Abstract
Waste dumpsites in developing countries are primary pollution sources impacting nearby ecosystems. This study assessed seasonal changes in soils surrounding the Hulene-B landfill (Maputo, Mozambique) and evaluated the potential for surface water contamination by leachates. A total of 71 samples were collected during the rainy and dry periods and analyzed for pH, electrical conductivity (EC), organic matter (OM), and color. The contamination potential (Pbci) was determined considering the landfill’s characteristics and local hydrological context. During the dry season, soils exhibited higher EC and OM, indicating greater retention of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) and a strong tendency for accumulation. In the rainy season, leaching processes prevailed, leading to reduced EC and OM but increased potential for contaminant mobility. The Pbci values were consistently high across both periods, confirming elevated contamination risk. Overall, the Hulene-B landfill exerts a marked influence on surrounding soils and nearby surface waters, underscoring the urgent need for structural measures to control leachate release and ash dispersion.
1. Introduction
The rapid urbanization of many developing countries is often accompanied by insufficient infrastructure for managing municipal solid waste, a heterogeneous mixture of discarded materials generated by households, urban services, and institutions (including hospitals), which is collected, transported, and disposed of in engineered or non-engineered landfill sites, where it undergoes physical, chemical, and biological degradation over time. The lack of adequately planned disposal facilities, including controlled dumping sites, has become a significant source of environmental pollution [1]. Elevated contamination levels near such facilities pose serious risks to human health [2,3]. Understanding how leachate generation and dispersion vary over time is crucial in this context. These processes change in both volume and chemical composition. Monitoring them is essential for evaluating contamination associated with these environments [4,5].
Uncontrolled dumps produce large amounts of leachate, especially during rainy periods when high temperatures accelerate waste decomposition [6,7]. As a result, these hydrological fluctuations promote contaminant transport into surrounding soils and water bodies. Furthermore, the concentration of metal ions changes with waste composition, water infiltration, and dilution effects [8,9].
Soils act as a barrier between leachates and the environment, regulating contaminant spread. As natural filters, they trap and reduce potentially toxic elements (PTEs) like Zn, Cu, Cr, and Pb. Soil’s ability to immobilize contaminants depends on both pollutant levels and properties such as pH, organic matter (OM), texture, and electrical conductivity (EC), which vary with climate [3,10,11,12]. For example, with pH above 6, H+ dissociates from OM and Fe/Al oxides, enhancing metal binding and reducing bioavailability [13]. OM and texture influence how metals are held or leached [10,14], while EC indicates ion levels and contamination [15]. Changing rainfall and drought further affect how PTEs move and accumulate [16,17].
Several frameworks have been proposed to evaluate environmental risks near waste disposal areas. For example, Rapti-Caputo [18] introduced a hydrogeological-based risk assessment model, while Calvo et al. [19] developed a diagnostic methodology that integrates multiple indices to assess potential impacts across environmental compartments. Despite these approaches, detailed soil characterization remains essential, as it is needed to elucidate mechanisms of contaminant retention, migration, and transformation around dumpsites.
In Mozambique, urban centers still lack efficient waste management systems, leading to the accumulation of rejected materials in open areas [20]. In Maputo, Mozambique’s capital, the Hulene-B dump, currently the country’s largest one, receives over 1000 tons of unsorted waste daily [21]. Previous research in this area has reported significant enrichment in PTEs, including Zn, Cu, Cr, Zr, Pb, Ni, and Mn, in both soils and adjacent waters [22,23,24,25,26,27,28]. Building on these findings, the present study examines seasonal changes in key soil parameters around the Hulene-B site and estimates a surface-water contamination index. Monitoring these variables helps clarify how climatic seasonality influences contaminant retention and mobility, providing essential information for the development of mitigation and remediation strategies [3,29,30].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Hulene-B waste dump (Figure 1), located in Maputo, is the largest in Mozambique [20]. It is surrounded by the Hulene-B neighborhood, which has approximately 49,000 inhabitants [31]. The dump was established in an abandoned quarry without any preparation for waste disposal and has expanded rapidly westwards [32]. Waste is deposited onto heterogeneous sandy soils [23]. The site receives all types of waste generated in Maputo’s urban area, including domestic, industrial, construction, and hospital waste [33]. According to CMCM [21], the composition of deposited waste is estimated at 68% organic matter, 13.2% paper, 9% plastics, 7.5% glass, 2.8% metals, and 1.5% rubber. The dump has an estimated height ranging from ~6 to 15 m and covers an area of about 17 ha. Surrounding soils on the western border have been used for subsistence horticulture, sustained by the continuous accumulation of surface water in the depression, which keeps soils moist.
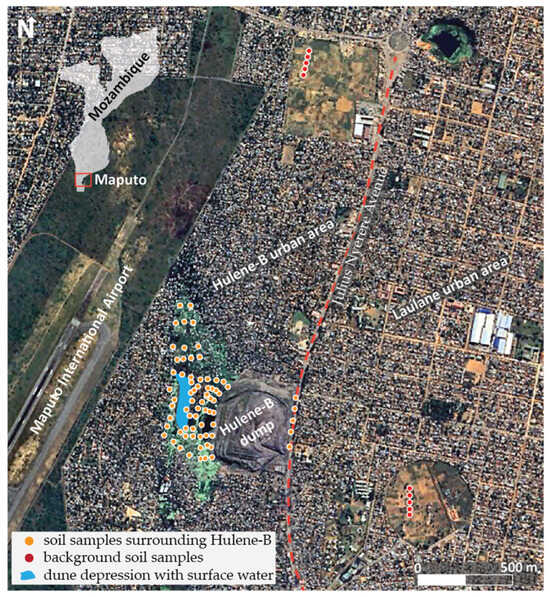
Figure 1.
Location of the Hulene-B waste dump and the distribution of sampled soils (orange dots) and background soils (red dots). The study area lies within densely urbanized zones that encompass two major residential communities (Hulene-B and Laulane urban areas) and the Maputo International Airport.
Geologically, the area around the Hulene-B dump belongs to the Meso–Cenozoic sedimentary basin of southern Mozambique. It is located at the contact zone between the Ponta Vermelha Formation and the Malhazine Formation, on a moderate dune slope with an E–W orientation [22,34,35]. Hydrogeologically, the Hulene-B area is part of the Tertiary–Quaternary aquifer system [34], with a substrate composed of clayey marl to gray clay layers [36]. A semi-impermeable layer of clayey sands has been identified, which promotes water circulation between the two sectors [36]. In some areas, coarse sands directly overlie the clay layer, creating semi-confined conditions [37]. Groundwater depth in local wells varies between 1.5 and 9.3 m, with an average of 3.8 m [34]. The western margin of the dump, due to its morphological configuration (intradune depression), is permanently covered by surface water. In contrast, in the northern part of the study area, periodic flooding occurs, particularly during the rainy season [24].
