Abstract
This study addresses the challenges of uneven recovery in strongly water-sensitive reservoirs through the development of a time-dependent two-phase flow model capturing the dynamic evolution of permeability and relative permeability. Based on laboratory core flooding experiments and integrated into a black-oil simulator, the model accurately reproduces reservoir behavior under long-term water flooding, significantly improving the history matching of water cut and pressure—especially in high water-cut stages. Results demonstrate that water sensitivity causes staged damage: initial reduction in heterogeneity is followed by intensified interlayer conflict and earlier water breakthrough. The relative permeability curve shifts rightward, accompanied by reduced residual oil saturation. These findings overcome the limitations of conventional static-property models and provide a reliable basis for optimizing enhanced oil recovery strategies. Further validation with field data will enhance the model’s applicability under diverse geological conditions.
1. Introduction
Water sensitivity, a common challenge in oilfield development, threatens reservoir development efficiency worldwide. Industry statistics show that over 60% of sandstone reservoirs and about 30% of carbonate reservoirs exhibit varying degrees of water sensitivity. The major risk arises when reservoirs are exposed to low-salinity fluids (such as injection water), which can trigger a sharp decline in permeability—commonly referred to as water-sensitive damage [1,2]. This problem is particularly severe in low-permeability and ultra-low-permeability reservoirs, often manifested as poor injectivity (with continuously increasing injection pressure) and rapid production decline [3]. In extreme cases, the injectivity index of injection wells may drop by more than 80% within a month. The dynamic evolution of water-sensitive damage generally follows a three-stage process: an initial latent period (where reservoir energy masks the damage), a rapid damage period (characterized by steep production decline and permeability loss of more than 50% within hours), and a final stabilization period [4]. Such damage not only reduces oil production and increases development costs but can also severely impair the overall economic value of the reservoir.
Waterflooding, a conventional recovery method, often induces clay mineral migration and swelling due to incompatibility issues, thereby causing water-sensitive damage in reservoirs. This not only alters reservoir permeability but also drives key flow characteristics—especially oil–water relative permeability (relperm) curves—to vary significantly over time [5,6]. Relperm curves comprehensively reflect changes in reservoir pore structure and flow capacity, and thus serve as a core indicator for evaluating development potential and performance [1,7]. Conventional simulations typically regard relative permeability as a static function dependent solely on saturation, neglecting its dynamic evolution with reservoir development, such as pore–throat structure alteration and cumulative injection volume (expressed as pore volumes injected, PV) [8,9]. To address this limitation, the IMPES (Implicit Pressure Explicit Saturation) method is often employed, requiring multiple sets of relperm curves derived from experiments or simulations at different water-cut stages. However, this approach presents challenges in terms of both operational complexity and predictive accuracy. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a numerical simulation model capable of capturing the time-dependent evolution of reservoir parameters under water-sensitive damage [10]. Such a model enables more accurate characterization of flow field distribution, enhances the reliability of production performance forecasts, and provides a solid scientific basis for designing effective development adjustment strategies.
The simulation approach incorporating time-dependent reservoir properties is a key technique for overcoming the above bottleneck [11]. The core procedure is as follows. After each iteration step (n ≥ 1), the cumulative water throughput of each grid block is calculated based on its instantaneous flow rate. The permeability field is then updated using the quantitative relationship between permeability variation factor and cumulative water throughput. Subsequently, the oil–water relative permeability curves are modified by adjusting their end-point values (e.g., end-point relative permeability) according to the updated permeability. Finally, the next time step (n + 1) is initiated using the revised reservoir property parameters [12,13]. This time-coupled dynamic updating mechanism provides a solid foundation for effectively simulating the complex development dynamics of water-sensitive reservoirs.
Wang et al. [14] quantitatively characterized the evolution patterns of permeability, porosity, and relative permeability with increasing injection volume during the ultra-high water cut stage through systematic displacement experiments, and further developed an end-point relative permeability model using the Alternating Conditional Expectation (ACE) transformation. The results indicate that, as injection volume accumulates, the relative permeability curves shift systematically to the right, rock wettability evolves toward a more water-wet state, and residual oil saturation decreases significantly. Meanwhile, permeability in high-permeability streaks continues to increase, intensifying interlayer heterogeneity and aggravating water channeling, which deteriorates development performance. This finding overcomes the limitations of the traditional “static permeability” assumption and provides an experimental foundation for introducing time-variant algorithms.
Building on this, Cui et al. [15], focusing on the pronounced non-Darcy flow behavior in heavy oil reservoirs of the Bohai Bay area, coupled the time-variant permeability effect with the threshold pressure gradient (TPG) to establish a co-evolution model. The results demonstrate that the continuous increase in permeability with injection history markedly reduces the TPG, further amplifying the flow dominance of main channels. When both effects are considered, the predicted ultimate recovery factor is about 20% lower than that of the conventional black-oil model, highlighting that neglecting time-variant properties would severely overestimate recovery performance. This study first introduced the concept of a “waterflood-dependent threshold pressure gradient,” providing a new theoretical basis for refined numerical simulation of heavy oil reservoirs.
From an engineering perspective, Xun et al. [16] addressed the stability and efficiency of numerical algorithms incorporating time-variant permeability. Based on well-test data from three production wells, they fitted an exponential empirical relationship between permeability and scouring time, discretized the oil–water two-phase model using the Mimetic Finite Difference (MFD) scheme, and solved it efficiently with the IMPES method. Simulation results show that, after incorporating time-variant permeability, the average water saturation of the reservoir decreased from 0.718 to 0.639, the sweep efficiency of waterflooding improved by 12.3%, and the recovery factor increased from 22.5% to 26.3%, representing a 16.9% improvement. This comparison clearly demonstrates that the time-variant algorithm not only improves the prediction accuracy of remaining oil distribution, but also provides a quantitative basis for rational infill well placement and optimization of injection–production strategies in the field.
