applications [4]. However, when directly applied to RS scenes, these architectures often suffer from reduced mAP scores for small objects, elevated false negative rates, and limited real-time processing capacity. This underscores the necessity for novel architectures that are scale-aware, computationally efficient, and particularly sensitive to small object detection.
Within this context, attention mechanisms and especially lightweight yet effective methods such as Efficient Attention (EA) have gained prominence. Compared to conventional self-attention mechanisms, EA offers a broader contextual representation at a lower computational cost, thereby facilitating improved learning of small and medium scale objects in conjunction with their surrounding cues. Nevertheless, the commonly adopted attention integration at every level paradigm in the literature substantially increases the number of parameters and computational overhead, leading to significant reductions in frames per second [5,6,7,8]. Therefore, the strategic placement of attention modules solely at critical scale levels emerges as a design choice that optimizes the trade-off between accuracy and efficiency. The AERIS-ED architecture proposed in this study has been developed with these requirements in mind. Built upon a C3 based backbone, the model integrates Efficient Attention modules exclusively at the P3 and P4 levels, thereby delivering substantial performance gains for small- and medium-scale targets. In this way, accuracy is enhanced, parameter overhead remains limited, and real time processing capability is preserved.
The forthcoming experimental analyses evaluate AERIS-ED on the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets to assess potential improvements in detection accuracy and inference efficiency.
1.2. Related Works
The literature on remote sensing (RS) object detection fundamentally revolves around two central questions: how multi-scale representations are constructed, and where as well as how attention mechanisms should be integrated within these representations. Early two-stage approaches, followed by one-stage families (both anchor-based and anchor-free), have addressed RS specific challenges such as scene complexity, pronounced scale variation, and the disappearance of small targets due to aggressive downsampling through pyramid structures including FPN, PANet, and BiFPN. In parallel, channel and/or spatial attention mechanisms (e.g., SE, ECA, CBAM, coordinate/dilated variants), together with Transformer-derived attentions, aim to enhance sensitivity particularly at small and medium scales by learning “which channel and where” to strengthen the signal. However, the common practice of symmetrically inserting attention modules at every pyramid level increases computational cost and often conflicts with real-time constraints.
This study prioritizes placement rather than mere addition of attention. In particular, it seeks to achieve consistent improvements for small- and medium-scale targets without compromising speed by strategically applying a lightweight attention design only at the P3 and P4 levels through single-level (E3/E4) and dual-level (ED) configurations. In this way, the principle shifts from “attention everywhere” to “the right attention at the right level,” thereby jointly optimizing small-object sensitivity and real-time feasibility within RS contexts. Representative studies in the literature include the following:
Fu et al. [3] proposed a YOLOv8-based architecture aimed at enhancing small object sensitivity by combining a Downsample Difference Upsample (DDU) flow with the PNOC attention module. Their evaluations were conducted on VOC07 test and MAR20 datasets. The reported results include mAP@0.5, 75.8% on VOC and an overall mAP, 89.3% on MAR20. Ablation studies on VOC, performed with a 640 × 640 input size and a 100 epoch training protocol, showed that the DDU + PNOC combination achieved the best performance.
Hu et al. [9] introduced a two-stage framework leveraging opticalSAR complementarity. In the first stage, pixel-aligned SAR images are generated from unpaired optical inputs using SFEG, which incorporates physical scattering priors. In the second stage, feature fusion is performed with CFFDNet, DFSC, and GWF units, modeling the differences and complementarities of the two modalities in both spatial and channel dimensions. This framework demonstrates superior performance over unimodal and multimodal baselines on CORS-ADD and MAR20, reporting mAP50 values of 89.57% and 87.63%, respectively.
Xu et al. [10] introduced C2IDet, a single-stage, anchor-free fine-grained airplane detector composed of three components: R2CD (region-internal content interaction), CDFL (class-aware discrete focal loss), and CS3 (cross-shaped sampling space). The model achieved mAP@0.5, 84.16% on MAR20 and mAP@0.5, 88.98% on FAIRPlane11.
Jiang et al. [11] presented MFCANet, an RTMDet-based framework comprising three components: FFCA (focused feature context aggregation), ODCLayer (context enhancement via multi-dimensional dynamic convolution), and MFFM (multi-scale feature fusion). The model achieved mAP, 85.96% on MAR20, mAP 66.28% with near 18.3 FPS on SRSDD, 90.48/97.84 (VOC07/12) on HRSC, and mAP 69.82% on DIOR-R. Reported improvements over baselines were +2.13, +10.28, +1.46, and +1.13 points, respectively.
Wang et al. [12] proposed a two-stage framework for fine-grained oriented object detection, extending the Oriented R-CNN (ResNet-50-FPN) with three additional components: RGAM (relevance-guided attention module) for capturing global context through relevance pooling, CBC (class-balance–aware correction) for addressing class imbalance, and ECL (enhanced contrastive learning) for sharpening inter-class discrimination. Evaluations conducted on FAIR1M and MAR20 reported mAP scores of 46.44% and 85.05%, respectively.
Zhao et al. [13] proposed MMFDet, a detection framework tailored for low-light environments and small-scale targets by integrating both RGB and infrared (IR) data. The system employs a three-stream feature extractor, where RGB, IR, and an early pixel-level fusion branch operate in parallel. To refine the extracted information, it incorporates MDCM, which accounts for inter-modality differences, and HFSHM, which restructures high-level features through a split-and-shuffle mechanism. Evaluation on the VEDAI and Drone Vehicle benchmarks demonstrated clear improvements: MMFDet achieved 77.9% and 82.5% mAP, corresponding to increases of +14.7 and +11.1 points compared with baseline methods. These results suggest that the model can more effectively capture fine details and detect small objects in challenging low-light conditions by explicitly exploiting cross-modal differences.
Wang et al. [14] introduced CM-YOLO, a lightweight detector designed to operate exclusively on infrared (IR) inputs while leveraging RGB–IR pairs during training. The model incorporates a PMT module for IR-to-RGB transformation and an IV-gate module to achieve cross-modal alignment. On the VEDAI dataset, CM-YOLO attained an mAP@50 of 72.5%, outperforming YOLOX-S by +12 points, with an additional +4.1 point gain when the IV-gate was integrated. Furthermore, the approach demonstrated strong generalization on the FLIR dataset.
Similarly, Nie et al. [15] proposed CrossYOLO, a dual-branch architecture that processes RGB and IR images in parallel. By combining CNN and Transformer blocks, the model effectively captures both local and global contextual cues, which are subsequently fused through the CFFIM module at a uniform scale. On the VEDAI dataset, CrossYOLO achieved an mAP of 79.8%, surpassing single-modality YOLOv7 (74.7%) as well as other multi-modal detectors such as SuperYOLO (75.1%) and YOLOFusion (78.6).
Zhang et al. [16] introduced FFCA-YOLO, an architecture built upon YOLOv5 for small-object detection, incorporating simplified downsampling in the backbone and three lightweight modules in the neck. FEM enriches local context, FFM improves multi-scale feature fusion, and SCAM models global relations across spatial and channel dimensions. Evaluations were conducted using mAP50, mAP50:95, and APs for small objects. On the VEDAI dataset, the model achieved mAP50 = 0.748 and APs = 44.6, with additional improvements observed across mAPvt/mAPt/mAPs metrics.
Recently, Zhang et al. [17] proposed the Progressive Sample Selection with Contrastive Loss (PSSCL) framework, which combines robust pre-training and contrastive learning to effectively mitigate overfitting caused by noisy labels, achieving competitive results across multiple computer vision benchmarks.
While recent RS detection frameworks have achieved remarkable progress through multi-scale fusion, attention, and multimodal integration, several methodological limitations persist. Multi-scale pyramids such as FPN and PANet, despite enhancing contextual richness, often degrade small-object representations due to excessive downsampling. Symmetric attention insertion across all pyramid levels, a common practice in CBAM, SE, and Transformer-based variants, introduces redundant computations and may saturate attention responses without proportional accuracy gain. Likewise, multimodal fusion frameworks (e.g., Optical–SAR, RGB–IR) offer complementary cues but suffer from registration complexity, modality imbalance, and increased hardware dependency. Finally, recent transformer-based detectors (e.g., RT-DETR, RF-DETR) provide strong accuracy but remain computationally expensive, limiting real-time feasibility and reproducibility on mid-range GPUs.
To address these limitations, our proposed AERIS-ED emphasizes selective attention placement—restricting attention to critical feature levels (P3–P4)—to jointly preserve sensitivity to small/medium targets and sustain real-time performance. This design shifts the focus from global architectural expansion to targeted efficiency optimization, positioning AERIS-ED as a lightweight yet analytically grounded alternative among contemporary RS detectors.
