Abstract
Pneumonia remains a major global health concern, particularly among pediatric populations in low-resource settings where radiological expertise is limited. This study investigates the enhancement of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) for automated pneumonia diagnosis from chest X-ray images through the integration of a novel module combining Inception blocks, Mish activation, and Batch Normalization (IncMB). Four state-of-the-art transfer learning models—InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, MobileNetV2, and DenseNet201—were evaluated in their base form and with the proposed IncMB extension. Comparative analysis based on standardized classification metrics reveals consistent performance improvements across all models with the addition of the IncMB module. The most notable improvement was observed in InceptionResNetV2, where the IncMB-enhanced model achieved the highest accuracy of 0.9812, F1-score of 0.9761, precision of 0.9781, recall of 0.9742, and strong specificity of 0.9590. Other models also demonstrated similar trends, confirming that the IncMB module contributes to better generalization and discriminative capability. These enhancements were achieved while reducing the total number of parameters, indicating improved computational efficiency. In conclusion, the integration of IncMB significantly boosts the performance of CNN-based pneumonia classifiers, offering a promising direction for the development of lightweight, high-performing diagnostic tools suitable for real-world clinical application, particularly in underserved healthcare environments.
1. Introduction
Pneumonia is an acute infection affecting the alveolar regions of the lungs and represents a leading cause of childhood morbidity and mortality worldwide [1,2]. It is typically caused by bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens and manifests clinically with fever, cough, tachypnea, chest retractions, pleuritic pain, and abnormal breath sounds such as crackles or wheezing [3,4,5]. The severity of pneumonia in children can vary significantly, ranging from mild and self-limiting to life-threatening conditions involving respiratory failure and acute respiratory distress syndrome [6]. Prompt diagnosis and timely intervention are therefore essential for reducing complications and improving clinical outcomes [7]. Statistical data highlights the ongoing burden of pediatric pneumonia on global health systems. In 2019 alone, pneumonia accounted for approximately 740,000 deaths among children under five, representing 14% of all under-five mortality [8], and disproportionately affecting regions such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa [6,9]. Pneumonia remains a major cause of pediatric hospitalizations, contributing significantly to healthcare utilization and child mortality [10]. Risk factors that predispose children to pneumonia include malnutrition, incomplete immunization coverage, indoor air pollution, and limited access to quality healthcare services [11]. Treatment strategies for pediatric pneumonia mainly depend on the underlying etiology. Bacterial infections typically require antimicrobial therapy, with macrolides or beta-lactam antibiotics frequently used [12], depending on the age of the patient and the likely causative organism [13]. For example, macrolides are preferred in school-aged children when atypical pathogens such as Mycoplasma pneumoniae are suspected [14]. In contrast, viral pneumonia is managed primarily with supportive care, including oxygen therapy, hydration, and antiviral agents when appropriate [15,16]. Severe cases may necessitate hospitalization and intensive care support, including mechanical ventilation.
Radiological imaging is considered essential for the diagnosis of pneumonia, with chest radiography (CXR) recognized as the gold standard imaging modality [17]. The presence of new pulmonary infiltrates on a chest X-ray provides objective evidence of alveolar involvement and supports a definitive pneumonia diagnosis. Although limited in sensitivity and specificity, chest radiography is the most common instrument because of availability, speed, and the relative affordability to perform [18,19]. It enables differentiation between pneumonia and other respiratory conditions, and plays a central role in clinical decision-making, particularly in acute care settings [2]. While computed tomography (CT) of the chest offers higher sensitivity for detecting parenchymal changes, it is rarely employed in pediatric practice due to concerns about ionizing radiation and limited accessibility [17]. Lung ultrasound (LUS) has emerged as a potential alternative, offering the advantages of portability, absence of radiation, and suitability for point-of-care use [13,20]. However, despite its high sensitivity, LUS suffers from relatively low specificity and limited negative predictive value, making it unreliable as a standalone diagnostic tool. Studies have shown that although a positive LUS finding strongly suggests pneumonia, a negative result does not reliably exclude the disease [21,22]. Therefore, in cases with high clinical suspicion and negative ultrasound findings, additional imaging with CXR or CT is often warranted [17]. As such, chest radiography remains the reference standard for confirming pneumonia, especially in pediatric patients [23].
Because pneumonia diagnosis relies heavily on imaging, researchers have explored automating chest X-ray interpretation using artificial intelligence, particularly deep learning approaches. The CNNs have demonstrated great performance in the classification of thoracic pathologies such as pneumonia [24,25,26]. These models have demonstrated the ability to extract hierarchical image features that may not be apparent to human observers, facilitating more accurate and efficient diagnosis [27,28]. The application of CNNs in pediatric imaging has the potential to enhance diagnostic accuracy, reduce interpretation time, and alleviate the workload on radiologists [29,30]. In addition, deep learning has shown a powerful performance of processing high-dimensional data, noisy data, and non-stationary data in a wide range of fields. Multi-scale architectures are robust and generalizable as adaptive neural structures have been used in structural health monitoring to adapt to environmental variability and signal distortions using hierarchical feature optimization [31]. Despite notable progress, the broader clinical adoption of AI-driven models for pediatric pneumonia diagnosis remains constrained by several persistent limitations [32]. One primary concern is computational complexity. Advanced hybrid frameworks and transformer-based architectures, while delivering strong diagnostic performance, often rely on resource-intensive components such as fuzzy inference systems, multi-head attention mechanisms, or ensemble learning strategies [24,33,34]. These introduce significant latency and memory consumption, which can limit deployment in low-resource clinical environments [35]. Even relatively streamlined models require sophisticated fine-tuning procedures and optimized activation functions, further complicating their practical implementation. Equally critical is the limited adaptability of many models to pediatric-specific imaging features [36,37]. Deep learning architectures trained predominantly on adult datasets may not generalize well to pediatric chest radiographs, which differ in anatomical scale, developmental variability, and disease manifestation patterns [34]. Pediatric pneumonia often presents with viral features that are more diffuse and less radiographically distinct, making the recognition task inherently more challenging [18]. Consequently, models optimized on adult populations may exhibit reduced sensitivity or specificity when applied to pediatric cases [34]. Furthermore, structural features of the medical imaging data present further complications. Unlike the natural RGB images, chest radiography is a monochromatic image with diagnostically valuable information encoded into subtle shades of grayscale level differences [38,39]. Many existing CNN-based solutions, including architectures like Inception and EfficientNet, were originally tailored for color image recognition and thus do not inherently accommodate the lower-dimensional and contrast-dependent nature of grayscale medical data [40]. This mismatch can diminish feature extraction efficiency, particularly in subtle or small lesion recognition scenarios. Furthermore, current models often fail to leverage the statistical and textural signatures that distinguish radiographic findings in pediatric pneumonia. Lesions in this population are frequently small, ill-defined, and distributed heterogeneously across the lung fields [41]. Standard modules lack adaptive mechanisms to integrate multi-scale contextual information from such complex grayscale inputs [42]. This gap suggests an underexplored need for architectural components specifically designed to enhance multi-scale feature learning in monochromatic images.
These challenges highlight the need for deep learning frameworks that are diagnostically accurate, computationally efficient, and specifically adapted to pediatric and grayscale imaging characteristics. In response to these challenges, we investigate the adaptation of the IncMB (Inception–Mish activation function–Batch Normalization) module—a lightweight and scalable architectural block originally designed for color image classification, in the context of pediatric pneumonia recognition using chest radiographs. The key contributions of this paper are as follows:
- This study adapts the IncMB module for grayscale pediatric chest X-ray analysis, overcoming the limitations of traditional CNNs designed for RGB images. By leveraging the Mish activation function for smoother gradients and Batch Normalization for robust regularization, the module achieves enhanced feature extraction in monochromatic medical images, improving pneumonia classification accuracy.
- This study rigorously evaluates the IncMB module’s integration into established CNN architectures on a publicly available pediatric CXR dataset, demonstrating its balanced trade-off between computational efficiency and diagnostic performance. The module’s design inherently reduces parameter growth compared to conventional multi-branch architectures while maintaining competitive accuracy.
- This work bridges the gap between adult-trained deep learning models and pediatric-specific diagnostic needs by optimizing feature learning for subtle, diffuse radiographic patterns unique to children. The adapted IncMB module enhances sensitivity to small lesions and viral pneumonia manifestations, supporting more accurate and accessible AI-driven diagnosis in pediatric healthcare.
This paper is organized into distinct sections. Section 2 surveys existing literature concerning deep learning approaches for diagnosing pediatric pneumonia. Section 3 details our proposed model and its methodologies. Subsequently, Section 4 presents experimental findings and a comparative analysis of the model’s performance. The paper concludes in Section 5 with a summary of our findings and suggestions for future research.
2. Related Works
Advances in deep learning have significantly enhanced the diagnostic performance of CNNs in the analysis of pediatric chest radiographs, particularly for pneumonia recognition. These models have demonstrated promising results in terms of accuracy and sensitivity; however, the challenge of balancing diagnostic robustness, interpretability, and computational efficiency continues to hinder real-world deployment, especially in resource-constrained clinical environments that demand rapid and reliable diagnostic support.
