Abstract
The integration of 3D printers into food production represents an unprecedented innovation, envisaging applications from the industry to missions in space to home cooking, with no geographical or sectoral limits. Extrusion food 3D printers are designed to use ‘food inks’ that must be produced from raw materials possessing a range of suitable characteristics (viscosity, elasticity, and others) that make them printable. Not all food matrices possess such characteristics, and additives are often needed to formulate food inks, which must also adapt to the complexity of the 3D model to be printed. Initially, mainly food matrices such as potatoes, chocolate, cereal, and legume flours and soluble-fiber-rich additives were tested with this new technology, with promising results. In recent years, alternative food matrices (e.g., based on insects, algae, cultured meat, and food waste) have begun to be experimented with, as 3D printing appears to be a suitable way to exploit their potential. This review aims to highlight recent studies that have investigated the development of innovative food ink formulations and trace a picture of the new food raw materials that are being tested for 3D food printing, the opportunities they represent, their nutritional properties, safety, and technological challenges. This review considered a total of 46 papers, selected from 330 papers published in the last 8 years (2018–2025) on the generic subject of 3D food printing.
1. Introduction
Three-dimensional printing applied to food is a recent technology that has the potential to enable the creation of a wide range of printed food products with different textures, colors, and shapes, ranging from more traditional foods to customized foods that adapt to individual nutritional needs [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Extrusion-based 3D food printers are designed to use a wide variety of food raw materials to produce formulations (‘food inks’) possessing characteristics, like viscosity and elasticity, that make them printable [2,3]. Not all food matrices are suitable for this technology on their own, and additives are often required; additionally, the results depend not only on the starting ingredients but also on the complexity of the 3D model to be printed [7]. A good knowledge of the technological properties of ingredients for 3D ink formulation is the necessary basis to understand the behavior of the ink systems, which directly affects the quality of the final printed product.
Initially, food matrices such as mashed potatoes, chocolate, cereal and legume flours, and soluble-fiber-rich additives were tested with this new technology, with encouraging results [1,8]. However, in recent years, alternative food matrices based on insects, algae, cultured meat, and food waste have begun to be experimented with, as 3D printing appears to be a suitable way to exploit their potential as food ingredients of high nutritional quality and increased sustainability.
This review aims to highlight recent studies that have investigated the development of innovative food ink formulations and trace a picture of the new food raw materials that are being tested for extrusion-based 3D food printing, the opportunity they represent, their nutritional properties, safety, and technological challenges.
2. Methodology
This review considered a total number of 46 papers, selected from 330 Scopus-indexed papers published in the last 8 years (2018–2025; see Figure 1) on the generic subject of 3D food printing (search keywords: ‘3D food printing’ and ‘inks’).
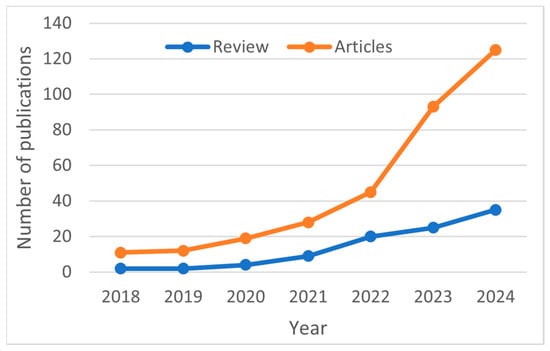
Figure 1.
Publication trends in the application of 3D printing in food. Source: Online Scopus database (www.scopus.com) using the keywords ‘inks’ AND ‘3D printing’.
Recent years have seen a clear shift in eating habits toward more sustainable diets, driven by both consumer awareness and the introduction of innovative raw materials. This transition is characterized by a move away from traditional, animal-based, and resource-intensive foods toward plant-based, novel, and environmentally friendly ingredients. There is a growing trend toward plant-based diets and the use of innovative raw materials, which are mainly algae, insects, and by-products from food processing (food waste). These alternatives are associated with lower environmental impacts compared with traditional animal-based ingredients [9,10]. Research on cultured meat is going in the same direction of reducing the environmental impact, alongside answering ethical challenges, although it is still at an early stage at present [11,12].
Innovative inks for food 3D printing currently include those derived from edible insects, algae, and food waste. Therefore, all papers having as an object the use of ingredients based on edible insects, algae, and by-products from food processing (food waste) to produce inks for extrusion food 3D printing were retained. Since we wanted to maintain focus on recent innovation, studies centered on traditional plant-based protein products, meat analogs, and commonly used matrices (e.g., chocolate and mashed potato) were excluded, as these topics are well-established and do not represent the cutting edge of 3D food printing research. Papers in which 3D printing was used to extrude animal cells for cultured meat production were also retained.
A total of 46 papers were thus retained, offering a panorama of what is being experimented with in novel food inks for food 3D printing. Despite the promise of these innovative inks, at the moment, the literature remains limited, highlighting the need for further research on alternative protein and food waste ingredient-based inks. It was also evident during the selection that such innovative ingredients were used only as inks in extrusion-based printing.
Figure 2 shows the number of articles reviewed for each different ink category.

Figure 2.
Number of articles examined for each group of novel inks (based on insects, algae, cultivated meat, and food waste).
3. Food 3D Printing Process
Three-dimensional printing is an additive-manufacturing (AM) method used to produce three-dimensional objects, involving the application of consecutive layers of material [2]. Originating in 1984, this technology was initially used to construct replacement components for the industry [13,14]. In a short period of time, this technology was able to revolutionize numerous sectors such as medicine, manufacturing, art, education, gastronomy, and engineering, and eventually even reach into space [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Regarding food applications, 3D printing represents the only technology that makes it possible to translate digital images into food products, opening the way to the realization of innovative shapes and sizes, and improving the design, appearance, and attractiveness of products [23].
Three main components make up a 3D printer: a computer, which allows the user to be able to interact with the printer by means of specific software; the software, which allows the computer to communicate with the motor control system; and the printer’s motors, controlled by the control system. The specificity of a food 3D printer lies not only in the geometry of the extruding components and in the characteristics of the motor system, but particularly in the fact that all components coming into contact with food are made of suitable materials and are designed to be easy to clean, like all devices for food processing.
3.1. Steps of Food 3D Printing
The steps leading to the creation of a 3D-printed food model are shown in Figure 3 [1].

Figure 3.
Scheme of the food 3D-printing process (Pereira et al., 2021 [1]).
The first step is the preparation of the food materials, which can be in the form of ink, liquid, or powder, according to the printing technology to be used. For extrusion food 3D printing, a ‘food ink’ can be defined as the final printable form of an edible substance prepared from one or more raw materials [24]. Generally, the materials from which inks are formulated fall into three categories: natively printable foods (gels, pastes, and doughs), non-printable foods (meat, fish, and vegetables), and alternative ingredients (insects and algae) [25].
The second step (modeling phase) is the creation of the 3D model to be printed [23]. Three-dimensional geometry can be created by software (such as AutoCAD, vers. 2026—www.autodesk.com, accessed 7 November 2025, or Tinkercad, vers. 2025—https://www.tinkercad.com, accessed 7 November 2025, where there are several options available, from those for beginners to those for expert users) or by a 3D scan of a real object using the reverse-engineering technique [26].
Once the 3D model is created in the form of computer-aided design (CAD) data, it is converted into a stereolithographic format (.stl file) and sent to a slicing software, where the model layers are created and the printing parameters are set (speed, filling, temperature, and nozzle height). At this level, the slicing program transforms the STL data into a G-code file, a computer programming language, which is used to send instructions to the computer, providing information to the printer on the movements to be performed [1,27,28].
The third step is printing, which can be performed by extrusion, which is currently the most common method, but also by ink jetting, binder jetting, or selective laser sintering [1]. These are different technologies, each adapted to specific kinds of products, currently applicable or not to home or industrial production, and making use of viscous liquid or semisolid edible formulations (‘inks’) or of powdered food materials (see subparagraph below).
The fourth step, when necessary, is the further processing of the printed product, like cooking (baking, boiling, frying, etc.), drying, or others. For this step, the stability of the printed shape under the processing technique is critical.
3.2. Available 3D-Printing Technologies
Figure 4 represents the main 3D food-printing technologies currently in use: binder jetting, selective laser sintering (SLS), inkjet printing, and extrusion [25,29].

Figure 4.
The main technologies currently used for 3D food printing [14].
Binder jetting technology uses powdered food material deposited layer by layer, stabilized with a fine mist of water [21]. Next, the print head applies a liquid binder that connects the powder particles [14]. After binder deposition, the powder bed is exposed to heat via a thermal lamp to provide mechanical strength and enable the next layer to be added. This process is repeated until the object matches the CAD design [30].
The main advantages of binder jetting include the ability to use a wide range of materials, print in color with various flavors, achieve short production times, and create complex 3D geometries. However, limitations include a rough and granular surface, the need for post-processing to remove moisture, low mechanical strength, and reduced nutritional content compared with other processes [30]. Commonly used materials are sugar, vanilla, mint, and chocolate, mainly for confectionery with intricate geometric designs [25,31].
Commercial examples include the ChefJet printer by 3D Systems. The Australian company 3DChef produces decorative sweets using binder jetting with powdered sugar [32].
