Biodata-Driven Knowledge Graph Recommendation System: Fusing Foot and Leg Characteristics for Personalised Shoe Recommendation
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Background and Related Work
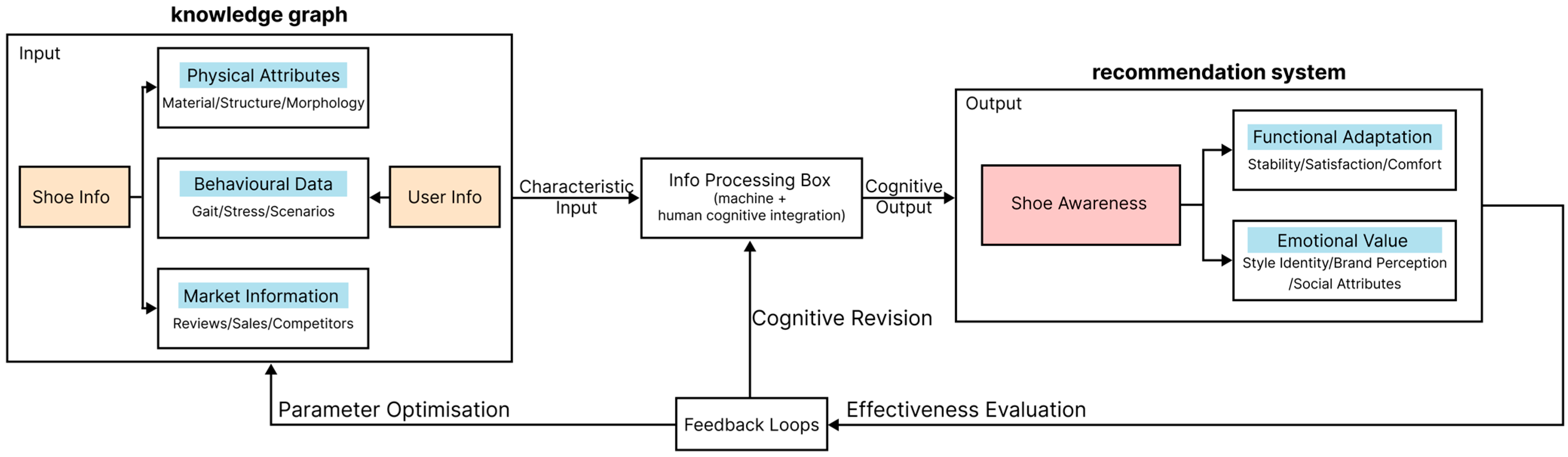
2.1. Cognitive Pathways in Shoe Selection
2.2. Biometric Data and the Mapping of Shoe Features
2.2.1. Deconstructing Shoe Features
2.2.2. Analysis of Biometric Data
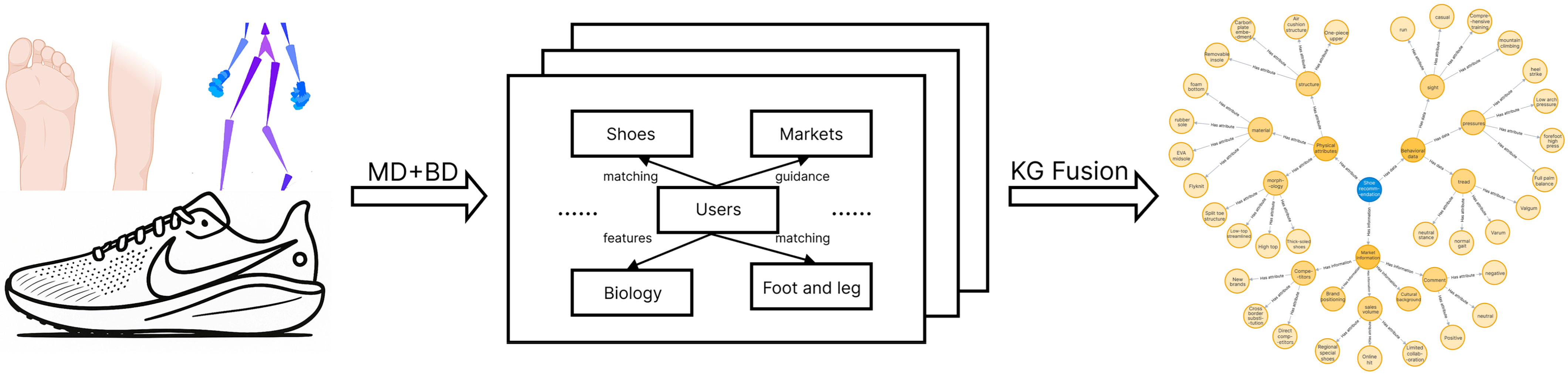
2.2.3. Mapping of Shoe Features and Biometric Data
2.3. Shoe Recommendation Approach Integrating Biological Data
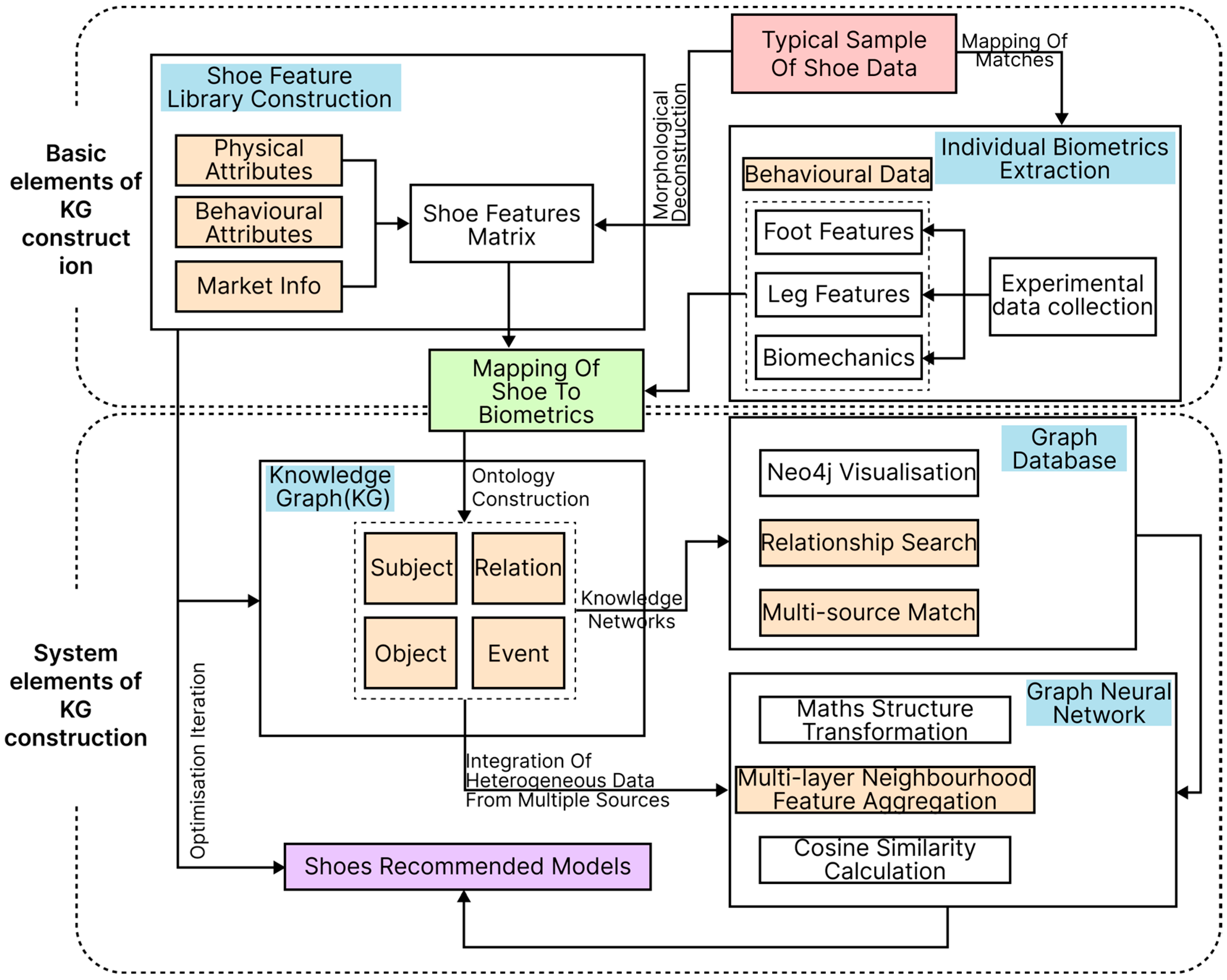
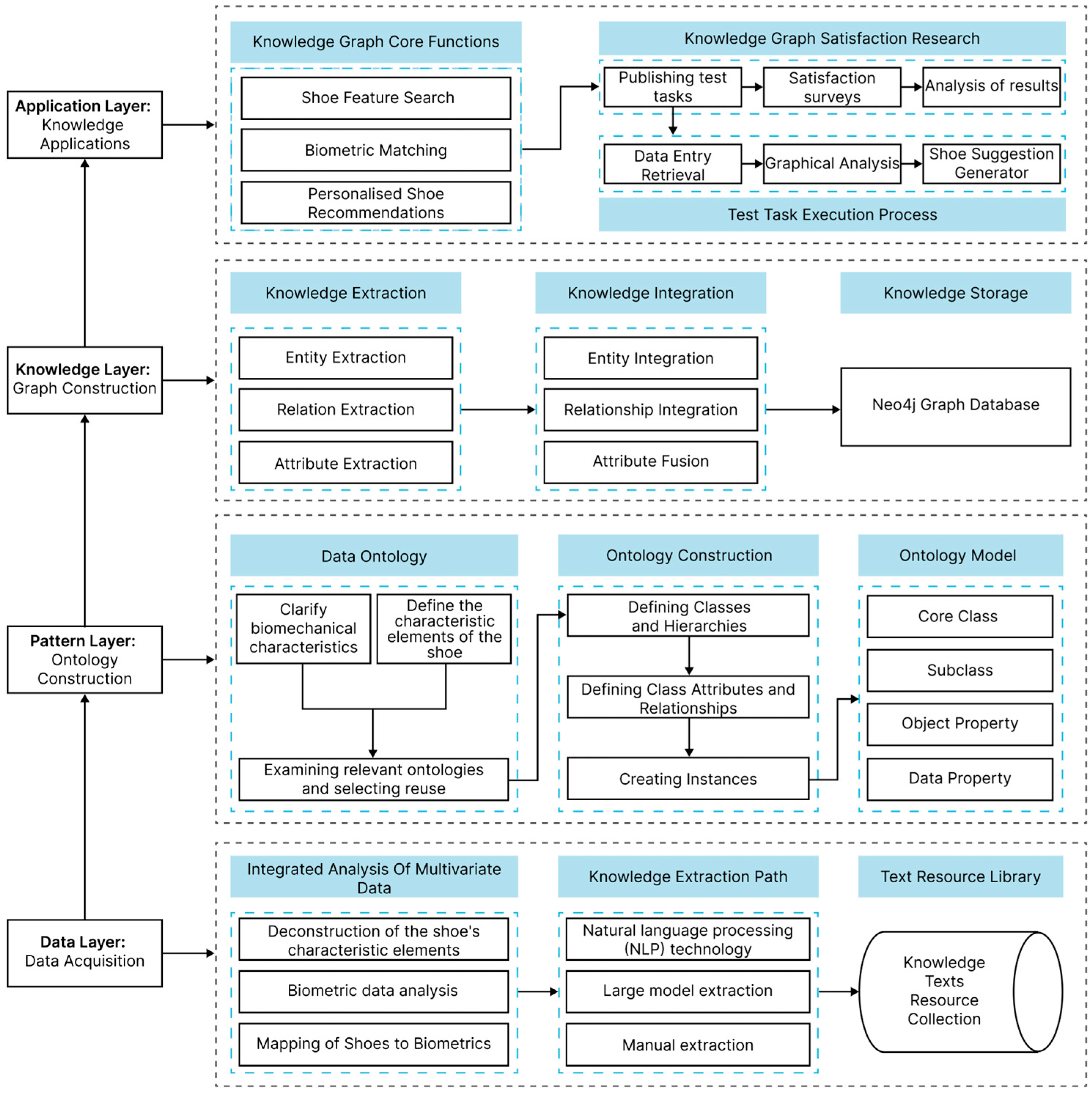
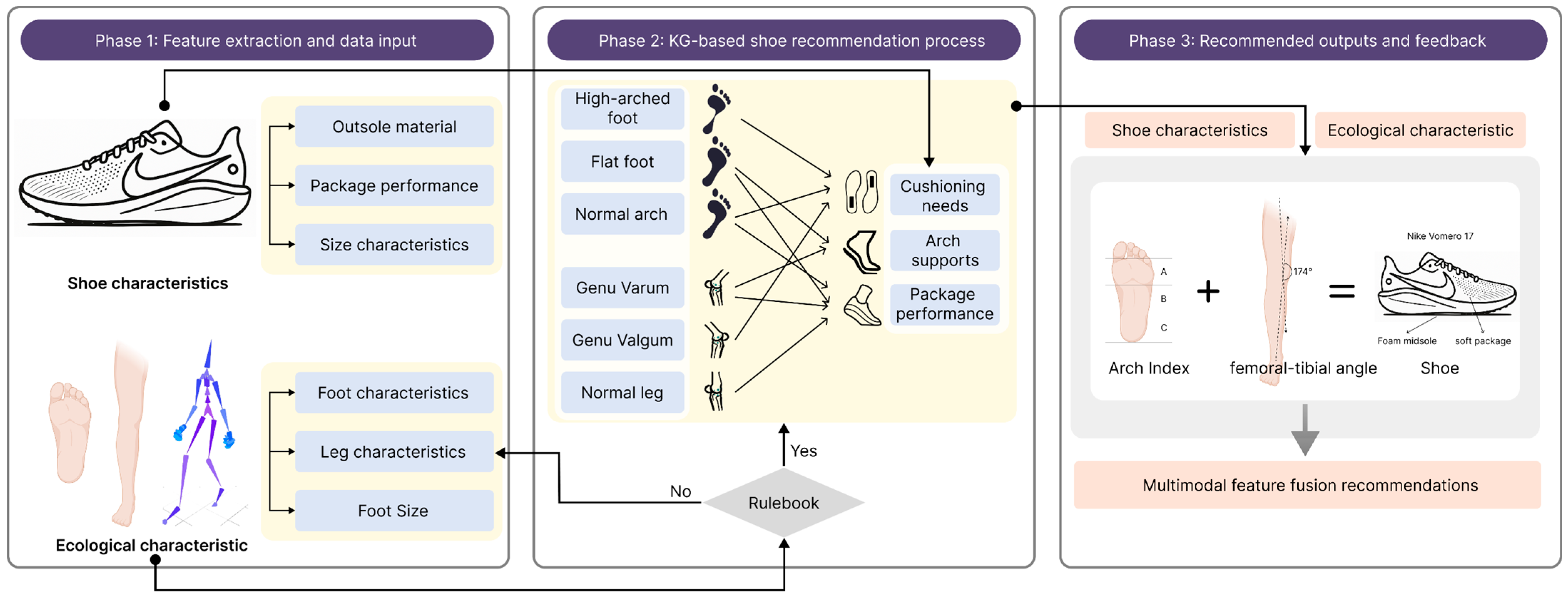
3. Construction of a Biometric Data-Driven Footwear Recommendation System
3.1. Extraction of Footwear Features
3.1.1. Acquisition of Core Elements
3.1.2. Technical Approaches to Feature Extraction
3.2. Construction of the Biometric Data-Driven Footwear Recommendation Knowledge Graph
3.2.1. Pathway for Building the Footwear Recommendation Knowledge Graph
3.2.2. NLP-Based Footwear Information Extraction
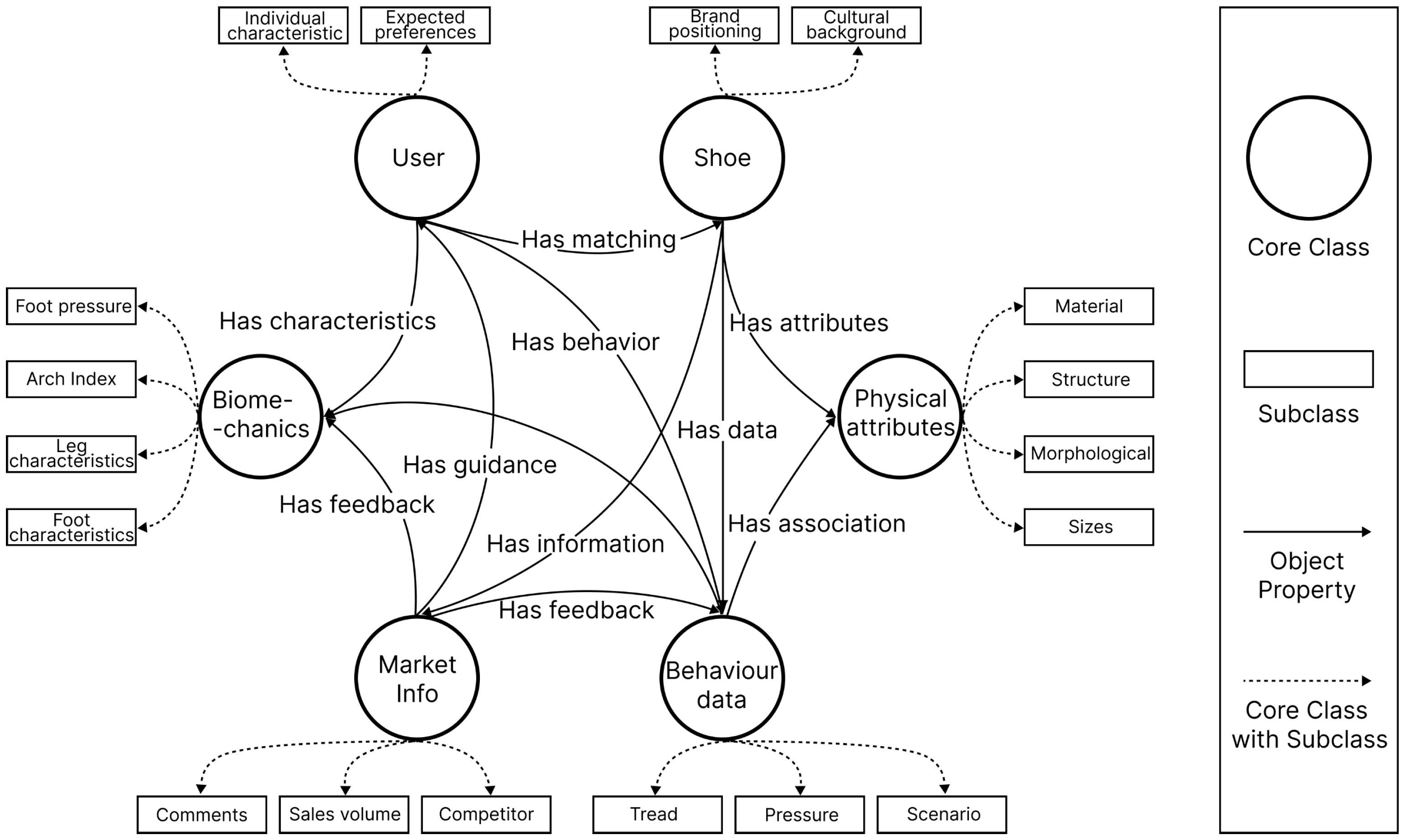
3.2.3. Ontology Construction for Footwear Recommendation KG
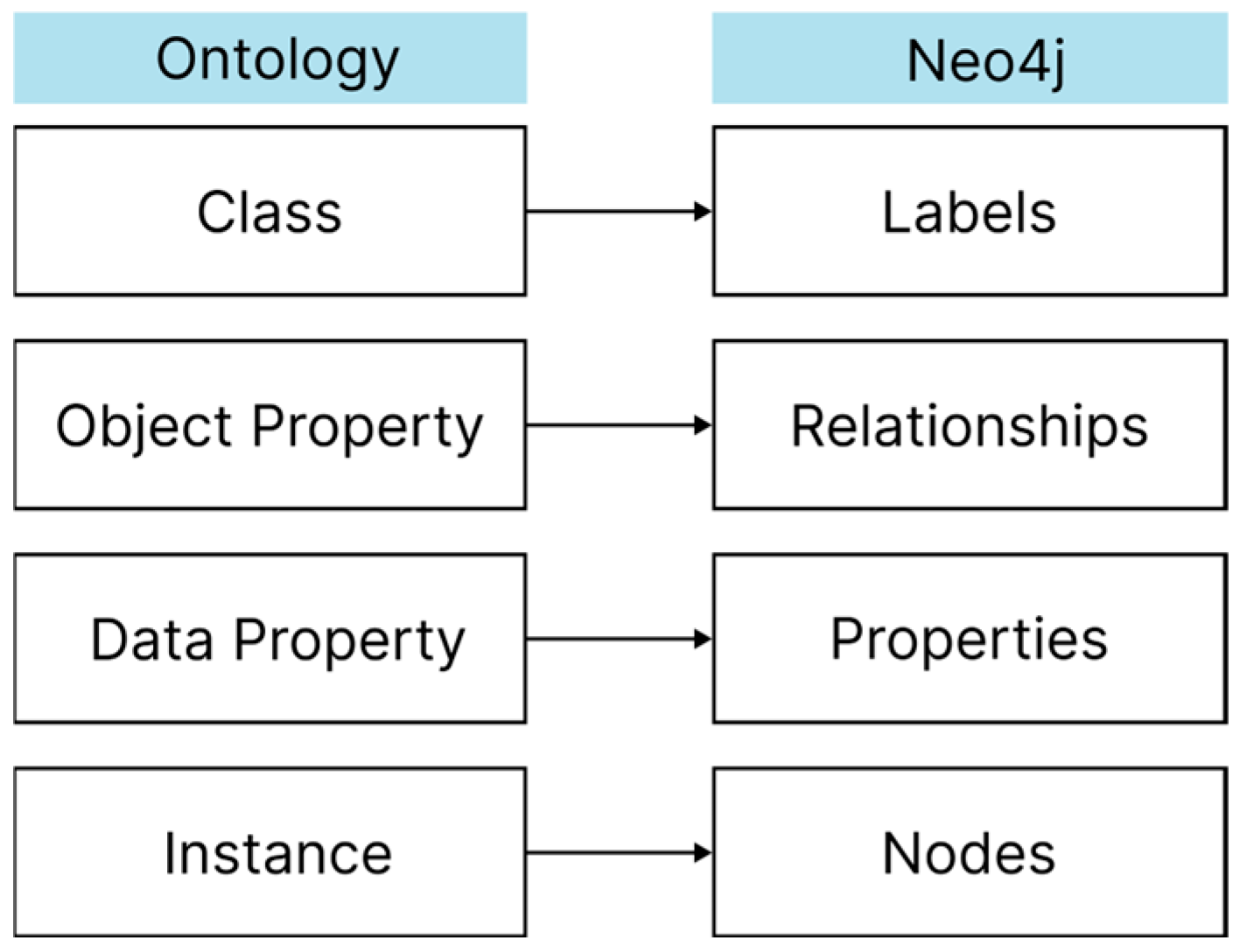
3.2.4. Ontology and Graph Database Mapping
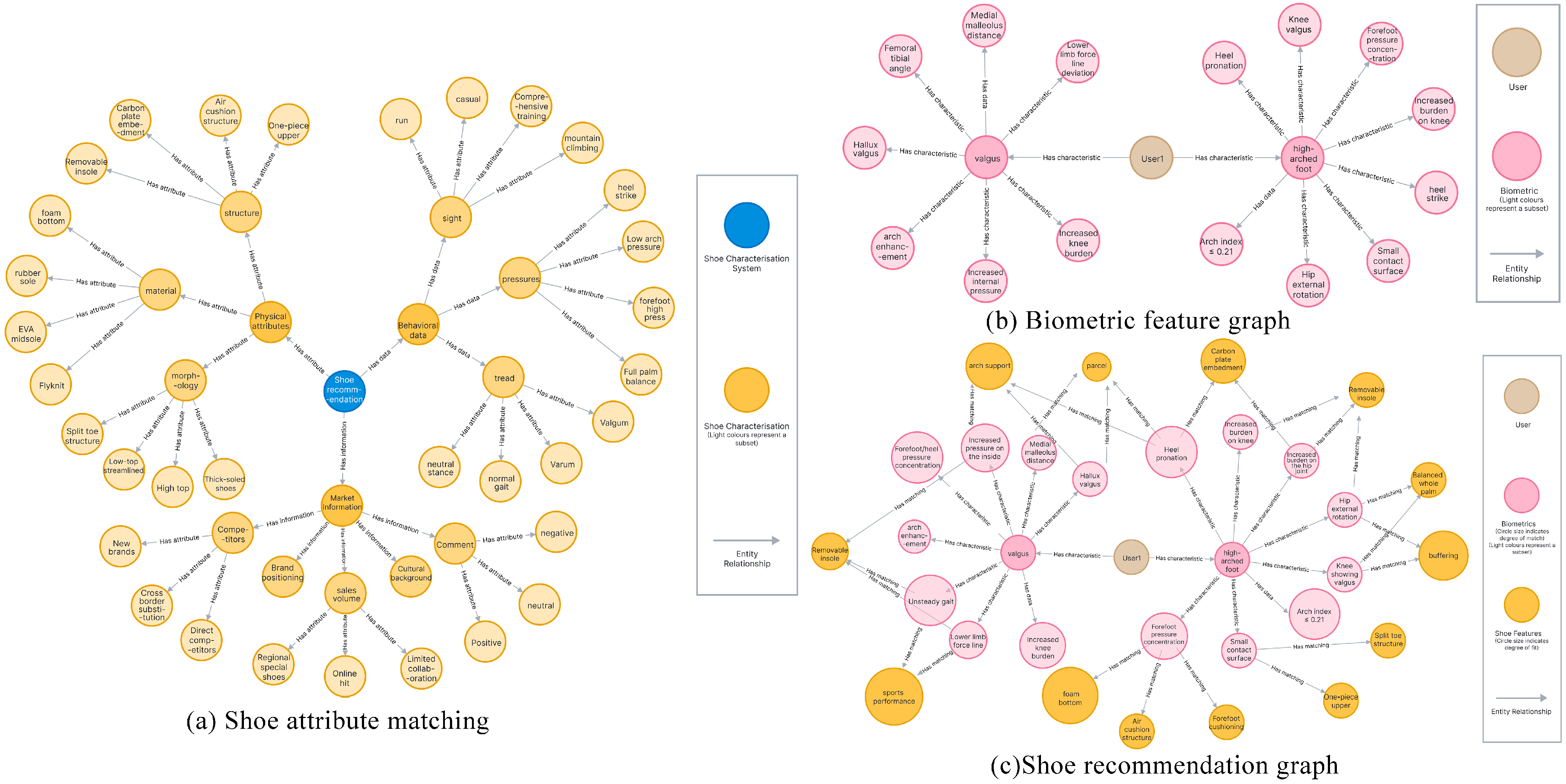
3.2.5. Neo4j-Based KG Visualization
4. Results and Discussion on the Practical Application
4.1. Questionnaire Collection and Participant Selection
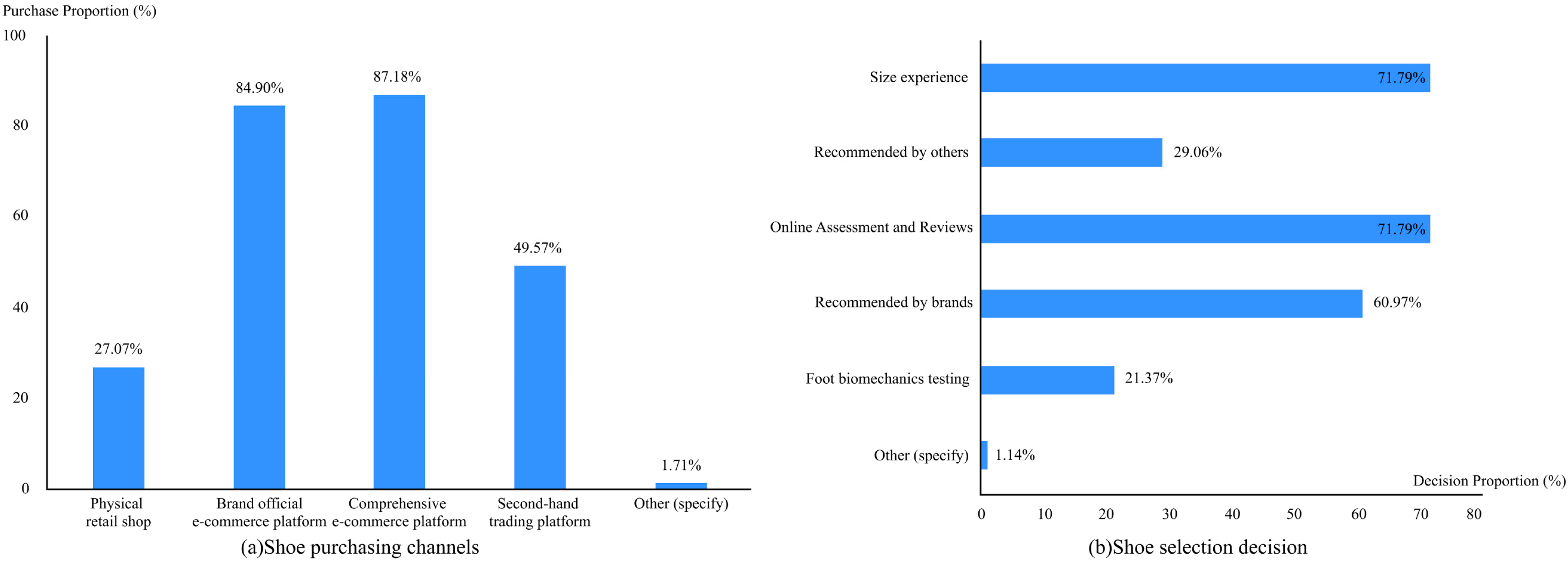
4.1.1. Questionnaire Results
4.1.2. Participant Selection
4.2. Application Testing of the Recommendation System
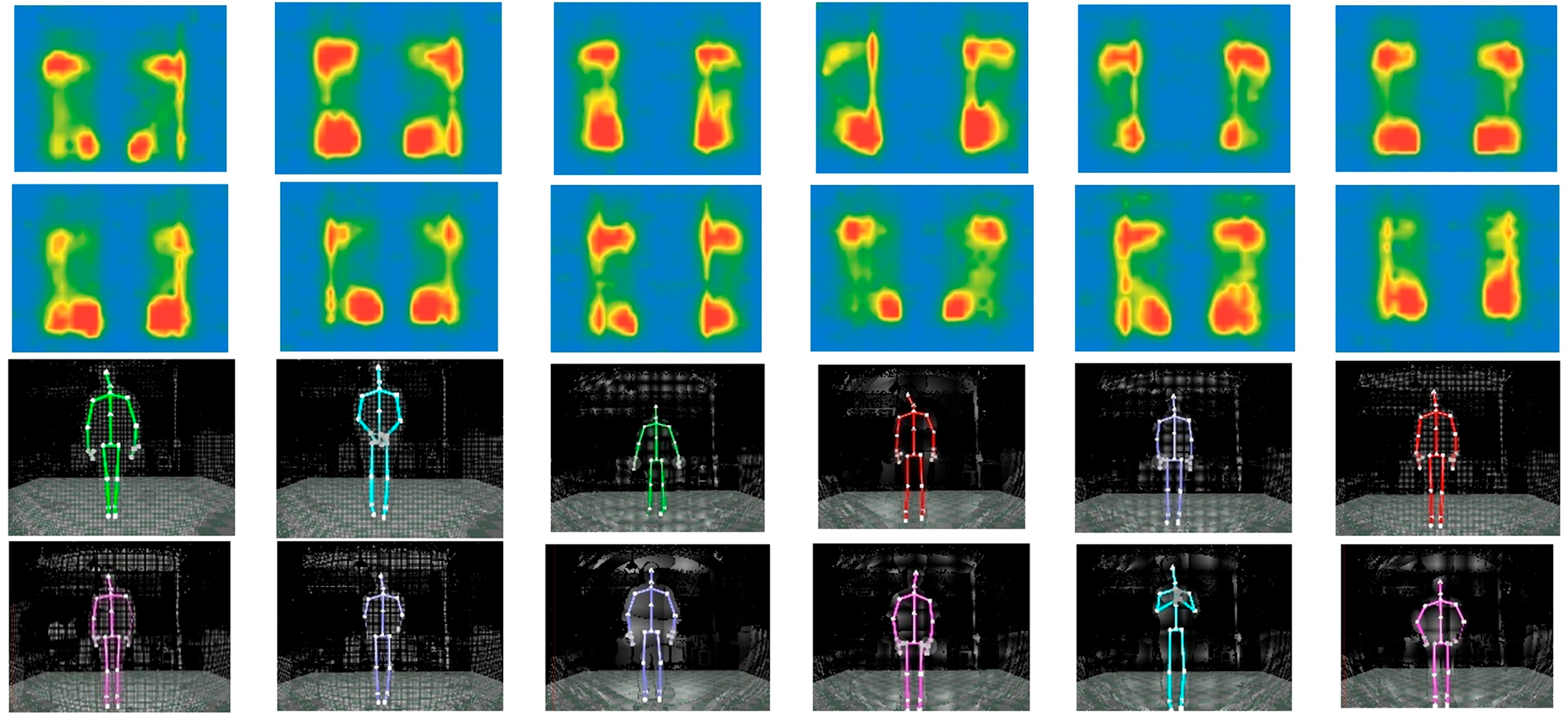
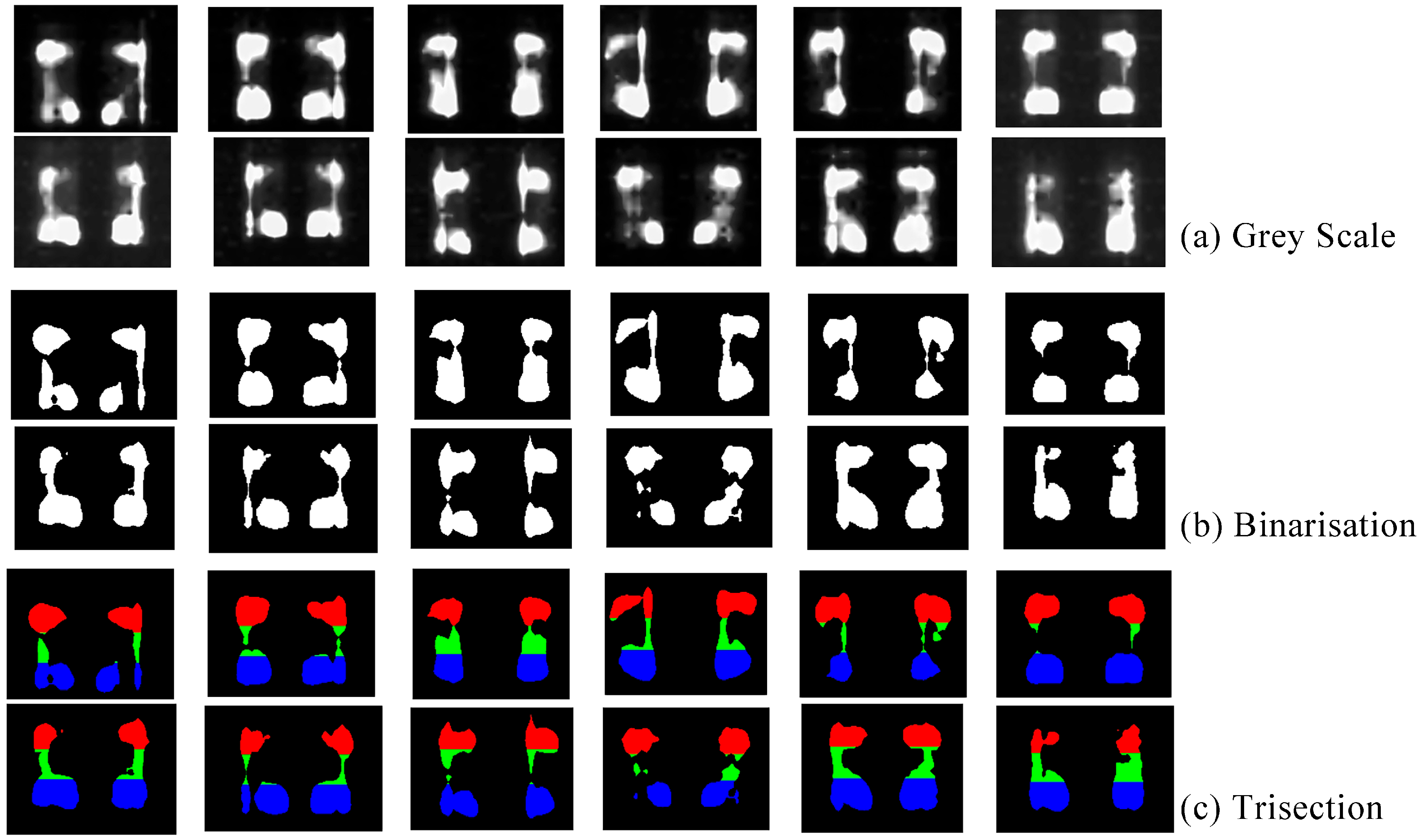
4.2.1. Experiment Acquisition and Analysis of Biometric Data
4.2.2. Biometric Data-Driven Shoe Recommendation Process and Results
4.2.3. Shoe Recommendation Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KG | Knowledge graph |
| MD | Multimodal Data |
| BD | Biometric Data |
| NLP | Natural Language Processing |
| AI | Arch Index |
| FTA | Femoral Tibial Angle |
References
