Self-Supervised Depth and Ego-Motion Learning from Multi-Frame Thermal Images with Motion Enhancement
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose a self-supervised multi-frame depth and ego-motion learning framework for monocular thermal videos. It successfully leverages the temporal advantages of multiple thermal frames by constructing the multi-view stereo. The accuracy of prediction results is further improved through the integration of motion hints and multi-spectral properties.
- We design a motion enhancement module that utilizes self-generated motion constraints to complement self-supervised signals. It enhances the stability of motion hints within the framework, consequently improving the accuracy of pose estimation.
- We employ an efficient objective function that combines photometric loss, thermal loss, and motion loss to address the challenges in real-world scenarios, including unavoidable low-light conditions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Self-Supervised Depth and Ego-Motion Learning
2.2. Depth and Ego-Motion Learning with Thermal Images
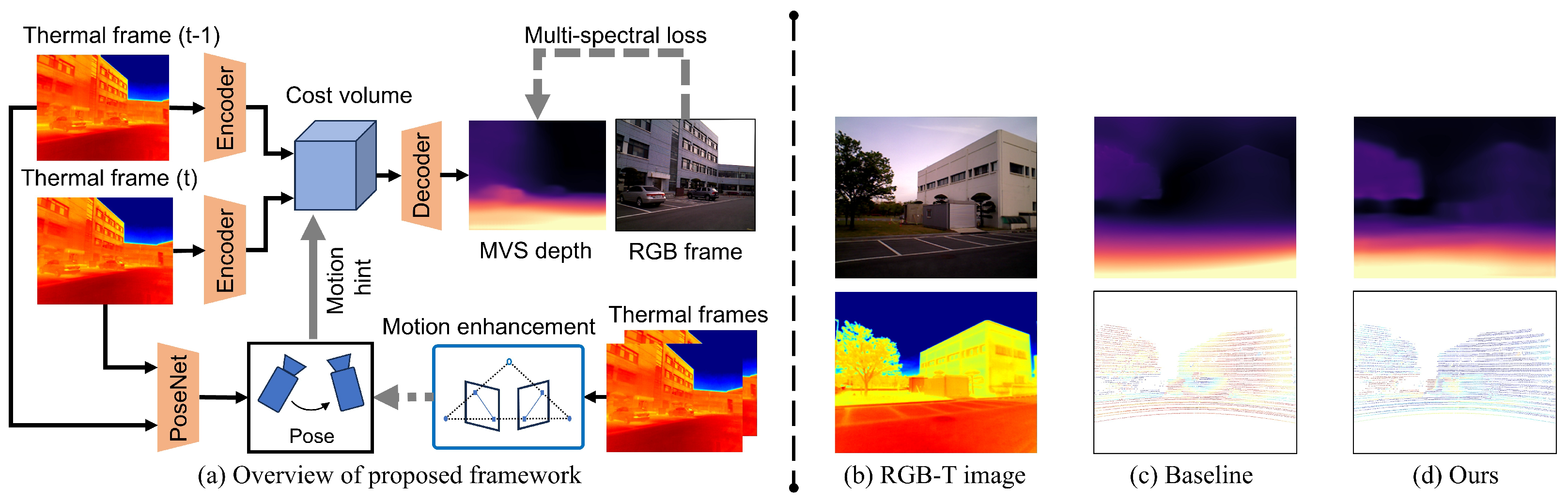
3. Method
3.1. Method Overview
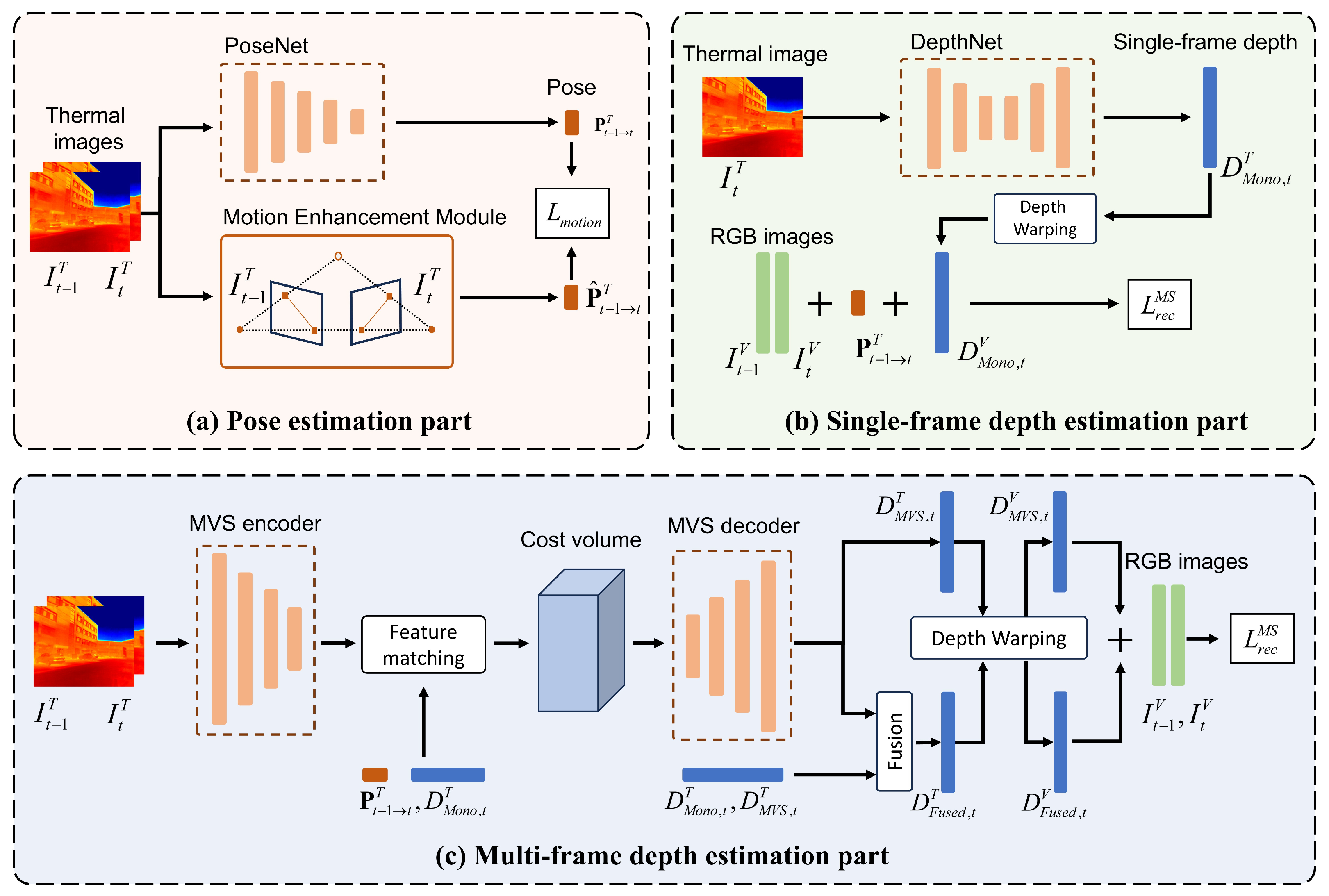
3.2. Single-Frame Self-Supervised Depth Learning
3.3. Multi-Frame Depth Learning from Thermal Images with Motion Hint
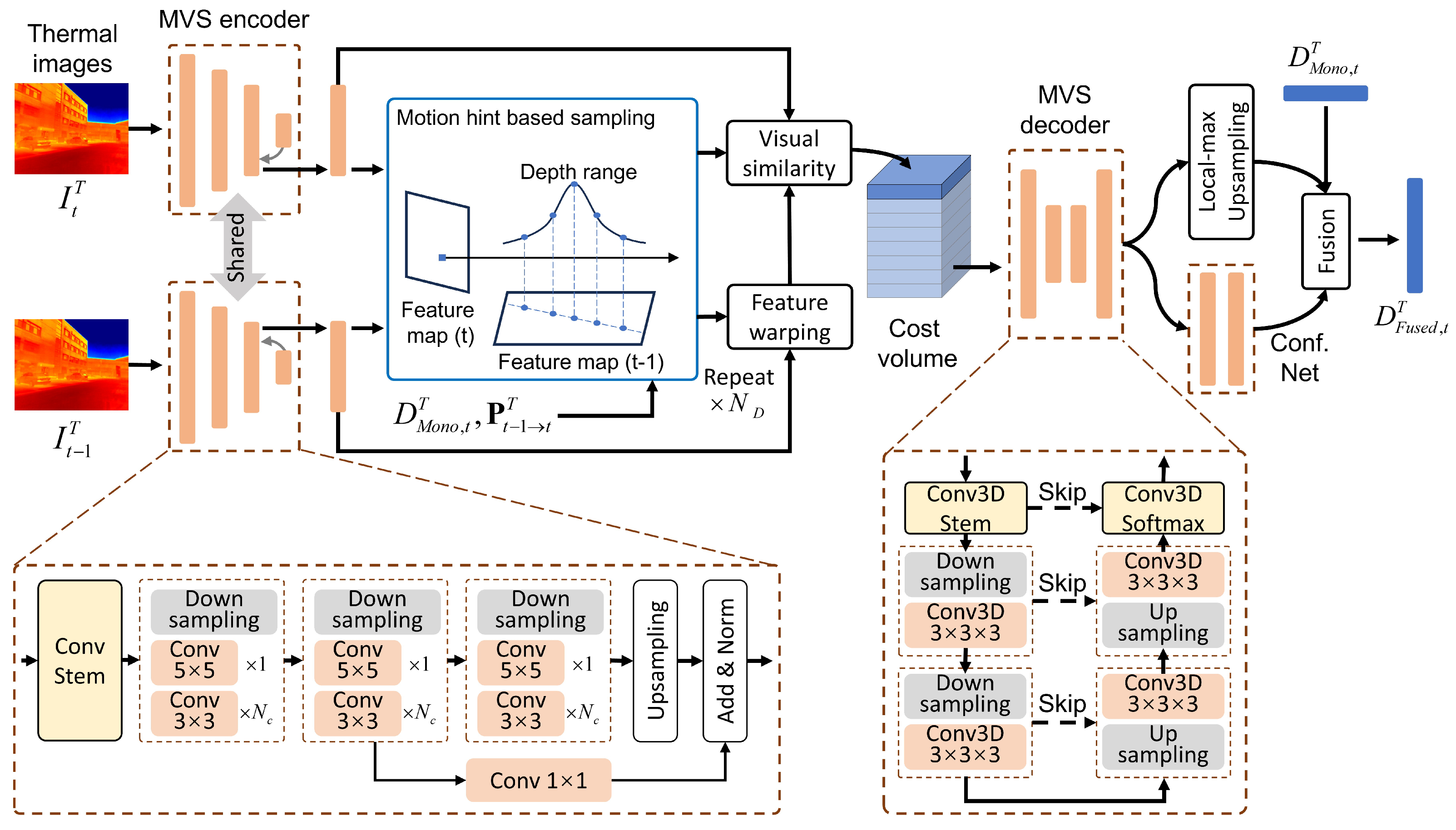
3.3.1. Cost Volume Construction
3.3.2. Depth Sampling with Motion Hint
3.3.3. Depth Fusing
3.4. Motion Enhancement Using Epipolar Geometry Constraint
3.4.1. Epipolar Geometry Constraint
3.4.2. Matrix Scoring and Selection
3.4.3. Montion Recovery
3.4.4. Motion Loss
3.5. Multi-Spectral Loss
3.5.1. Thermal Reconstruction Loss
3.5.2. Depth Warping
3.5.3. Photometric Reconstruction Loss
3.5.4. Total Loss Function
4. Experiments
4.1. Datasets
4.2. Thermal Image Preprocessing
4.3. Implementation Details
Training Configuration
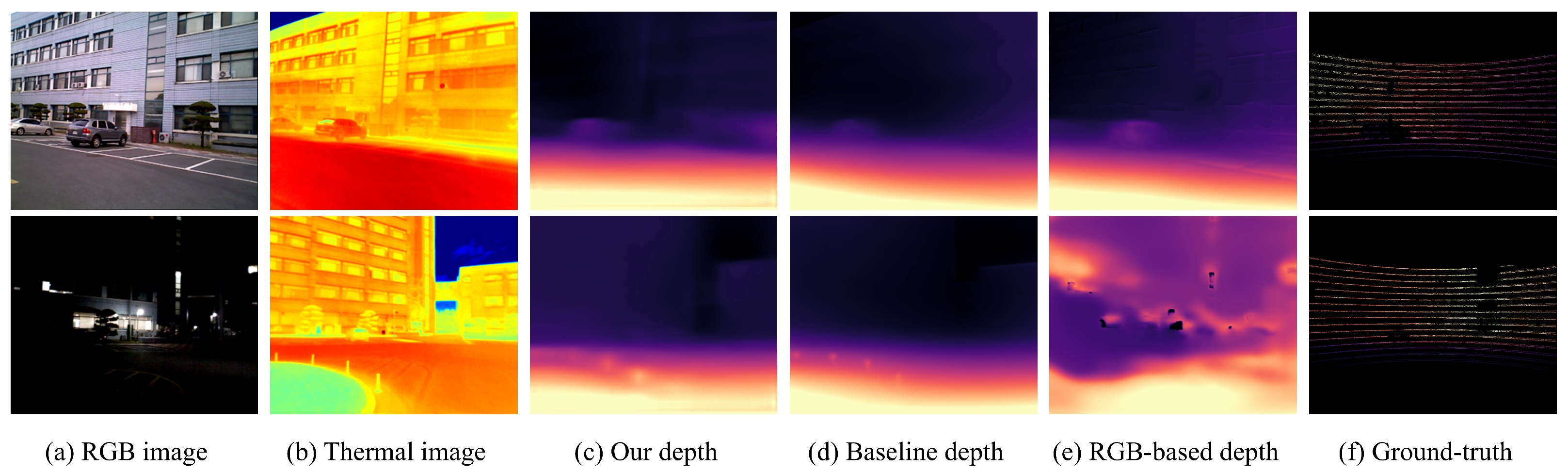
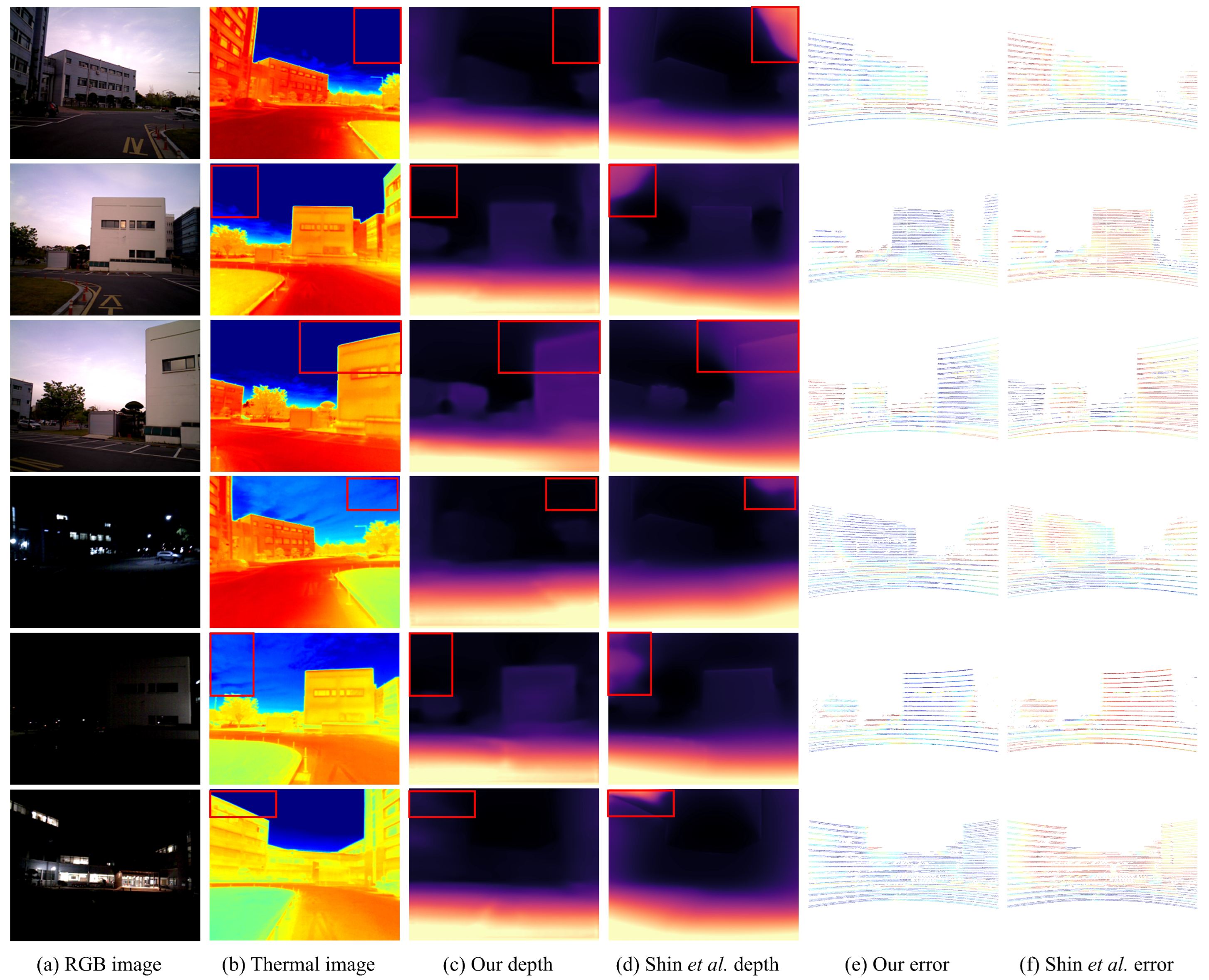
4.4. Depth Prediction Results
4.5. Pose Estimation Results
4.6. Ablation Study
4.6.1. Effect of Each Component
4.6.2. Effect of Each Loss Term