In summary, recent studies in remote sensing converge along two main directions for capturing small and fine-grained objects:
- Scale-aware feature enrichment and attention/context aggregation (e.g., lightweight modular necks, content-interaction units, class-aware losses), and
- Multimodal integration (RGB–IR, Optical–SAR) that leverages complementary cues through fusion or translation.
Across datasets such as MAR20, VEDAI, FAIRPlane11, AI-TOD, and FAIR1M, consistent improvements have been reported in both mAP@0.5 and mAP@[0.5:0.95], with particularly notable gains in the small-object domain (APs) while maintaining practical inference speeds. This body of evidence underscores the central objective of balancing accuracy and efficiency—preserving sensitivity to small and medium objects without sacrificing real-time applicability. Within this context, our proposed AERIS-ED aims to enhance APs/APm performance by employing lightweight attention selectively at specific pyramid levels and adopting a streamlined training–testing protocol, while remaining balanced in terms of FPS, parameter count, and GFLOPs.
1.3. Motivation and Main Contributions
The primary motivation of this study is to develop an architecture that compensates for accuracy losses in small-object detection without compromising processing speed, and that is, in fact, adaptable to real-time scenarios. To this end, the proposed AERIS-ED architecture is built upon a C3-based backbone and is founded on the idea of strategically placing Efficient Attention (EA) modules only at critical scale levels (P3 and P4). In this way, the contextual representational capacity for small- and medium-scale objects is enhanced, parameter overhead is constrained, and the accuracy–speed trade-off is effectively optimized. The original contributions of this work can be summarized as follows:
- Latency-Reducing EA Design: By substituting the conventional 3 × 3 dense mixing with a combination of 1 × 1 dimensionality reduction, depthwise operations, and linearized attention at the P3–P4 levels, we achieved approximately 31% lower latency and 45% higher FPS.
- Hybrid Channel–Spatial Attention Mechanism: We designed an enhanced EA module that jointly exploits channel-based and spatial attention pathways. This dual-path design was developed to capture critical spatial relationships and channel dependencies that are often overlooked by single-path attention approaches.
- Multi-Scale Feature Enrichment Framework: We developed a comprehensive multi-scale detection framework capable of effectively addressing objects of varying size categories through intelligent feature fusion and attention-guided processing. This framework is deliberately designed to address the unique difficulties of remote sensing, in which objects appearing within a single scene frequently display considerable differences in scale.
- Scale-Aware Selective Attention Architecture: Instead of applying attention mechanisms uniformly across every feature stage, we introduced a focused placement strategy where Efficient Attention (EA) is incorporated solely at the P3 and P4 levels of the feature pyramid. By concentrating attention at these scales, the model effectively tackles the persistent difficulties in detecting small- and medium-sized objects, while simultaneously maintaining high computational efficiency.
2. Background Theories
2.1. Architectural Overview
The proposed AERIS-ED is a scale-aware detection framework, built upon the YOLOv12 backbone, and specifically developed to reduce the accuracy loss commonly encountered when identifying small and medium objects in remote sensing imagery. The guiding idea of the model is to maintain strong feature extraction capacity while channeling contextual information only into critical layers, thus achieving a favorable balance between accuracy and inference speed.
The network is organized into three principal components: Backbone, Neck, and Head. In the backbone, convolutional layers together with C3 blocks generate multi-scale feature maps from the input image. With increasing depth, the spatial resolution becomes coarser, while the semantic representation is enriched. At the deepest stage, the Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast (SPPF) module aggregates multi-scale context, producing a compact representation that strengthens the discrimination of small objects within cluttered backgrounds. The multi-scale outputs of the backbone are then fused and propagated through a PANet-based neck, ensuring the flow of information across different resolutions.
The distinctive design of AERIS-ED lies in its selective use Efficient Attention (EA). Unlike conventional approaches that insert attention modules across all pyramid levels, EA is deliberately applied only at P3 and P4. Traditional self-attention enriches global context but typically introduces high computational overhead, reducing real-time performance. In contrast, EA provides contextual enhancement with lower parameter complexity, enabling improved recognition of small and medium objects without compromising efficiency. Specifically, the P3-level EA strengthens fine-grained detail for separating small objects, while the P4-level EA stabilizes the learning of spatial relations for medium-sized targets. By confining attention to the levels where it delivers the most impact, the model secures consistent gains in both accuracy and processing speed.
Finally, the Head stage produces multi-scale predictions using features from the P3, P4, and P5 levels, where each detection head estimates class probabilities and bounding boxes to generate the final outputs.
This design enables robust performance across a wide spectrum of object sizes, from small to large. The overall structure of the architecture is illustrated in Figure 1.
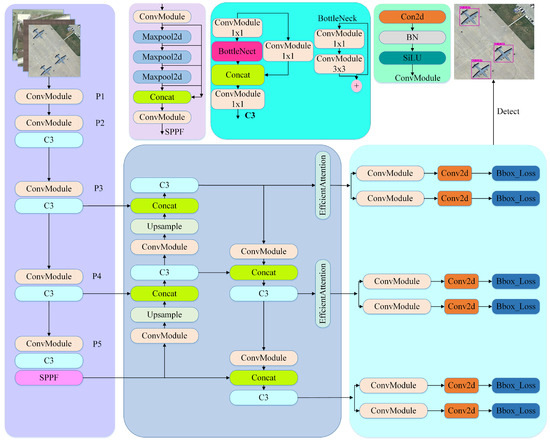
Figure 1.
General overview of the AERIS-ED architecture.
The modular details of the architecture are summarized in Table 1, which presents the output scale, channel dimensions, and modules used at each stage. The backbone is structured across three resolution levels, generating multi-scale features from the P3, P4, and P5 layers. At the P5 stage, the Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast (SPPF) module is employed to aggregate contextual information across multiple scales, resulting in a compact yet informative representation. The derived multi-scale features are then merged and transmitted across different resolutions via a PANet-based neck. It is at this point that the distinct innovation of the proposed model becomes clear: Efficient Attention (EA) modules are selectively positioned only at the P3 and P4 levels. This targeted placement strengthens the separation of small objects from cluttered backgrounds by refining high-resolution details and, at the same time, supports more consistent learning of spatial relationships for medium-sized objects. By confining EA to the most impactful layers, the architecture avoids unnecessary parameter growth and computation, thereby sustaining a strong trade-off between accuracy and inference efficiency.

Table 1.
Structural Summary of The AERIS-ED Architecture.
In the final Head stage, the network exploits the features extracted from P3, P4, and P5 to generate class predictions and bounding boxes, ensuring robust detection performance across multiple object scales.
The architectural specifications summarized in Table 1 emphasize the selective attention strategy adopted in AERIS-ED, which is tailored to enhance the detection of small- and medium-sized objects. In terms of model complexity, AERIS-ED contains approximately 14.59 million parameters and 27.9 GFLOPs, demonstrating its lightweight and computationally efficient design compared to conventional YOLO-based detectors. The overall training procedure employed for the model is depicted in Figure 2.
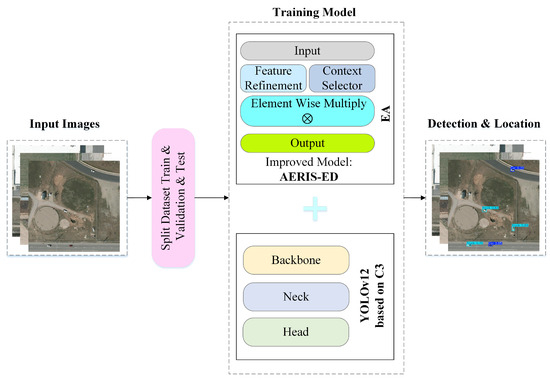
Figure 2.
Overview of the proposed object detection framework.
In summary, the AERIS-ED model is designed to achieve high detection and localization accuracy in remote sensing imagery through systematic training and validation. Its architecture is intended to effectively select multi-scale features and exploit contextual information with enhanced efficiency. As such, the model aims to provide a dependable and real-time solution for remote sensing applications while demonstrating strong potential for competitive performance compared with recent state-of-the-art approaches.
2.2. The Efficient Attention (EA) Module
The Efficient Attention (EA) module introduced in this work is a lightweight mechanism that improves feature representations while maintaining low computational cost by modeling channel and spatial dependencies in sequence. While conceptually related to CBAM [18] it departs from prior approaches by employing structural simplification techniques together with a novel scale-aware integration strategy.
During the channel attention phase, global context is extracted at the channel level by applying global average pooling to the input feature map .
The resulting summary vector is processed by a two-layer 1 × 1 convolutional block, which applies dimensionality reduction followed by expansion using a predefined reduction ratio r. Subsequently, the channel weights are obtained through the combined application of the ReLU activation function and the sigmoid function.