Selective laser sintering (SLS) uses a 3D device and an infrared laser (or a hot air beam in the case of hot-air sintering (HAS)) connected to a scanner. The laser scans the cross-section of the powder bed, which is evenly spread on the printing platform, fusing particles to create a solid structure through sintering [33,34]. Sintering involves heating powders or granules to a temperature below their melting point but high enough to bond particles together. After scanning the first layer, the powder bed is lowered, a new layer is deposited, and the process continues until the desired shape is completed according to the CAD design [14].
SLS enables extremely fast production of three-dimensional objects [34]. A study by Jonkers et al. [35] analyzed starch-based foods sintered by a selective laser and observed that mechanical properties varied with laser parameters. One of the main advantages of powder-based techniques like SLS is the ability to create highly complex geometries, as unsintered powder supports the product itself. These technologies also provide higher spatial resolution in product design [35]. Fresh ingredients are unsuitable for this type of printing and must be dehydrated and converted into powder form [14].
The Dutch company TNO developed the Food Jetting Print system, applying SLS to sugar and Nesquik powders [17], where unsintered powder remained as structural support [21]. In 2014, CandyFab used low-speed hot-air sintering to melt sugar and create decorative sweets with intricate designs [21].
Inkjet printing (IJP) consists of depositing liquid droplets onto a substrate through a computer-assisted process [2]. The printer dispenses the material in the form of tiny drops via a thermally heated print head, directing them to specific regions to create the internal structure or surface decoration of foods.
This technology is suitable for low-viscosity materials and does not allow the production of complex structures. Commonly used materials include chocolate, liquid dough, jams, cheese, meat paste, and sugar glaze. The main advantages are the wide range of possible applications and the preservation of the food’s quality characteristics, while limitations include the reduced ability to design elaborate geometric shapes and its current use mainly for image decoration and surface filling [25].
An example of an industrial application is the Dutch company FoodJet, which uses Inkjet technology to produce numerous food products sold worldwide.
Extrusion-based printing (FDM) is a widely used technology in 3D food printing. The process consists of the continuous extrusion of soft materials through a moving nozzle, with temperature and viscosity control, depositing successive layers onto the printing platform [14]. It can occur at high temperatures (hot melt), as in the case of chocolate [2], or at room temperature for foods such as cheese, mashed potatoes, and meat-based mixtures [33,36].
The main advantages are the wide variety of materials and the possibility of customization, while limitations include low precision and rheological issues. Too-low viscosity compromises shape retention, whereas high viscosity can cause nozzle clogging [25,30]. Some printers allow multi-extrusion, enabling the creation of multi-material and multi-flavor products [37].
Due to the great versatility of extrusion printing in handling complex inks and its widespread use, we focused our review on exploring the use of alternative/innovative matrices with this technology.
3.3. Printability of Foods
For foods, ‘printability’ means the possibility to give a permanent desired shape and structure to a food compound that initially appears as a viscous solution or paste (an ‘ink’). Printability is tightly linked to the rheological properties of food materials, which determine how well a material can be extruded and hold its shape post-deposition during printing. Key rheological parameters influencing printability include viscosity, yield stress, shear-thinning behavior, storage modulus, loss modulus, and viscoelastic properties. These factors govern the extrusion ease, shape fidelity, layer adhesion, and ultimate structural stability of the printed food [3,38,39]. When formulating complex foodstuffs including several materials/ingredients, one must take into account how they will interact with each other and always consider the rheological characteristics of the food ink, as specific viscoelastic properties are required for the extrusion of the material from the nozzle [29,39]. The composite effects of starch type and concentration, protein source, and hydrocolloid additives substantially modify these rheological parameters [40]. Process parameters, including nozzle diameter, extrusion speed, ambient and bed temperature, and layer height, must be set accordingly to the ink rheological properties to positively affect dimensional accuracy and print consistency. Consequently, successful extrusion-based 3D food printing necessitates finely tuned edible inks exhibiting a rheological profile balancing elasticity, yield stress, and shear-thinning behavior to enable effective extrusion, layer adhesion, and retention of the intended geometrical form [3,14,39,41].
4. Innovative Raw Materials for 3D Food Printing
4.1. Insect Powder
Edible insects represent a promising solution to meet the growing demand for protein [42]. Currently, about 2 billion people consume insects as part of their traditional diet, particularly in Africa, Asia, and Latin America, where more than 1900 species used as food have been identified [43,44]. Insects are a rich source of proteins, lipids, vitamins, and minerals. Their composition varies depending on species, age, and diet, but in general, they offer high-quality protein [44,45]. For example, mealworms contain omega-3 and omega-6 unsaturated fatty acids comparable to fish and higher than pork and beef. Furthermore, their vitamin and mineral content is similar to that of meat and fish [43].
There are some concerns about food safety when considering edible insects. There is potential to develop serious allergic reactions, and different kinds of bacteria that are known to make people sick have been found in insects. In addition to bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi are also possible forms of biological contamination. Because many insects are eaten whole, they are especially vulnerable to chemical contamination. In the EU, insect regulation, as it relates to food, is the responsibility of the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and has played a key role in evaluating the safety of edible insects as a food source. The EFSA focuses on assessing the safety of insects in terms of contaminants, allergens, nutritional properties, and microbiological risks. In 2021, the EFSA approved a number of edible insect species, including the house cricket (Acheta domesticus), yellow mealworm (Tenebrio molitor), and black soldier fly (Hermetia illucens). This approval allows these insects to be legally used as food ingredients in processed products such as snacks, flours, bars, and baked goods.
The taste, flavor, texture, and color of edible insects are widely variable as they are influenced by species, developmental stage, diet, and cooking methods. In Western countries, entomophagy is often viewed with mistrust, associated with cultural prejudices and negative perceptions related to food appearance [43,46]. To overcome these barriers, insect flours rather than whole insects are increasingly being incorporated into common foods, such as snacks and baked goods, so that the original insect is no longer recognizable. Studies show that insects hidden in processed products are more easily accepted. Hartmann and Siegrist showed that the level of acceptance in the consumption of insects increased when hidden within processed products, observing that people who had consumed processed insect foods were more willing to eat unprocessed insects as well [47]. Many sensory tests show that products are well-received by non-habitual consumers when containing insect flour at up to 30% [48].
These flours, in addition to being added to normal food formulations, can be used as a possible ingredient for formulating inks for food 3D printers. From a nutritional, safety, and acceptability point of view for the Western consumer, what has already been said for flours is valid; then, 3D printers certainly increase the possibilities for creating innovative foods with appealing shapes and could increase acceptability to Western consumers. Innovative projects such as ‘Insects Au Gratin’ [49] explore new ways of eating insects through 3D printing (Figure 5). Susana Soares, in collaboration with London South Bank University and the University of West England, has overseen the design and development of several prototypes of 3D-printed, ready-to-eat, and ready-to-cook insect doughs made by mixing insect powders with glazed butter, cream cheese, water, and gelling agent to achieve the right consistency to pass through the nozzle, allowing for proper extrusion [44,49,50].

Figure 5.
Designer food made from insect flour (Susana Soares: Insect Au Gratin/Project [51]).
This approach not only helps to mask the unusual insect flavor but also improves the nutritional profile of foods. Singh et al. highlighted the advantages of Drosophila as a sustainable protein source compared with other conventional sources, being tasteless and smell-less in comparison with other unpleasant-smelling insects [42]. The authors concluded the analysis by noting that the acceptability of Drosophila-based foods by consumers can be improved by customizing the shape, taste, and nutritional quality according to specific needs/demands, and that Drosophila-based protein has all the potential to be an excellent alternative source that is nutritionally valid and also compatible with 3D-printing processes.
From a nutritional point of view, as previously stated, the use of insect flour as ink offers significant advantages. Azzolini et al. found that enrichment of extruded wheat-based snacks with 10% Tenebrio molitor larvae flours improved the microstructure of the product and ensured sufficient protein content to be classified as a ‘protein source’ according to European standards. However, higher percentages (20%) compromised the structural properties of the snack due to the high lipid content of the larvae [52].
Severini et al. also experimented with 3D printing to create enriched snacks that significantly improved the contents of essential amino acids such as lysine, methionine, and cysteine with the addition of up to 20% Tenebrio molitor larvae flour [53].
Recently, Herdeiro et al. developed doughs suitable for printing that combined insect flours (Tenebrio molitor and Alphitobius diaperinus) with other raw materials [54]. At the end of their work, they observed that the incorporation of insect flour had a significant impact on the dough flow during printing; the hardness of the insect-based samples was significantly higher than that of the control samples, resulting in a more stable internal structure. Furthermore, the insect-based snacks, compared with the control, all had a higher protein content, sufficient to qualify as a ‘protein source’, and an increased mineral profile.
From a technological point of view, insect flours modify the rheological characteristics of the dough in cereal-based inks, an effect probably attributed to the weakening of the gluten network. In the study of Severini et al. [53], an increase in softness of the ink formulated with the addition of insect flour was observed, which caused over-deposition during the printing phase, with a consequent loss of shape of the object due to the lack of the required mechanical strength to ensure stability after printing. Furthermore, the cooking conditions also influenced the attributes of the 3D-printed snacks, modifying their microstructure, inducing non-enzymatic browning reactions, and altering their mechanical properties.
The effects of different percentages of insect powder on the rheological properties of inks were evaluated by Adedeji in 2022 [55]. In their study, the structural, morphological, and rheological properties of bioinks formulated with varying proportions (0–75%) of cricket (Acheta domesticus) powder in a wheat flour (WF) matrix were examined. The results showed that incorporating high insect powder levels increased the water absorption capacity, amino acid content, and color attributes. Rheological analysis revealed that only the printed material using 50% of cricket flour showed adequate viscoelastic properties, as a high dough stiffness maintained the shape stability, which is crucial for 3DFP applications.
