Sound-Absorbing Thermoplastic Composite with Helmholtz Resonance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
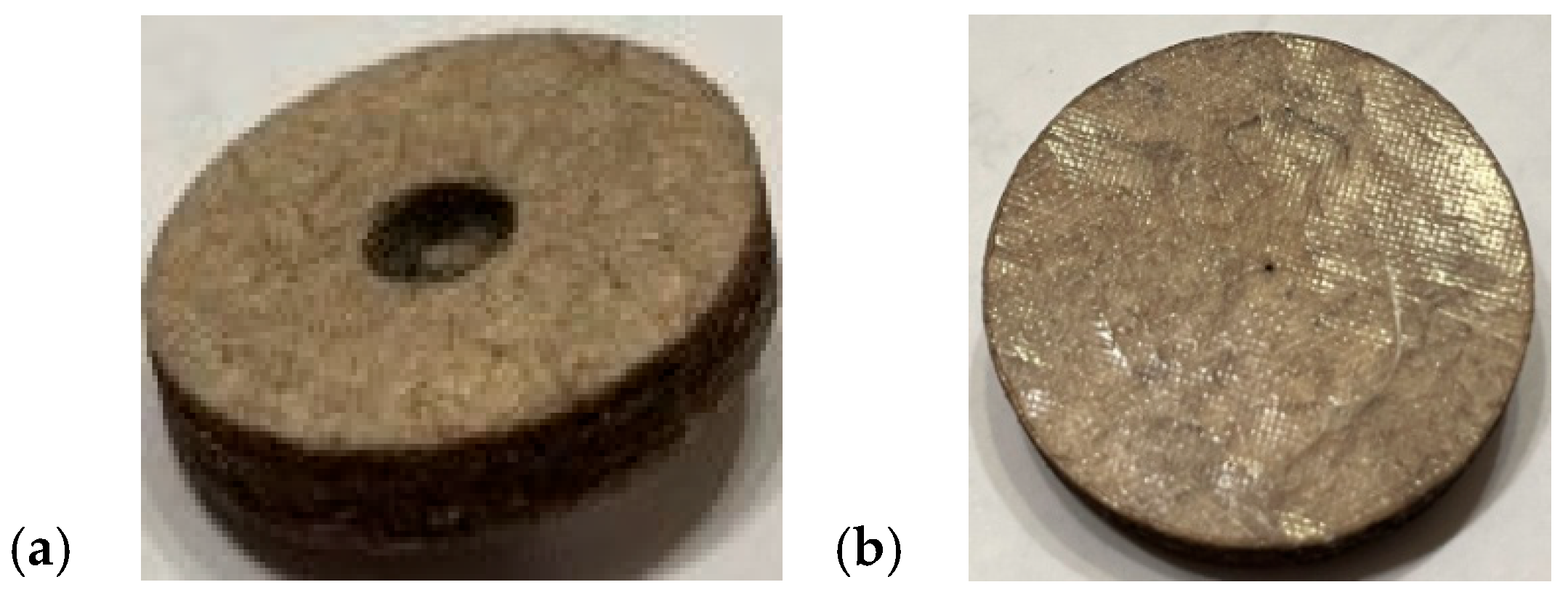
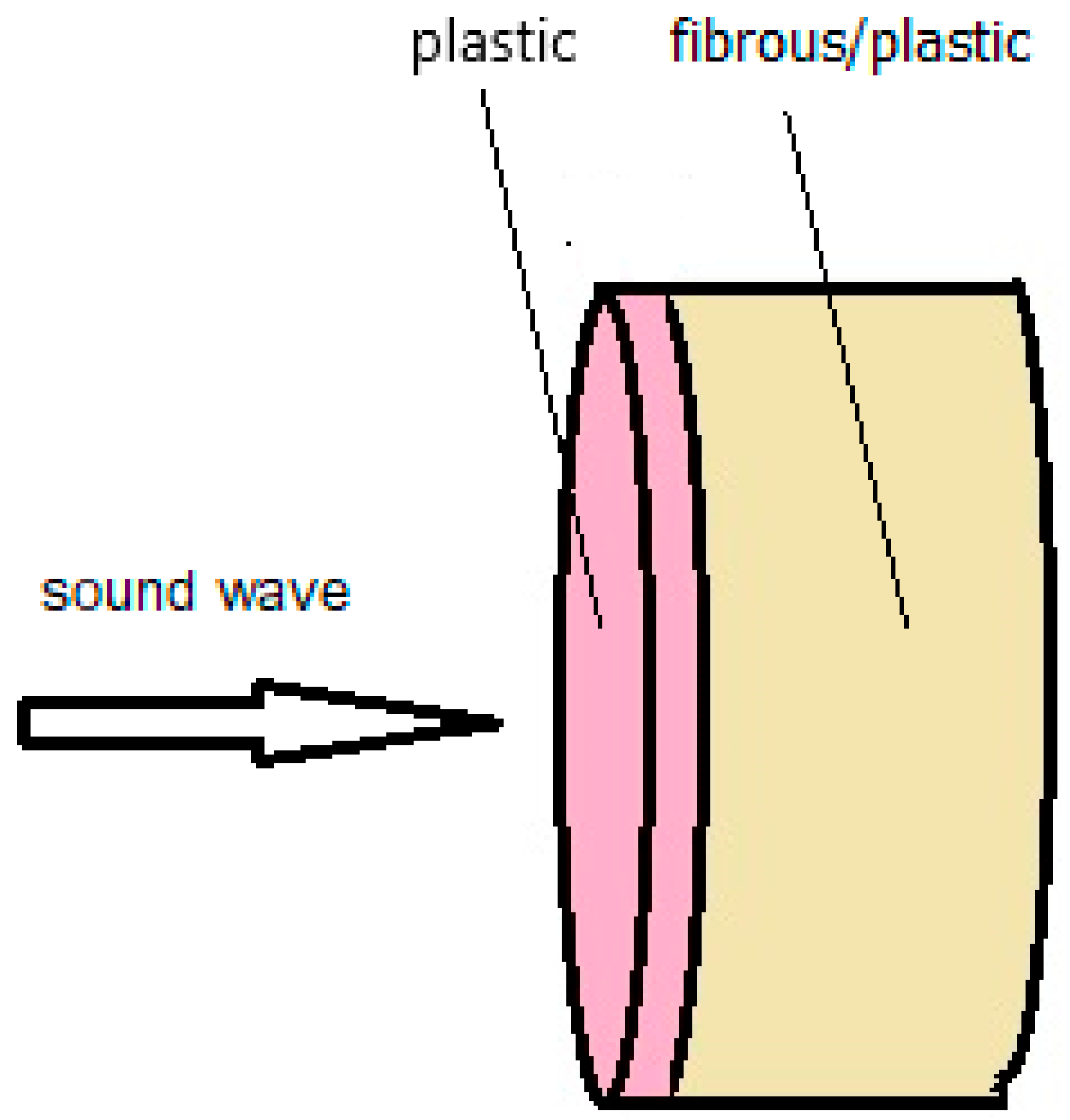
2.1. Composite Manufacturing
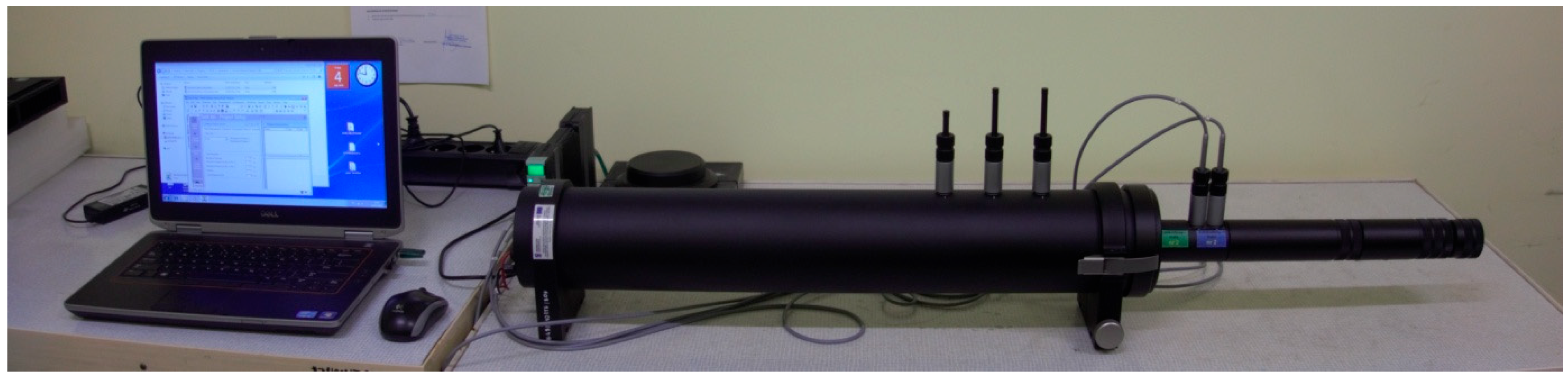
2.2. Measurements
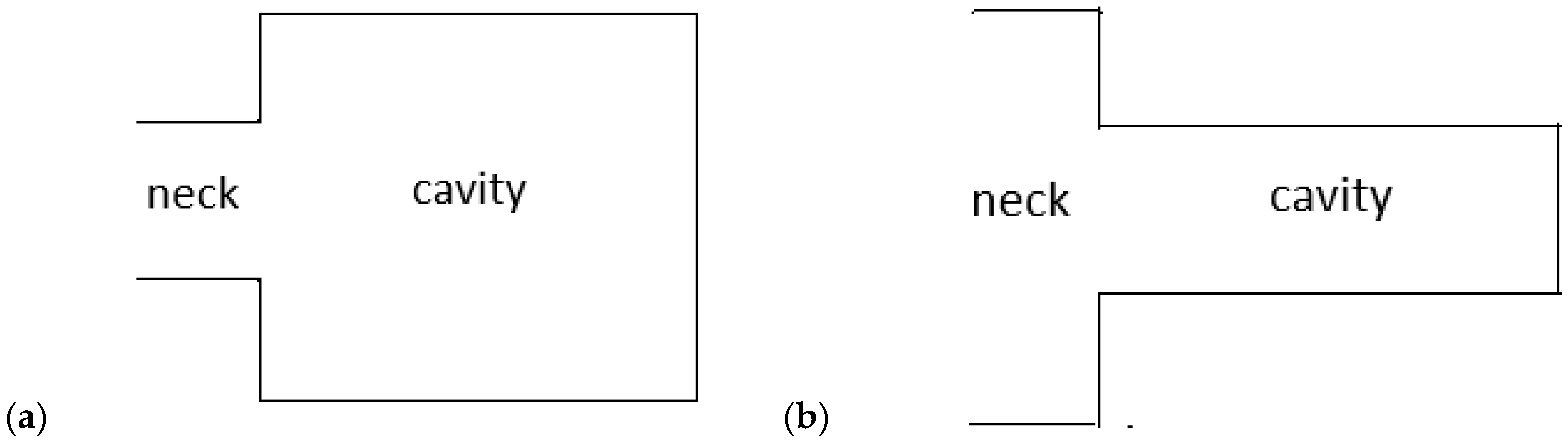
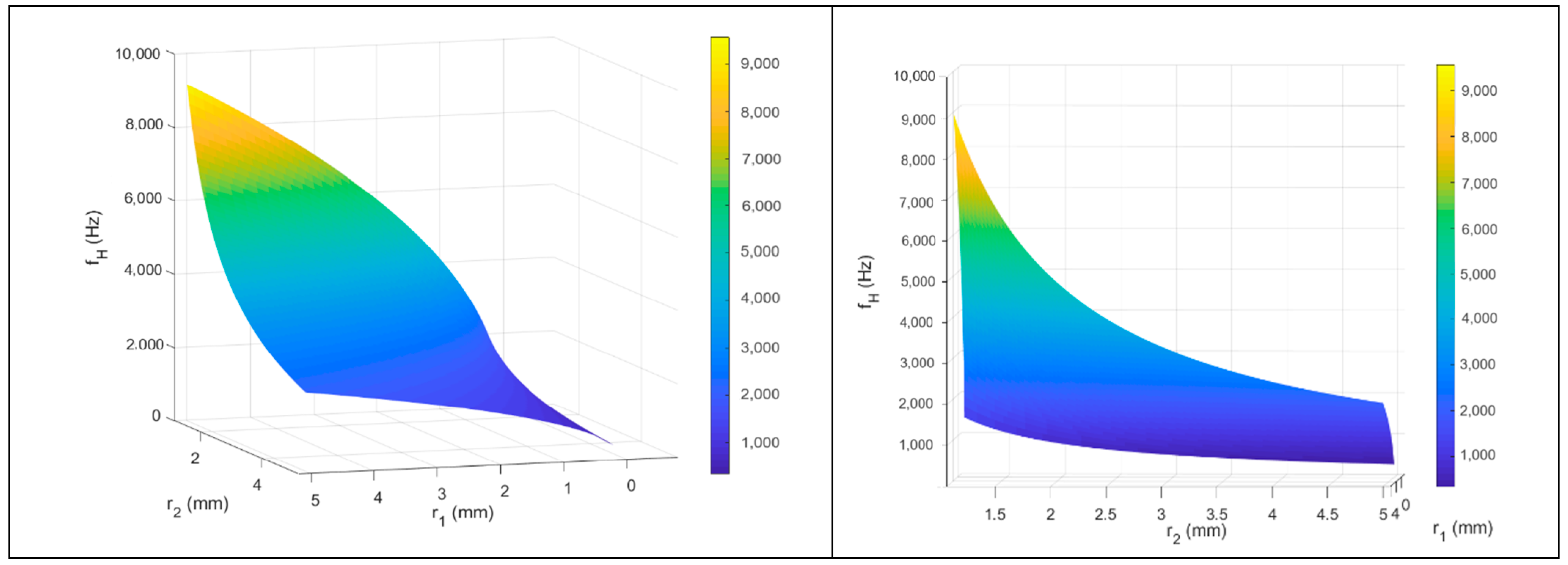
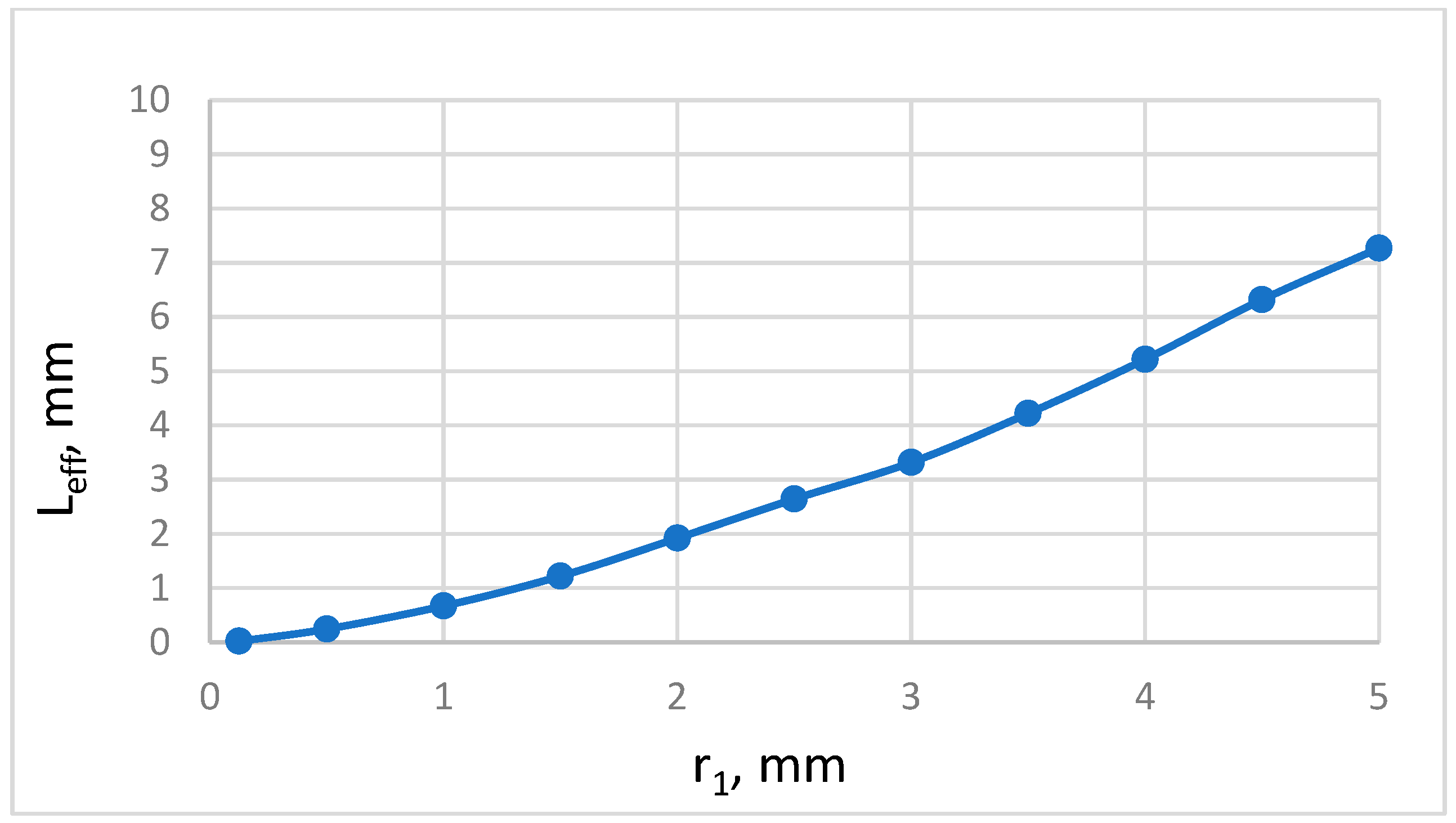
3. Helmholtz Resonance
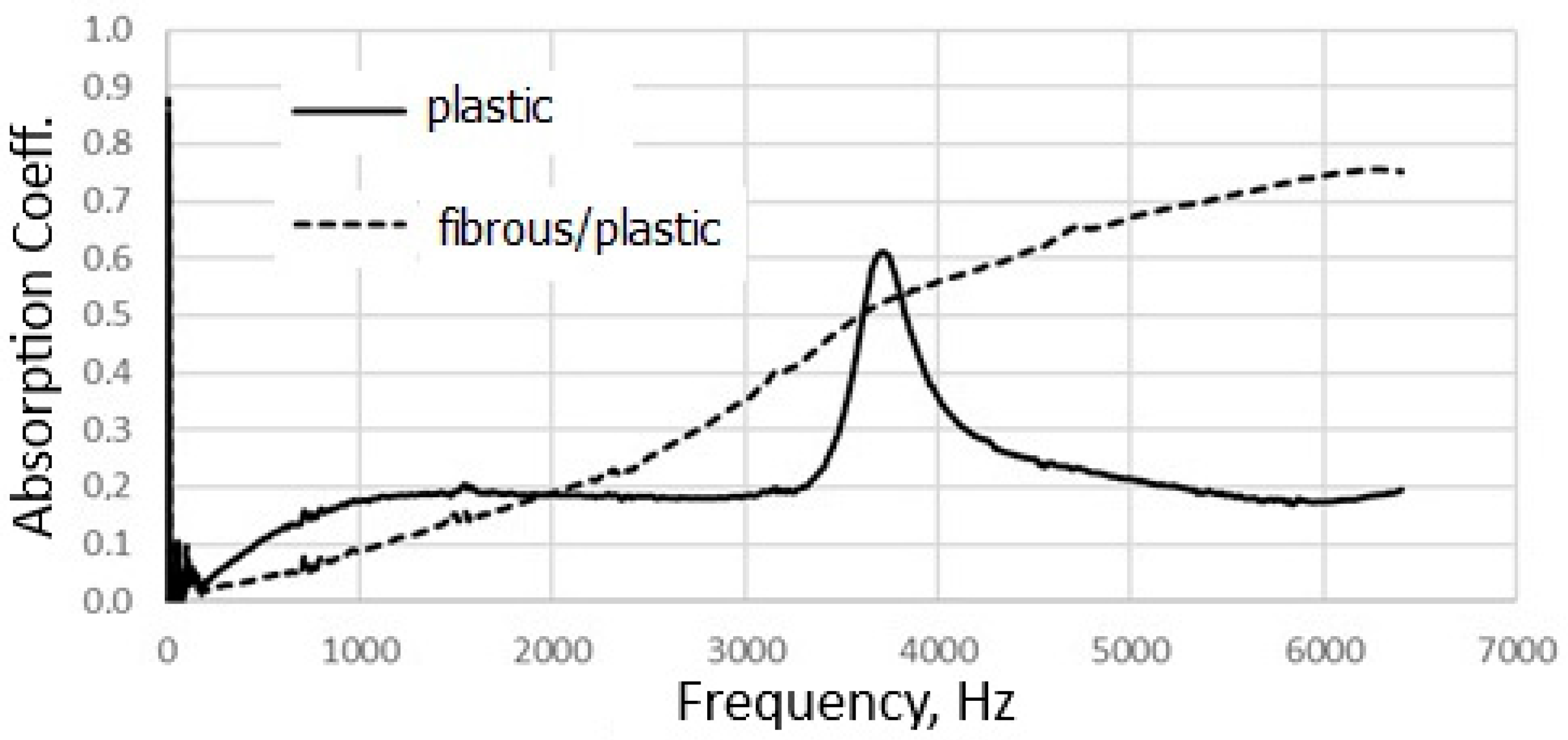
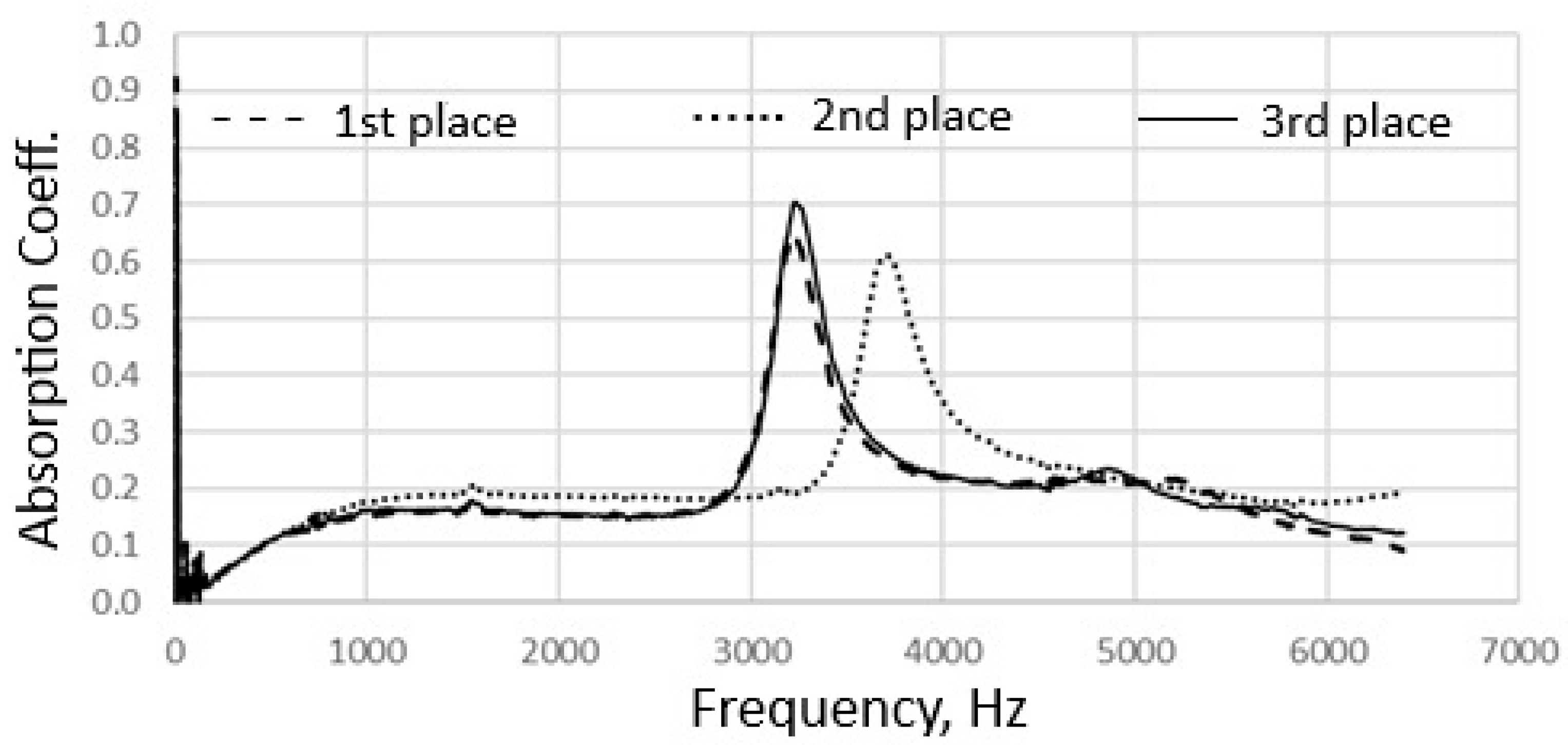
4. Results and Discussions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azimi, M. Noise reduction in buildings using sound absorbing materials. J. Archit. Eng. Technol. 2017, 6, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miodragović, T.; Erić-Cekić, O.; Radičević, B.; Grković, V. Composite materials that are good sound absorbers. In Proceedings of the X International Conference “Heavy Machinery-HM 2021”, Vrnjačka Banja, Serbia, 23–25 June 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sikora, J.; Turkiewicz, J. Sound absorption coefficients of granular materials. Mech. Control 2010, 29, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Yahya, M.N.; Chin, D.D.V.S. A Review on the potential of natural fibre for sound absorption application, International Research and Innovation Summit (IRIS2017). IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 226, 012014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fu, Q.; Si, Y.; Ding, B.; Yu, J. Porous materials for sound absorption. Compos. Commun. 