Monitoring Landslide Deformation in the Xiluodu Reservoir Area Using Combined Ascending and Descending Orbit Time-Series InSAR Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
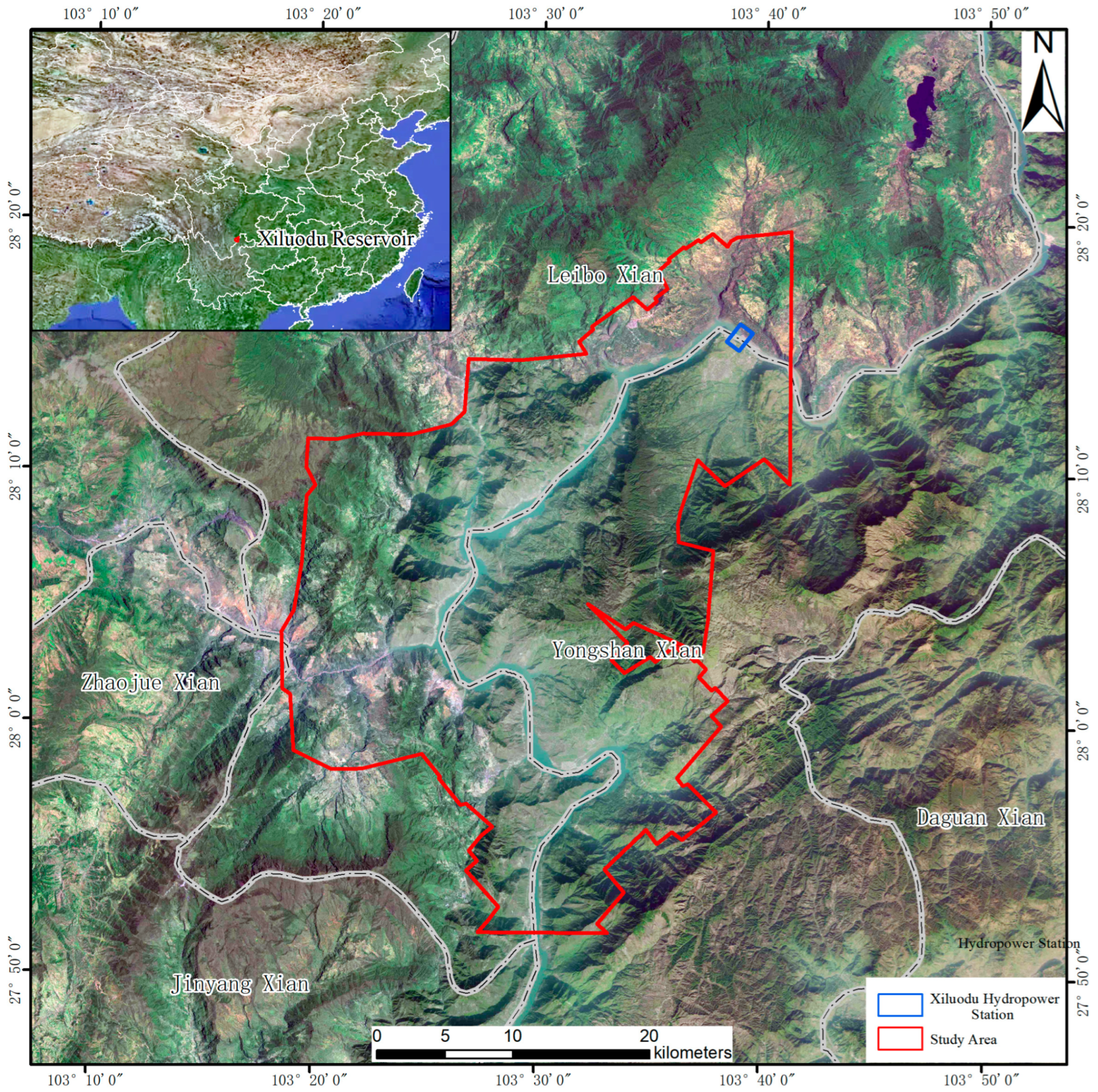
2.1. Study Area
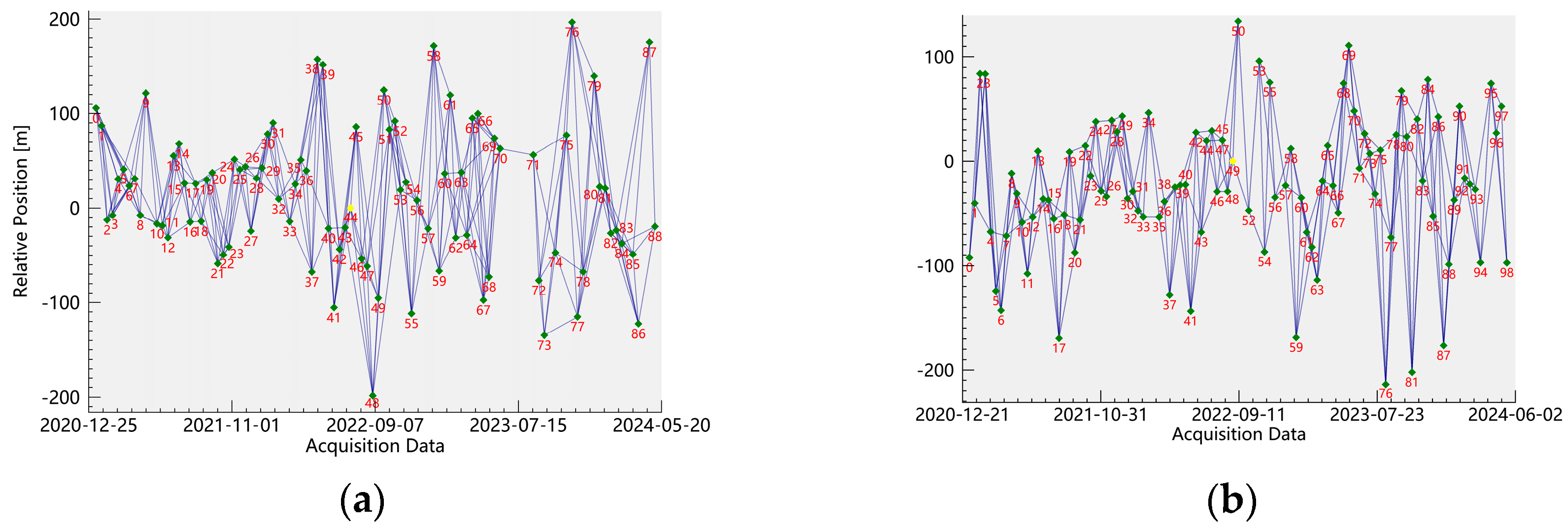
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. The SBAS-InSAR Principles and Processing Flow
2.3.2. Two-Dimensional Deformation Decomposition
3. Results
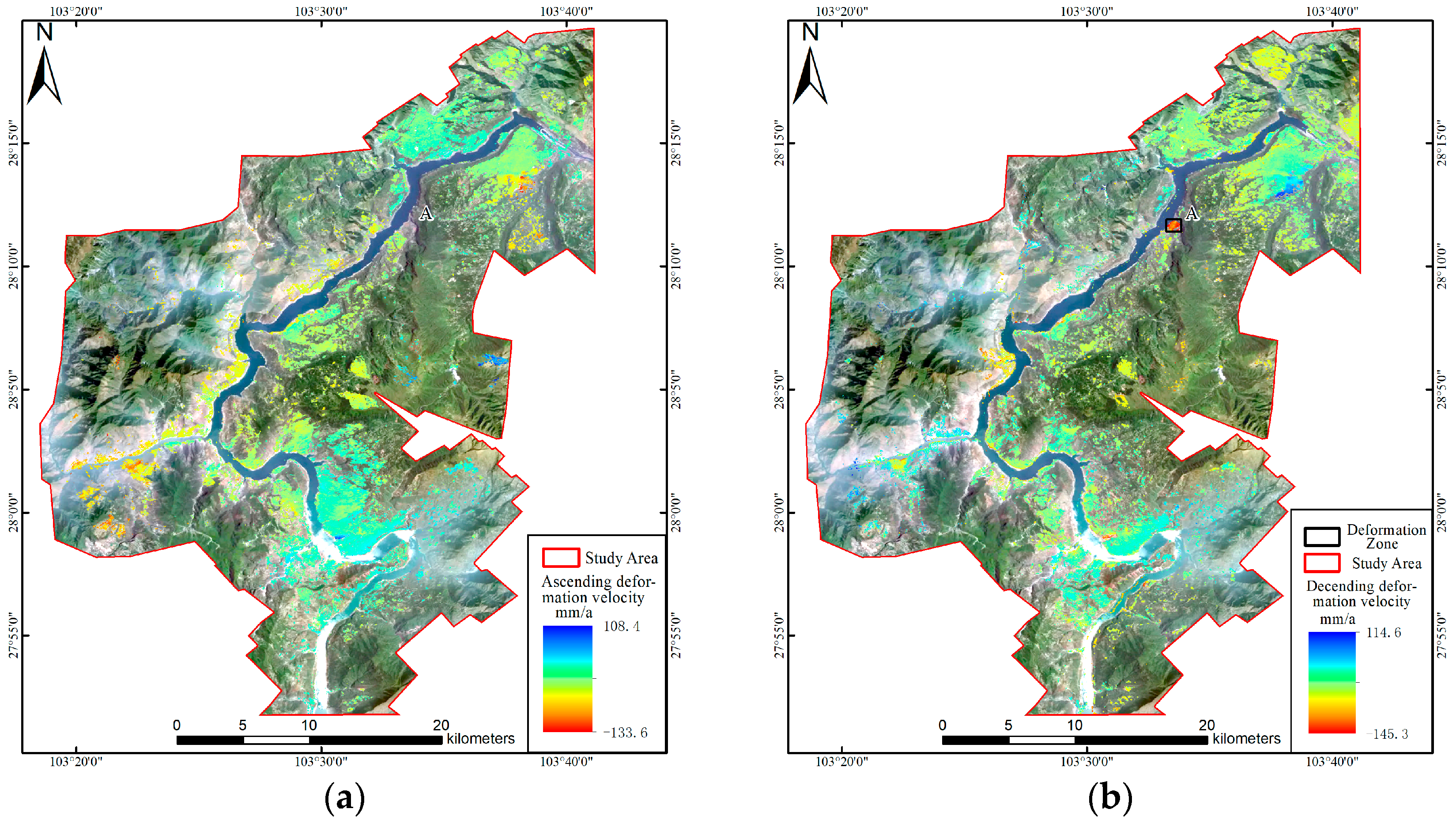
3.1. Analysis of the LOS Deformation Results