A study by García Gutiérrez in 2024 [56] investigated the effect of adding two edible insect species (A. diaperinus and L. migratoria) on the fluidity and viscoelastic properties of doughs, in this case, made with chickpea flour, to produce a 3D-printed salty snack, and found an increase in viscosity as the percentage of insect increased. Similar results were reported in a paper by Sundarsingh A. in the same year [57], in which various additions of insect powder, in particular, Alphitobius diaperinus and Locusta migratoria, were evaluated to enrich chickpea-based doughs and produce salty snacks by 3D printing. The addition of insect powders changed the rheological properties of the doughs; in particular, the increase in the powder concentration resulted in an increase in viscosity and pseudoplasticity, improving the structural stability required for 3D printing. However, Locusta migratoria, while contributing to a greater increase in dough elasticity than Alphitobius diaperinus, presented limitations in printability at high concentrations. Furthermore, snacks printed with Alphitobius diaperinus exhibited a higher crispiness compared with the snack without insects.
The use of insect powders as ‘ink’ for food printing represents a unique opportunity to develop sustainable and nutritionally rich products. However, several challenges must be addressed before large-scale adoption can be realized. From a technological point of view, optimizing ink rheology and ensuring structural stability are crucial for achieving high-quality prints. Further research is needed to refine formulation techniques, improve extrusion properties, and develop post-processing methods that maintain both nutritional value and texture. Furthermore, consumer acceptance remains a significant hurdle to be addressed through sensory enhancement, and strategic food design will be essential for market penetration. Furthermore, regulatory compliance and food safety measures must be established to ensure the consistency and security of insect-based food products. By overcoming these challenges, insect-based inks have the potential to revolutionize sustainable food production and contribute to global food security.
4.2. Algae Biomass and Algal Extracts
In recent years, the growing consumer focus and trend toward the consumption of healthy products have increased interest in integrating natural ingredients into food. These include products such as algae and microalgae, which are considered innovative and promising compounds rich in beneficial nutrients and bioactive molecules [50].
It was demonstrated that there is the possibility of extracting bioactive compounds from algae using emerging extraction technologies that are already being used for food waste (ultrasound-assisted extraction, pulsed electric field, and microwave-assisted extraction), with the aim of producing functional 3D-printed food [58].
Particularly in the field of 3D food printing, the use of new proteins as raw materials became a current research topic, leading to the development and use of new food products, such as ‘plant meat’ [59].
We can divide algae into macroalgae and microalgae. Macroalgae are rich in dietary fiber, vitamins, and minerals, while microalgae are abundant in proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and diverse bioactive compounds [60]. Otherwise, microalgae are good sources of vitamins A, C, E, B1, B2, B6, and B12, and minerals such as iron, potassium, magnesium, iodine, and calcium [61].
Some species of algae are considered a valid source of protein that contain protein levels similar to meat, eggs, soya, and milk, but with poor bioavailability in their raw and unprocessed form. It has been observed that microalgae have a remarkable capacity to accumulate protein, surpassing most other algae [62]. Some species of Chlorella and Spirulina can contain up to 70% protein by dry weight, making dried algae powders comparable to concentrated protein powders [63].
Their functional properties, such as emulsifying, foaming, and gelling capabilities, make algae versatile for use in food applications [64].
It is well known that algae can be used either as biomass or as a source of extracts, depending on the needs of the food industry. Algal biomass is used directly or after minor processing, usually to produce flaked or hydrated algae for sushi or broths, for example, or ground into a powder to be added to supplements, flours, pasta, or snacks.
Seaweed extracts, conversely, are used for their technological and nutritional properties, either as food additives and gelling agents (carrageenan, agar, and alginates) or as protein and lipid extracts to nutritionally enrich foods [65].
The studies we reviewed point to the possibility of using algae for the formulation of food inks for 3D printing food. In general, however, a known problem concerning the incorporation of bioactive functional ingredients into food is that their biological activity naturally decreases during the cooking process.
The study of Oliveira et al. in 2021 [66] demonstrated that 3D printing of foodstuffs with pores (in the case observed by the authors, it was a 3D-printed biscuit dough, enriched with grape skin derivatives and whose extract was encapsulated) reduces the effects of loss of bioactivity from the cooking-induced degradation process.
Vieira et al. [67] developed functional biscuits, formulated with the extract of microalgae Arthrospira platensis, with antioxidant properties. By means of ultrasound-assisted extraction in hydroalcoholic solutions, the antioxidants were extracted from the microalgae and then encapsulated with alginate microspheres to improve their stability to heat, light, and oxygen during the baking process. Encapsulation of the extract promoted an improvement in the ORAC (oxygen radicals absorbance capacity) value and color stability compared with all other formulations, revealing the potential of A. platensis for the development of a functional 3D food ink [50,67] (Figure 6).

Figure 6.
Effects of using functional 3D ink obtained by encapsulating antioxidants from A. platensis (Vieira et al., 2020 [67]).
The effect of the addition of algae inside biscuits was also evaluated by Uribe-Wandurraga et al. [68], who analyzed the rheological and structural characteristics of 3D-printed biscuit doughs to which microalgae biomasses, such as Arthrospira platensis and Chlorella vulgaris, were added. The authors observed a higher extrusion force during printing, greater mechanical strength, and an increase in the elastic component, concluding that the addition of algae led to an improvement in printability, resulting in biscuits with greater stability and resistance to baking.
An et al. [69] investigated the use of Nostoc sphaeroides biomass in food 3D printing, using its nutritional and rheological properties as a natural gel material for 3D-FP ink. The results showed that the fresh biomass gel was printable but had instability and non-uniformity. The resulting inks had a less fluid print due to reduced elasticity and viscosity. An improvement in printability was observed with a 24 h rehydration period using seaweed powder. The addition of pre-gelatinized potato starch (1–100 g/kg) improved the print quality, with the best result obtained at 40 g/kg.
In recent years, since awareness that overfishing is leading to a dangerous loss of biodiversity, causing ecological effects that are detrimental to our planet, has been rising, algae have also been used for the production of fish analogs [70,71,72,73,74,75]. A recent study highlighted the potential of macroalgae as a major component and protein source for the 3D-printed production of a prototype ‘salmon fillet’ analog and a two-color ‘smoked’ salmon slice analog: proteins and polysaccharides were co-extracted from the red marine macroalgae Gracilaria cornea, also known as Irish moss or Ogonori [76], the use of the extract in 3D printing of which was intended to form two different types of bioinks: a red bioink dyed with microalgal astaxanthin, for muscle tissue, and a white bioink dyed with CaCO3, for intramuscular adipose tissue [77].
Several studies highlight the integration of microalgae as a source of blue food with the use of 3D food printing, as it could be an attractive way to expand the area of microalgae-based 3D food products to meet socio-economic development while ensuring environmental stability [78].
In 2019, the start-up Open Meals, specialized in food 3D-printing technology, presented ‘Sushi Singularity’, a sushi project printed in 3D, where the proposed new technology aims to customize food using a printer whose food cartridges mainly contain plant ingredients, seaweed, enzymes, and fibers, and pays special attention to food design as, in addition to creating attractive shapes, it can incorporate nutrients, flavorings, and impart certain organoleptic characteristics [79] (Figure 7).

Figure 7.
Three-dimensional-printed sushi made from small edible gel cubes, which are assembled and used to design foods (Open Meals website [80]).
In a recent review paper [81], the authors explored the effects of adding modified starch to meat analog products made from microalgae as a solution to improve the rheological and mechanical properties of inks, facilitating 3D printing and improving the structure of final products. The study analyzed different combinations of ingredients to create inks based on microalgae (Auxenochlorella protothecoides, Chlorella, and Arthrospira), including microalgae proteins [82], hydrocolloids [83], and texture modifiers. The results show that the inclusion of modified starch in microalgae-based inks significantly improves printing properties, allowing the creation of more stable and defined structures.
There are not yet many studies employing the use of algae in 3D-printed products, but certainly, some aspects to be explored in future studies should include technological, regulatory, and consumer acceptability issues, such as taste and smell dislike, suggesting strategies to overcome these obstacles through innovative and sustainable formulation approaches.
4.3. Cultured Cells
In recent years, cultured meat has attracted increased interest in the scientific community, due to the fact that it represents a possible alternative to conventional animal protein products and can be used to meet the growing demand for food attributable to global population growth [11,84]. Cultured meat, also referred to as clean meat, cell-based meat, or cell-culture meat [85], is meat produced outside of a live animal. Animal stem cells are cultured in a medium that contains nutrients and energy sources necessary for the cells to divide and differentiate into muscle cells, which are then transformed into tissues [12]. The application of 3D food printing to cultured meat is a promising frontier for sustainable food production, but it faces several unresolved limitations and challenges. Recent advances include the use of 3D printers both for the fabrication of edible scaffolds that serve as a support for cell growth and for the direct printing of bioinks containing living animal cells, i.e., the cultured meat itself [86]. In practice, there are two main approaches:
Printing of scaffolds only: The 3D printer is used to create porous, edible scaffolds made from plant proteins, hydrogels, or other biocompatible materials. After printing, animal cells are seeded onto these scaffolds and cultured in bioreactors, where they proliferate and differentiate to form muscle tissue [87,88,89].