The region has a subtropical climate, with a mean annual precipitation of approximately 789 mm [38]. Two main climatic seasons are distinguished: (a) a hot and rainy period, from December to March, with a mean temperature of 25 °C and accounting for more than 60% of the annual precipitation, reaching a peak in January (~125 mm); and (b) a dry and cooler season, from April to September, with the lowest mean temperatures recorded in June and July (~21 °C), and minimal precipitation in August (~12 mm). The prevailing winds in the area predominantly blow from the southeast [33].
2.2. Sampling
Soil sampling was conducted during the rainy season (January 2020) and the dry season (May 2021). A total of 142 samples (71 per season; ±1.5 kg each) were collected at 0–20 cm depth in the area surrounding the Hulene-B dump, where soils were accessible, without houses and streets covering the soils (Figure 1). Samples were sequentially numbered: 1I to 71I for the rainy season and 1II to 71II for the dry season. The 2020 sampling took place during heavy rainfall, with a monthly average of 123 mm, whereas the 2021 sampling occurred under dry conditions, with a monthly average of 25 mm [38]. In addition, background samples (n = 10) were collected during both seasons from areas considered not directly affected by the dump. All samples were georeferenced, stored in plastic bags, and transported for laboratory processing. Although the rainy- and dry-season samplings were a year apart, both represent the typical seasonal extremes under the stable subtropical climate of Maputo, where interannual variability is minimal. The design aimed to capture process-based differences (leaching during wet periods vs. evaporation during dry periods). However, we acknowledge that minor non-seasonal factors, such as gradual waste accumulation, may have contributed to variability and were considered a limitation of this study.
2.3. Samples Analysis
In the laboratory of the Pedagogical University of Maputo (Mozambique), samples were oven-dried at ~40 °C and sieved to <2000 µm. Subsequently, they were transported to the GeoBioTec Research Center, University of Aveiro (Portugal), for detailed analyses and characterization.
Soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC) were determined in a 1:2.5 soil/water suspension using a multiparametric meter Hanna, HI 98494 model (Hanna Instruments®, Inc., Woonsocket, RI, USA). Organic matter (OM) content was quantified following the method described by Reeuwijk [39]. The clay fraction was determined using a Sedigraph III Plus grain size analyzer (Micromeritics®, Norcross, GA, USA), which calculates the relative mass distribution of particles based on sedimentation theory (Stokes’ law) and X-radiation absorption (Beer–Lambert law). Soil color was assessed using the Munsell soil color chart [40], with classifications defined according to color intensity, ranging from least to most intense.
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) was performed on the grounded samples, oxides Al2O3, CaO, Fe2O3, K2O, MgO, MnO, Na2O, P2O5, SiO2, SO3, TiO2, and trace elements Ba, Br, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Pb, Sb, Sn, and Zn. A Panalytical Axios PW4400/40 (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, Worcestershire, UK) was used with Rh radiation. Loss of ignition (LOI) was assessed by calcination in a muffle at 1000 °C for 3 h. Mineral phases were identified by X-ray diffraction (XRD), using a Philips/Panalytical powder diffractometer (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, Worcestershire, UK), model X’ Pert Pro MPD, with a Cu–X-ray tube operated at 50 kV and 30 mA, data collected from 2 to 70° 2θ with a step size of 0.01°, and a counting interval of 0.02 s [41]. After diffractogram interpretation, the relative abundance of each mineral phase was semi-quantitatively estimated based on the reflection intensities using the peak area method [42]. Soil chemical and mineralogical analysis results are presented in Tables S1–S3.
2.4. Chemical Alteration Indices
The degree of chemical alteration of the soils samples was assessed through four complementary geochemical weathering indices: the Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA), the Chemical Index of Weathering (CIW), the Plagioclase Index of Alteration (PIA), and the Weathering Index of Parker (WIP). These indices quantify the removal of mobile cations (Ca, Na, K, Mg) relative to the immobile Al fraction during chemical weathering or leaching [43,44,45,46]. In soils developed near waste dumps, chemical alteration indices provide a valuable tool to distinguish natural weathering processes from anthropogenic modifications induced by leachate infiltration. Elevated CIA, CIW, and PIA values may reflect the progressive leaching of alkali and alkaline-earth cations, but in landfill environments these apparent weathering signals can also result from carbonate and sulfate enrichment, alkali displacement, and secondary mineral precipitation. The complementary use of WIP combining CIA-type ratios with mineralogical and electrical conductivity data enables the recognition of leachate-driven alteration, characterized by alkali loss, salinization, and secondary carbonate accumulation, rather than by purely pedogenic clay formation. This integrative approach supports environmental interpretation of soils influenced by urban waste contamination.
2.4.1. Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA)
The CIA expresses the extent of feldspar alteration to clay minerals by comparing the proportion of immobile Al2O3 to the total of major base cations. It is computed on a molar basis using the following equation:
where CaO* represents Ca in silicate minerals only (Ca from carbonate, phosphate, and sulfate minerals is excluded). The index varies from ~50 for unweathered feldspars to 100 for highly weathered materials, in which alkali and alkaline-earth cations have been largely leached (Table 1) [43,47].

Table 1.
The CIA, CIW, PIA, and WIP indices typical alteration ranges [43,44,45,46,47].
2.4.2. Chemical Index of Weathering (CIW)
The CIW, introduced by Harnois [45], removes K2O from the denominator, as K can be secondarily reintroduced during illitization or adsorption. It is defined as follows:
The CIW generally yields slightly higher values than CIA for the same material. Values above 80 indicate advanced chemical alteration and alkali leaching, while lower values (<60) suggest fresh or weakly weathered detrital feldspars (Table 1).
2.4.3. Plagioclase Index of Alteration (PIA)
The PIA [44] isolates the alteration of plagioclase feldspars by excluding potassium. It is expressed as follows:
PIA values of ~50 indicate unweathered plagioclase, while values approaching 100 reflect complete transformation to kaolinite or gibbsite. The PIA is particularly sensitive to Na and Ca loss in the early stages of weathering (Table 1).