Numerous innovative approaches have been proposed to address the challenges inherent in pediatric chest X-ray analysis. Sotirov et al. [43] introduced a hybrid framework that integrates CNNs with intuitionistic fuzzy estimators (IFEs) to improve robustness against data ambiguity and noise. By leveraging CNNs for feature extraction and IFEs for uncertainty modeling, their system achieved a classification accuracy of 0.9493, surpassing traditional CNNs in both sensitivity and specificity. Despite achieving higher accuracy, the inclusion of fuzzy inference layers increases computational cost, introducing latency and memory overhead that limit real-time clinical use. Ensemble learning approaches have also shown considerable promise. Prakash et al. [44] developed a stacking ensemble model incorporating five channel-attention-based CNNs—ResNetV2, Xception, and DenseNet169 among them. These feature representations were refined using kernel principal component analysis, with classification performed via support vector machines and XGBoost. The architecture yielded a high classification accuracy of 0.9615 and an AUC of 0.9624. However, the operational complexity associated with deploying multiple CNNs concurrently, along with the overhead from feature fusion and dimensionality reduction, imposes significant constraints on clinical integration, particularly in settings where computational resources and inference time are limited. Transfer learning has emerged as a viable strategy for improving diagnostic performance, particularly when pediatric data is scarce. Lan et al. [45] conducted a comparative analysis of ResNet50, DenseNet121, and EfficientNetV2-S for Mycoplasma pneumonia detection, finding ResNet50 to be the most effective with an accuracy of 0.8265. Their study highlighted the critical role of domain-specific pretraining on pediatric datasets over generic datasets such as ImageNet, underscoring the importance of contextual feature learning in medical imaging. However, the moderate AUC scores ranging from 0.822 to 0.758, and specificity ranging from 0.655 to 0.814 suggest ongoing difficulties in accurately distinguishing between different pneumonia subtypes and other thoracic pathologies. Further optimization of transfer learning was demonstrated by Khan et al. [46], who refined the EfficientNetB1 architecture through three principal innovations: the replacement of ReLU with Swish activation, extensive hyperparameter tuning, and classification head regularization. This approach yielded a 0.9613 accuracy in a four-class classification task involving COVID-19, viral pneumonia, lung opacity, and normal cases. Importantly, the regularization strategy effectively mitigated overfitting—a common issue in pediatric imaging due to limited dataset sizes. However, continuing to use RGB-based architectures for grayscale chest X-rays may constrain performance, suggesting potential benefits from grayscale-optimized designs. Architectural enhancements were also explored by Wang et al. [47], who improved DenseNet by integrating Squeeze-and-Excitation (SE) blocks, replacing average pooling with max-pooling to preserve lesion-level detail, and employing PReLU activation to address neuron deactivation. Their modifications resulted in a 2.4% increase in accuracy over baseline DenseNet, reaching 0.928 with high precision of 0.926 and recall of 0.962. Nevertheless, their validation was limited to adult CXR datasets, raising concerns about direct applicability to pediatric cases due to notable anatomical and pathological differences. More recently, transformer-based models have pushed the boundaries of diagnostic performance. Chen et al. [33] introduced a Mixed-Scale Dynamic Attention Transformer for pediatric pneumonia diagnosis, incorporating dynamic local attention, hierarchical multi-scale feature integration, and large language model (LLM)-driven attention amplification. This architecture achieved state-of-the-art performance with 0.952 accuracy and 0.990 AUC. Despite these impressive metrics, the integration of LLMs and advanced attention mechanisms necessitates substantial computational resources, limiting deployment in real-world healthcare settings, particularly in low- and middle-income regions where pediatric pneumonia is most prevalent.
Studies have further explored the impact of domain-specific pretraining and foundation models on medical imaging performance. Models trained on large-scale radiology datasets such as RadiologyNET have demonstrated slightly higher accuracy than ImageNet-pretrained counterparts, particularly in data-limited scenarios [48]. Similarly, the RadImageNet initiative, trained on 1.35 million annotated medical images, reported measurable AUC gains across multiple classification tasks, including thyroid, breast, and pulmonary conditions [49]. Despite these improvements, both approaches remain limited by their high computational demands and reliance on extremely large pretraining datasets, which restricts their practical reproducibility and accessibility. In parallel, foundation models like BiomedCLIP have achieved state-of-the-art few-shot classification results in pediatric and thoracic imaging; however, their vast parameter counts and dependence on multimodal training data render them impractical for real-time clinical deployment [50].
Across approaches, several critical limitations persist. High computational complexity continues to hinder the integration of state-of-the-art models into real-time clinical workflows. Moreover, many architectures are not optimally tailored to the unique challenges of pediatric imaging, including subtle lesion presentation and age-dependent anatomical variability. In addition, a large proportion of existing models were originally developed for color image classification and may insufficiently exploit the structural and textural properties of grayscale chest radiographs, potentially limiting their diagnostic effectiveness in medical imaging contexts. In response to these challenges, the present study investigates the adaptation of the IncMB module, originally developed for color image classification, for application in pediatric chest radiograph analysis. This module integrates components from the Inception architecture, the Mish activation function, and Batch Normalization, all tailored to leverage the statistical and spatial properties of grayscale medical imaging. The proposed framework evaluates the incorporation of IncMB within standard CNN pipelines to enhance feature extraction and classification accuracy in pediatric pneumonia recognition, while maintaining computational efficiency suitable for potential integration into real-world diagnostic systems.
3. Materials and Methods
In this study, we evaluate the feasibility of adapting the IncMB module for grayscale chest radiographs to support pediatric pneumonia classification. Although originally developed for RGB image processing [51], we integrate IncMB into medical deep learning workflows and assess its effectiveness in enhancing feature extraction from monochromatic data. Our goal is to determine whether this lightweight, multi-scale module can improve diagnostic accuracy and efficiency when applied to pediatric chest X-rays.
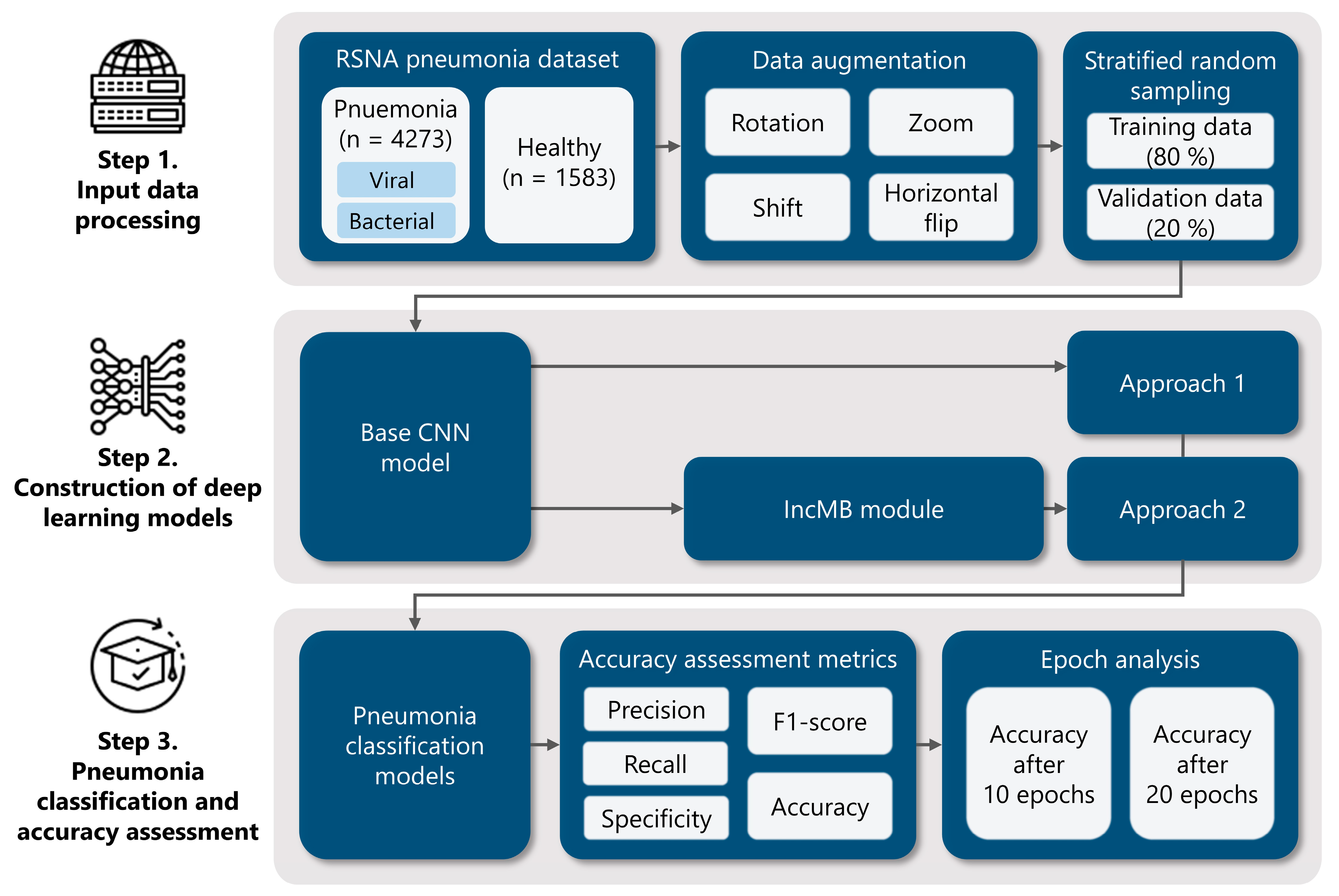
To achieve this, we employ four widely used CNN architectures—InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, DenseNet201, and MobileNetV2—as both baseline models and modified versions incorporating the IncMB module. This dual evaluation allows us to directly compare performance gains introduced by IncMB. The module of IncMB is appended directly to backbone convolutional feature maps and precedes the classification head. This position enables the module to boost multi-scale properties without compromising the ability to extract features in the backbone network that is pretrained. The experimental workflow consists of three main stages, as illustrated in Figure 1: (1) Data preprocessing and preparation, using the publicly available Chest X-ray Images (Pneumonia) dataset to classify images into two categories: pneumonia and healthy. We apply preprocessing techniques and data augmentation to improve generalization and mitigate overfitting; (2) Model implementation, where we integrate the IncMB module into the selected CNN architectures and fine-tune both the base and modified models using transfer learning; (3) Performance evaluation, where we assess and compare both baseline and IncMB-enhanced models using classification metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall (sensitivity), F1 score and specificity.
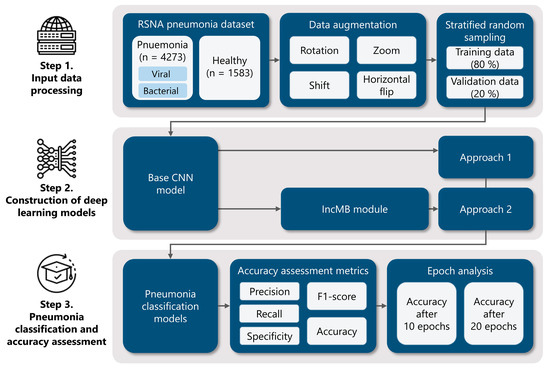
Figure 1.
Comprehensive methodology for deep learning pneumonia classification: (1) Initial data preparation, encompassing augmentation techniques and the division of the dataset into training and validation subsets via stratified random sampling; (2) Development of deep learning models utilizing established architectures such as InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, DenseNet201, and MobileNetV2, integrated into two distinct modeling strategies, including an IncMB module; (3) Evaluation of pneumonia classification performance through various accuracy metrics and an analysis of model behavior across different training epochs.