This study breaks through the limitations of existing time-variant permeability models primarily focused on high-permeability unconsolidated sandstone reservoirs, and for the first time concentrates on water-sensitive reservoirs, revealing their fundamentally different physical property evolution mechanisms. Unlike the phenomenon in sandstones where particle migration leads to increasing permeability and continuous expansion of high-permeability channels, water-sensitive reservoirs are controlled by the hydration, expansion, and migration of clay minerals, manifesting as a continuous decrease in permeability and a staged evolution characteristic of interlayer heterogeneity “initially alleviated and subsequently intensified”. Based on laboratory water sensitivity experimental data, this study innovatively established a dual time-variant characterization model for permeability and relative permeability, which was successfully coupled into a numerical simulator, achieving high-precision characterization of dynamic parameters during long-term water injection. This model not only significantly enhances prediction accuracy by quantifying the variation patterns of physical properties under different injection pore volumes, but also dynamically simulates the spatiotemporal evolution of damaged zones, providing a scientific basis for guiding water injection quality monitoring, optimizing the timing of clay stabilizer application, and managing layer series. Compared to traditional models, the dual time-variant coupling method proposed in this study more accurately reflects the physicochemical nature and dynamic flow behavior of water-sensitive reservoirs, offering an integrated solution from mechanistic research to production application for the efficient development of such complex reservoirs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Relative Permeability Experimental Measurement
To evaluate reservoir water sensitivity, core samples from wells Bei-31 and Bei-42 were selected for experimental testing [17]. A total of 18 samples, comprising four lithologies conglomerate, coarse sandstone, medium sandstone, and fine sandstone were used, with gas permeability ranging from 0.01 to 65 mD.
The experiments were conducted at room temperature. Initially, the cores were saturated with formation water (salinity: 12,460 mg/L) to determine the initial permeability. Subsequently, injection water (low-salinity water, salinity: 6914 mg/L) was introduced at a flow rate controlled between 0.1 and 0.5 mL/min, adjusted based on the core permeability. The standard dimensions of the cores were 2.5 cm in diameter and 5–7 cm in length. To ensure data reliability, all displacement tests under each condition were performed in triplicate.
The core flooding experimental procedure (Figure 1) is as follows:
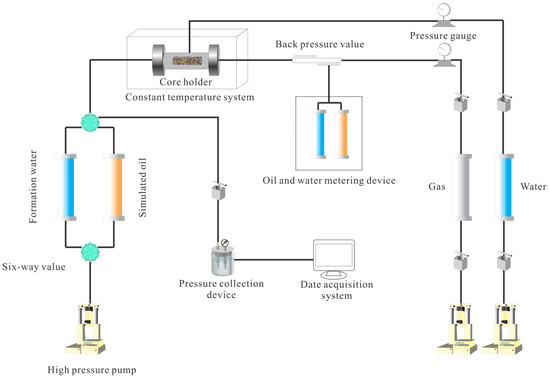
Figure 1.
Core Flooding Analysis Flowchart.
Step 1: The core is dried and weighed. Gas permeability is then measured, followed by vacuum saturation with formation water.
Step 2: After weighing, the fully saturated core is placed into the core holder, maintaining a confining pressure 2.0 MPa higher than the inlet pressure throughout the test.
Step 3: The initial liquid permeability of the core is measured using formation water. Subsequently, low-salinity water (injection water) or distilled water is injected at a flow rate consistent with the initial rate. After the displacement is completed, the confining pressure and temperature are kept constant to allow sufficient interaction between the fluid and rock minerals for at least 12 h. The flow rate is then restored to the initial value to measure permeability, and the wet weight is used to determine porosity.
Step 4: Pressure, flow rate, time, and temperature are monitored. Once steady-state flow is achieved, the test data are recorded.
2.2. Establishment of Relative Permeability Characterization Model
Considering the significant differences in the time-variant seepage behavior between water-sensitive reservoirs and loose sandstone reservoirs during waterflood development, a time-variant seepage model for water-sensitive reservoirs was constructed. This model incorporates the time-dependent characteristics of both permeability and relative permeability. The process of establishing the mathematical model is outlined as follows:
The governing equations are:
The parameters are defined as follows: The saturations of oil and water phases are and , respectively. The absolute permeability tensor is . The relative permeabilities of oil and water phases are and (dimensionless), respectively. The viscosities of oil and water phases are and , respectively. The pressures of oil and water phases are and (MPa), respectively. The densities of oil and water phases are and (kg/m3), respectively. The flow sources of oil and water phases are and (m3/s), respectively. The velocities of oil and water phases are and , respectively. Additionally, there are the gravitational acceleration g (m/s2), vertical depth z (m), and porosity (%).
Combining Equations (2) and (3) for velocity v:
Based on the new insights into the time-variant seepage patterns presented in Section 2.2, the time-variant permeability and time-variant relative permeability were incorporated into the governing equations (Figure 2). This integration led to the development of a mathematical model and numerical simulation method that can account for the dynamic changes in both permeability and relative permeability over time. The model is capable of accurately depicting the dynamic variations in reservoir properties and fluid seepage capacity during the water injection development process in water-sensitive oil reservoirs. It provides a more precise characterization of the production dynamics of water-sensitive reservoirs during long-term water injection development. Moreover, it offers a theoretical foundation for the dynamic adjustment of development plans and the optimization of technical policies in subsequent stages.
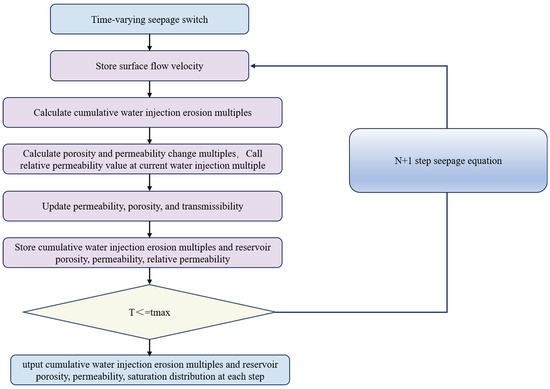
Figure 2.