2.4.4. Weathering Index of Parker (WIP)
The WIP [46] uses cation valence and mobility factors to quantify overall base-cation depletion. It incorporates the relative abundance of the major alkalis and alkaline earths according to the equation:
All oxides are in molar proportions (per 100 g of sample). Unlike CIA-type indices, higher WIP values denote fresher material, and the index decreases with increasing chemical weathering intensity (Table 1).
2.4.5. Data Treatment
All indices were calculated on an anhydrous molar basis, using XRF major-oxide data. The correction for CaO* was performed by subtracting the Ca contributions from carbonate (calcite, dolomite), sulfate (anhydrite), and phosphate (apatite) phases determined with XRD and P2O5 contents [44]. When these minerals were absent, CaO* was approximated as the lesser of measured CaO and Na2O (in molar proportion), assuming plagioclase stoichiometry [43].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Descriptive statistics, independent-samples t-tests, one-way ANOVA, discriminant analysis, and principal component analysis (PCA) were performed using SPSS® v.25 software (IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). The t-test and one-way ANOVA were applied to evaluate statistical differences between samples and between sampling seasons. Discriminant analysis was employed to assess the accuracy of classifying soil samples into their respective season based on the measured variables, providing a predictive model for seasonal identification. PCA, a dimensionality reduction technique, was applied to identify a smaller set of independent variables (principal components) that explain most of the data variation [48]. Promax rotation was used in the PCA to account for potential correlations among variables, as soil and environmental parameters are rarely independent. This oblique rotation improves the interpretability of components compared with orthogonal rotations such as Varimax.
2.6. Surface Water Contamination Risk by Landfill
The surface water contamination risk (Pbci) from landfills was calculated using the landfill contamination environmental assessment parameters proposed by Calvo et al. [19]. To estimate contamination probability, landfill variables were selected according to their sensitivity to biochemical and physical processes that directly or indirectly affect the surrounding environment [49]. In this study, eight factors related to surface water were considered: (1) degree of compaction, (2) final cover, (3) leachate control, (4) type of waste and percentage of organic matter, (5) precipitation, (6) surface drainage systems, (7) waterproofing at the discharge point, and (8) distance to surface water. These variables were used to assess landfill contamination risk through the probability of each contamination variable (Pbcj), calculated as (Pbcj), by , where Wj is the weighting of variable j, Cj is the classification of variable j, dependent on the variable state, and providing information on the status of the interaction between disposal processes and environmental characteristics related to the variable, and N is the number of variables of each parameter. Weight values were assigned based on the characteristics of the evaluated factor, including contamination risk (Tables S4–S11). Risk classification corresponds to Pbci = 0 non-existent; 0 < Pbci < 0.3 low; 0.3 < Pbci < 0.6 mean; 0.6 < Pbci ≤ 1 high [19].
3. Results and Discussion
Dry season samples with higher clay content, between 2.5 and 5.4%, were ranked 1II > 67II > 2II > 11II > 21II > 66II > 4II, being collected on the SW and SE borders of the dump (Figure S1), while in rainy season, only one sample was detected with maximum clay content (2.6%; sample 65I), collected on the N sector of the study area. The sand fraction, prevalent in all soil samples from both sampling seasons (Table 2), showed higher values in samples collected in areas farther from the dump, suggesting an influence of waste in the proximity of the dump. The differences in silty and clayey fractions between seasons can be attributed to reduced/absent precipitation during the dry season, a significant factor in acceptable particle leaching, and fly ash deposition and accumulation on the soil surface, resulting from continuous open-air waste incineration occurring on the top of the dump. Dry season samples displayed slightly higher metal adsorption potential due to the content of clay and silt fractions, which can influence the adsorption of heavy metals in soils [29]. Background samples were also classified as sandy (93.8 to 95.4%) for both seasons.

Table 2.
Soil samples’ granulometric fractions descriptive statistics (in %).
The pH, EC, and OM of the background samples from the two sampling seasons revealed no significant differences (ANOVA 1-way; p > 0.05), suggesting that no significant impact factors substantially altered the analyzed parameters (Table 3).

Table 3.
Background soil samples’ parameters of dry (n = 10) and rainy (n = 10) seasons.
Soil samples surrounding the Hulene-B dump, collected during the rainy season, ranged from 6.7 to 8.0 in pH with a mean of 7.4 (Figure 2). The dry season samples’ sandy fraction varied from 7.6 to 10.5, being classified as neutral to alkaline. Soil samples’ pH showed a tendency to migration of PTEs [50]. In tropical regions, heavy metal retention in soils can occur under higher pH conditions due to the predominance of oxidic (Al, Fe, and Mn) and kaolinitic mineralogy, which increases metal adsorption capacity [51]. Bernardo et al. [26] suggested a predominance of Al, Fe, and Mn oxides, along with the presence of clay minerals, in the Hulene-B dump surrounding soils. This represents an essential factor in the PTEs adsorption and absorption even under mildly-alkaline-to-moderate conditions. Naveen et al. [52], in a similar study in India, suggested that soil alkalinity was linked to ash accumulation from waste incineration and the flow of leachates from waste biodegradation, representing potential factors in contamination and alteration of soil pH. Škrbić et al. [53] identified a greater heavy metal retention in soils with high pH, attributed to reduced metal solubility.

Figure 2.
Soil samples’ pH variation in the two sampling seasons.
Rainy season soil samples, EC, varied between 43 and 725 µS/cm, with an average of 221 µS/cm, revealing higher values in samples collected near the dumpsite (Figure 3). Samples collected during the dry season presented higher EC than rainy season, ranging from 90 to 9510 µS/cm, and an average of 1150 µS/cm. Spatially, dry season samples presented higher EC values near the dump, suggesting contamination accumulation. Electrical resistivity assays on the study area during the same periods [23] reported higher anomalies in depth during the dry period compared to the rainy period. These differences were associated with the poor superficial leaching occurring during the dry period. Ashraf et al. [54], in a study of soil contamination in the surroundings of a landfill in Pakistan, reported similar results. During dry periods, higher accumulation of heavy metals in the topsoil layer occurred, leading to higher EC and contamination [3,55]. Wu et al. [56] and Naveen et al. [52] suggested that in areas with sources of contamination, such as waste dumps, during dry periods, higher amount of waste transported and deposition of contaminants on the soil surface occur, which are related to higher EC in soils.

Figure 3.
Soil samples’ electrical conductivity (in µS/cm) variation in the two sampling seasons.