- Tedeschi, R.; Giorgi, F.; Donati, D. Footwear and Foot Health: Unveiling the Role of Proper Shoe Fit in Preventing Podiatric Issues and Enhancing Well-Being. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murley, G.S.; Landorf, K.B.; Menz, H.B.; Bird, A.R. Effect of foot posture, foot orthoses and footwear on lower limb muscle activity during walking and running: A systematic review. Gait Posture 2009, 29, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldt, A.K.; Menz, H.B. Incorrectly fitted footwear, foot pain and foot disorders: A systematic search and narrative review of the literature. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2018, 11, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boppana, A.; Anderson, A.P. Dynamic foot morphology explained through 4D scanning and shape modeling. J. Biomech. 2021, 122, 110465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luximon, A.; Jiang, L.; Luximon, Y. Sizing and grading methods with consideration of footwear styles. Int. J. Ind. Erg. 2020, 78, 102960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, H.; Idrees, W.; Umar, W.; Khalil, A.; Rizvi, Z.A. Impact of routine footwear on foot health: A study on plantar fasciitis. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2022, 11, 3851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Lü, J.; Chen, T.; Jiang, F.; Chen, J.; Chen, S. Assessment of plantar arch index and prevalence of fiat feet in 3 226 school-age children in Shanghai. Chin. J. Sch. Health 2020, 41, 1328–1361, 1364. [Google Scholar]
- Inamdar, P.; Fatnani, D.; Rajiwate, F.; Shaikh, B.; Deshpande, B.; Shaikh, S.; Ranka, B.; Dhansay, S. Prevalence of flat foot and high arched foot in normal working individuals using footprint method. Int. J. Physiother. Res. 2018, 6, 2754–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woźniacka, R.; Oleksy, Ł.; Jankowicz-Szymańska, A.; Mika, A.; Kielnar, R.; Stolarczyk, A. The association between high-arched feet, plantar pressure distribution and body posture in young women. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 17187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.T.; Zhu, J.D.; Chern, J.S. Dynamic and Static Balance in Persons with Different Arch Height and Impacts of an Arch Support. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Taichung, Taiwan, 31 October–2 November 2016; pp. 282–285. [Google Scholar]