The channel weights are multiplied with the input to produce the channel-attention–refined output, formulated as: Equation (1) illustrates the derivation of the channel summary, while Equation (2) presents the computation of the channel weights. This process determines the relative importance of each channel, enabling the model to focus on more discriminative features.
In the spatial attention stage, channel-wise average pooling and channel-wise max pooling are applied to , producing two complementary spatial maps:
The two maps are concatenated to form a tensor of size , which is then passed through a 7 × 7 convolutional layer to generate the spatial attention map.
As a result, channel and spatial attention are applied sequentially to derive the final output:
Equations (3) and (4) illustrate the summarization of spatial context and the construction of the spatial attention map, whereas Equation (5) represents the output obtained from the integration of all stages of the EA module.
This design is optimized to maintain a low parameter count by employing only a single global average pooling operation together with lightweight convolutional blocks. Its computational complexity is on the order of , which is significantly more efficient compared to the classical self-attention mechanisms with complexity .
In AERIS-ED, the EA modules are strategically positioned at the Backbone–Neck transition, in contrast to the more common “in-block” implementations found in the literature. Selectively deployed at the P3 level, which is sensitive to small objects, and the P4 level, which is suited for medium-scale objects, the EA modules enrich the features propagated through PANet with contextual information, thereby delivering more discriminative representations to the detection heads.
Overall, the EA module provides a distinctive architectural contribution to AERIS-ED through its structural simplicity and its unique scale-based integration strategy. The internal design of the module is schematically illustrated in Figure 3.
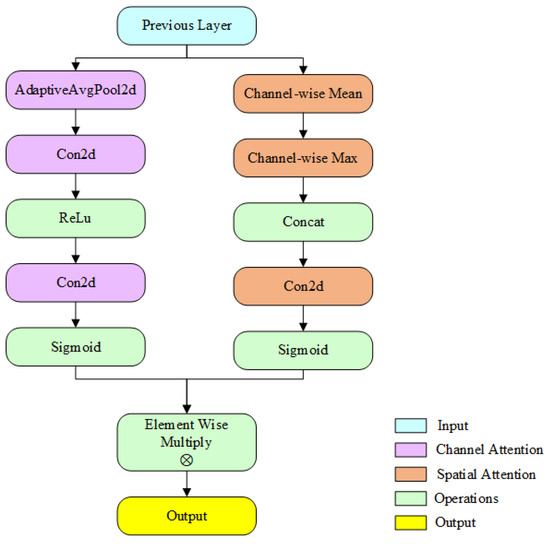
Figure 3.
Efficient Attention Module.
As illustrated in Figure 3, the Efficient Attention module employs a dual-branch architecture that processes input feature maps through two complementary attention mechanisms. Given an input feature map , the module produces an attention-refined output Y, where B denotes the batch size, C the number of channels, H the height, and W the width.
The core design philosophy of the module is first to identify which channels are most relevant, and subsequently to determine which spatial regions within those channels are most critical. This sequential approach yields optimal outcomes in terms of both computational efficiency and feature quality.
The channel-attention branch focuses on modeling inter-channel relationships to capture “what” is meaningful in the feature map. This process consists of three main stages: global spatial information aggregation, channel dimensional modulation, and channel-wise feature recalibration.
In the first stage, the input feature map X undergoes adaptive global average pooling, which compresses its spatial dimensions. This step is expressed as Xpooled = GlobalAvgPool2D(X), yielding a channel descriptor of size C × 1 × 1 that encodes global spatial context. The use of global average pooling is advantageous because it captures the overall activation level of each channel while keeping the computational burden minimal.
The second stage performs channel dimensional modulation through a bottleneck structure. Here, the channel dimension is first reduced by a factor of r and subsequently restored to its original size. Mathematically, this can be expressed as: and, .
This design substantially decreases computational complexity while retaining the ability to model inter-channel dependencies.
In the final stage of channel attention, the weights Z2 are applied to the original features through element-wise multiplication, = Z2, leading to channel-wise recalibration. This adjustment enhances discriminative power by strengthening informative channels and suppressing those with limited contribution.
The spatial attention branch then operates on the channel-refined features Xca to capture spatial relationships, i.e., where the network should focus. It proceeds in four steps. First, channel information aggregation is performed: both average pooling and max pooling are applied along the channel dimension to form two complementary spatial descriptors. While Favg = Mean (, dim = 1) captures global activation tendencies, Fmax = Max (, dim = 1) highlights the most salient responses at each spatial position. Together, they provide a more comprehensive spatial context. In the second step, these descriptors are concatenated, Fconcat = Concat ([Favg,Fmax]) yielding a spatial map of size 2 × H × W.
The third step generates spatial attention weights. The concatenated feature is processed by a 7 × 7 convolution and activated by a sigmoid function: .
The relatively large kernel captures sufficient spatial context, while the sigmoid ensures the weights fall within [0, 1].
Finally, in the fourth step, these weights are applied to the channel-attended features to produce the final refined output: where the operator denotes element-wise multiplication. This operation highlights informative regions while attenuating irrelevant ones, thereby enhancing the overall feature representation.
The design philosophy of the Efficient Attention module combines effectiveness with efficiency. By applying channel attention first, the most informative feature dimensions are emphasized, and spatial attention subsequently pinpoints relevant regions in this refined space. This sequential process maximizes the impact of each mechanism.
From an efficiency standpoint, the module minimizes cost by employing a bottleneck ratio of r = 16 in the channel path and lightweight pooling-based operations in the spatial branch. The dual use of average and max pooling ensures complementary information fusion, with average pooling capturing global context and max pooling emphasizing salient cues.
Following the principle of minimal parameter overhead, the module adds only a small number of extra parameters yet substantially improves feature discriminability. This makes the design easy to integrate into existing CNN frameworks without significantly increasing model complexity.
The main hyperparameters include the channel-reduction ratio 7 × 7 kernel in spatial attention, and the ReLU and Sigmoid activations used for channel and spatial modulation.
The computational complexity can be approximated as: , where the first term corresponds to channel attention and the second to spatial attention. Compared to conventional self-attention mechanisms with complexity , this is substantially lower, making the module practical for real-world scenarios.
In conclusion, the Efficient Attention module provides a lightweight, end-to-end trainable, and plug-and-play solution that significantly enhances feature quality through its dual attention strategy, while maintaining efficiency and adaptability for integration into modern CNN architectures.
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Dataset Description
In this section, we present a detailed overview of the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets, two widely adopted benchmarks in remote sensing object detection. These datasets play a crucial role as evaluation platforms for assessing the performance of the proposed AERIS-ED model, especially with respect to detecting small- and medium-sized objects in complex and cluttered environments.
To further illustrate their characteristics, we provide a representative example image in Figure 4 that contains both near and distant objects. Such visual diversity highlights the challenges posed by scale variation: small targets at greater distances often appear with limited pixel resolution, while nearby objects occupy larger regions with more distinctive structural features. This discrepancy underscores the importance of designing detection frameworks that can effectively capture fine-grained details without compromising contextual awareness.
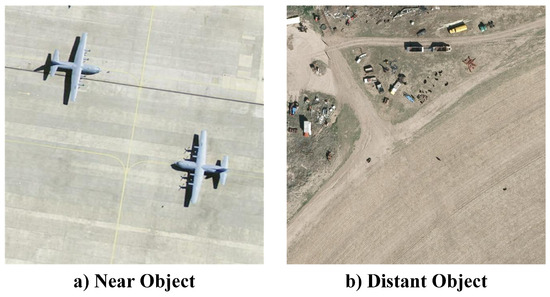
Figure 4.
Illustration of object instances across different scales: (a) Near-object instances; (b) Distant-object instances.
Three selected examples from each dataset are presented in Figure 5. These visuals clearly illustrate the aircraft diversity of MAR20 and the multi-class vehicle compositions of VEDAI across different scene types.

Figure 5.
Sample imagery drawn from the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets.
The presented visuals highlight high-resolution aircraft samples from MAR20 alongside the diverse vehicle categories included in VEDAI. Together, these examples illustrate the inherent scale variability and scene complexity of the datasets. As such, they pose a substantial challenge for evaluating whether the AERIS-ED architecture can consistently deliver strong performance, from detecting small-scale targets to handling scenes characterized by dense background clutter.
3.1.1. MAR20
The MAR20 dataset [19], occupies an important place in the literature as one of the most extensive open resources specifically created for the recognition of military aircraft in remote sensing imagery. It contains 3842 high-resolution images encompassing 20 different aircraft models and a total of 22,341 annotated instances. Each target is labeled with both horizontal and oriented bounding boxes, a dual-annotation scheme that improves detection accuracy in aerial imagery where orientation is crucial, while also enabling fair comparisons across different detection algorithms.
