Robust Vehicle Pose Estimation Through Multi-Sensor Fusion of Camera, IMU, and GPS Using LSTM and Kalman Filter
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We propose an integrated localization architecture that combines local relative motion estimation and global GPS data using a deep neural network and Kalman filter, improving pose estimation accuracy and reliability.
- We introduce a novel fusion strategy that leverages latent vectors from auxiliary pose estimators to assess sensor data reliability, enabling robust performance in the presence of sensor failures or missing data.
- We develop a staged training approach that enhances fusion performance by ensuring the module operates on high-quality inputs from pretrained auxiliary networks.
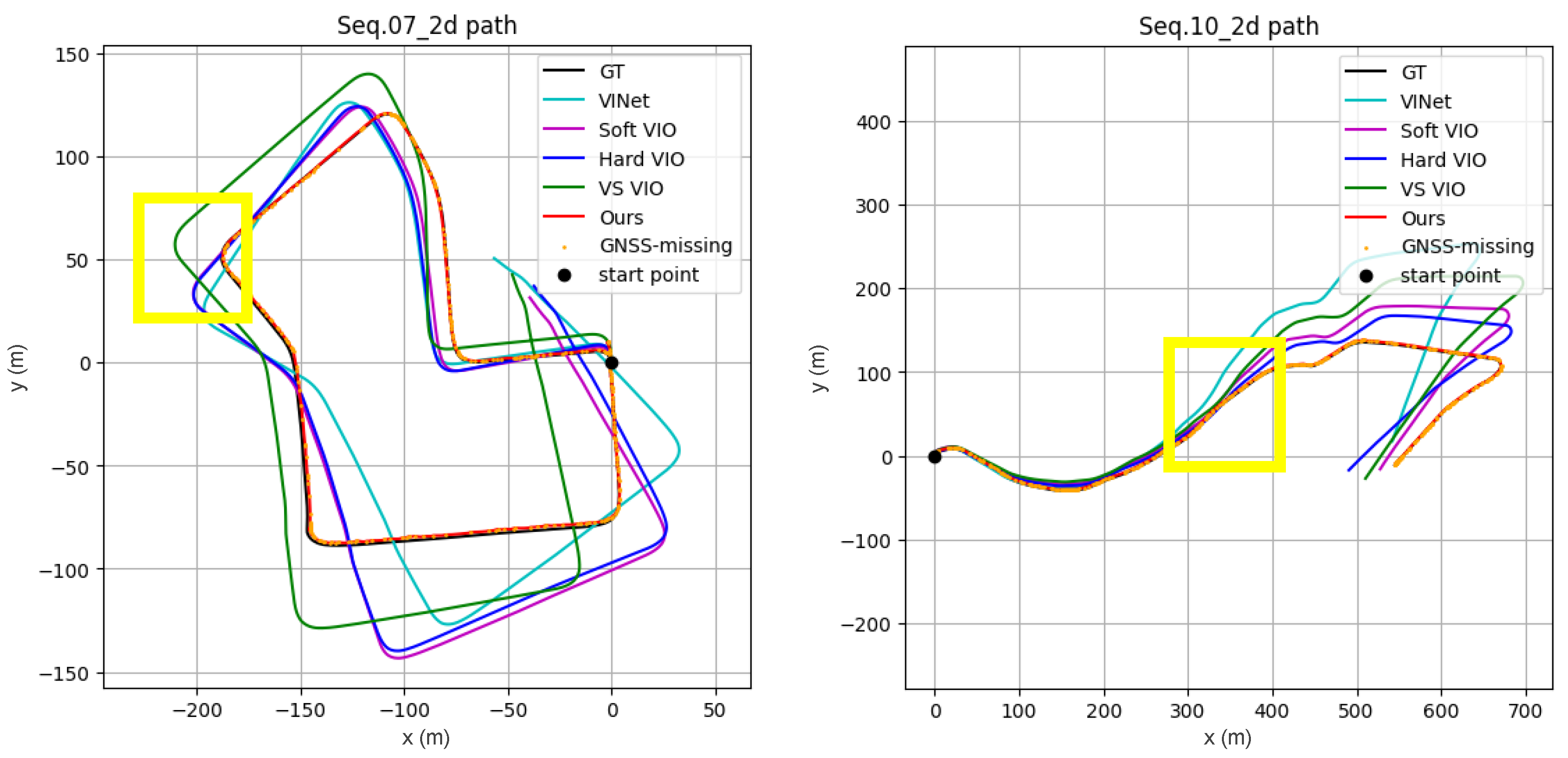
- We validate our method through extensive experiments, demonstrating stable performance in challenging scenarios. On KITTI sequences 07 and 10, our method reduced the average position RMSE by 79–91% compared to four state-of-the-art baselines (VS VIO, Hard VIO, Soft VIO, and VINet), confirming its effectiveness for real-world deployment in autonomous systems.
2. Proposed Robust Vehicle Pose Estimation Algorithm
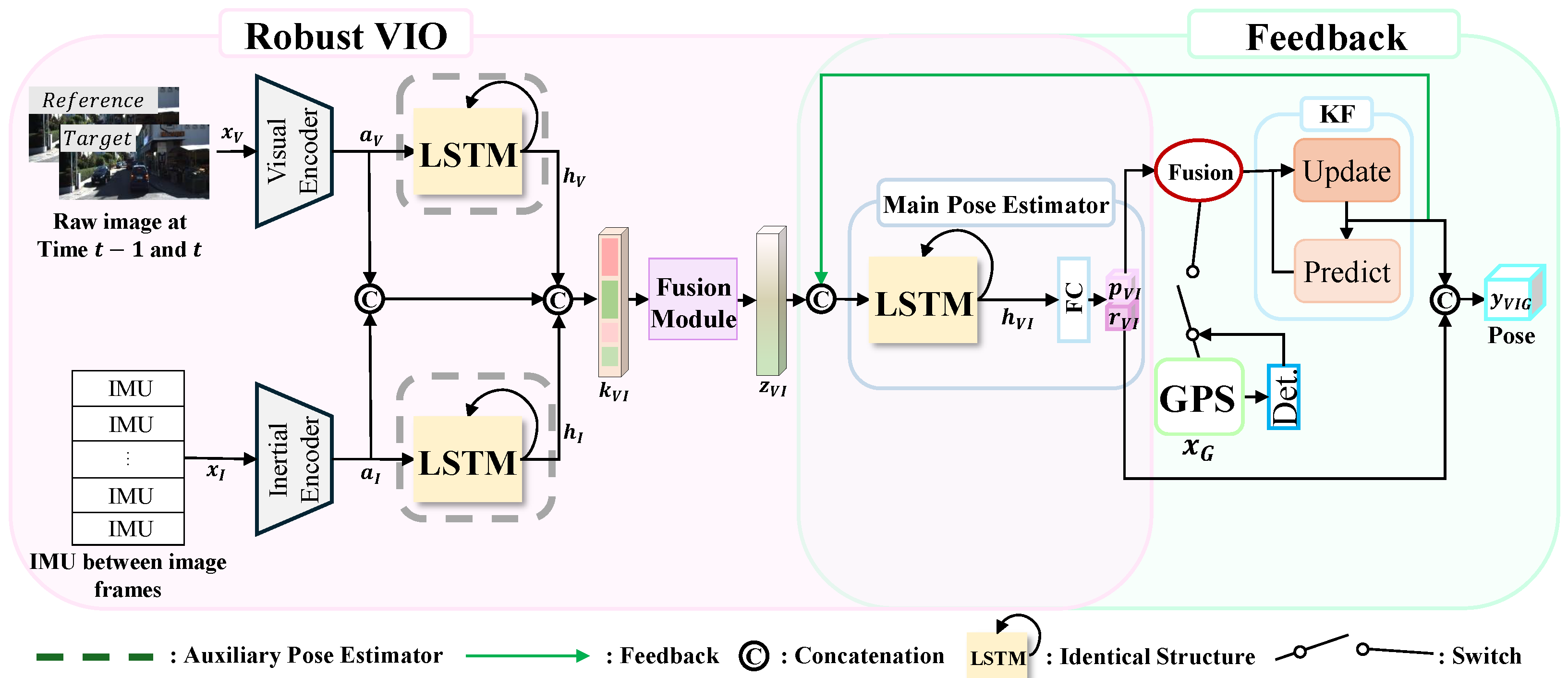
2.1. Overall System Architecture
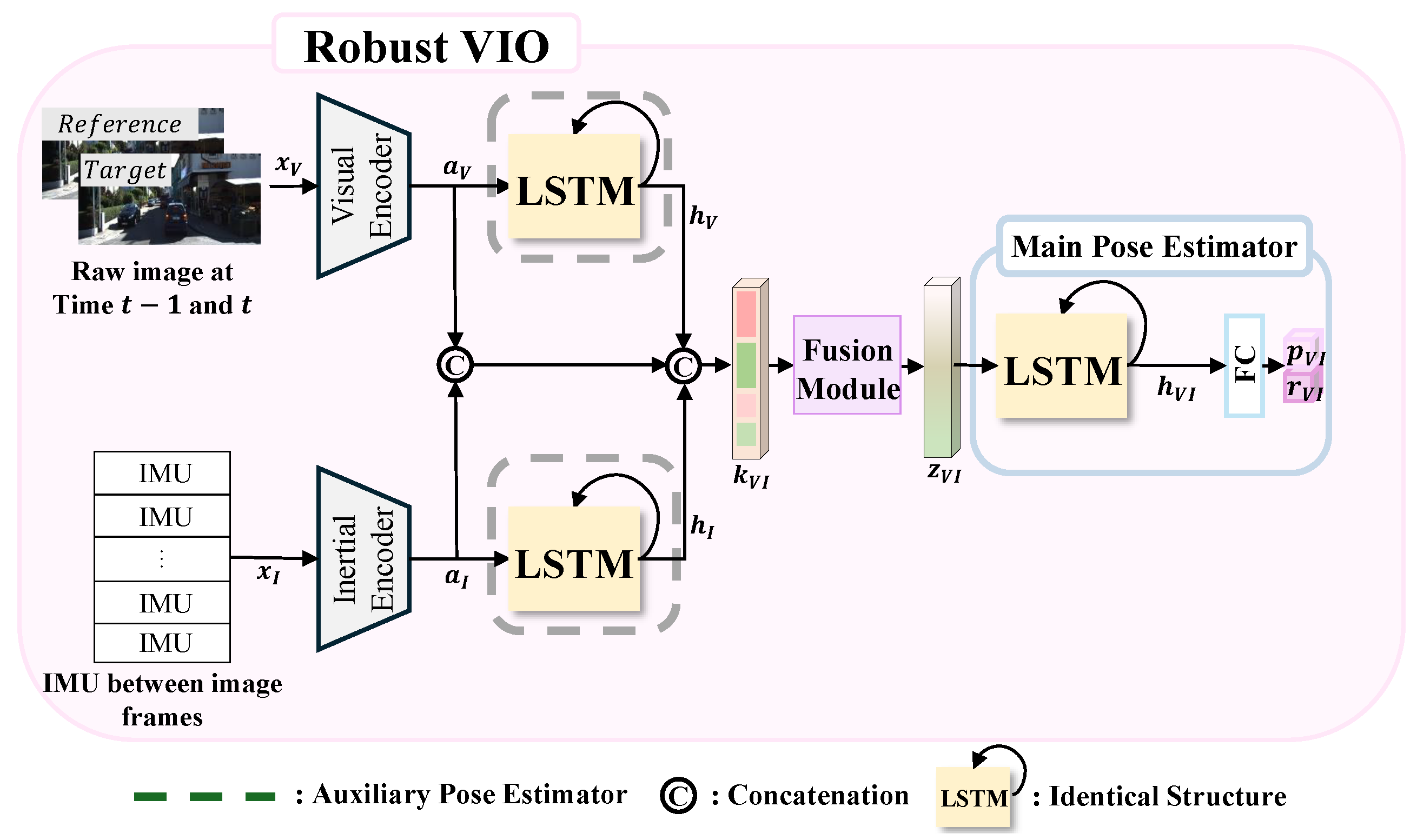
2.2. Robust VIO: Fusion of Multi-Sensor Data for Robust Localization
2.2.1. Feature Encoder
Visual Feature Encoder
Inertial Feature Encoder
2.2.2. Temporal Modeling and Pose Estimation
Auxiliary Pose Estimator
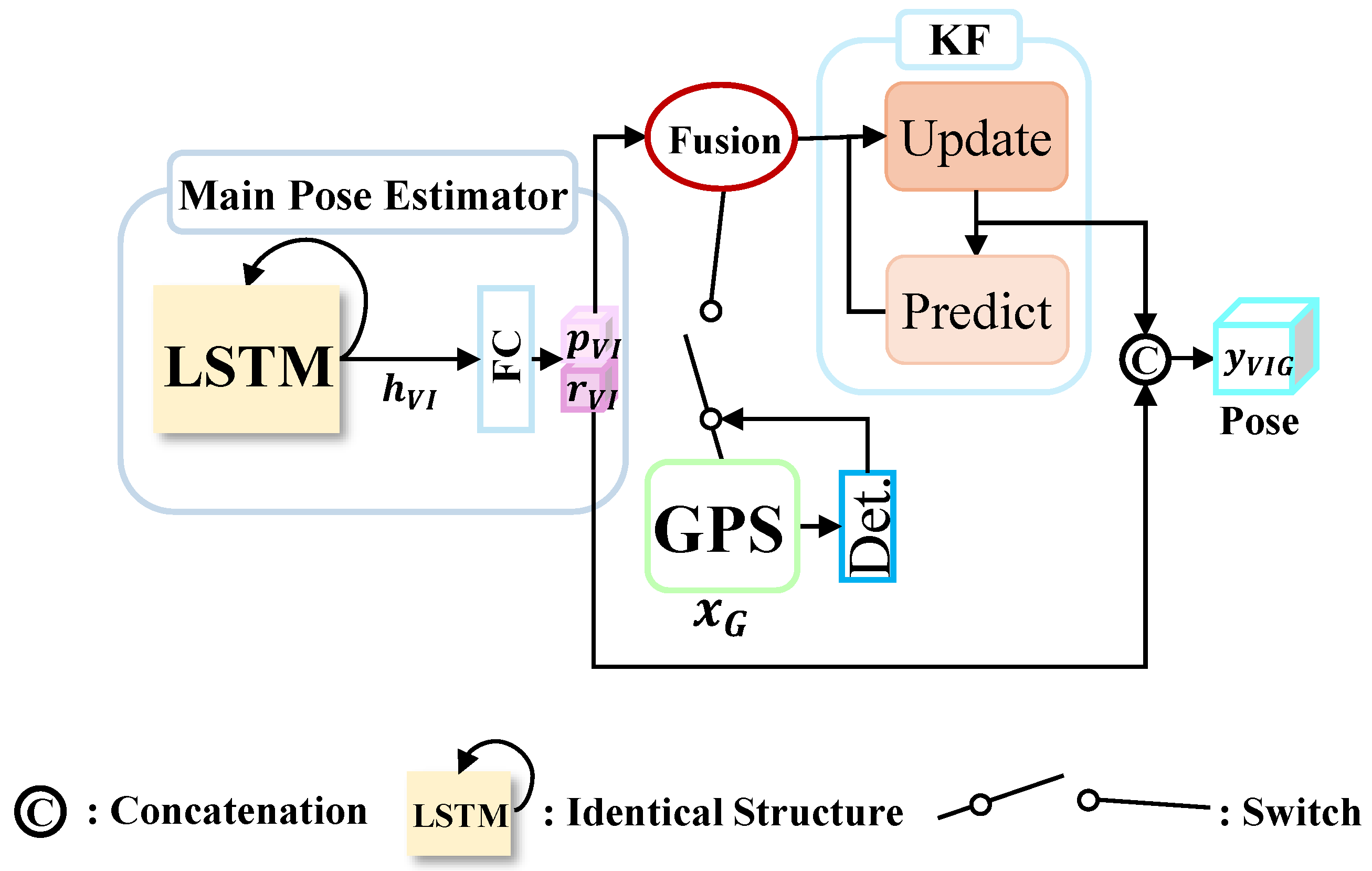
Main Pose Estimator

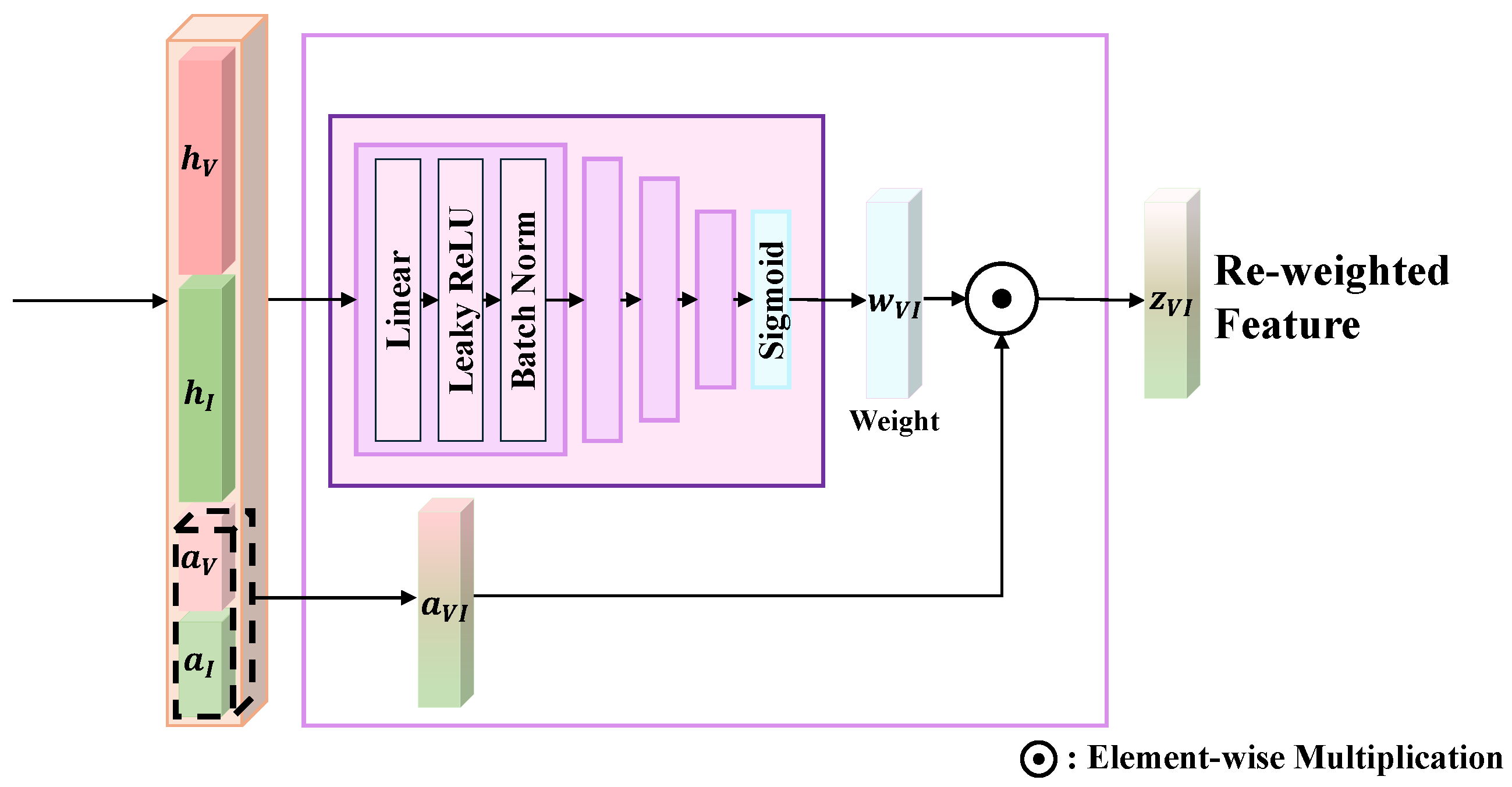
2.2.3. Fusion Module
Fusion Function
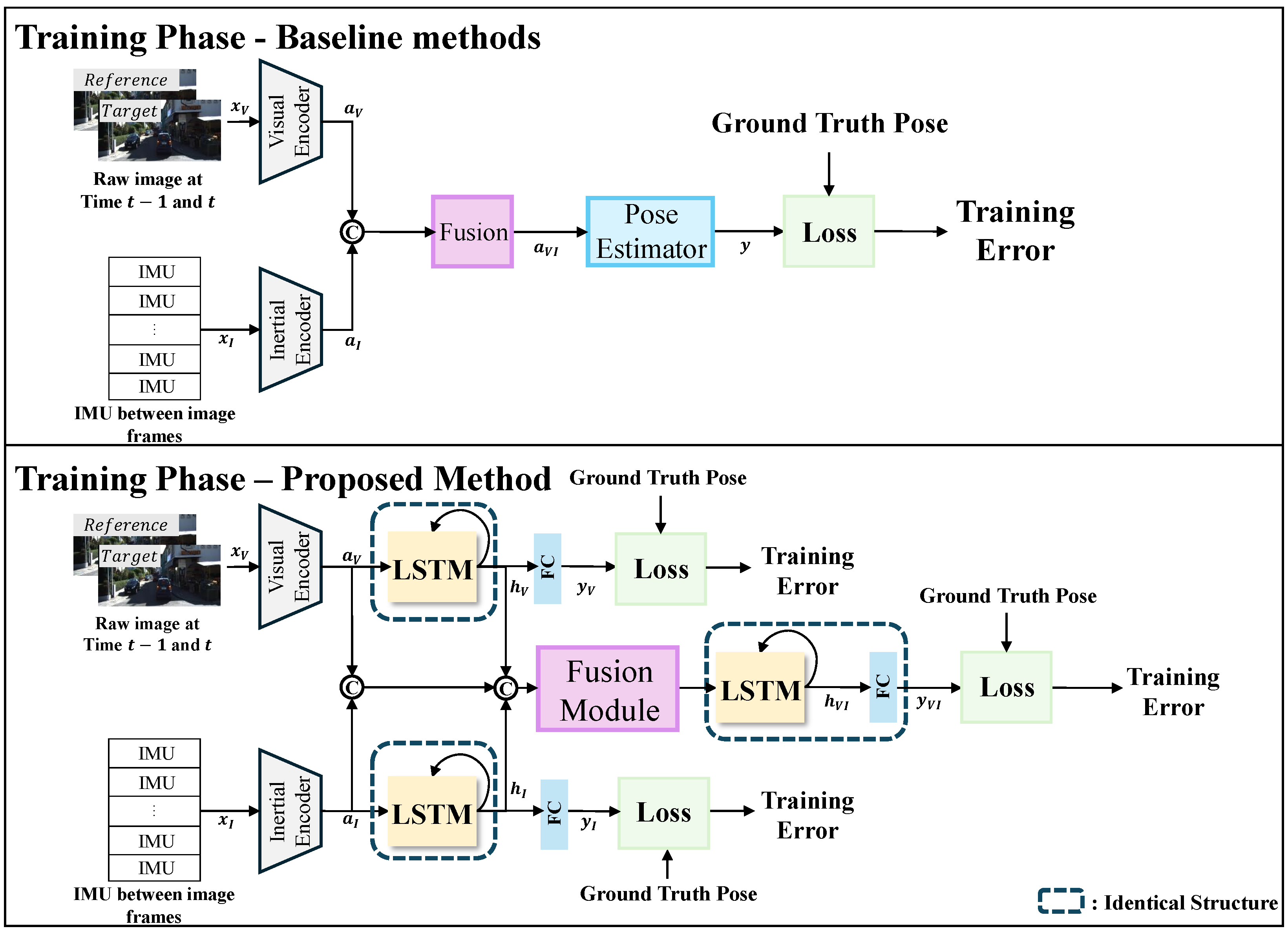
2.2.4. Learning Methods
Stage-Wise Training
Loss Function
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Experimental Setups
3.1.1. Implementation Details
3.1.2. Comparison Algorithms
- VINet concatenates features from different sensors without evaluating their reliability and uses the combined features for state estimation.
- Soft VIO uses an MLP followed by a sigmoid activation to assign continuous weights in the range to each sensor feature before state estimation.
- Hard VIO adopts the Gumbel-Softmax trick to assign discrete weights, giving a weight of 1 to high-quality features and 0 to low-quality ones.
- Visual-Selective VIO relies primarily on inertial features for state estimation, temporarily incorporating visual features only to correct accumulated inertial drift.
3.1.3. Dataset
KITTI Odometry Dataset
Synthetic Data Missing
3.1.4. Evaluation Metrics
Position Error RMSE
Orientation Error RMSE
3.1.5. Total Position Errors
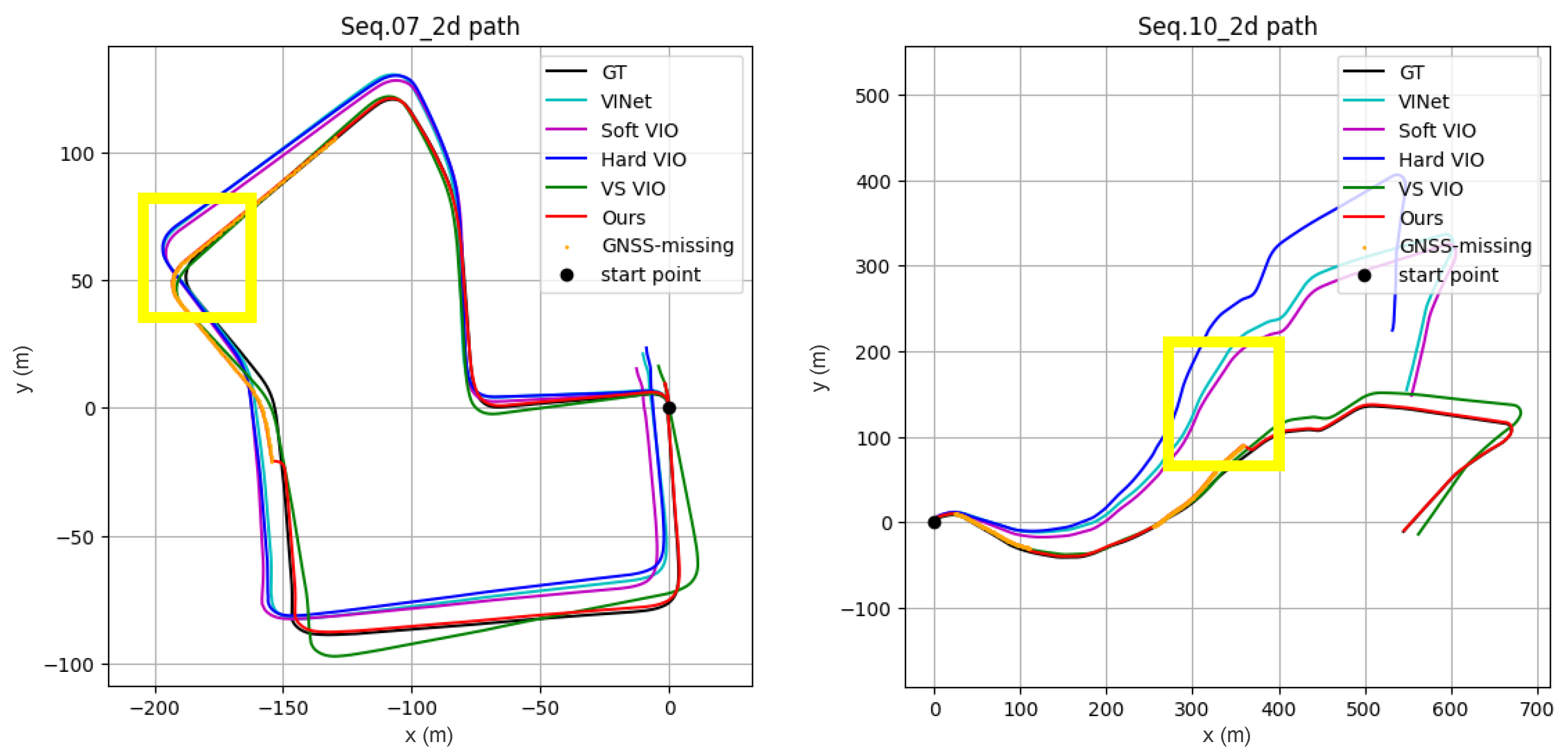
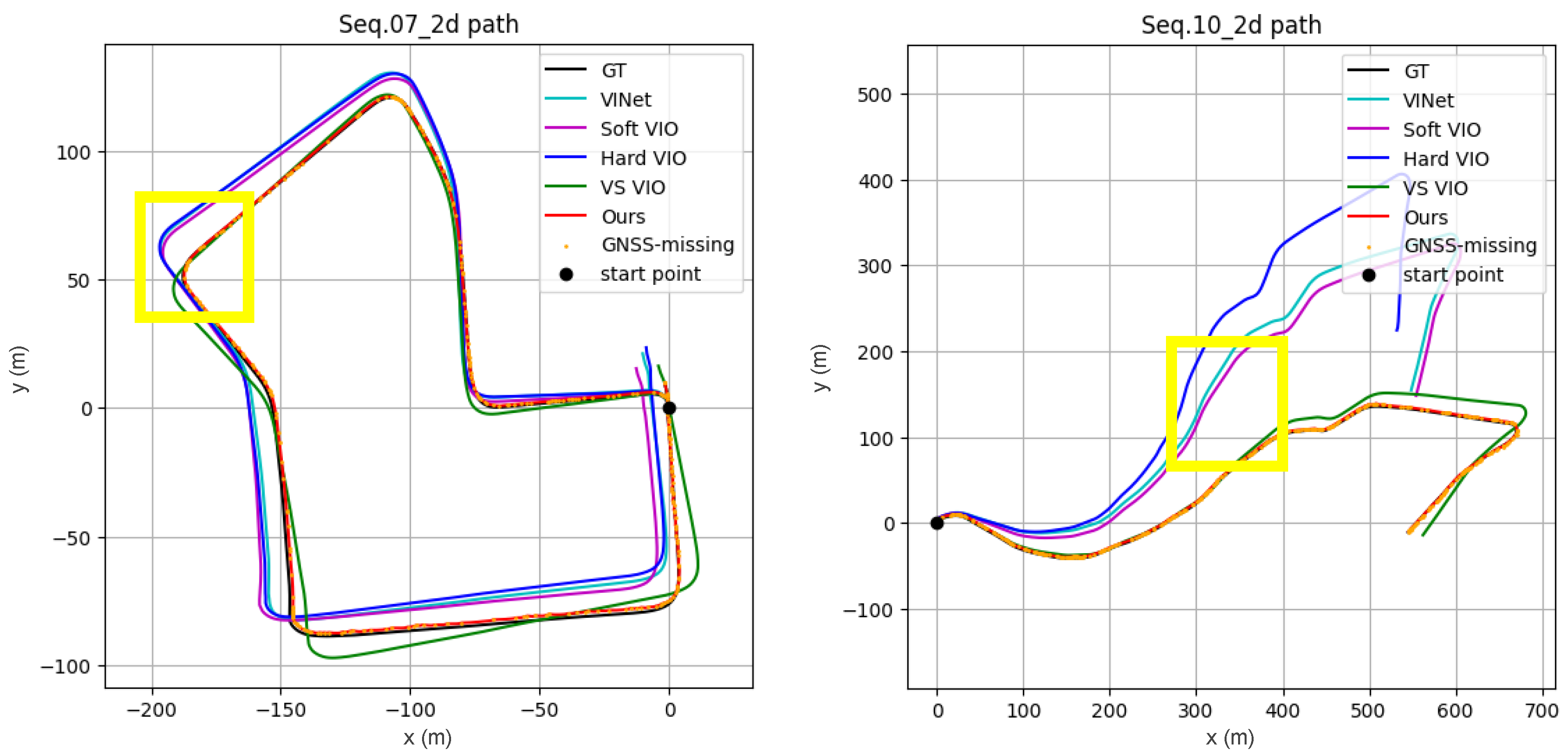
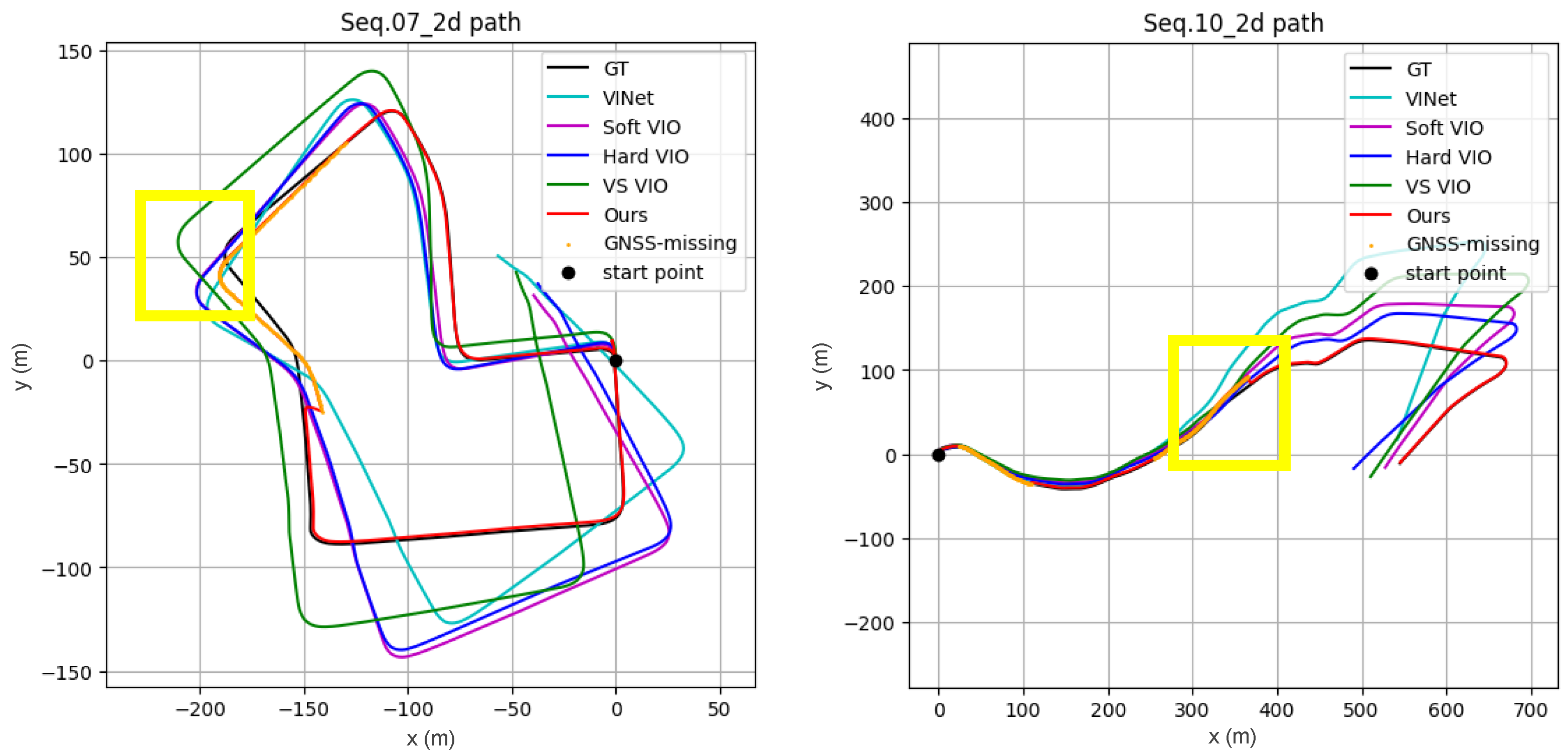