Algorithm Flowchart.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Time-Variant Behavior of Permeability and Relative Permeability
Water sensitivity experiments were conducted on conglomerate, coarse sandstone, medium sandstone, and fine sandstone from the North 31 area to investigate the changes in porosity and permeability under different injected pore volumes (PV). Overall, permeability decreased significantly with increasing injected PV. When PV ≤ 100, permeability experienced a rapid reduction; beyond 100 PV, the decline tended to stabilize. The conglomerate, with higher reservoir quality, exhibited the highest permeability retention under the same injected PV, while medium sandstone, containing more clay, showed the lowest retention. Coarse and fine sandstones displayed similar retention behaviors (Figure 3A).
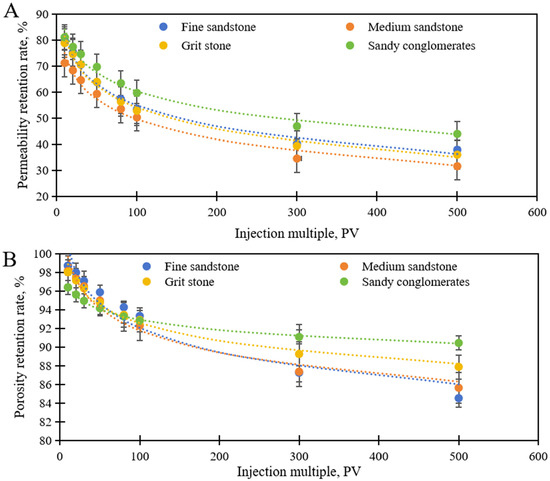
Figure 3.
(A) Permeability Variation Curves under Different Injected PV Multiples; (B) Porosity Variation Curves under Different Injected PV Multiples.
Compared to permeability, the variations in porosity were smaller but followed a similar trend. It is noteworthy that when the injected PV exceeded 100, the porosity of all samples tended to stabilize, indicating the existence of a critical threshold for pore structure damage (Figure 3B).
These results suggest that rock particle composition and pore structure are key factors controlling the degree of water sensitivity. The time-variant porosity and permeability curves for each lithology were averaged, and time-variant models were subsequently established for fine sandstone, medium sandstone, coarse sandstone, and conglomerate, respectively (Table 1).

Table 1.
Time-Variant Porosity and Permeability Models of Fine, Medium, and Coarse Sandstones and Conglomerate.
3.2. Relative Permeability Behavior Under High Waterflooding Multiples
High waterflooding multiple experiments were conducted, and the relative permeability of conglomerate, medium sandstone, and fine sandstone at high waterflooding multiples was obtained using the JBN algorithm. The results indicate that when the injection multiple is increased to 500, the oil displacement efficiency of conglomerate, medium sandstone, and fine sandstone increases by 12.5%, 8.45%, and 2.33%, respectively. At higher injection multiples, the water-phase relative permeability at the same water saturation decreases (Figure 4). As the injection multiple increases, the two-phase co-flow region expands, and the residual oil saturation decreases. However, the water-phase relative permeability at residual oil saturation does not follow a consistent pattern. This reflects a “contradiction” in the seepage process: higher injection multiples lead to greater water sensitivity damage and reduced residual oil, but simultaneously lower water-phase flow resistance.
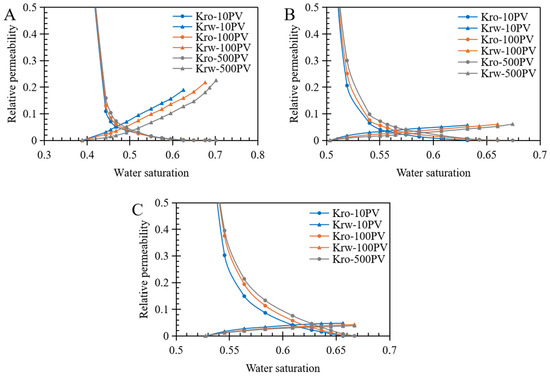
Figure 4.
Relative permeability variation in different lithologies under high waterflooding multiples. (A): Conglomerate; (B): medium sandstone; (C): fine sandstone.
In the conglomerate system (Figure 4A), with increasing waterflooding multiples, the oil and water phase flow capacities exhibit a trend of coordinated improvement. The oil-phase relative permeability curve shifts significantly to the right, and the water saturation corresponding to the equal-permeability point increases markedly, while the water-phase relative permeability shows a steady increase. This indicates that during long-term waterflooding, the conglomerate reservoir primarily undergoes optimization and modification of pore structure. The coarse-grained skeleton provides good stability, allowing the reservoir to withstand strong fluid scouring. Consequently, the two-phase flow interval broadens, residual oil saturation decreases, and the reservoir demonstrates good development potential.
The medium sandstone samples (Figure 4B) display moderate water sensitivity. As the injection multiple increases, the oil-phase relative permeability gradually decreases, whereas the water-phase relative permeability exhibits a more complex behavior: it increases at low water saturations but decreases at high water saturations. The leftward shift in the equal-permeability point indicates a change in rock wettability, the two-phase co-flow region narrows, and the micro-pore structure undergoes irreversible adjustments. These responses suggest that hydration expansion and particle migration of fine-grained components in medium sandstone begin to affect pore–throat connectivity.
The fine sandstone system (Figure 4C) exhibits the strongest waterflooding sensitivity. The oil-phase relative permeability decreases sharply, maintaining only a small fraction of the initial value under high waterflooding multiples. Conversely, the water-phase relative permeability increases significantly, and the equal-permeability point shifts markedly to the left, indicating that the rock surface wettability becomes strongly water-wet. This trend reflects the hydration expansion of abundant clay minerals in fine sandstone, leading to a drastic reduction in effective flow channels and fundamental changes in micro-pore structure, severely limiting oil-phase mobility.