A defining feature of MAR20 is the interplay between high intra-class similarity among aircraft of the same type and substantial intra-class variability caused by images captured from diverse geographical locations. This duality increases the difficulty of the task: aircraft models appear visually similar to one another yet are embedded within heterogeneous backgrounds. Additional challenges such as atmospheric conditions, changes in illumination, shadows, and climatic variability further reinforce MAR20’s role as a demanding benchmark for the reliable detection of small- and medium-scale targets.
The dataset was compiled from imagery collected at 60 distinct military airfields via Google Earth, ensuring coverage not only of uniform scenes but also of a wide range of geographical and environmental contexts. These characteristics establish MAR20 as a critical benchmark for both academic investigations and applied research in remote sensing–based aircraft detection.
3.1.2. VEDAI
The VEDAI dataset [20], is recognized as a distinctive benchmark for multi-class vehicle detection in aerial imagery, capturing the complexity of real-world scenarios. It contains vehicle samples recorded under diverse conditions, including variations in orientation, illumination, shadows, glare, and partial occlusion. As such, VEDAI is not only a conventional dataset for object detection but also a robust platform for testing the ability of models to detect small objects in challenging environments.
A notable strength of VEDAI lies in its multimodal composition, as it provides imagery in the visible spectrum, infrared, and multispectral bands, thereby facilitating comparative studies across different detection strategies. In terms of spatial resolution, images are available in both 512 × 512 and 1024 × 1024 formats, allowing for flexible evaluation across scales. The dataset was collected over the Salt Lake City region in the United States and encompasses both rural and urban areas, ensuring a wide variety of visual contexts.
Overall, VEDAI comprises approximately 1240 images and includes multiple categories such as cars, pick-ups, trucks, planes, camping cars, vans, and an “other” class. On average, each image contains about 5.5 vehicles. making it a diverse and challenging resource for vehicle detection research. While the dataset does not feature extremely dense object clustering, it provides sufficient variability within scenes to pose a balanced challenge for both single-object and multi-object detection tasks.
This multidimensional structure makes the detection of small vehicles particularly challenging, while simultaneously offering an ideal environment for evaluating a model’s ability to generalize across scales. Consequently, VEDAI has become one of the widely recognized benchmark datasets in the remote sensing object detection literature.
3.2. Performance Evaluation Indicators
To assess the performance of the AERIS-ED model, we employed standard evaluation metrics that are widely used in the object detection literature. These measures provide a holistic perspective, enabling the analysis of both detection accuracy and computational efficiency.
In this study, the evaluation framework supports a multidimensional examination of detection models with respect to accuracy, sensitivity, scale awareness, and processing speed. The key definitions underlying this framework are as follows: true positives (TP) denote correctly detected objects, false positives (FP) refer to instances incorrectly predicted as present, and false negatives (FN) correspond to ground-truth objects that the model fails to detect. Additionally, the intersection over union (IoU) is defined as the ratio between the overlapping area and the union area of the predicted bounding box and the ground-truth box. A detection is regarded as correct if its IoU surpasses a predefined threshold.
Based on these definitions, the study adopts the following performance indicators. Precision quantifies the proportion of correctly identified positive instances relative to all predicted positives, thereby reflecting the model’s ability to minimize false alarms.
Recall measures the fraction of ground-truth objects that the model successfully detects, indicating its effectiveness in minimizing missed targets.
mAP@0.5 is obtained by first calculating the average precision (AP) of each class at an IoU threshold of 0.5, and then taking the mean value across all classes.
mAP@[0.50:0.95], consistent with the COCO standard, is calculated by measuring average precision at IoU thresholds from 0.5 to 0.95 with increments of 0.05, and then averaging these values. This metric offers a more demanding and comprehensive assessment of detection performance.
Average Precision (AP) is defined as the area under the Precision–Recall (P–R) curve for a given category. For a more fine-grained evaluation, AP is also reported across different object scales: APs for small, APm for medium, and APl for large objects. According to the COCO standard, small objects are those with an area less than 322 pixels, medium objects fall between 322 and 962 pixels, and large objects correspond to areas greater than or equal to 962 pixels.
Inference Time (ms/img) represents the mean processing duration per image.
Frames Per Second (FPS) expresses the average rate of images processed in one second and is obtained as the reciprocal of the inference time
3.3. Comparative Results
3.3.1. Comparative Analysis of YOLOv12s and AERIS-ED on Different Datasets
In this section, we present a comprehensive comparison between the proposed AERIS-ED model and the baseline YOLOv12s to rigorously validate the effectiveness of the proposed approach. To ensure fairness, both models were trained under identical settings: 200 epochs on the VEDAI dataset and 50 epochs on the MAR20 dataset. Their performance was evaluated using a suite of standard metrics, including Precision, Recall, mAP@0.5, mAP@[0.5:0.95], APs, APm, and APl. Together, these measures provide a thorough view of each model’s detection capability, indicating how effectively they maximize true positives while limiting false detections.
Table 2 summarizes the experimental results for YOLOv12s and AERIS-ED across both datasets. The findings show that AERIS-ED not only improves detection accuracy but also achieves clear gains in inference efficiency, thereby reinforcing its suitability for real-time applications.

Table 2.
The Comparison Results of AERIS -ED And YOLOv12s Models For Both Datasets.
The performance gains of the proposed AERIS-ED model over the baseline YOLOv12s were thoroughly evaluated on both the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets. To ensure a fair comparison, training conditions were kept identical, with 50 epochs on MAR20 and 200 epochs on VEDAI. The evaluation relied on standard metrics Precision, Recall, mAP@0.5, mAP@[0.5:0.95], inference time (ms/img), and FPS which together provide a comprehensive assessment of each model’s capability to minimize false positives, maximize true detections, and maintain real-time processing performance. This translates into absolute improvements of +0.038 in mAP@0.5 and +0.039 in mAP@[0.5:0.95]. From a computational perspective, the inference time decreased from 5.4 ms/img to 3.8 ms/img (29.6% faster), while the processing speed rose from 185 FPS to 263 FPS (42% higher).
A similar trend is observed on the VEDAI dataset: YOLOv12s recorded Precision of 0.791, Recall of 0.755, mAP@0.5 of 0.772, and mAP@[0.5:0.95] of 0.488, whereas AERIS-ED raised these metrics to 0.842, 0.792, 0.830, and 0.532, respectively. This indicates absolute improvements of +0.058 in mAP@0.5 and +0.044 in mAP@[0.5:0.95]. Moreover, inference time decreased from 5.5 to 3.8 ms/img (≈30.9% faster), and FPS increased from 181 to 263 (≈45% higher).
Overall, the results on both datasets demonstrate that AERIS-ED not only enhances object detection accuracy but also provides lower latency and higher FPS, making it more suitable for real-time applications. By exhibiting strong generalization across datasets with diverse object class distributions, AERIS-ED consistently outperforms the baseline in both accuracy and speed. As summarized in Figure 6, the model achieves higher Precision, Recall, and mAP scores compared to YOLOv12s on both benchmarks.
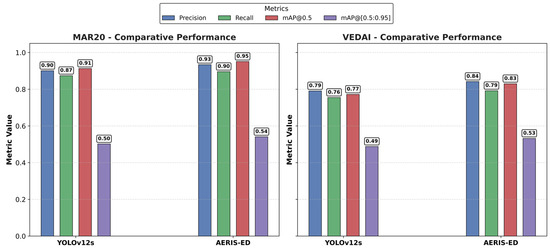
Figure 6.
Bar chart comparing the performance of AERIS-ED and YOLOv12s.
Figure 6 illustrates the comparative performance of YOLOv12s and AERIS-ED on the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets. Despite their distinct class distributions, AERIS-ED consistently achieves higher values of Precision, Recall, mAP@0.5, and mAP@[0.5:0.95] than the baseline YOLOv12s, underscoring its effectiveness as a detection model. Notably, the improvements in mAP@0.5 across both datasets demonstrate the model’s capability to reduce false positives, enhance true positives, and provide more accurate localization. These advantages establish AERIS-ED as a strong candidate for applications requiring high detection accuracy. Moreover, the decrease in inference time coupled with the increase in FPS validates its efficiency and robustness for real-time object detection. The corresponding training process for the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets are depicted in Figure 7.
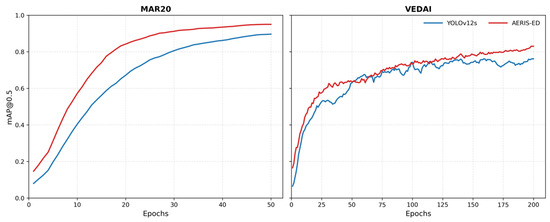
Figure 7.
Training curves of YOLOv12s and AERIS-ED models on MAR20 and VEDAI datasets.
