Multi-Agent Multimodal Large Language Model Framework for Automated Interpretation of Fuel Efficiency Analytics in Public Transportation
Abstract
1. Introduction
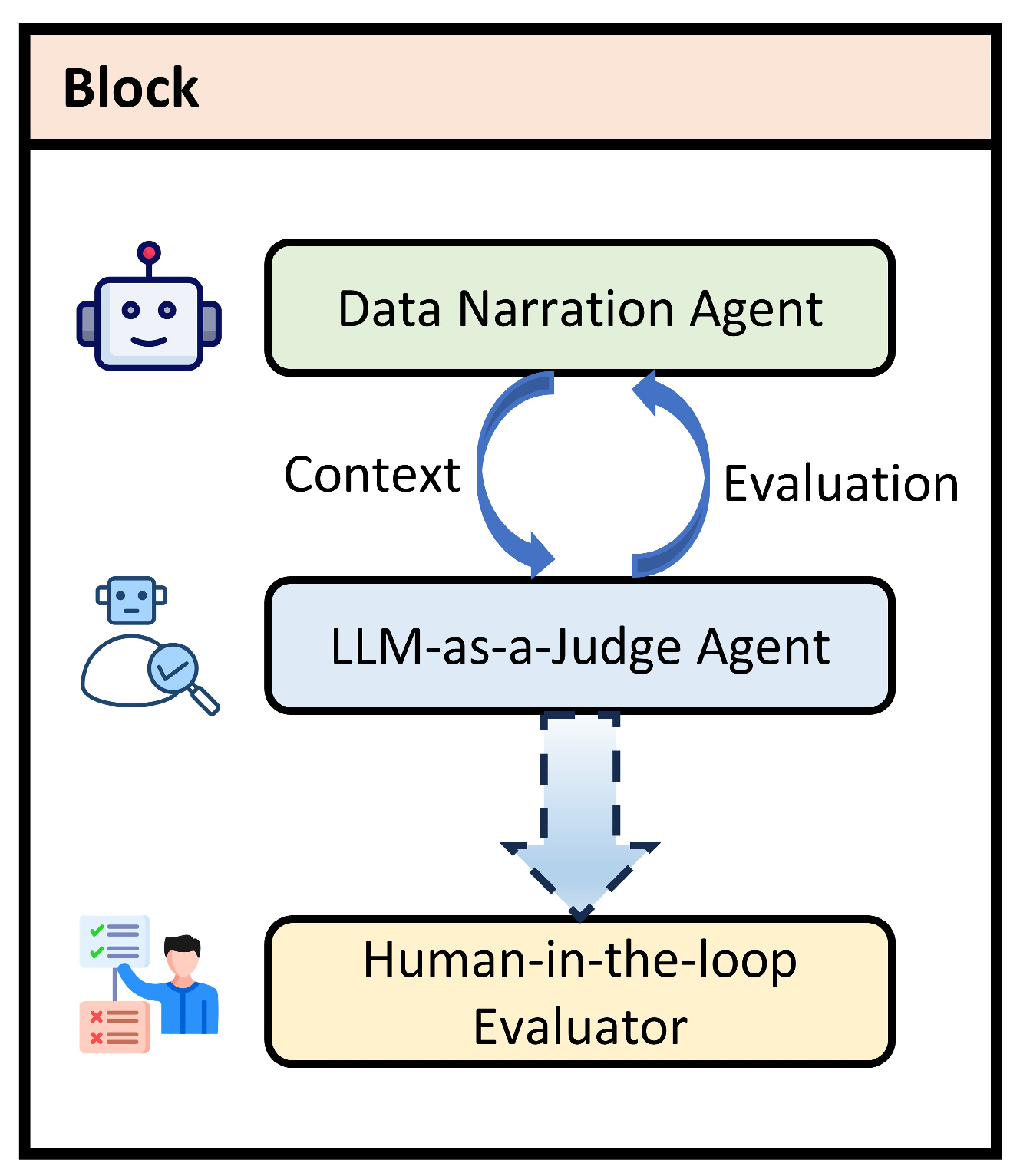
- A data narration agent, which interprets multimodal inputs and generates textual narratives;
- An LLM-as-a-judge agent, which evaluates narrative quality, coherence, and relevance;
- An optional human-in-the-loop evaluator, which enables expert refinement in sensitive applications.
