Enhancing Stance Detection with Target-Stance Graph and Logical Reasoning
Abstract
1. Introduction
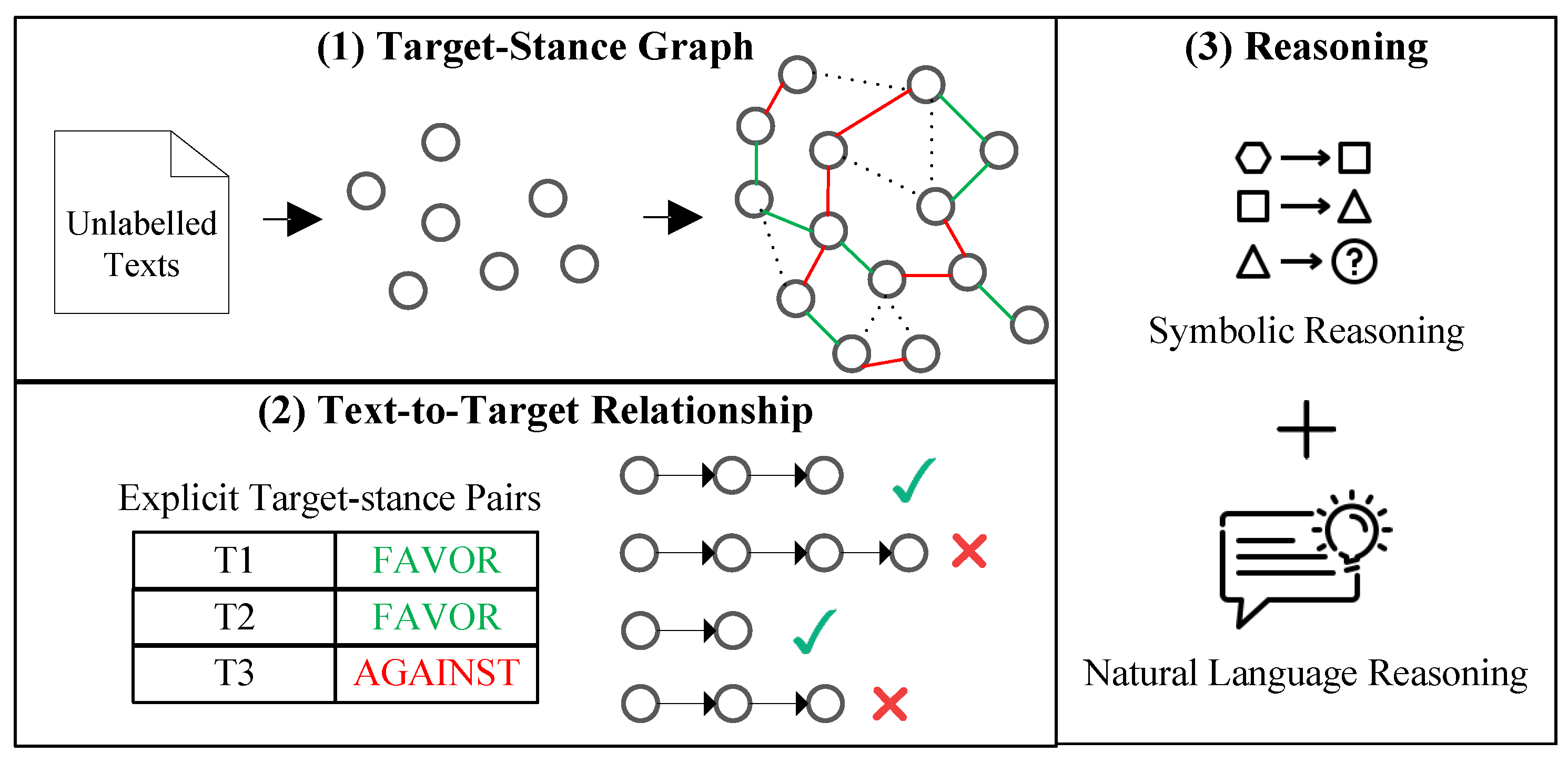
- We achieve the stance reasoning process by extracting open target-stance pairs and the stance between target pairs.
- We take advantage of the transitivity of stance to transform stance reasoning into a more credible and interpretable logical reasoning process.
- Extensive experimental results on three datasets demonstrate that our proposed framework significantly outperforms existing methods. Further analysis shows that our method has the potential to apply to the implicit target scenarios.
