Digital-Driven New Quality Productivity and Its Impact on Supply Chain Resilience: A Complex Network Approach Integrating the Hadamard Product
Abstract
1. Introduction
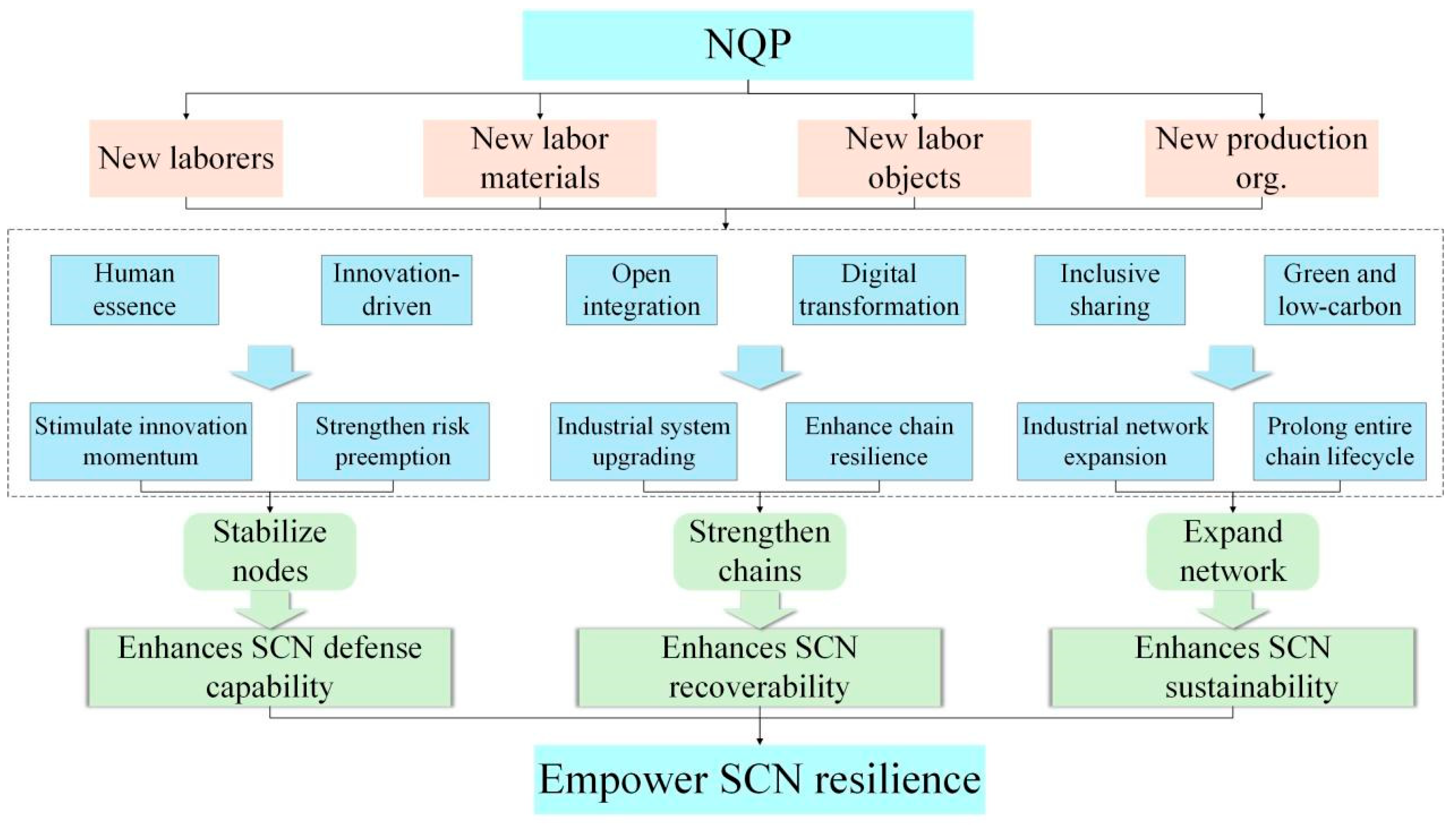
2. Theoretical Pathways of NQP on SCN Resilience
2.1. Stabilize Nodes: NQP Enhances SCN Defense Capability
2.2. Strengthen Chains: NQP Enhances SCN Recoverability
2.3. Expand Network: NQP Enhances SCN Sustainability
3. Research Design and Model Construction
3.1. SCN Model Construction
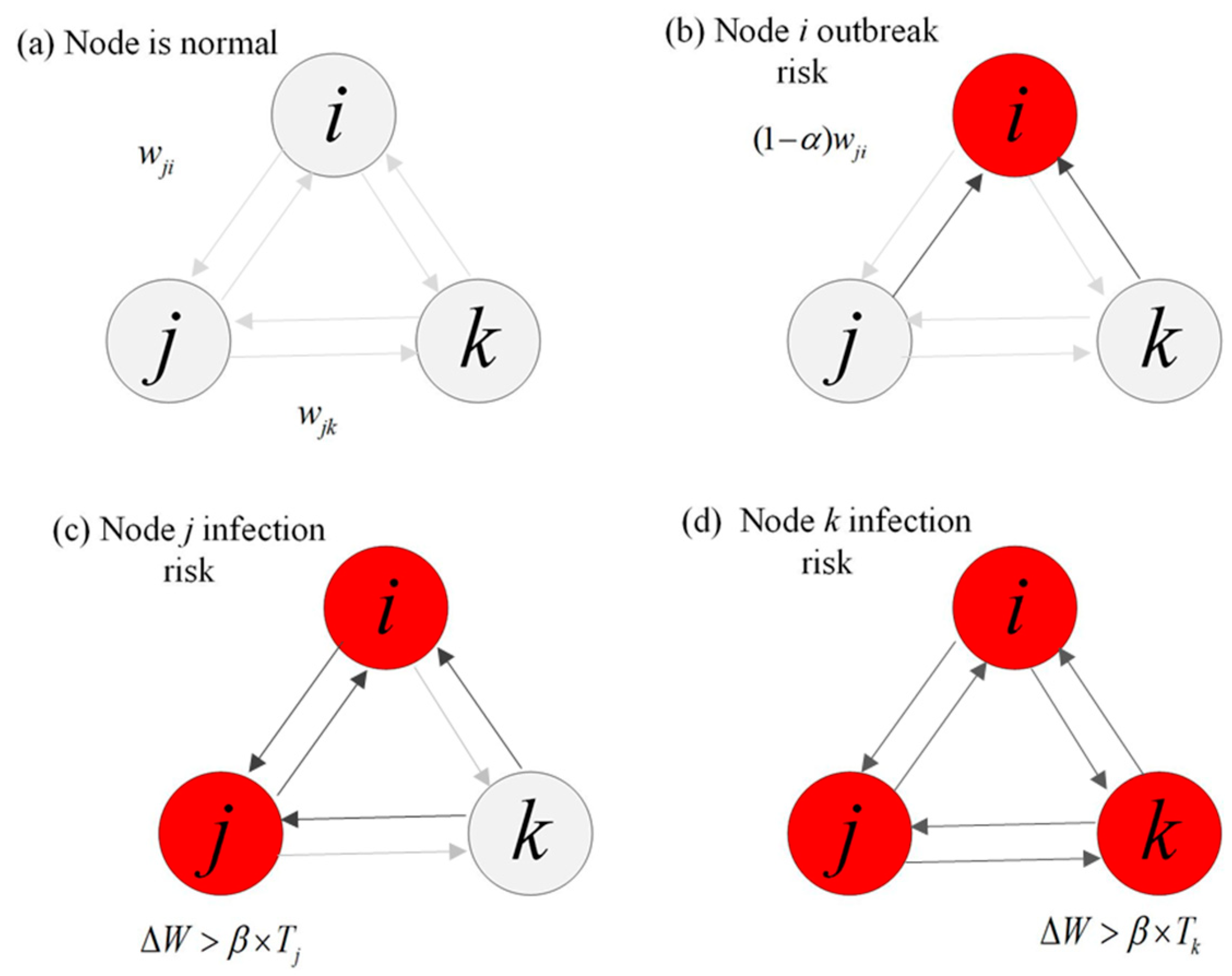
3.2. SCN Resilience Indicators
3.3. NQP Impacts SCN Model Construction
4. Result Analysis
4.1. Measurement Results of SCN Resilience
4.1.1. Data Sources and Processing
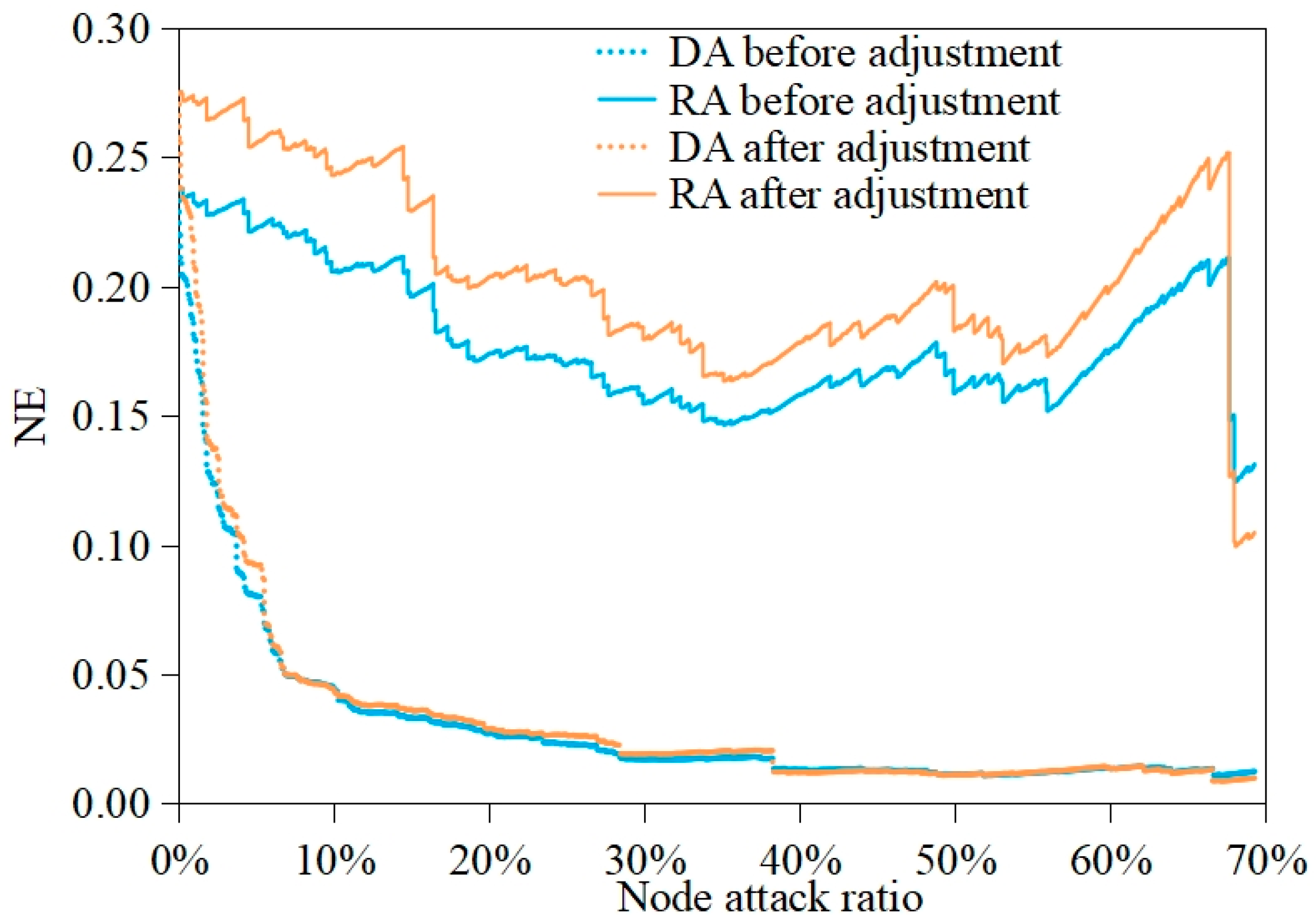
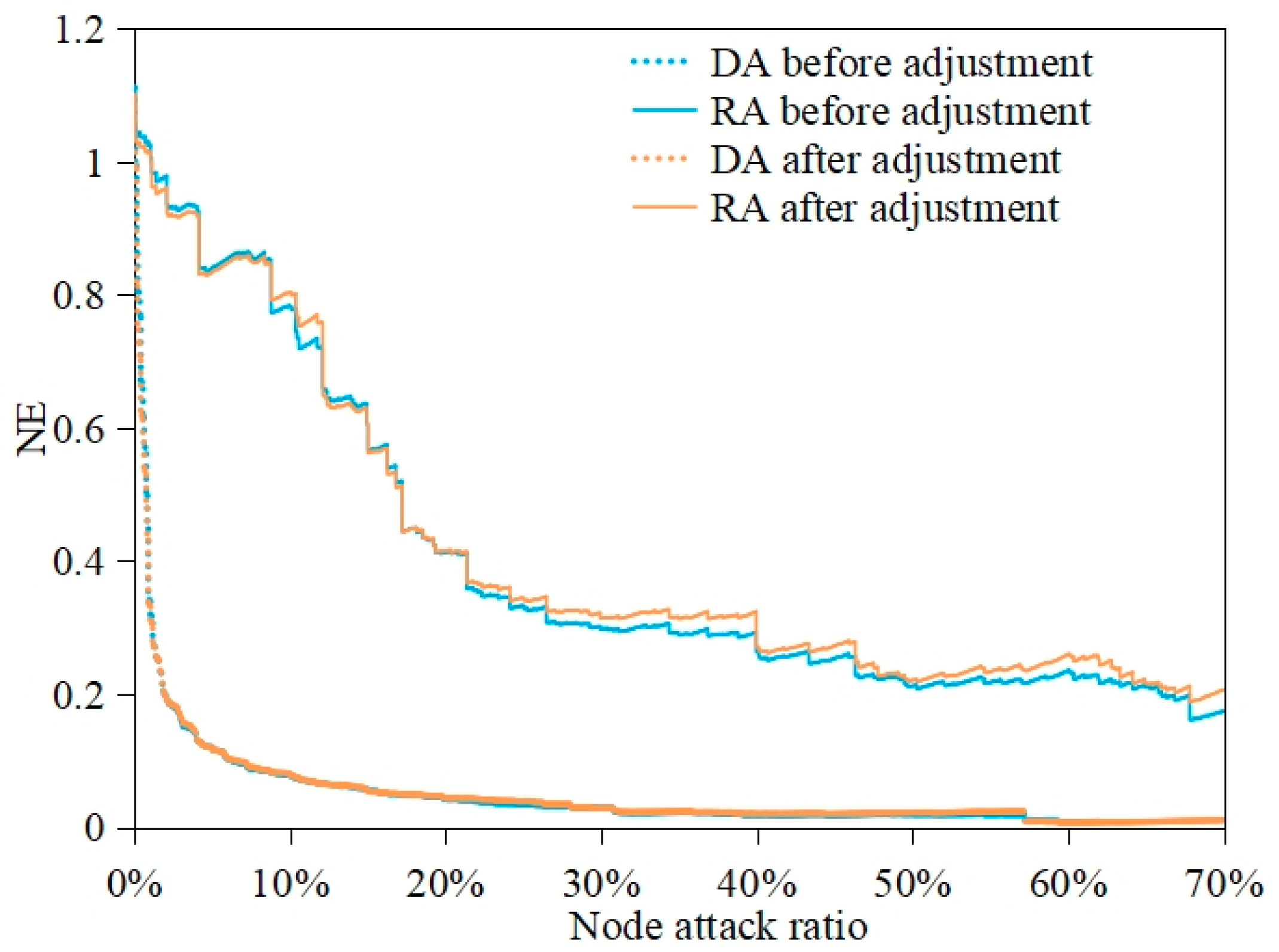
4.1.2. Measurement Results of SCN Resilience
4.2. Impact of NQP on SCN Defense Capability
4.3. Impact of NQP on SCN Recoverability
4.4. Impact of NQP on SCN Sustainability
5. Conclusions and Policy Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, C.; Zhang, L.; You, L.; Tian, W. A review of supply chain resilience: A network modeling perspective. Appl. Sci. 2024, 15, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Gu, T.; Shi, Y. The Influence of New Quality Productive Forces on High-Quality Agricultural Development in China: Mechanisms and Empirical Testing. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, N.; Nayak, B.S. Rethinking of Marxist perspectives on big data, artificial intelligence (AI) and capitalist economic development. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2021, 166, 120576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Chiarini, A. Building Sustainable Supply Chain Resilience: Insights From a Mixed-Method Study. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2024, 34, 2103–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.M.H.; Islam, M.T.; Ali, I.; Quaddus, M. The role of social capital, resilience, and network complexity in attaining supply chain sustainability. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 33, 2621–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnadi, M.; Gheith, M.H.; Troise, C.; Abdallah, Y.O.; Abdelaziz, M.A.A. Digital Transformation and Sustainable Supply Chain Performance for Sustainable Development: The Mediating Role of Supply Chain Capabilities. Sustain. Dev. 2025. online version of record before inclusion in an issue. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearnshaw, E.J.; Wilson, M.M. A complex network approach to supply chain network theory. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2013, 33, 442–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guntuka, L.; Carnovale, S.; Falcone, E. Supply Chain Plasticity: A Responsive Network Capability to Ensure Resilience. J. Bus. Logist. 2024, 45, e12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrucco, A.S.; Picanço Rodrigues, V.; Fransoo, J.C.; Mejia-Argueta, C. Resilient Supply Chains Amid Uncertainty: Do Agility, Adaptability, and Alignment Mitigate the Effects of Major Disruptions? J. Bus. Logist. 2025, 46, e70037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Q. Developing supply chain resilience through integration: An empirical study on an e-commerce platform. J. Oper. Manag. 2022, 69, 477–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, Z.; Mangla, S.K.; Song, M. Robot Built Different: How It Affects Supply Chain Resilience. J. Bus. Logist. 2025, 46, e70028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.K.; Daultani, Y.; Pratap, S. Blockchain technology enabled critical success factors for supply chain resilience and sustainability. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2023, 33, 1533–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Yang, G.; Chen, T. The role of green finance and digital inclusive finance in promoting economic sustainable development: A perspective from new quality productivity. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Ran, R.; Wu, W. New energy policy and new quality productive forces: A quasi-natural experiment based on demonstration cities. Econ. Anal. Policy 2024, 84, 1670–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hua, Z.; He, Z.; Wei, X.; Sun, H. The impact of local government attention on green total factor productivity: An empirical study based on System GMM dynamic panel model. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K. The Promoting Role of New Quality Productive Forces in Rural Revitalization and Its Mechanism Analysis—An Empirical Study Based on the Effects of Innovation Spillover and Industrial Upgrading. Adv. Econ. Manag. Res. 2025, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Tang, Q.; Jin, G. Labor protection and the efficiency of human capital investment. Econ. Anal. Policy 2021, 69, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y. Research on Collaborative Performance of Green Supply Chain Enabled by New Quality Productivity. Sustainability 2025, 17, 3793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, H.; ur Rehman, A.; Iftikhar, A.; ul Haq, M.Z.; Akbar, U.; Kamal, M.M. Digital transformation: Unlocking supply chain resilience through adaptability and innovation. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2025, 219, 124234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y.; Li, H.; Dong, J.; Zhou, J.; Hu, L. Impacts of intellectual capital, supply chain knowledge sharing on supply chain resilience: Evidence from China. J. Intellect. Cap. 2025, 26, 1013–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issa, A.; Khadem, A.; Alzubi, A.; Berberoğlu, A. The path from green innovation to supply chain resilience: Do structural and dynamic supply chain complexity matter? Sustainability 2024, 16, 3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, A.B.M.; Ali, H.A.A.; Aly, S.A.S.; Ali, M.A.S. The Interplay between Digital Technologies, Supply Chain Resilience, Robustness and Sustainable Environmental Performance: Does Supply Chain Complexity Matter? Sustainability 2024, 16, 6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, T.M.; Mathivathanan, D.; Arun SJ, C.J.; Ramasubramaniam, M.; Alathur, S. Influence of supply chain resilience, information technology capabilities and agility on cost and delivery performance in construction supply chains: An Indian perspective. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2023, 34, 1050–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Raut, R.D.; Gunasekaran, A.; Venkateshwarlu, M.; Choubey, V.K. Developing supply chain capabilities through digitalization and viability for controlling the ripple effect. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 10341–10357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Bao, H. Digital transformation and resilience of supply chain in manufacture listed firms: A backward spillover effects in the vertical supply chain relationship. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 65, 105516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Luo, X.; Xi, M. The impact of regional artificial intelligence development on the resilience of enterprise supply chains. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 102, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Li, J. How does digital collaboration impact supply chain resilience. Financ. Res. Lett. 2024, 66, 105684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, Y. Corporate financialization, digital transformation, and industrial supply chain resilience: Mechanisms based on R&D investment and financial regulation. Int. Rev. Financ. Anal. 2025, 102, 104119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.; Ran, W. Supply chain diversification, digital transformation, and supply chain resilience: Configuration analysis based on FSQCA. Sustainability 2022, 14, 7690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effah, D.; Bai, C.; Asante, W.A.; Quayson, M. The role of artificial intelligence in coping with extreme weather-induced cocoa supply chain risks. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2023, 71, 9854–9875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, D.; Li, H. Efficiency measurement and productivity progress of regional green technology innovation in China: A comprehensive analytical framework. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2022, 34, 1432–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini, S.; Ivanov, D.; Blackhurst, J. Conceptualization and measurement of supply chain resilience in an open-system context. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2020, 69, 3111–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, S.; Rahman, M.S.; Chan, H.-L.; Sharma, J. Effect of Supply Chain Flexibility and Supply Chain Endurance on Supply Chain Resilience in Extreme Weather Events: An Empirical Study. IEEE Trans. Eng. Manag. 2025, 72, 2150–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Q. Developing supply chain resilience: A supply network perspective. Supply Chain Manag. Int. J. 2025, 30, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavassani, K.M.; Boyd, Z.M.; Movahedi, B.; Vasquez, J. Ten-tier and multi-scale supply chain network analysis of medical equipment: Random failure & intelligent attack analysis. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2023, 61, 8468–8492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G. A Study on the Measurement of China’s Manufacturing Industry Chain Toughness and Regional Heterogeneity from a Dynamic Perspective. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2025, 102, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wei, L.; Yi, Z. The impact of embedded global innovation networks on manufacturing value chains. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 28275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsolakis, N.; Schumacher, R.; Dora, M.; Kumar, M. Artificial intelligence and blockchain implementation in supply chains: A pathway to sustainability and data monetisation? Ann. Oper. Res. 2023, 327, 157–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Li, G.; Ivanov, D. Digital transformation in the blockchain era: Balancing efficiency and resilience in operations management. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2025, 282, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouari, D.; Ruel, S.; Viale, L. Does digitalising the supply chain contribute to its resilience? Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2021, 51, 149–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; He, Z. Synergistic industrial agglomeration, new quality productive forces and high-quality development of the manufacturing industry. Int. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2024, 94, 103373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, C. Digital transformation, firm boundaries, and market power: Evidence from China’s listed companies. Systems 2023, 11, 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Wei, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, X. Mitigating supply-demand mismatch: The relationship between inventory sharing and demand learning. Decis. Sci. 2024, 55, 533–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Sui, Q.; Liu, H.; Yu, G.; Qu, J. Promoting environmental risk assessment and control of emerging contaminants in China. Engineering 2024, 37, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. The