2. Related Work
2.1. Multimodal Large Language Models
2.2. Prompt Engineering
2.3. Multimodal LLMs for Data Narration
3. Materials and Methods
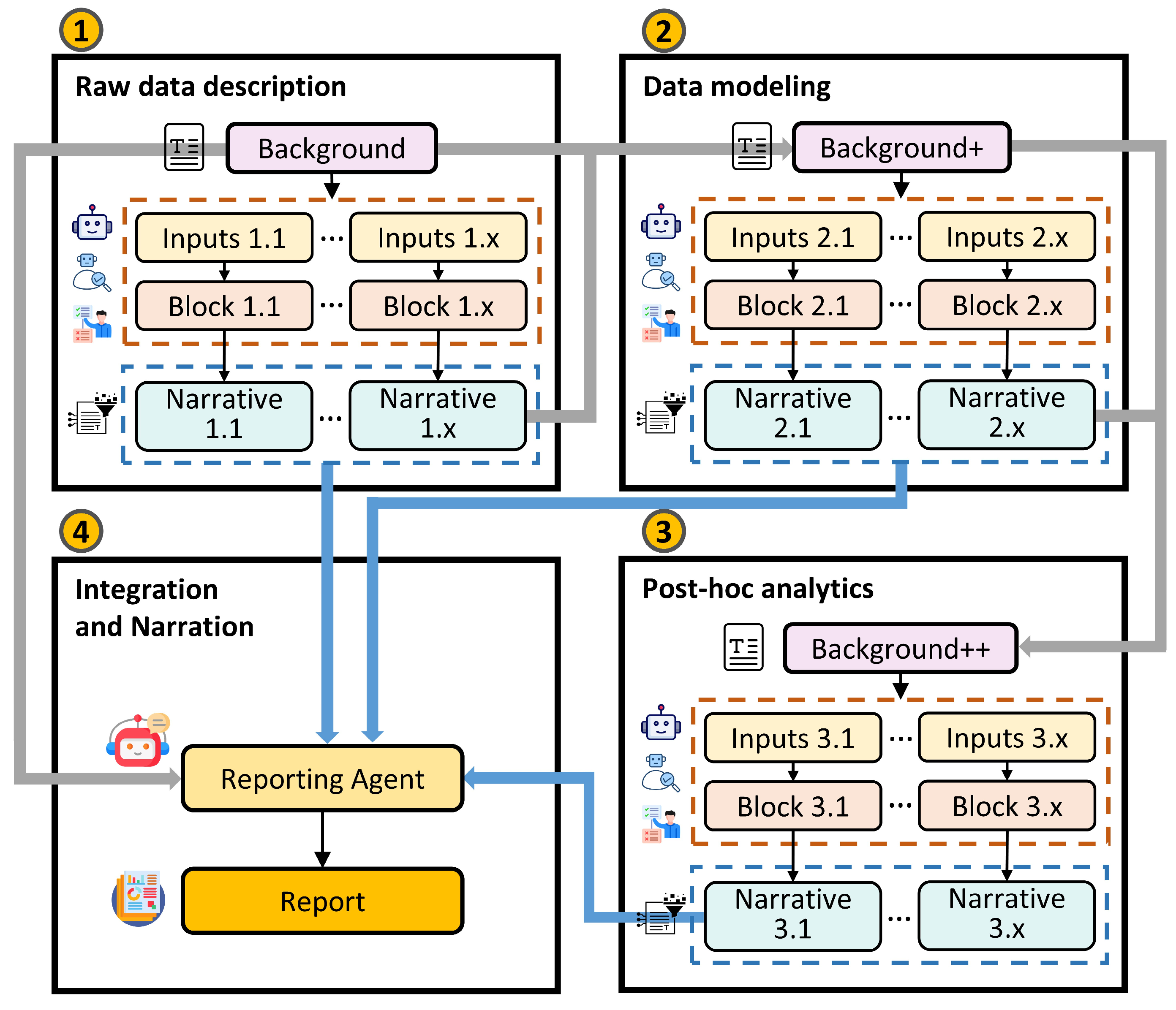
3.1. Multi-Agent Architecture
3.2. Workflow of the Multi-Agent Framework
4. Case Study
5. Experiments and Results
5.1. Experiment Design and Settings
- Execution time, measured in seconds, quantifies the time required to generate each narrative;
- Cost, measured in cents (0.01 USD), reflects the expense of using the model based on its API pricing;
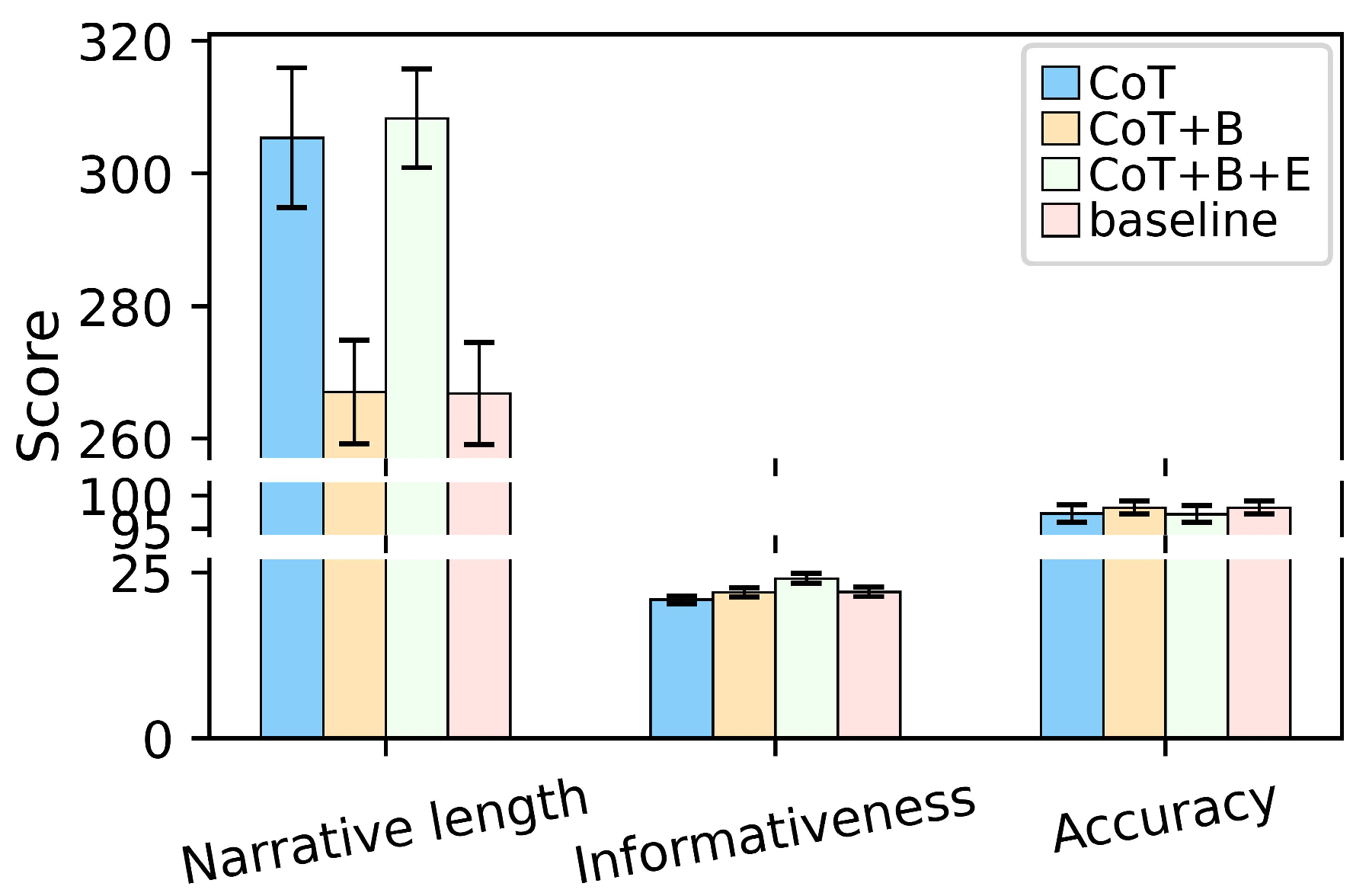
- Narrative length, defined as the total word count of the generated output;
- Informativeness, measured as the number of distinct information points extracted from the visual input;
- Accuracy, calculated as the percentage of correct information points relative to the total number of points generated.
- Accurate Narrative Information Density (ANID), defined as the number of correct distinct information points per 100 words in a generated narrative.
- Flesch Reading Ease (FRE) [37]: A readability score that indicates how easy a text is to read, with higher values corresponding to easier reading (typically ranging from 0 to 100).
- Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level (FKGL) [37]: A metric that estimates the U.S. school grade level required to understand the text, with lower values indicating greater accessibility.
- Automated Readability Index (ARI) [38]: Another readability measure based on word and sentence length, providing a numeric grade level; lower values reflect simpler language.
- Cost: The monetary cost of generating each report, measured in cents (USD 0.01), based on API pricing for each model.
- Report length (RL): The total word count of the generated report, reflecting the amount of explanatory content produced.
- Number of recommendations with data support (NRDS): The subset of recommendations explicitly grounded in the data narratives.
- Percentage of recommendations with data support (PRDS): The percentage of recommendations explicitly grounded in the data narratives relative to the total number of actionable suggestions included in the report.