Organic matter content on rainy season soil samples ranged from 0.4 to 1.8%, with an average of 1.0%. Samples collected during the dry season ranged from 1.7 to 8.6%, with a mean of 1.9%. Samples located on the E and W borders of the dumpsite presented OM > 4% (Figure 4). Siddiqi et al. [9] proposed that OM in sandy soil is susceptible to leaching, which explains the relatively lower predominance of OM content during the rainy season. However, high OM content in topsoil may lead to contaminants uptake, as heavy metals bind easily to OM [57], which decreases toxicity levels [58].

Figure 4.
Soil samples’ organic matter (in %) variation in the two sampling seasons.
Soil samples’ color from the rainy season was mainly brownish (Figure 5), changing to grayish in dry season samples, and becoming blackish at the immediate limit of the dump. In general, areas with dark and brownish soil colors, near contamination sources such as dumps, have been associated with a greater capacity of the soil to absorb PTES. According to Nisari and Sujatha [58], soils exhibiting darker coloration near waste dumps often contain higher Fe–Mn oxide content, promoting PTE retention. Kanmani and Gandhimathi [59] and Hussein et al. [60] reported that leachate migration from open dumps and landfills leads to the accumulation of organic matter and metal oxides in adjacent soils, resulting in darkened surface horizons and enhanced metal adsorption capacity. Therefore, darker soil colors in areas adjacent to dumps can reflect enhanced potential for PTE absorption and accumulation. Grayish soil color in areas with leachates is associated with leaching processes, consistent with the dry season samples. In the surroundings of dumpsites, color is also influenced by solid waste incineration and ash deposition [61]. Weibel et al. [62] revealed that waste burning contributes to the dispersion of Hg-contaminated ash, which is subsequently deposited in topsoil, causing its enrichment and color variation. In the Hulene-B dump, waste burning occurs daily, with the wind softly transporting the resulting dust into the surrounding areas.

Figure 5.
Soil samples’ color variation in the two sampling seasons.
The ANOVA one-way analysis of the soil samples revealed significant differences (p < 0.01; Table S12) between sampling seasons. All the variables analyzed in this study showed higher values during the dry season, except for sand fraction, which was more representative during the rainy season. Additionally, the discriminant analyses of the two seasons showed that all samples were classified according to the sampling season, except for dry season 12II, 40II, and 52II (4.8%), which presented variables in agreement with the rainy season samples’ characteristics. Taking this into consideration, principal components analysis (PCA) was conducted separately for each sampling season group for variables sand, silt, clay, pH, EC, and OM.
The PCA was performed separately for both seasons, using the variables sand, silt, clay, OM, EC, and pH. For both seasons, two components were extracted, accounting for 82.05% (rainy period) and 83.80% (dry season) of the total variance. The first component (PC1) explained 61.82% (rainy season) and 63.95% (dry season) of total variance, grouping OM, silt, and clay, with sand in opposition (Figure 6). In this study, soil sand was the predominant fraction, being prevalent in samples more distant from the dumpsite. Samples closer to the Hulene-B waste dump showed higher content of OM and thinner fractions, partially related to the incorporation of leachates and ashes resulting from the incineration of solid wastes. The link established between these variables (PC1) can be related to their significance in soil and plant productivity [63], with different types of edible plants being continuously cultivated near the dump [28]. The second component (PC2) explained 17.32% (rainy season) and 19.85% (dry season) of total variance, with positive loadings by pH and EC. This PC can be explained by the lack of significant pH variation, predominantly alkaline conditions, with higher values near the dump. The soil samples’ high pH can be used as an indicator of soil contamination by heavy metals, particularly in tropical areas with a higher significance of Al and Fe oxides. The EC values were predominantly high in all samples, being more significant in samples collected near the dump, with values over the world average EC for sandy soils (<100 µS/cm).
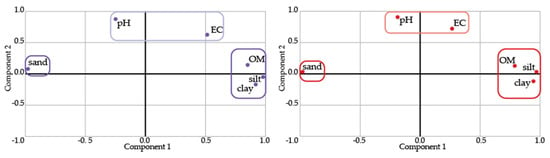
Figure 6.
Projection of principal component analysis variables by component of dry (left plot) and rainy (right plot) seasons.
- Chemical alteration indices
The chemical alteration indices of the soils around the Hulene-B waste dump revealed distinct seasonal variations related to climatic conditions and leachate–soil dynamics (Table 4). During the rainy season (I), CIA, CIW, and PIA values ranged from 2.3 to 75.9, 2.4–96.1, and 1.4–94.7, respectively, with mean values of 63.0, 84.6, and 79.4. In the dry season (II), these indices ranged from 46.8 to 83.2, 66.6–94.4, and 42.1–93.3, with slightly higher mean values (67.0, 86.3, and 80.4). These values suggested a moderate-to-high degree of apparent alteration in both seasons [43,44], but were promoted by different controlling mechanisms. During the rainy season, the lower quartile values of CIA, CIW, and PIA, together with the low CaO content (0.07–4.37%) and the predominance of quartz (>90%) (Tables S1 and S3), reflected significant leaching of mobile cations due to intense rainfall, surface runoff, and leachate percolation. The presence of residual feldspar and minor calcite in rainy season samples suggested incomplete alteration of detrital silicates. These leaching-dominated conditions, the removal of Na+, K+, and Ca2+, enhanced the apparent alteration indices despite clay neoformation remained limited. Similar seasonal trends have been described in tropical and subtropical landfills where seasonal rainfall accelerates cation removal through leachate percolation [5,9]. In contrast, dry-season samples displayed slightly higher mean CIA and CIW values, associated with higher CaO (up to 19.3%), and MgO (up to 1.05%) content, and abundant calcite, dolomite, and anhydrite content. These minerals were products of secondary carbonate and sulfate precipitation rather than continued silicate weathering. The increase in alteration indices during the dry season reflected chemical enrichment due to ion concentration and evaporative processes under limited rainfall, consistent with the semi-arid subtropical climate of Maputo [38]. Such enrichment processes can simulate natural weathering, but represent the anthropogenic alteration and salinization induced by leachate evaporation [15]. Mineralogically (Table S3), the dry-season soils (II) displayed a higher abundance of Σphyllosilicates and zeolitic phases, indicating partial feldspar alteration and the formation of secondary hydrated aluminosilicates and amorphous phases from leachate–soil reactions [29]. The higher EC and OM content in the dry period (II) suggested the accumulation of soluble ions and organic residues, enhancing cation exchange capacity and the immobilization of certain metals. Overall, both seasons exhibited a moderate alteration (mean CIA 63 (I)/70 (II)) characteristic of sandy, quartz-rich soils periodically affected by leachate infiltration and carbonate accumulation. The slightly higher dry-season indices were not indicative of intensified silicate weathering, but rather of post-evaporative enrichment in dissolved bases, producing elevated CIA/CIW/PIA ratios despite the low clay fraction (<5%). Similar behavior was reported for landfill-affected soils in subtropical regions [1,3].