- Madzhi, N.K.; Mhd Nor, A.A.B.M.; Abdullah, N.E. Preliminary Investigation on the Effect of Speed Variation to Pressure Distribution for Flat, Medium and High Foot Arch. In Proceedings of the 2018 4th International Conference on Electrical, Electronics and System Engineering (ICEESE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 8–9 November 2018; pp. 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Norton, A.A.; Callaghan, J.J.; Amendola, A.; Phisitkul, P.; Wongsak, S.; Liu, S.S.; Fruehling-Wall, C. Correlation of Knee and Hindfoot Deformities in Advanced Knee OA: Compensatory Hindfoot Alignment and Where It Occurs. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2015, 473, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güven, E.; Çıtaker, S.; Alsancak, S. The effect of orthotics on plantar pressure in children with infantile tibia vara (Blount’s disease). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Yu, L.; Gao, Z.; Liu, W.; Mei, Q.; Gu, Y. Understanding the Role of Children’s Footwear on Children’s Feet and Gait Development: A Systematic Scoping Review. Healthcare 2023, 11, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puszczalowska-Lizis, E.; Zarzyczna, P.; Mikulakova, W.; Migala, M.; Jandzis, S. Influence of footwear fitting on feet morphology in 9 year old girls. BMC Pediatr. 2020, 20, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwan, R.L.C.; Zheng, Y.P.; Cheing, G.L.Y. The effect of aging on the biomechanical properties of plantar soft tissues. Clin. Biomech. 2010, 25, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellema, A.H.; Huysmans, T.; Hartholt, K.; van der Cammen, T.J.M. Shoe design for older adults: Evidence from a systematic review on the elements of optimal footwear. Maturitas 2019, 127, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, R.H.R.; Davies-Jones, G.R.; Brock, J.; Satheesh, V.; Robertson, G.A. Surgical management of the diabetic foot: The current evidence. World J. Orthop. 