2. Related Works
2.1. External Knowledge
2.2. Stance Reasoning
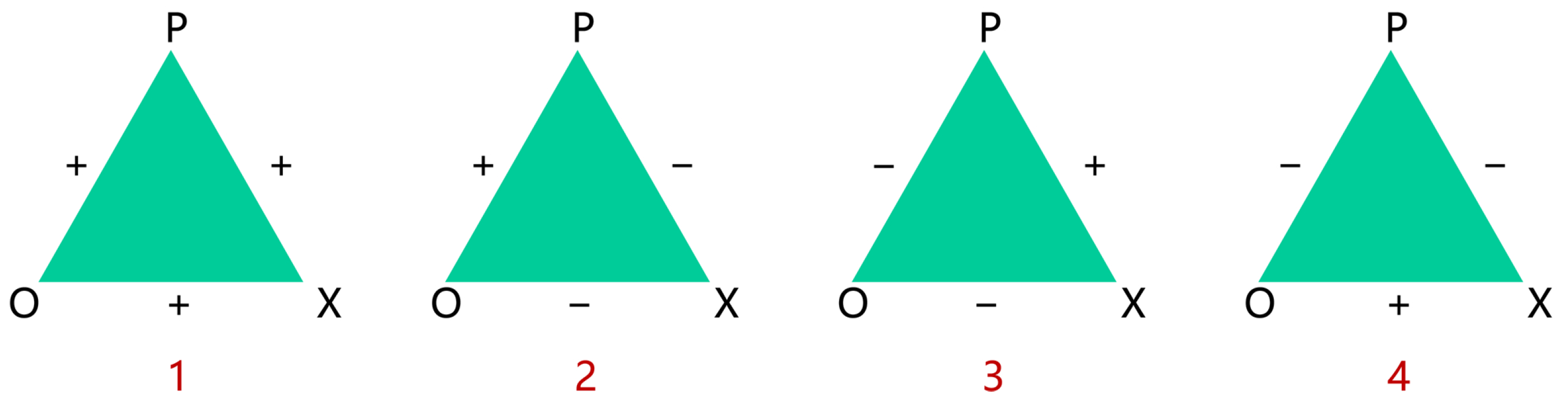
2.3. Stance Transitivity
3. Method
3.1. Task Description
3.2. Target-Stance Graph Construction
3.3. Text-to-Target Relationship Acquisition
Analyze the following tweet, generate the target for this tweet, and determine its stance towards the generated target. The target follows the following rules:
The target stance pair can be more than one. The output format should be: “<target1>: <stance1>, <target2>: <stance2>”. |
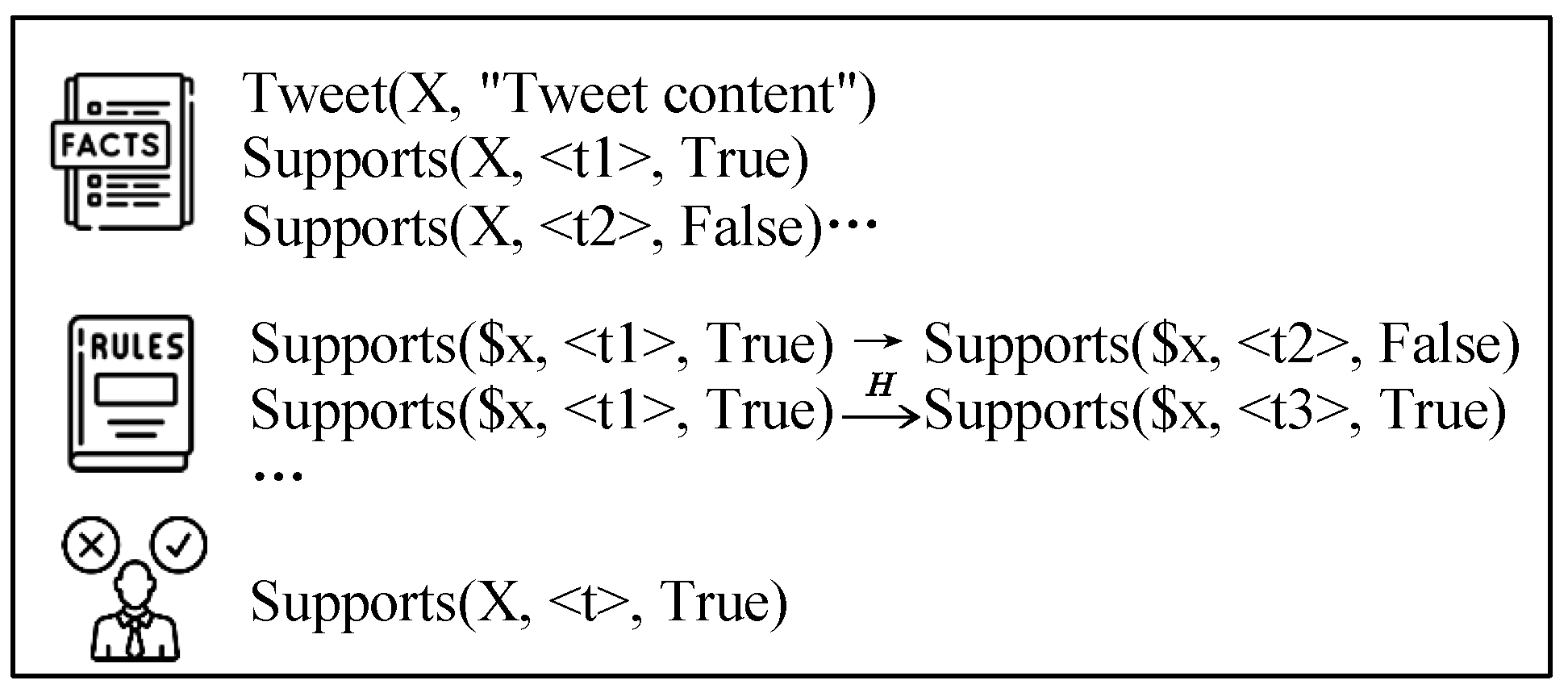
3.4. Logical Stance Reasoning
| Execution: Let’s execute the plan step by step, applying first-order logic inference rules and logical operators to determine the truth value of the statement. Step 1: Identify the Goal Step 2: Define the Relevant Rules and Predicates Step 3: Review the Given Facts Step 4: Analyze the Rules Step 5: Apply the Rules to the Given Facts Step 6: Determine if the Statement Can Be Inferred Step 7: Evaluate the Content of the Tweet Step 8: Conclude the result **Final answer: true|false|unknown** |
4. Experimental Setup
4.1. Experimental Dataset
4.2. Experimental Implementation
4.3. Comparison Models
5. Results
5.1. Main Results
5.2. Ablation Study
5.3. Impact of the Values of k
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. A Reasoning Example
Appendix B. Detailed Experimental Statistical Analysis
| Methods | Sem16 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | CC | FM | HC | LA | DT | |
| COLA-LLaMA3 | 33.1 ± 0.4 | 61.9 ± 4.4 | 63.9 ± 0.5 | 73.4 ± 1.3 | 61.8 ± 0.5 | 56.7 ± 0.2 |
| LSD-LLaMA3 | 74.3 ± 3.3 | 71.2 ± 0.8 | 67.8 ± 3.3 | 78.4 ± 1.2 | 64.2 ± 0.8 | 61.3 ± 0.8 |
| p-value | 0.0001 | 0.0229 | 0.1153 | 0.0011 | 0.0168 | 0.0014 |
| Methods | COVID-19 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask | Fauci | School | Home | |
| COLA-LLaMA3 | 71.0 ± 0.8 | 53.5 ± 0.8 | 38.1 ± 2.4 | 68.0 ± 1.2 |
| LSD-LLaMA3 | 77.6 ± 0.6 | 78.3 ± 2.5 | 69.3 ± 2.2 | 72.0 ± 1.8 |
| p-value | 0.0012 | 0.0004 | 0.0004 | 0.0066 |
References
- Mohammad, S.M.; Sobhani, P.; Kiritchenko, S. Stance and Sentiment in Tweets. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1605.01655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatt, G.; Sharma, A.; Sharma, S.; Nagpal, A.; Raman, B.; Mittal, A. Combining Neural, Statistical and External Features for Fake News Stance Identification. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2018—WWW ’18, Lyon, France, 23–27 April 2018; pp. 1353–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Ma, J.; Lin, H.; Gao, W. A Weakly Supervised Propagation Model for Rumor Verification and Stance Detection with Multiple Instance Learning. In Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval—SIGIR ’22, Madrid, Spain, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 1761–1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Zha, Z.J. ESCNet: Entity-enhanced and Stance Checking Network for Multi-modal