5.2. Prompts and LLM Selection
| LLM | Prompting | Time (s) | Cost (cent) | Narrative Length | Informativeness | Accuracy (%) | ANID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4.1 mini | CoT | 13.27 0.849 | 0.24 0.008 | 305.4 10.54 | 20.91 0.567 | 97.31 1.295 | 6.73 0.267 |
| CCoT | 41.48 2.383 | 0.62 0.020 | 288.2 13.14 | 20.36 0.646 | 98.52 1.056 | 7.13 0.384 | |
| DN | 10.91 0.411 | 0.23 0.007 | 315.9 10.83 | 25.55 0.999 | 95.45 1.518 | 7.75 0.273 | |
| o4-mini | CoT | 14.53 0.595 | 0.96 0.023 | 285.1 11.37 | 21.91 0.698 | 96.97 1.158 | 7.55 0.334 |
| CCoT | 39.17 1.823 | 2.37 0.056 | 257.6 11.92 | 20.45 0.754 | 96.17 1.776 | 7.76 0.397 | |
| DN | 19.17 1.301 | 1.10 0.038 | 308.9 17.42 | 25.45 1.474 | 94.43 1.830 | 7.80 0.232 | |
| Claude 3.5 Haiku | CoT | 9.80 0.417 | 0.42 0.002 | 207.3 5.20 | 16.70 0.736 | 84.46 4.597 | 6.94 0.539 |
| CCoT | 21.69 0.617 | 1.05 0.040 | 192.2 4.81 | 17.10 0.767 | 91.14 4.895 | 8.35 0.700 | |
| DN | 12.65 1.667 | 0.45 0.002 | 230.8 3.97 | 19.60 0.710 | 91.48 3.014 | 7.84 0.475 | |
| Gemini 2.5 Flash | CoT | 8.96 0.623 | 0.11 0.007 | 287.5 11.14 | 20.55 0.965 | 92.91 0.018 | 6.67 0.300 |
| CCoT | 22.87 1.297 | 0.29 0.007 | 227.2 8.30 | 16.82 6.533 | 90.16 3.404 | 6.82 0.469 | |
| DN | 5.14 0.249 | 0.07 0.003 | 278.9 16.49 | 21.27 1.554 | 90.60 3.011 | 7.19 0.304 | |
| Llama 4 Maverick | CoT | 26.00 2.615 | N/A | 220.1 13.41 | 18.64 0.412 | 88.64 2.756 | 7.71 0.398 |
| CCoT | 56.17 4.459 | N/A | 228.7 7.79 | 17.91 0.537 | 91.36 2.938 | 7.19 0.304 | |
| DN | 27.24 2.387 | N/A | 242.4 11.57 | 19.18 0.861 | 89.83 2.409 | 7.13 0.247 |
5.3. Ablation Study
6. Discussion
6.1. Interpretation of Results and Integration with Prior Work
6.2. Scientific Contributions and Novelty
6.3. Methodological Limitations
6.4. Domain-Specific Challenges, Generalizability, and Ethical Implications
6.4.1. Generalizability and Practical Adaptation
6.4.2. Ethical and Human-in-the-Loop Considerations
6.5. Future Research Directions
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANID | Accurate Narrative Information Density |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| ARI | Automated Readability Index |
| CCoT | Contrastive Chain-of-Thought |
| CoT | Chain-of-Thought |
| DN | DataNarrative (prompting strategy) |
| DS-Agent | Data Science Agent |
| FKGL | Flesch-Kincaid Grade Level |
| FRE | Flesch Reading Ease |
| GMM | Gaussian Mixture Model |
| IT | Information Technology |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| NRDS | Number of Recommendations with Data Support |
| PDE | Probability Density Estimate |
| PRDS | Percentage of Recommendations with Data Support |
| RAG | Retrieval-Augmented Generation |
| RL | Report Length |
| RLHF | Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback |
| SHAP | SHapley Additive exPlanations |
| SQL | Structured Query Language |
| USD | United States Dollar |
Appendix A. Prompt Engineering
| Listing A1. The prompt used to generate data narratives. |
| [System Prompt] You are a genius data analyst who can process and explain multimodal scientific data. You have domain specific knowledge in transportation and fuel efficiency. Firstly, I will give you a background file, introducing the project background and raw data. Next, I will give you an image, which can be a chart or another type of data representation. Please describe and interpret the context of this image. [User Prompt] Here is the background file: {background} Firstly, based on the content in the file and your global knowledge, please generate the domain knowledge in this field and store this knowledge in your mind. Secondly, based on your generated domain knowledge and the background file, please think step by step to solve the following task. The task is as follows:
|
| Listing A2. The prompt used to evaluate data narratives. |
| [System Prompt] You are a genius and experienced data analyst who can process text files and write high-quality report. The report is aimed to make recommendations and decision support for the stakeholders in bus companies without technical background. [User Prompt] Based on the project introduction in the file: {background}, and your global knowledge, please generate the global domain knowledge in this field and store the knowledge in your mind. Now, please read and analyze the following files: …, which store the analysis and explanation of scientific figures related to this project. The project description and motivation are in {background}. Please write a high-quality report to make recommendations for the stakeholders in bus companies. The report should follow the following tasks:
|
| Listing A3. The prompt used to generate the report. |
| [System Prompt] You are a genius and fair data analyst and evaluator that can process and assess text files generated by another LLM agent accurately. I will give you two files. The first one is the project introduction. The second is the generated context waiting for your evaluation. Please return the results as the JSON output. [User Prompt] Based on the project introduction in the file: {background}, and your global knowledge, please generate the global domain knowledge in this field and store the knowledge in your mind. Next, based on the project introduction, please evaluate the file {text}, generated by another LLM agent, which explains an image of data analytics results in this project following the following steps:
{“evaluation_scores”: { “Clarity”: <score>, “Relevance”: <score>, “Insightfulness”: <score>, “Contextualization”: <score>, “Overall_score”: <average score of above four>, }, “evaluation_report”: <providing scores of each criterion, explanation of scores of each criterion, overall evaluation results and summary>} |
| Listing A4. Evaluation criteria in the LLM-as-a-judge agent. |
| 1. Clarity: Clarity refers to how well the descriptions convey the message without ambiguity. Information should be presented logically and in a way that is easily understood by the intended audience. - **0—Inadequate**: Information is confusing and unclear. - **1—Needs Improvement**: Some parts are clear, but overall understanding is hindered. - **2—Satisfactory**: Generally clear but lacks depth or contains minor ambiguities. - **3—Proficient**: Very clear, easy to understand, logical flow, with minimal effort needed for comprehension. - **4—Excellent**: Exceptionally clear; no ambiguity, and very engaging in presentation. 2. Relevance: Relevance assesses whether the content directly pertains to the project objectives and the data being analyzed. - **0—Inadequate**: Content is largely irrelevant and does not relate to the project objectives. - **1—Needs Improvement**: Some relevant points, but many unrelated aspects. - **2—Satisfactory**: Mostly relevant, with some minor digressions. - **3—Proficient**: Highly relevant, with all points supporting project objectives. - **4—Excellent**: Entirely relevant; addresses the core analytic objectives with precision. 3. Insightfulness: Insightfulness measures how well the content provides unique or valuable insights derived from the data. - **0—Inadequate**: No insights are provided; merely descriptive. - **1—Needs Improvement**: Some insights, but largely superficial or expected. - **2—Satisfactory**: Provides some valuable insights but lacks depth. - **3—Proficient**: Strong insights that provoke thought or highlight significant implications. - **4—Excellent**: Deep insights that provide new avenues of thought. 4. Contextualization: This evaluates how well the data and conclusions are placed within a broader context, such as environmental or policy implications. - **0—Inadequate**: No contextual information provided. - **1—Needs Improvement**: Minimal context; does not fully connect findings to the broader implications. - **2—Satisfactory**: Some contextual elements present, but could be enhanced for better clarity. - **3—Proficient**: Good contextualization, connecting findings to relevant implications. - **4—Excellent**: Comprehensive context that frames the findings within larger environmental and policy discussions. |
| Listing A5. Template for data narration. |
| 1. [Chart] Type and Purpose This is a [type of chart] showing [very brief statement of what is being compared or analyzed]. 2. Key Variables and Metrics If it is a chart, the output should be: The x-axis denotes [list main variables/metrics] with [units or scale if applicable]. The y-axis denotes [list main variables/metrics] with [units or scale if applicable]. 3. Main Findings and Trends The primary observation is [dominant pattern or trend]. [Mention any secondary or more observations if needed]. The observed trend shows [the insights and explanations of trends and outliers]. 4. Statistical Insights The [type of chart] indicates [basic statistical result, e.g., p-value, R2, mean, etc.]. The [type of chart] illustrates [insights and analysis of interconnected attributes]. 5. Contextual Implications This suggests [main relevance or application in industrial/data science context]. |
Appendix B. Examples
| No. | Narratives | Model and Prompting Method | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | This is a histogram showing the distribution of fuel efficiency values measured in liters per 100 km (L/100 km). | CoT + GPT-4.1 mini | N/A |
| This is a histogram showing the distribution of fuel efficiency for a dataset of vehicles. | CoT + Gemini 2.5 flash | It is short and misses some information. | |
| 2 | The y-axis denotes the number of occurrences or frequency of vehicles within each fuel efficiency range, with values ranging from 0 to 2500. | CoT + GPT-4.1 mini | N/A |
| The y-axis denotes the number of observations or frequency. | CoT + Llama 4 maverick | It does not describe a specific chart. | |
| 3 | This is a ternary scatter plot showing the distribution and clustering of data points based on three variables: Rural, Urban, and Highway. | CoT + GPT-4.1 mini | N/A |
| This is a triangular scatter plot showing the distribution of data points across three categorical dimensions: Urban, Rural, and Highway. | CoT + Claude 3.5 haiku | “triangular scatter plot” is not a formal and accurate name. | |
| 4 | The distribution illustrates that while some routes have low entropy, indicating predictability, others have moderate to high entropy, reflecting more variability in route types within the cluster. | CoT + GPT-4.1 mini | It is detailed and has better explanations. |
| The histogram illustrates the distribution shape and highlights multiple common entropy levels rather than a uniform spread. | CCoT + GPT-4.1 mini | This explanation focuses on statistics. | |