3.1. Data Preparation and Experimental Setup
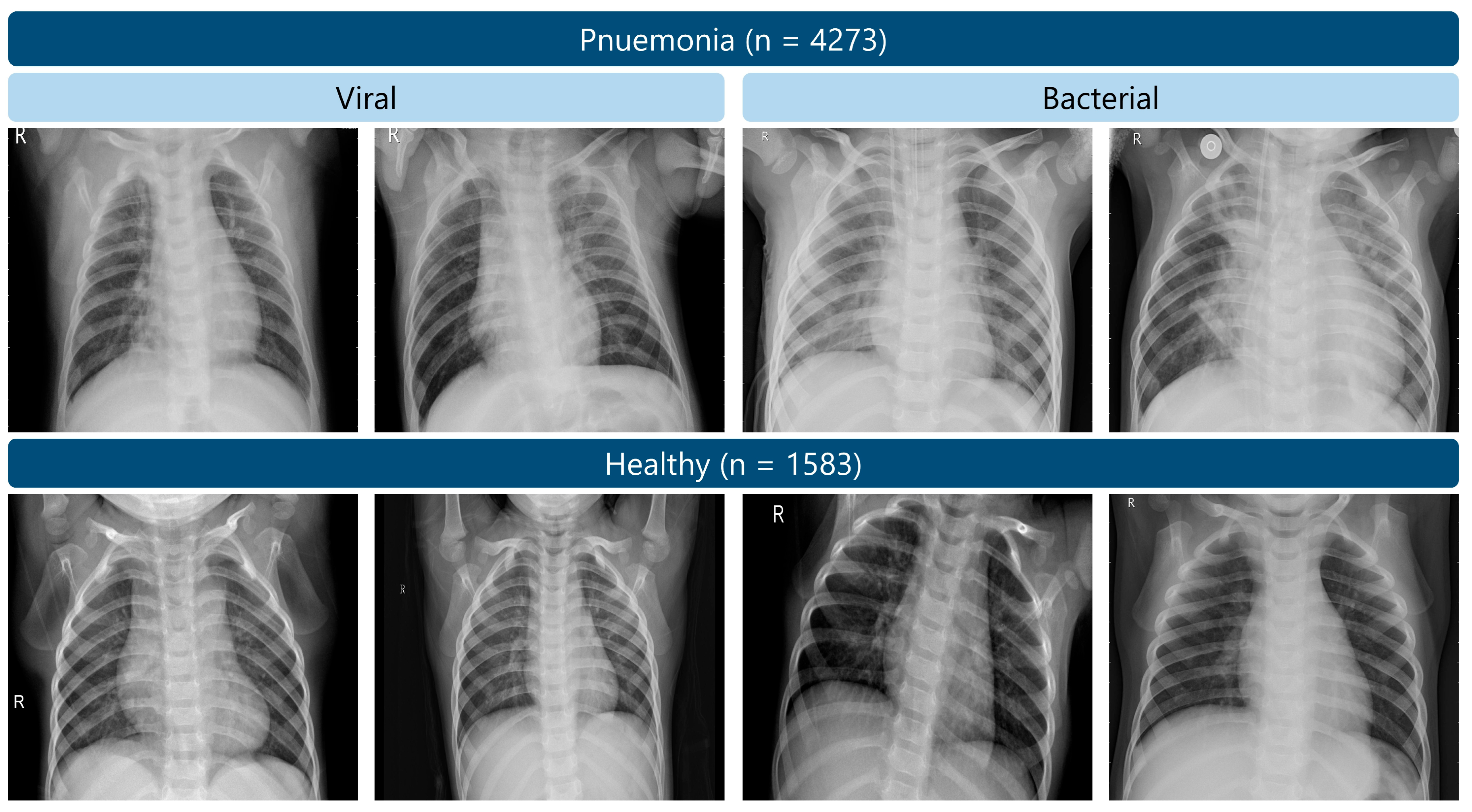
In the given study, we used publicly available Chest X-ray Images (Pneumonia) dataset [52], which consists of 5856 chest X-rays taken of pediatric patients (one to five years old) in Guangzhou Woman and Children Hospital. There are 4273 cases of pneumonia and 1583 healthy controls in this data [52]. While the dataset includes both viral and bacterial pneumonia labels, these were combined into a single pneumonia class, and all models were trained using binary cross-entropy loss to distinguish pneumonia from healthy cases. Figure 2 shows some of the samples. The quality of the data and reliability of the diagnosis has been considered by screening of all X-ray images prior to their use to extract low-quality scans or those that are unreadable. Two expert physicians made the diagnoses, and a third expert would confirm the check to reduce the possibility of errors.
Figure 2.
Examples of chest X-ray images from the RSNA pneumonia dataset.
The dataset was partitioned using a stratified random split method at an 80:20 ratio for training and validation, thereby preserving the original class distribution. Despite the inherent class imbalance, several strategies were implemented to mitigate its impact. Firstly, extensive data augmentation techniques, including rotation (±30°), width and height shifts (±10%), zooming (up to 20%), and horizontal flipping, were applied equally across both classes. This artificially expanded the training set and reduced overfitting, particularly benefiting the minority (healthy) class. Secondly, evaluation focused on metrics sensitive to class imbalance, such as precision, recall, and F1-score, rather than solely accuracy, providing a more reliable assessment of model performance across both classes. Thirdly, stratified splitting ensured consistent representation of the imbalance in both sets, preventing bias toward the majority class during evaluation. Due to computational resource limitations and the dataset’s scale, a single 80:20 split was chosen over k-fold cross-validation, which would have significantly increased training time without proportional benefits. All chest X-ray images were resized to 224 × 224 pixels, matching the input dimensions commonly used by convolutional neural networks such as InceptionV3, DenseNet201, and MobileNetV2. This resizing provides a standardized input for deep learning models, while retaining sufficient detail for the detection of radiographic findings relevant to pneumonia. Although fine interstitial changes may be partially blurred at this resolution, larger opacities and consolidations, which are typically the focus of pneumonia diagnosis, remain discernible [9,18].
We developed and trained the deep learning models in a Python environment (Python 3.10; Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, DE, USA), leveraging the Keras-GPU [53] and TensorFlow-GPU [54] frameworks on the Google Colab platform. Google Colab facilitated efficient training through its NVIDIA Tesla K80 GPUs (NVIDIA Corporation, Santa Clara, CA, USA) with 12 GB of memory. Training details, optimizer, loss function, and other hyperparameters are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Summary of model hyperparameters.
3.2. Model Architecture and Adapted IncMB Module
CNNs have been established as foundational in medical image analysis, primarily because of their capacity to hierarchically extract spatial and contextual features from input data [24,43,44]. In this study, four CNN architectures—InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, DenseNet201, and MobileNetV2—were adopted through transfer learning, utilizing pre-trained ImageNet weights. Instead of the fine-tuning of the entire layers, the pre-trained convolutional bases were left as fixed feature extraction modules, but custom classification heads were added and learnt on the pediatric pneumonia data. Although domain-specific pretraining can be beneficial, using ImageNet-pretrained models offers several advantages: they are extensively validated, widely available, and provide rich low-level visual representations that generalize well to medical imaging tasks. This approach also ensures methodological consistency and comparability across related studies [36,37].
A critical challenge arises from the fundamental difference between the grayscale nature of CXRs and the color RGB images on which traditional CNNs are typically trained. This distinction manifests in terms of dimensionality (single channel for grayscale vs. three channels for RGB), contrast sensitivity, and the intricate representation of texture. Consequently, directly applying CNNs trained on color images often leads to suboptimal feature extraction when confronted with grayscale medical images [38,39]. Pediatric CXRs present further complexities, including age-related anatomical variability, inherently lower contrast in pathological regions, and the subtle, diffuse, and often small-scale lesion presentations that are less radiographically distinct compared to those commonly observed in adult populations [34].
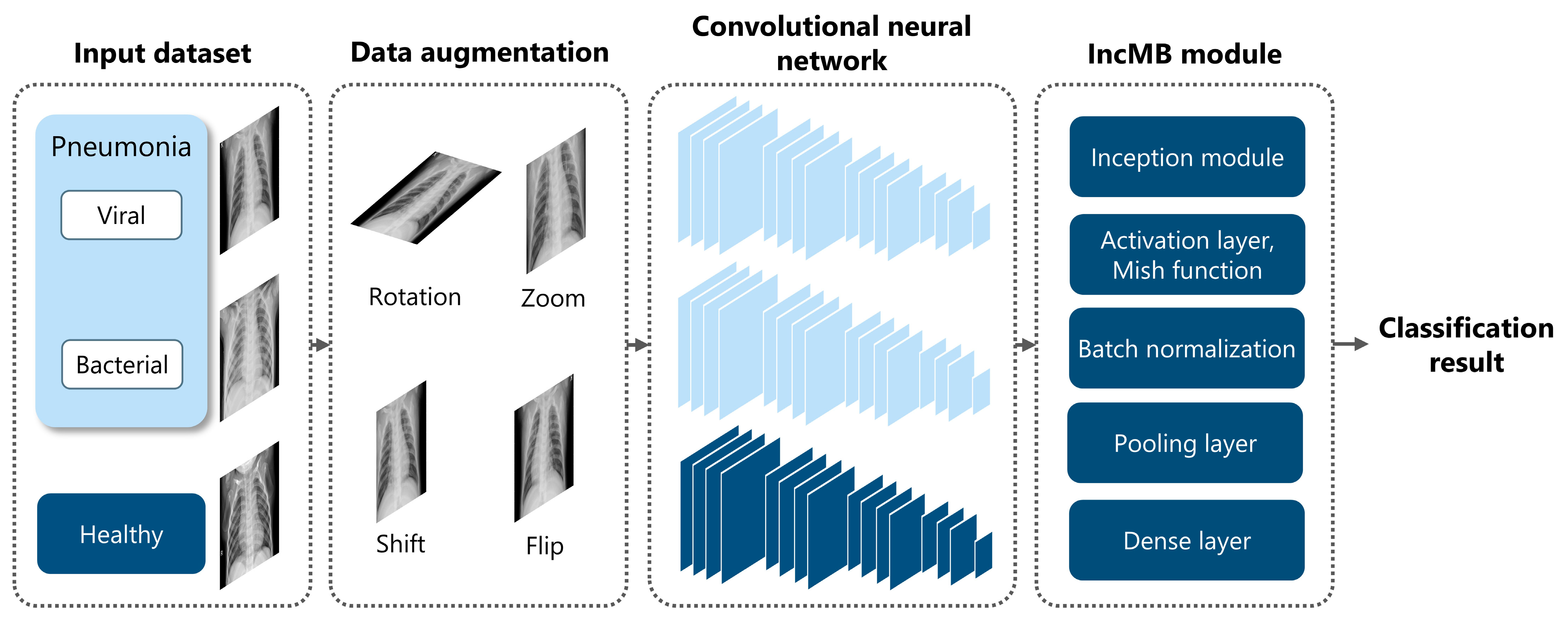
To address these challenges, we introduce the IncMB module, a lightweight architectural unit specifically designed to enhance multi-scale feature learning in grayscale medical images. Overall architecture is shown in Figure 3.
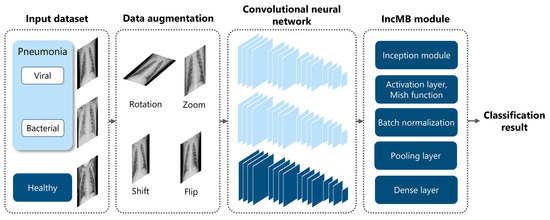
Figure 3.
Overview of the proposed framework for pediatric pneumonia classification, highlighting the integration and role of the IncMB module.