In summary, a comparison of the three lithologies reveals a clear trend of increasing water sensitivity from conglomerate to fine sandstone. This variation primarily results from differences in mineral composition and pore structure: conglomerate is dominated by coarse grains and possesses a stable framework; medium sandstone contains more fine-grained components, displaying moderate sensitivity; fine sandstone is rich in clay minerals, exhibiting strong water–rock interactions.
3.3. Analysis of Changes in Permeability and Relative Permeability Under High Waterflooding Multiples
To further elucidate the mechanisms behind the changes in permeability and relative permeability of the North 31 Wutonggou Formation oil reservoir under high waterflooding multiples, CT scans were performed on core samples in their initial state and after 100 PVs of waterflooding. The scans provided quantitative pore–throat structure parameters before and after water sensitivity damage (Figure 5).
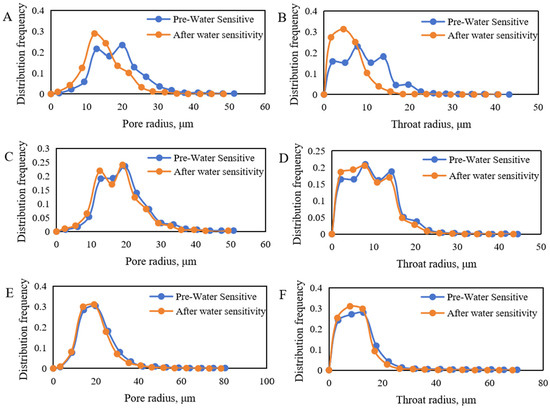
Figure 5.
Pore–throat structure changes before and after water sensitivity. (A): Pore size distribution frequency curves of fine sandstone before and after water sensitivity; (B): throat radius distribution frequency curves of fine sandstone before and after water sensitivity; (C): pore size distribution frequency curves of medium sandstone before and after water sensitivity; (D): throat radius distribution frequency curves of medium sandstone before and after water sensitivity; (E): pore size distribution frequency curves of conglomerate before and after water sensitivity; (F): throat radius distribution frequency curves of conglomerate before and after water sensitivity.
The results indicate that after water sensitivity damage, the average pore radius decreased by 11%, and the throat radius decreased by 17.3%. Comparing the changes among fine sandstone, medium sandstone, and conglomerate, it was observed that reservoirs with poorer physical properties experienced more severe water sensitivity damage, whereas better-quality reservoirs showed less damage. This finding suggests that water sensitivity further exacerbates reservoir heterogeneity, increasing disparities in permeability.
The deterioration of the pore–throat structure—manifested as throat blockage and reduction in effective seepage channels—is a direct consequence of water sensitivity damage, leading to decreased permeability [18]. Pore–throat structure also strongly influences two-phase flow capacity. Typically, water sensitivity damage reduces the two-phase co-injection area, and relative permeability curves reflect decreases in both oil and water phase permeability [19].
In the present study, this pattern was observed. However, under very high waterflooding multiples (up to 500 PVs), despite the presence of water sensitivity damage, the two-phase co-injection area still exhibited an increasing trend, and residual oil saturation tended to decrease. Furthermore, the study revealed that water sensitivity damage occurs in two stages: a rapid damage period and a slow damage period, with approximately 100 PVs as the critical threshold. Consequently, a “contradiction” arises in the seepage process: high injection multiples induce significant water sensitivity damage while simultaneously reducing residual oil.
3.4. Mineral Response of Water-Sensitive Core—Characteristics of Clay Mineral Reactions
The occurrence of water sensitivity damage is closely related to the microscopic response behavior of clay minerals. The direct mechanisms include the hydration and expansion of montmorillonite and illite–montmorillonite mixed-layer minerals, as well as the migration and pore–throat blockage caused by movable minerals such as illite and kaolinite. Experimental results indicate that after water sensitivity damage, the average pore radius decreases by 11%, and the throat radius significantly reduces by 17.3%, reflecting a notable deterioration in physical properties.
During the water sensitivity process, montmorillonite and illite–montmorillonite mixed-layer minerals exhibit significant hydration expansion (Figure 6A,B). When the core comes into contact with distilled water or low-salinity water, these layered silicate minerals undergo an irreversible increase in interlayer spacing. Specifically, as observed in scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images, montmorillonite appears as filmy, flocculent, or sheet-like fillings in intergranular spaces before water sensitivity damage. After water sensitivity occurs, these minerals expand in volume, severely blocking pores and throat channels, leading to a sharp decline in permeability.
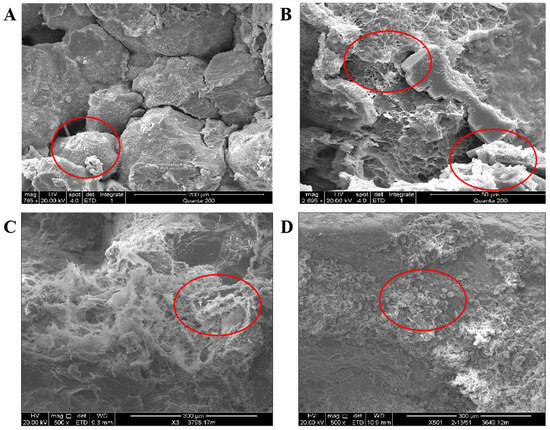

Figure 6.
(A): Scanning Electron Micrograph of Core Sample Before Water Sensitivity Damage; (B): Scanning Electron Micrograph of Core Sample After Water Sensitivity Damage—Illustrating Hydration Expansion of Illite–Montmorillonite Mixed-Layer and Honeycomb-Structured Montmorillonite; (C): Scanning Electron Micrograph of Core Sample After Water Sensitivity Damage—Depicting Illite Filling Intergranular Pores; (D): Scanning Electron Micrograph of Core Sample After Water Sensitivity Damage—Showing Kaolinite Filling Intergranular Pores.