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Lee, D. EASD: Exposure Aware Single-Step Diffusion Framework for Monocular Depth Estimation in Autonomous Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, P.; Dong, X.; Ge, R.; Liu, Z.; Yang, A. Dp-M3D: Monocular 3D object detection algorithm with depth perception capability. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 318, 113539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.J.; Tsai, H.; Chan, D.Y. High-Precision Depth Estimation Networks Using Low-Resolution Depth and RGB Image Sensors for Low-Cost Mixed Reality Glasses. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Brown, M.; Snavely, N.; Lowe, D.G. Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from video. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godard, C.; Mac Aodha, O.; Firman, M.; Brostow, G.J. Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 3828–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peng, S.; Chen, J.; Peng, S.; Sun, J.; Liu, M.; Bao, H.; Feng, J.; Zhou, X.; Kang, B. Prompting depth anything for 4k resolution accurate metric depth estimation. In Proceedings of the Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 11–15 June 2025; pp. 17070–17080. [Google Scholar]
- Aditya, N.; Dhruval, P. Thermal voyager: A comparative study of rgb and thermal cameras for night-time autonomous navigation. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Yokohama, Japan, 13–17 May 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 14116–14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Khan, S.; Daud, M.; Asim, M.; Anwar, G.A.; Shahid, A.R.; Ho, H.P.A.; Chan, T.; Pak Kong, D.; Yuan, W. Improving Autonomous Vehicle Cognitive Robustness in Extreme Weather With Deep Learning and Thermal Camera Fusion. IEEE Open J. Vehic. Tech. 2025, 6, 426–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Lu, G. An alternative of lidar in nighttime: Unsupervised depth estimation based on single thermal image. In Proceedings of the Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Virtual, 5–9 January 2021; pp. 3833–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Choi, Y.; Hwang, S.; Kweon, I.S. Multispectral transfer network: Unsupervised