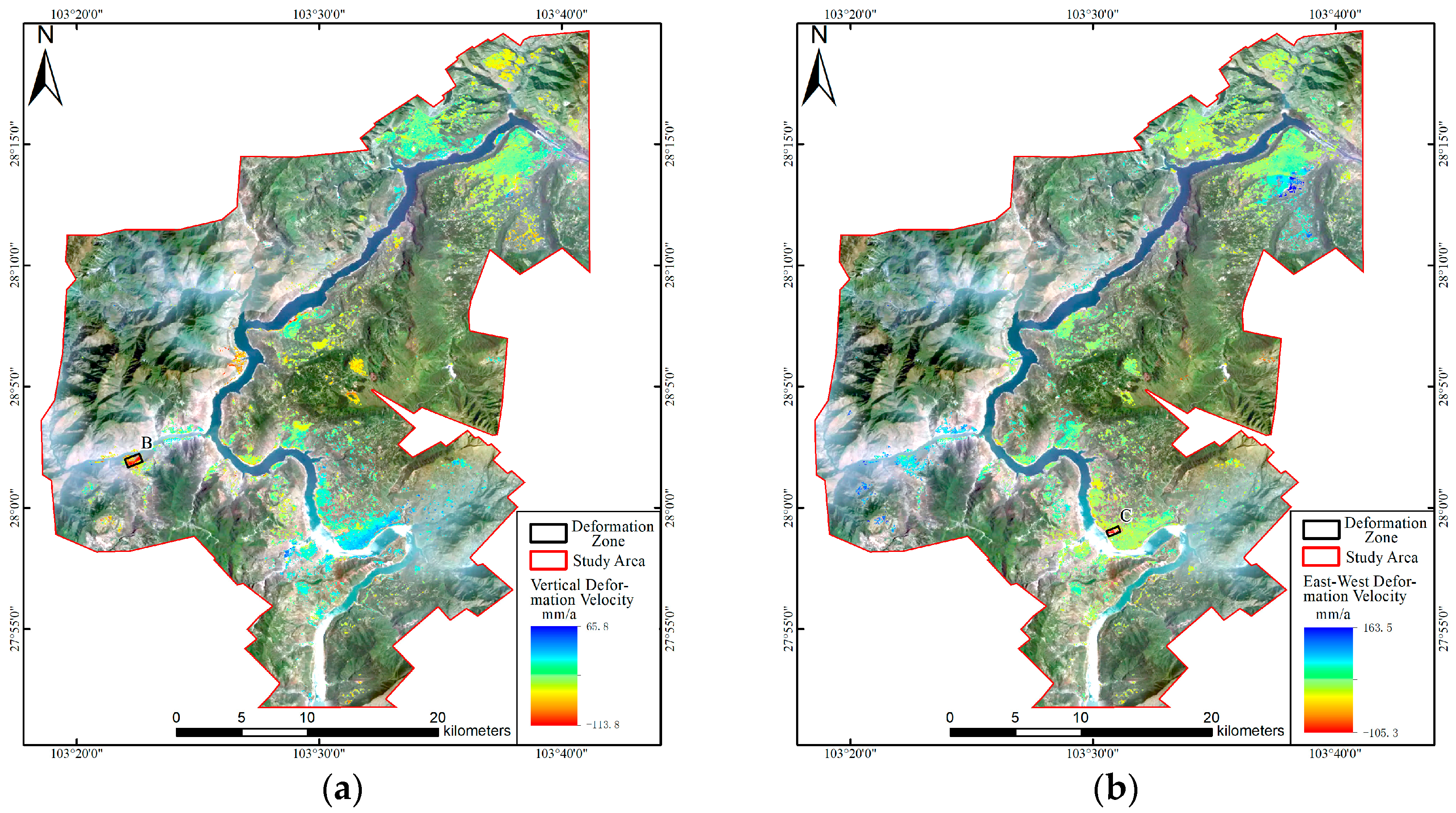
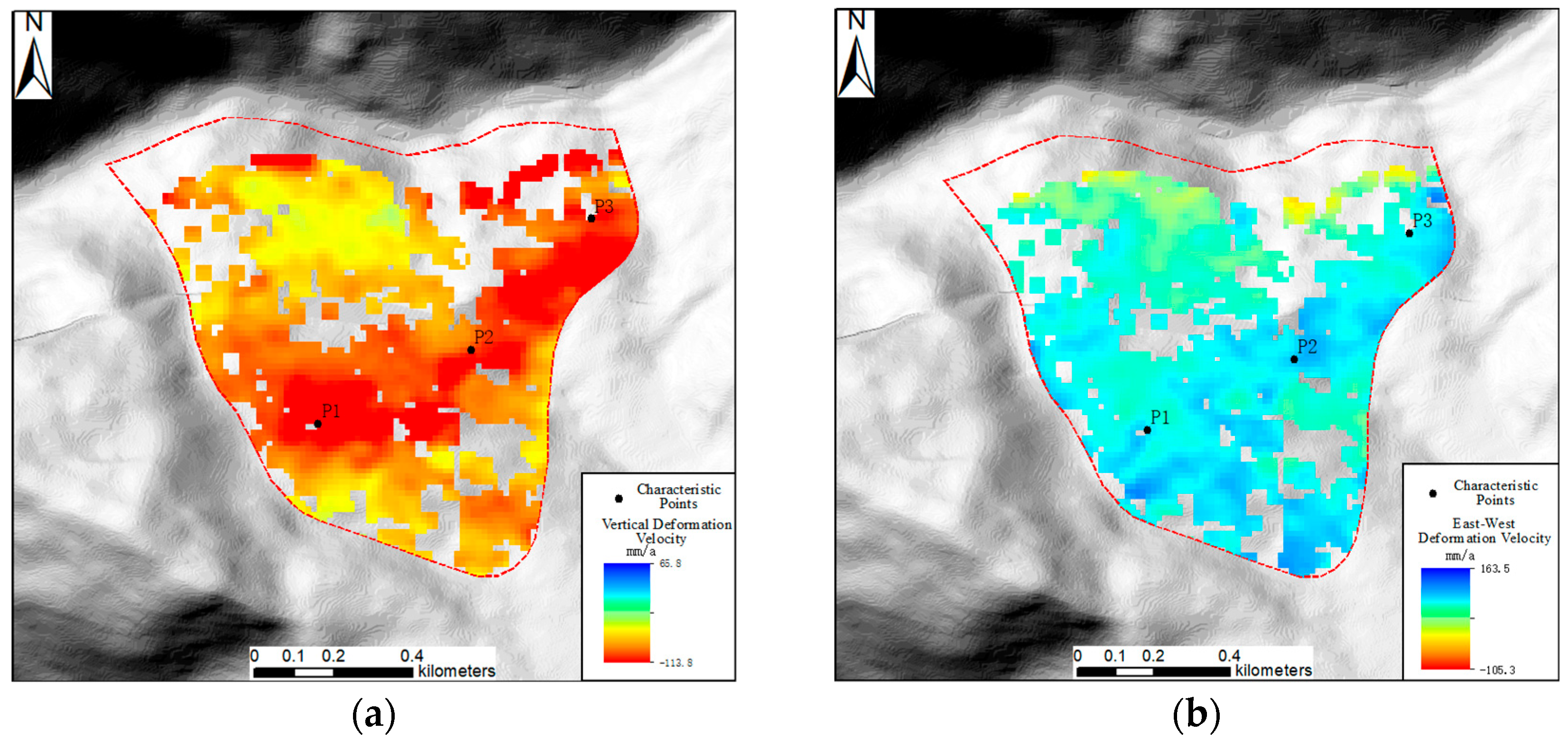
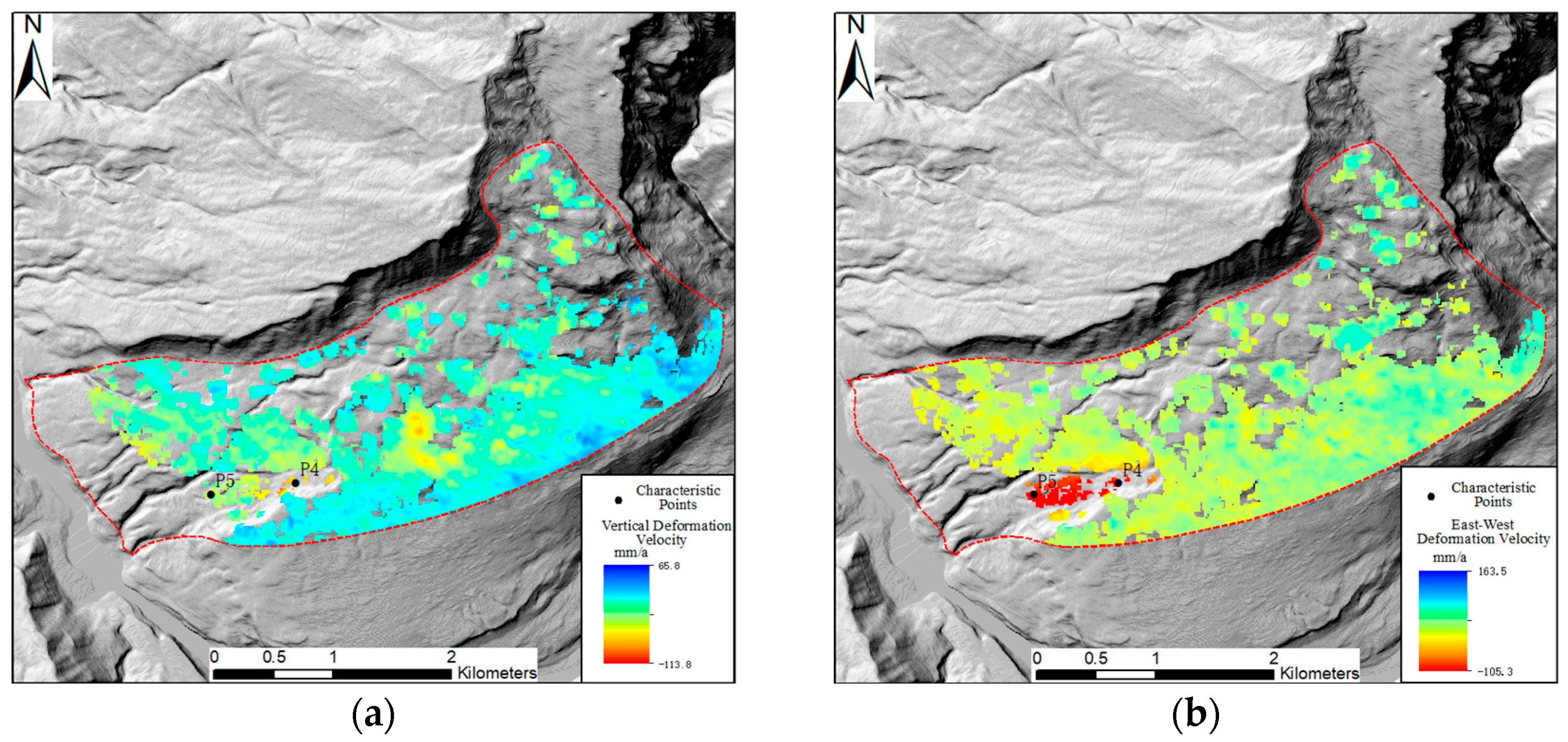
3.2. Analysis of Two-Dimensional Deformation Results
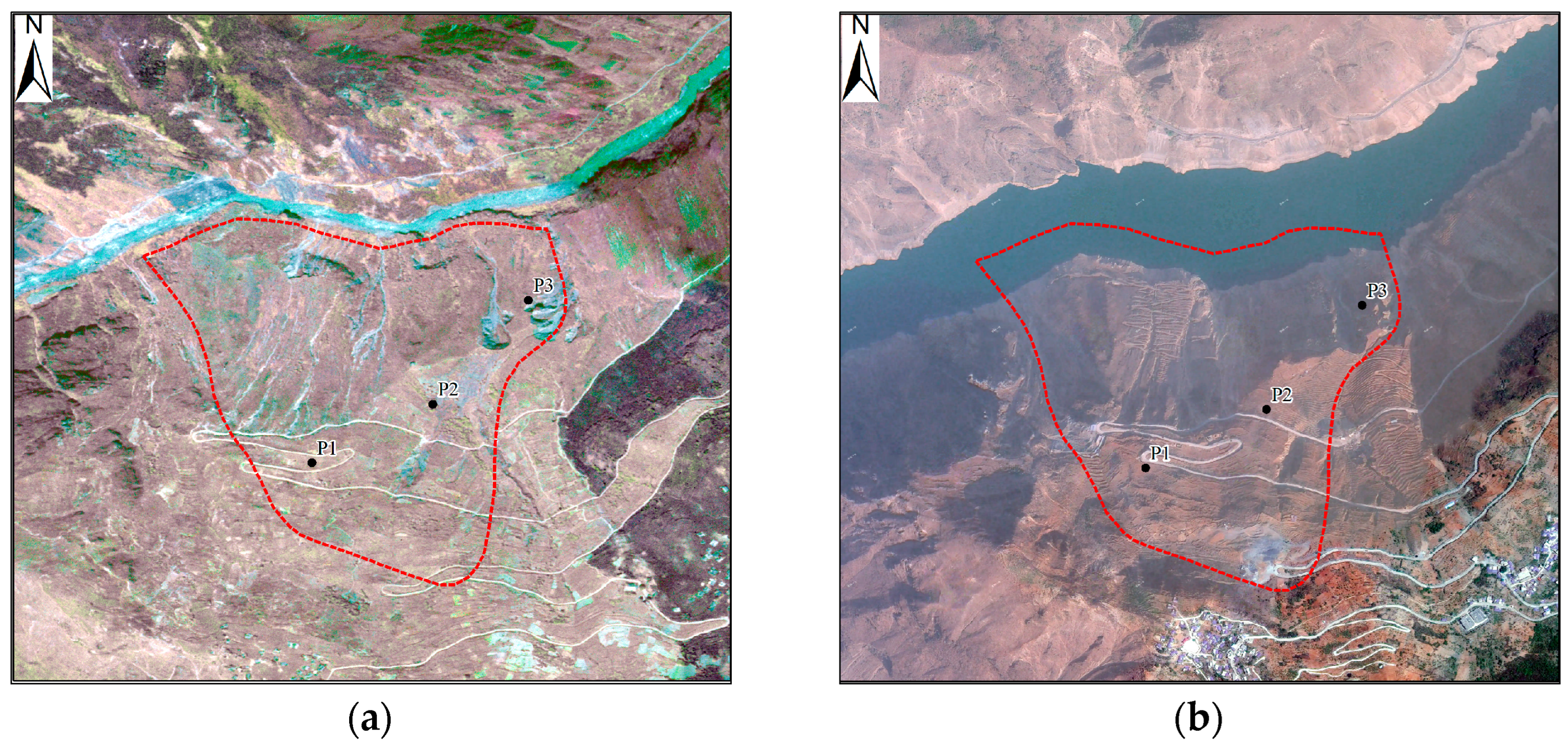
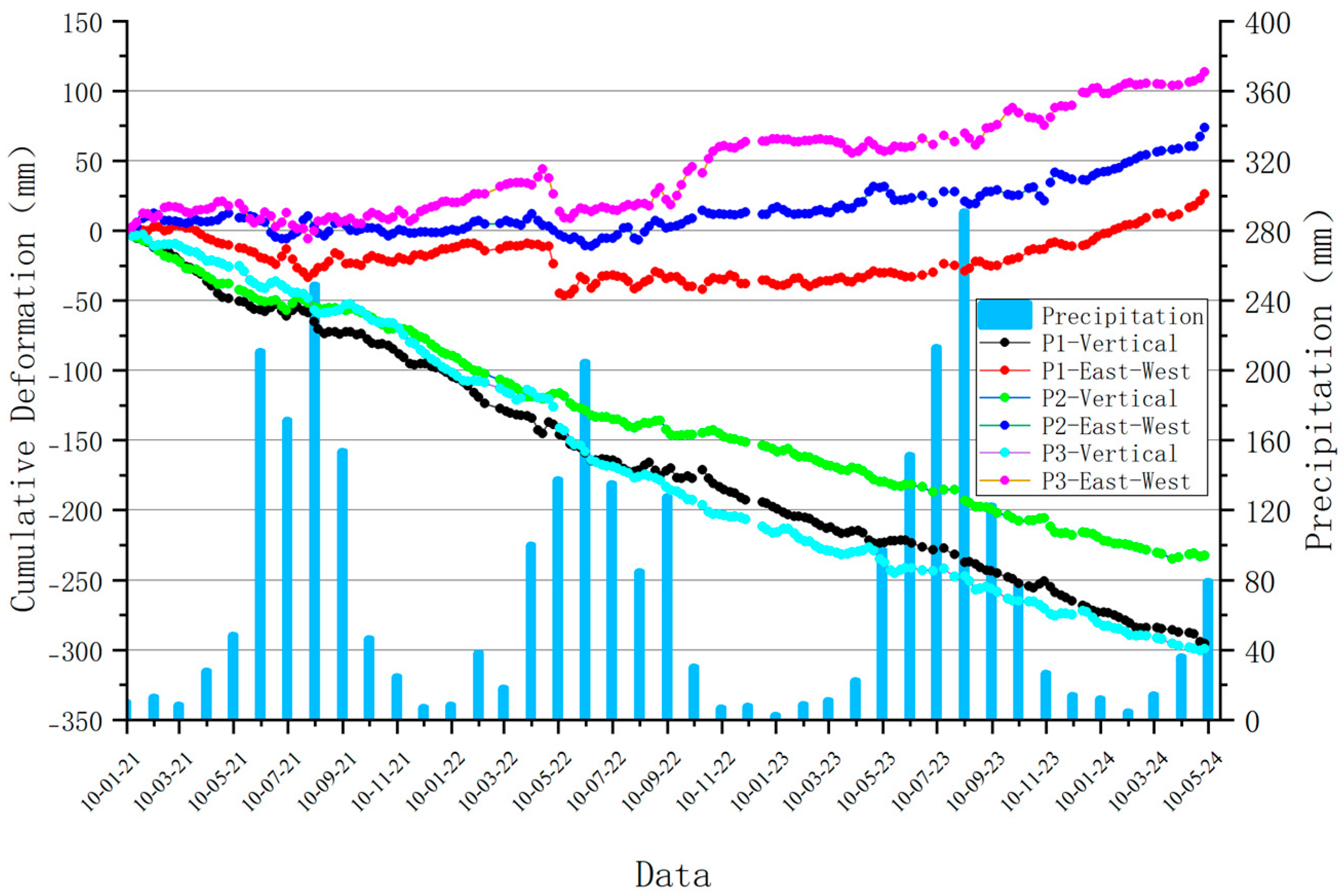
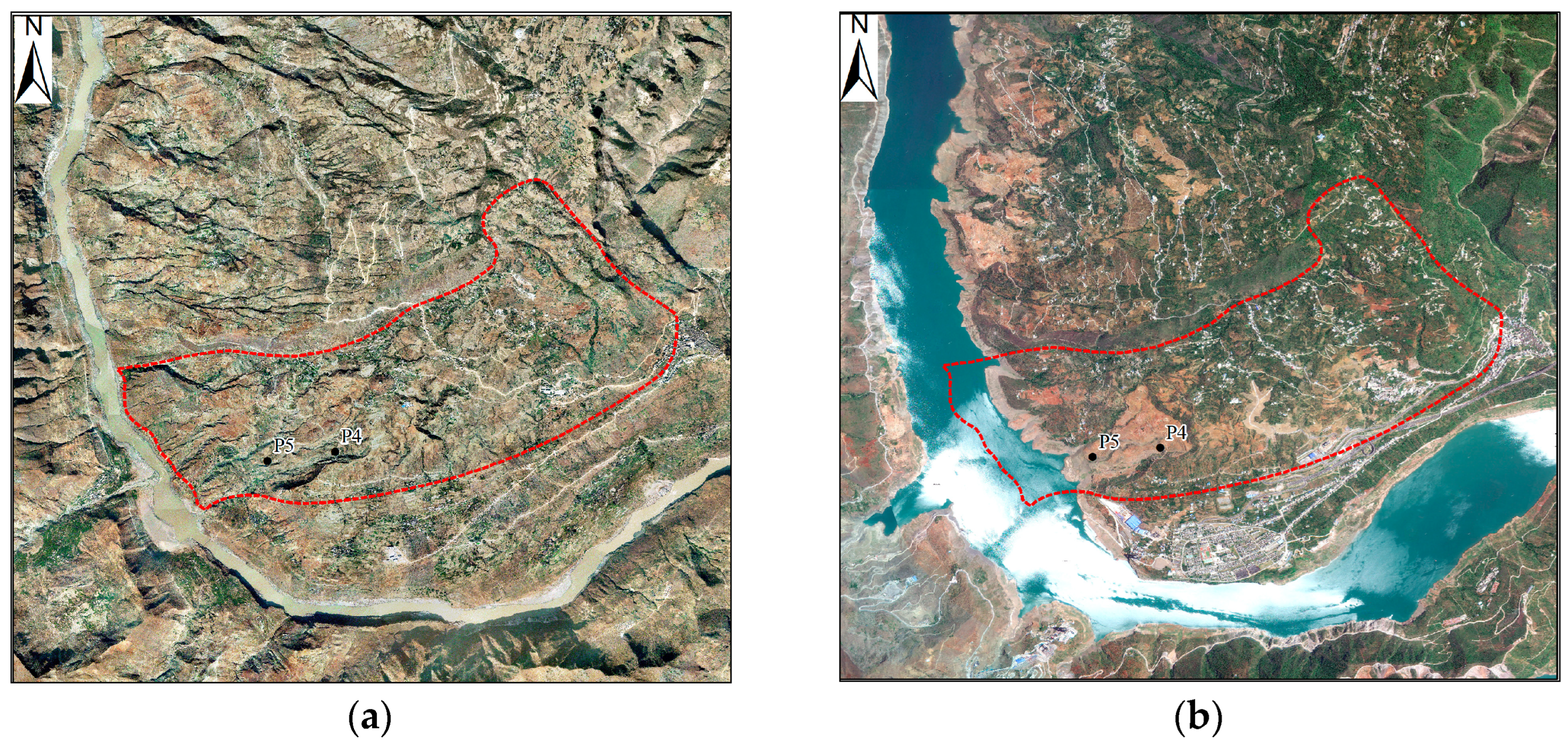
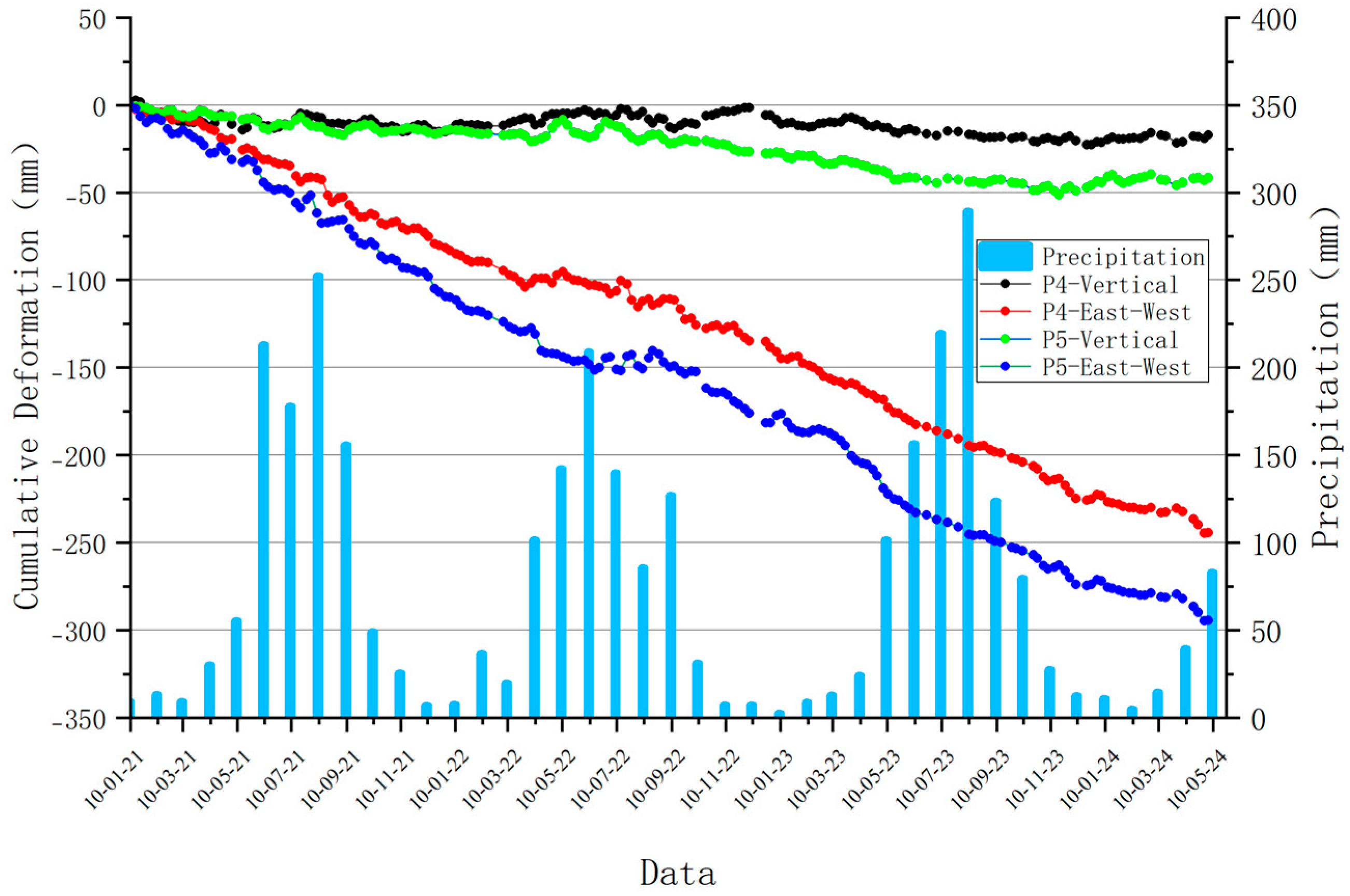
3.3. Characterization of Typical Deformation Areas
4. Discussion
- (1)
- Compared to single-orbit monitoring approaches commonly used in alpine canyon regions, the integration of ascending and