In contrast, illite and kaolinite contribute to water sensitivity damage primarily through migration and blockage mechanisms (Figure 6C,D). Kaolinite typically exists as loose granular particles, while illite appears as fine flakes or fibrous forms distributed within intergranular pores. Their weak crystalline structures make them easily detached by hydraulic flow. Once mobilized, these mineral particles tend to bridge and become physically trapped at throat constrictions, further restricting fluid flow capacity.
In summary, the mineral response mechanisms in water-sensitive cores involve multiple minerals and coexisting processes. Montmorillonite and illite–montmorillonite mixed-layer minerals reduce effective flow space through volumetric expansion, whereas illite and kaolinite cause physical blockage of pores and throats via particle migration and redeposition. These combined effects significantly alter the pore structure characteristics, ultimately leading to a sharp reduction in core permeability and adversely impacting reservoir development efficiency. This understanding provides critical mineralogical and microscopic mechanistic insights for designing effective strategies to mitigate water sensitivity damage and optimize development approaches.
3.5. Application and Computational Testing
The North Santai oilfield is characterized by medium porosity, low permeability, strong heterogeneity, and pronounced water sensitivity. The reservoir exhibits an average porosity of 19.9% and a permeability of 25.9 mD (ranging from 11.65 to 113.35 mD). The average surface crude oil viscosity at 50 °C is 41.0 mPa·s. Clay minerals account for 10% of the formation, primarily consisting of montmorillonite and illite–smectite interlayers. With a water sensitivity index of 0.898, the reservoir displays strong water-sensitive behavior. Currently, the oilfield is in a high water-cut development stage, facing challenges such as low planar and vertical sweep efficiency, limited profile modification options, and strong reservoir heterogeneity. Focusing on this block, time-variant numerical simulation studies were conducted to provide accurate guidance for optimizing enhanced oil recovery strategies.
3.5.1. Construction of Time-Variant Numerical Model
Based on the latest high-resolution three-dimensional geological model, a compositional–time-variant coupled numerical simulation model was established for the North 31 area. The model consists of 418 × 149 × 231 grid cells, with a planar grid spacing of 10 m and a vertical spacing of 0.5 m, totaling 14,387,142 cells. It incorporates 22 injection wells and 65 production wells, with data encompassing perforation, fracturing, oil, water, and gas production, water injection, and production timelines. Using PVTi regression, a seven-component EOS fluid model was constructed and integrated with porosity, permeability, and relative permeability curves that continuously evolve with cumulative pore volumes (PV), achieving a dynamic, time-variant representation of reservoir properties and two-phase flow behavior. In the numerical simulation studio, the grid was roughened, with a grid size of 209 × 74 × 115, totaling 1,778,590 grids (Figure 7).
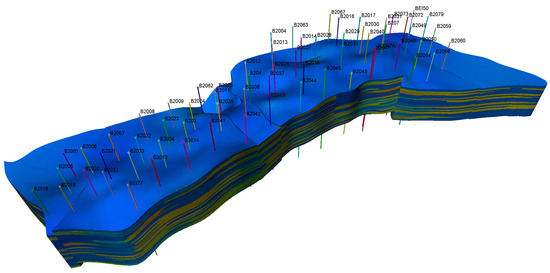
Figure 7.
Numerical Model Grid Distribution.
3.5.2. History Matching
In this study, a compositional–time-variant coupled numerical simulation platform was established (Figure 8) to perform history matching for the entire North 31 area. This included matching the overall water cut and reservoir pressure, as well as single-well water cut for 58 wells and single-well pressure for 60 wells. The overall matching accuracy reached 88.1%, with water cut and pressure-matching accuracies of 86.5% and 89.5%, respectively. The time-variant model outperformed the non-time-variant model in history matching, demonstrating improved agreement for both daily oil and water production (Table 2, Figure 9). These results indicate that the time-variant model effectively captures the dynamic reservoir behavior during long-term water injection, particularly providing high-fidelity simulation of water cut and pressure during the high water cut stage.
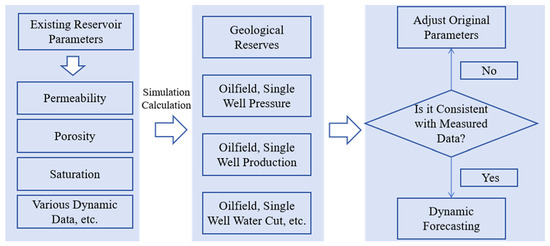
Figure 8.
History-Matching Workflow.

Table 2.
Evaluation of RMSE and R2 for Static and Time-Variant Models.
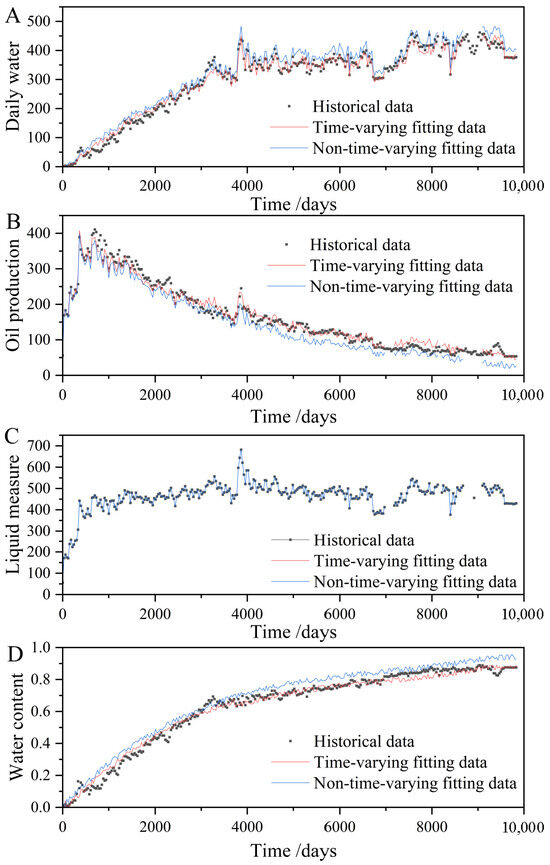
Figure 9.