Structure and Function of Complex Networks. SIAM Rev. 2003, 45, 167–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.S.; Bell, M.G.; Piraveenan, M.; Kasthurirathna, D.; Parhi, M. Topological structure of manufacturing industry supply chain networks. Complexity 2018, 2018, 3924361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, Y. The impact of digital infrastructure on industrial chain resilience: Evidence from China’s manufacturing. Technol. Anal. Strateg. Manag. 2024, 37, 1112–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ma, D.; Wang, Y. Structural resilience evolution and vulnerability assessment of semiconductor materials supply network in the global semiconductor industry. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2024, 270, 109172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.U.; Daipeng, M.A.; Xianmei, W. International trade network resilience for products in the whole industrial chain of iron ore resources. Resour. Sci. 2022, 44, 2006–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X. Research on the Statistical Properties and Stability of Complex Interindustrial Networks. Complexity 2024, 2024, 9220756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Sun, X.; He, C.; Liu, G. Systematic risks of the global lithium supply chain network: From static topological structures to cascading failure dynamics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 22135–22147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Ren, B. Supply risk propagation in international trade networks of the tungsten industry chain. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2025, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysos, G.G.; Wu, Y.; Pascanu, R.; Torr, P.; Cevher, V. Hadamard product in deep learning: Introduction, Advances and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2025, 47, 6531–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, Y.; Yao, N.; Lin, O.; Li, Q.; Liu, B. Impact of policy interventions on low-carbon technology innovation diffusion in supply networks. Manag. Decis. Econ. 2024, 45, 5040–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Hua, Q.; Xu, S.; Lin, W. The mechanism of green finance in promoting China’s new quality productive forces: Technological innovation and data factor. Res. Int. Bus. Financ. 