depth estimation for all-day vision. In Proceedings of the Conference AAAI, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; pp. 6983–6991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, U.; Lee, K.; Lee, S.; Kweon, I.S. Self-supervised depth and ego-motion estimation for monocular thermal video using multi-spectral consistency loss. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönberger, J.L.; Zheng, E.; Frahm, J.M.; Pollefeys, M. Pixelwise view selection for unstructured multi-view stereo. In Proceedings of the European Conference, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 11–14 October 2016; pp. 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fu, Z.; Yang, D.; Deng, J. Single-image depth perception in the wild. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2016, 29, 730–738. [Google Scholar]
- Eigen, D.; Puhrsch, C.; Fergus, R. Depth map prediction from a single image using a multi-scale deep network. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2014, 27, 2366–2374. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, L. A Survey on Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation Based on Deep Neural Networks. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2025, 36, 15622–15642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guizilini, V.; Ambrus, R.; Pillai, S.; Raventos, A.; Gaidon, A. 3D packing for self-supervised monocular depth estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2485–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, N.; Zhan, H.; Shen, C.; Cheng, M.M.; Reid, I. Unsupervised scale-consistent depth and ego-motion learning from monocular video. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 33, 35–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, J.; Zhan, H.; Wang, N.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Shen, C.; Cheng, M.M.; Reid, I. Unsupervised scale-consistent depth learning from video. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2548–2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM2: An open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2017, 33, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wu, M.; Lam, S.K.; Wang, C.; Wang, R. EDS-Depth: Enhancing Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation in Dynamic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2025, 26, 5585–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; Lu, K.; Ge, L. Self-Supervised Monocular Depth Estimation With Dual-Path Encoders and Offset Field Interpolation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2025, 34, 939–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Yin, W.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Yang, X. Adaptive Fusion of Single-View and Multi-View Depth for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 10138–10147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, G.; Chi, X.; Ye, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X. Crafting monocular cues and velocity guidance for self-supervised multi-frame depth learning. In Proceedings of the Conference AAAI, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 2689–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, J.; Mac Aodha, O.; Prisacariu, V.; Brostow, G.; Firman, M. The temporal opportunist: Self-supervised multi-frame monocular depth. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Virtual, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 1164–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, G.; Budvytis, I.; Cipolla, R. Multi-view depth estimation by fusing single-view depth probability with multi-view geometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 2842–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wei, H.; He, H. IAFMVS: Iterative Depth Estimation with Adaptive Features for Multi-View Stereo. Neurocomputing 2025, 629, 129682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, Q.; Che, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, G. IFDepth: Iterative fusion network for multi-frame self-supervised monocular depth estimation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2025, 318, 113467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Edge-Based Monocular Thermal-Inertial Odometry in Visually Degraded Environments. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2078–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doer, C.; Trommer, G.F. Radar visual inertial odometry and radar thermal inertial odometry: Robust navigation even in challenging visual conditions. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Prague, Czech Republic, 27 September–1 October 2021; pp. 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (MICCAI), Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; Volume 9351, pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Galliani, S.; Vogel, C.; Pollefeys, M. IterMVS: Iterative probability estimation for efficient multi-view stereo. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 8606–8615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Luo, Z.; Fang, T.; Yao, Y. Vis-mvsnet: Visibility-aware multi-view stereo network. Int. J. Comput. Vision 2023, 131, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mur-Artal, R.; Montiel, J.M.M.; Tardos, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system. IEEE Trans. Robot. 2015, 31, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Zhu, C.; Huang, Q.; Ren, B.; Liu, J. A review of monocular visual odometry. Vis. Comput. 2020, 36, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, D.G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2004, 60, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z. Eight-Point Algorithm. In Computer Vision: A Reference Guide; Ikeuchi, K., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 370–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, R.; Zisserman, A. Multiple View Geometry in Computer Vision; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faugeras, O.D.; Lustman, F. Motion and structure from motion in a piecewise planar environment. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 1988, 2, 485–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Bovik, A.C.; Sheikh, H.R.; Simoncelli, E.P. Image quality assessment: From error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2004, 13, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Siyao, L.; Sun, W.; Yin, Q.; Yang, M.H. Quadratic video interpolation. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A.; Kavukcuoglu, K. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 29, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Godard, C.; Mac Aodha, O.; Brostow, G.J. Unsupervised monocular depth estimation with left-right consistency. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.J.; Cho, Y.; Shin, Y.S.; Kim, A.; Myung, H. ViViD++: Vision for visibility dataset. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 6282–6289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paszke, A.; Gross, S.; Massa, F.; Lerer, A.; Bradbury, J.; Chanan, G.; Killeen, T.; Lin, Z.; Gimelshein, N.; Antiga, L.; et al. PyTorch: An Imperative Style, High-Performance Deep Learning Library. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 8–14 December 2019; Curran Associates, Inc.: Nice, France, 2019; Volume 32. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J.L. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), San Diego, CA, USA, 7–9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Scaramuzza, D. A tutorial on quantitative trajectory evaluation for visual (-inertial) odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Madrid, Spain, 1–5 October 2018; pp. 7244–7251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Scene | Methods | Input | Error (Lower Is Better) | Accuracy (Higher Is Better) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abs. Rel. | Sq. Rel. | RMSE | RMSElog | ||||||
| Outdoor day1 | SfMLearner [4] | V | 0.200 | 1.549 | 6.394 | 0.248 | 0.684 | 0.922 | 0.975 |
| Monodepth2 [5] | V | 0.436 | 6.318 | 9.967 | 0.454 | 0.491 | 0.719 | 0.840 | |
| Bian et al. [17] | V | 0.136 | 1.464 | 5.638 | 0.179 | 0.844 | 0.977 | 0.991 | |
| Watson et al. [24] | V | 0.166 | 1.472 | 6.358 | 0.220 | 0.754 | 0.945 | 0.986 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (T) | T | 0.143 | 0.766 | 4.547 | 0.180 | 0.790 | 0.979 | 0.996 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (MS) | T | 0.142 | 0.792 | 4.730 | 0.181 | 0.788 | 0.980 | 0.996 | |
| Ours | T | 0.115 | 0.683 | 4.310 | 0.159 | 0.869 | 0.980 | 0.996 | |
| Outdoor day2 | SfMLearner [4] | V | 0.192 | 1.652 | 6.511 | 0.235 | 0.702 | 0.941 | 0.978 |