descending InSAR tracks significantly enhances both spatial coverage and monitoring reliability by identifying a greater number of deforming areas and accurately separating deformation components in different line-of-sight directions. This provides robust data support for precisely characterizing landslide kinematics and understanding their underlying mechanisms. Furthermore, when combined with visual interpretation of remote sensing imagery, this approach enables early warning of potential landslide hazards, offering proactive measures for disaster prevention and mitigation.
- (2)
- Surveillance data from two selected typical deformation zones indicate that reservoir water level fluctuation is one of the primary triggering factors for landslide development and deformation in the reservoir area. In future work, integrating in situ monitoring data with numerical simulations—such as hydro-mechanical coupled models—would enable more rigorous quantitative analysis of landslide deformation mechanisms. Furthermore, incorporating advanced machine learning approaches, such as deep learning algorithms, could enhance the predictive capability of landslide behavior under varying reservoir operation schedules and rainfall scenarios.
- (3)
- The SBAS-InSAR technology has successfully reconstructed the spatiotemporal evolution of landslide deformation in deep canyon reservoirs, demonstrating its capability to detect deformation risks early, quantify deformation rates, and analyze triggering factors in large-scale, complex environments. This provides scientific evidence and technical solutions for ensuring the safe operation of reservoirs with similar geological conditions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.X.; Xiao, J.Z.; Xu, C.; Xie, Q.Z.; Yuan, H. Deformation mechanism and stability analysis of landslides under the influence of reservoir impoundment and construction activities. J. Eng. Geol. 2014, 22, 386–395. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, F.J.; Qi, S.W.; Guo, S.F.; Zou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, X.; Hou, X. Spatiotemporal distribution Patterns and susceptibility of reservoir-induced landslides in the Xiluodu reservoir area of the Jinsha River. J. Eng. Geol. 2022, 30, 609–620. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Y.H.; Zheng, D.; Wu, Z.L.; Li, Q.F.; Pan, Y.Y.; Liu, J.F. Study on the Reactivation Mechanism of Typical Reservoir Bank Deposits under High Water Level and Large Amplitude Fluctuations. Yangtze River 2025, 1–13. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/42.1202.TV.20250414.2206.002 (accessed on 30 September 2025).