Direct printing of cultured meat (cellular bioink): The 3D printer can directly deposit bioinks composed of a mixture of living animal cells and support materials (such as hydrogels), enabling the creation of three-dimensional structures in which the cells are already distributed according to a precise pattern. This approach allows for the production of more complex products that closely resemble real meat, as the cells can be organized in a controlled manner during the printing process [90,91].
Both approaches are currently under research and development. Printing of only scaffolds is more established and widespread, while direct printing of cultured meat represents a technological frontier that enables products with a microstructure more faithful to natural meat, but requires highly optimized bioinks to ensure cell viability and differentiation [86,88,91].
The first demonstration of cultured meat by Mosa Meat in 2013 cost more than USD 300,000, and this highlighted the need for more economic methods of providing nutrients for cell growth through serum-free culture media (Figure 8) [92].

Figure 8.
First cultured meat burger presented by Mosa Meat (Jo and Nie, 2021 [92]).
Over time, several companies have invested in the experimentation and production of cultured meat. The Israeli company Aleph Farms collaborated with 3D bioprinting solutions to conduct a 3D-printed meat test in a microgravity environment. Astronauts were able to grow and 3D print muscle tissue using cells provided by Aleph Farms [93]. In 2020, US start-up Eat Just launched and sold cell-grown chicken products in Singapore [94]. The future application of 3D printing in cultured meat production holds significant promise for addressing sustainability, animal welfare, and food security challenges. However, a critical analysis reveals that this technology is still in a nascent phase and faces substantial scientific, technological, economic, and social hurdles.
Achieving faithful reproduction of texture, taste, and nutritional value is still challenging [11,86]. The scalability of the process is hindered by the high cost of materials (such as growth factors and culture media), the need for advanced bioreactors, and the complexity of producing large volumes efficiently and safely [91,95,96,97]. From a sustainability perspective, although cultured meat promises a lower environmental impact than traditional livestock, current production remains energy-intensive and requires thorough life cycle assessments [11,86]. Regulatory frameworks and food safety standards for 3D-printed cultured meat are still under development, representing a significant barrier to market entry [11,97]. Finally, consumer acceptance is uncertain: perceptions of ‘unnaturalness,’ doubts about safety, taste, and nutritional benefits, and reluctance toward highly processed foods are significant cultural obstacles [98].
4.4. Food Waste
The world population, as reported by the FAO, is continuously expanding and will grow by about 33% in 2030 to reach almost ten billion people in 2050 [99]. Food resources are decreasing, and in 2022, about 9.2% of the world’s population suffered from chronic hunger compared with 7.9% in 2015 [100]. The increase in the world of population will inevitably cause an increase in food demand, especially in more developed areas that have an unsustainable food consumption pattern, using more food than necessary, mainly based on animal products, processed foods, and saturated fats that inevitably have an impact on raw materials, such as water, but also on land use and gas emissions [101]. Three-dimensional food printing may be one of the emerging and innovative solutions to respond to the increasing food insecurity; 3DFP technology can improve and enhance food utilization and food waste by utilizing discarded food from the supply chain and by-products to make more appealing food products for consumers [102,103]. Fruit, vegetable, and wholegrain by-products are promising sources of dietary fiber and functional compounds, have high water retention capacity, and exhibit a high swelling ratio with good physiological activity [104,105]. Feng et al. investigated the possibility of using the by-products of ground potatoes, mixed with yam powder (Dioscorea), to prepare 3D-printed air-fried snacks [106]. In 2023, DaTan et al. conducted an analysis on the revalorization of orange peel by making 3D-printed snacks. The authors formulated a food matrix based on orange peel, which was dried in an oven, then pulverized, filtered, and fortified with deionized water and different concentrations of xanthan gum to modify its rheology and to assess any change in the antioxidant and bioflavonoid content of the printed food product, observing that the nutritional value remained unchanged [107]. A further analysis on the use of 3DFP for waste valorization was conducted by Molina-Montero et al. [108], where the aim of the study was the valorization of orange peel (OB P) in 3D-printed apricot pulp gels by means of extrusion at a constant temperature of 25 °C to obtain a final fiber-enriched snack. The study investigated rheological characteristics before and after printing, printing precision, and post-treatment (assessing color, shear strength, and the presence of bioactive substances) [108]. Also, from the peels, a food ink obtained from the durian fruit was developed. The study observed printability in terms of ease of extrusion through the nozzle and the shape fidelity of printed structures. Improved printability can be achieved by reducing the particle size of the durian peel and adding xanthan gum as a rheology modifier to the ink [109].
Another study characterized the rheological properties (shear thinning and yield stress) of food inks formulated from spinach stems and kale stems, common green leafy vegetable wastes, which, both industrially and domestically, are usually disposed of because of their hard composition. The food ink formulations discussed in the study were designed by competitors who participated in a local (Singapore) 3D-printing competition called SUTD X Armstrong 3D Printing Design & Innovation: Digital Gastronomy. The competition was organized to encourage the use of AM technologies in the food industry [110].
Another study on waste valorization was conducted in 2021 by Jagadiswaran et al., with the aim of making functional, three-dimensional molded cookies using pomace and broken wheat as ingredients that would otherwise have been destined for animal feed. The study was purely rheological, with the aim of being able to obtain a finished product with structural and organoleptic characteristics that could pass a positive evaluation by a panel of tasters [111].
Not only can parts that are not commonly used in food preparation be used in the formulation of food inks, but fruits and vegetables with imperfect shapes, which are, therefore, discarded by the food sales market, can be used as well. In fact, another work used vegetables with imperfect shapes, such as broccoli and carrots, which were recycled into freeze-dried powders to improve their shelf life before being processed into food inks for 3D printing. Rheology of food inks, color analysis of raw and cooked designs, and texture analysis of cooked designs were determined [112]. The resulting product is shown in Figure 9.

Figure 9.
Three-dimensional-printed baked goods, each with a different food ink formulation obtained from broccoli and carrot food waste. (a): control; (b): 25 carrot:75 flour; (c): 25 broccoli:75 flour; (d): 25 broccoli/carrot:75 flour; (e): 50 carrot:50 flour; (f): 50 broccoli:50 flour; (g): 50 broccoli/carrot:50 flour; (h): 75 carrot:25 flour; (i): 75 broccoli:25 flour; (j): 75 carrot/broccoli:25 flour, mass ratios). The scale bars in all images represent 1 cm (from Ahmadzadeh et al., 2024 [112]).
The problem of raw material waste associated with the meat industry can be solved through the development and utilization of its by-products, such as offal, skin, feet, and fat, which account for 52 percent to 66 percent of the live weight of cattle and pigs, respectively. The use of this organic material as ink for 3D printing presents a challenge because some of these by-products, such as heart, liver, and kidney, have high nutritional value but, at the same time, an unpleasant taste, resulting in being disliked by consumers. Food formulas with large amounts of tendons and connective tissue inside limit the rheological characteristics of the formulas, impacting the printability of the extrudates [113].
In 2022, Carvajal-Mena et al. [114] used 3D-printing technology to develop an edible product made from the by-products of the salmon industry. The aim of the study was to evaluate the printability at different concentrations of salmon skin-based gels by studying their physical properties and analyzing dimensional stability over time.
In a paper by Wang et al. in 2023 [115], a new 3D-printing material was developed using Spirulina platensis residues obtained after phycocyanin extraction, with characteristics of shear thinning, high viscosity, and rapid recovery. The effects of the moisture content and pretreatment method on the rheological properties of Spirulina platensis residues were examined. Scanning electron microscopy allowed the microstructure to be observed, while texture analysis evaluated the structural characteristics of the residues. The rheological properties determined the key factors for 3D printing, such as the viscosity and modulus of the residues.
5. Discussion and Perspectives
Three-dimensional food printing is leading the way for future food, offering edible products made from insect meals, microalgae, and food waste, making them appealing in appearance, customized, and accessible to all. Additionally, 3D food printing shows the potential to reduce food waste through the revalorization of waste from supply chains, which can be used to formulate printing inks. The 2030 Agenda, adopted by all United Nations (UN) member states in 2015, has at its core 17 goals (SDGs), which are an urgent call to action by all countries, developed and developing, in a global partnership to promote sustainable development. As 3D food printing scales up and becomes a widely used technology, it will be able to contribute to the achievement of sustainability goals.
Currently, however, notwithstanding its great potential, there are still a number of obstacles that slow down its global expansion, and they mainly concern food formulas (optimization of inks, improvement of printability, and the stability of compounds), the post-printing phase (alteration of the shape and mechanical strength of the product), limitations of a more technical nature, related to the computer–software–printer interface, and limitations of a regulatory nature, related to food safety, besides consumer acceptance.
5.1. Safety and UE Regulation
With regard to the safety of food 3D printing, two aspects need to be clarified. One concerns the safety of the ink to be used, and the other relates to the correct cleaning of the printer that extrudes the food.
For the first aspect, the innovative food ingredients referred to in this review, namely, insects, algae, food waste, and cultured meat, present specific food safety issues, with microbiological, bacteriological, and allergenic risks (Table 1).
As previously stated, edible insects can be a good source of protein and micronutrients, but they pose a microbiological risk if contaminated with pathogenic bacteria or can accumulate heavy metals and environmental contaminants [116,117]. In addition, they can cause allergic reactions in some people, as the presence of proteins such as tropomyosin and arginine kinase can cause allergic reactions, especially due to cross-reactivity with crustaceans and dust mites. Their safety depends on proper breeding and hygienic treatment [118,119,120].