3.2. Comparison with VIO Methods
3.2.1. Quantitative and Qualitative Results
3.2.2. Real-Time Performance and Resource Consumption
3.3. Ablation Studies
- Auxiliary Pose Estimator: This component was designed to enhance the assessment of sensor reliability by generating hidden latent vectors. As shown in Table 14, incorporating the auxiliary pose estimator led to noticeable performance gains, particularly in scenarios where sensor data was missing. These results demonstrate its effectiveness in supporting accurate pose estimation under data-deficient conditions.
- Fusion Module: The integration of the fusion module further enhanced performance by dynamically adjusting the weights of sensor features according to their estimated reliability. This adaptive mechanism proved particularly effective in scenarios involving simultaneous sensor data losses—such as GD-V and GS-V missing—where it significantly reduced localization errors by prioritizing more trustworthy inputs.
- Stage-wise Learning: The stage-wise learning strategy improved overall model performance by sequentially optimizing individual components. In this approach, the feature encoders and the primary pose estimator were trained first, followed by the activation of the fusion module. This structured training process facilitated more stable and efficient learning. As shown in Table 14, this incremental refinement yielded consistent performance improvements across all evaluated scenarios and sequences.
3.4. Visualization of Adaptive Weighting Mechanism
4. Limitations and Future Work
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K.W.; Im, J.H.; Jee, G.I. Tunnel facility based vehicle localization in highway tunnel using 3D LIDAR. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 17575–17583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Jiang, K.; Wijaya, B.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, D. TM 3 Loc: Tightly-coupled monocular map matching for high precision vehicle localization. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 20268–20281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreau, A.; Piasco, N.; Tsishkou, D.; Stanciulescu, B.; de La Fortelle, A. Coordinet: Uncertainty-aware pose regressor for reliable vehicle localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 3–8 January 2022; pp. 2229–2238. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Li, L.; Fürsterling, A.; Durocher, H.J.; Mouridsen, J.; Zhang, X. Learning-based object detection and localization for a mobile robot manipulator in SME production. Robot. -Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2022, 73, 102229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savci, I.H.; Yilmaz, A.; Karaman, S.; Ocakli, H.; Temeltas, H. Improving navigation stack of a ros-enabled industrial autonomous mobile robot (amr) to be incorporated in a large-scale automotive production. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 120, 3647–3668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Cong, Q. Kinematic and dynamic control model of wheeled mobile robot under internet of things and neural network. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 8678–8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Mottola, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; He, Y. Indoor drone localization and tracking based on acoustic inertial measurement. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2023, 23, 7537–7551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Chen, G.; Li, Y.; Dong, W. Agile formation control of drone flocking enhanced with active vision-based relative localization. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 6359–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cioffi, G.; Bauersfeld, L.; Kaufmann, E.; Scaramuzza, D. Learned inertial odometry for autonomous drone racing. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2023, 8, 2684–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.; Ventura, J.; Langlotz, T.; Gul, S.; Mills, S.; Zollmann, S. Localization and tracking of stationary users for augmented reality. Vis. Comput. 2024, 40, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhao, L.; Peng, Z.; Xie, W.; Jiang, M.; Zha, H.; Bao, H.; Zhang, G. A low-cost and scalable framework to build large-scale localization benchmark for augmented reality. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 34, 2274–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Jung, C.; Lee, K.; Seo, S. A study on recognizing multi-real world object and estimating 3D position in augmented reality. J. Supercomput. 2022, 78, 7509–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, H.; Meng, M.Q.H. Inertial odometry using hybrid neural network with temporal attention for pedestrian localization. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2022, 71, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, R.; Tian, Y.; Tian, J.; Wang, J.; Li, N.; Jiang, Y. ResMixer: A lightweight residual mixer deep inertial odometry for indoor positioning. IEEE Sens. J. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yan, D.; Li, T.; Xia, M.; Shi, C. Pedestrian gait information aided visual inertial SLAM for indoor positioning using handheld smartphones. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 19845–19857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teed, Z.; Lipson, L.; Deng, J. Deep patch visual odometry. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36, 39033–39051. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Lan, X.; Chen, S.; Ming, Y.; Yu, X.; Bao, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, G. PVO: Panoptic visual odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 9579–9589. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, L.; Shangguan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ohn-Bar, E. XVO: Generalized visual odometry via cross-modal self-training. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 10094–10105. [Google Scholar]
- Von Stumberg, L.; Cremers, D. DM-VIO: Delayed marginalization visual-inertial odometry. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 1408–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, R.; Agrawal, V.; Camurri, M.; Dellaert, F.; Fallon, M. Deep imu bias inference for robust visual-inertial odometry with factor graphs. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 8, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiskari, O.; Rantalankila, P.; Kannala, J.; Ylilammi, J.; Rahtu, E.; Solin, A. HybVIO: Pushing the limits of real-time visual-inertial odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa, HI, USA, 4–8 January 2022; pp. 701–710. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Lopez, B.T.; Agha-mohammadi, A.A.; Mehta, A. Direct lidar odometry: Fast localization with dense point clouds. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2022, 7, 2000–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H. Efficient 3d deep lidar odometry. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2022, 45, 5749–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Jiang, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H. Translo: A window-based masked point transformer framework for large-scale lidar odometry. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 1683–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Peng, S.; Larsson, V.; Xu, W.; Bao, H.; Cui, Z.; Oswald, M.R.; Pollefeys, M. Nice-slam: Neural implicit scalable encoding for slam. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 12786–12796. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Agapito, L. Co-slam: Joint coordinate and sparse parametric encodings for neural real-time slam. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 13293–13302. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, C.; Qu, D.; Xu, D.; Zhao, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Li, X. Gs-slam: Dense visual slam with 3d gaussian splatting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 17–21 June 2024; pp. 19595–19604. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Jin, X. Gravity-Shift-VIO: Adaptive Acceleration Shift and Multi-Modal Fusion with Transformer in Visual-Inertial Odometry. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Gold Coast, QLD, Australia, 18–23 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Ding, G.; Qiu, Y.; Yoshiyasu, Y.; Kanehiro, F. TransFusionOdom: Transformer-based LiDAR-inertial fusion odometry estimation. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 22064–22079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaygusuz, N.; Mendez, O.; Bowden, R. AFT-VO: Asynchronous fusion transformers for multi-view visual odometry estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Kyoto, Japan, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 2402–2408. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Qiao, X.; Ma, Y.; Tafazolli, R. Transformer-based self-supervised monocular depth and visual odometry. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 23, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, B.; Zang, T. A global pose and relative pose fusion network for monocular visual odometry. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 108863–108875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Z.; Chen, C.; Pan, X.; Liu, R.; Cui, J.; Mao, J. Ema-vio: Deep visual–inertial odometry with external memory attention. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 20877–20885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, X.Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, K.C.; Lee, C.Y. Dynamic attention-based visual odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW), Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 36–37. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Li, G.; Li, T.H. Atvio: Attention guided visual-inertial odometry. In Proceedings of the ICASSP 2021–2021 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), Toronto, ON, Canada, 6–11 June 2021; pp. 4125–4129. [Google Scholar]
- Dahal, P.; Mentasti, S.; Paparusso, L.; Arrigoni, S.; Braghin, F. Fault resistant odometry estimation using message passing neural network. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Anchorage, AK, USA, 4–7 June 2023; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Rosa, S.; Miao, Y.; Lu, C.X.; Wu, W.; Markham, A.; Trigoni, N. Selective sensor fusion for neural visual-inertial odometry. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 10542–10551. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.; Ye, G.; Yang, P.; Yu, W. Application of multi-sensor fusion localization algorithm based on recurrent neural networks. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Zhuang, Y.; Huai, J. Multi-sensor fusion for robust localization with moving object segmentation in complex dynamic 3D scenes. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2023, 124, 103507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ušinskis, V.; Nowicki, M.; Dzedzickis, A.; Bučinskas, V. Sensor-fusion based navigation for autonomous mobile robot. Sensors 2025, 25, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Urtasun, R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 3354–3361. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Fischer, P.; Ilg, E.; Hausser, P.; Hazirbas, C.; Golkov, V.; Van Der Smagt, P.; Cremers, D.; Brox, T. Flownet: Learning optical flow with convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2758–2766. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.; Wang, S.; Wen, H.; Markham, A.; Trigoni, N. Vinet: Visual-inertial odometry as a sequence-to-sequence learning problem. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–9 February 2017; Volume 31. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Rosa, S.; Lu, C.X.; Wang, B.; Trigoni, N.; Markham, A. Learning selective sensor fusion for state estimation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2022, 36, 4103–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, Y.; Kim, H.S. Efficient deep visual and inertial odometry with adaptive visual modality selection. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Cham, Switzerland, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 233–250. [Google Scholar]




| Scenario | Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO [45] | Hard VIO [44] | Soft VIO [44] | VINet [43] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | |
| Normal | Position (m) | 2.07 | 8.63 | 6.34 | 16.77 | 11.96 | 129.18 | 10.46 | 121.88 | 10.85 | 122.1 |
| Orientation (°) | 9.43 | 9.10 | 4.64 | 4.26 | 2.70 | 27.78 | 2.51 | 23.32 | 2.41 | 23.52 | |
| GD Missing | Position (m) | 3.61 | 11.76 | 6.34 | 16.77 | 11.96 | 129.18 | 10.46 | 121.88 | 10.85 | 122.1 |
| Orientation (°) | 9.43 | 9.10 | 4.64 | 4.26 | 2.70 | 27.78 | 2.51 | 23.32 | 2.41 | 23.52 | |
| GS Missing | Position (m) | 1.64 | 8.62 | 6.34 | 16.77 | 11.96 | 129.18 | 10.46 | 121.88 | 10.85 | 122.1 |
| Orientation (°) | 9.43 | 9.10 | 4.64 | 4.26 | 2.70 | 27.78 | 2.51 | 23.32 | 2.41 | 23.52 | |
| GD-V Missing | Position (m) | 4.11 | 13.14 | 26.17 | 63.23 | 27.05 | 33.21 | 27.77 | 36.58 | 36.46 | 78.88 |
| Orientation (°) | 10.11 | 2.13 | 4.48 | 7.38 | 15.01 | 2.57 | 15.03 | 5.57 | 24.58 | 16.09 | |
| GS-V Missing | Position (m) | 1.66 | 8.65 | 26.17 | 63.23 | 27.05 | 33.21 | 27.77 | 36.58 | 36.46 | 78.88 |
| Orientation (°) | 10.11 | 2.13 | 4.48 | 7.38 | 15.01 | 2.57 | 15.03 | 5.57 | 24.58 | 16.09 | |
| Scenario | Error | Ours | VS VIO [45] | Hard VIO [44] | Soft VIO [44] | VINet [43] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sequence | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | |
| Normal | (%) | 1.44 | 3.23 | 2.87 | 5.24 | 4.87 | 15.20 | 4.46 | 14.84 | 4.52 | 14.85 |
| (°) | 2.46 | 2.42 | 1.64 | 1.57 | 1.21 | 4.51 | 1.14 | 4.16 | 1.09 | 4.18 | |