Fact-Checking. In Proceedings of the 2024 ACM on Web Conference, Singapore, 13–17 May 2024; pp. 2429–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimminger, L.; Klinger, R. Hate Towards the Political Opponent: A Twitter Corpus Study of the 2020 US Elections on the Basis of Offensive Speech and Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 11th Workshop on Computational Approaches to Subjectivity, Sentiment and Social Media Analysis, Virtual, 19 April 2021; pp. 171–180. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, A.; Riedl, J.; Drews, W. Real-Time Stance Detection and Issue Analysis of the 2021 German Federal Election Campaign on Twitter. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Electronic Government, Linköping, Sweden, 6–8 September 2022; pp. 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kwak, H.; Gao, W.; An, J. Wearing Masks Implies Refuting Trump?: Towards Target-specific User Stance Prediction across Events in COVID-19 and US Election 2020. In Proceedings of the 15th ACM Web Science Conference 2023, Austin, TX, USA, 30 April–1 May 2023; pp. 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Li, S.Z.; Zhang, Y. Exploiting Sentiment and Common Sense for Zero-shot Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 12–17 October 2022; pp. 7112–7123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Q.; Liang, B.; Sun, J.; Du, J.; Zhou, L.; Xu, R. Enhancing Zero-Shot Stance Detection via Targeted Background Knowledge. In Proceedings of the 45th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval—SIGIR ’22, Madrid, Spain, 11–15 July 2022; pp. 2070–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Lin, Z.; Tan, Y.; Wang, W. Enhancing Zero-shot and Few-shot Stance Detection with Commonsense Knowledge Graph. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL-IJCNLP 2021; Zong, C., Xia, F., Li, W., Navigli, R., Eds.; Association for Computational Linguistics: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 3152–3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatto, J.; Sharif, O.; Preum, S.M. Chain-of-Thought Embeddings for Stance Detection on Social Media. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.19750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Ding, D.; Jing, L.; Huang, H. A Logically Consistent Chain-of-Thought Approach for Stance Detection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Qin, B. SSR: Utilizing Simplified Stance Reasoning Process for Robust Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Gyeongju, Republic of Korea, 12–17 October 2022; pp. 6846–6858. [Google Scholar]