Table 4.
Chemical Index of Alteration (CIA), Chemical Index of Weathering (CIW), and Plagioclase Index of Alteration (PIA) statistical results of the studied samples for rainy (I) and dry (II) seasons.
The Weathering Index of Parker (WIP) results were consistently low across all samples, ranging 0.1–0.6 (Table 4), corresponding to severe base-cation depletion [46]. However, this depletion was primarily due to alkali leaching and Ca sequestration in secondary carbonates and sulfates phases, rather than advanced pedogenesis. The inverse correlation between CIA/CIW and WIP is typical of soils influenced by alternating wet–dry leachate cycles, where soluble cations were lost during the rainy season and reprecipitated during the dry period [44,45]. Therefore, the WIP results supported the interpretation that the soils surrounding Hulene-B were under anthropogenic chemical alteration, characterized by leachate-derived salinity, carbonate accumulation, and alkali depletion during intense rainfall. The persistence of extremely low WIP values confirmed that base-cation removal and replacement by non-silicate phases were dominant alteration pathways, leading to apparent high CIA/CIW values even under limited natural weathering.
- The A–CN–K diagram
The A–CN–K ternary system (Al2O3–(CaO* + Na2O)–K2O) (Figure 7) of the studied soil samples revealed a mixed natural–anthropogenic alteration trend, controlled by seasonal hydrology, leachate infiltration, and secondary carbonate formation. Both rainy- and dry-seasons samples clustered along the A–K axis, extending toward the A vertex, corresponding to kaolinite–gibbsite–illite compositional fields [44,47]. This proximity indicated significant depletion in mobile alkalis (Na, K) and relative enrichment of Al2O3 during alteration. However, this trend did not represent advanced pedogenic weathering, but rather an apparent alteration driven by Na and K leaching under alkaline conditions, and Ca incorporation into carbonates and sulfates rather than silicate matrices. The rainy-season samples exhibited lower and more variable Al2O3 content (1.2–4.6%) and low K2O and Na2O, reflecting intense leaching during periods of high precipitation and runoff. These conditions can enhance alkali removal, with higher CIA, CIW, and PIA values, with samples near the A vertex. These patterns are common in tropical soils subjected to cyclic wetting, where the combined influence of natural weathering and leachate percolation generated high alteration indices even with minimal clay formation [64]. Conversely, the dry-season soils revealed higher Al2O3 and K2O content, and a slight increase in mean CIA, CIW, and PIA (Table 4). This pattern can result from evaporative enrichment and secondary carbonate formation, rather than progressive feldspar alteration. The mineral content confirmed abundant calcite, dolomite, and anhydrite, together with Σphyllosilicates and zeolitic phases, indicating precipitation from leachate-rich solutions during the lowering of the water table. In the A–CN–K diagram (Figure 7), these processes produced a horizontal trend toward the K vertex, reflecting partial K enrichment and residual illitization, consistent with the geochemical environment and mineral assemblage [15]. Overall, the A–CN–K system defined a restricted compositional field near the A–K merge, reflecting moderate apparent alteration. The absence of clear plagioclase weathering (from feldspar join to A vertex) confirmed that the chemical signatures were predominantly anthropogenic rather than purely pedogenic. These soils can be classified as leachate-altered materials, with seasonal chemical variability controlled by leaching intensity during wet months and evaporative concentration during dry periods.
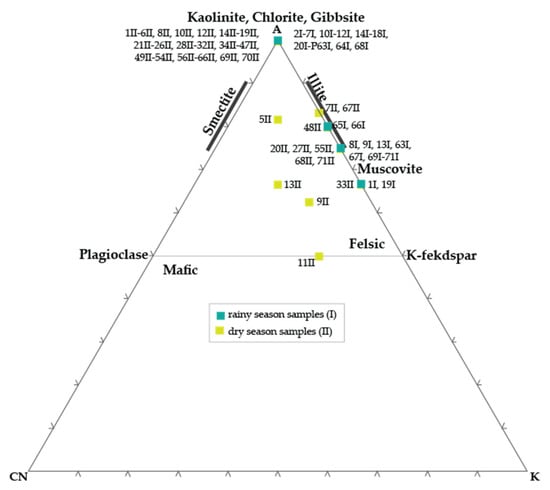
Figure 7.
Rainy (I) and dry (II) season samples projected in the A–CN–K ternary diagram (Al2O3–(CaO* + Na2O)–K2O). Mineral fields from Obasi et al. [65].
- Potentially toxic elements
The potentially toxic elements (PTEs) concentration showed marked differences between the rainy (I) and dry (II) seasons (Table S2), reflecting the combined influence of leachate composition, climate, and soil geochemistry. Median concentrations were considerably lower in the rainy season than in the dry season. Maximum values (Cu = 5970, Zn = 16,100, Pb = 1230, Cr = 1080 mg/kg) suggested episodic metal enrichment due to landfill leachate influx [27,28]. Seasonal contrasts can be linked to hydrological concentration mechanisms, once infiltration and runoff promote dilution and lateral dispersion of soluble metals during the rainy season, while in the dry season, low rainfall and strong evapotranspiration enhance solute concentration and secondary precipitation of metals in the upper soil layers. The elevated Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cr contents during the dry period coincide with the high CaO and SO3 levels and abundant carbonate–sulfate phases, suggesting metal co-precipitation or absorption onto carbonates and Fe–Mn oxyhydroxides [1,3]. Elevated Sb and Sn (up to 200 and 740 mg/kg) further indicate inputs from electronic and battery waste, consistent with the composition of the Hulene-B rejected materials. Soils proximal to the landfill boundaries, characterized by alkaline pH and high EC, exhibited a significant PTEs accumulation, linked to reduced metal mobility under high ionic strength and carbonate buffering. These geochemical conditions favor the formation of insoluble metal carbonates (e.g., ZnCO3, PbCO3) and hydroxide complexes, limiting vertical migration but enhancing local retention [15,29].
