Design of a Six-Phase Surface Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor with Chamfer-Shaped Magnet to Reduce Cogging Torque and Torque Ripple for Large-Ship Propulsion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Six-Phase SPMSM for Large-Ship Propulsion
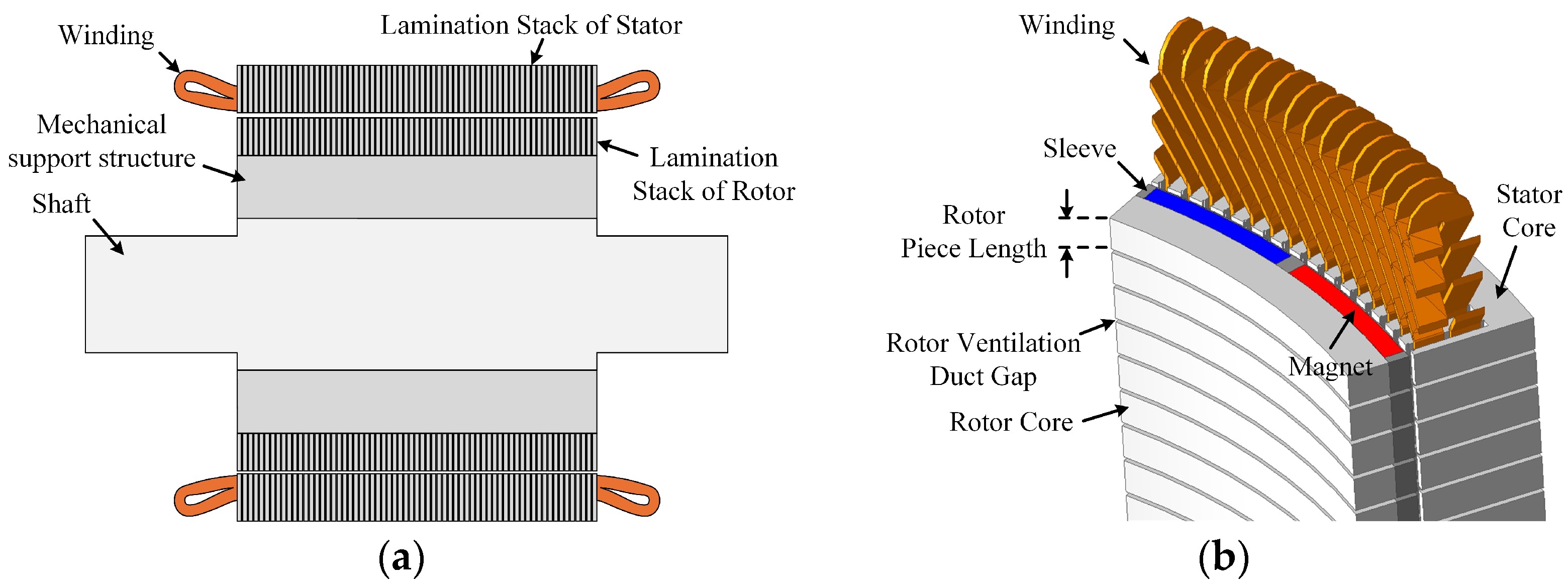
2.1. Machine Structure for Large-Ship Propulsion
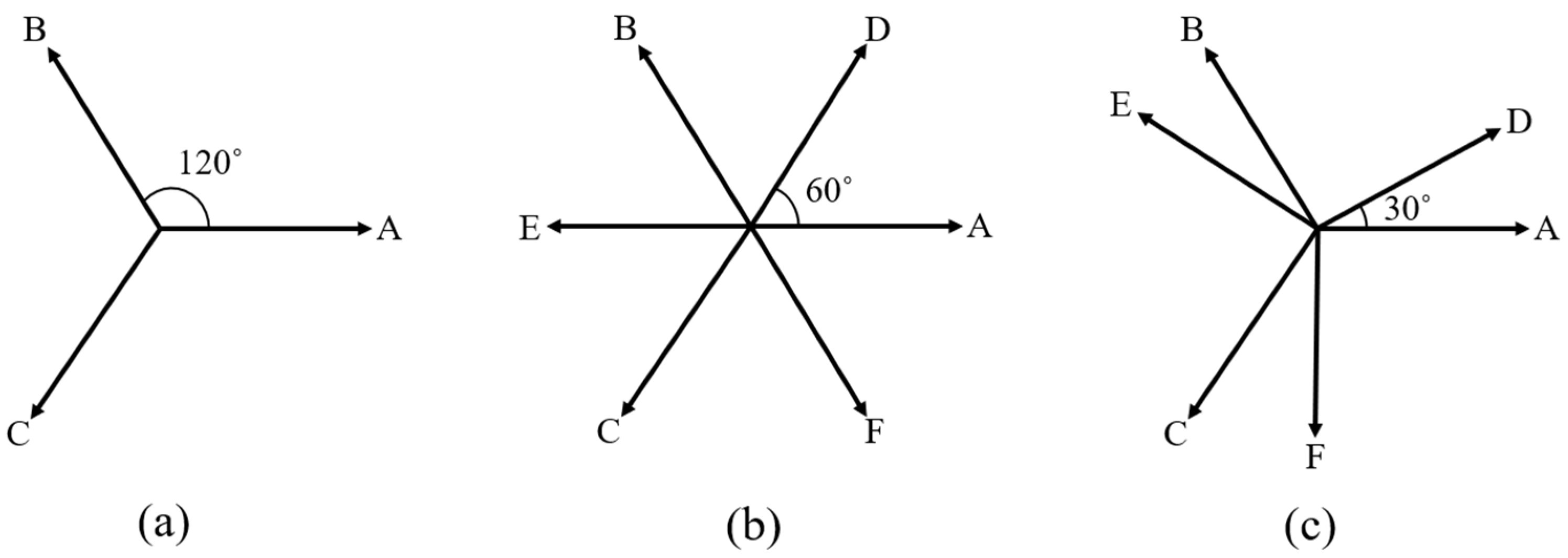
2.2. Six-Phase Configuration
- (a)
- BEMF of three-phase winding:
- (b)
- BEMF of symmetric six-phase winding:
- (c)
- BEMF of asymmetric six-phase winding:
2.3. Cogging Torque
2.4. Electromagnetic Torque
- (a)
- Current of three-phase winding:
- (b)
- Current of symmetric six-phase winding:
- (c)
- Current of asymmetric six-phase winding:
- (a)
- Electromagnetic torque of three-phase winding:
- (b)
- Electromagnetic torque of symmetric six-phase winding:
- (c)
- Electromagnetic torque of asymmetric six-phase winding:
3. Design of Six-Phase SPMSM with Chamfered Magnet Shape
3.1. Basic Design Specification
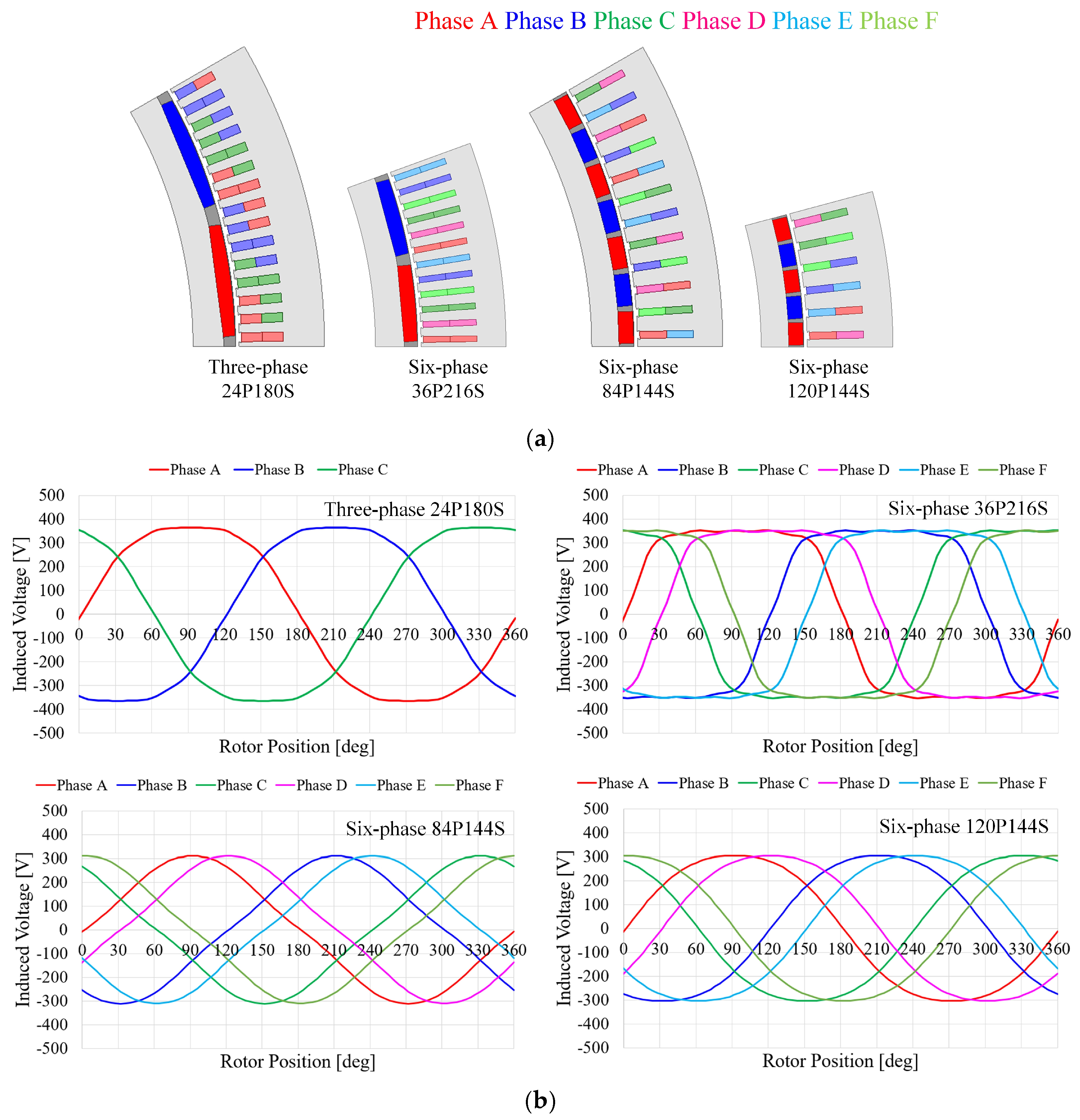
3.2. Pole–Slot Combination for Six-Phase Winding
3.3. Chamfered Magnet Shape Design
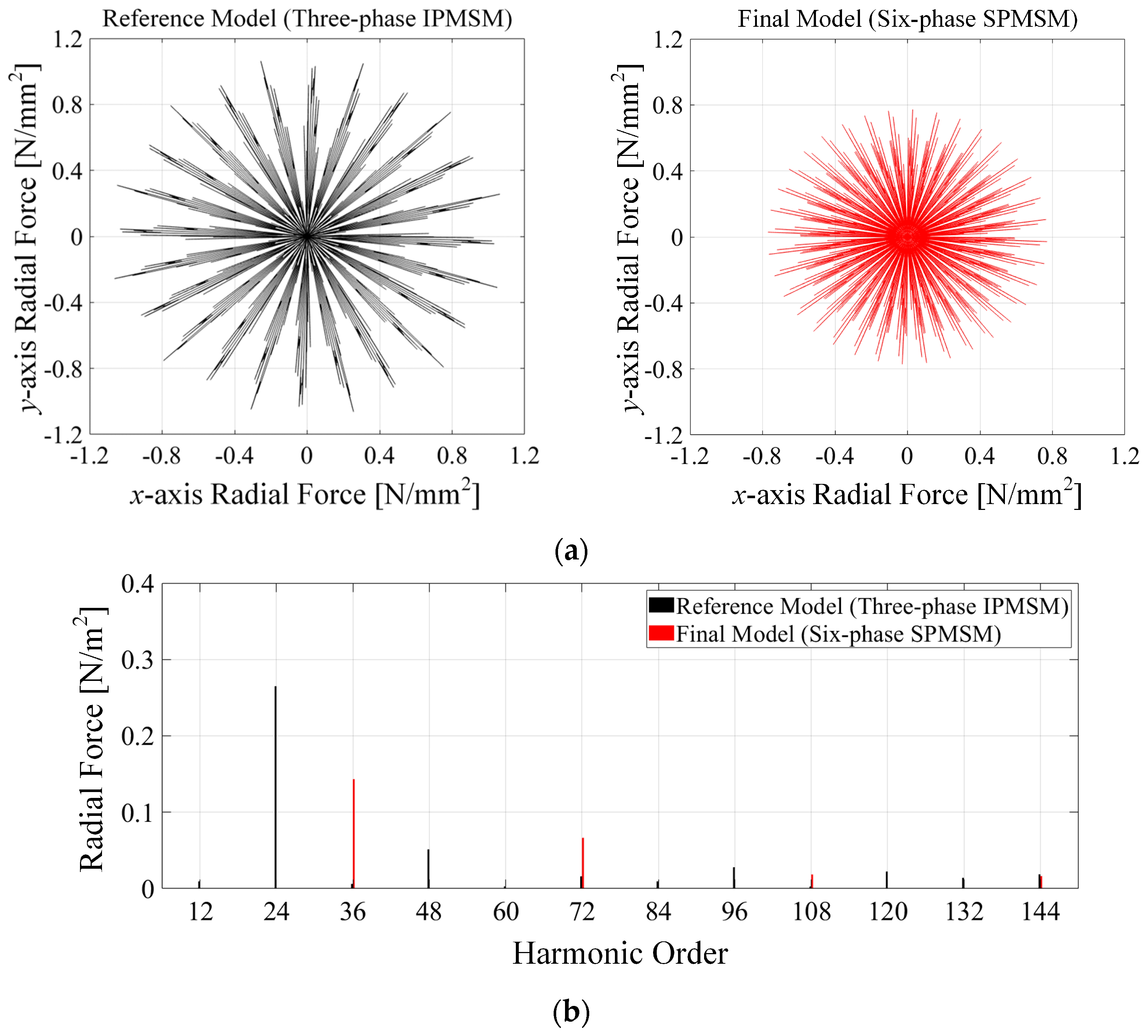
4. Performance Comparison
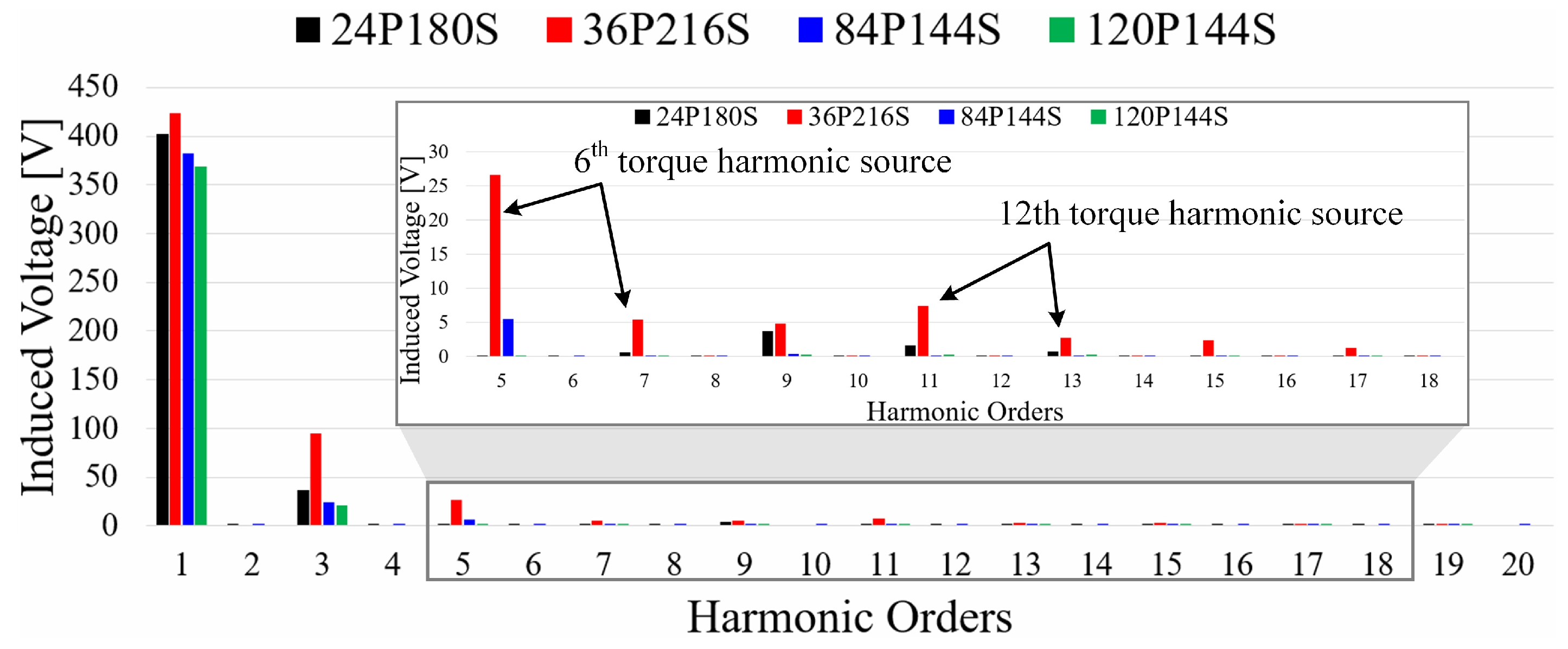
4.1. No-Load Characteristics
4.2. Load Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sjerić, M.; Tomić, R.; Martić, I.; Degiuli, N.; Grlj, C.G. Environmental and Economic Aspects of a Containership Engine Performance in Off-Design Conditions. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modabberian, A.; Storm, X.; Shamekhi, A.-M.; Vasudev, A.; Zenger, K.; Hyvönen, J.; Mikulski, M. Low Temperature Combustion Modeling and Predictive Control of Marine Engines. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.; Oh, J. Carbon Dioxide Emission Characteristics and Operation Condition Optimization for Slow-Speed and High-Speed Ship Engines. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 6134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shi, G.; Wu, J.; Cao, C.; Zhou, L.; Xu, W.; Wang, S.; Li, X. Combustion and Emission Characteristics of a Diesel Engine with a Variable Injection Rate. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lu, T.; Han, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, X.; Li, W. Improving Ship Fuel Consumption and Carbon Intensity Prediction Accuracy Based on a Long Short-Term Memory Model with Self-Attention Mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Park, Y.; Oh, S.-T.; Jin, C.-S.; Lee, J.; Kim, W.-H. Study on the Design of Six-Phase Surface Inset Permanent Magnet Synchronous Generator and Motor Considering the Power Factor and Torque Ripple. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2022, 58, 8202005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Jiang, C.; Zhu, Y.; Li, G. Research on Design Method and Electromagnetic Vibration of Six-Phase Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Winding PM Motor Suitable for Ship Propulsion. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 8535–8543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arish, N.; Kamper, M.J.; Wang, R.-J. Design and Optimisation of a 5 MW Permanent Magnet Vernier Motor for Podded Ship Propulsion. World Electr. Veh. J. 2024, 15, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojaghlu, P.; Vahedi, A. Specification and Design of Ring Winding Axial Flux Motor for Rim-Driven Thruster of Ship Electric Propulsion. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2019, 68, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakatsanis, T.S. Optimization and Performance Evaluation of PM Motor and Induction Motor for Marine Propulsion Systems. Appl. Syst. Innov. 