- Akash, A.U.; Fahmy, A.; Trabelsi, A. Can Large Language Models Address Open-Target Stance Detection? In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2025; Association for Computational Linguistics: New York, NY, USA, 2025; pp. 971–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, S.; Li, P.; Liu, Y. DEEM: Dynamic Experienced Expert Modeling for Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 4530–4541. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Cui, Z.; Du, C.; Chiang, C.E. CL-ISR: A Contrastive Learning and Implicit Stance Reasoning Framework for Misleading Text Detection on Social Media. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2506.05107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yap, Y.K.; Chieu, H.L.; Chen, N. Guiding Computational Stance Detection with Expanded Stance Triangle Framework. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 3987–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taranukhin, M.; Shwartz, V.; Milios, E. Stance Reasoner: Zero-Shot Stance Detection on Social Media with Explicit Reasoning. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 15257–15272. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Wu, P.; Pan, L. CRAVE: A Conflicting Reasoning Approach for Explainable Claim Verification Using LLMs. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2504.14905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Liao, J.; Zhao, S.; Fu, X.; Peng, X.; Huang, H.; Zhang, B. Large Language Model Enhanced Logic Tensor Network for Stance Detection. Neural Netw. 2025, 183, 106956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Hovy, E.; Hauptmann, A. Transitive Consistency Constrained Learning for Entity-to-Entity Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; pp. 1467–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Fei, H.; Pan, L.; Liu, Q.; Lee, M.L.; Hsu, W. Faithful Logical Reasoning via Symbolic Chain-of-Thought. In Proceedings of the 62nd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Bangkok, Thailand, 11–16 August 2024; pp. 13326–13365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glandt, K.; Khanal, S.; Li, Y.; Caragea, D.; Caragea, C. Stance Detection in COVID-19 Tweets. In Proceedings of the 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 11th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing, Bangkok, Thailand, 1–6 August 2021; pp. 1596–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stab, C.; Miller, T.; Schiller, B.; Rai, P.; Gurevych, I. Cross-topic Argument Mining from Heterogeneous Sources. In Proceedings of the 2018 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Brussels, Belgium, 31 October–4 November 2018; pp. 3664–3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.Q.; Vu, T.; Tuan Nguyen, A. BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Virtual, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, P.; Gao, J.; Chen, W. DeBERTaV3: Improving DeBERTa using ELECTRA-Style Pre-Training with Gradient-Disentangled Embedding Sharing. In Proceedings of the The Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations, Kigali, Rwanda, 1–5 May 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, B.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, M.; Gui, L.; He, Y.; Xu, R. JointCL: A Joint Contrastive Learning Framework for Zero-Shot Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Dublin, Ireland, 22–27 May 2022; pp. 