- Risk of surface water contamination (Pbci)
The weights (W) and ranking levels (C) were assigned to the studied variables, based on the characteristics of the landfill and its surroundings [19]: (1) compaction, given its precariousness processes at Hulene-B dump, was characterized by being partial, being assigned as W = 2, and C = 3; (2) cover material, once being an open-air landfill without any mechanism to cover the waste, was assigned as W = 2, and C = 4; (3) leachate control, at the N, S, and W borders of the landfill, where leachates drain, being in open air and cyclically overflowing, with no underground isolation, likely contributing to migration of leachates in depth (Figure 7), was attributed W = 2 to surface water, and W = 1 to soil, and C = 4; (4) age and percentage of OM, once the landfill dates from 1973 (~50 years of age), assuming little leachate generation but >1 t of miscellaneous waste deposited daily, and an estimated 50% of organic, was attributed W = 2 and C = 4; (5) impermeability of discharge point, being a landfill that is neither itself nor its surroundings waterproofed, increasing the potential risk of soil, ground, and surface water contamination, W = 1 for soils, W = 2 for surface water, and C = 4; (6) being Hulene-B dump located in flood-prone areas, the surroundings of the dump is susceptible to inundation, given the lack of mechanisms to adequately control surface flows leading to widespread flooding by surface leachate from Hulene-B dump, W = 4 and C = 2 (Figure 8); (7) rainfall, average annual precipitation of ~789 mm, with precipitation influencing decomposition and leachate production, W = 2 and C = 2 were assigned; and (8) existence and distance of surface water, W of the dump surface water occupying the surface of the dune depression every year and other cyclically floods at more distant areas, W = 2 and C = 4. Thus, the contamination risk of surface water was 0.91 (Table 5), with almost all factors contributing to higher values, except for the compaction factor, given the process of waste compaction by bulldozer that has taken place in recent years.

Figure 8.
Field images illustrating (a) leachates along the western boundary of the Hulene-B waste dump, (b) leachate seepage at the southern boundary, and (c) adjacent surface water potentially influenced by leachate migration.

Table 5.
Variables weight and contamination risk (Pbci) result of surface water around Hulene-B waste dump.
A high risk of surface water contamination was identified, taking into consideration Hulene-B dump characteristics and contamination processes occurring by leachate-free circulation at various points of the W boundary (Figure 7). This risk is also taking into consideration ashes deposition on the surrounding soils of Hulene-B dump, originating from the uncontrolled incineration of continuously deposited waste. These represent vectors of contamination and alteration of soil properties. Bernardo et al. [24] suggested a high risk of soil and groundwater contamination, mainly by leachate in the surrounding area of Hulene-B waste dump. Naveen et al. [66] showed high levels of surface water and soil contamination in the surroundings of a landfill in Bangalore (India) and associated it with the contaminant content in leachates. Although the Pbci index is based on landfill management criteria rather than direct pollutant measurements, its high-risk result (0.91) was consistent with the measured geochemical evidence, including high EC, pH, and metal (Cu, Zn, Pb, Cr) contents in the surrounding soils. The risk of surface water contamination was selected as a complementary indicator that reflected field-observed contamination patterns while acknowledging its qualitative and non-quantitative nature.
4. Conclusions
The temporal variation in soil properties around the Hulene-B waste dump revealed a clear seasonal contrast promoted by rainfall and leachate dynamics. Soils collected during the rainy season exhibited characteristics indicative of intense leaching, with lower organic matter, electrical conductivity, clay, and silt contents, compared to the dry season. In contrast, the dry-season soils showed conditions more favorable for contaminant accumulation in the upper horizons, consistent with reduced leaching and evaporative concentration. The predominance of blackish-to-brownish coloration in dry-season samples further supports limited percolation and the retention of leachate-derived compounds.
Geochemically, the alteration indices (CIA, CIW, PIA, WIP) suggested a moderate to high degree of alteration, dominated by alkali leaching and carbonate–sulfate enrichment related to landfill processes. The A–CN–K ternary diagram confirmed that most samples cluster near the Al–K compositional field, showing significant depletion of mobile cations (Ca, Na, K) and relative Al2O3 enrichment typical of soils affected by cyclic wetting–drying and leachate percolation. Results showed that the chemical variability reflected anthropogenic alteration rather than pedogenic weathering.
The risk of surface water contamination (Pcbi) was classified as high, consistent with field observations of uncontrolled leachate flow and ash deposition around the dump. The Pcbi confirmed that the Hulene-B waste dump acts as a persistent source of soil and water contamination, influencing both surface and groundwater quality. Further research should integrate seasonal monitoring of potentially toxic elements and hydrochemical tracing of leachates to refine contamination pathways. Overall, the findings emphasize the urgent need for structural remediation and containment measures at the Hulene-B dump, particularly targeting leachate drainage, ash management, and improved waste compaction, to mitigate ongoing environmental degradation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app152111663/s1, Figure S1. Samples by collection location; Table S1. Major elements chemical composition of the studied samples for rainy (I) and dry (II) seasons (in %); Table S2. Potentially toxic elements chemical composition of the studied samples for rainy (I) and dry (II) seasons (in mg/kg); Table S3. Mineral phases identified in the studied samples for rainy (I) and dry (II) seasons (in %); Table S4. Compaction Ranking–Assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, factor selected considering the dump characteristics); Table S5. Daily Coverage–Assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, factor selected considering the dump characteristics); Table S6. Control Leachate–Assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, factor selected considering the dump characteristics); Table S7. Final Cover–Assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, factor selected considering the dump characteristics); Table S8. Type of waste–Assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, factor selected considering the dump characteristics); Table S9. Waterproofing the discharge point–Assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, factor selected considering the dump characteristics); Table S10. Rainfall assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, indicating the factor selected based on dump characteristics); Table S11. Distance to surface water bodies assessment criteria and assigned scores (in green, factor selected considering the dump characteristics); Table S12. Anova 1-way analysis, test of homogeneity of variances.