2025, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, Y.; Aydin, M. A Novel Asymmetric and Unconventional Stator Winding Configuration and Placement for a Dual Three-Phase Surface PM Motor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2017, 53, 8111805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Wang, X.; Azeem, M.; Abubakar, U. Evaluation of Magnetomotive Force and Torque Ripples in Modular Type IPMSM with Multi Three-Phase Winding Configurations. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 1577–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Wu, Z.-y. Modelling and Vector Control of Dual Three-Phase PMSM with One-Phase Open. IET Electr. Power Appl. 2021, 15, 847–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, M.; Li, B.; Sun, X.; Jiang, F. Optimized Fault-Tolerant Control of Dual Three-Phase PMSM Under Open-Switch Faults. Energies 2024, 17, 5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Wang, S.; Shao, B.; Yan, L.; Xu, P.; Ren, Y. Advances in Dual-Three-Phase Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines and Control Techniques. Energies 2021, 14, 7508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Jiang, D.; Zou, T.; Qu, R.; Yang, K. Two-Segment Three-Phase PMSM Drive with Carrier Phase-Shift PWM for Torque Ripple and Vibration Reduction. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 588–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, Z.Q. Design Tradeoff between Cogging Torque and Torque Ripple in Fractional Slot Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8108704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R.; Husain, I.; Fardoun, A.; McLaughlin, K. Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor Magnet Designs with Skewing for Torque Ripple and Cogging Torque Reduction. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Industry Applications Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–27 September 2007; pp. 1552–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsunata, R.; Takemoto, M. Skewing Technology for Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors: A Comprehensive Review and Recent Trends. IEEE Open J. Ind. Electron. Soc. 2024, 5, 1251–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. High Torque Density and Low Torque Ripple Shaped-Magnet Machines Using Sinusoidal Plus Third Harmonic Shaped Magnets. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2019, 55, 2601–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, Q. Design and Analysis of a Low Torque Ripple Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine for Flywheel Energy Storage Systems. Energies 2024, 17, 6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.Q.; Zhu, Z.Q. Reduction of On-Load Torque Ripples in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machines by Improved Skewing. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2013, 49, 3822–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Z.S.; Lipo, T.A. Reducing Torque Ripple Using Axial Pole Shaping in Interior Permanent Magnet Machines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2020, 56, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, O.; Aydin, M. An Innovative Semi-FEA-Based, Variable Magnet-Step-Skew to Minimize Cogging Torque and Torque Pulsations in Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 210775–210783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, K.; Zhu, S.; Liu, C. Performance Comparisons of Fractional Slot Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Machines with Slot-Harmonic-Only Windings. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Li, G.J. Influence of Stator Topologies on Average Torque and Torque Ripple of Fractional-Slot SPM Machines with Fully Closed Slots. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, C. Effect of Flux Density Harmonics on Torque Characteristics of Integer Slot and Fractional Slot PMSMs. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2025, 40, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, P.; Boroujeni, S.T.; Khoshtarash, J. Expansion of the Feasible Slot/Pole Combinations in the Fractional Slot PM Machines by Applying Three-Slot Pitch Coils. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2019, 34, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhu, Z.Q.; Cai, S.; Wang, L.; Wei, F.R.; Shao, B. Influence of Stator Slot and Rotor Pole Number Combination on Field Winding Induced Voltage Ripple in Hybrid Excitation Switched Flux Machine. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2021, 36, 1245–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, W.; Ji, J.; Liu, G.; Lee, C.H.T. Design to Reduce Modulated Vibration in Fractional-Slot Concentrated-Windings PM Machines Considering Slot–Pole Combination. IEEE Trans. Transport. Electrific. 2023, 9, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Pei, Y.; Chai, F.; Doppelbauer, M. Analysis of Back EMF Harmonics Influenced by Slot–Pole Combinations in Permanent Magnet Vernier In-Wheel Motors. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2023, 70, 4461–4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Khalik, A.S.; Ahmed, S.; Massoud, A.M. Low Space Harmonics Cancelation in Double-Layer Fractional Slot Winding Using Dual Multiphase Winding. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8104710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Sala, G.; Zhang, H.; Gu, C.; Buticchi, G.; Formentini, A.; Gerada, C.; Wheeler, P. Torque Ripple Reduction in Sectored Multi Three-Phase Machines Based on PWM Carrier Phase Shift. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 4315–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, R.-W.; Lee, J. Alternative Surface-Mounted Permanent Magnet Topology for Reducing Voltage and Torque Harmonics in Shaft Generators. Energies 2023, 16, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

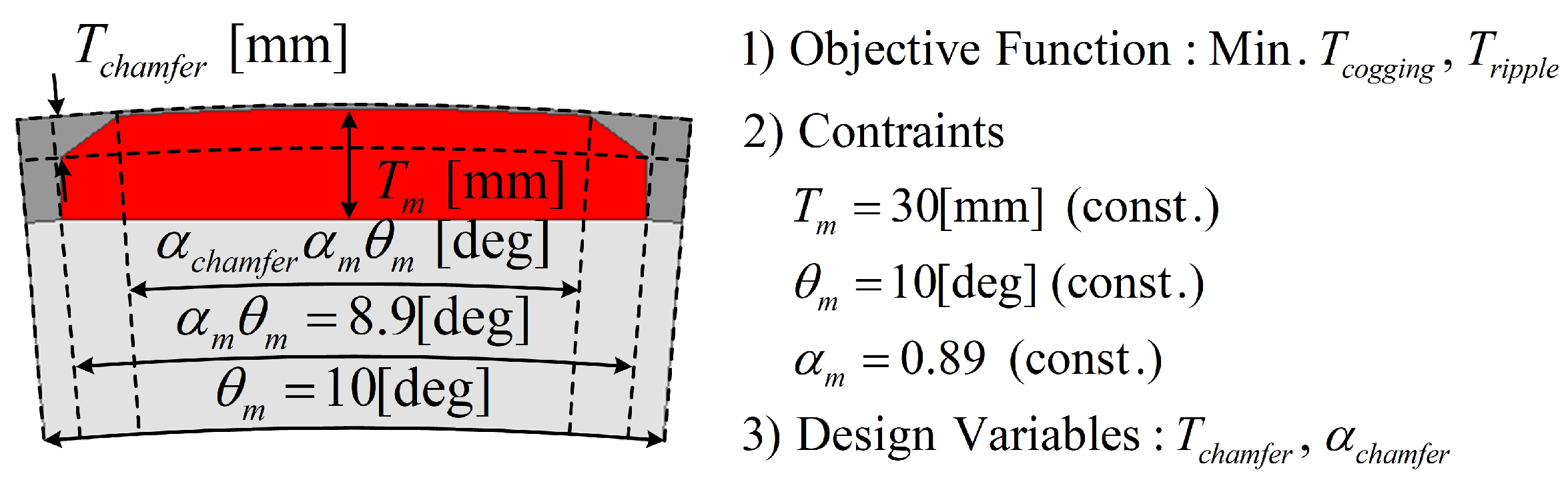
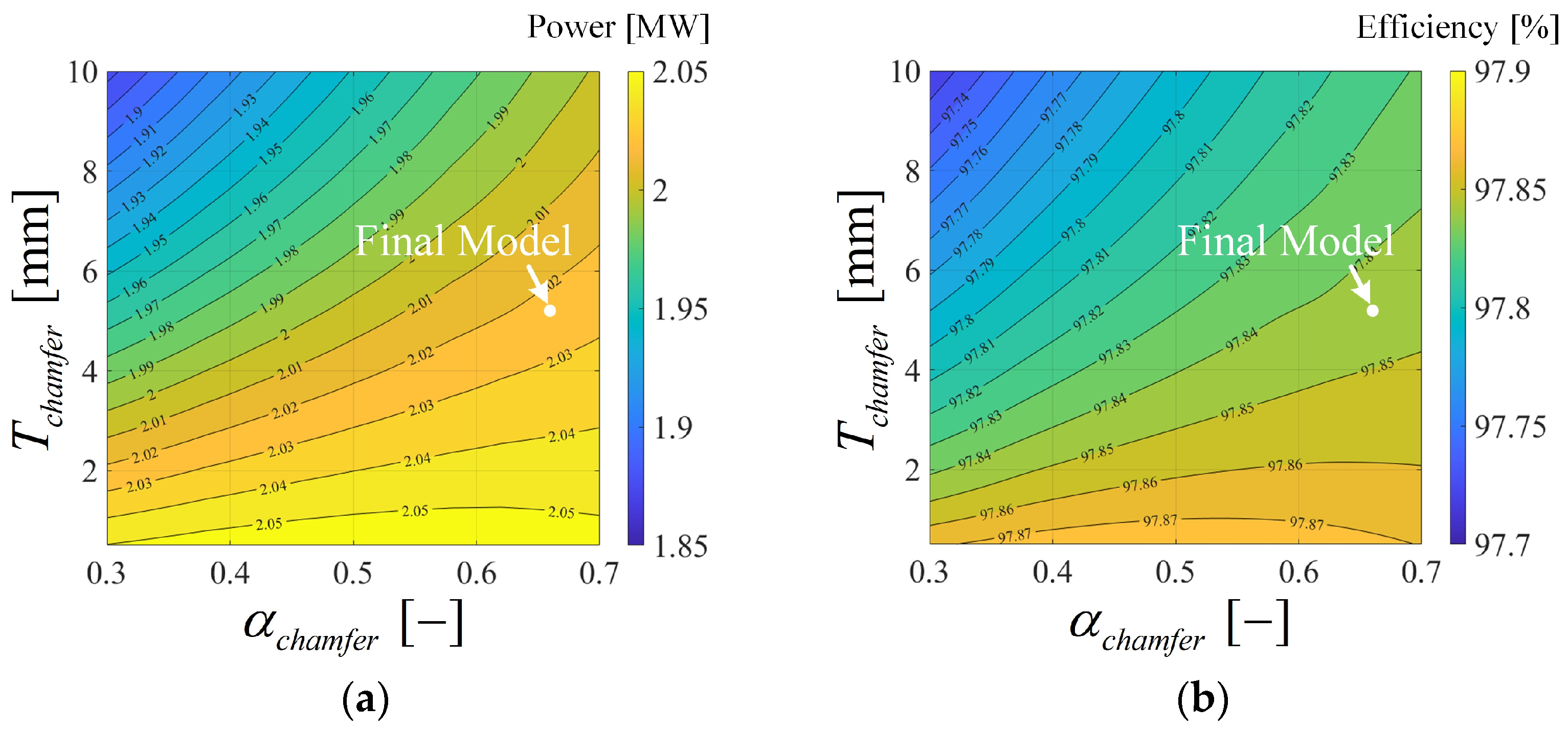
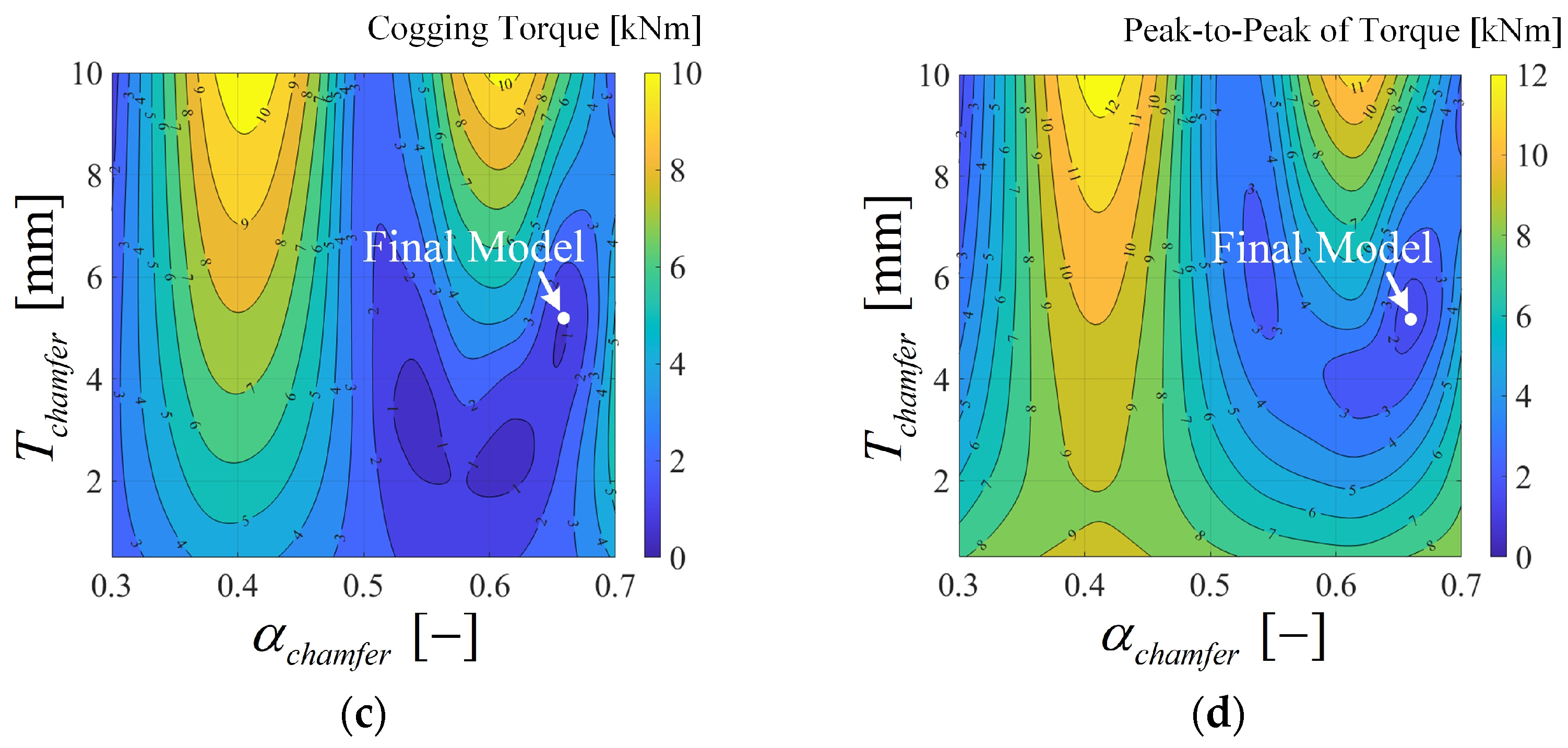

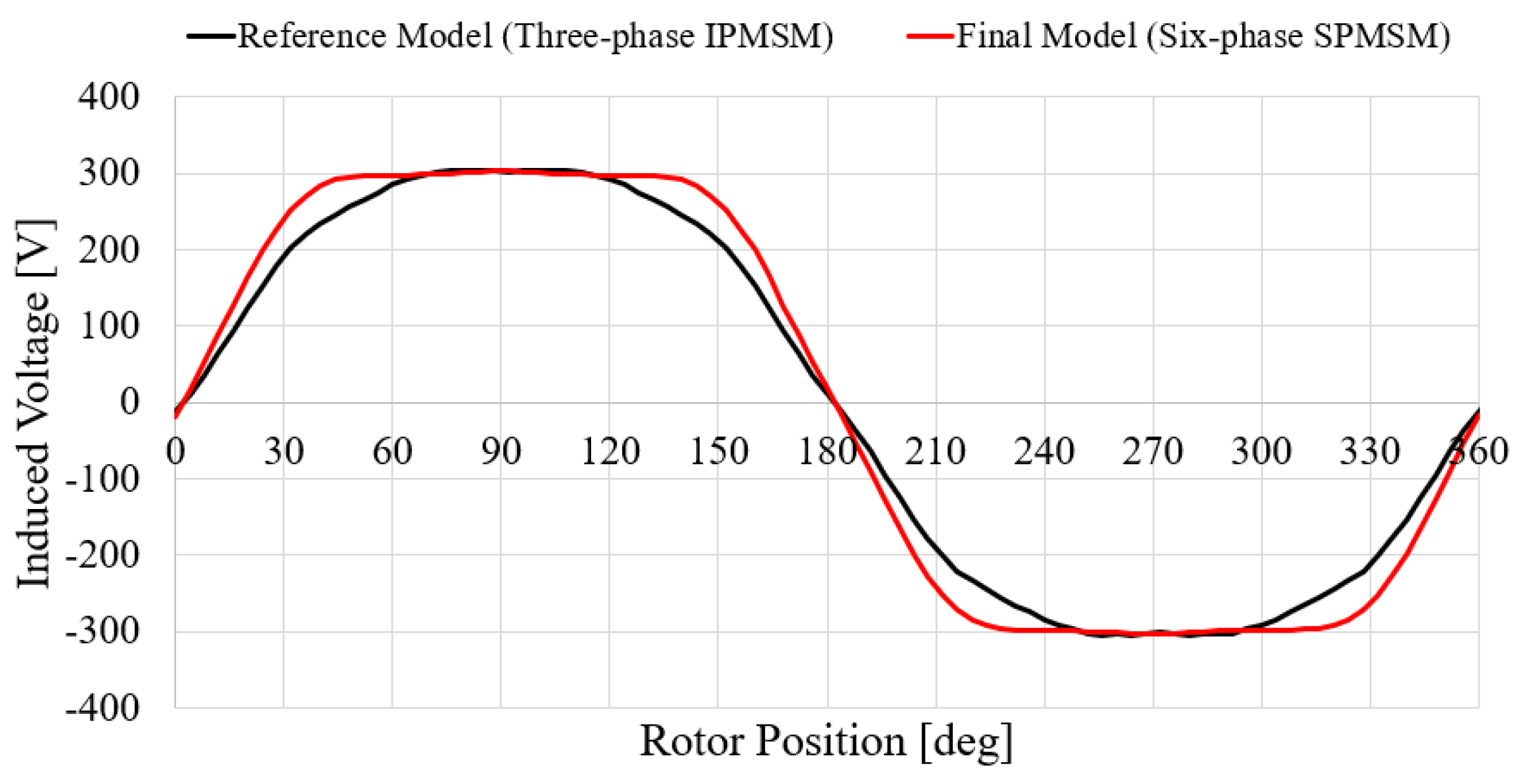
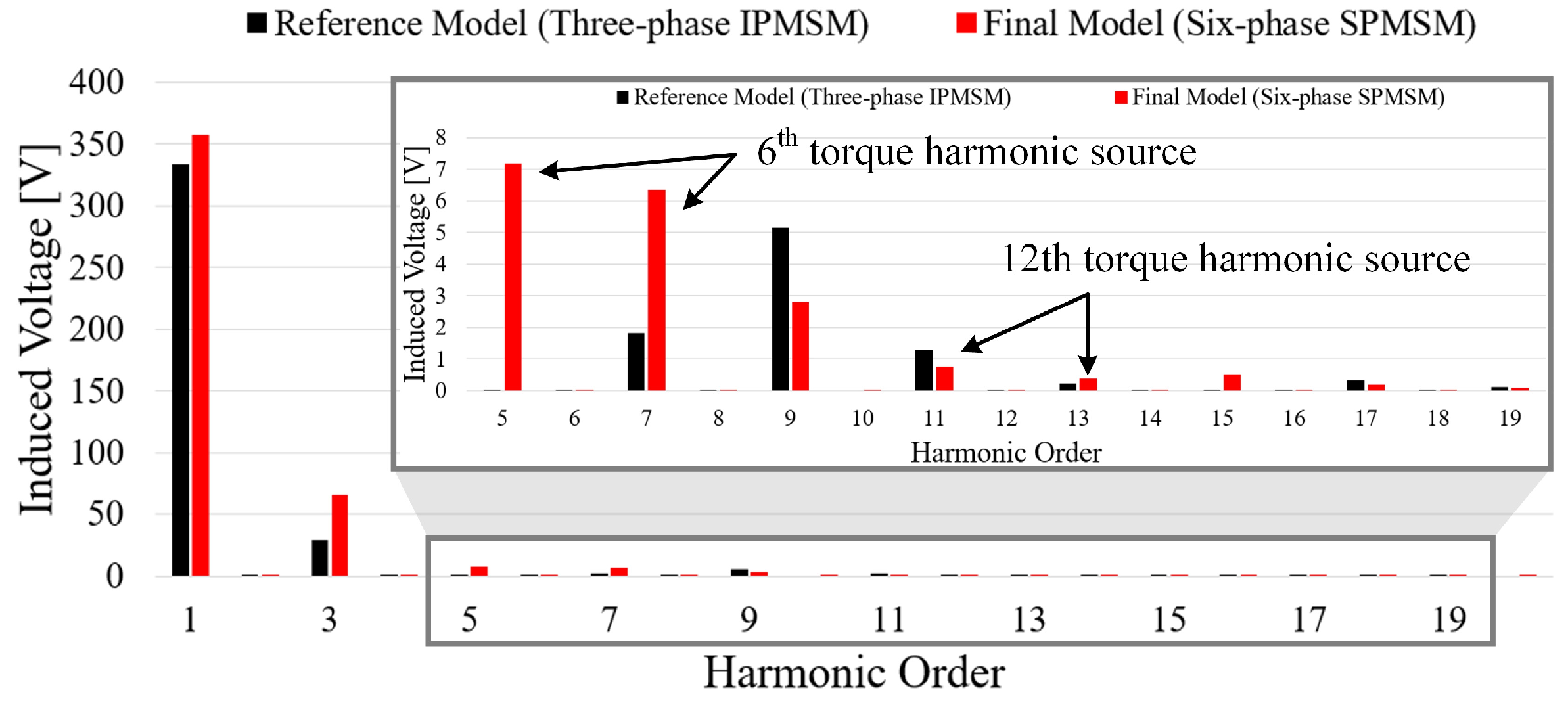
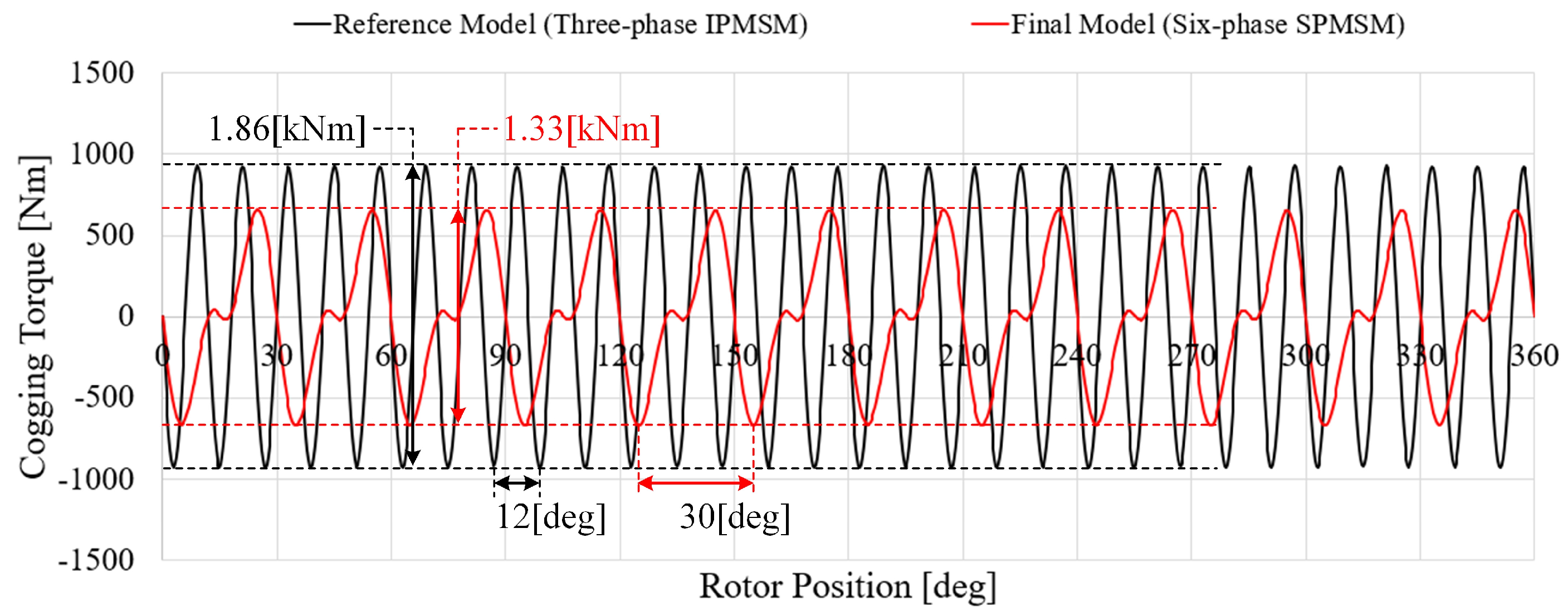
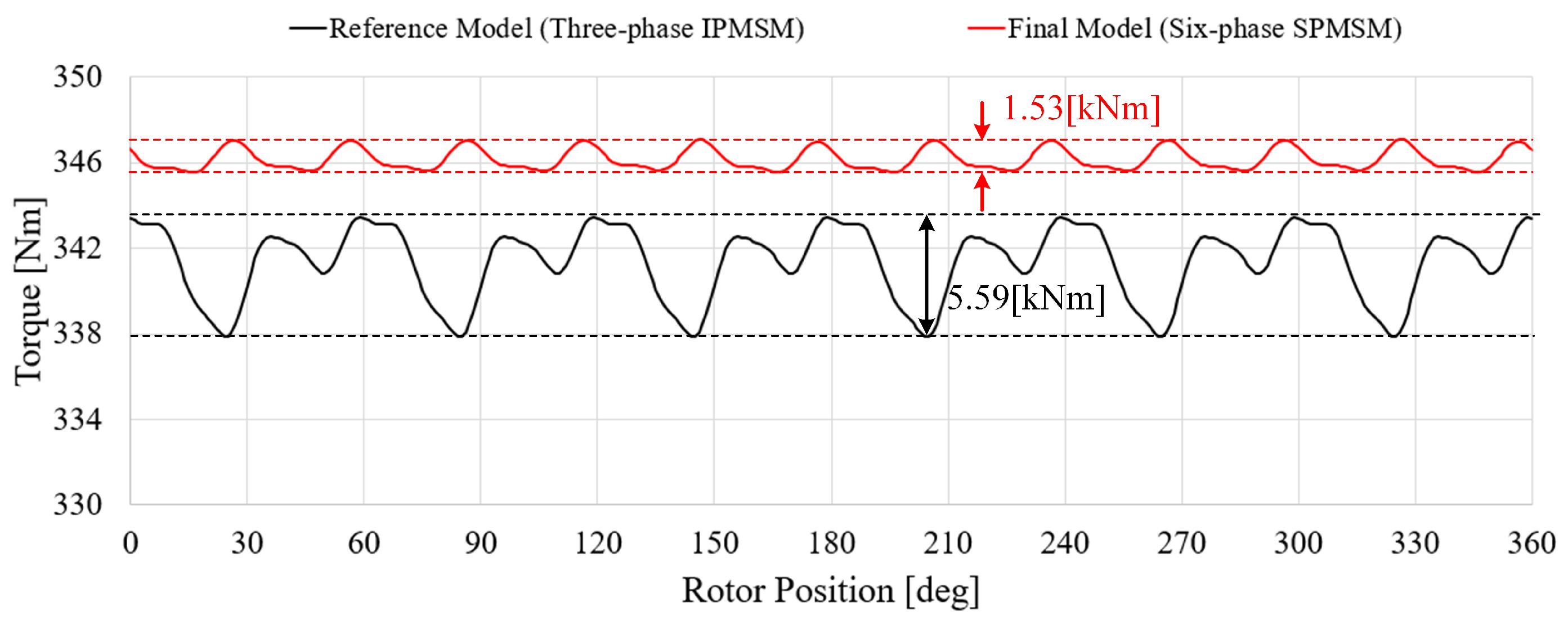
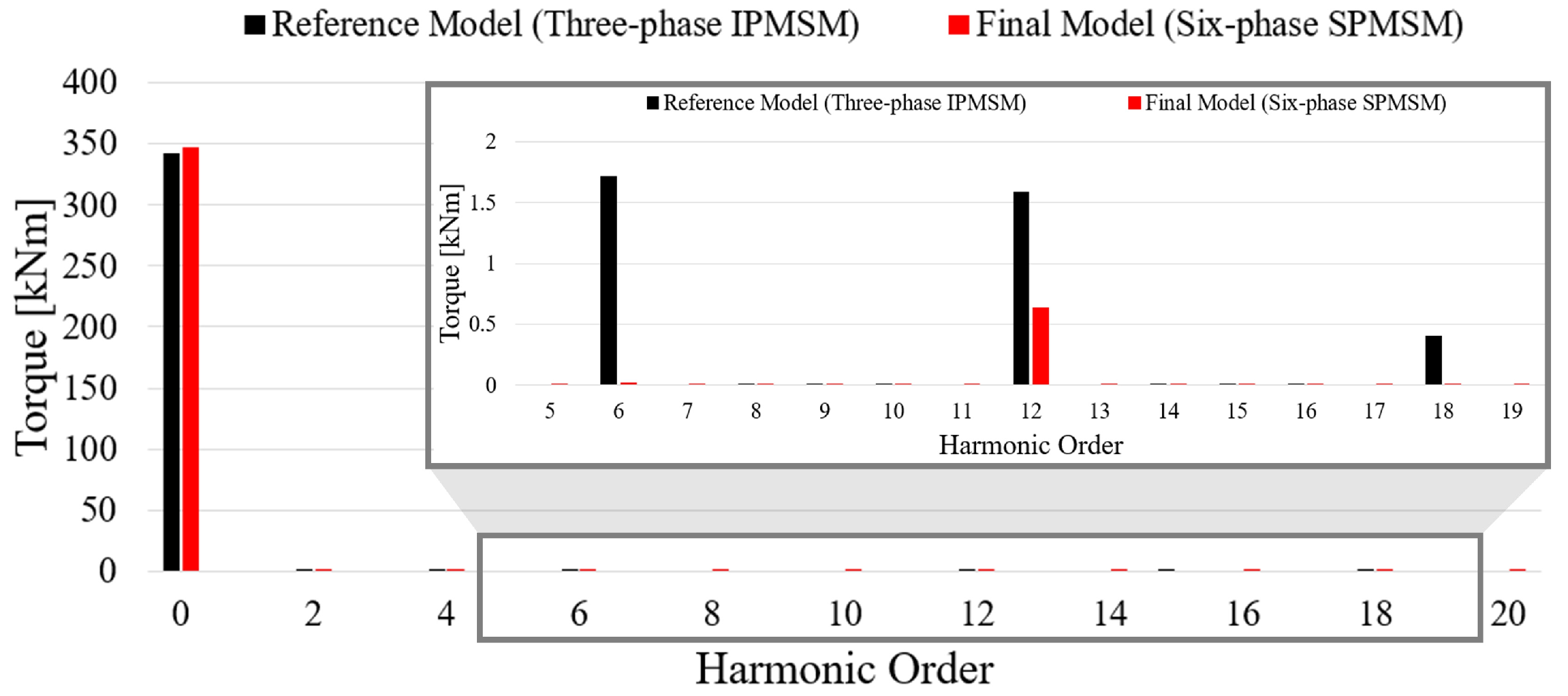
| Parameter | Value | Unit | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated power | 2 | MW | |
| Rated speed | 56 | rpm | |
| Rated torque | 341 | kNm | |
| Maximum | Three-phase | 2850 | Arms |
| current | Six-phase | 1425 | Arms |
| Stator outer/inner diameter | 2450/2100 | mm | |
| Rotor outer/inner diameter | 2086/1740 | mm | |
| Stack length with/without ducts | 1210/1354 | mm | |
| Airgap length | 7 | mm | |
| Number of poles/slots | 24/180 | - | |
| Rotor core material | 50PN600 | - | |
| Stator core material | 50PN400 | - | |
| Magnet material | N35UH | - | |
| Copper and magnet temperature | 80 | ℃ | |
| Parameter | Reference Model (IPMSM) | SPMSM | Unit | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arc-Shaped | Arc-Tapering-Shaped | Bread-Shaped | Bread-Tapering-Shaped | |||
| Total series turns | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 | - |