2024, 15, 404–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, S.; Wilkes, B.; Poulton, L.; Roser, M.; Draper, S.; Creer, A.; Standifird, T. Effect of Sex-Specific Running Shoes on Female Recreational Runners. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, M.S.; Raghavan, S.; Jha, S. Role of tactile and visual inputs in product evaluation: A multisensory perspective. Asia Pac. J. Mark. Logist. 2011, 23, 513–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loriette, C.; Amengual, J.L.; Ben Hamed, S. Beyond the brain-computer interface: Decoding brain activity as a tool to understand neuronal mechanisms subtending cognition and behavior. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 811736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Fang, X.; Huang, X.; Guo, C.; Wu, J. A solution and practice for combining multi-source heterogeneous data to construct enterprise knowledge graph. Front. Big Data 2023, 6, 1278153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Cai, Y.; Liu, J.; Zou, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xie, J.; Cai, Y.; Li, Q. Integration of Multi-Source Medical Data for Medical Diagnosis Question Answering. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2025, 44, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Duan, N.; Liu, S.; Shum, H.Y. Progress in Neural NLP: Modeling, Learning, and Reasoning. Engineering 2020, 6, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Jia, S.; Xiang, Y. A review: Knowledge reasoning over knowledge graph. Expert. Syst. Appl. 2020, 141, 112948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Li, G. Aging-Friendly Design Research: Knowledge Graph Construction for Elderly Advantage Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujang, M.A.; Omar, E.D.; Baharum, N.A. A Review on Sample Size Determination for Cronbach’s Alpha Test: A Simple Guide for Researchers. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 25, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nkansah, B.K. On the Kaiser-Meier-Olkin’s measure of sampling adequacy. Math. Theory Model. 2018, 8, 52–76. [Google Scholar]