Author Contributions
Methodology, C.C., F.R.; validation, C.C., F.R.; formal analysis, B.B., C.C.; investigation, C.C., F.R.; writing—original draft preparation, C.C.; writing—review and editing, C.C., B.B., F.R.; supervision, C.C., F.R.; funding, F.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was partially supported by GeoBioTec (UIDB/04035) Research Centre, funded by FEDER funds through the Operational Program Competitiveness Factors COMPETE and by National funds through FCT. The first author acknowledges a grant from the Portuguese Institute Camões and FNI (National Investigation Fund—Mozambique).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data is not publicly available due to privacy concerns.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Souza, V.; Hollas, C.; Bortoli, M.; Manosso, F.; Souza, D. Heavy metal contamination in soils of a decommissioned landfill in southern Brazil: Ecological and health risk assessment. Chemosphere 2023, 339, 139689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audu, P.; Wuana, R. Evaluating the Levels and Human Health Risks of Heavy Metals in Soils around Onne Landfill, Rivers State, Nigeria. Int. Res. J. Pure Apl. Chem. 2021, 22, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, A.; Singh, D.; Shukla, S. Assessment of human health risk due to leachate contaminated soil at solid waste dumpsite, Kanpur (India). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 21, 909–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toha, M.; Sikder, S.; Rahman, M. An Overview of Existing Municipal Landfill Leachate Treatment Techniques: Opportunities and Challenges. In Landfill Leachate Treatment Techniques; Souabi, S., Anouzla, A., Eds.; Springer Water: Cham, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaki, K.; Karhat, Y.; Falaki, K. Temporal Monitoring and Effect of Precipitation on the Quality of Leachate from the Greater Casablanca Landfill in Morocco. Pollution 2022, 8, 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, T.; Mahmood, N.; Othman, F. Estimation of leachate generation from MSW landfills in Selangor. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotech. Environ. Sci. 2017, 19, 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Wijekoon, P.; Koliyabandara, P.; Cooray, A.; Lam, S.; Athapattu, B.; Vithanage, M. Progress and prospects in mitigation of landfill leachate pollution: Risk, pollution potential, treatment and challenges. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Lin, S.; Ye, L.; Qu, D.; Yang, H.; Chang, H.; Yu, H.; Yan, Z.; Rong, H.; Qu, F. Landfill leachate treatment by direct contact membrane distillation: Impacts of landfill age on contaminant removal performance, membrane fouling and scaling. Desalination 2024, 577, 117407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, S.; Al-Mamun, A.; Sana, A.; Baawain, M.; Choudhury, M. Characterization and pollution potential of leachate from urban landfills during dry and wet periods in arid regions. Water Supply 2022, 22, 3462–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udoh, U.; Babatunde, O.; Ibrahim, I.; Fidelis, G.; Eke, C. The Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination and Ecological Risks in Soils Surrounding Dumpsites in Ikwuano LGA, Abia State. Int. J. Adv. Biol. Biomed. Res. 2025, 13, 405–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Balajiang, G.; Dang, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhao, W.; Cong, Y.; Ai, S. Spatial distribution, pollution assessment and source identification of heavy metals in Yarlung Zangbo River, Tibet. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2025, 202, 107768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouhakki, H.; Hmouni, D.; El Fallah, K.; El Mejdoub, N.; Adiba, A. Groundwater quality dynamics in Doukkala, Morocco—Exploring seasonal and temporal variations in physicochemical and bacteriological traits. J. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 26, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagnanelli, F.; Esposito, A.; Toro, L. Metal speciation and pH effect on Pb, Cu, Zn and Cd biosorption onto Sphaerotilus natans: Langmuir-type empirical model. Water Res. 2003, 37, 627–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobadi, R.; Altaee, A.; Zhou, J.; Karbassiyazdi, E.; Ganbat, N. Effective remediation of heavy metals in contaminated soil by electrokinetic technology incorporating reactive filter media. J. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 794, 148668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagwar, P.; Dutta, D. Landfill leachate a potential challenge towards sustainable environmental management. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 926, 171668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Gao, Y.; Yang, Y. Leaching of heavy metals from lead-zinc mine tailings and the subsequent migration and transformation characteristics in paddy soil. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoya, A.; Kamelia, M.; Sari, I. Analysis of the amount of leachate pollution on the environmental health of settlements at Bakung final disposal site Bandar Lampung City. J. Eduhealth 2023, 14, 707–712. Available online: https://ejournal.seaninstitute.or.id/index.php/healt/article/view/2092 (accessed on 3 February 2025).
- Rapti-Caputo, A.; Sdao, F.; Masi, S. Pollution risk assessment based on hydrogeological data and management of solid waste landfills. Eng. Geol. 2006, 85, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvo, F.; Moreno, B.; Zamorano, M.; Szanto, M. Environmental diagnosis methodology for municipal waste landfills. Waste Manag. 2005, 25, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, C. Da Problemática Ambiental à Mudança: Rumo à um Mundo Melhor; Escolar Editora, Ed.; Universidade Católica de Moçambique (UCM): Maputo, Mozambique, 2012. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- CMCM Quadro da Política de Reassentamento—QPR Novembro de 2020. Conselho Municipal da Cidade de Maputo, 2020. Available online: https://documents1.worldbank.org/curated/en/964181607106676324/pdf/Revised-Resettlement-Framework-Maputo-Urban-Transformation-Project-P171449.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2022).
- Vicente, E.; Jermy, C.; Schreiner, H. Urban geology of Maputo, Mozambique. Eng. Geol. Tomorrow’s Cities Geol. Soc. Lond. Eng. Geol. Spec. Publ. 2006, 338, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Integration of Electrical Resistivity and Modified DRASTIC Model to Assess Groundwater Vulnerability in the Surrounding. Water 2022, 14, 1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Application of Geophysics in geo-environmental diagnosis on the surroundings of the Hulene-B waste dump, Maputo, Mozambique. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2022, 185, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Soil properties and environmental risk assessment of soils in the surrounding area of Hulene-B waste dump, Maputo (Mozambique). Environ. Earth Sci. 2022, 81, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Characterization of the Dynamics of Leachate Contamination Plumes in the Surroundings of the Hulene-B Waste Dump in Maputo, Mozambique. Environments 2022, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. Soil Risk Assessment in the Surrounding Area of Hulene-B Waste Dump, Maputo (Mozambique). Geosciences 2022, 12, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardo, B.; Candeias, C.; Rocha, F. The Contribution of the Hulene-B Waste Dump (Maputo, Mozambique) to the Contamination of Rhizosphere Soils, Edible Plants, Stream Waters, and Groundwaters. Environments 2023, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoai, S.; Lan, H.; Viet, N.; Hoang, G.; Kawamoto, K. Characterizing seasonal variation in landfill leachate using leachate pollution index (LPI) at nam son solid waste landfill in Hanoi, Vietnam. Environments 2021, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbay, G.; Jones, M.; Gadde, M.; Isah, S.; Attarwala, T. Design and operation of effective landfills with minimal effects on the environment and human health. J. Environ. Public Health 2021, 2021, 6921607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INE Boletim de Estatísticas Demográficas e Sociais, Maputo Cidade 2019. Instituto Nacional de Estatistica, 2020. Available online: https://www.ine.gov.mz/ (accessed on 22 October 2022).