History-Matching Results: (A): Daily Water Production; (B): Daily Oil Production; (C): Total Liquid Production; (D): Water Cut.
Sensitivity analysis further highlighted the significant influence of parameters such as permeability, relative permeability curves, aquifer size, and conductivity on matching results. Adjustments of these parameters were critical in enhancing the matching accuracy. Analysis of the results across different regions allowed for clear identification of development characteristics and potential issues, providing a solid basis for zonal management strategies.
Although the time-variant model demonstrates excellent matching performance, its equations are derived from statistical regression based on the North 31 area. Therefore, extrapolation to the entire oilfield requires further verification. Additionally, long-term chemical agent–rock interactions affecting permeability have not yet been incorporated. Future work will focus on calibration using additional field data and experimental studies. Overall, the history-matching results validate the reliability of the time-variant model, providing a robust theoretical foundation for evaluating enhanced oil recovery (EOR) strategies. Subsequent studies will further optimize and validate the model, integrating more field and experimental data to improve its applicability and predictive accuracy under varying geological conditions.
3.5.3. Analysis of Water Sensitivity Damage in Reservoirs
Water sensitivity damage has a significant impact on reservoir development and is closely linked to reservoir properties. Reservoirs with poor physical properties are more susceptible to water sensitivity damage, which in turn exacerbates heterogeneity and increases the disparity in permeability, adversely affecting development efficiency. In low-permeability reservoirs, particle migration, blockage, and stress-induced pore deformation can reduce permeability. The greater the extent of pore–throat blockage and pore deformation [20], the larger the reduction in permeability.
Water sensitivity damage is also strongly related to the magnitude of waterflooding multiples. Long-term water injection can increase core porosity and permeability, enlarge pore sizes, and reduce clay content, with changes in clay minerals and particle migration being the primary causes [19]. In practical reservoir development, the average waterflooding multiples between wells are typically concentrated between 10 and 50 PVs, while near-wellbore multiples can reach up to 500 PVs, and inter-well maximum multiples exceed 100 PVs. The results of this study indicate that rapid permeability damage primarily occurs within 100 PVs. By mapping these areas, the regions most prone to rapid permeability deterioration during ongoing water injection can be clearly identified. For similar nearby reservoirs, it is recommended that during the early stages of water injection, strict monitoring of injected water quality should be conducted, water compatibility studies should be initiated in advance, and the early addition of anti-swelling agents should be considered to slow the rate of reservoir damage. Field experience by Wang et al. [1] has shown that in the early stages of water injection in water-sensitive reservoirs, proper technical measures—including selecting appropriate injection water sources and adding cations to the injected water—can effectively mitigate water sensitivity damage. Compared to single-approach mitigation strategies—such as chemical treatments (e.g., clay stabilizers, which are costly and exhibit efficacy decay) or injection strategy adjustments (e.g., pulsed injection, which is operationally complex)—the time-variant model proposed in this study couples geological characteristics with dynamic flow behavior. This model quantitatively defines the damage threshold under varying water flush multiples, enabling early prediction and targeted prevention of damage zones. With its predictive and quantifiable advantages, the approach provides a systematic decision-making basis for optimizing injected water quality, timing of clay stabilizer application, and layer-specific management, thereby effectively delaying reservoir damage and enhancing development efficiency.
Permeability changes may also induce variations in oil saturation. As permeability decreases, fluid flow resistance increases, the oil phase relative permeability declines, and oil saturation correspondingly rises. Water sensitivity damage is influenced by both reservoir properties and waterflooding multiples, with the latter affecting the extent of damage (Figure 10A,B). The phenomenon is inherently complex and variable.
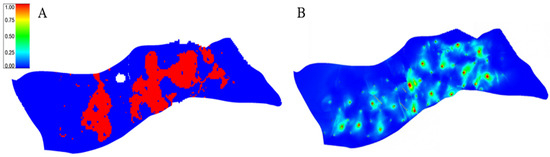
Figure 10.
(A): Rapid Damage Zones of the North 31 Well Area Wutonggou Formation; (B): Average Waterflooding Multiples of the North 31 Well Area Wutonggou Formation.
Therefore, in sensitive reservoirs such as water-sensitive formations, it is particularly critical to consider the time-variant characteristics of reservoir properties and two-phase flow capacity. Accurate understanding of the dynamic response of water-sensitive reservoirs during water injection development is essential for implementing targeted, dynamic, and precise adjustments. Subsequent development strategies should be tailored to specific well groups, taking into account detailed reservoir behavior to optimize recovery.
3.5.4. Residual Oil Distribution Patterns
Considering time-variant effects during reservoir development is crucial for understanding reservoir characteristics and the distribution of residual oil. Studies indicate that when time-variant factors are incorporated, the overall reservoir permeability tends to decline, while local residual oil saturation correspondingly increases. For instance, in wells B3013 and B2033IW, planar and cross-sectional residual oil maps clearly show that the combined effect of strong water sensitivity and high-rate water injection leads to attenuation of the permeability in preferential flow channels. Consequently, residual oil predominantly accumulates in low-permeability zones and non-mainstream regions (see Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13). In wells B3013 and B2033IW, the combined influence of strong water sensitivity and high-rate water injection leads to attenuation of the permeability in preferential flow channels. During water injection, as the number of injected pore volumes (PVs) increases, the pore structure and permeability of various lithologies in water-sensitive reservoirs—such as conglomerate, coarse sandstone, medium sandstone, and fine sandstone—undergo significant changes due to water sensitivity. When the injection multiple is relatively low (PV ≤ 100), permeability declines rapidly, and the preferential flow channels are quickly damaged. This alters the distribution of water within the reservoir, causing water to bypass high-permeability but already damaged regions and preferentially flow into lower-permeability zones. As the injection multiple exceeds 100 PVs, the overall decline in permeability slows, but by this stage the preferential channels have already experienced substantial permeability reduction. Consequently, water distribution becomes more complex, water fingering intensifies, and residual oil predominantly accumulates in low-permeability zones and non-mainstream regions.