- Tsang, N.W.H.; Lam, K.Y.; Qureshi, U.M.; Ng, J.K.Y.; Papavasileiou, I.; Han, S. Indoor activity tracking for elderly using intelligent sensors. In Intelligent Data Sensing and Processing for Health and Well-Being Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 197–222. [Google Scholar]
- Keatsamarn, T.; Visitsattapongse, S.; Pintavirooj, C.; Aoyama, H. Optical-based foot plantar pressure measurement with application in human postural balance, gait and recognition analysis. In Proceedings of the 2020 6th International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences and Technology (ICEAST), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 1–4 July 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Paley, D. Principles of Deformity Correction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Murley, G.S.; Menz, H.B.; Landorf, K.B. A protocol for classifying normal- and flat-arched foot posture for research studies using clinical and radiographic measurements. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2009, 2, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, H.B.; Bonanno, D.R. Footwear comfort: A systematic search and narrative synthesis of the literature. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2021, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zeng, Q.; Lai, J.; Zhang, X. Effects of arch support doses on the center of pressure and pressure distribution of running using statistical parametric mapping. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1051747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, F.; Lu, B.; Kuang, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhao, J.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Ma, J.X.; Ma, X.L. A systematic review and meta-analysis into the effect of lateral wedge arch support insoles for reducing knee joint load in patients with medial knee osteoarthritis. Medicine 2017, 96, e7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeighami, A.; Dumas, R.; Aissaoui, R. Knee loading in OA subjects is correlated to flexion and adduction moments and to contact point locations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Feature Classification | Feature | Serial Number | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | ||
