A Small Linear Accelerator for Charged Microparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
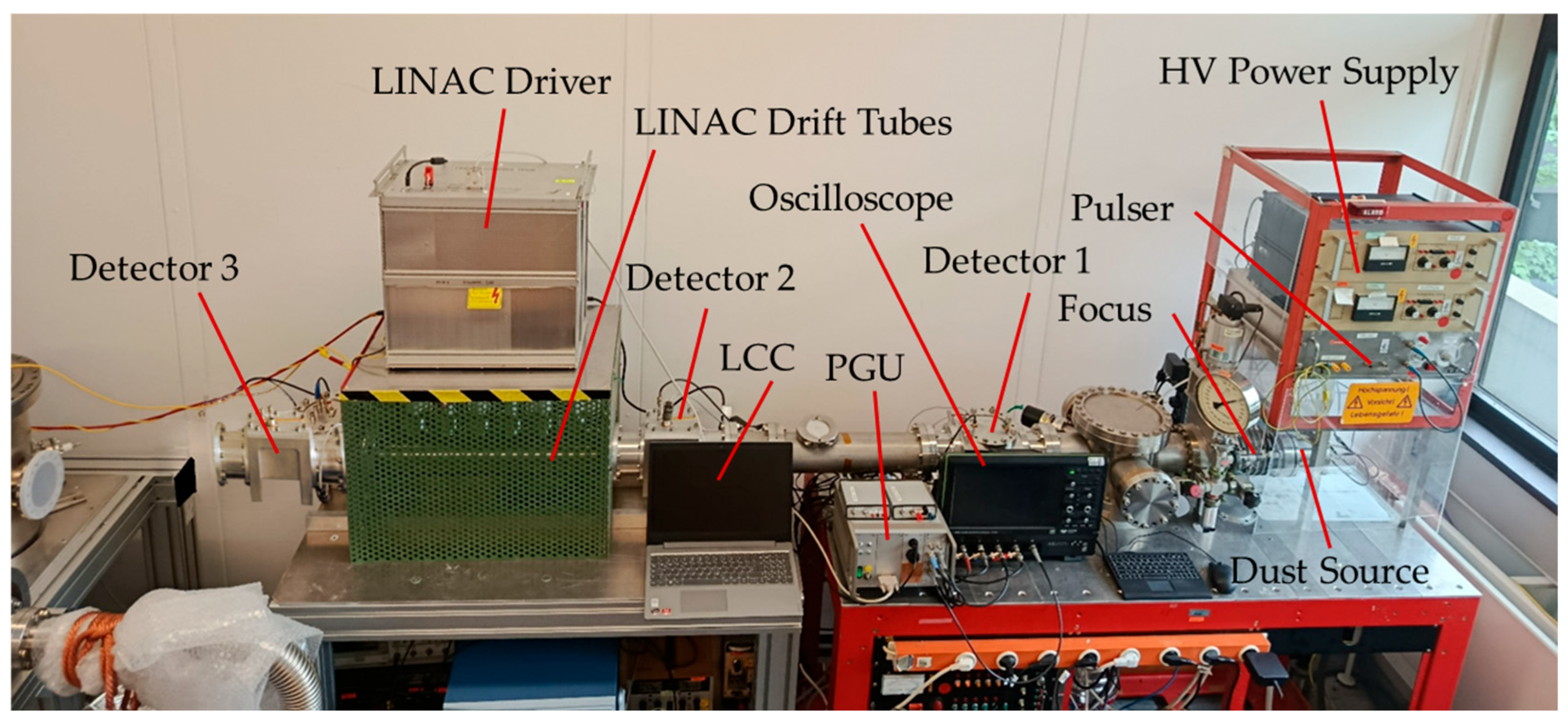
2. Materials and Methods
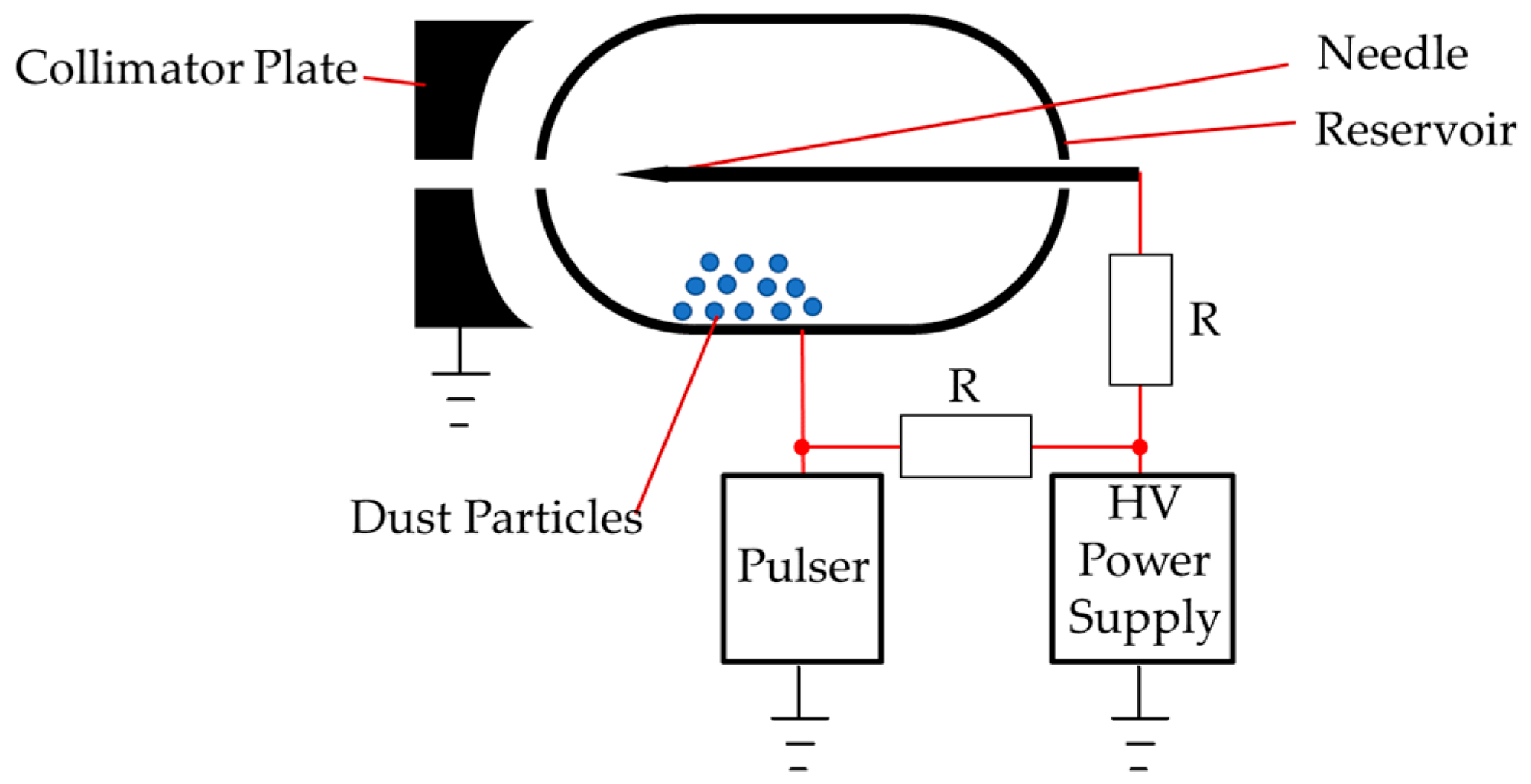
2.1. Dust Source
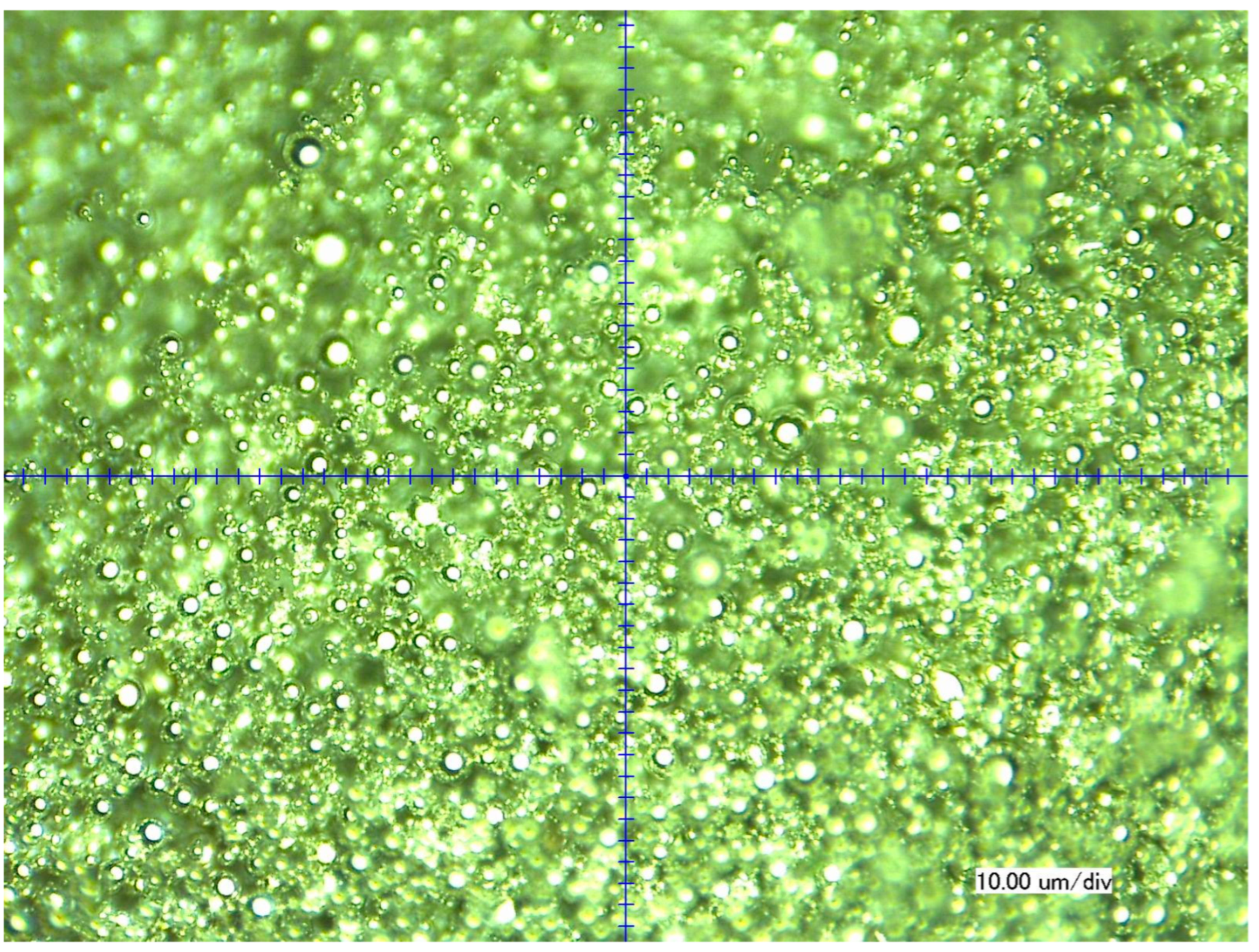