In Europe, edible insects fall under the novel foods legislation, mainly regulated by Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 [121], which provides for a rigorous approval procedure based on scientific safety assessments conducted by the EFSA in 2015 [122]. Only insects included in the official list can be placed on the European market as novel foods. To date, seven types of insects are authorized on the EU market, including Tenebrio molitor larvae (yellow mealworm), Locusta Migratoria (grasshopper), Acheta domesticus (house cricket), and Alphitobius diaperinus larvae (lesser mealworm). The permitted forms include whole, dried, frozen, and powdered insects, including those treated with UV rays, such as the new Tenebrio molitor larva powder authorized in January 2025.
In Europe, edible seaweed is regulated by Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 on novel foods, which authorizes its marketing as food or supplements. The regulation sets limits for chemical contaminants and heavy metals such as lead, cadmium, and mercury, and recommends informing consumers about iodine levels, ensuring safe consumption. Contamination from heavy metals in seaweed products intended for human consumption has been known for some time [123]. The main food safety risk associated with mycoproteins concerns the presence of allergens. In some individuals allergic to mold, adverse reactions, such as urticaria, and, in rare cases, anaphylaxis, have been reported [124]. Microalgae can become contaminated with toxins when they grow in environments where cyanobacteria that produce harmful substances are present. Some species produce them directly, while others can contaminate them indirectly [125]. Production and harvesting are also regulated to ensure quality and safety, providing complete control over nutritional and environmental aspects (Recommendation (EU) 2018/464 [126]).
The EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) guidelines on the safety of reused food waste focus primarily on the assessment and management of microbiological, chemical, physical, and toxicological risks related to the destination of food waste, especially when it is reintroduced into the food chain or used for animal feed production [127,128]. The EFSA recommends strict control of food waste collection, treatment, and processing to prevent contamination by pathogenic microorganisms such as Salmonella, Listeria, or Escherichia coli.
Cultured meat is subject to major microbiological risks, such as contamination from Salmonella, Campylobacter, Escherichia coli, and other pathogens, during the production process. The most obvious safety issues may arise from the use of animal serum in the culture medium, due to the presence of viruses [125]. However, with rigorous hygiene controls, sterilization, and monitoring, these risks can be minimized. It is also necessary to assess the origin and health status of the animal cells from which the cultured meat is derived. Attention should also be paid to possible cross-contamination and other biological contamination.
In summary, the safety of these foods requires thorough checks of microbial load, monitoring of allergens and chemical contaminants (heavy metals), and rigorous production, storage, and processing practices to minimize risks to human health.
An important aspect that is overlooked in the reviewed papers on food 3D printers is the physicochemical characteristics of the food inks that are used, such as moisture content, water activity, and microbial contamination, which limit the practical application of the results [129]. Another current challenge is the affordability of this technology, due to costs that are currently still too high. To overcome these limitations, many research and R&D laboratories have adapted 3D printers that were created for other uses for food production [130,131]. Over the years, this has led to the ability to purchase 3D printers for a few hundred dollars and focus no longer on the cost of the hardware, but rather on customizing the machine itself to fit a wide variety of needs [132,133]. However, we need to point out here a very important aspect that brings us back to the safety of use of this equipment. The parts of a 3D printer that come into contact with food must meet the requirements of conventional food equipment; therefore, food safety depends on the type of 3D printer and the application of effective cleaning protocols. Three-dimensional printers built specifically for food use meet all these requirements, whereas 3D printers that have additional food printing functions are relatively inexpensive, but many of their components are often made of materials not suitable for food production [7,134].
One can easily incur contamination by foodborne pathogens, such as Salmonella Typhimurium and Listeria monocytogenes or a surrogate for human norovirus, Tulane virus (TuV), which is transmitted by food between surfaces and food inks, as some studies have observed [135,136].

Table 1.
Safety issues of food 3D printing.
Table 1.
Safety issues of food 3D printing.
| Physical Hazards | Allergens | Chemical Contaminants | Microbiological Contaminants * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algae | Rzymski et al., 2015 [124] | Al Dhabi, 2013 [123] | Hadi and Brightwell, 2021 [125] | |
| Insects | De Gier and Verhoeckx, 2018 [119] He et al., 2021 [120] | Ribeiro et al., 2018 [117] | Kooh et al., 2020 [116] | |
| Food waste | O’Connor et al., 2022 [128] | O’Connor et al., 2022 [128] | O’Connor et al., 2022 [128] | |
| Cultured meat | Hadi and Brightwell, 2021 [125] Singh et al., 2022 [42] |
* Microbiological contaminants include bacteria, viruses, parasites, fungi, and their toxins.
5.2. Consumer Acceptance of 3D-Printed Foods
Consumer acceptance of 3D-printed foods is shaped by a complex interplay of psychological, cultural, and technological factors. Recent studies underscore that positive attitudes, perceived usefulness, and openness to innovation significantly increase consumers’ willingness to try and pay for 3D-printed foods, whereas novel food technology neophobia (NFTN) and concerns about the naturalness of food remain substantial barriers. In fact, negative perceptions often associate 3D-printed foods with highly processed products containing multiple ingredients, which further hinders acceptance [137,138,139,140].
Trust in scientific advances and transparent communication about the technology’s safety and benefits can mitigate these barriers effectively.
Theoretical models like the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and the Theory of Planned Behavior (TPB) support the hypothesis that consumer attitudes, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and the intention to adopt new technologies are significant predictors of acceptance. Marketing strategies that emphasize benefits such as reduced food waste and nutritional customization can positively shape consumer perceptions and drive adoption. As well as a targeted communication to reduce neophobia and enhance trust, along with transparent labeling and information on product components and health benefits [141,142].
In addition, consumer acceptance improves when 3D-printed foods align with local culinary traditions and cultural preferences, making the novel technology perceived as more relatable and less intimidating [140]. Positioning 3D food printers as accessible home-use devices that enable easy recipe customization and promote zero food waste can transform consumer perceptions and unlock mainstream adoption [143,144].
Research on the subject, then, is growing rapidly and evolving continuously: from the study of home-format printers to studying beyond Earth’s frontiers, exploring possibilities for production even in microgravity conditions.
6. Conclusions
As this study highlights, 3DFP and the use of innovative inks are revolutionizing food presentation, composition, and customization, allowing a wide range of possibilities. Customization of food formulas and sensory properties is opening the way toward on-demand production of food, where consumers can co-create their food with the producer according to their needs/desires, eliminating much of the waste in production and consumption. Three-dimensional food printing can improve the dining experience by creating attractive and nutritionally optimized dishes. It can provide ad hoc solutions not only in design, color, and shape, but also in texture, promoting the feeding of the elderly, patients with dysphagia, and children with food neophobia. It can enable the production of healthy foods suitable for athletes or for consumers with specific nutritional needs. It can find applications for astronauts. In conclusion, food 3D printing technology still has limitations and has a long way to go; it offers numerous possibilities for designing foods and maximizing the field of customization and represents an answer to current and not-so-distant future problems.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M. and V.T.; bibliographic research, M.R., G.C., S.M., V.T., V.N., and S.R.; writing—original draft preparation, S.M., V.T., and G.C.; writing—review and editing, S.M. and V.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pereira, T.; Barroso, S.; Gil, M.M. Food Texture Design by 3D Printing: A Review. Foods 2021, 10, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoi, F.C.; Bhandari, B.R.; Prakash, S.; Zhang, M. Chapter 1—An Introduction to the Principles of 3D Food Printing. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 1–18. ISBN 978-0-12-814564-7. [Google Scholar]
- Pérez, B.; Nykvist, H.; Brøgger, A.F.; Larsen, M.B.; Falkeborg, M.F. Impact of Macronutrients Printability and 3D-Printer Parameters on 3D-Food Printing: A Review. Food Chem. 2019, 287, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, D.; Yan, L. 3D Food Printing: Perspectives. In Polymers for Food Applications; Gutiérrez, T.J., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 725–755. ISBN 978-3-319-94625-2. [Google Scholar]
- Jeltema, M.; Beckley, J.; Vahalik, J. Food Texture Measurement and Consumer Choice. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-0-08-100596-5. [Google Scholar]
- Stokes, J.R.; Boehm, M.W.; Baier, S.K. Oral Processing, Texture and Mouthfeel: From Rheology to Tribology and Beyond. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Yan, L.; Huang, D.; Lin, L. Extrusion-Based Food Printing for Digitalized Food Design and Nutrition Control. J. Food Eng. 2018, 220, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanaro, M.; Desselle, M.R.; Woodruff, M.A. Chapter 6—3D Printing Chocolate: Properties of Formulations for Extrusion, Sintering, Binding and Ink Jetting. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 151–173. ISBN 978-0-12-814564-7. [Google Scholar]