Figure 7 provides a comprehensive illustration of the training dynamics of YOLOv12s and the proposed AERIS-ED across the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets. The depicted learning curves not only demonstrate the overall convergence tendencies of both architectures but also reveal the manner in which AERIS-ED consistently achieves smoother and more stable optimization. In particular, the plotted trajectories underscore the model’s superior ability to suppress loss values over successive epochs while simultaneously attaining higher levels of accuracy. This indicates that AERIS-ED does not merely converge faster but also stabilizes at a performance plateau that is more favorable for generalization to unseen data.
Figure 8 presents representative detection results obtained from both networks on complex, real-world scenes. Visual comparisons reveal that while YOLOv12s occasionally produces false detections—such as identifying non-existent objects within cluttered regions—the proposed AERIS-ED effectively suppresses these errors. AERIS-ED provides more accurate bounding-box localization and demonstrates a marked reduction in false positives, particularly in challenging small—and medium-scale targets affected by scale variation, low resolution, and background clutter. These qualitative results complement the quantitative findings by illustrating that AERIS-ED maintains stronger spatial consistency, delineates object boundaries more precisely, and avoids spurious detections observed in YOLOv12s. Collectively, Figure 7 and Figure 8 provide a holistic perspective on the training robustness and detection efficacy of the proposed architecture, reinforcing its potential for practical deployment in real-time remote sensing scenarios.
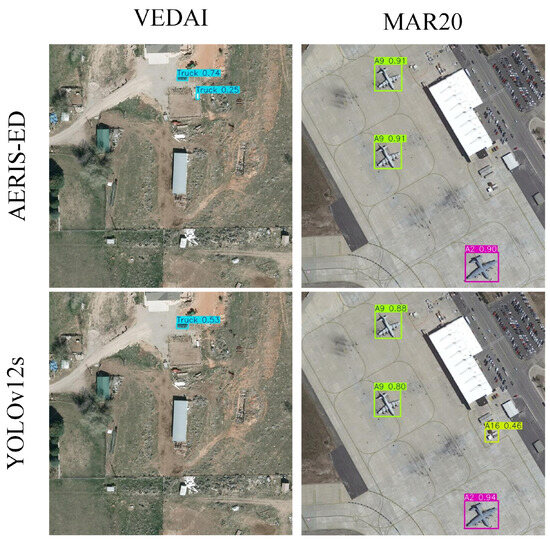
Figure 8.
Visualization of detection outcomes for AERIS-ED and YOLOv12s.
In addition to convergence and qualitative analyses, the Precision–Recall (PR) curve serves as a key metric for evaluating object detection performance, especially in imbalanced datasets where positive samples are limited compared to abundant background instances. Unlike the ROC curve, which focuses primarily on the balance between true and false positive rates, the PR curve directly reflects the relationship between precision and recall, making it more informative in scenarios where false positives and false negatives impose unequal costs, as in safety-critical or mission-driven applications. The area under the PR curve (AUC-PR) thus provides a reliable measure of model robustness by quantifying its ability to sustain high precision levels while simultaneously maintaining strong recall.
Figure 9 illustrates the PR curves of YOLOv12s and AERIS-ED on MAR20 and VEDAI. YOLOv12s exhibits a steep drop in precision as recall increases, indicating a vulnerability under high-recall conditions and reduced reliability in demanding scenarios. In contrast, AERIS-ED maintains a smoother, more balanced curve, ensuring stable performance across thresholds and confirming its stronger capacity for generalization. Overall, these results demonstrate that AERIS-ED improves accuracy and stability while achieving a more favorable precision–recall trade-off, validating its effectiveness as a robust solution for remote sensing object detection.
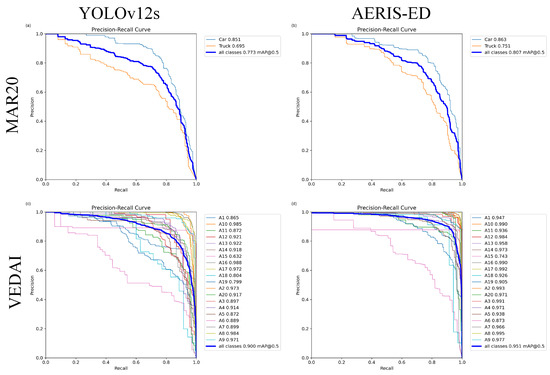
Figure 9.
Precision–Recall (PR) curves of the AERIS-ED and YOLOv12s models. (a) PR curves of YOLOv12s on the MAR20 dataset. (b) PR curves of AERIS-ED on the MAR20 dataset. (c) PR curves of YOLOv12s on the VEDAI dataset. (d) PR curves of AERIS-ED on the VEDAI dataset.
3.3.2. Comparison of AERIS-ED Against Other Models
In this section, the performance of the proposed AERIS-ED model is benchmarked against several state-of-the-art object detection approaches on the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets. To ensure consistency and fairness, all methods were trained and evaluated under identical experimental settings: 50 epochs for MAR20, 200 epochs for VEDAI, a batch size of 8, and an input resolution of 640 × 640, running on Ubuntu 22.04 with an NVIDIA RTX 4060 GPU and a fixed random seed of 42. The SGD optimizer was employed with an initial learning rate of 0.001, momentum of 0.937, while no additional data augmentation techniques were applied beyond standard preprocessing (resizing and normalization). The loss function followed the standard YOLO detection objective, combining CIoU loss for bounding-box regression, binary cross-entropy for classification, and an objectness loss term. Comparisons were conducted across accuracy metrics (mAP@0.5, mAP@[0.5:0.95, Precision, Recall), computational efficiency (ms/img, FPS), and scale sensitivity (APs, APm, APl).
In addition, an ablation study was performed to demonstrate the specific contribution of the proposed ED module.
An examination of the results presented in Table 3 shows that the AERIS-ED model consistently outperforms competing methods on both datasets. On MAR20, AERIS-ED achieved the highest accuracy with 0.951 mAP@0.5 and 0.735 mAP@[0.5:0.95], while also maintaining a strong balance between Precision (0.906) and Recall (0.919). Although YOLOv5s was the fastest model with 3.2 ms/img, AERIS-ED, offered a clear advantage in the accuracy–speed trade-off, achieving substantially higher accuracy (0.951 vs. 0.886 mAP@0.5) at a still efficient runtime. Scale-based evaluations further confirmed the superiority of AERIS-ED. The results on the VEDAI dataset reveal a similar pattern. AERIS-ED once again reached the highest accuracy, with 0.830 mAP@0.5 and 0.532 mAP@[0.5:0.95], and delivered balanced Precision (0.756) and Recall (0.771). With an inference time of 3.8 ms/img, the model also demonstrated real-time applicability, significantly outperforming two-stage detectors such as RetinaNet and Faster R-CNN in terms of efficiency. Overall, the findings in Table 3 highlight that AERIS-ED achieves a well-balanced performance across both accuracy and speed in diverse scenarios. While its accuracy advantage is most pronounced on MAR20, the results on VEDAI demonstrate superiority in both accuracy and efficiency, positioning AERIS-ED as a strong solution for real-time object detection.

Table 3.
Benchmark Results of AERIS-ED Against Recent Detectors on MAR20 And VEDAI.
These outcomes confirm the potential of the proposed architecture for both academic research and practical applications. Figure 9 further illustrates the performance of AERIS-ED against other models across key evaluation metrics. The results in Figure 10 demonstrate that the proposed AERIS-ED model consistently outperforms competing methods on both the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets.
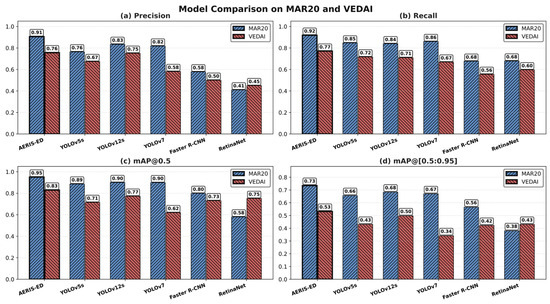
Figure 10.
Performance comparison of AERIS-ED and competing models in terms of evaluation metrics.
On MAR20, the model achieved 0.951 mAP@0.5 and 0.735 mAP@[0.5:0.95], marking a clear margin in accuracy, while also attaining balanced Precision and Recall scores of 0.906 and 0.919, respectively. A similar trend was observed on VEDAI, where AERIS-ED surpassed alternative approaches with 83% mAP@0.5 and 0.532 mAP@[0.5:0.95]. The figure further highlights the distinction between single-stage and two-stage detectors. While Faster R-CNN and RetinaNet appear competitive in certain scenarios in terms of accuracy, their higher inference times (approximately 52 ms/img and 35 ms/img, respectively) limit their applicability in real-time contexts. In contrast, AERIS-ED delivers an inference speed of 3.8 ms/img (≈263 FPS), providing a balanced trade-off between accuracy and efficiency.