2.2. Particles
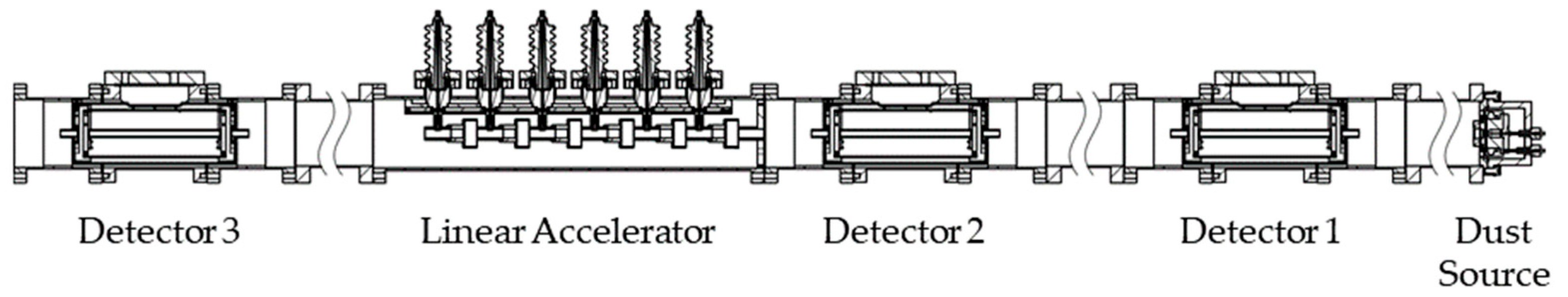
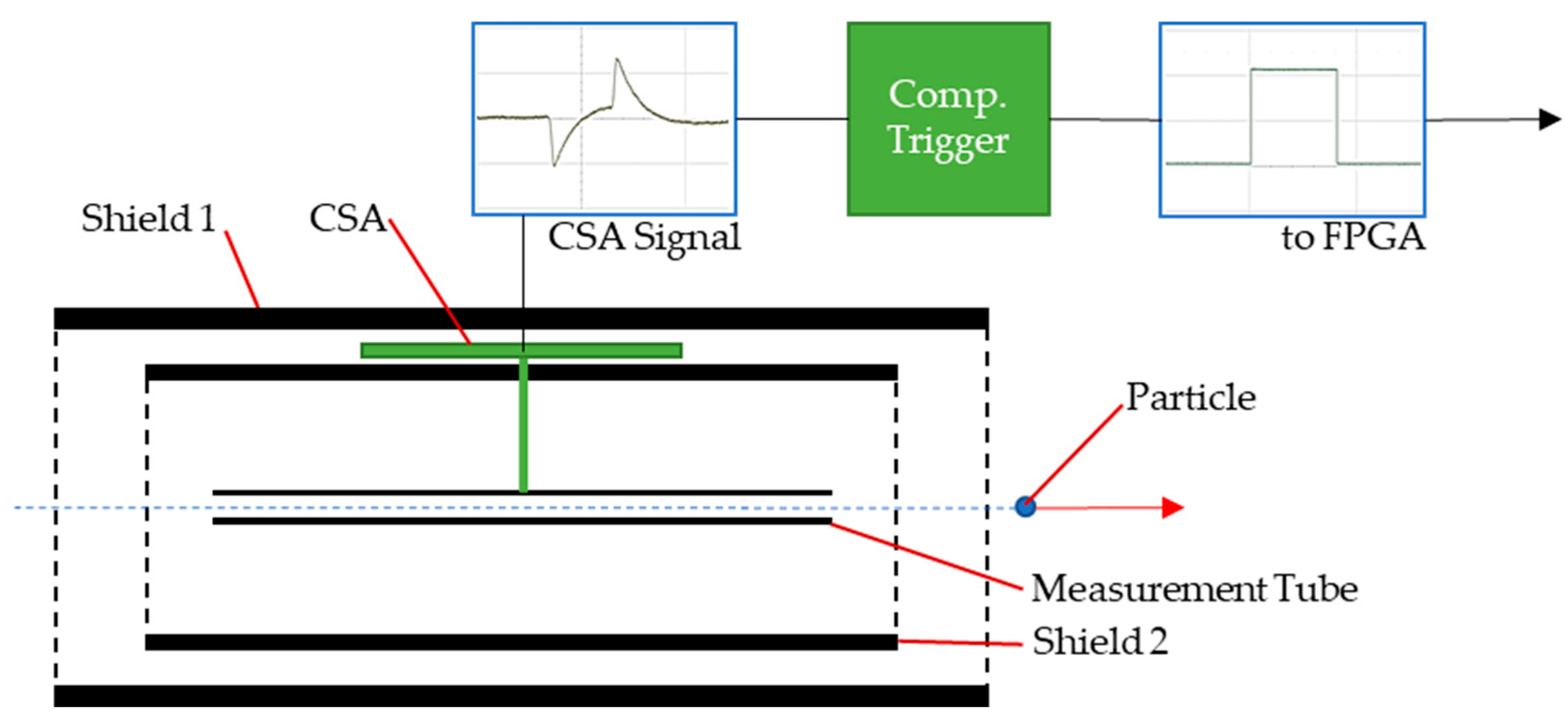
2.3. Beam Detectors
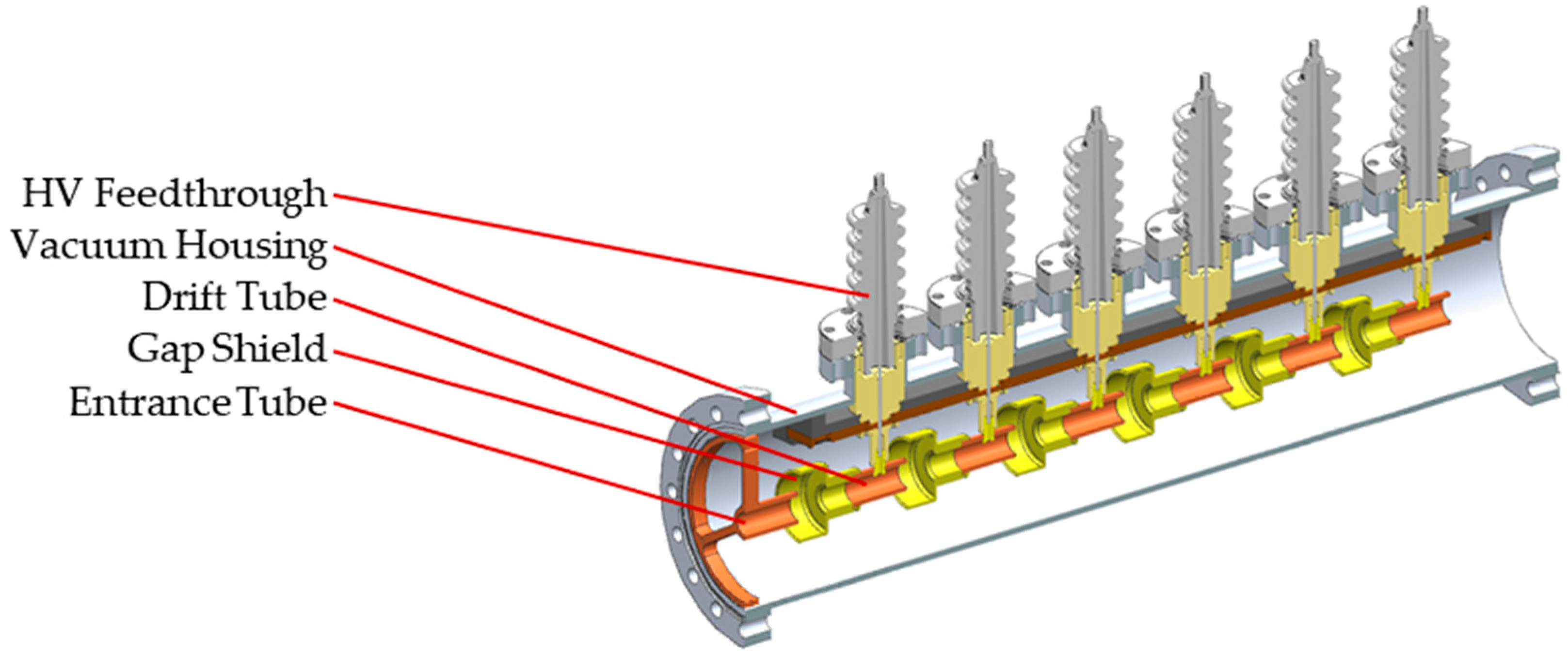
2.4. Linear Accelerator
2.4.1. Electrode Assembly
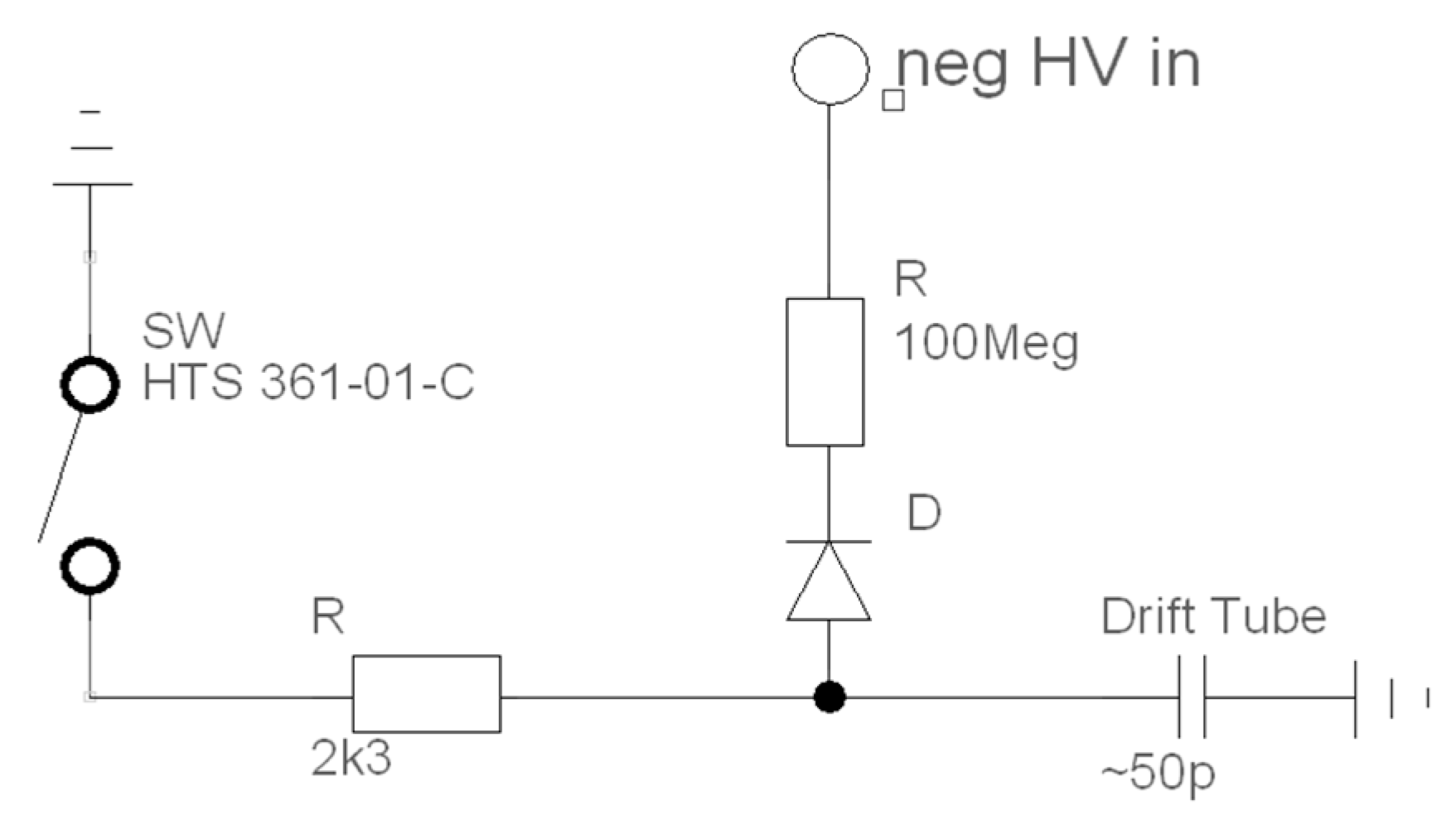