| Monodepth2 [5] | V | 0.435 | 6.915 | 9.576 | 0.438 | 0.591 | 0.752 | 0.843 | |
| Bian et al. [17] | V | 0.131 | 1.376 | 5.899 | 0.185 | 0.822 | 0.976 | 0.991 | |
| Watson et al. [24] | V | 0.197 | 2.281 | 7.707 | 0.241 | 0.695 | 0.922 | 0.982 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (T) | T | 0.148 | 0.933 | 4.736 | 0.188 | 0.802 | 0.970 | 0.991 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (MS) | T | 0.145 | 0.917 | 4.784 | 0.187 | 0.804 | 0.971 | 0.991 | |
| Ours | T | 0.122 | 0.957 | 4.787 | 0.170 | 0.855 | 0.968 | 0.991 | |
| Outdoor night1 | SfMLearner [4] | V | 0.429 | 4.584 | 8.624 | 0.445 | 0.468 | 0.698 | 0.834 |
| Monodepth2 [5] | V | 0.704 | 11.75 | 12.53 | 0.636 | 0.362 | 0.559 | 0.701 | |
| Bian et al. [17] | V | 0.520 | 6.413 | 10.40 | 0.516 | 0.381 | 0.596 | 0.755 | |
| Watson et al. [24] | V | 0.469 | 5.690 | 10.96 | 0.466 | 0.332 | 0.612 | 0.839 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (T) | T | 0.158 | 0.844 | 4.634 | 0.192 | 0.754 | 0.977 | 0.996 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (MS) | T | 0.156 | 0.856 | 4.813 | 0.192 | 0.752 | 0.976 | 0.996 | |
| Ours | T | 0.119 | 0.747 | 4.189 | 0.162 | 0.850 | 0.979 | 0.996 | |
| Outdoor night2 | SfMLearner [4] | V | 0.373 | 4.215 | 8.294 | 0.396 | 0.548 | 0.773 | 0.879 |
| Monodepth2 [5] | V | 0.602 | 10.84 | 11.72 | 0.562 | 0.477 | 0.650 | 0.759 | |
| Bian et al. [17] | V | 0.464 | 6.376 | 9.887 | 0.472 | 0.511 | 0.685 | 0.807 | |
| Watson et al. [24] | V | 0.416 | 4.860 | 10.16 | 0.428 | 0.383 | 0.692 | 0.873 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (T) | T | 0.159 | 1.084 | 5.115 | 0.204 | 0.772 | 0.957 | 0.989 | |
| Shin et al. [11] (MS) | T | 0.156 | 1.049 | 5.166 | 0.202 | 0.775 | 0.957 | 0.989 | |
| Ours | T | 0.124 | 0.899 | 4.694 | 0.179 | 0.829 | 0.963 | 0.990 | |
| Methods | Input | Outdoor Day1 | Outdoor Day2 | Outdoor Night1 | Outdoor Night2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. | Mean | Std. | Mean | Std. | Mean | Std. | ||
| SfMLearner [17] | V | 0.0774 | 0.0407 | 0.0867 | 0.0414 | 0.0657 | 0.0342 | 0.0579 | 0.0279 |
| Monodepth2 [5] | V | 0.0525 | 0.0305 | 0.0544 | 0.0266 | 0.0552 | 0.0302 | 0.0545 | 0.0277 |