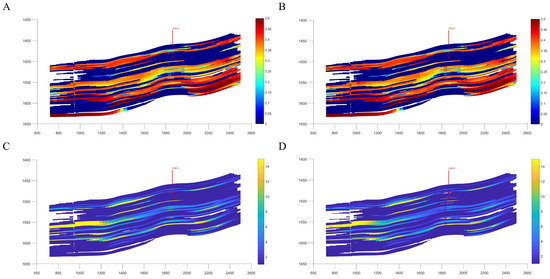
Figure 11.
Original Saturation Field (A), Time-Variant Saturation Field (B), Original Permeability Field (C), and Time-Variant Permeability Field (D) of Well B3013.
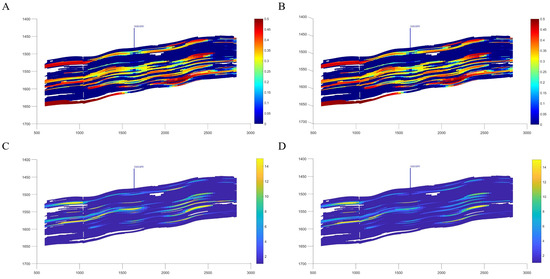
Figure 12.
Original Saturation Field (A), Time-Variant Saturation Field (B), Original Permeability Field (C), and Time-Variant Permeability Field (D) of Well B2033IW.
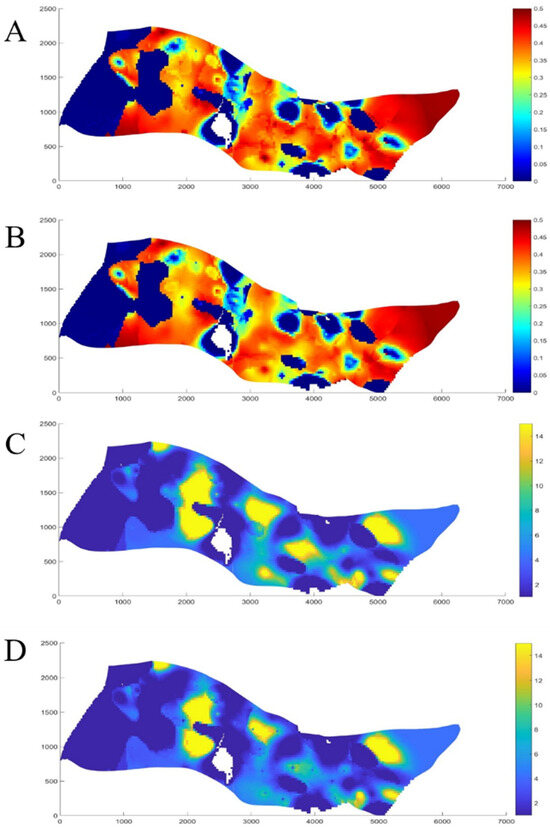
Figure 13.
Original Saturation Field (A), Time-Variant Saturation Field (B), Original Permeability Field (C), and Time-Variant Permeability Field (D) of the Study Area.
From the perspective of residual oil saturation, as the injection multiple increases, the co-injection area of the two phases expands and the overall residual oil saturation decreases. However, the water-phase relative permeability at residual oil saturation exhibits spatial variability. This indicates that during water injection, although the total residual oil saturation declines, the flow resistance of water within the reservoir changes due to water sensitivity damage, resulting in a more complex residual oil distribution. In regions where the permeability of preferential flow channels has diminished, water flow resistance increases, reducing the displacement efficiency of residual oil. Conversely, in low-permeability zones and non-mainstream regions, water flow resistance is relatively lower, leading to higher displacement efficiency. Nevertheless, continued water injection induces further water sensitivity in these areas, exacerbating water fingering and causing residual oil saturation to remain relatively high [21].
The upscaling of laboratory-derived time-variant permeability relationships to field-scale applications introduces significant uncertainties due to differences in spatial heterogeneity, flow dynamics, and mineral distribution between core samples and reservoir conditions. While regression-based models (e.g., permeability retention vs. PV injected in Table 1) effectively capture trends observed in core floods, their reliance on empirical fitting may overlook underlying physical complexities such as localized clay mobilization, pore–throat reorganization, and scale-dependent fluid–rock interactions.
Furthermore, these models assume uniform damage progression across lithologies, whereas field-scale heterogeneity (e.g., fractures, permeability contrasts) may amplify deviations. The regression approach also struggles to extrapolate beyond experimental PV ranges (e.g., >500 PV) or account for long-term chemical/biological processes. Future work should integrate mechanistic models with multi-scale data to reduce scaling biases and improve predictive robustness.
4. Conclusions
This study integrates experimental and numerical approaches to investigate time-variant reservoir parameter behavior during long-term waterflooding in water-sensitive reservoirs, establishing a dynamic simulation model. The key findings are:
- (1)
- Increasing water injection multiples enhance permeability in high-permeability zones, intensifying interlayer heterogeneity. Concurrently, relative permeability curves shift rightward, reducing residual oil saturation. These phenomena provide critical experimental validation for time-variant algorithms.