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.; Hauptmann, A. Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Stance Detection on Varied Topics via Conditional Generation. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; pp. 1491–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, S. SEGP: Stance-Emotion Joint Data Augmentation with Gradual Prompt-Tuning for Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Computational Science, London, UK, 21–23 June 2022; pp. 577–590. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, J. Generative Data Augmentation with Contrastive Learning for Zero-Shot Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 2022 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 7–11 December 2022; pp. 6985–6995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Zhao, X.; Xie, F.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Tian, L. Zero-Shot Stance Detection via Sentiment-Stance Contrastive Learning. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 34th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Macao, China, 31 October–2 November 2022; pp. 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; Caragea, C. TTS: A Target-based Teacher-Student Framework for Zero-Shot Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023, Austin, TX, USA, 30 April–4 May 2023; pp. 1500–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Dong, L.; Huang, Z.; Xu, G.; Huang, X.; Liu, B.; Jing, L.; Zhang, B. EDDA: An Encoder-Decoder Data Augmentation Framework for Zero-Shot Stance Detection. In Proceedings of the 2024 Joint International Conference on Computational Linguistics, Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC-COLING 2024), Torino, Italy, 20–25 May 2024; pp. 5484–5494. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Gao, C.; Jin, D.; Li, Y. Stance Detection with Collaborative Role-Infused LLM-Based Agents. Proc. Int. AAAI Conf. Web Soc. Media 2024, 18, 891–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fu, X.; Ding, D.; Huang, H.; Li, Y.; Jing, L. Investigating Chain-of-thought with ChatGPT for Stance Detection on Social Media. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Datasets | Target | Train | Test | Val | All | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Favor | Against | None | All | Favor | Against | None | All | Favor | Against | None | All | |||
| Sem16 | Atheism | 81 | 250 | 108 | 439 | 32 | 160 | 28 | 220 | 11 | 54 | 9 | 74 | 733 |
| Climate Change is a Real Concern | 181 | 12 | 143 | 336 | 123 | 11 | 35 | 169 | 31 | 3 | 25 | 59 | 564 | |
| Feminist Movement | 191 | 266 | 112 | 569 | 58 | 183 | 44 | 285 | 19 | 62 | 14 | 95 | 949 | |
| Hillary Clinton | 103 | 336 | 152 | 591 | 45 | 172 | 78 | 295 | 15 | 57 | 26 | 98 | 984 | |
| Legalization of Abortion | 108 | 291 | 162 | 561 | 46 | 189 | 45 | 280 | 13 | 64 | 15 | 92 | 933 | |