- Rabadán, A.; Nieto, R.; Bernabéu, R. Food Innovation as a Means of Developing Healthier and More Sustainable Foods. Foods 2021, 10, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Boukid, F.; Pasqualone, A.; Bryant, C.J.; García, G.G.; Parra-López, C.; Jagtap, S.; Trollman, H.; Cropotova, J.; Barba, F.J. Emerging Trends in the Agri-Food Sector: Digitalisation and Shift to Plant-Based Diets. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2022, 5, 2261–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, W.; Correia, P.; Vieira, J.; Leal, I.; Rodrigues, L.; Nery, T.; Barbosa, J.; Soares, M. Trends and Technological Challenges of 3D Bioprinting in Cultured Meat: Technological Prospection. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, P.; Brown, C.; Arneth, A.; Dias, C.; Finnigan, J.; Moran, D.; Rounsevell, M.D.A. Could Consumption of Insects, Cultured Meat or Imitation Meat Reduce Global Agricultural Land Use? Glob. Food Secur. 2017, 15, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attarin, S.; Attaran, M. Food Printing: Evolving Technologies, Challenges, Opportunities, and Best Adoption Strategies. J. Int. Technol. Inf. Manag. 2020, 29, 25–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvara, R.-A.; Szabo, K.; Vodnar, D.C. 3D Food Printing: Principles of Obtaining Digitally-Designed Nourishment. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, S.; Vahabzadeh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Bone Tissue Engineering Using 3D Printing. Mater. Today 2013, 16, 496–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dankar, I.; Haddarah, A.; Omar, F.E.L.; Sepulcre, F.; Pujolà, M. 3D Printing Technology: The New Era for Food Customization and Elaboration. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 75, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoi, F.C.; Prakash, S.; Bhandari, B.R. 3d Printing Technologies Applied for Food Design: Status and Prospects. J. Food Eng. 2016, 179, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Dong, H.; Su, J.; Han, J.; Song, B.; Wei, Q.; Shi, Y. A Review of 3D Printing Technology for Medical Applications. Engineering 2018, 4, 729–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Shen, F.; Chua, C.K.; Zhou, K. Polymeric Composites for Powder-Based Additive Manufacturing: Materials and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2019, 91, 141–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flowers, P.F.; Reyes, C.; Ye, S.; Kim, M.J.; Wiley, B.J. 3D Printing Electronic Components and Circuits with Conductive Thermoplastic Filament. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 18, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhou, W.; Huang, D.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Hong, G.S. An Overview of 3D Printing Technologies for Food Fabrication. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1605–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. Medical Applications for 3D Printing: Current and Projected Uses. Pharm. Ther. 2014, 39, 704–711. [Google Scholar]
- Derossi, A. 3D Food Printing: Opportunities, Principles, Limitations, and New Ways in Food Production. IUFoST Sci. Inf. Bull. SIBs 2021. Available online: https://iufost.org/news/3d-food-printing-new-sib (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Voon, S.L.; An, J.; Wong, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chua, C.K. 3D Food Printing: A Categorised Review of Inks and Their Development. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2019, 14, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Bhattacharjee, S. Fundamentals of Food Printing. In Food Printing: 3D Printing in Food Industry; Sandhu, K., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 19–34. ISBN 978-981-16-8121-9. [Google Scholar]
- Derossi, A.; Corradini, M.G.; Caporizzi, R.; Oral, M.O.; Severini, C. Accelerating the Process Development of Innovative Food Products by Prototyping through 3D Printing Technology. Food Biosci. 2023, 52, 102417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morya, S.; Kumari, J.; Kumar, D.; Syed, A.; Awuchi, C.G. Three-Dimensional (3D) Printing Technology: 3D Printers, Technologies, and Application Insights in the Food Diligence. In Food Printing: 3D Printing in Food Industry; Sandhu, K., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 81–100. ISBN 978-981-16-8121-9. [Google Scholar]
- Derossi, A.; Caporizzi, R.; Ricci, I.; Severini, C. Chapter 3—Critical Variables in 3D Food Printing. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 41–91. ISBN 978-0-12-814564-7. [Google Scholar]
- Waseem, M.; Tahir, A.U.; Majeed, Y. Printing the Future of Food: The Physics Perspective on 3D Food Printing. Food Phys. 2024, 1, 100003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitayachaval, P.; Sanklong, N.; Thongrak, A. A Review of 3D Food Printing Technology. MATEC Web Conf. 2018, 213, 01012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kour, R.; Singh, H. Food Printing: Unfolding a New Paradigm for Designer and User. In Food Printing: 3D Printing in Food Industry; Sandhu, K., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 47–63. ISBN 978-981-16-8121-9. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, S.; Foster, T.; Tuck, C. Chapter 9—Creation of Food Structures Through Binder Jetting. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 257–288. ISBN 978-0-12-814564-7. [Google Scholar]
- Gunjal, M.; Rasane, P.; Singh, J.; Kaur, S.; Kaur, J. Three-Dimensional (3D) Food Printing: Methods, Processing and Nutritional Aspects. In Food Printing: 3D Printing in Food Industry; Sandhu, K., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 65–80. ISBN 978-981-16-8121-9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M. Chapter 2—3D Food Printing Technologies and Factors Affecting Printing Precision. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 19–40. ISBN 978-0-12-814564-7. [Google Scholar]
- Jonkers, N.; van Dijk, W.J.; Vonk, N.H.; van Dommelen, J.A.W.; Geers, M.G.D. Anisotropic Mechanical Properties of Selective Laser Sintered Starch-Based Food. J. Food Eng. 2022, 318, 110890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangalakshmi, S.; Arora, V.K. Three-Dimensional (3D) Food Printing and Its Process Parameters. In Food Printing: 3D Printing in Food Industry; Sandhu, K., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 35–45. ISBN 978-981-16-8121-9. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, C. Dual Extrusion 3D Printing of Mashed Potatoes/Strawberry Juice Gel. LWT 2018, 96, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Fu, Y.; Ma, L.; Yap, P.L.; Losic, D.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Rheology of Edible Food Inks from 2D/3D/4D Printing, and Its Role in Future 5D/6D Printing. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 132, 107855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejada-Ortigoza, V.; Cuan-Urquizo, E. Towards the Development of 3D-Printed Food: A Rheological and Mechanical Approach. Foods 2022, 11, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdov, A.D.; deClaville Christiansen, J. Rheology of Plant Protein–Polysaccharide Gel Inks for 3D Food Printing: Modeling and Structure–Property Relations. J. Food Eng. 2024, 380, 112150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugday, Z.Y.; Venkatachalam, A.; Anderson, P.D.; van der Sman, R.G.M. Rheology of Paste-like Food Inks for 3D Printing: Effects of Nutrient and Water Content. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 9, 100847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Ramniwas, S.; Kumar, R. Development of Cost-Effective and Sustainable Alternative Protein from Drosophila and Consumer Acceptability of Drosophila Protein Using 3D Printing. In Food Printing: 3D Printing in Food Industry; Sandhu, K., Singh, S., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2022; pp. 141–154. ISBN 978-981-16-8121-9. [Google Scholar]
- van Huis, A.; Van Itterbeeck, J.; Klunder, H.; Mertens, E.; Halloran, A.; Muir, G.; Vantomme, P. Edible Insects. Future Prospects for Food and Feed Security; FAO Forestry Paper; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2013; ISBN 978-92-5-107595-1. [Google Scholar]
- Caporizzi, R.; Derossi, A.; Severini, C. Chapter 4—Cereal-Based and Insect-Enriched Printable Food: From Formulation to Postprocessing Treatments. Status and Perspectives. In Fundamentals of 3D Food Printing and Applications; Godoi, F.C., Bhandari, B.R., Prakash, S., Zhang, M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 93–116. ISBN 978-0-12-814564-7. [Google Scholar]
- Orkusz, A. Edible Insects versus Meat—Nutritional Comparison: Knowledge of Their Composition Is the Key to Good Health. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparros Megido, R.; Sablon, L.; Geuens, M.; Brostaux, Y.; Alabi, T.; Blecker, C.; Drugmand, D.; Haubruge, É.; Francis, F. Edible Insects Acceptance by Belgian Consumers: Promising Attitude for Entomophagy Development. J. Sens. Stud. 2014, 29, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, C.; Siegrist, M. Becoming an Insectivore: Results of an Experiment. Food Qual. Prefer. 2016, 51, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carcea, M.; Narducci, V.; Turfani, V. Consumer Attitudes towards Insects as Food. In Edible Insects Processing for Food and Feed; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, S.; Forkes, A. Insects Au Gratin—An Investigation into the Experiences of Developing a 3D Printer That Uses Insect Protein Based Flour as a Building Medium for the Production of Sustainable Food. In Proceedings of the 16th International conference on Engineering and Product Design Education (E&PDE14), Design Education and Human Technology Relations, Enschede, The Netherlands, 4–5 September 2014; pp. 426–431. [Google Scholar]