- The Inception architecture: This foundational design enables efficient multi-branch processing, allowing the network to concurrently extract features at different spatial scales. This is achieved through parallel convolutions employing various kernel sizes and a pooling branch [55,56]. Moreover, its inherent multi-scale capacity is particularly well-suited for pediatric pneumonia recognition, where pathologies can manifest as small, poorly defined opacities or as broader, more diffuse patterns [28].
- The Mish activation function: To further adapt the module for grayscale image processing, Mish is employed as the activation function. Mish is a non-monotonic, self-regularizing activation function [57,58] as mathematically defined in Equation (1):
Unlike traditional activation functions such as ReLU, Mish maintains a smooth, continuous gradient flow, even for negative input values, thereby preventing abrupt transitions that could impede network convergence [57]. Its formulation fosters better feature representation by enabling richer information propagation across layers, especially in deeper networks or when the input features contain subtle grayscale variations, as is characteristic of chest radiographs. Studies have compellingly demonstrated that Mish activation significantly outperforms both ReLU and Swish in tasks demanding the capture of fine-grained patterns, such as grayscale medical image classification [26,58]. Its smooth curvature and non-zero gradient across all real inputs contribute to more stable optimization and ultimately, higher classification accuracy. In the specific context of pediatric CXR analysis, where abnormalities may reside in low-contrast or texturally ambiguous regions, Mish ensures that these subtle diagnostic cues are meticulously preserved and amplified across convolutional layers, rather than being clipped or nullified as might occur with ReLU-based activations [58]. This property is particularly advantageous when combined with multi-scale feature extraction, as it empowers the network to retain crucial diagnostic details that might otherwise be lost through shallower or narrower activations.
- Batch Normalization: The IncMB module also incorporates Batch Normalization after the convolution and activation stages. This crucial regularization mechanism ensures that internal covariate shift is minimized and that feature distributions remain stable throughout the training process [59]. This leads to faster convergence, the ability to utilize higher learning rates, and a reduced risk of overfitting—all critical considerations when working with relatively small and potentially imbalanced pediatric datasets.
Structurally, the IncMB module comprises four distinct branches: a 1 × 1 convolutional pathway, a 1 × 1 followed by 3 × 3 convolutional pathway, a 1 × 1 followed by 5 × 5 convolutional pathway, and a 3 × 3 max-pooling followed by a 1 × 1 convolution. Each of these branches captures features at distinct receptive fields, which are subsequently concatenated to form a rich, multi-scale representation of the input image [55]. This composite feature map is then passed through the Mish activation function and Batch Normalization before being processed by the downstream CNN layers. A single IncMB module is positioned after the backbone feature extraction layers and before the global pooling and classification layers.
In adapting the IncMB module to the grayscale pediatric pneumonia dataset, it is strategically inserted into the selected CNN backbone, either replacing or complementing traditional convolutional blocks. This deliberate integration allows the network to more effectively accommodate the unique radiological characteristics of pediatric CXRs, including heterogeneous lesion distribution and the often-subtle textural differences between pathological and healthy tissues. The overall methodology is outlined in Appendix A.
3.3. Pediatric Pneumonia Performance Evaluation
The assessment of deep learning model efficacy in the classification of pediatric pneumonia from chest radiographs necessitated the application of a comprehensive set of quantitative metrics. These indicators, including precision, recall (sensitivity), specificity, F1-score, and overall accuracy, were systematically derived from the confusion matrix to facilitate a granular evaluation of the models’ diagnostic capabilities, as defined in Equations (2)–(6) [60,61].
The model’s classifications were precisely compared against the established ground truth. True Positives (TP) denoted instances where the presence of pneumonia was correctly identified. Conversely, True Negatives (TN) represented accurate determinations of the absence of pneumonia. Errors in classification were delineated as False Positives (FP), occurring when a non-pneumonic condition was erroneously assigned the pneumonia label, and False Negatives (FN), signifying a failure to detect actual pneumonia cases.
4. Results and Discussion
This section presents a comprehensive evaluation of the proposed pneumonia classification models using multiple transfer learning backbones—InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, MobileNetV2, and DenseNet201—under two approaches: a base model and the base model with the IncMB.
Across all networks, the integration of the IncMB module led to a consistent and notable improvement in classification performance metrics, underscoring its effectiveness in enhancing deep learning models for pneumonia recognition as detailed in Table 2. Among the evaluated models, InceptionResNetV2 with IncMB achieved the highest scores across several key metrics—accuracy of 0.9812, F1-score of 0.9761, and recall of 0.9742—demonstrating its superior ability to generalize and accurately classify pneumonia cases. These results highlight the synergy between the deep architecture of InceptionResNetV2 and the feature-enriching capabilities of IncMB. In addition to absolute performance gains, IncMB integration significantly boosted performance for lighter models. Notably, MobileNetV2 with IncMB exhibited the largest improvement in accuracy, with a jump of +4.69% from its base model from 0.9113 to 0.9582. This substantial gain reinforces the utility of IncMB, especially for resource-constrained settings where lightweight models are preferred. Moreover, improvements in precision and F1-score were consistently observed across all models with IncMB. However, some trade-offs became apparent. For instance, MobileNetV2 with IncMB experienced a decrease in specificity from 0.9779 to 0.8675. Despite this, its recall increased significantly from 0.8865 to 0.9918, which is a desirable outcome in clinical scenarios where minimizing false negatives is paramount. In such contexts, especially in pneumonia diagnosis, capturing as many true cases as possible is often more critical than avoiding false positives [62]. Overall, the inclusion of IncMB led to improved robustness and diagnostic value across various deep learning backbones.

Table 2.
Performance evaluation of the proposed pneumonia classification approaches based on overall accuracy metrics.
As detailed in Table 3, the base models generally demonstrated higher recall for the pneumonia class compared to the healthy class, indicating a tendency to better identify diseased cases while occasionally misclassifying healthy ones. This imbalance poses a challenge in clinical settings, where both false negatives and false positives can have serious implications. After incorporating the IncMB, recall for the healthy class improved notably across most models, suggesting enhanced discrimination between the two classes. For example, InceptionV3’s healthy class recall increased from 0.9117 to 0.9369, and DenseNet201 saw a significant jump from 0.9022 to 0.9590. These improvements reflect a reduction in false positives—healthy patients incorrectly flagged as having pneumonia. The pneumonia class also showed improvements or maintained high recall values after IncMB integration. MobileNetV2 with IncMB achieved the highest pneumonia recall of 0.9918, marking a substantial improvement from its base recall of 0.8865. Interestingly, DenseNet201’s base model already exhibited a high pneumonia recall of 0.9918, which remained robust after IncMB inclusion. These results suggest that IncMB not only improves the network’s ability to detect healthy cases but also maintains or enhances its strength in identifying pneumonia. Overall, the IncMB contributes to a more balanced classification performance, reducing bias toward one class and improving the model’s reliability for real-world clinical applications where accurate identification of both healthy and diseased cases is essential.

Table 3.
Detailed recall scores for pneumonia classification for each CNN within the evaluated approaches.
Training and validation trends over 10 and 20 epochs demonstrated smoother convergence and lower validation loss for all IncMB-enhanced models as presented in Table 4. A key observation is the marked reduction in validation loss, an indicator of improved model generalization and reduced overfitting. Most notably, InceptionResNetV2 with IncMB achieved the lowest validation loss of 0.0547 after 20 epochs, significantly outperforming its base counterpart, which recorded a validation loss of 0.0665. This suggests that the model not only converged more effectively but also retained better generalization capacity on unseen data. Similar positive trends were observed in InceptionV3 and DenseNet201. For instance, InceptionV3’s validation loss dropped from 0.1235 for base model to 0.0739 for base model with IncMB after 20 epochs, reflecting more efficient learning and better representation of data distributions. DenseNet201 with IncMB also exhibited enhanced performance, with its validation loss reducing from 0.0857 to 0.0794, while validation accuracy increased from 0.9679 to 0.9731. Even for lightweight architectures like MobileNetV2, IncMB contributed to meaningful improvements. Validation loss decreased from 0.2459 to 0.1610 over 20 epochs, and validation accuracy improved from 0.9288 to 0.9601, demonstrating that IncMB facilitates more robust learning dynamics even in computationally efficient models. Overall, these results demonstrate that IncMB positively influences the training trajectory, enabling faster convergence, lower validation error, and higher validation accuracy across varying architectures. This enhanced training behavior positions IncMB as a valuable module for improving both performance and reliability in deep learning-based medical image classification tasks.

Table 4.
Training dynamics illustrating the progression of accuracy and validation loss over 10 and 20 epochs for the different proposed classification approaches.