Moreover, when Precision and Recall are jointly considered, AERIS-ED not only reduces false positives but also achieves higher true positive detections, thereby reinforcing its overall reliability and robustness across varying conditions. These findings further underscore the model’s applicability beyond academic benchmarks, clearly demonstrating its strong potential for deployment in diverse and complex real-world scenarios where accuracy and stability are critical. Example detection results for the evaluated models are also presented in Figure 11.
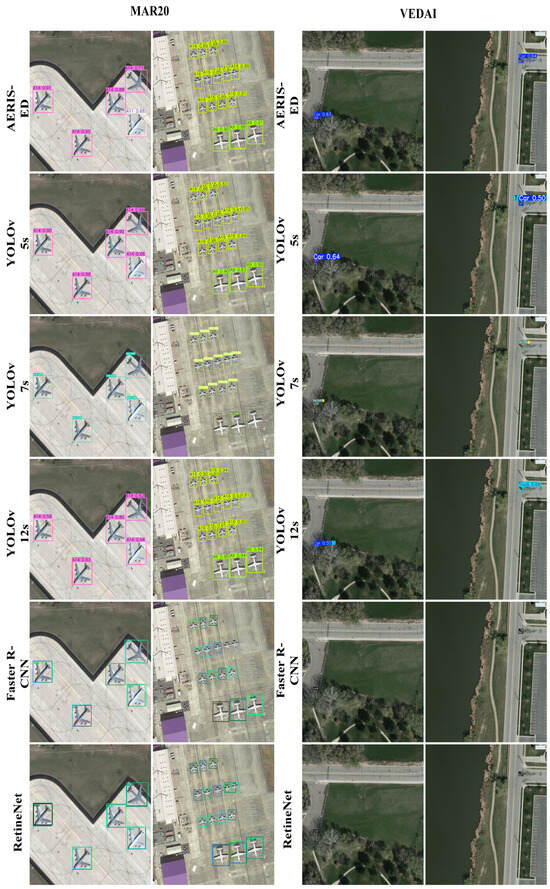
Figure 11.
Predicted outcomes of the models across the two datasets.
The figure presents a visual comparison of six detectors on the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets. From top to bottom, the rows correspond to AERIS-ED, YOLOv5s, YOLOv7, YOLOv12s, Faster R-CNN, and RetinaNet. For each row, the outputs of the models are displayed side by side on the same two test scenes, allowing for a qualitative assessment of differences in the number of detections, bounding box placements, and confidence scores.
3.3.3. Scale-Based Performance Analysis
In remote sensing imagery, objects appear across a wide range of scales; due to ground sampling distance (GSD), flight altitude, and scene complexity, small targets (S) are prone to loss of detail, medium-scale (M) targets are sensitive to the balance between localization and classification, and large targets (L) are affected by saturation and redundant context. Consequently, a single “overall mAP” value may not fully capture model behavior across all scales, as improvements at certain scales may obscure declines at others. The purpose of this section is to disentangle the performance of AERIS-ED and strong baselines across small, medium, and large object ranges (APs, APm, APl), in order to identify where the gains are concentrated and how they translate into applications such as vehicles, rooftops, or infrastructure representing small targets. The scope of the analysis covers two datasets MAR20 and VEDAI allowing the assessment of scale sensitivity and generalization trends under diverse scene distributions. A detailed summary of the scale-based accuracy comparisons is provided in Table 4, which compiles mAP@0.5, mAP@[0.5:0.95], and scale metrics for each model on both datasets.

Table 4.
Scale-Based (APs, APm, APl) Accuracy Comparisons On MAR20 And VEDAI Datasets.
According to Table 4, AERIS-ED consistently ranks first in overall accuracy (mAP@[0.5:0.95]) on both the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets, achieving a margin of 0.052 on MAR20 (0.735) and 0.035 on VEDAI (0.532) over the nearest competitor. When performance is broken down by scale, the superiority of AERIS-ED is particularly pronounced for small and medium objects: on MAR20, it attains APs = 0.483 and APm = 0.715, surpassing competing methods by 0.033 and 0.063 points, respectively; on VEDAI, APs = 0.484 and APm = 0.395 are maintained with margins of 0.030 and 0.034 points. This pattern reflects the scale-sensitive behavior of the architecture, which preserves detail for small targets and balances localization–classification trade-offs at medium scales. For large objects, AERIS-ED achieves APl = 0.714 on MAR20, demonstrating that the gains at smaller scales can be sustained without practical degradation at larger scales. Since APl is not reported in the VEDAI dataset, the scale-based evaluation there is limited to APs and APm. Model differences also become apparent within this analytical framework; for example, RetinaNet attains an APs of 0.189 on the VEDAI dataset, clearly suggesting that its small-object localization struggles under stricter IoU thresholds. Taken together, the holistic interpretation of Table 5 shows that AERIS-ED delivers consistent and meaningful improvements for small and medium objects across two distinct distributions, while maintaining competitive accuracy for large objects under diverse real-world scenarios.

Table 5.
Performance comparison between AERIS-ED and existing methods in the literature on the VEDAI and MAR20 datasets.
3.3.4. Comparison of Existing Studies
To validate the effectiveness of newly proposed methods in object detection, it is essential to conduct comprehensive comparisons not only with baseline models but also with widely adopted approaches in the literature. Such comparisons reveal the extent to which the proposed architecture can generalize across different datasets and scenarios, thereby reinforcing the overall rigor and credibility of the study and ensuring its scientific soundness. In this context, the AERIS-ED model is evaluated on the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets against well-known methods including YOLOv5s, YOLOv7, YOLOv12s, Faster R-CNN, and RetinaNet. The comparisons cover accuracy metrics (Precision, Recall, mAP@0.5, mAP@[0.5:0.95]) as well as inference time and FPS, which are critical for real-time applications and deployment in practical settings. In this way, the advantages of the proposed method over both traditional two-stage detectors and contemporary single-stage approaches are comprehensively demonstrated. The results in Table 6 provide a detailed assessment, confirming that AERIS-ED achieves competitive performance on these benchmarks and validating its effectiveness in object detection tasks.

Table 6.
Ablation Study Results Showing the Impact of The ED Module on the AERIS Architecture.
To comparatively assess the performance of the proposed AERIS-ED model against recent state-of-the-art methods, extensive experiments were conducted on the VEDAI and MAR20 datasets. The results summarized in Table 6 demonstrate that AERIS-ED delivers competitive performance on these challenging benchmarks, confirming its effectiveness in object detection tasks.
On VEDAI, AERIS-ED achieved an mAP@0.5 of 0.830, outperforming methods such as FFCA-YOLO (0.748) and DKDNet (0.779), while maintaining a narrow margin behind the leading LF-MDet (0.808). Notably, AERIS-ED attained the second-highest mAP@0.5 score among all compared methods, with only a 2.2% difference from the top-performing model. Its balanced performance is further confirmed by an mAP@[0.5:0.95] of 0.532, which substantially surpasses FFCA-YOLO (0.448) and DKDNet (0.492). These results highlight the model’s strong localization capability and consistent detection quality across different IoU thresholds.
On the more challenging MAR20 dataset, AERIS-ED achieved an outstanding mAP@0.5 of 0.951, exceeding OPT2SAR (0.876) by 8.6% and approaching the performance ceiling of this dataset. With an mAP@[0.5:0.95] of 0.735, AERIS-ED surpasses OPT2SAR (0.637) by a margin of 15.4%, highlighting its superior precision across a broad range of IoU thresholds. The precision–recall analysis further reinforces its balanced detection capability: on VEDAI, the model achieves 0.756 precision with 0.771 recall, while on MAR20 it attains 0.906 precision and 0.919 recall. This balance demonstrates the model’s effectiveness in minimizing both false positives and false negatives, an essential property for real-world applications where accuracy and completeness carry equal importance.
The consistently strong results across datasets indicate that AERIS-ED incorporates architectural innovations that generalize well to diverse detection scenarios. Its ability to maintain competitive accuracy while offering computational efficiency advantages makes it a practical solution for deployment. Moreover, the inclusion of scale-specific evaluations such as APs provides a more transparent and rigorous assessment compared with competing methods that report only limited metrics. This comprehensive evaluation framework enhances reliability and reproducibility, aligning with best practices in computer vision research.
In conclusion, the comparative analysis positions AERIS-ED as a highly competitive detector that consistently delivers strong performance on challenging datasets. Its robust mAP values across multiple IoU levels, combined with well-balanced precision–recall characteristics, underscore its theoretical soundness and practical applicability.