| The distribution is bimodal, suggesting two dominant patterns of route type diversity within the cluster. | DN + GPT-4.1 mini | It is incorrect, there are three dominant patterns. |
| No. | Narratives | Model and Prompting Method | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | This is a density plot combined with a scatter plot showing the distribution and clustering of fuel efficiency values for bus trips in public transportation. | CoT+B/baseline | “CoT+B” and baseline are same in this sentence. “bus trips in public transportation” is generated from background. |
| This is a density plot combined with a scatter plot showing the distribution and clustering of fuel efficiency values (measured in liters per 100 km) across different clusters. | CoT | No background information. | |
| 2 | The primary observation is that a large proportion of drivers have very low entropy values close to 0, indicating that these drivers tend to have bus trips concentrated in a single cluster. | CoT+B/baseline | “CoT+B” and baseline are same in this sentence. More concise. |
| The primary observation is that a large proportion of drivers have very low entropy values close to 0, indicating that most drivers tend to have bus trips concentrated in a single cluster rather than spread evenly across all four clusters. | CoT+B+E | Longer but do not provide more useful information. | |
| 3 | The initial Cluster 0 is divided into two distinct clusters: Cluster 0 and Cluster 3. Cluster 0 shows a wider spread with lower density at moderate fuel efficiency values, while Cluster 3 appears at higher fuel efficiency values (above 80 L/100 km). | Baseline | This is provided through human intervention, which cannot be generated through data reasoning. |
Appendix C. Report
| Listing A6. Generated technical report. |
| Report on Fuel Efficiency Analysis in Public Bus Transportation: Insights and Recommendations for Stakeholders Introduction This report presents a comprehensive analysis of fuel efficiency in public bus transportation based on data collected from 4006 bus trips …, during the week of … The primary objective of the study is to … Employing Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM) clustering, … Subsequent post hoc analyses explore …, providing actionable insights for stakeholders … Data Description The dataset comprises fuel efficiency measurements expressed in liters per 100 km (L/100 km) for each bus trip, defined as … The distribution of fuel efficiency values reveals that …. Notably, the distribution is right-skewed, with a long tail extending towards … This pattern indicates that …, suggesting variability in … Clustering Analysis The application of GMM clustering effectively partitions the bus trips into four distinct clusters, …. Cluster 0, … Cluster 1, the largest cluster encompassing 2857 trips, centers around moderate fuel efficiency with a mean of 46.03 L/100 km and a range from 29.16 to 56.02 L/100 km. Cluster 2 …, while Cluster 3, … The density plot and scatter visualization confirm that … Post Hoc Analysis: Driver Distribution Examining the distribution of clusters across individual drivers reveals that most drivers predominantly operate within Cluster 1, indicating … Entropy analysis of driver trip distributions further supports these findings … Post Hoc Analysis: Route Distribution The distribution of clusters across bus routes shows that … Entropy analysis of routes reveals that … These insights imply that … Post Hoc Analysis: Route Type Distribution The analysis of route type composition across clusters highlights … Cluster 2 trips show moderate route type diversity, with a tendency towards … Recommendations Based on the comprehensive analysis, several recommendations emerge for stakeholders in bus companies aiming to enhance fuel efficiency: 1. Driver-Focused Interventions: … 2. Route-Specific Strategies: … 3. Route Type Considerations: … 4. Monitoring and Continuous Analysis: … Conclusion This study demonstrates that fuel efficiency in public bus transportation is influenced by … The use of GMM clustering reveals … By leveraging these insights, bus companies can … |
References
- Sahu, G.; Puri, A.; Rodriguez, J.; Abaskohi, A.; Chegini, M.; Drouin, A.; Taslakian, P.; Zantedeschi, V.; Lacoste, A.; Vazquez, D.; et al. Insightbench: Evaluating business analytics agents through multi-step insight generation. In Proceedings of the The Thirteenth International Conference on Learning Representations, Singapore, 24–28 April 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, C.; Gao, S. MDSF: Context-Aware Multi-Dimensional Data Storytelling Framework based on Large language Model. arXiv 2025, arXiv:250101014. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.; Ouyang, C.; Jing, Y.; Fang, H.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R. Application of LLM Techniques for Data Insights in DHP. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 4th International Conference on Digital Twins and Parallel Intelligence (DTPI), Wuha, China, 18–20 October 2024; pp. 656–661. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.S.; Laskar, M.T.; Parvez, M.R.; Hoque, E.; Joty, S. DataNarrative: Automated data-driven storytelling with visualizations and texts. In Proceedings of the 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, Miami, FL, USA, 12–16 November 2024; pp. 19253–19286. [Google Scholar]