- Zhang, E.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Physical model experimental study on the deformation mechanism of Baijiabao landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2025, 32, 218–230. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, Q.L.; Wang, B.; Deng, M.L.; Dong, Q.; Liu, K.X.; Zhang, J.X.; Lai, X.M. Deformation characteristics and mechanism of landslides induced by rainfall raising groundwater level in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area. J. China Three Gorges Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2023, 45, 105–115. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Wang, T.; Da, S.; Yang, A.P.; Li, J.S.; Zhu, J.D. Application of SBAS-InSAR technology in the deformation monitoring of a super-large landslide: A case study of Pangcun landslide in Tibet Autonomous Region. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 14927–14935. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.J.; Zuo, X.Q.; Li, Y.F.; Zhang, J.M.; Chen, K. Deformation monitoring and landslide identification in a reservoir area of a Southwest China power station based on DS-InSAR. Remote Sens. Inf. 2024, 39, 104–111. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-series algorithms, applications, and challenges. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Ren, S. Research progress on the application of InSAR technology in landslide identification and monitoring. Geol. China 2025, 52, 513–526. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhao, R.Z.; Wang, H.B.; Li, X.G.; Lü, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.Y. Early identification and dynamic monitoring of geological hazards by remote sensing technology: A case study of the Changbo Township to Yangla Township section. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 1823–1836. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, B.A.; Zhao, C.; Kakar, N.; Chen, X. SBAS-InSAR Monitoring of Landslides and Glaciers Along the Karakoram Highway Between China and Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Dun, J.; Yi, X.; Zhang, G.Q. Deformation analysis of the Woda Village giant ancient landslide in Jinsha River Basin based on SBAS-InSAR technology. J. Eng. Geol. 2020, 28, 384–393. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Li, W.L.; Lu, H.Y.; Zhou, S.; Li, W.M.; Xu, S.M. Response relationship between deformation characteristics of active landslides in reservoir area and reservoir water level variation based on SBAS-InSAR: A case study of Maoergai Hydropower Station in Heishui County, Sichuan Province. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2024, 24, 11991–12002. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.S.; Wei, C.R.; Wei, Y.J.; Li, Z.F.; Ding, H.L. Whole-process deformation monitoring before and after the instability of the Baige landslide in Tibet based on multi-source remote sensing images. Remote Sens. Nat. Resour. 2025, 37, 203–211. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.H.; Chen, B.; Liu, Y.P.; Peng, J.B.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, L.W.; Du, J.T.; Song, C.; Ding, M.T.; Zhu, W. Long-term 3D deformation monitoring and risk assessment of the Guba landslide on the Tibetan Plateau. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2025, 55, 3421–3437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.L.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.W.; Yang, Y.H.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, J. Monitoring the slope-oriented deformation velocity field of Taoping ancient landslide using ascending and descending Sentinel-1A data. J. Eng. Geol. 2022, 30, 1350–1361. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, A.; Wang, T.; Xiang, W.; Liu, G.X. Potential landslide identification of Jinsha River landslide group by joint time-series InSAR of ascending and descending orbits. J. Beijing Inst. Technol. 2023, 43, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.R.; Sha, Y.L.; Xin, R.F.; Zhang, X.; Sui, J.; Sun, H. Early identification and characteristic analysis of landslide hazards in Tongren City, Qinghai Province based on time-series InSAR. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2023, 23, 15158–15170. [Google Scholar]
- Dun, J.W.; Feng, W.K.; Yi, X.Y.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wu, M.T. Early identification of active landslides by InSAR before impoundment in Baihetan Reservoir Area: A case study from Hukou Town to Xiangbiling section. J. Eng. Geol. 2023, 31, 479–492. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.Y.; He, S.S.; Wang, P.S.; Sun, L. Early identification of landslide hazards in Southwest mountainous areas based on ascending and descending Sentinel-1A SBAS-InSAR. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 42, 892–897. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Yan, L.; Su, P.D.; Qiu, P.; Long, W.; Wang, Y.L. Deformation characteristics and formation mechanism of thehekou landslide in the Xiluodu reservoir area. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2021, 21, 14500–14507. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Gan, S.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, X. Identification of landslide hazards in Dongchuan District by integrating ascending and descending InSAR data. Prog. Geophys. 2023, 38, 137–146. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S. 1-km monthly precipitation dataset for China (1901–2024). Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2019, 11, 1931–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Xi, W.; Yang, Z.; Shi, Z.; Huang, G.; Yang, Z.; Yang, D. Landslide hazard susceptibility evaluation based on SBAS-InSAR technology and SSA-BP neural network algorithm: A case study of Baihetan Reservoir Area. J. Mt. Sci. 2024, 21, 952–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Yin, K.L.; Liang, X.; Xie, X.X.; Liao, Y.X.; Wang, N.N.; Yin, H. Time-series deformation characteristics analysis of the Outang landslide hazard based on PS-SBAS-InSAR. Saf. Environ. Eng. 2025, 32, 216–229. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.J.; Sun, J.B.; Xue, L.; Shen, Z.K. Monitoring land surface deformation in the North China Plain using wide-area InSAR time-series analysis. Acta Sci. Nat. Univ. Pekin. 2023, 59, 934–944. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.J.; Yao, X.; Zhou, Z.K.; Wang, D.F. Suitability evaluation of Sentinel-1 data for InSAR monitoring of deformation slopes in reservoir areas of southwestern mountainous regions: A case study of Xiluodu Reservoir. J. Geomech. 2022, 28, 281–293. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Luo, H.H.; Jiang, P.; Li, L.Z.; Fan, J.Y.; Liao, H.S.; An, R.H.; Tu, J.; Chen, J.; Yan, B.; et al. Monitoring and application of reservoir bank landslides in large hydropower stations using time-series InSAR technology. Geospat. Inf. 2025, 23, 13–17. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.H.; Li, W.L.; Wu, Z.L.; Zhou, S.S.; Wang, X.; Li, X.Q.; Li, Y.S. Identification of active landslides and analysis of deformation influencing factors in the Baihetan reservoir area. Bull. Geol. Sci. Technol. 2025, 44, 62–77. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.R.; Xi, W.F.; Shi, Z.T.; Xiao, B.; Zhou, D.Y. Deformation analysis of potential reservoir bank landslides at the Baihetan Hydropower Station based on SBAS-InSAR. Chin. J. Geol. Hazard Control 2022, 33, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
| Orbit | Band | Resolution/m | Incidence Angle /(°) | Heading Angle /(°) | Polarization | Number of Acquisitions | Monitoring Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending Orbit | C | 5 × 20 | 37.0 | 347.39 | VV | 89 | 10 January 2021–6 May 2024 |
| Descending Orbit | 37.2 | 192.62 | 98 | 5 January 2021–13 May 2024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Liang, Y.; Dai, F.; Wang, Z. Monitoring Landslide Deformation in the Xiluodu Reservoir Area Using Combined Ascending and Descending Orbit Time-Series InSAR Technology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111698
Wang X, Liang Y, Dai F, Wang Z. Monitoring Landslide Deformation in the Xiluodu Reservoir Area Using Combined Ascending and Descending Orbit Time-Series InSAR Technology. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111698
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaodong, Yunchang Liang, Fuchu Dai, and Zihan Wang. 2025. "Monitoring Landslide Deformation in the Xiluodu Reservoir Area Using Combined Ascending and Descending Orbit Time-Series InSAR Technology" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111698
APA StyleWang, X., Liang, Y., Dai, F., & Wang, Z. (2025). Monitoring Landslide Deformation in the Xiluodu Reservoir Area Using Combined Ascending and Descending Orbit Time-Series InSAR Technology. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111698