2.4.2. High Voltage Supply
2.4.3. Linear Accelerator Driver
- Behlke HTS 361-01-C (Behlke Power Electronics GmbH, 61476 Kronberg im Taunus, Germany) high voltage Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor (MOSFET) switches,
- high voltage resistors,
- high voltage diodes to prevent voltage polarity errors and discharging through unwanted current paths,
- MOSFET-drivers, and
- opto-couplers to reduce noise output to peripherals generated by the high-speed switching.
2.4.4. Pulse Generating Unit
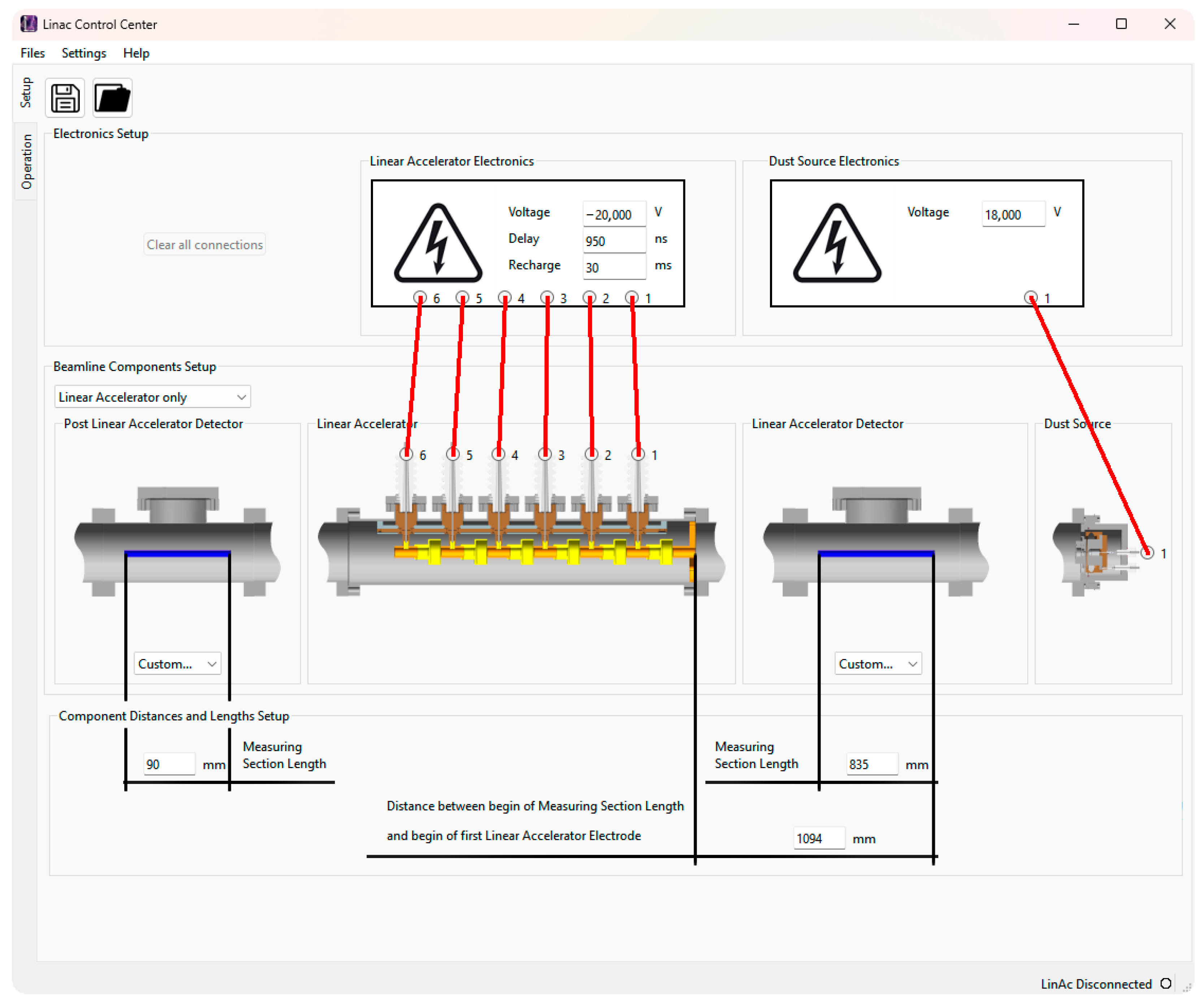
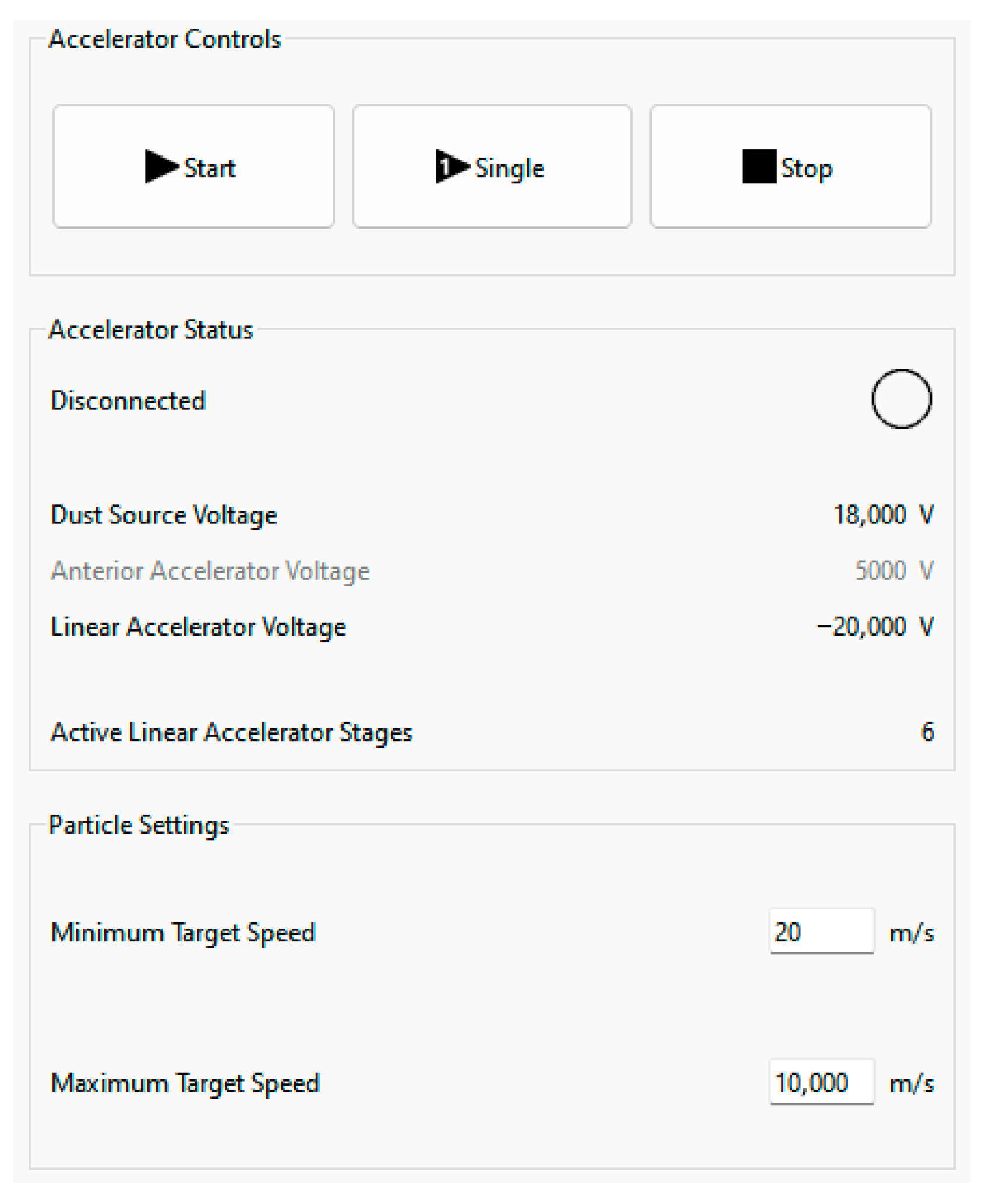
2.4.5. LINAC Control Center
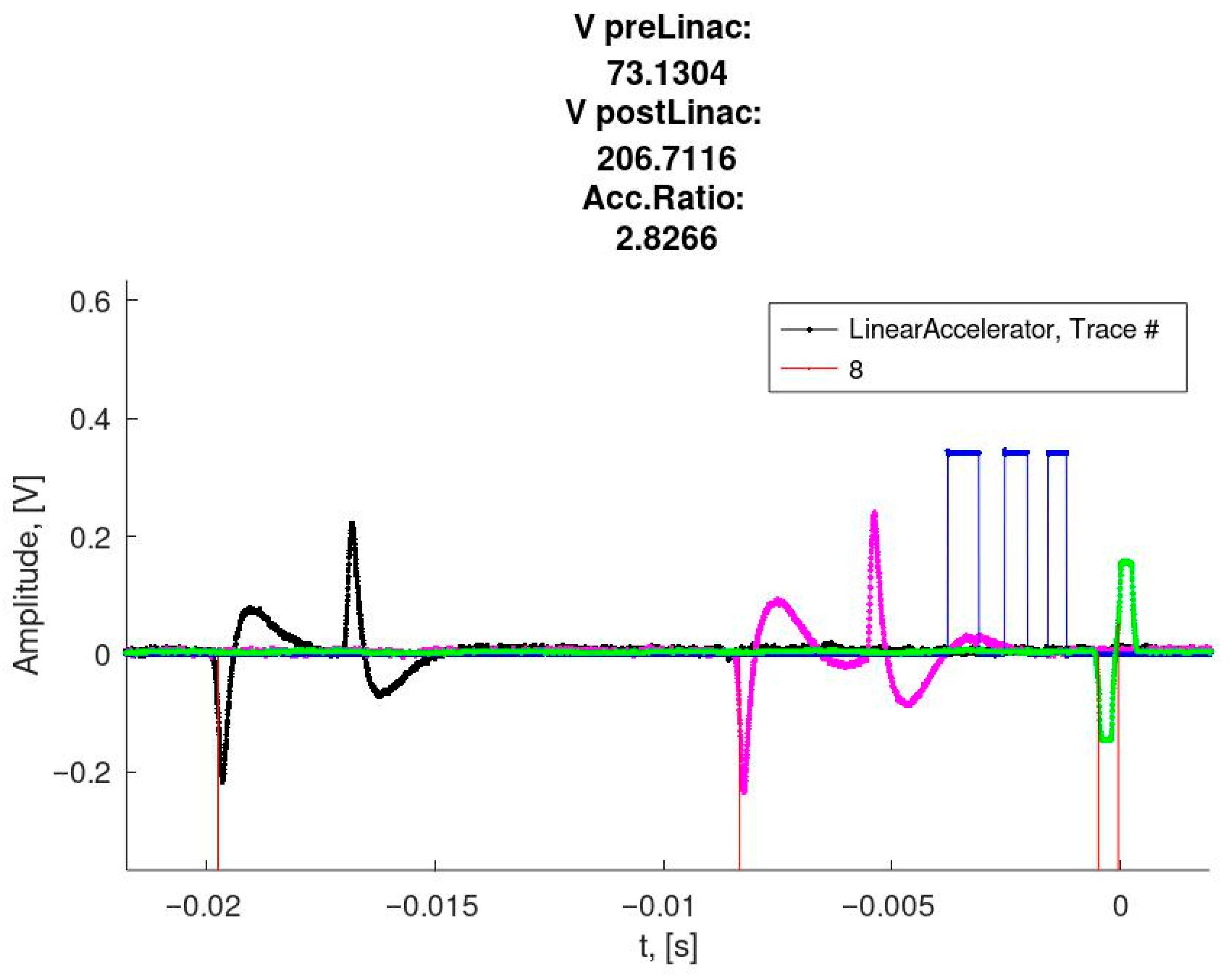
2.5. Data Recording and Evaluation
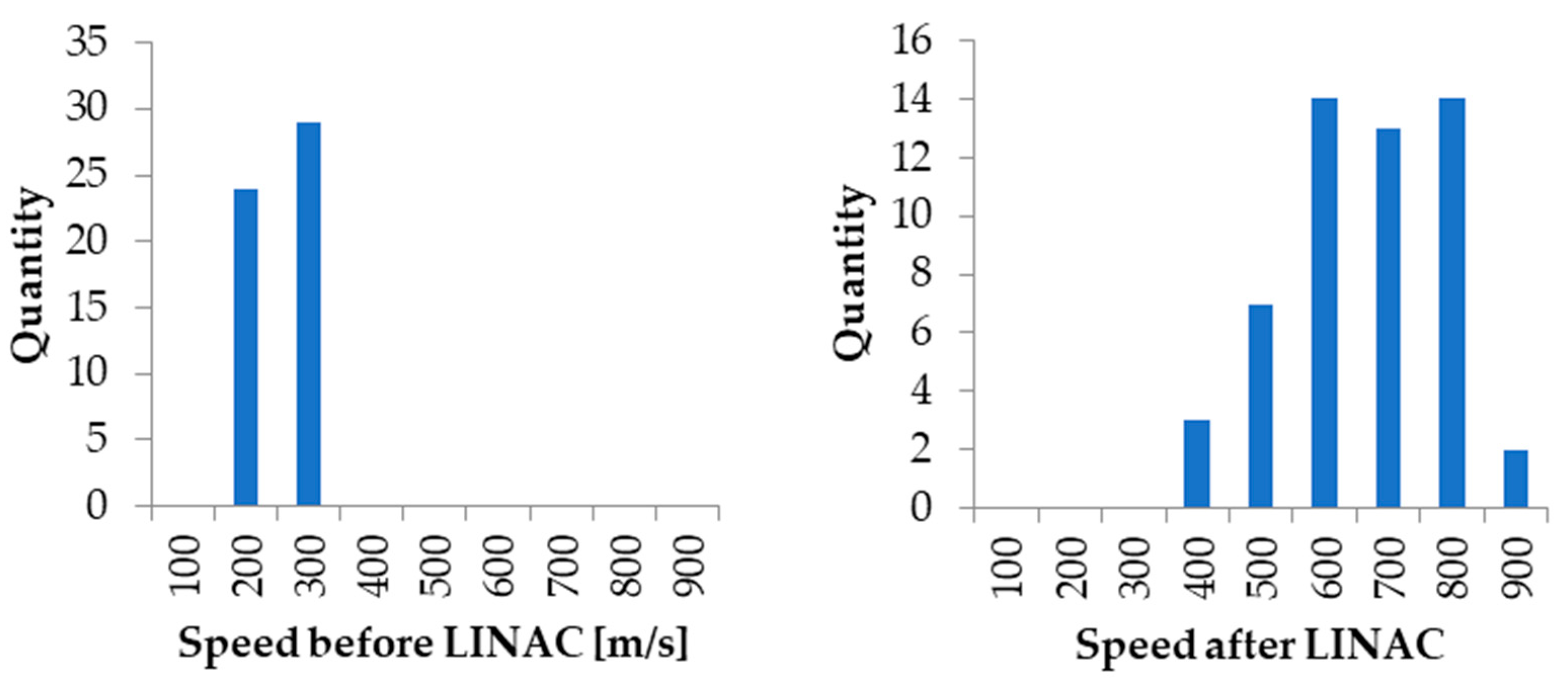
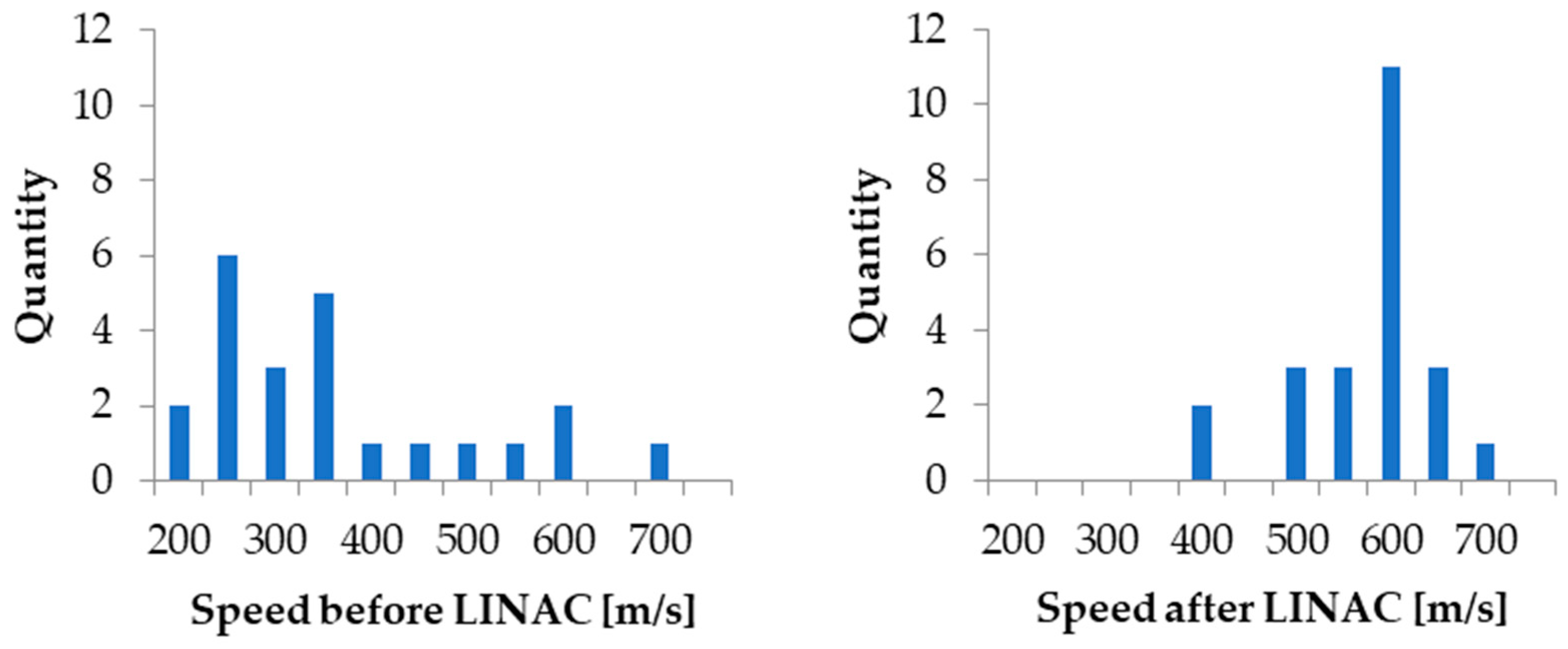
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- particles in the size range of 0.6 to 1.8 µm,
- pre-LINAC speed range of 170–530 m/s,
- post-LINAC speed range of 200–1300 m/s,
- LINAC potentials from 20 to 120 kV, and
- acceleration ratios up to 3.