- Otten, J.J.; Cheng, K.; Drewnowski, A. Infographics and public policy: Using data visualization to convey complex information. Health Aff. 2015, 34, 1901–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Lim, E.P.; Wang, Y. LLM4Vis: Explainable Visualization Recommendation using ChatGPT. In Proceedings of the 2023 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: Industry Track, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 675–692. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, D.; Chen, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Zhou, P.; Sun, L. Mllm-as-a-judge: Assessing multimodal llm-as-a-judge with vision-language benchmark. In Proceedings of the Forty-first International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024; pp. 6562–6595. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.Y.; Chang, K.J.; Yang, C.F.; Wu, H.Y.; Chen, W.; Bansal, H.; Chen, L.; Yang, Y.P.; Chen, Y.C.; Chen, S.P.; et al. Towards a holistic framework for multimodal LLM in 3D brain CT radiology report generation. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, R.; Hasan, R.; Farhad, A.A.; Laskar, M.T.; Ashmafee, M.H.; Kamal, A.R. ChartSumm: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Automatic Chart Summarization of Long and Short Summaries. In Proceedings of the 36th Canadian Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Montreal, QC, Canada, 5–9 June 2023; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, K.; Riedl, M. Creating Suspenseful Stories: Iterative Planning with Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the 18th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics, St. Julian’s, Malta, 17–22 March 2024; Volume 1, pp. 2391–2407. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, A.; Shi, Y.; Xu, H.; Ye, J.; Ye, Q.; Yan, M.; Li, C.; Qian, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F. mplug-paperowl: Scientific diagram analysis with the multimodal large language model. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Melbourne, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024; pp. 6929–6938. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Qu, H. From data to story: Towards automatic animated data video creation with llm-based multi-agent systems. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE VIS Workshop on Data Storytelling in an Era of Generative AI (GEN4DS), St. Pete Beach, FL, USA, 13 October 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 20–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Tang, J.; Zang, C.; Pei, M.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, Z. Let storytelling tell vivid stories: A multi-modal-agent-based unified storytelling framework. Neurocomputing 2025, 622, 129316. [Google Scholar]
- Shojaee, P.; Mirzadeh, I.; Alizadeh, K.; Horton, M.; Bengio, S.; Farajtabar, M. The illusion of thinking: Understanding the strengths and limitations of reasoning models via the lens of problem complexity. arXiv 2025, arXiv:250606941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satpute, A.; Gießing, N.; Greiner-Petter, A.; Schubotz, M.; Teschke, O.; Aizawa, A.; Gipp, B. Can llms master math? investigating large language models on math stack exchange. In Proceedings of the 47th International ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and Development in Information Retrieval, Washington, DC, USA, 14–18 July 2024; pp. 2316–2320. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, C.L.; Eisenschlos, J.M.; Perot, V.; Wang, Z.; Miculicich, L.; Fujii, Y.; Shang, J.; Lee, C.Y.; et al. Chain-of-table: Evolving tables in the reasoning chain for table understanding. arXiv 2024, arXiv:240104398. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z.; Jorgensen, B.N.; Ma, Z. A Scoping Review of Energy-Efficient Driving Behaviors and Applied State-of-the-Art AI Methods. Energies 2024, 17, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Jørgensen, B.N.; Ma, Z. Fuel Efficiency Analysis of the Public Transportation System Based on the Gaussian Mixture Model Clustering. In Proceedings of the EPIA Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Viana do Castelo, Portugal, 3–6 September 2024; pp. 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Dong, J.; Li, C.; Su, D.; Chu, C.; Yu, D. MM-LLMs: Recent Advances in MultiModal Large Language Models. In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2024; Association for Computational Linguistics: Brooklyn, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 12401–12430. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI Introducing GPT-4.1 in the API. Available online: https://openai.com/index/gpt-4-1/ (accessed on 14 April 2025).
- Anthropic. Introducing Claude 4. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com/news/claude-4 (accessed on 22 May 2025).
- Google DeepMind. Gemini 2.5 Pro. Available online: https://deepmind.google/models/gemini/pro/ (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- OpenAI Introducing OpenAI o3 and o4-mini. Available online: https://openai.com/index/introducing-o3-and-o4-mini/ (accessed on 16 April 2025).
- Anthropic. Introducing Computer Use, a New Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Claude 3.5 Haiku. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com/news/3-5-models-and-computer-use (accessed on 22 October 2024).