- Eswaran, H.; Ponnuswamy, R.D.; Kannapan, R.P. Perspective Approaches of 3D Printed Stuffs for Personalized Nutrition: A Comprehensive Review. Ann. 3D Print. Med. 2023, 12, 100125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susana Soares: Insects Au Gratin/Project. Available online: http://www.susanasoares.com/index.php?id=82 (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Azzollini, D.; Derossi, A.; Fogliano, V.; Lakemond, C.M.M.; Severini, C. Effects of Formulation and Process Conditions on Microstructure, Texture and Digestibility of Extruded Insect-Riched Snacks. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2018, 45, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, C.; Azzollini, D.; Albenzio, M.; Derossi, A. On Printability, Quality and Nutritional Properties of 3D Printed Cereal Based Snacks Enriched with Edible Insects. Food Res. Int. 2018, 106, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herdeiro, F.M.; Carvalho, M.O.; Nunes, M.C.; Raymundo, A. Development of Healthy Snacks Incorporating Meal from Tenebrio Molitor and Alphitobius Diaperinus Using 3D Printing Technology. Foods 2024, 13, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedeji, O.E.; Lee, H.E.; Kim, Y.; Kang, H.J.; Kang, M.D.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.S.; Ezekiel, O.O.; Kim, W.-C.; Lee, S.-J.; et al. Three-Dimensional Printing of Wheat Flour and Acheta Domesticus Powder Blends. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 57, 6279–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, N.; Salvador, A.; Sanz, T.; Ferrando, M.; Güell, C.; Méndez, C.; de Lamo-Castellví, S. Rheological and Textural Characterisation of Chickpea Dough and Baked 3D-Printed Snacks Enriched with Alphitobius Diaperinus and Locusta Migratoria Powders. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 5199–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundarsingh, A.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S.; Li, J. Research Progress in Printing Formulation for 3D Printing of Healthy Future Foods. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 3408–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donn, P.; Prieto, M.A.; Mejuto, J.C.; Cao, H.; Simal-Gandara, J. Functional Foods Based on the Recovery of Bioactive Ingredients from Food and Algae By-Products by Emerging Extraction Technologies and 3D Printing. Food Biosci. 2022, 49, 101853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, H.; Li, C. Potential Sources of Novel Proteins Suitable for Use as Ingredients in 3D Food Printing, along with Some of the Food Safety Challenges. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2024, 37, 100983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyande, A.K.; Chew, K.W.; Rambabu, K.; Tao, Y.; Chu, D.-T.; Show, P.-L. Microalgae: A Potential Alternative to Health Supplementation for Humans. Food Sci. Hum. Wellness 2019, 8, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, E.W. Microalgae for Human and Animal Nutrition. In Handbook of Microalgal Culture; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 461–503. ISBN 978-1-118-56716-6. [Google Scholar]
- Seyidoglu, N.; Inan, S.; Aydin, C.; Seyidoglu, N.; Inan, S.; Aydin, C. A Prominent Superfood: Spirulina Platensis. In Superfood and Functional Food—The Development of Superfoods and Their Roles as Medicine; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; ISBN 978-953-51-2942-4. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, P.-J.; Tan, C.H.; Lo, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-C.; Show, P.L.; Lin, C.-H.; Chang, J.-S. Improving Protein Production of Indigenous Microalga Chlorella Vulgaris FSP-E by Photobioreactor Design and Cultivation Strategies. Biotechnol. J. 2015, 10, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, F.; Tul Zohra, K.; Naveed, K.; Zia, A.; Khaliq, M.; Noor, Z.; Khaliq, K.; Ali, M.A. Algal Proteins for Sustainable Nutrition and Functional Food Innovation. Appl. Food Res. 2025, 5, 100752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleakley, S.; Hayes, M. Algal Proteins: Extraction, Application, and Challenges Concerning Production. Foods 2017, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, S.M.; Gruppi, A.; Vieira, M.V.; Matos, G.S.; Vicente, A.A.; Teixeira, J.A.C.; Fuciños, P.; Spigno, G.; Pastrana, L.M. How Additive Manufacturing Can Boost the Bioactivity of Baked Functional Foods. J. Food Eng. 2021, 294, 110394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.V.; Oliveira, S.M.; Amado, I.R.; Fasolin, L.H.; Vicente, A.A.; Pastrana, L.M.; Fuciños, P. 3D Printed Functional Cookies Fortified with Arthrospira Platensis: Evaluation of Its Antioxidant Potential and Physical-Chemical Characterization. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 107, 105893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uribe-Wandurraga, Z.N.; Igual, M.; Reino-Moyón, J.; García-Segovia, P.; Martínez-Monzó, J. Effect of Microalgae (Arthrospira Platensis and Chlorella Vulgaris) Addition on 3D Printed Cookies. Food Biophys. 2021, 16, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.-J.; Guo, C.-F.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, Z.-P. Investigation on Characteristics of 3D Printing Using Nostoc Sphaeroides Biomass. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2019, 99, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Feng, Y.; Xu, Y. Production of Fish Analogues from Plant Proteins: Potential Strategies, Challenges, and Outlook. Foods 2023, 12, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwaha, N.; Beveridge, M.C.M.; Phillips, M.J. Fad, Food, or Feed: Alternative Seafood and Its Contribution to Food Systems. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2022, 6, 750253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BettaFish—The Best Fish Alternatives from Seaweed. Available online: https://bettafish.co (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- Hooked Foods—Enkelt, Gott & Näringsrikt. 100% Veganskt Såklart, För Allas Bästa! Available online: https://www.hookedfoods.com (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- Mimic Seafood|Plant-Based Seafood That Saves Oceans. Available online: https://mimicseafood.com/ (accessed on 7 November 2025).
- Accueil. Available online: https://www.odontella.com/ (accessed on 22 October 2025).
- Global Production Gracilaria. Seaweed Insights. Available online: https://seaweedinsights.com/global-production-gracilaria/ (accessed on 7 November 2025).
- Alasibi, S.; Kazir, M.; Israel, Á.; Livney, Y.D. Algal Protein-Based 3D-Printed Fish-Analogs as a New Approach for Sustainable Seafood. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 9, 100905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisht, B.; Begum, J.P.S.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Kurbatova, A.; Singh, N.; Nishinari, K.; Nanda, M.; Kumar, S.; Vlaskin, M.S.; Kumar, V. Unlocking the Potential of Future Version 3D Food Products with next Generation Microalgae Blue Protein Integration: A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S. Digital Food Revolution: Japanese Startup Open Meals Is 3D-Printing Sustainable Sushi; Green Queen: Hong Kong, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Open Meals. Available online: http://www.open-meals.com/ (accessed on 23 October 2025).
- Mirzapour-Kouhdasht, A.; Biparva, P.; McClements, D.J.; Garavand, F.; Garcia-Vaquero, M. Formulation of Inks for 3D Printing of Microalgae-Based Meat Analogues and the Role of Modified Starch: A Review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 59, 8618–8629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tang, T.; Shi, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Fan, J. The Potential and Challenge of Microalgae as Promising Future Food Sources. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 126, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B. Materials Properties of Printable Edible Inks and Printing Parameters Optimization during 3D Printing: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 3074–3081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, Z.F.; Morton, J.D.; Kumar, S.; Bhat, H.F.; Aadil, R.M.; Bekhit, A.E.-D.A. 3D Printing: Development of Animal Products and Special Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 118, 87–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, S.; Choudhury, D.; Naing, M.W. Cell-Based Meat: Current Ambiguities with Nomenclature. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 102, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, D.; He, B.; Hu, L.; Jiang, G. 3D Bioprinting of Cultured Meat: A Promising Avenue of Meat Production. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024, 17, 1659–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomkamp, C.; Skaalure, S.C.; Fernando, G.F.; Ben-Arye, T.; Swartz, E.W.; Specht, E.A. Scaffolding Biomaterials for 3D Cultivated Meat: Prospects and Challenges. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2102908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianovici, I.; Zagury, Y.; Redenski, I.; Lavon, N.; Levenberg, S. 3D-Printable Plant Protein-Enriched Scaffolds for Cultivated Meat Development. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handral, H.K.; Hua Tay, S.; Wan Chan, W.; Choudhury, D. 3D Printing of Cultured Meat Products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurel, M.; Rathod, N.; Cabrera, L.Y.; Voyton, S.; Yeo, M.; Ozogul, F.; Ozbolat, I.T. A Narrative Review: 3D Bioprinting of Cultured Muscle Meat and Seafood Products and Its Potential for the Food Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 152, 104670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.; Seo, J.W.; Lee, H.-G.; Jung, W.K.; Park, Y.H.; Bae, H. Efficient Myogenic/Adipogenic Transdifferentiation of Bovine Fibroblasts in a 3D Bioprinting System for Steak-Type Cultured Meat Production. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2202877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, B.; Nie, M.; Takeuchi, S. Manufacturing of Animal Products by the Assembly of Microfabricated Tissues. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlota, V. Aleph Farms and 3D Bioprinting Solutions Collaborate to Create Slaughter-Free Meat; 3Dnatives: Paris, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- GOOD Meat|GOOD Meat Partners with ADM to Build the World’s First Large-Scale Cultivated Meat Facility. Available online: https://www.goodmeat.co/all-news/good-meat-partners-with-industry-leader-to-build-first-large-scale-cultivated-meat-facility (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Zhang, Y.S.; Oklu, R.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A. Three-Dimensional Bioprinting Strategies for Tissue Engineering. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a025718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleymani, S.; Naghib, S.M.; Mozafari, M.R. An Overview of Cultured Meat and Stem Cell Bioprinting: How to Make It, Challenges and Prospects, Environmental Effects, Society’s Culture and the Influence of Religions. J. Agric. Food Res. 2024, 18, 101307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-Y.; Hu, Z.-N.; Zhou, G.-H. A Review: Analysis of Technical Challenges in Cultured Meat Production and Its Commercialization. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2025, 65, 1911–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanz, M.; Hartmann, C.; Egan, P.; Siegrist, M. Consumer Acceptance of Cultured, Plant-Based, 3D-Printed Meat and Fish Alternatives. Future Foods 2024, 9, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searchinger, T.; Waite, R.; Hanson, C.; Ranganathan, J.; Matthews, E. Creating a Sustainable Food Future; World Resources Institute (WRI): Washington, DC, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-56973-963-1. [Google Scholar]