- (2)
- The developed compositional time-variant model outperforms conventional static models, achieving significantly higher accuracy in matching high water-cut stage performance (e.g., water-cut and pressure responses), thus better capturing long-term injection dynamics.
- (3)
- Water sensitivity damage evolves through distinct stages. Early rapid permeability decline exacerbates heterogeneity and impairs development efficiency, trapping residual oil predominantly in low-permeability/non-mainstream areas. This understanding supports optimized injection-production strategies for enhanced recovery.
- (4)
- The combined experimental-numerical approach effectively characterizes dynamic parameter evolution, providing scientific guidance for the North Santai Wutonggou Formation and serving as a reference for other water-sensitive reservoirs.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: H.X. and S.W.; Methodology: J.D.; Software: E.Y.; Validation: X.H. and S.W.; Formal Analysis: F.Y.; Investigation: J.Y. and F.Y.; Resources: S.W.; Data Curation: E.Y. and F.Y.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation: H.X.; Writing—Review and Editing: S.W.; Visualization: F.Y.; Supervision: S.W.; Project Administration: S.W.; Funding Acquisition: S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Joint Fund for Enterprise Innovation and Development of NSFC (Grant No. U24B2037) and the Fund for General Program of NSFC (Grant No. 52374051).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to sincerely thank those who have contributed to this research.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Hui Xie, Jie Du, Enlai Yuan, Xiaodie Hu, Jianghua Le and Fenggang Yuan are employed by company, Xinjiang Oilfield Company. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Peng, X.; Wang, P.; Zhao, N.; Chu, S.; Wang, X.; Kong, L. Water-sensitive damage mechanism and the injection water source optimization of low permeability sandy conglomerate reservoirs. Pet. Explor. Dev. 2019, 46, 1218–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J. Investigation of Water-Sensitivity Damage for Tight Low-Permeability Sandstone Reservoirs. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 11197–11204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, B.; Wang, B.; Wang, M.; Teng, J.; He, B.; Liang, T. Characterization of Water-Rock Interaction in Water-Sensitive Tight Oil Reservoirs and its Mitigation Method with Pilot Tests. In Proceedings of the 58th U.S. Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, Golden, CO, USA, 23–26 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Zhao, A.; Wei, Y. The dominant mineralogical triggers hindering the efficient development of the world’s largest conglomerate oilfield. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 60, 688–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Pu, C.; Li, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, L.; Jing, C. Permeability recovery of damaged water sensitive core using ultrasonic waves. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2017, 38, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jiang, G.; Li, X.; Yang, L. Quantitative Investigation of Water Sensitivity and Water Locking Damages on a Low-Permeability Reservoir Using the Core Flooding Experiment and NMR Test. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 4444–4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kang, Z.; Liu, H.; Kang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Jiang, L.; Ali, S.M.F.; Wang, S. A method to consider capillary end effect in relative permeability curves. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 493, 144906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, J.; Zijun, H.; Ruxiang, G.; Jibo, R.; Gaoming, Y.; Yu, Z. Time-varying Numerical Simulation Of Reservoir Physical Properties Based On Surface Flux. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1894, 012077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, M.; Wang, K. Mechanism of Permeability Evolution for Reservoir Sandstone with Different Physical Properties. Geofluids 2018, 2018, 5327895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, J.; Kühn, M.; Schneider, W.; Clauser, C.; Pape, H.; Meyn, V.; Lajcsak, I. Core flooding laboratory experiment validates numerical simulation of induced permeability change in reservoir sandstone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 34-1–34-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheng, G.; Liu, N.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Wang, X.; Dou, X.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Shi, X. Numerical Simulation of Time-Varying Characteristics in a High-Permeability Sandstone Reservoir: A Case of Gaoqian Southern Area. Geofluids 2024, 2024, 4886286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Zhang, W.; Zhao, P.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, M.; Tao, Z.; Zhao, M.; Ni, T.; Xu, J.; Cui, Y.; et al. Characterization of the reservoir property time-variation based on ‘surface flux’ and simulator development. Fuel 2018, 234, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X. Numerical Simulation and Flow Field Evaluation Considering Physical Properties Time Variation for Waterflooding Reservoir. Master’s Thesis, China University of Petroleum (East China), Qingdao, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.-C.; Zhang, N.; Tang, Z.-H.; Zou, X.-F.; Sun, Q.; Liu, W. Time-dependent model for two-phase flow in ultra-high water-cut reservoirs: Time-varying permeability and relative permeability. Pet. Sci. 2024, 21, 2536–2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhou, W.; Liu, C. Integrated Modeling of Time-Varying Permeability and Non-Darcy Flow in Heavy Oil Reservoirs: Numerical Simulator Development and Case Study. Processes 2025, 13, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xun, Y.; Xiao, J.; Shi, L. A novel numerical simulation method for oil reservoir considering time-varying permeability. Geosyst. Eng. 2024, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wang, S.; You, Q.; Yu, C. A New Measurement of Anisotropic Relative Permeability and Its Application in Numerical Simulation. Energies 2021, 14, 4731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Zhu, Y.; Jiao, T.; Qi, Z.; Luo, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L. Microscopic pore throat structures and water flooding in heterogeneous low-permeability sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Jurassic Yan’an Formation in the Huanjiang area, Ordos Basin, Northern China. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2021, 219, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Zhang, G.; Sun, D.; Li, B.; Wang, F. The influence of water flooding multiples on reservoir micro pore structure. Exp. Pet. Geol. 2020, 42, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Z.; Wang, J. Analysis of reservoir damage and microscopic seepage simulation in low permeability oil and gas reservoirs based on pore topology structure. J. Eng. Res. 2024, 13, 2730–2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Shen, Z.; Cai, M.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, M.; Lu, F.; Li, X.; He, S.; Li, P. A comprehensive reservoir simulation technique based on time-varying petro-physical parameters characterized by effective displacement flux. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2022, 46, 89–96. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).