- Google DeepMind. Gemini 2.5 Flash. Available online: https://deepmind.google/models/gemini/flash/ (accessed on 20 May 2024).
- Sahoo, P.; Singh, A.K.; Saha, S.; Jain, V.; Mondal, S.; Chadha, A. A systematic survey of prompt engineering in large language models: Techniques and applications. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.07927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.D.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language models are few-shot learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Xia, F.; Chi, E.; Le, Q.V.; Zhou, D. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 24824–24837. [Google Scholar]
- Chia, Y.K.; Chen, G.; Tuan, L.A.; Poria, S.; Bing, L. Contrastive chain-of-thought prompting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:231109277. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Lee-Urban, S.; Johnston, G.; Riedl, M. Story generation with crowdsourced plot graphs. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Bellevue, WA, USA, 14–18 July 2013; pp. 598–604. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.J.; Boggust, A.; Satyanarayan, A. Vistext: A benchmark for semantically rich chart captioning. In Proceedings of the 61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Toronto, ON, Canada, 9–14 July 2023; Volume 1, pp. 7268–7298. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Choi, H.J.; Hsu, T.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Kim, S.; Rossi, R.; Yu, T.; Giles, C.L.; Huang, T.H.; et al. Multi-LLM Collaborative Caption Generation in Scientific Documents. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2501.02552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Deng, C.; Wen, Y.; Chen, H.; Chang, Y.; Wang, J. DS-agent: Automated data science by empowering large language models with case-based reasoning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Vienna, Austria, 21–27 July 2024; pp. 16813–16848. [Google Scholar]
- Michalowski, M.; Wilk, S.; Bauer, J.M.; Carrier, M.; Delluc, A.; Le Gal, G.; Wang, T.F.; Siegal, D.; Michalowski, W. Manually-Curated Versus LLM-Generated Explanations for Complex Patient Cases: An Exploratory Study with Physicians. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 9–12 July 2024; pp. 313–323. [Google Scholar]
- Meta, A.I. The Llama 4 Herd: The Beginning of a New Era of Natively Multimodal AI Innovation. Available online: https://ai.meta.com/blog/llama-4-multimodal-intelligence/ (accessed on 5 April 2025).
- Marulli, F.; Campanile, L.; de Biase, M.S.; Marrone, S.; Verde, L.; Bifulco, M. Understanding readability of large language models output: An empirical analysis. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2024, 246, 5273–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.A.; Senter, R. Automated Readability Index; Aerospace Medical Research Laboratories, Aerospace Medical Division, Air Force Systems Command: Dayton, OH, USA, 1967; Volume 66, pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Chkirbene, Z.; Hamila, R.; Gouissem, A.; Devrim, U. Large language models (llm) in industry: A survey of applications, challenges, and trends. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 21st International Conference on Smart Communities: Improving Quality of Life using AI, Robotics and IoT (HONET), Doha, Qatar, 3–5 December 2024; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, C.I.; DiBattista, M.A.; Letelier, T.A.; Halloran, H.D.; Camelio, J.A. Framework for LLM applications in manufacturing. Manuf. Lett. 2024, 41, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LLM | FRE | FKGL | ARI | Cost | RL | NRDS | PRDS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-4.1 | 21.26 | 14.88 | 16.64 | 2.52 | 1080 | 5 | 100 |
| GPT-4.1 mini | 19.45 | 14.63 | 16.37 | 0.47 | 1127 | 5 | 100 |
| o4-mini | 28.50 | 12.95 | 14.77 | 1.52 | 982 | 3 | 75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, Z.; Bahja, A.R.; Burgdorf, A.; Pomp, A.; Meisen, T.; Jørgensen, B.N.; Ma, Z.G. Multi-Agent Multimodal Large Language Model Framework for Automated Interpretation of Fuel Efficiency Analytics in Public Transportation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111619
Ma Z, Bahja AR, Burgdorf A, Pomp A, Meisen T, Jørgensen BN, Ma ZG. Multi-Agent Multimodal Large Language Model Framework for Automated Interpretation of Fuel Efficiency Analytics in Public Transportation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111619
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Zhipeng, Ali Rida Bahja, Andreas Burgdorf, André Pomp, Tobias Meisen, Bo Nørregaard Jørgensen, and Zheng Grace Ma. 2025. "Multi-Agent Multimodal Large Language Model Framework for Automated Interpretation of Fuel Efficiency Analytics in Public Transportation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111619
APA StyleMa, Z., Bahja, A. R., Burgdorf, A., Pomp, A., Meisen, T., Jørgensen, B. N., & Ma, Z. G. (2025). Multi-Agent Multimodal Large Language Model Framework for Automated Interpretation of Fuel Efficiency Analytics in Public Transportation. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11619. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111619