| Donald Trump | - | - | - | - | 148 | 299 | 260 | 707 | - | - | - | - | 707 | |
| COVID-19 | Wearing a Face Mask | 531 | 512 | 264 | 1307 | 81 | 78 | 41 | 200 | 81 | 78 | 41 | 200 | 1707 |
| Anthony S. Fauci, M.D | 388 | 480 | 596 | 1464 | 52 | 65 | 83 | 200 | 52 | 65 | 83 | 200 | 1864 | |
| Keeping Schools Closed | 409 | 166 | 215 | 790 | 103 | 42 | 55 | 200 | 103 | 42 | 55 | 200 | 1190 | |
| Stay at Home Orders | 136 | 284 | 552 | 972 | 27 | 58 | 115 | 200 | 27 | 58 | 115 | 200 | 1372 | |
| ArgMin | Abortion | 490 | 591 | 1746 | 2827 | 136 | 165 | 486 | 787 | 54 | 66 | 195 | 315 | 3929 |
| Cloning | 508 | 604 | 1075 | 2187 | 142 | 168 | 299 | 609 | 56 | 67 | 120 | 243 | 3039 | |
| Death Penalty | 316 | 789 | 1522 | 2627 | 103 | 232 | 396 | 731 | 38 | 90 | 165 | 293 | 3651 | |
| Gun Control | 566 | 479 | 1359 | 2404 | 158 | 133 | 378 | 669 | 63 | 53 | 152 | 268 | 3341 | |
| Marijuana Legalization | 422 | 450 | 908 | 1780 | 118 | 126 | 253 | 497 | 47 | 50 | 101 | 198 | 2475 | |
| Minimum Wage | 414 | 396 | 968 | 1778 | 116 | 111 | 270 | 497 | 46 | 44 | 108 | 198 | 2473 | |
| Nuclear Energy | 436 | 613 | 1524 | 2573 | 122 | 171 | 424 | 717 | 48 | 68 | 170 | 286 | 3576 | |
| Methods | Sem16 | COVID-19-Stance | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | CC | FM | HC | LA | DT | Avg | Mask | Fauci | School | Home | Avg | |
| BERT-FT | 55.2 | 37.3 | 41.9 | 49.6 | 44.8 | 47.0 | 46.0 | 52.1 | 48.2 | 44.8 | 56.0 | 50.3 |
| BERTweet-FT | 42.1 | 21.4 | 39.1 | 44.8 | 31.9 | 47.4 | 37.8 | 49.7 | 49.6 | 44.4 | 65.4 | 52.3 |
| Deberta-FT | 40.6 | 52.1 | 49.9 | 28.8 | 40.2 | 60.4 | 45.3 | 60.2 | 63.2 | 52.5 | 66.9 | 60.7 |
| JointCL | 54.5 ♮ | 39.7 ♮ | 53.8 ♮ | 54.8 ♮ | 49.5 ♮ | 50.5 ♮ | 50.5 ♮ | 49.7 | 51.8 | 40.8 | 57.9 | 50.1 |
| VTCG | 42.4 | 35.9 | 37.8 | 24.4 | 46.9 | 51.7 | 39.9 | 61.2 | 44.7 | 52.4 | 52.7 | 52.8 |
| SEGP | 67.4 | 44.1 | 59.7 | 37.7 | 56.7 | 44.7 | 51.7 | 54.4 | 51.4 | 45.9 | 68.8 | 55.1 |
| GDA-CL | 43.8 ♯ | 43.7 ♯ | 53.4 ♯ | 54.8 ♯ | 55.4 ♯ | 50.3 ♯ | 50.2 ♯ | 45.2 | 52.3 | 37.7 | 61.6 | 49.2 |
| SSCL | 55.4 ℸ | 53.4 ℸ | 53.5 ℸ | 59.7 ℸ | 55.6 ℸ | 50.4 ℸ | 54.7 | 59.5 ℸ | 51.8 ℸ | 53.7 ℸ | 54.5 ℸ | 54.9 |
| TTS | 34.9 | 22.2 | 33.9 | 44.1 | 48.9 | 37.6 | 36.9 | 56.6 | 52.8 | 52.1 | 69.1 | 57.7 |
| DAQ-GPT3.5 | 9.1 † | 31.1 † | 44.7 † | 68.7 † | 51.5 † | 62.5 † | 41.0 | 56.4 | 46.4 | 25.2 | 58.3 | 46.6 |
| DAQ-LLaMA3 | 55.2 | 47.4 | 59.0 | 65.4 | 63.8 | 52.4 | 57.2 | 65.2 | 61.2 | 23.7 | 46.2 | 49.1 |
| EDDA | - | - | 69.2 ‡ | 80.1 ‡ | 62.4 ‡ | 69.5 ‡ | - | 52.9 | 43.6 | 34.7 | 57.2 | 47.1 |
| COLA-GPT3.5 | 70.8 † | 65.5 † | 63.4 † | 81.7 † | 71.0 † | 68.5 † | 70.2 | 76.0 | 70.0 | 49.4 | 77.9 | 72.6 |
| COLA-LLaMA3 | 33.1 * | 61.9 * | 63.9 | 73.4 * | 61.8 * | 56.7 * | 58.5 | 71.0 * | 53.5 * | 38.1 * | 68.0 * | 57.6 |
| LSD | 74.3 * | 71.2 * | 67.8 | 78.4 * | 64.2 * | 61.3 * | 69.5 | 77.6 * | 78.3 * | 69.3 * | 72.0 * | 74.3 |
| Methods | ArgMin | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AB | CL | DP | GC | ML | MW | NE | SU | Avg | |