2018, 10, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egab, L.; Wang, X.; Fard, M. Acoustical characterisation of porous sound absorbing materials: A review. Int. J. Veh. Noise Vib. 2014, 10, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Fang, X.; Wang, X.; Assouar, B.; Cheng, Q.; Li, Y. Acoustic perfect absorbers via Helmholtz resonators with embedded apertures. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 145, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, S.; Huang, Z.; Wen, J. Ultra-broadband sound-absorbing metastructure with Helmholtz resonator and porous material modulation crown. Mater. Des. 2024, 246, 113351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Yu, C.; He, W.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. Perfect sound absorption of Helmholtz resonators with embedded channels in petal shape. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 130, 135102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Q. Application of microperforated-panel absorber in communication products. J. Appl. Math. Phys. 2018, 6, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ye, C.; Liu, X.; Xin, F.; Lu, T.J. Underwater acoustic absorption of composite anechoic layers with inner holes. J. Vib. Acoust. 2019, 141, 041006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.B.; Song, C.H.; Wu, J.H. Reducing cavity dependence in helmholtz resonators via compact neck arrays. Appl. Acoust. 2026, 242, 111070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Liang, H.; Chu, J.; Jin, F. Sound absorber based on a sonic black hole and multi-layer micro-perforated panels. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 065960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-F.; Li, Z.-H.; Zhou, Y.-J.; Zhang, Q.-F.; Liu, B.; Liu, F.; Pei, S.-C.; Shi, K.; Bai, P.-K. Improved sound absorption with 3D-printerd micro-perforated sandwich structures. J. Mater. Technol. 2025, 34, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Yan, X. Multi-layer fibrous structures for noise reduction. J. Text. Inst. 2017, 108, 2096–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliścińska, E.; Sankowski, D.; Krucińska, I.; Gocławski, J.; Michalak, M.; Rowińska, Z.; Sekulska-Nalewajko, J. Optical coherence tomography image analysis of polymer surface layers in sound-absorbing fibrous composite materials. Polym. Test. 2017, 63, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliścińska, E.; Michalak, M.; Krucińska, I.; Strąkowska, M.; Kopeć, M.; Więcek, B. A new thermographic method for determining the thickness of the polymer surface layer in sound-absorbing fibrous composite materials. Polym. Test. 2022, 115, 107748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, X.; Wen, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, F. Enhanced sound absorption properties of a semi-open underwater periodic acoustic metamaterial. Compos. Struct. 2025, 354, 118831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, Y.; Gao, T.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Jin, Y. Broadband low-frequency sound absorption of multifunctional composite metastructure. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2025, 68, 1220206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlack, K.H.; Bauhofer, A.; Krödel, S.; Palermo, A.; Daraio, C. Composite 3D-printed meta-structures for low frequency and broadband vibration absorption. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 130, 8386–8390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, J.; Ma, T.; Wei, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Z. Composite structure with porous material and parallel resonators for broadband sound absorption at low-to-mid frequencies. Appl. Acoust. 2024, 225, 110193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.-H.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.-W.; Du, S.-Z.; Liu, Z.-E. Comparison analysis and optimization of composite micro-perforated absorbers in sound absorption bandwidth. Acoust. Aust. 2018, 46, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wu, Q. Enhanced low-frequency sound absorption of a porous layer mosaicked with perforated resonator. Polymers 2022, 14, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwalla, D.K.; Mohanty, A.R. Low-frequency wideband sound absorption properties of composite layer micro-perforated panel absorber. J. Vib. Eng. Technol. 2024, 12, 6251–6271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, D.; Liang, X.; Liang, H.; Chu, J.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, G.; Duan, J.; Chen, J. Broadband sound absorption using acoustic black holes with micro-perforated panels. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2024, 38, 2450243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelat, A.; Gautier, F.; Conlon, S.C.; Semperlotti, F. The acoustic black hole: A review of theory and applications, Special Issue: Recent Advances in Acoustic Black Hole Research. J. Sound Vib. 2020, 476, 115316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafique, F.; Wu, J.H.; Liu, C.R.; Ma, F. Low-frequency sound absorption of an inhomogeneous micro-perforated panel with J-shaped cavities of different depths. Acoust. Aust. 2022, 50, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Donda, K.; Fan, S.; Cao, L.; Assouar, B. Broadband ultra-thin acoustic metasurface absorber with coiled structure. Appl. Phys. Express 2019, 12, 114002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero-Durá, I.; Cebrecos, A.; Picó, R.; Romero-García, V.; García-Raffi, L.M.; Sánchez-Morcillo, V.J. Sound absorption and diffusion by 2D arrays of Helmholtz resonators. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donda, K.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, S.-W.; Cao, L.; Li, Y.; Assouar, B. Extreme low-frequency ultrathin acoustic absorbing metasurface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2019, 115, 173506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, N.; Huang, R.-R.; Fan, S.-W.; Wang, Y.-F.; Wang, Y.-S. Resonance-based acoustic ventilated metamaterials for sound insulation. Acoustics 2025, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, J.-F.; Marigo, J.-J.; Maurel, A. Influence of the neck shape for Helmholtz resonators. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2017, 142, 3703–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanga, D.; Wang, X.; Zhu, M. The impact of the neck material on the sound absorption performance of Helmholtz resonators. J. Sound Vib. 2014, 333, 6843–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selamet, A.; Lee, I. Helmholtz resonator with extended neck. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2003, 113, 1975–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soegijono, H.; Soegijono, B. Investigation on the composite of pumice and alumina equipped by quarter wavelength and Helmholtz resonators as noise absorber material. Res. J. Mater. Sci. 2013, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Corning, E. Resonance and neck length for a spherical resonator. ISB J. Phys. 2011, 5, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Basirjafari, S. Innovative solution to enhance the Helmholtz resonator sound absorber in low-frequency noise by nature inspiration. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2020, 18, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yu, C.; Xin, F. Gradually perforated porous materials backed with Helmholtz resonant cavity for broadband low-frequency sound absorption. Compos. Struct. 2021, 263, 113647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Zhao, H.; Lv, L.; Yuan, B.; Wang, G.; Wen, X. Effects of locally resonant modes on underwater sound absorption in viscoelastic materials. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2011, 130, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xin, F. Broadband low-frequency sound absorption via Helmholtz resonators with porous material lining. J. Sound Vib. 2024, 578, 118330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaodan, Z.; Xiangqian, F. Enhancing low frequency sound absorption of micro-perforated panel absorbers by using mechanical impedance plates. Appl. Acoust. 2015, 18, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romadhona, I.C.; Yahya, I.; Ubaidillah, H. On the use of coupled cavity Helmholtz resonator inclusion for improving absorption performance of wooden sound diffuser element. Procedia Eng. 2017, 170, 458–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, H.; Chen, W.; Jiang, D. Broaden noise reduction range in low frequency by a HR + MPP structure based on impedance matching method. Appl. Acoust. 2025, 232, 110572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 9073-1:2023; Textiles—Test Methods for Nonwovens. Part 1: Determination of Mass per Unit Area. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- ISO 10534-2:2023; Acoustics—Determination of Acoustic Properties in Impedance Tubes. Part 2: Two-Microphone Technique for Normal Sound Absorption Coefficient and Normal Surface Impedance. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland.
- Bykov, A.; Komkin, A. Design of Helmholtz resonator with required characteristics. MATEC Web Conf. 2020, 320, 00012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Sun, Z. Several explanations on the theoretical formula of Helmholtz resonator. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2017, 114, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strutt, J.W. The theory of the Helmholtz resonator. Proc. R. Soc. A 1916, 92, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Shen, X.; Wang, E.; Yang, F.; Zhang, X.; Yin, Q. Acoustic multi-layer Helmholtz resonance metamaterials with multiple adjustable absorption peaks. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 241904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalebek, N.A. Sound Absorbing Polyester Recycled Nonwovens for the Automotive Industry. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2016, 24, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Shen, J.; Lee, H.P.; Yan, X. Sound absorption performance and mechanism of flexible PVA microperforated membrane. Appl. Acoust. 2022, 185, 108420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaodan, Z.; Xin, W.; Yong-Jie, Y. Enhancing low-frequency sound absorption of micro-perforated panel absorbers by combining parallel mechanical impedance. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 130, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gliścińska, E.; Michalak, M.; Michalak, A. Sound-Absorbing Thermoplastic Composite with Helmholtz Resonance. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111349
Gliścińska E, Michalak M, Michalak A. Sound-Absorbing Thermoplastic Composite with Helmholtz Resonance. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111349
Chicago/Turabian StyleGliścińska, Eulalia, Marina Michalak, and Anna Michalak. 2025. "Sound-Absorbing Thermoplastic Composite with Helmholtz Resonance" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111349
APA StyleGliścińska, E., Michalak, M., & Michalak, A. (2025). Sound-Absorbing Thermoplastic Composite with Helmholtz Resonance. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11349. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111349