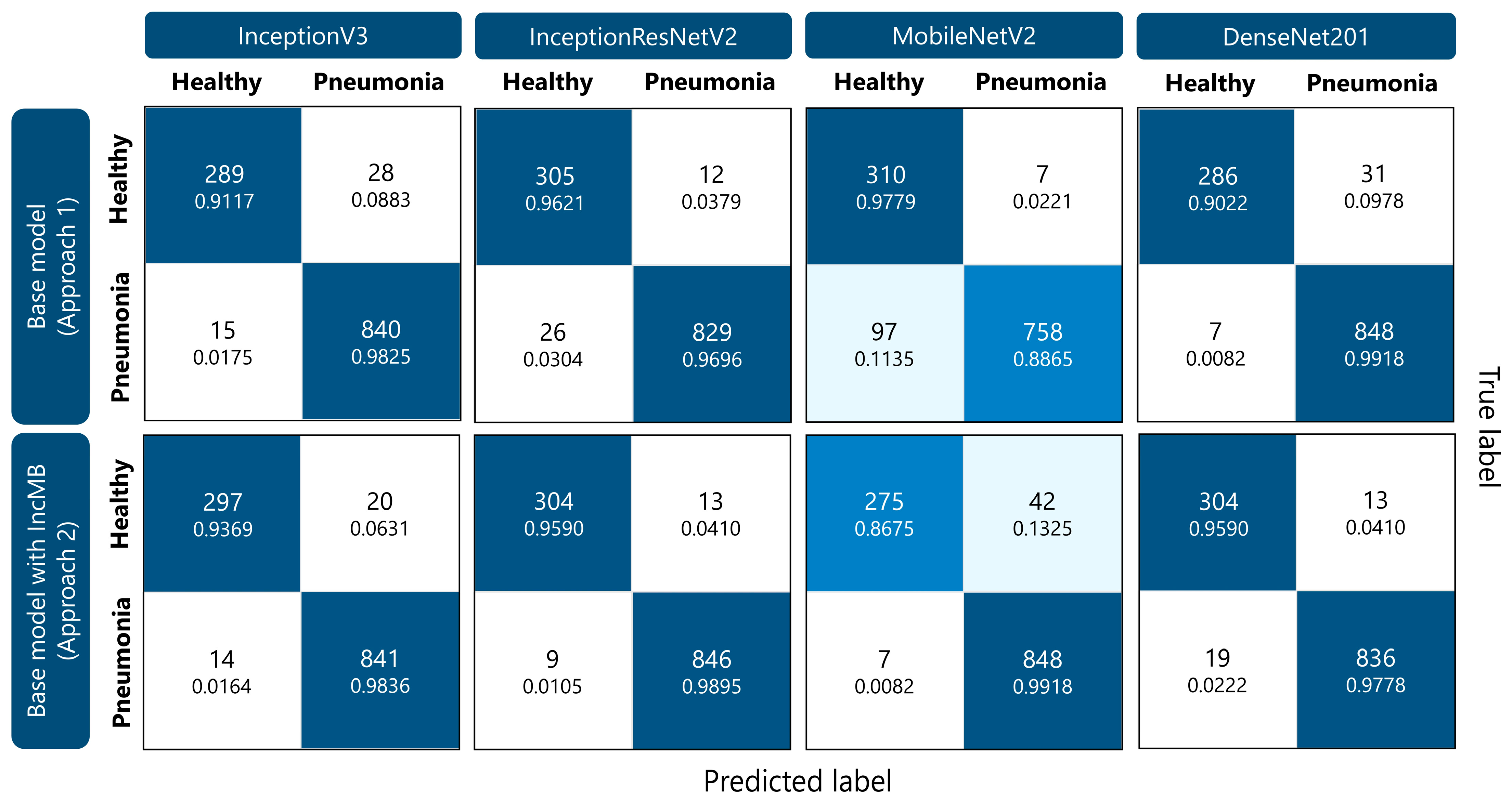
As demonstrated in Figure 4, IncMB significantly decreased the number of pneumonia cases misclassified as healthy across all networks, for example, InceptionResNetV2’s FNs dropped from 26 to 9, and MobileNetV2’s from 97 to just 7, showing over 90% improvement in FN rate for the latter. True negative counts also improved for most models with IncMB, especially for DenseNet201 from 286 to 304 and InceptionV3 from 289 to 297, resulting in improved specificity. While some models experienced a slight increase in false positives, this was often accompanied by a more clinically acceptable reduction in false negatives. For instance, MobileNetV2 with IncMB improved pneumonia recall from 0.8865 to 0.9918 at the cost of a moderate drop in healthy recall. Overall, the confusion matrices clearly demonstrate that the proposed IncMB module not only boosts aggregate performance metrics but also leads to a clinically meaningful redistribution of errors—favoring the reduction in false negatives, which is critical in pneumonia recognition.
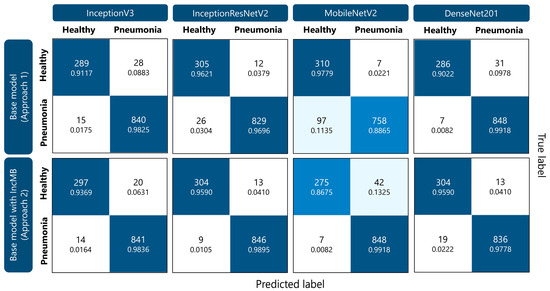
Figure 4.
Confusion matrices illustrating the performance of different CNN models (InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, MobileNetV2, and DenseNet201) for pediatric pneumonia classification. Within each cell, the top number indicates the count of classified instances, while the lower number presents the corresponding percentage for that specific class.
Incorporating the IncMB module across different CNN architectures produced consistent improvements in accuracy, generalization, and computational efficiency. The observed gains are attributable to the synergistic interaction of three architectural enhancements: multi-branch Inception-style convolutions, Batch Normalization, and the Mish activation function. Together, these components provide a more expressive, stable, and generalizable feature extraction framework, particularly well-suited for the heterogeneous and fine-grained visual patterns encountered in pediatric chest radiographs. The Inception component of IncMB employs parallel convolutional paths with varying kernel sizes, allowing the network to simultaneously capture features at multiple spatial resolutions [55,63]. This capacity for multi-scale representation is critical in medical imaging, where pathological features such as infiltrates or consolidations may present with variable size, shape, and intensity. Furthermore, the use of 1 × 1 convolutions as bottleneck layers enables dimensionality reduction prior to computationally intensive operations, thereby lowering the total number of parameters without compromising feature richness [64]. Batch Normalization contributes to both training stability and generalization. By normalizing the intermediate feature distributions, Batch Normalization reduces internal covariate shift and smooths the loss landscape, which facilitates faster convergence and allows for the use of higher learning rates [65,66]. Moreover, its implicit regularization effect helps prevent overfitting, particularly in smaller or imbalanced datasets common in medical imaging [65]. The Mish activation function complements these benefits by introducing a smooth, non-monotonic, and self-regularizing nonlinearity [57]. Unlike traditional ReLU, Mish retains negative information while preserving gradient flow across layers. Its continuous differentiability and curvature near zero enable improved learning dynamics, particularly in deep architectures [57]. These properties have been shown to enhance representation learning in vision tasks and are reflected in the improved recall and specificity achieved across all IncMB-augmented models in the present study. The performance metrics support these architectural improvements. Models incorporating IncMB consistently demonstrated higher recall and specificity relative to their baseline counterparts, indicating improved sensitivity to pneumonia cases and enhanced discrimination of healthy instances. Such balanced performance is essential for clinical applicability, where both false negatives and false positives carry significant consequences [28,41]. Furthermore, training trajectories showed smooth and consistent convergence, with validation performance closely tracking training accuracy and loss. This behavior suggests an absence of significant overfitting and indicates that the models learned robust, generalizable features. The regularizing effects of Batch Normalization, the smoother optimization facilitated by Mish, and the use of data augmentation collectively contributed to this outcome.
The integration of the IncMB module resulted in more parameter-efficient network architectures across all evaluated models. As summarized in Table 5, each base convolutional neural network exhibited a modest reduction in total parameter count when modified with the IncMB block. For instance, the InceptionV3 model decreased from approximately 22.98 million parameters (87.67 MB) to 22.30 million parameters (85.09 MB). The MobileNetV2 architecture demonstrated a more substantial reduction, from 2.99 million parameters (11.43 MB) to 2.60 million (9.93 MB), representing a decrease of approximately 13%. InceptionResNetV2 and DenseNet201 also showed reductions of about 0.87% and 3.2%, respectively. These reductions can be attributed to the architectural design of the IncMB module, particularly the use of 1 × 1 bottleneck convolutions and efficient feature compression strategies characteristic of Inception-style modules [55]. Such mechanisms effectively reduce the number of trainable parameters while preserving the network’s representational capacity. Importantly, this finding confirms that the improved classification performance observed with IncMB-enhanced models does not stem from increased model capacity or a higher number of trainable parameters. Instead, the gains primarily result from the module’s multi-scale feature extraction, grayscale-adaptive processing, and refined feature re-encoding capabilities. Moreover, these gains in compactness were achieved without any degradation in classification performance. On the contrary, accuracy and other performance metrics consistently improved with the IncMB-enhanced models. This demonstrates that the IncMB contributes meaningful architectural efficiency and feature-level adaptability rather than serving as a source of additional trainable complexity. From a deployment perspective, the reduced parameter count implies lower memory requirements and potentially faster inference times, facilitating integration into real-time or resource-constrained clinical environments [67,68]. Additionally, the decreased model complexity may help mitigate overfitting, contributing to improved generalization in unseen data settings.

Table 5.
Total parameters for transfer deep learning models across different classification approaches.
The technical enhancements introduced by the IncMB module hold practical relevance for pediatric pneumonia screening. High recall ensures that true pneumonia cases are reliably identified, reducing the risk of missed diagnoses, while high specificity minimizes false positives, preventing unnecessary interventions [69]. This balanced performance supports the use of IncMB-enhanced models as effective triage tools. Additionally, the reduction in model parameters enables deployment on resource-constrained devices, such as portable systems in rural or low-resource settings. These lightweight yet accurate models could facilitate faster, automated chest X-ray interpretation, assisting clinicians in prioritizing cases and improving diagnostic efficiency.
In comparative analysis with prior state-of-the-art approaches, the proposed IncMB-augmented models demonstrate performance that is both competitive and methodologically robust. Barakat et al. [70] evaluated a Quadratic SVM-based framework on a pediatric chest X-ray dataset comprising approximately 5856 images, achieving an accuracy of 0.9758. Although several performance measures were reported, the study emphasized accuracy as the primary indicator of model quality, without providing a deeper per-class breakdown or confusion matrix analysis to elucidate diagnostic trade-offs. Furthermore, no training–validation progression curves were presented, limiting the ability to assess potential overfitting or the stability of convergence. Similarly, Alsharif et al. [71] employed a deep learning–based model on 5852 pediatric X-ray images, attaining an accuracy of 0.9970, sensitivity of 0.9974, and an AUC of 0.9812. While Alsharif et al. reported marginally higher overall accuracy and sensitivity than our best-performing InceptionResNetV2 + IncMB configuration, its lower specificity and the absence of per-class recall metrics or confusion matrix analysis hinder a nuanced evaluation of diagnostic trade-offs [71]. Notably, neither Barakat et al. nor Alsharif et al. presented epoch-wise validation trends, whereas our results explicitly document smooth and stable convergence across training and validation values, with no evidence of significant overfitting [70,71]. These findings underscore that the observed performance gains in our models are not attributable to instability or over-optimization, but rather to the multi-scale, grayscale-adaptive feature enhancement capabilities introduced by the IncMB module. In addition to the aforementioned studies, several recent deep learning methodologies have reported commendable performance in pediatric pneumonia classification, employing diverse architectural and training paradigms. Ha Pham and Tran [72] implemented an ensemble of three pre-trained convolutional neural networks: InceptionResNetV2, DenseNet201, and VGG16, achieving an accuracy of approximately 95% and a 3% enhancement in the F1-score relative to single-model baselines. Their ensemble strategy effectively integrates complementary representational features, whereas the proposed IncMB-augmented InceptionResNetV2 architecture attains superior overall accuracy while preserving an equitable sensitivity–specificity balance, thereby exemplifying an alternative yet methodologically robust design approach. Kareem et al. [73] investigated a federated learning framework encompassing multiple pre-trained CNN architectures (AlexNet, DenseNet, ResNet50, Inception, and VGG19) trained on distributed pediatric chest X-ray datasets. The ResNet-50 model within their study achieved an accuracy of approximately 93%, highlighting both the potential and inherent complexities of decentralized medical data learning. In contrast, the present centralized IncMB-based configuration exhibits marginally higher accuracy under controlled conditions, suggesting that multi-scale feature enrichment could serve as a complementary mechanism in prospective federated or hybrid learning paradigms. Patidar et al. [74] introduced a hybrid ensemble model combining MobileNetV2, ResNet152, and DenseNet169 for pediatric pneumonia detection, achieving 95.03% classification accuracy. Their results demonstrate the effectiveness of ensemble strategies in leveraging complementary network features. In comparison, our IncMB-augmented InceptionResNetV2 model attains 98.12% accuracy with stable convergence and detailed per-class evaluation, reflecting the complementary strengths of ensemble-based and feature-enhancement approaches.