| Bian et al. [17] | V | 0.0503 | 0.0255 | 0.0514 | 0.0285 | 0.0886 | 0.0439 | 0.0888 | 0.0390 |
| Shin et al. [11] (T) | T | 0.0751 | 0.0371 | 0.0784 | 0.0391 | 0.0744 | 0.0417 | 0.0793 | 0.0402 |
| Shin et al. [11] (MS) | T | 0.0541 | 0.0307 | 0.0643 | 0.0365 | 0.0590 | 0.0315 | 0.0604 | 0.0315 |
| Ours | T | 0.0429 | 0.0251 | 0.0450 | 0.0248 | 0.0464 | 0.0288 | 0.0442 | 0.0252 |
| Methods | Abs. Rel. | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ours (full) | 0.127 | 4.305 | 0.831 |
| Ours (w/o depth warping) | 0.144 | 4.729 | 0.815 |
| Ours (w/o motion enhancement) | 0.138 | 4.763 | 0.824 |
| Ours (w/o motion hint) | 0.140 | 4.798 | 0.816 |
| Ours (w/o remapping) | 0.140 | 4.832 | 0.813 |
| Ours (w/o depth fusing) | 0.136 | 4.478 | 0.816 |
| Methods | Abs. Rel. | RMSE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ours (full) | 0.127 | 4.305 | 0.831 |
| Ours (w/o thermal loss) | - | - | - |
| Ours (w/o motion loss) | 0.138 | 4.763 | 0.824 |
| Ours (w/o smoothness loss) | 0.140 | 4.742 | 0.799 |
| Ours (w/o RGB loss) | 0.144 | 4.729 | 0.815 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, R.; Ma, G.; Guo, J.; Xu, L. Self-Supervised Depth and Ego-Motion Learning from Multi-Frame Thermal Images with Motion Enhancement. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211890
Yu R, Ma G, Guo J, Xu L. Self-Supervised Depth and Ego-Motion Learning from Multi-Frame Thermal Images with Motion Enhancement. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):11890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211890
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Rui, Guoliang Ma, Jian Guo, and Lisong Xu. 2025. "Self-Supervised Depth and Ego-Motion Learning from Multi-Frame Thermal Images with Motion Enhancement" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 11890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211890
APA StyleYu, R., Ma, G., Guo, J., & Xu, L. (2025). Self-Supervised Depth and Ego-Motion Learning from Multi-Frame Thermal Images with Motion Enhancement. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 11890. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211890