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2022. Repurposing Food and Agricultural Policies to Make Healthy Diets More Affordable; The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World (SOFI); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022; ISBN 978-92-5-136499-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aureli, V.; Nardi, A.; Palmieri, N.; Peluso, D.; Di Veroli, J.N.; Scognamiglio, U.; Rossi, L. Sustainability Perception of Italian Consumers: Is It Possible to Replace Meat, and What Is the Best Alternative? Nutrients 2023, 15, 3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Iskandar, M.M.; Baeghbali, V.; Kubow, S. Three-Dimensional Printing of Foods: A Critical Review of the Present State in Healthcare Applications, and Potential Risks and Benefits. Foods 2023, 12, 3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoha, K.S.; Moses, J.A. 3D Printing Approach to Valorization of Agri-Food Processing Waste Streams. Foods 2023, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, N.A.; Pareek, S.; Sharma, S.; Yahia, E.M.; Lobo, M.G. Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Bioactive Compounds, Their Extraction, and Possible Utilization. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 512–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, J.L.; Lloyd, B. Health Benefits of Fruits and Vegetables. Adv. Nutr. 2012, 3, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, M.; Bhandari, B.; Ye, Y. Use of Potato Processing By-Product: Effects on the 3D Printing Characteristics of the Yam and the Texture of Air-Fried Yam Snacks. LWT 2020, 125, 109265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.D.; Lee, C.P.; Foo, S.Y.; Tan, J.C.W.; Tan, S.S.Y.; Ong, E.S.; Leo, C.H.; Hashimoto, M. 3D Printability and Biochemical Analysis of Revalorized Orange Peel Waste. Int. J. Bioprinting 2023, 9, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Montero, C.; Vicente-Jurado, D.; Igual, M.; Martínez-Monzó, J.; García-Segovia, P. Fiber Enrichment of 3D Printed Apricot Gel Snacks with Orange By-Products. Gels 2023, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.D.; Lee, C.P.; Leo, C.H.; Hashimoto, M. Enhancing Three-Dimensional (3D) Printablity of Durian Husk Inks. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 70, 698–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, A.; Ni Leam, P.X.; Chua, C.K.; Tan, U.-X. Valorisation of Vegetable Food Waste Utilising Three-Dimensional Food Printing. Virtual Phys. Prototyp. 2023, 18, e2146593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadiswaran, B.; Alagarasan, V.; Palanivelu, P.; Theagarajan, R.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Valorization of Food Industry Waste and By-Products Using 3D Printing: A Study on the Development of Value-Added Functional Cookies. Future Foods 2021, 4, 100036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadzadeh, S.; Clary, T.; Rosales, A.; Ubeyitogullari, A. Upcycling Imperfect Broccoli and Carrots into Healthy Snacks Using an Innovative 3D Food Printing Approach. Food Sci. Nutr. 2024, 12, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Wang, P.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X. 3D Printing Based on Meat Materials: Challenges and Opportunities. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 6, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal-Mena, N.; Tabilo-Munizaga, G.; Pérez-Won, M.; Lemus-Mondaca, R. Valorization of Salmon Industry By-Products: Evaluation of Salmon Skin Gelatin as a Biomaterial Suitable for 3D Food Printing. LWT 2022, 155, 112931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Lu, X.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.; Wang, L.; Qian, Y.; Zeng, M. Rheological and Physicochemical Properties of Spirulina Platensis Residues-Based Inks for Extrusion 3D Food Printing. Food Res. Int. 2023, 169, 112823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooh, P.; Jury, V.; Laurent, S.; Audiat-Perrin, F.; Sanaa, M.; Tesson, V.; Federighi, M.; Boué, G. Control of Biological Hazards in Insect Processing: Application of HACCP Method for Yellow Mealworm (Tenebrio Molitor) Powders. Foods 2020, 9, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.C.; Cunha, L.M.; Sousa-Pinto, B.; Fonseca, J. Allergic Risks of Consuming Edible Insects: A Systematic Review. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2018, 62, 1700030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, F.; Doyen, V.; Debaugnies, F.; Mazzucchelli, G.; Caparros, R.; Alabi, T.; Blecker, C.; Haubruge, E.; Corazza, F. Limited Cross Reactivity among Arginine Kinase Allergens from Mealworm and Cricket Edible Insects. Food Chem. 2019, 276, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Gier, S.; Verhoeckx, K. Insect (Food) Allergy and Allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 100, 82–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; Li, S.; He, K.; Sun, F.; Mu, L.; Li, Q.; Yi, J.; He, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wu, X. Identification of Potential Allergens in Larva, Pupa, Moth, Silk, Slough and Feces of Domestic Silkworm (Bombyx Mori). Food Chem. 2021, 362, 130231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) 2015/2283 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 November 2015 on Novel Foods, Amending Regulation (EU) No 1169/2011 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Repealing Regulation (EC) No 258/97 of the European Parliament and of the Council and Commission Regulation (EC) No 1852/2001 (Text with EEA Relevance); 2015; Volume 327. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2015/2283/oj/eng (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Committee, E.S. Risk Profile Related to Production and Consumption of Insects as Food and Feed. EFSA J. 2015, 13, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dhabi, N.A. Heavy Metal Analysis in Commercial Spirulina Products for Human Consumption. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 20, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rzymski, P.; Niedzielski, P.; Kaczmarek, N.; Jurczak, T.; Klimaszyk, P. The Multidisciplinary Approach to Safety and Toxicity Assessment of Microalgae-Based Food Supplements Following Clinical Cases of Poisoning. Harmful Algae 2015, 46, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, J.; Brightwell, G. Safety of Alternative Proteins: Technological, Environmental and Regulatory Aspects of Cultured Meat, Plant-Based Meat, Insect Protein and Single-Cell Protein. Foods 2021, 10, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Commission. Commission Recommendation (EU) 2018/464 of 19 March 2018 on the Monitoring of Metals and Iodine in Seaweed, Halophytes and Products Based on Seaweed (Text with EEA Relevance.). Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, L 078, 16–18. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32018H0464 (accessed on 5 November 2025).
- Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, R.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, J.; Wang, G. Physiological Responses of Lettuce (Lactuca Sativa L.) to Microplastic Pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 30306–30314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, J.; Mickan, B.S.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Rinklebe, J.; Kirkham, M.B.; Bolan, N.S. Physical, Chemical, and Microbial Contaminants in Food Waste Management for Soil Application: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 300, 118860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Pandya, J.K.; McClements, D.J.; Lu, J.; Kinchla, A.J. Advancements in 3D Food Printing: A Comprehensive Overview of Properties and Opportunities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 4752–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severini, C.; Derossi, A.; Azzollini, D. Variables Affecting the Printability of Foods: Preliminary Tests on Cereal-Based Products. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 38, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeleny, P.; Ruzicka, V. The Design of the 3D Printer for Use in Gastronomy. MM Sci. J. 2017, 2017, 1744–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhou, W.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Hong, G.S.; Chiu, A. A Review on 3D Printing for Customized Food Fabrication. Procedia Manuf. 2015, 1, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bégin-Drolet, A.; Dussault, M.-A.; Fernandez, S.A.; Larose-Dutil, J.; Leask, R.L.; Hoesli, C.A.; Ruel, J. Design of a 3D Printer Head for Additive Manufacturing of Sugar Glass for Tissue Engineering Applications. Addit. Manuf. 2017, 15, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiano, A. 3D Printed Foods: A Comprehensive Review on Technologies, Nutritional Value, Safety, Consumer Attitude, Regulatory Framework, and Economic and Sustainability Issues. Food Rev. Int. 2022, 38, 986–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, A.N.; Gibson, K.E. Efficacy of Manufacturer Recommendations for the Control of Salmonella Typhimurium and Listeria monocytogenes in Food Ink Capsules Utilized in 3D Food Printing Systems. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, A.N.; Gibson, K.E. Transfer Rates of Salmonella Typhimurium, Listeria monocytogenes, and a Human Norovirus Surrogate Impacted by Macronutrient Composition of Food Inks in 3D Food Printing Systems. Food Microbiol. 2023, 113, 104268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegrist, M.; Hartmann, C. Consumer Acceptance of Novel Food Technologies. Nat. Food 2020, 1, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blutinger, J.D.; Tsai, A.; Storvick, E.; Seymour, G.; Liu, E.; Samarelli, N.; Karthik, S.; Meijers, Y.; Lipson, H. Precision Cooking for Printed Foods via Multiwavelength Lasers. Npj Sci. Food 2021, 5, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellali, W.; Korai, B. Understanding Consumer’s Acceptability of the Technology behind Upcycled Foods: An Application of the Technology Acceptance Model. Food Qual. Prefer. 2023, 110, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.; Pereira, T.; Mendes, S.; Gordo, L.; Gil, M.M. Consumer’s Perceptions and Motivations on the Consumption of Fortified Foods and 3D Food Printing. Future Foods 2024, 10, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Gao, J.; Yang, Q.; Al Mamun, A.; Masukujjaman, M.; Hoque, M.E. Modeling the Intention to Consume and Willingness to Pay Premium Price for 3D-Printed Food in an Emerging Economy. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, M.M.; Collins, A.M.; McCarthy, M.B.; Kelly, A.L. Overcoming Barriers to Consumer Acceptance of 3D-Printed Foods in the Food Service Sector. Food Qual. Prefer. 2022, 100, 104615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, F.T.; Garrett, B. Technology for Sustainable Urban Food Ecosystems in the Developing World: Strengthening the Nexus of Food–Water–Energy–Nutrition. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2018, 2, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blutinger, J.D.; Cooper, C.C.; Karthik, S.; Tsai, A.; Samarelli, N.; Storvick, E.; Seymour, G.; Liu, E.; Meijers, Y.; Lipson, H. The Future of Software-Controlled Cooking. Npj Sci. Food 2023, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).