| BERT-FT | 53.0 | 66.2 | 55.1 | 52.1 | 61.9 | 61.8 | 62.8 | 65.3 | 59.8 |
| VTCG | 53.6 | 69.0 | 57.8 | 50.4 | 65.2 | 72.1 | 68.1 | 71.9 | 63.5 |
| SEGP | 53.0 | 70.2 | 52.9 | 50.7 | 60.4 | 61.5 | 63.6 | 64.7 | 59.6 |
| JointCL | 34.9 | 67.0 | 53.4 | 52.2 | 57.7 | 65.6 | 61.1 | 67.1 | 57.4 |
| GDA-CL | 32.4 | 64.3 | 52.7 | 49.9 | 57.8 | 54.9 | 56.6 | 50.1 | 52.3 |
| TTS | 32.5 | 66.2 | 57.0 | 51.2 | 57.2 | 34.8 | 59.5 | 60.1 | 52.3 |
| DAQ-LLaMA3 | 62.2 | 74.6 | 57.3 | 49.1 | 72.7 | 63.4 | 66.4 | 71.9 | 64.7 |
| COLA-LLaMA3 | 63.9 | 78.2 | 69.3 | 44.4 | 75.8 | 68.9 | 70.0 | 73.4 | 68.0 |
| LSD | 67.9 | 76.8 | 68.6 | 68.6 | 78.4 | 72.7 | 70.6 | 75.4 | 72.4 |
| Methods | Sem16 | COVID-19 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | CC | FM | HC | LA | DT | Mask | Fauci | School | Home | |
| LSD | 74.3 | 71.2 | 67.8 | 78.4 | 64.2 | 61.3 | 77.6 | 78.3 | 69.3 | 72.0 |
| 70.0 | 51.2 | 58.7 | 74.2 | 58.8 | 54.8 | 67.7 | 54.6 | 56.8 | 60.4 | |
| 65.3 | 48.2 | 68.6 | 78.6 | 68.8 | 64.5 | 59.8 | 70.8 | 19.8 | 49.1 | |
| Methods | Sem16 | COVID-19 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | CC | FM | HC | LA | DT | Mask | Fauci | School | Home | |
| k = 0 | 55.2 | 47.4 | 59.0 | 65.4 | 63.8 | 52.4 | 65.2 | 61.2 | 23.7 | 46.2 |
| k = 1 | 58.7 | 47.9 | 68.2 | 79.8 | 70.0 | 62.4 | 57.7 | 52.1 | 26.0 | 53.4 |
| k = 2 | 61.1 | 50.7 | 68.5 | 80.1 | 71.5 | 62.9 | 55.6 | 52.7 | 22.7 | 51.3 |
| k = 3 | 62.8 | 50.8 | 68.5 | 79.3 | 69.8 | 62.1 | 57.8 | 52.3 | 23.8 | 51.6 |
| Methods | Sem16 | COVID-19 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AT | CC | FM | HC | LA | DT | Mask | Fauci | School | Home | |
| k = 1 | 70.0 | 51.2 | 58.7 | 74.2 | 58.8 | 54.8 | 67.9 | 54.6 | 56.8 | 60.4 |
| k = 2 | 68.7 | 53.2 | 57.8 | 71.7 | 59.8 | 55.5 | 65.9 | 61.7 | 54.7 | 59.8 |
| k = 3 | 74.3 | 71.2 | 67.8 | 78.4 | 64.2 | 61.3 | 77.6 | 78.3 | 69.3 | 72.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, X.; Hu, H. Enhancing Stance Detection with Target-Stance Graph and Logical Reasoning. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11784. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111784
Cai Y, Ma X, Liu B, Chen X, Hu H. Enhancing Stance Detection with Target-Stance Graph and Logical Reasoning. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11784. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111784
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Yiqing, Xingkong Ma, Bo Liu, Xinyi Chen, and Huaping Hu. 2025. "Enhancing Stance Detection with Target-Stance Graph and Logical Reasoning" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11784. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111784
APA StyleCai, Y., Ma, X., Liu, B., Chen, X., & Hu, H. (2025). Enhancing Stance Detection with Target-Stance Graph and Logical Reasoning. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11784. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111784