| Parallel circuit | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | 12 | - |
| No-load BEMF | 236.75 | 288.16 | 274.19 | 285.25 | 267.93 | Vrms |
| Power | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2.05 | 1.99 | MW |
| Torque | 341.33 | 343.46 | 341.78 | 349.79 | 340.15 | kNm |
| Torque ripple | 1.63 | 2.11 | 1.13 | 1.92 | 1.09 | % |
| Current | 2700 | 2380 | 2485 | 2450 | 2530 | Arms |
| Copper loss | 54.8 | 42.54 | 46.38 | 45.08 | 48.07 | kW |
| Eddy current loss | 0.02 | 11.31 | 14.8 | 9.94 | 14 | kW |
| Iron loss | 5.5 | 4.8 | 4.41 | 4.83 | 4.34 | kW |
| Efficiency | 97.07 | 97.16 | 96.82 | 97.16 | 96.77 | % |
| Power factor | 80.76 | 95.38 | 94.38 | 94.13 | 92.86 | - |
| Magnet total area | 0.167 | 0.166 | 0.164 | 0.163 | 0.164 | m2 |
| Parameter | Basic Machine | Six-Phase | Unit | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36poles-216slots | 84poles-144slots | 120poles-144slots | |||
| Poles/slots | 24/180 | 36/216 | 84/144 | 120/144 | - |
| Power | 2.05 | 2.06 | 2.09 | 2 | MW |
| No-load BEMF | 285.25 | 306.7 | 270.36 | 260.61 | Vrms |
| Current | 2450 | 1160 | 1355 | 1356 | Arms |
| Cogging torque | 2885.6 | 2500.5 | 24.63 | 93.73 | Nm |
| Torque | 349.78 | 352.45 | 359.22 | 345.04 | kNm |
| Torque ripple | 1.92 | 2.74 | 16.27 | 23.02 | % |
| Copper loss | 45.08 | 34.22 | 89.54 | 68.1 | kW |
| Eddy current loss | 9.94 | 3.6 | 15.76 | 27.86 | kW |
| Iron loss | 4.83 | 7.1 | 1627 | 23.02 | kW |
| Efficiency | 97.16 | 97.87 | 94.5 | 94.73 | % |
| Parameter | Reference Model (Three-Phase IPMSM) | Final Model (Six-Phase SPMSM) | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pole/Slot | 24/180 | 36/216 | - |
| Power | 2 | 2.02 | MW |
| Cogging Torque | 1.86 | 1.33 | kNm |
| No-load BEMF | 236.75 | 257.86 | Vrms |
| Current | 2700 | 1350 | Arms |
| Power Factor | 80.76 | 93.7 | % |