3.3.5. Ablation Study
This section provides a detailed examination of the contribution of the proposed ED module to the AERIS architecture. Within the scope of the ablation study, different variants of the AERIS architecture (E3, E4, ED) were evaluated on both the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets, thereby clearly demonstrating the benefits introduced by the module. In the E3 variant, Efficient Attention (EA) is integrated exclusively at the P3 scale head, improving sensitivity to small objects. By contrast, the E4 variant applies EA only at the P4 scale, enabling more stable detection of medium-sized targets. The ED variant incorporates EA at both P3 and P4 simultaneously, thereby strengthening multi-scale feature representations and offering a distinct advantage in the balance between accuracy and speed. These results demonstrate that the AERIS family delivers flexible solutions adaptable to different application needs, with the ED variant in particular enhancing cross-scale representational capacity and achieving a more robust, well-balanced performance on both MAR20 and VEDAI compared with alternative approaches. This clearly validates its broad and practical versatility.
Figure 12 presents Grad-CAM–based visualizations illustrating the feature activation responses at the P3 and P4 levels of the AERIS-ED model. The first column shows the original samples, while the second and third columns correspond to the P3 and P4 feature heatmaps, respectively. The P3 map highlights fine-grained regions corresponding to small aircraft targets, whereas the P4 map captures broader contextual areas, indicating the model’s sensitivity to medium-scale structures. These Grad-CAM results visually confirm that the selective integration of Efficient Attention modules at these levels strengthens discriminative learning across multiple scales, consistent with the quantitative improvements shown in Table 5.
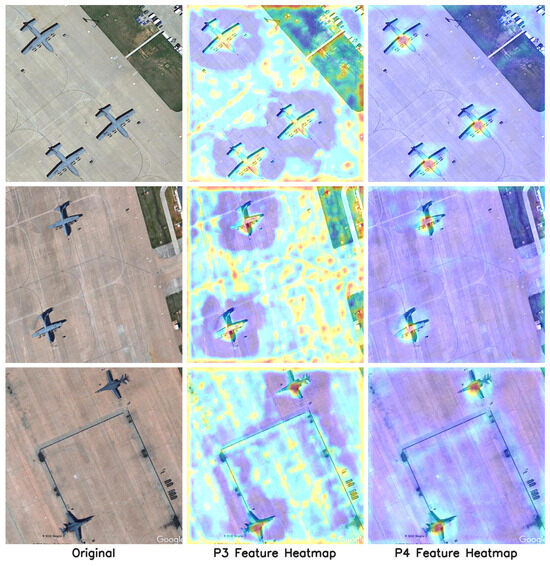
Figure 12.
Visualization of multi-scale attention responses at different feature pyramid levels (P3 and P4) for representative.
The ablation study results in Table 5 show that all three variants of the AERIS family outperform the YOLOv12s baseline, providing measurable benefits in both scale-specific accuracy and runtime efficiency. On the MAR20 dataset, the AERIS-ED variant achieves the most substantial improvements, with a marked increase in mAP@0.5 as well as notable gains in sensitivity to small and medium scale objects. Specifically, the ED variant strengthens performance on small objects while also providing additional benefits at the medium scale, effectively combining the strengths of the P3-focused E3 and the P4-focused E4 within a single architecture. Runtime indicators reinforce this outcome, as ED not only improves accuracy but also achieves faster inference and higher FPS compared to the baseline, thereby enhancing the overall accuracy–speed balance. A consistent trend is observed on VEDAI. While both E3 and E4 deliver measurable improvements over YOLOv12s, ED attains the highest overall accuracy and, importantly, exhibits stronger representation for both small and medium objects. The combination of scale-specific strengths within ED results in a more balanced performance profile across object sizes. At the same time, ED maintains superior runtime efficiency, again surpassing the baseline in inference speed and throughput. Since APl is not reported on VEDAI, large-scale analysis is limited to MAR20, where ED demonstrates the ability to preserve large-object accuracy while retaining its advantages on smaller scales.
Overall, the table highlights that strategically applying the ED module at both P3 and P4 enhances cross-scale information flow, translating into simultaneous improvements in accuracy and efficiency. Whereas single-focus variants (E3, E4) yield benefits at specific scales, the ED variant consolidates these effects into a consistently superior and well-balanced performance across two distinct datasets, establishing itself as a strong candidate for real-time remote sensing applications.
4. Discussion
The Efficient Attention (EA) mechanism developed in this study, along with its integration into the AERIS-ED architecture, has yielded substantial improvements over the baseline on both the MAR20 and VEDAI datasets. The findings clearly indicate that the proposed approach provides an effective solution for the challenge of small-object detection.
On the VEDAI dataset, experimental results show that AERIS-ED achieved an mAP@0.5 of 0.830, outperforming the baseline by 0.057 points (7.37%). The improvement is especially pronounced in the small-object (APs) category, where an increase of 0.108 points was recorded, representing a notable success. Likewise, on the MAR20 dataset, the model attained an mAP@0.5 of 0.951, exceeding the baseline value of 0.900 by 0.051 points (5.67%), thereby confirming its consistent performance across different datasets.
The contribution of selectively positioning EA modules at the P3 and P4 levels was further highlighted by the ablation studies. In the AERIS-E3 configuration, where EA was applied only at P3, the model achieved an improvement of 0.024 points on the VEDAI dataset. In the AERIS-E4 configuration, with EA integrated solely at P4, the improvement reached 0.034 points. When applied simultaneously at both levels in the AERIS-ED configuration, the model achieved the highest improvement of 0.057 points, explicitly demonstrating the synergistic effect of the EA modules.
In comparative analyses against other widely used object detection models, the superior performance of AERIS-ED becomes even more apparent. On the VEDAI dataset, YOLOv5s achieved an mAP@0.5 of 0.715, YOLOv7 reached 0.620, Faster R-CNN achieved 0.731, and RetinaNet obtained 0.752. In contrast, AERIS-ED achieved 0.830, thereby proving the effectiveness of the proposed approach. Notably, when compared to the two-stage detectors Faster R-CNN and RetinaNet, AERIS-ED not only delivered higher accuracy but also provided significantly faster inference (3.8 ms/img versus 52.1 ms/img and 35.7 ms/img, respectively).
While transformer-based and hybrid detectors such as RT-DETR, RTMDet, and ReDet have recently demonstrated remarkable performance on complex vision benchmarks, their computational requirements remain considerably high for mid-range GPUs such as the RTX 4060.
In contrast, AERIS-ED maintains a strong balance between detection accuracy and efficiency, achieving competitive mAP scores with substantially lower FLOPs and parameter counts. This balance highlights AERIS-ED’s practical suitability for resource-constrained environments, while future work will focus on extending its compatibility with transformer-based detection frameworks to further enhance small object recognition capability.
One of the key advantages of the Efficient Attention mechanism is its ability to deliver performance gains with minimal computational overhead. The AERIS-ED model’s inference time of 3.8 ms/img and throughput of 263 FPS represent a 31% speedup compared to the baseline model’s 5.5 ms/img and 182 FPS. The fact that this improvement was achieved despite the addition of EA modules provides clear evidence of the computationally efficient design of the proposed mechanism.
From the perspective of real-time applications, the 263 FPS achieved by AERIS-ED underscores its potential usability in time-critical domains such as drone-based surveillance, autonomous vehicle systems, and industrial quality control. While YOLOv5s achieves a slightly higher throughput of 312 FPS, the 0.115-point advantage in mAP@0.5 achieved by AERIS-ED establishes it as an optimal solution in terms of the speed–accuracy trade-off.
The effectiveness of the Efficient Attention mechanism in small-object detection is most clearly reflected in the APs improvements. On the VEDAI dataset, AERIS-ED achieved an APs of 0.562 compared to the baseline’s 0.454, corresponding to a 0.108-point (23.8%) increase. This demonstrates the success of strategically placing EA modules at the backbone–neck transition and employing a dual-path attention mechanism to enhance the discriminative features of small objects.
Similarly, on the MAR20 dataset, the APs improvement of 0.222 points (85.1%) reveals the model’s consistent performance across different imaging conditions and object types. These results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed approach in addressing the small-object detection problem, which is of critical importance in remote sensing and aviation applications.
The rationale for positioning Efficient Attention (EA) modules specifically at the P3 and P4 levels is strongly supported by the experimental findings. The P3 stage enhances sensitivity to small objects through its high-resolution feature maps, whereas P4 provides the most effective contextual information for medium-scale targets. By contrast, the exclusion of EA from the P5 level is intentional, since large objects are already represented with sufficient features, and additional attention at this scale would only introduce unnecessary computational overhead.
Another critical design decision is the sequential application of channel and spatial attention. Applying channel attention first identifies the most important feature channels, thereby providing higher-quality inputs for the subsequent spatial attention. Compared to parallel applications, this design produces results that are both more effective and computationally more efficient, ultimately ensuring superior feature utilization and a better balance between accuracy and speed.