| Physical Attributes | Materials L1 | Foam sole | Rubber sole | EVA midsole | Flyknit |
| Structure L2 | One-piece upper | Air cushion structure | Carbon plate embedded | Removable insole | |
| Morphology L3 | Ankle-high shoes | Low-top streamlined | Thick-soled pops | Split-toe construction | |
| Behavioral Data | Gait patterns L4 | Normal gait | Knee Varus | Knee Valgus | Neutral gait |
| Plantar pressure L5 | Forefoot high pressure | Heel high pressure | Low arch pressure | Balanced whole palm | |
| Usage scenarios L6 | Casual | Running | Hiking | Comprehensive training | |
| Market Information | User reviews L7 | Positive | Neutral | Negative | Wait and see |
| Sales figures L8 | Online pop-ups | Regional special shoes | Limited edition | Regular style | |
| Competing products L9 | Direct competitor | Cross-border substitution | New brands | Traditional upgrade | |
| User Features | Experimental Data | Foot Features | Leg Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| High-arched foot | Arch index ≤ 0.21 | Focused forefoot/heel pressure Smaller contact surface Heel pronation | Increased burden on knee and hip joints Knee shows valgus and hip external rotation |
| Flat foot | Arch index ≥ 0.26 | Increased pressure on mid-foot Larger contact surface Forefoot pronation | Increased burden on knee and hip joints Knee shows Varus and hip internal rotation |
| Normal arch | Arch index between 0.21–0.26 | Even pressure distribution | Straight legs and stable gait |
| Genu varum | Distance between inside of both knees > 30 mm Femoral-tibial angle > 179° | Foot eversion Arch collapse Increased lateral plantar pressure | Increased burden on the lateral aspect of the knee Lower limb force lines shifted outwards Unstable gait |
| Genu valgum | Distance between medial ankle bones > 30 mm Femoral-tibial angle < 174° | Foot pronation Arch increase Increased medial plantar pressure | Increased burden on the medial aspect of the knee Lower limb force lines shifted inwards Unstable gait |
| User Features | Foot Features | Leg Features |
|---|---|---|