- Ferrão, D. Evaluation of Removal and Disposal of Solid Waste in Maputo City, Mozambique. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Cape Town, Cape Town, South Africa, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Muchangos, L.; Tokai, A.; Hanashima, A. Analyzing the structure of barriers to municipal solid waste management policy planning in Maputo city, Mozambique. Environ. Dev. 2015, 16, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cendón, D.I.; Haldorsen, S.; Chen, J.; Hankin, S.; Nogueira, G.; Momade, F.; Achimo, M.; Muiuane, E.; Mugabe, J.; Stigter, T. Hydrogeochemical aquifer characterization and its implication for groundwater development in the Maputo district, Mozambique. Quat. Int. 2020, 547, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momade, F.; Ferrara, M.; Oliveira, J. Notícia Explicativa da Carta Geológica 2532 Maputo (Escala 1:50000); Direcção Nacional de Geologia (DNG), Ministério dos Recursos Minerais e Energia: Maputo, Mozambique, 1996. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Muchimbane, A. Estudo dos Indicadores da Contaminação das Aguas Subterrâneas por Sistemas de Saneamento in Situ—Distrito Urbano 4. Ph.D. Dissertation, São Paulo University, Cidade de Maputo, Moçambique, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Nogueira, G.; Stigter, T.; Zhou, Y.; Mussa, F.; Juizo, D. Understanding groundwater salinization mechanisms to secure freshwater resources in the water-scarce city of Maputo, Mozambique. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 661, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CIAT. Climate-Smart Agriculture in Mozambique. Center for Tropical Agriculture, 2017. Available online: https://climateknowledgeportal.worldbank.org/sites/default/files/2019-06/CSA-in-Mozambique.pdf (accessed on 8 October 2022).
- Reeuwijk, L. Procedures for Soil Analysis; International Soil Reference and Information Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Munsell Soil Color Charts: With Genuine Munsell Color Chips; Munsell Color, X-Rite, Inc.: Grand Rapids, MI, USA, 2009.
- Candeias, C.; Santos, I.; Rocha, F. Characterization and Suitability for Ceramics Production of Clays from Bustos, Portugal. Minerals 2025, 15, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biscaye, P. Mineralogy and Sedimentation of Recent Deep-Sea Clay in the Atlantic Ocean and Adjacent Seas and Oceans. GSA Bull. 1965, 76, 803–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.; Young, G. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites. Nature 1982, 299, 15–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedo, C.; Nesbitt, H.; Young, G. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance. Geology 1995, 23, 921–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnois, L. The CIW index: A new chemical index of weathering. Sediment. Geol. 1988, 55, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, A. An Index of Weathering for Silicate Rocks. Geol. Mag. 1970, 107, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesbitt, H.; Young, G. Prediction of some weathering trends of plutonic and volcanic rocks based on thermodynamic and kinetic considerations. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1984, 48, 1523–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groth, D.; Hartmann, S.; Klie, S.; Selbig, J. Principal Components Analysis. In Computational Toxicology. Methods in Molecular Biology; Reisfeld, B., Mayeno, A., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012; Volume 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryampa, S.; Maheshwari, B.; Sabiiti, E.; Olobo, C.; Bateganya, N. Adaptation of EVIAVE methodology to landfill environmental impact assessment in Uganda—A case study of Kiteezi landfill. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2021, 183, 104310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rieuwerts, J.; Ashmore, M.; Farago, M.; Thornton, I. The influence of soil characteristics on the extractability of Cd, Pb and Zn in upland and moorland soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 366, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alleoni, L.; Iglesias, C.; Mello, S.; Camargo, O.; Casagrande, J.; Lavorenti, N. Soil attributes related to cadmium and copper adsorption in tropical soils. Acta Sci. Agron. 2005, 27, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Naveen, B.; Mahapatra, D.; Sitharam, T.; Sivapullaiah, P.; Ramachandra, T. Physico-chemical and biological characterization of urban municipal landfill leachate. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škrbić, B.; Čupić, S. Trace Metal Distribution in Surface Soils of Novi Sad and Bank Sediment of the Danube River. J. Environ. Sci. Health 2004, 39, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.; Zeshan, M.; Hafeez, S.; Hussain, R.; Qadir, A.; Majid, M.; Ahmad, S. Temporal variation in leachate composition of a newly constructed landfill site in Lahore in context to environmental pollution and risks. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 37129–37143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeez, J.; Hassan, O.; Egunjobi, P. Soil contamination at dumpsites: Implication of soil heavy metals distribution in municipal solid waste disposal system: A case study of Abeokuta, southwestern Nigeria. Soil Sediment Contam. 2011, 20, 370–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Wang, L.; Yang, R.; Hou, W.; Zhang, S.; Guo, X.; Zhao, W. Pollution characteristics and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil of a construction waste landfill site. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmo, D.; Lima, L.; Silva, C. Soil Fertility and Electrical Conductivity Affected by Organic Waste Rates and Nutrient Input. Soil. Use Manag. 2016, 40, e0150152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisari, A.; Sujatha, C. Assessment of trace metal contamination in the Kol wetland, a Ramsar site, Southwest coast of India. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 47, 101953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanmani, S.; Gandhimathi, R. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in soil due to leachate migration from an open dumping site. Appl. Water Sci. 2013, 3, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.; Yoneda, K.; Mohd-Zaki, Z.; Amir, A.; Othman, N. Heavy metals in leachate, impacted soils and natural soils of different landfills in Malaysia: An alarming threat. Chemosphere 2021, 267, 128874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Deng, H.; Li, M.; Chai, X. Mercury transport and fate in municipal solid waste landfills and its implications. Biogeochemistry 2020, 148, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weibel, G.; Eggenberger, U.; Schlumberger, S.; Mäder, U. Chemical associations and mobilization of heavy metals in fly ash from municipal solid waste incineration. Waste Manag. 2017, 62, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Paepe, J.; Alvarez, R. Development of a Regional Soil Productivity Index Using an Artificial Neural Network Approach. Agron. J. 2013, 105, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buggle, B.; Glaser, B.; Hambach, U.; Gerasimenko, N.; Marković, S. An evaluation of geochemical weathering indices in loess–paleosol studies. Quat. Int. 2011, 240, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obasi, R.; Madukwe, H.; Nnabo, P. Geochemistry, weathering intensity and palaeoclimatic conditions of soils around dumpsites from Ibadan, Oyo State, Nigeria. Eur. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2020, 7, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Naveen, B.; Sumalatha, J.; Malik, R. A study on contamination of ground and surface water bodies by leachate leakage from a landfill in Bangalore, India. Int. J. Geo-Eng. 2018, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).