| Torque | 341.33 | 346.16 | kNm |
| Torque Ripple | 1.63 | 0.44 | % |
| Copper Loss | 54.8 | 34.06 | kW |
| Eddy Current Loss | 0.02 | 3.79 | kW |
| Iron Loss | 5.5 | 6.81 | kW |
| Efficiency | 97.07 | 97.84 | % |
| Total cost | 134.03 | 124.46 | k$ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, D.-H.; Jo, C.; Han, H.-S.; Kim, H.-G.; Kim, W.-H.; Kim, H. Design of a Six-Phase Surface Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor with Chamfer-Shaped Magnet to Reduce Cogging Torque and Torque Ripple for Large-Ship Propulsion. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11400. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111400
Choi D-H, Jo C, Han H-S, Kim H-G, Kim W-H, Kim H. Design of a Six-Phase Surface Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor with Chamfer-Shaped Magnet to Reduce Cogging Torque and Torque Ripple for Large-Ship Propulsion. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11400. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111400
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Do-Hyeon, Chaewon Jo, Hyung-Sub Han, Hyo-Gu Kim, Won-Ho Kim, and Hyunwoo Kim. 2025. "Design of a Six-Phase Surface Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor with Chamfer-Shaped Magnet to Reduce Cogging Torque and Torque Ripple for Large-Ship Propulsion" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11400. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111400
APA StyleChoi, D.-H., Jo, C., Han, H.-S., Kim, H.-G., Kim, W.-H., & Kim, H. (2025). Design of a Six-Phase Surface Permanent-Magnet Synchronous Motor with Chamfer-Shaped Magnet to Reduce Cogging Torque and Torque Ripple for Large-Ship Propulsion. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11400. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111400