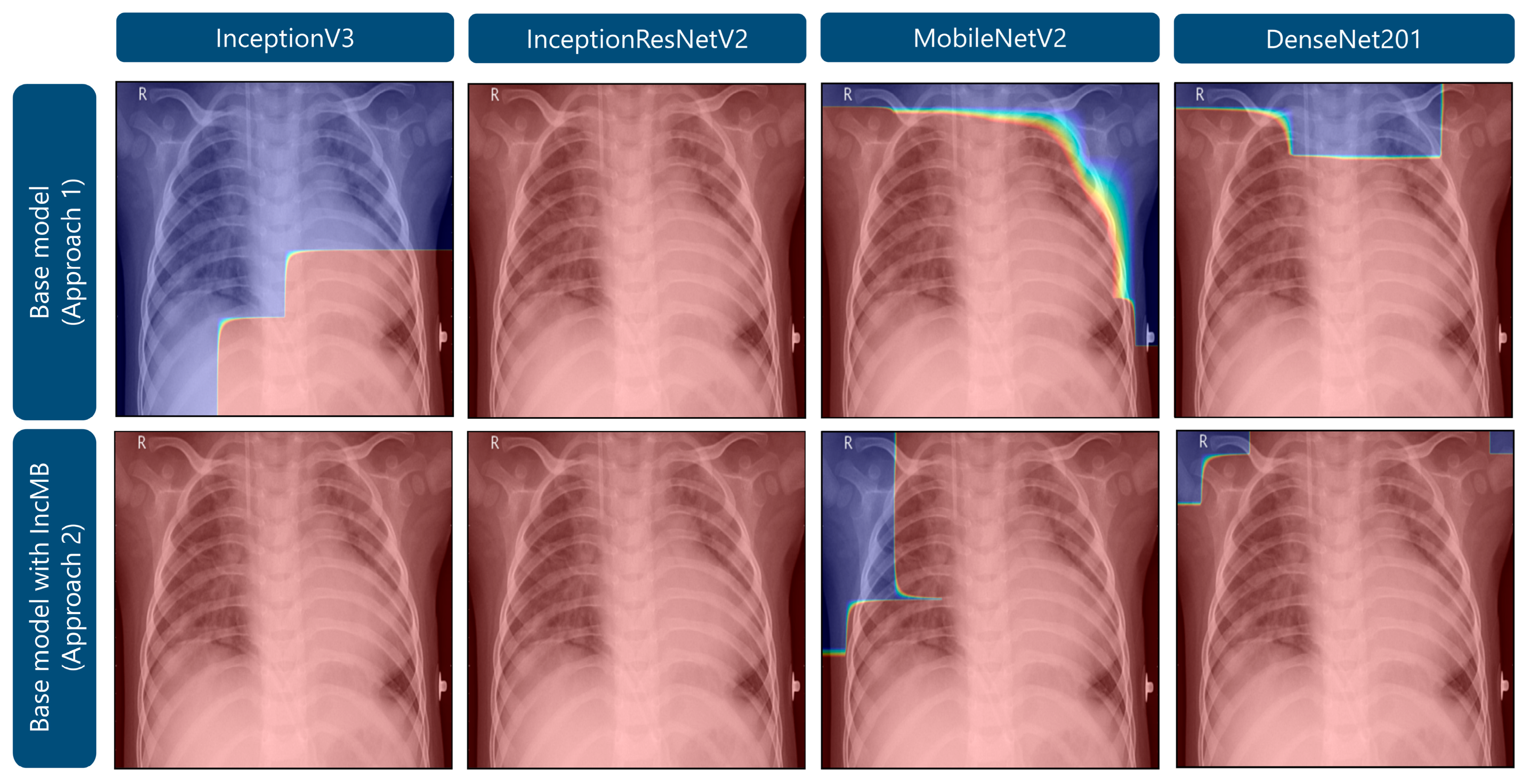
As demonstrated in Figure 5, Grad-CAM visualizations illustrating the attention maps of four convolutional neural network architectures—InceptionV3, InceptionResNetV2, MobileNetV2, and DenseNet201—under two approaches: the base model and the base model augmented with the adaptive IncMB module. The example shown corresponds to a confirmed case of bacterial pneumonia, which on pediatric chest radiographs typically manifests as focal or lobar consolidation with increased opacity, often localized to one lung zone and associated with air bronchograms. In the base configurations, several models, particularly InceptionV3, MobileNetV2, and DenseNet201, exhibit partial or peripheral focus on non-pathological regions, such as the upper thoracic border and areas outside the lung fields. This misdirected attention is especially evident in MobileNetV2, where the heatmap concentrates along the image margins, suggesting suboptimal feature localization. Following the integration of IncMB, all four architectures demonstrate markedly improved focus, with activation maps more precisely covering the lung parenchyma and the region of consolidation, reflecting better alignment with radiological markers of bacterial pneumonia. This shift indicates that the IncMB module enhances the network’s ability to attend to clinically relevant structures, reducing reliance on extraneous image features. The refined attention is consistent with the observed improvements in recall, specificity, and overall accuracy reported in Table 1, Table 2 and Table 3 and supports the hypothesis that IncMB facilitates more discriminative and pathology-centered feature extraction in pediatric pneumonia classification tasks.
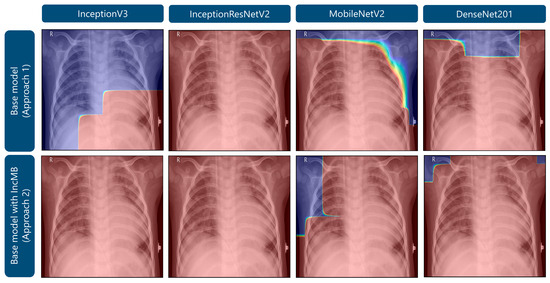
Figure 5.
Grad-CAM visualizations highlighting areas of attention in images of bacterial pneumonia.
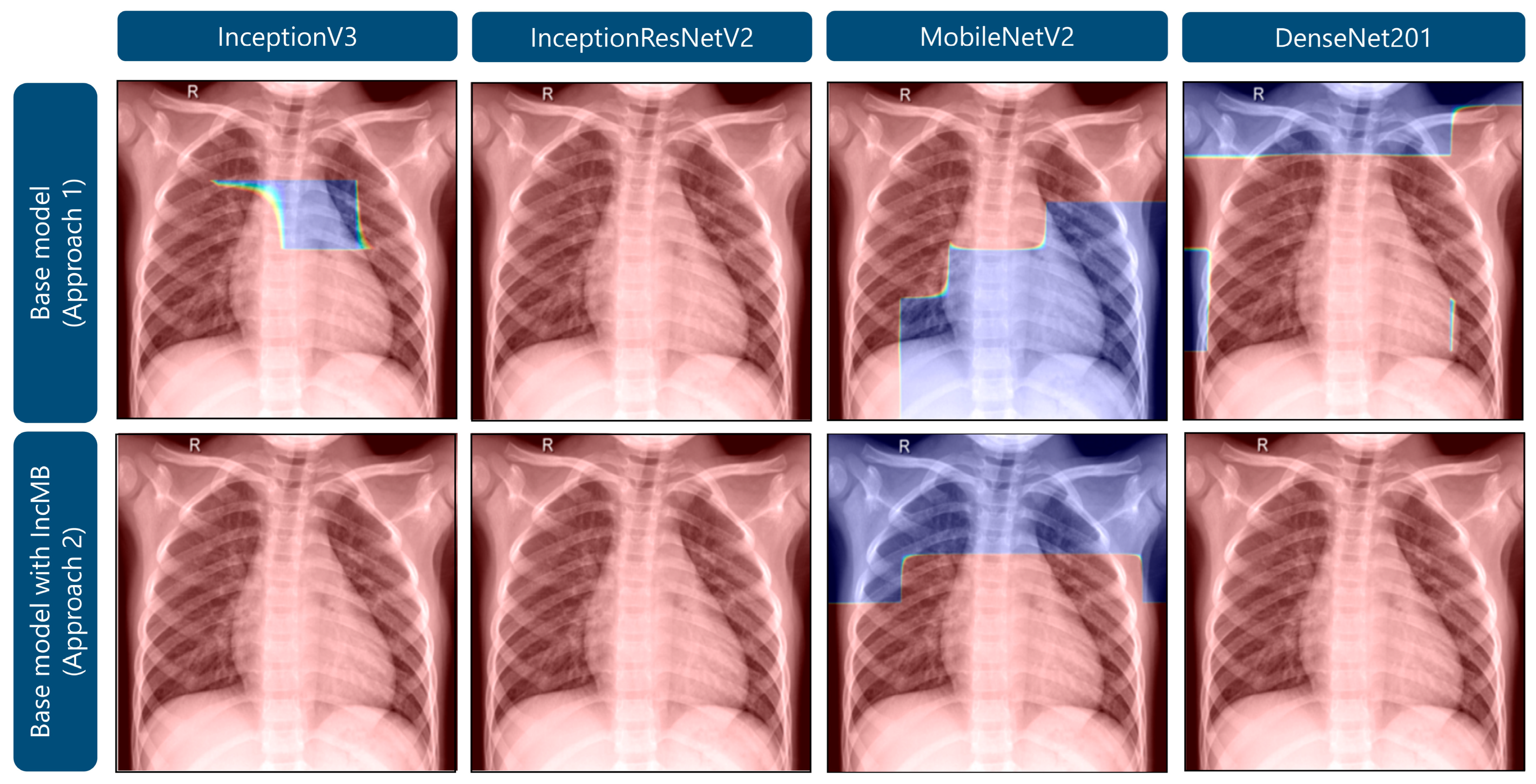
As demonstrated in Figure 6, Grad-CAM visualizations for a representative healthy pediatric chest radiograph provide a comparative perspective on the distribution of model attention in non-pathological versus pathological cases. In the base configurations, several architectures display dispersed and irregular activation patterns, with emphasis along the lung apices and peripheral thoracic margins, suggesting nonspecific or contextually irrelevant feature attribution. After the integration of the adaptive IncMB module, the overall activation intensity markedly decreases and becomes confined to anatomically plausible pulmonary regions, with minimal focus on extraneous structures. Although IncMB-based activation maps may appear to encompass broader areas of the lung fields, this behavior reflects the module’s multi-scale receptive design, which encourages contextual integration of bilateral and parenchymal patterns rather than a loss of spatial precision. This results in anatomically coherent, context-aware attention that enhances lesion localization in abnormal images (Figure 5) while concurrently suppressing false-positive responses in normal radiographs. Collectively, the comparison between Figure 5 and Figure 6 demonstrates that the IncMB module promotes balanced and semantically meaningful feature attention across distinct clinical categories.