| High-arched foot | Focused forefoot/heel pressure ↔ L1(1), L2(2), L5(1) Smaller contact surface ↔ L2(1), L3(4) Heel pronation ↔ L2(3), L4(2), L5(3) | Increased burden on knee and hip joints ↔ L2(3), L6(3) Knee shows valgus and hip external rotation ↔ L4(3), L5(2), L6(3) |
| Flat foot | Increased pressure on mid-foot ↔ L1(3), L2(3) Larger contact surface ↔ L3(3), L1(2) Forefoot pronation ↔ L3(1), L2(4) | Increased burden on knee and hip joints ↔ L2(4), L5(3) Knee shows Varus and hip internal rotation ↔ L4(2), L5(3), L6(4) |
| Normal arch | Even pressure distribution ↔ L5(4) | Straight legs and stable gait ↔ L3(2), L5(4) |
| Genu varum | Foot eversion ↔ L4(3), L5(4) Arch collapse ↔ L2(4), L3(2) Increased lateral plantar pressure ↔ L5(1), L2(2) | Increased burden on the lateral aspect of the knee ↔ L4(3), L5(4) Lower limb force lines shifted outwards ↔ L6(3), L2(2) Unstable gait ↔ L6(4), L2(4) |
| Genu valgum | Foot pronation ↔ L4(2), L5(3) Arch increase ↔ L1(3), L2(3) Increased medial plantar pressure ↔ L5(3), L2(4) | Increased burden on the medial aspect of the knee ↔ L4(2), L5(3) Lower limb force lines shifted inwards ↔ L6(4), L2(4) Unstable gait ↔ L6(4), L2(4) |
| Gender | Number | Age | Education Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 8 | 22~26 | Master’s degree |
| Female | 4 | 22~25 | Master’s degree |
| Participants | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left Foot AI | 0.119 | 0.188 | 0.274 | 0.214 | 0.157 | 0.095 | 0.067 | 0.033 | 0.256 | 0.077 | 0.149 | 0.125 |
| Right Foot AI | 0.115 | 0.197 | 0.263 | 0.217 | 0.123 | 0.138 | 0.163 | 0.065 | 0.329 | 0.124 | 0.181 | 0.088 |
| Left Leg FTA | 182° | 178° | 179° | 181° | 178° | 179° | 181° | 177° | 173° | 179° | 172° | 173° |
| Right Leg FTA | 180° | 175° | 179° | 180° | 177° | 179° | 182° | 173° | 171° | 179° | 173° | 173° |
| Participants | Recommended Shoes | Reason for Recommendation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nike Air Max 270 | Featuring a foam sole and air cushion construction with a low-top shape |
| 2 | Nike ZoomX Vaporfly | Combines a foam sole, air cushion construction, carbon plate technology |
| 3 | Asics Gel-Nimbus 23 | EVA midsole and rubber sole provide comfort and abrasion resistance |