- isometric tubes to keep it short,
- negative voltages,
- no capacitor banks, and
- high voltage MOSFET switches.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| [C] | Coulombs |
| CSA | Charge Sensitive Amplifier |
| EMI | Electromagnetic Interference |
| FPGA | Field-Programmable Gate Array |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface |
| HV | High Voltage |
| [kg] | Kilograms, 1 kg = 1000 g |
| [km/s] | Kilometers per Second, 1 km/s = 1000 m/s |
| [kV] | Kilovolts, 1 kV = 1000 V |
| LCC | LINAC Control Center |
| LINAC | Linear Accelerator |
| [m/s] | Meters per Second |
| [mA] | Milliamperes, 1 mA = 0.001 A |
| [mbar] | Millibars, 1 mbar = 0.001 bar |
| [MHz] | Megahertz, 1 MHz = 1 × 106 Hz |
| [µm] | Micrometers, 1 µm = 1 × 10−6 m |
| [µs] | Microseconds, 1 µs = 1 × 10−6 s |
| MOSFET | Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor |
| MSL | Measuring Section Length |
| [Ω] | Ohms, 1 Ω = 1 × 10−3 kΩ = 1 × 10−6 MΩ |
| PEEK | Polyether Ether Ketone |
| PGU | Pulse Generating Unit |
| PSU | Particle Selection Unit |
| [s] | Seconds |
| SF6 | Sulfur Hexafluoride |
| TOF | Time Of Flight |
| USB | Universal Serial Bus |
Appendix A
References
- Friichtenicht, J.F. Micrometeoroid Simulation using Nuclear Accelerator Techniques. Nucl. Instrum. Methods 1964, 28, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burchell, M.J.; Cole, M.J.; McDonnell, J.A.M.; Zarnecki, J.C. Hypervelocity impact studies using the 2 MV Van de Graaff accelerator and two-stage light gas gun of the University of Kent at Canterbury. Meas. Sci. Technol. 1999, 10, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hörz, F. Cratering and penetration experiments in aluminum and teflon: Implications for space-exposed surfaces. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 2012, 47, 763–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsworthy, B.; Burchell, M.; Cole, M.; Green, S.; Leese, M.; McBride, N.; McDonnell, J.; Müller, M.; Grün, E.; Srama, R.; et al. Laboratory Calibration of the Cassini Cosmic Dust Analyser (CDA) using new, low density Projectiles. Adv. Space Res. 2002, 29, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takechi, S.; Nogami, K.; Miyachi, T.; Fujii, M.; Hasebe, N.; Iwai, T.; Sasaki, S.; Ohashi, H.; Shibata, H.; Grün, E.; et al. Laboratory calibration measurements of a piezoelectric lead zirconate titanate cosmic dust detector at low velocities. Adv. Space Res. 2009, 43, 905–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göller, J.R.; Grün, E. Calibration of the Galileo/Ulysses dust detectors with different projectile materials and at varying impact angles. Planet. Space Sci. 1989, 37, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fechtig, H.; Gault, D.E.; Neukum, G.; Schneider, E. Laboratory Simulation of Lunar Craters. Naturwissenschaften 1972, 59, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veysset, D.; Sun, Y.; Kooi, S.E.; Lem, J.; Nelson, K.A. Laser-Driven High-Velocity Microparticle Launcher in Atmosphere and Under Vacuum. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2020, 137, 103465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, A.; Collette, A.; Drake, K.; Grün, E.; Horányi, M.; Kempf, S.; Mocker, A.; Munsat, T.; Northway, P.; Srama, R.; et al. 3 MV hypervelocity dust accelerator at the Colorado Center for Lunar Dust and Atmospheric Studies. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 075108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocker, A.; Bugiel, S.; Auer, S.; Baust, G.; Colette, A.; Drake, K.; Fiege, K.; Grün, E.; Heckmann, F.; Helfert, S.; et al. A 2 MV Van de Graaff accelerator as a tool for planetary and impact physics research. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2011, 82, 095111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horányi, M.; Szalay, J.R.; Kempf, S.; Schmidt, J.; Grün, E.; Srama, R.; Sternovsky, Z. A permanent, asymmetric dust cloud around the Moon. Nature 2015, 522, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, A.; Krasowski, M.J.; Prokop, N.; Greer, L.C.; Adams, C.M.; Rennó, N.O. Instrument to Study Plume Surface Interactions (PSI) on the Lunar Surface: Science Motivation, Requirements, Instrument Overview, and Test Plans. Aerospace 2024, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Molla, T.; Brandl, C.; Watts, J.; McCully, R.; Tang, C.; Schaffer, G. Critical velocity and deposition efficiency in cold spray: A reduced-order model and experimental validation. J. Manuf. Process. 2025, 134, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assadi, H.; Gärtner, F.; Stoltenhoff, T.; Kreye, H. Bonding mechanism in cold gas spraying. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 4379–4394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slattery, J.C.; Becker, D.G.; Hamermesh, B.; Roy, N.L. A Linear Accelerator for Simulated Micrometeors. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1973, 44, 755–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkin, N.D.; Piyakov, A.V.; Voronov, K.E.; Bogoyavlenskii, N.L.; Goryunov, D.V. A linear accelerator for simulating micrometeorites. Instrum. Exp. Tech. 2007, 50, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamson, B.D.; Miller, M.E.C.; Continetti, R.E. The aerosol impact spectrometer: A versatile platform for studying the velocity dependence of nanoparticle-surface impact phenomena. EPJ Tech. Instrum. 