| GD Missing | (%) | 2.09 | 4.81 | 2.87 | 5.24 | 4.87 | 15.20 | 4.46 | 14.84 | 4.52 | 14.85 |
| (°) | 2.46 | 2.42 | 1.64 | 1.57 | 1.21 | 4.51 | 1.14 | 4.16 | 1.09 | 4.18 | |
| GS Missing | (%) | 1.28 | 3.23 | 2.87 | 5.24 | 4.87 | 15.20 | 4.46 | 14.84 | 4.52 | 14.85 |
| (°) | 2.46 | 2.42 | 1.64 | 1.57 | 1.21 | 4.51 | 1.14 | 4.16 | 1.09 | 4.18 | |
| GD-V Missing | (%) | 2.23 | 5.02 | 7.43 | 10.75 | 7.52 | 8.14 | 7.60 | 8.45 | 8.44 | 11.77 |
| (°) | 2.64 | 0.97 | 1.62 | 2.15 | 3.30 | 1.15 | 3.30 | 1.84 | 4.27 | 3.46 | |
| GS-V Missing | (%) | 1.29 | 3.24 | 7.43 | 10.75 | 7.52 | 8.14 | 7.60 | 8.45 | 8.44 | 11.77 |
| (°) | 2.64 | 0.97 | 1.62 | 2.15 | 3.30 | 1.15 | 3.30 | 1.84 | 4.27 | 3.46 | |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 1.20 | 4.26 | 6.84 | 7.95 | 6.10 |
| y (m) | 1.69 | 4.69 | 9.81 | 6.80 | 8.97 |
| (°) | 9.43 | 4.64 | 2.70 | 2.51 | 2.41 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 7.37 | 11.62 | 32.24 | 26.58 | 26.88 |
| y (m) | 4.49 | 12.09 | 125.09 | 118.95 | 119.10 |
| (°) | 9.10 | 4.26 | 27.78 | 23.32 | 23.52 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 2.69 | 4.26 | 6.84 | 7.95 | 6.10 |
| y (m) | 2.41 | 4.69 | 9.81 | 6.80 | 8.97 |
| (°) | 9.43 | 4.64 | 2.70 | 2.51 | 2.41 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 9.27 | 11.62 | 32.24 | 26.58 | 26.88 |
| y (m) | 7.24 | 12.09 | 125.09 | 118.95 | 119.10 |
| (°) | 9.10 | 4.26 | 27.78 | 23.32 | 23.52 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 1.20 | 4.26 | 6.84 | 7.95 | 6.10 |
| y (m) | 1.11 | 4.69 | 9.81 | 6.80 | 8.97 |
| (°) | 9.43 | 4.64 | 2.70 | 2.51 | 2.41 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 7.31 | 11.62 | 32.24 | 26.58 | 26.88 |
| y (m) | 4.56 | 12.09 | 125.09 | 118.95 | 119.10 |
| (°) | 9.10 | 4.26 | 27.78 | 23.32 | 23.52 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 1.99 | 17.22 | 19.11 | 18.92 | 30.29 |
| y (m) | 3.60 | 19.71 | 19.15 | 20.32 | 20.29 |
| (°) | 10.11 | 4.48 | 15.01 | 15.03 | 24.58 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 10.04 | 25.91 | 21.00 | 13.70 | 12.10 |
| y (m) | 8.48 | 57.68 | 25.73 | 33.92 | 77.95 |
| (°) | 2.13 | 7.38 | 2.57 | 5.57 | 16.09 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 1.23 | 17.22 | 19.11 | 18.92 | 30.29 |
| y (m) | 1.11 | 19.71 | 19.15 | 20.32 | 20.29 |
| (°) | 10.11 | 4.48 | 15.01 | 15.03 | 24.58 |
| Error (RMSE) | Ours | VS VIO | Hard VIO | Soft VIO | VINet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x (m) | 7.39 | 25.91 | 21.00 | 13.70 | 12.10 |
| y (m) | 4.49 | 57.68 | 25.73 | 33.92 | 77.95 |
| (°) | 2.13 | 7.38 | 2.57 | 5.57 | 16.09 |
| Method | Processing Time (s) | FPS | CPU Mem (MB) | GPU Alloc. (MB) | GPU Reserv. (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VINet | 0.0250 | 40 | 1030.09 | 464.86 | 632.00 |