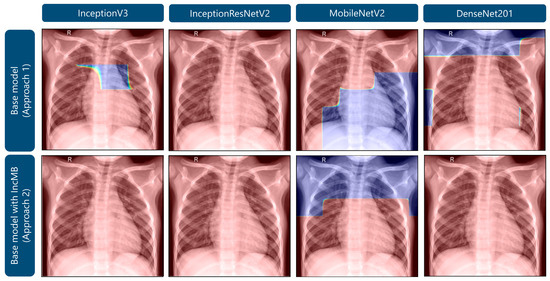
Figure 6.
Grad-CAM visualizations highlighting areas of attention in images of healthy lungs.
While our findings are promising, a significant limitation of this study is the dataset’s scope. The chest X-ray images were sourced exclusively from a single publicly available pediatric dataset collected at one hospital. Although the dataset is extensive, it does not fully represent the demographic, geographic, and clinical diversity found in real-world medical practice. The lack of variability in imaging equipment, patient populations, and acquisition settings may constrain the model’s generalizability to different clinical environments. To improve robustness and applicability, future work should focus on evaluating these models using larger, multi-center datasets that include a wider range of age groups, disease presentations, and imaging protocols.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we proposed an improved pneumonia classification framework based on transfer learning models enhanced with a custom IncMB module, which integrates Inception blocks, the Mish activation function, and Batch Normalization. Among the evaluated architectures, the InceptionResNetV2 model with IncMB achieved the highest performance, recording an accuracy of 0.9812 and F1-score of 0.9761, outperforming all baseline counterparts. Additionally, the IncMB module consistently improved model generalization while reducing the number of parameters across all tested networks—for instance, lowering InceptionResNetV2’s parameter counts by nearly half a million—thus contributing to computational efficiency without compromising predictive accuracy. These advances support the use of this approach in low-resource and point-of-care settings where compact, reliable diagnostic tools are required.
Despite these promising outcomes, several limitations must be acknowledged. The dataset, while sizable, may not fully capture the diversity encountered in global clinical practice, potentially limiting the generalizability of the models across different demographic, geographic, or equipment-specific contexts. In addition, the experimental design employed a single train–validation split without additional repetitions or cross-validation, which may limit the assessment of statistical variability and model stability. Nevertheless, consistent settings, standardized hyperparameters, and extensive data augmentation were applied to enhance reliability and mitigate potential bias.
Future research should focus on validating the proposed models using multi-center datasets that capture broader demographic, geographic, and equipment variability, ensuring robust generalization across different clinical settings. Beyond retrospective evaluation, prospective clinical trials are needed to assess real-world performance, including workflow integration and diagnostic impact in routine practice. Integrating additional imaging modalities, such as lung ultrasound, may further enhance clinical applicability by enabling multimodal diagnosis. Furthermore, integration with clinical decision support systems could facilitate seamless adoption into clinical workflows, improving interpretability and user trust. From a deployment perspective, efforts should include edge computing solutions and mobile platforms equipped with intuitive user interfaces tailored for healthcare professionals, allowing for real-time decision support in both hospital and resource-limited environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, P.R.; methodology, P.R.; software, P.R.; validation, D.R. and G.M.; formal analysis, P.R.; investigation, P.R.; resources, P.R.; data curation, P.R.; writing—original draft preparation, P.R.; writing—review and editing, P.R., D.R. and G.M.; visualization, D.R. and P.R.; supervision, G.M.; project administration, G.M.; funding acquisition, D.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The code developed in this study is available on request from the corresponding author. The open access Chest X-Ray Images (Pneumonia) repository containing images collected from pediatric patients is divided into two categories—Pneumonia/Healthy—and is available at https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/paultimothymooney/chest-xray-pneumonia (accessed on 9 October 2025).
Conflicts of Interest
Author Petra Radočaj was employed by the company Layer d.o.o. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
Appendix A. Detailed Pseudocode for CNN Training and Evaluation with Adapted IncMB Module
| Algorithm A1: Training and Evaluation of CNN with Adapted IncMB Module |
|
References
- Altalhi, A. Review: Pediatric Pneumonia, Etiology, Diagnosis and Management. 2020. Available online: https://www.iajps.com/March-2020/issue_20march_171.php (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- Crame, E.; Shields, M.D.; McCrossan, P. Paediatric Pneumonia: A Guide to Diagnosis, Investigation and Treatment. Paediatr. Child Health 2021, 31, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barson, W.J.; Kaplan, S.; Torchia, M. Pneumonia in Children: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, and Etiology. UpToDate Walth. MAAccessed January 28 2018. 2014. Available online: http://bvndtp.org.vn/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/Pneumonia-in-childre1.doc (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- de Benedictis, F.M.; Kerem, E.; Chang, A.B.; Colin, A.A.; Zar, H.J.; Bush, A. Complicated Pneumonia in Children. Lancet 2020, 396, 786–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutzeler, C.R.; Bourguignon, L.; Weis, C.; Tong, B.; Wong, C.; Rieck, B.; Pargger, H.; Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Egli, A.; Borgwardt, K.; et al. Comorbidities, Clinical Signs and Symptoms, Laboratory Findings, Imaging Features, Treatment Strategies, and Outcomes in Adult and Pediatric Patients with COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2020, 37, 101825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkes, C.; Bava, M.; Graham, H.R.; Duke, T. ARI Review group What Are the Risk Factors for Death among Children with Pneumonia in Low- and Middle-Income Countries? A Systematic Review. J. Glob. Health 2023, 13, 05003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Rocha, B.M.; Kaimakamis, E.; Cheimariotis, G.-A.; Petmezas, G.; Chatzis, E.; Kilintzis, V.; Stefanopoulos, L.; Pessoa, D.; Marques, A.; et al. A Deep Learning Method for Predicting the COVID-19 ICU Patient Outcome Fusing X-Rays, Respiratory Sounds, and ICU Parameters. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 235, 121089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pneumonia in Children. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/pneumonia (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Frigati, L.; Greybe, L.; Andronikou, S.; Eber, E.; Sunder, B.; Venkatakrishna, S.; Goussard, P. Respiratory Infections in Low and Middle-Income Countries. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2025, 54, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, O.; Nisar, S.; Khattak Haroon Ur Rashid, S.; Ibne Ali Jaffari, S.M.; Haider, Z.; Fatima, F.; Zahra, S.E.; Ijaz, A.H.; Kaneez, M.; Shairwani, G.K. Clinical and Etiological Exploration of Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia in the Intensive Care Unit of a Developing Country. Cureus 2023, 15, e47515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudan, I.; O’brien, K.L.; Nair, H.; Liu, L.; Theodoratou, E.; Qazi, S.; Lukšić, I.; Walker, C.L.F.; Black, R.E.; Campbell, H. Epidemiology and Etiology of Childhood Pneumonia in 2010: Estimates of Incidence, Severe Morbidity, Mortality, Underlying Risk Factors and Causative Pathogens for 192 Countries. J. Glob. Health 2013, 3, 010401. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, R.; Xu, P.; Cai, Y.; Wang, F.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; Liu, C. A Deep Learning Model for the Diagnosis and Discrimination of Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Pneumonia for Children Using Chest Radiography Images and Clinical Information. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 4083–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guitart, C.; Bobillo-Perez, S.; Rodríguez-Fanjul, J.; Carrasco, J.L.; Brotons, P.; López-Ramos, M.G.; Cambra, F.J.; Balaguer, M.; Jordan, I. Lung Ultrasound and Procalcitonin, Improving Antibiotic Management and Avoiding Radiation Exposure in Pediatric Critical Patients with Bacterial Pneumonia: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, C.; Cavallo, A.; Rocca, A.; Pierantoni, L.; Antonazzo, D.; Dondi, A.; Gabrielli, L.; Lazzarotto, T.; Lanari, M. Pulmonary and Extrapulmonary Manifestations in Hospitalized Children with Mycoplasma Pneumoniae Infection. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geanacopoulos, A.T.; Lipsett, S.C.; Hirsch, A.W.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Neuman, M. Impact of Viral Radiographic Features on Antibiotic Treatment for Pediatric Pneumonia. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2022, 11, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Liu, X.; Shen, J.; Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Ye, L.; Wu, X.; Chen, T.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Deep-Learning Pipeline for the Diagnosis and Discrimination of Viral, Non-Viral and COVID-19 Pneumonia from Chest X-Ray Images. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2021, 5, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Nufaiei, Z.F.; Alshamrani, K.M. Comparing Ultrasound, Chest X-Ray, and CT Scan for Pneumonia Detection. Med. Devices 2025, 18, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayhan, G.İ.; Gülleroğlu, N.B.; Çetin, S.; Erat, T.; Yıldız, S.; Özen, S.; Konca, H.K.; Yahşi, A.; Dinç, B. Radiographic Findings of Adenoviral Pneumonia in Children. Clin. Imaging 2024, 108, 110111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fancourt, N.; Deloria Knoll, M.; Barger-Kamate, B.; de Campo, J.; de Campo, M.; Diallo, M.; Ebruke, B.E.; Feikin, D.R.; Gleeson, F.; Gong, W.; et al. Standardized Interpretation of Chest Radiographs in Cases of Pediatric Pneumonia From the PERCH Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 64, S253–S261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balk, D.S.; Lee, C.; Schafer, J.; Welwarth, J.; Hardin, J.; Novack, V.; Yarza, S.; Hoffmann, B. Lung Ultrasound Compared to Chest X-Ray for Diagnosis of Pediatric Pneumonia: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2018, 53, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereda, M.A.; Chavez, M.A.; Hooper-Miele, C.C.; Gilman, R.H.; Steinhoff, M.C.; Ellington, L.E.; Gross, M.; Price, C.; Tielsch, J.M.; Checkley, W. Lung Ultrasound for the Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Children: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 714–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, A.; Numis, F.G.; Visone, G.; Pirozzi, C.; Masarone, M.; Olibet, M.; Nasti, R.; Schiraldi, F.; Paladino, F. Lung Ultrasound for Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Emergency Department. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2015, 10, 851–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delijani, K.; Price, M.C.; Little, B.P. Community and Hospital Acquired Pneumonia. Semin. Roentgenol. 2022, 57, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafraxo, S.; El Ansari, M.; Koutti, L. A New Hybrid Approach for Pneumonia Detection Using Chest X-Rays Based on ACNN-LSTM and Attention Mechanism. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 73055–73077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzhaynakbaev, N.; Kurmanbekkyzy, N.; Baimakhanova, A.; Mussatayeva, I. 2D-CNN Architecture for Accurate Classification of COVID-19 Related Pneumonia on X-Ray Images. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. IJACSA 2024, 15, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radočaj, P.; Radočaj, D.; Martinović, G. Pediatric Pneumonia Recognition Using an Improved DenseNet201 Model with Multi-Scale Convolutions and Mish Activation Function. Algorithms 2025, 18, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlGhamdi, A.S. Efficient Deep Learning Approach for the Classification of Pneumonia in Infants from Chest X-Ray Images. Trait. Signal 2024, 41, 1245–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radočaj, P.; Martinović, G. Interpretable Deep Learning for Pediatric Pneumonia Diagnosis Through Multi-Phase Feature Learning and Activation Patterns. Electronics 2025, 14, 1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, H.; Wan, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, J.; Shen, Y. Efficient Federated Learning for Pediatric Pneumonia on Chest X-Ray Classification. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephen, O.; Sain, M.; Maduh, U.J.; Jeong, D.-U. An Efficient Deep Learning Approach to Pneumonia Classification in Healthcare. J. Healthc. Eng. 2019, 2019, 4180949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hu, J.; Lv, F.; Tang, Z. A New Method for Long-Term Temperature Compensation of Structural Health Monitoring by Ultrasonic Guided Wave. Measurement 2025, 252, 117310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, A.P.; Tadeu Braga, H.F. Artificial Intelligence: Learning and Limitations. WSEAS Trans. Adv. Eng. Educ. 2020, 17, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Chen, L.; Nie, W.; Li, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhong, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, R. A Mixed-Scale Dynamic Attention Transformer for Pediatric Pneumonia Diagnosis. Displays 2025, 87, 102953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcos, G.; Yi, P.H.; Jeudy, J. Applying Artificial Intelligence to Pediatric Chest Imaging: Reliability of Leveraging Adult-Based Artificial Intelligence Models. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. JACR 2023, 20, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, C.-L.; Hsin, C.; Wang, H.-H.; Tang, C.Y. Optimization of GPU Memory Usage for Training Deep Neural Networks. In Pervasive Systems, Algorithms and Networks; Esposito, C., Hong, J., Choo, K.-K.R., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 289–293. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, G.; Zheng, L. A Transfer Learning Method with Deep Residual Network for Pediatric Pneumonia Diagnosis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2020, 187, 104964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luján-García, J.E.; Yáñez-Márquez, C.; Villuendas-Rey, Y.; Camacho-Nieto, O. A Transfer Learning Method for Pneumonia Classification and Visualization. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, J.L.; Zaiman, Z.; Vanschaik, J.; Luo, G.; Peng, L.; Price, B.; Mathias, G.; Mittal, V.; Sagane, A.; Tignanelli, C.; et al. Ability of Artificial Intelligence to Identify Self-Reported Race in Chest X-Ray Using Pixel Intensity Counts. J. Med. Imaging Bellingham Wash 2023, 10, 061106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Tahmasebi, A.; Dave, J.K.; Parekh, M.R.; Kumaran, M.; Wang, S.; Eisenbrey, J.R.; Donuru, A. Comparison of Gray-Scale Inversion to Improve Detection of Pulmonary Nodules on Chest X-Rays Between Radiologists and a Deep Convolutional Neural Network. Curr. Probl. Diagn. Radiol. 2023, 52, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, D.; Patel, C.; Talsania, H.; Patel, J.; Vaghela, R.; Pandya, S.; Modi, K.; Ghayvat, H. CNN Variants for Computer Vision: History, Architecture, Application, Challenges and Future Scope. Electronics 2021, 10, 2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M.I.; Lee, E.Y.; Bixby, S.; Diperna, S.; Hellinger, J.; Markowitz, R.; Servaes, S.; Monuteaux, M.C.; Shah, S.S. Variability in the Interpretation of Chest Radiographs for the Diagnosis of Pneumonia in Children. J. Hosp. Med. 2012, 7, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, J.; Kpeyiton, K.G.; Shi, Q. Grayscale Images Colorization with Convolutional Neural Networks. Soft Comput. 2020, 24, 4751–4758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotirov, S.; Orozova, D.; Angelov, B.; Sotirova, E.; Vylcheva, M. Transforming Pediatric Healthcare with Generative AI: A Hybrid CNN Approach for Pneumonia Detection. Electronics 2025, 14, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, J.A.; Asswin, C.R.; Kumar, K.S.D.; Dora, A.; Ravi, V.; Sowmya, V.; Gopalakrishnan, E.A.; Soman, K.P. Transfer Learning Approach for Pediatric Pneumonia Diagnosis Using Channel Attention Deep CNN Architectures. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, W.; Shi, F.; Guo, W. Image-Based Deep Learning in Diagnosing Mycoplasma Pneumonia on Pediatric Chest X-Rays. BMC Pediatr. 2024, 24, 720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, E.; Rehman, M.Z.U.; Ahmed, F.; Alfouzan, F.A.; Alzahrani, N.M.; Ahmad, J. Chest X-Ray Classification for the Detection of COVID-19 Using Deep Learning Techniques. Sensors 2022, 22, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Jiang, P.; Meng, J.; Jiang, X. Attention-Based DenseNet for Pneumonia Classification. IRBM 2022, 43, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napravnik, M.; Hržić, F.; Urschler, M.; Miletić, D.; Štajduhar, I. Lessons Learned from RadiologyNET Foundation Models for Transfer Learning in Medical Radiology. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 21622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, X.; Liu, Z.; Robson, P.M.; Marinelli, B.; Huang, M.; Doshi, A.; Jacobi, A.; Cao, C.; Link, K.E.; Yang, T.; et al. RadImageNet: An Open Radiologic Deep Learning Research Dataset for Effective Transfer Learning. Radiol. Artif. Intell. 2022, 4, e210315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woerner, S.; Baumgartner, C.F. Navigating Data Scarcity Using Foundation Models: A Benchmark of Few-Shot and Zero-Shot Learning Approaches in Medical Imaging. In Foundation Models for General Medical AI; Deng, Z., Shen, Y., Kim, H.J., Jeong, W.-K., Aviles-Rivero, A.I., He, J., Zhang, S., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Radočaj, P.; Radočaj, D.; Martinović, G. Image-Based Leaf Disease Recognition Using Transfer Deep Learning with a Novel Versatile Optimization Module. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2024, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermany, D.S.; Goldbaum, M.; Cai, W.; Valentim, C.C.S.; Liang, H.; Baxter, S.L.; McKeown, A.; Yang, G.; Wu, X.; Yan, F.; et al. Identifying Medical Diagnoses and Treatable Diseases by Image-Based Deep Learning. Cell 2018, 172, 1122–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Team, K. Keras Documentation: Keras 3 API Documentation. Available online: https://keras.io/api/ (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Module: Tf|TensorFlow v2.16.1. Available online: https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going Deeper with Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- McNeely-White, D.; Beveridge, J.R.; Draper, B.A. Inception and ResNet Features Are (Almost) Equivalent. Cogn. Syst. Res. 2020, 59, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misra, D. Mish: A Self Regularized Non-Monotonic Activation Function. Misra, Diganta. In Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference 2020, Online, 7–10 September 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Radočaj, P.; Radočaj, D.; Martinović, G. Optimizing Convolutional Neural Network Architectures with Optimal Activation Functions for Pediatric Pneumonia Diagnosis Using Chest X-Rays. Big Data Cogn. Comput. 2025, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batch Normalization|Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning—Volume 37. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3045118.3045167 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Diallo, R.; Edalo, C.; Awe, O.O. Machine Learning Evaluation of Imbalanced Health Data: A Comparative Analysis of Balanced Accuracy, MCC, and F1 Score. In Practical Statistical Learning and Data Science Methods: Case Studies from LISA 2020 Global Network, USA; Awe, O.O., Vance, E.A., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 283–312. ISBN 978-3-031-72215-8. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, G.; Zuva, T.; Sibanda, E.M. A Review of Evaluation Metrics in Machine Learning Algorithms. In Artificial Intelligence Application in Networks and Systems; Silhavy, R., Silhavy, P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, R.; Pandey, D.R.; Singh, A.K. Comparative Analysis of Radiological and Machine Learning-Based Interpretations for Differentiating COVID-19 and Pneumonia. Recent Adv. Electr. Electron. Eng. 2025, 18, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inception-v4, Inception-ResNet and the Impact of Residual Connections on Learning|Proceedings of the Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3298023.3298188 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Lin, B.; Su, H.; Li, D.; Feng, A.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, H.; Gong, X.; Liu, T. PlaneNet: An Efficient Local Feature Extraction Network. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segu, M.; Tonioni, A.; Tombari, F. Batch Normalization Embeddings for Deep Domain Generalization. Pattern Recognit. 2023, 135, 109115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Understanding Batch Normalization|Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/10.5555/3327757.3327868 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Merkow, J.; Soin, A.; Long, J.; Cohen, J.P.; Saligrama, S.; Bridge, C.; Yang, X.; Kaiser, S.; Borg, S.; Tarapov, I.; et al. CheXstray: A Real-Time Multi-Modal Monitoring Workflow for Medical Imaging AI. In Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention—MICCAI 2023; Greenspan, H., Madabhushi, A., Mousavi, P., Salcudean, S., Duncan, J., Syeda-Mahmood, T., Taylor, R., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 326–336. [Google Scholar]
- Characterizing Parameter Scaling with Quantization for Deployment of CNNs on Real-Time Systems|ACM Transactions on Embedded Computing Systems. Available online: https://dl.acm.org/doi/full/10.1145/3654799 (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Singh, M.P.; Singh, J.; Ravi, V.; Gupta, A.D.; Alahmadi, T.J.; Shivahare, B.D.; Diwakar, M.; Tayal, M.; Singh, P. A Healthcare System Employing Lightweight CNN for Disease Prediction with Artificial Intelligence. Open Public Health J. 2024, 17, e18749445302023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, N.; Awad, M.; Abu-Nabah, B.A. A Machine Learning Approach on Chest X-Rays for Pediatric Pneumonia Detection. Digit. Health 2023, 9, 20552076231180008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsharif, R.; Al-Issa, Y.; Alqudah, A.M.; Qasmieh, I.A.; Mustafa, W.A.; Alquran, H. PneumoniaNet: Automated Detection and Classification of Pediatric Pneumonia Using Chest X-Ray Images and CNN Approach. Electronics 2021, 10, 2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, N.H.; Tran, G.S. Apply a Cnn-Based Ensemble Model to Chest-x Ray Image-Based Pneumonia Classification. J. Adv. Inf. Technol. 2024, 15, 1205–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kareem, A.; Liu, H.; Velisavljevic, V. A Federated Learning Framework for Pneumonia Image Detection Using Distributed Data. Healthc. Anal. 2023, 4, 100204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patidar, M.; Pandey, G.; Koolagudi, S.G.; S, K.K.; Chandra, V. Enhancing Paediatric Healthcare: Deep Learning-Based Pneumonia Diagnosis from Children’s Chest X-Rays. In Proceedings of the 2024 Sixteenth International Conference on Contemporary Computing, Noida, India, 8–10 August 2024; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 128–135. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).