5. Conclusions
In this study, an Efficient Attention mechanism was developed for small-object detection and successfully implemented within the AERIS-ED model. The proposed approach leverages channel and spatial attention mechanisms in a sequential manner, achieving substantial performance improvements with minimal computational cost.
Experimental results demonstrate that the AERIS-ED model achieved mAP@0.5 improvements of 7.37% and 5.67% on the VEDAI and MAR20 datasets, respectively. In terms of small-object detection, the APs metric recorded increases of 23.8% on VEDAI and 85.1% on MAR20. From the perspective of computational efficiency, the model delivered a 31% speedup over the baseline, reaching 263 FPS.
The strategic placement of EA modules at the P3 and P4 levels enabled effective feature enrichment at the backbone–neck transition. Compared to YOLOv5s, YOLOv7, Faster R-CNN, and RetinaNet, AERIS-ED exhibited superior performance in both accuracy and inference speed.
The primary advantages of the proposed Efficient Attention mechanism include minimal parameter overhead, ease of integration, real-time applicability, and its specific effectiveness in small-object detection. Future work may explore adaptation to transformer-based architectures, extensions to video applications, and optimizations for edge computing.
Overall, the Efficient Attention mechanism offers an effective and practical solution to small-object detection, providing valuable contributions to both academic research and industrial applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: A.A. and E.A.; Methodology: A.A. and E.A.; Software: A.A.; Validation: A.A.; Formal Analysis: A.A.; Investigation: A.A.; Resources: A.A.; Data Curation: A.A.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation: A.A.; Writing—Review and Editing: A.A. and E.A.; Visualization: A.A.; Supervision: E.A.; Project Administration: E.A.; Funding Acquisition: A.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no specific external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in public repositories. The MAR20 dataset is available at https://gcheng-nwpu.github.io/ [19], accessed on 2 September 2025 and the VEDAI dataset is available at https://downloads.greyc.fr/vedai/ [20], accessed on 12 September 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AERIS-ED | Attention-Enhanced Real-time Intelligence System for Efficient Detection |
| C3 | Cross Stage Partial with three convolutions |
| EA | Efficient Attention |
| Mar20 | Maritime Object Detection 2020 |
| VEDAI | Vehicle Detection in Aerial Imagery |
| mAP | mean Average Precision |
| IoU | Intersection over Union |
| RS | Remote Sensing |
| APs | Average Precision for Small objects (area smaller than 322 pixels) |
| APm | Average Precision for Medium-scale objects (area between 322 and 962 pixels) |
| APl | Average Precision for Large objects (area exceeding 962 pixels) |
| SPPF | Spatial Pyramid Pooling Fast |
| FPS | Frames Per Second |
| TP | true positives |
| FP | false positives |
| FN | false negatives |
| PR | Precision–Recall |
| GSD | ground sampling distance |
| IR | infrared |
| SAR | SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) |
| DDU | Downsample Difference Upsample |
| PNOC | PNOC attention module |
| SFEG | SFEG |
| CFFDNet | CFFDNet |
| DFSC | DFSC |
| GWF | GWF units |
| R2CD | region-internal content interaction |
| CDFL | class-aware discrete focal loss |
| CS3 | cross-shaped sampling space |
| FFCA | focused feature context aggregation |
| ODCLayer | context enhancement via multi-dimensional dynamic convolution |
| MFFM | multi-scale feature fusion |
| RGAM | relevance-guided attention module |
| CBC | class-balance–aware correction |
| ECL | enhanced contrastive learning |
| MDCM | MDCM |
| HFSHM | restructures high-level features through a split-and-shuffle mechanism |
| PMT | PMT module |
| IV-gate | IV-gate module |
| CFFIM | CFFIM module |
| FEM | FEM |
| FFM | FFM |
| SCAM | SCAM |
| CBAM | Convolutional Block Attention Module |
| GAP | global average pooling |
| AUC-PR | area under the PR curve |
| ROC | ROC curve |
| GenAI | AI-based language model |
References
- Acikgoz, H.; Korkmaz, D.; Talan, T. An Automated Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease from MRI Scans Based on Enhanced Residual Dense Network with Attention Mechanism. J. Imaging Inform. Med. 2025, 38, 1935–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Avaroğlu, E. Contact classification for human-robot interaction with densely connected convolutional neural network and convolutional block attention module. SIViP Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 4363–4374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Tao, X.; Deng, W.; Liu, H. Image Detection Network Based on Enhanced Small Target Recognition Details and Its Application in Fine Granularity. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydın, A.; Talan, T.; Aktürk, C. Vision-Based Amateur Drone Detection: Performance Analysis of New Approaches in Deep Learning. Acta Infologica 2023, 7, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acikgoz, H. An automatic detection model for cracks in photovoltaic cells based on electroluminescence imaging using improved YOLOv7. SIViP Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 18, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, A.; Salur, M.U.; Aydin, İ. Fine-tuning convolutional neural network based railway damage detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE EUROCON 2021-19th International Conference on Smart Technologies, Lviv, Ukraine, 6–8 July 2021; pp. 216–221. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9535585/ (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Dikici, B.; Bekciogullari, M.F.; Acikgoz, H.; Ozbay, S. A lightweight and improved you only look once model using GhostWise convolution and attention mechanism for accurate plant disease detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2025, 161, 112163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahveci, S.; Avaroğlu, E. An Adaptive Underwater Image Enhancement Framework Combining Structural Detail Enhancement and Unsupervised Deep Fusion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 7883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, Y.; Zhi, X.; Shi, T.; Zhang, W. Complementarity-Aware Feature Fusion for Aircraft Detection via Unpaired Opt2SAR Image Translation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G. Context-Aware Content Interaction: Grasp Subtle Clues for Fine-Grained Aircraft Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5641319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Luo, T.; Peng, H.; Zhang, G. MFCANet: Multiscale Feature Context Aggregation Network for Oriented Object Detection in Remote-Sensing Images. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 45986–46001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G. Relevance Pooling Guidance and Class-Balanced Feature Enhancement for Fine-Grained Oriented Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, M.; Ding, Y.; Gong, J. Differential multimodal fusion algorithm for remote sensing object detection through multi-branch feature extraction. Expert Syst. Appl. 2025, 265, 125826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, K. Cross-Modal Adaptation for Object Detection in Infrared Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2025, 22, 7000805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Sun, H.; Sun, X.; Ni, L.; Gao, L. Cross-Modal Feature Fusion and Interaction Strategy for CNN-Transformer-Based Object Detection in Visual and Infrared Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2024, 21, 5000405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ye, M.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P.; Yan, J. FFCA-YOLO for Small Object Detection in Remote Sensing Images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5611215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cordeiro, F.R.; Chen, Q. PSSCL: A progressive sample selection framework with contrastive loss designed for noisy labels. Pattern Recognit. 2025, 161, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.-Y.; Kweon, I.S. CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.06521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.Q.; Cheng, G.; Wang, M.J.; Yao, Y.Q.; Xie, X.X.; Yao, X.W.; Han, J.W. MAR20: A benchmark for military aircraft recognition in remote sensing images. Natl. Remote Sens. Bull. 2024, 27, 2688–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razakarivony, S.; Jurie, F. Vehicle Detection in Aerial Imagery: A small target detection benchmark. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2015. Available online: https://hal.science/hal-01122605 (accessed on 9 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhao, F.; Yao, G.; Jin, Z. FGA-YOLO: A one-stage and high-precision detector designed for fine-grained aircraft recognition. Neurocomputing 2025, 618, 129067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, G. Military Aircraft Recognition Method Based on Attention Mechanism in Remote Sensing Images. IET Image Process. 2025, 19, e70069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Nurmamat, P.; Chen, J.; Cao, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, Z. Fine-Grained Aircraft Recognition Based on Dynamic Feature Synthesis and Contrastive Learning. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Chen, H.; Lin, Z.; Han, J.; Ding, G. RepViT: Revisiting Mobile CNN From ViT Perspective. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2307.09283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, J.; Luo, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, P. Diffusion Mechanism and Knowledge Distillation Object Detection in Multimodal Remote Sensing Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 4408314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Guo, L.; Xiong, F.; Kuang, L.; Han, X. Physical-Simulation-Based Dynamic Template Matching Method for Remote Sensing Small Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, Q. Low-rank multimodal remote sensing object detection with frequency filtering experts. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2024, 62, 5637114. Available online: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10643097/?casa_token=pihNVrkMTCEAAAAA:JT1I5zjYq52CIT9Xn89w99_RE8UU9Rz0EkSdgDyMQzs_HWs99Hu6l7i1t4SP5O-Mz6_IuyZHzAFg8w (accessed on 10 September 2025). [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Ye, X.; Du, Z. Object detection in multispectral remote sensing images based on cross-modal cross-attention. Sensors 2024, 24, 4098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).