2017, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonnell, J.A.M.; Haddad, H.; Ashworth, D.G. A switched linear accelerator for microparticles: Design and computer simulated performance data. J. Phys. E Sci. Instrum. 1975, 8, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, D.G.; Friichtenicht, J.F.; Hamermesh, B.; Langmuir, R.V. Variable-Frequency Radially-Stable Micrometeoroid Accelerator. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1965, 36, 1480–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stübig, M.; Schäfer, G.; Ho, T.-M.; Srama, R.; GrunGrün, E. Laboratory simulation improvements for hypervelocity micrometeorite impacts with a new dust particle source. Planet. Space Sci. 2001, 49, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bauer, M.; Kelz, S.; Strack, H.; Simolka, J.; Mazur, C.; Sommer, M.; Mocker, A.; Srama, R. Upgrades of a Small Electrostatic Dust Accelerator at the University of Stuttgart. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srama, R.; Auer, S. Low-charge detector for the monitoring of hyper-velocity micron-sized dust particles. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2008, 19, 055203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strack, H. Entwicklung Eines Echtzeit-Triggersystems für Strahl- und Trajektoriensensoren zur Messung von Geladenen Mikropartikeln. Doctoral Dissertation, Universitätsbibliothek der Universität Stuttgart, Stuttgart, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kerby, J.D.; Daly, R.T.; Austin, D.E. A novel particle source based on electrospray charging for dust accelerators and its significance for cosmic dust studies. Earth Planets Space 2013, 65, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spesyvyi, A.; Žabka, J.; Polášek, M.; Charvat, A.; Schmidt, J.; Postberg, F.; Abel, B. Charged Ice Particle Beams with Selected Narrow Mass and Kinetic Energy Distributions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2023, 34, 878–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Type | Velocities [m/s] | Masses [g] |
|---|---|---|
| Light-Gas Gun | up to 1 × 104 | 10−3 to 101 |
| Plasma Gun | up to 2 × 104 | 10−8 to 10−4 |
| Laser-Driven Launcher | up to 3 × 103 | 10−13 to 10−10 |
| Electrostatic Accelerator | up to 1 × 105 | 10−17 to 10−9 |
| Attribute | Value |
|---|---|
| acceleration potential | up to 120 kV |
| acceleration stages | 1 to 6 |
| input voltage range | −20 to 0 kV |
| particle entrance speed range | 20 to 10,000 m/s |
| particle output speed range | 20 to 50,000 m/s |
| maximum particle frequency | up to 33 particles per second |
| LINAC Potential [kV] | Diam [µm] | Charge [C] | Mass [kg] | Speed Pre LINAC [m/s] | Speed Post LINAC [m/s] | Acceleration Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 0.682 | 7.19 × 10−15 | 1.30 × 10−15 | 459 | 664 | 1.45 |
| 0.673 | 8.66 × 10−15 | 1.25 × 10−15 | 513 | 755 | 1.47 | |
| 1.455 | 1.36 × 10−14 | 1.26 × 10−14 | 202 | 294 | 1.46 | |
| 1.460 | 2.73 × 10−14 | 1.27 × 10−14 | 285 | 410 | 1.44 | |
| 1.821 | 2.73 × 10−14 | 2.47 × 10−14 | 205 | 294 | 1.43 | |
| 40 | 1.539 | 1.83 × 10−14 | 1.49 × 10−14 | 216 | 388 | 1.80 |
| 1.244 | 5.89 × 10−15 | 7.85 × 10−15 | 168 | 302 | 1.80 | |
| 1.025 | 1.66 × 10−14 | 4.40 × 10−15 | 379 | 678 | 1.79 | |
| 1.391 | 2.55 × 10−14 | 1.10 × 10−14 | 297 | 527 | 1.77 | |
| 0.616 | 5.56 × 10−15 | 9.54 × 10−16 | 470 | 831 | 1.77 | |
| 60 | 1.085 | 1.52 × 10−14 | 5.21 × 10−15 | 332 | 677 | 2.04 |
| 1.495 | 2.73 × 10−14 | 1.36 × 10−14 | 275 | 561 | 2.04 | |
| 0.641 | 5.93 × 10−15 | 1.07 × 10−15 | 458 | 965 | 2.11 | |
| 1.649 | 2.09 × 10−14 | 1.83 × 10−14 | 208 | 430 | 2.07 | |
| 1.374 | 1.22 × 10−14 | 1.06 × 10−14 | 209 | 427 | 2.04 | |
| 80 | 0.746 | 1.11 × 10−14 | 1.69 × 10−15 | 499 | 1194 | 2.39 |
| 1.220 | 2.61 × 10−14 | 7.43 × 10−15 | 365 | 866 | 2.37 | |
| 0.641 | 8.00 × 10−15 | 1.08 × 10−15 | 531 | 1272 | 2.40 | |
| 0.607 | 6.20 × 10−15 | 9.14 × 10−16 | 507 | 1208 | 2.38 | |
| 1.633 | 2.73 × 10−14 | 1.78 × 10−14 | 241 | 558 | 2.32 | |
| 100 | 0.749 | 8.86 × 10−15 | 1.71 × 10−15 | 443 | 1152 | 2.60 |
| 0.856 | 1.30 × 10−14 | 2.56 × 10−15 | 439 | 1137 | 2.59 | |
| 0.665 | 6.07 × 10−15 | 1.20 × 10−15 | 438 | 1114 | 2.54 | |
| 1.666 | 2.73 × 10−14 | 1.89 × 10−14 | 234 | 595 | 2.54 | |
| 0.920 | 1.02 × 10−14 | 3.18 × 10−15 | 349 | 898 | 2.57 | |
| 120 | 1.509 | 2.48 × 10−14 | 1.40 × 10−14 | 259 | 709 | 2.74 |
| 0.628 | 6.21 × 10−15 | 1.01 × 10−15 | 482 | 1334 | 2.77 | |
| 1.348 | 2.51 × 10−14 | 1.00 × 10−14 | 308 | 869 | 2.82 | |
| 1.490 | 2.17 × 10−14 | 1.35 × 10−14 | 246 | 700 | 2.85 | |
| 0.857 | 8.03 × 10−15 | 2.57 × 10−15 | 344 | 966 | 2.81 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bauer, M.; Li, Y.; Srama, R.; Behrens, F.; Mocker, A.; Schäfer, F.; Simolka, J.; Strack, H. A Small Linear Accelerator for Charged Microparticles. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111709
Bauer M, Li Y, Srama R, Behrens F, Mocker A, Schäfer F, Simolka J, Strack H. A Small Linear Accelerator for Charged Microparticles. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111709
Chicago/Turabian StyleBauer, Marcel, Yanwei Li, Ralf Srama, Florian Behrens, Anna Mocker, Felix Schäfer, Jonas Simolka, and Heiko Strack. 2025. "A Small Linear Accelerator for Charged Microparticles" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111709
APA StyleBauer, M., Li, Y., Srama, R., Behrens, F., Mocker, A., Schäfer, F., Simolka, J., & Strack, H. (2025). A Small Linear Accelerator for Charged Microparticles. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11709. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111709