| Soft VIO | 0.0262 | 38 | 1093.02 | 466.37 | 738.00 |
| Hard VIO | 0.0278 | 36 | 1113.36 | 469.37 | 632.00 |
| VS VIO | 0.0244 | 41 | 1109.98 | 466.84 | 632.00 |
| Ours | 0.0346 | 29 | 1037.61 | 667.00 | 774.00 |
| Auxiliary pose estimator | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||
| Fusion module | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ||||||||
| Stage-wise learning | ✓ | ||||||||||
| Scenario | Error (RMSE) | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 | 7 | 10 |
| Normal | Position (m) | 2.32 | 8.81 | 2.20 | 8.72 | 2.20 | 8.72 | 2.17 | 8.68 | 2.07 | 8.63 |
| Orientation (°) | 14.21 | 19.20 | 10.07 | 10.61 | 10.11 | 10.82 | 10.00 | 10.50 | 9.43 | 9.10 | |
| GD Missing | Position (m) | 9.13 | 13.04 | 4.37 | 12.39 | 4.47 | 12.48 | 4.08 | 12.12 | 3.61 | 11.76 |
| Orientation (°) | 14.21 | 19.20 | 10.07 | 10.61 | 10.11 | 10.82 | 10.00 | 10.50 | 9.43 | 9.10 | |
| GS Missing | Position (m) | 1.84 | 8.92 | 1.79 | 8.81 | 1.80 | 8.83 | 1.75 | 8.74 | 1.64 | 8.62 |
| Orientation (°) | 14.21 | 19.20 | 10.07 | 10.61 | 10.11 | 10.82 | 10.00 | 10.50 | 9.43 | 9.10 | |
| GD-V Missing | Position (m) | 6.05 | 15.55 | 4.31 | 14.64 | 3.57 | 14.35 | 2.89 | 13.81 | 1.68 | 13.14 |
| Orientation (°) | 14.58 | 17.82 | 11.77 | 10.31 | 11.62 | 10.01 | 11.18 | 6.01 | 10.11 | 2.13 | |
| GS-V Missing | Position (m) | 1.93 | 8.92 | 1.88 | 8.89 | 1.83 | 8.85 | 1.80 | 8.83 | 1.66 | 8.65 |
| Orientation (°) | 14.58 | 17.82 | 11.77 | 10.31 | 11.62 | 10.01 | 11.18 | 6.01 | 10.11 | 2.13 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, T.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Ahn, W.-J.; Kang, T.-K.; Lim, M.-T. Robust Vehicle Pose Estimation Through Multi-Sensor Fusion of Camera, IMU, and GPS Using LSTM and Kalman Filter. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211863
Jeong T-H, Lee Y-J, Ahn W-J, Kang T-K, Lim M-T. Robust Vehicle Pose Estimation Through Multi-Sensor Fusion of Camera, IMU, and GPS Using LSTM and Kalman Filter. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):11863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211863
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Tae-Hyeok, Yong-Jun Lee, Woo-Jin Ahn, Tae-Koo Kang, and Myo-Taeg Lim. 2025. "Robust Vehicle Pose Estimation Through Multi-Sensor Fusion of Camera, IMU, and GPS Using LSTM and Kalman Filter" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 11863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211863
APA StyleJeong, T.-H., Lee, Y.-J., Ahn, W.-J., Kang, T.-K., & Lim, M.-T. (2025). Robust Vehicle Pose Estimation Through Multi-Sensor Fusion of Camera, IMU, and GPS Using LSTM and Kalman Filter. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 11863. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211863