| 4 | Adidas Ultraboost 22 | Streamlined low-top design combined with air-cushioned construction |
| 5 | Nike ZoomX Vaporfly | Same as 2 |
| 6 | Nike ZoomX Vaporfly | Same as 2 |
| 7 | Nike Air Max 1 | Low-top design with foam sole and air cushion construction |
| 8 | Nike Air Zoom Pegasus | Foam sole, air cushion construction and removable insole |
| 9 | Brooks Glycerin 19 | Features a combination of EVA midsole and rubber sole |
| 10 | Nike ZoomX Vaporfly | Same as 2 |
| 11 | Nike Air Zoom Pegasus | Same as 8 |
| 12 | Nike Air Zoom Pegasus | Same as 8 |
| Participants | Recommended Shoes | Participants | Recommended Shoes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | New Balance NB 327 | 7 | Timberland Motion6 |
| 2 | ERKE high-top boardshorts | 8 | Skechers D’Lites1 |
| 3 | Superstar Shoes | 9 | Balenciaga3xl |
| 4 | Air Force 1 | 10 | Air Jordan 1 |
| 5 | ERKE boardshorts | 11 | Nike Vomero17 |
| 6 | Air Jordan 1 | 12 | Air Force 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Li, X. Biodata-Driven Knowledge Graph Recommendation System: Fusing Foot and Leg Characteristics for Personalised Shoe Recommendation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11281. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011281
Zhang H, Li X. Biodata-Driven Knowledge Graph Recommendation System: Fusing Foot and Leg Characteristics for Personalised Shoe Recommendation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11281. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011281
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Haoyu, and Xiaoying Li. 2025. "Biodata-Driven Knowledge Graph Recommendation System: Fusing Foot and Leg Characteristics for Personalised Shoe Recommendation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11281. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011281
APA StyleZhang, H., & Li, X. (2025). Biodata-Driven Knowledge Graph Recommendation System: Fusing Foot and Leg Characteristics for Personalised Shoe Recommendation. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11281. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011281