2025, 79, 103038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, X.; Pan, Y. Global industrial chain resilience research: Theory and measurement. Systems 2023, 11, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Wang, G. Based On “Long Tail” Theory to Solve Finance Difficulties of SMEs with Internet Finance. Adv. Econ. Manag. Res. 2023, 6, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Research Method | Literature | Research Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Structural equation modeling (SEM) | [4,6,12,19,20,21,22,23,24] | Causal path analysis and empirical mechanism testing |
| Panel regression analysis | [9,25,26,27,28] | Dynamic heterogeneity and long-term resilience evolution |
| Configurational analysis (fsQCA) | [10,29,30] | Multiple pathways and complex conditional configurations |
| Complex network modeling | [8,31,32] | Topological structure and risk propagation characteristics |
| Research Perspective | Literature | Research Content |
|---|---|---|
| Digitalization and intelligence | [19,22,24,25,26,27,28] | Digital transformation, AI empowerment, and information interconnectivity for enhancing resilience |
| Greening and sustainability | [21,30] | Green innovation, eco-logistics optimization, and boundary effects of environmental complexity |
| Knowledge capital, flexibility, and organizational capability | [20,23,33] | Intellectual capital, knowledge sharing, and dynamic organizational capability for risk mitigation |
| Complex systems perspective | [29,32,34] | Structural holes, multi-path networks, and system openness for resilience improvement |
| Time Period | Enterprise | Number of Transactions | Average Transaction Value | Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012–2014 | 1296 | 1728 | 22,984.7 | 61 |
| 2015–2020 | 1448 | 2068 | 22,859.58 | 64 |
| 2021–2023 | 1206 | 1336 | 38,280.73 | 59 |
| 2012–2014 | 2015–2020 | 2021–2023 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DA | RA | DA | RA | DA | RA | ||
| NE | Max | 0.24 | 0.24 | 1.11 | 1.11 | 0.62 | 0.62 |
| Min | 0.01 | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.29 | |
| Mean | 0.03 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.40 | 0.07 | 0.39 | |
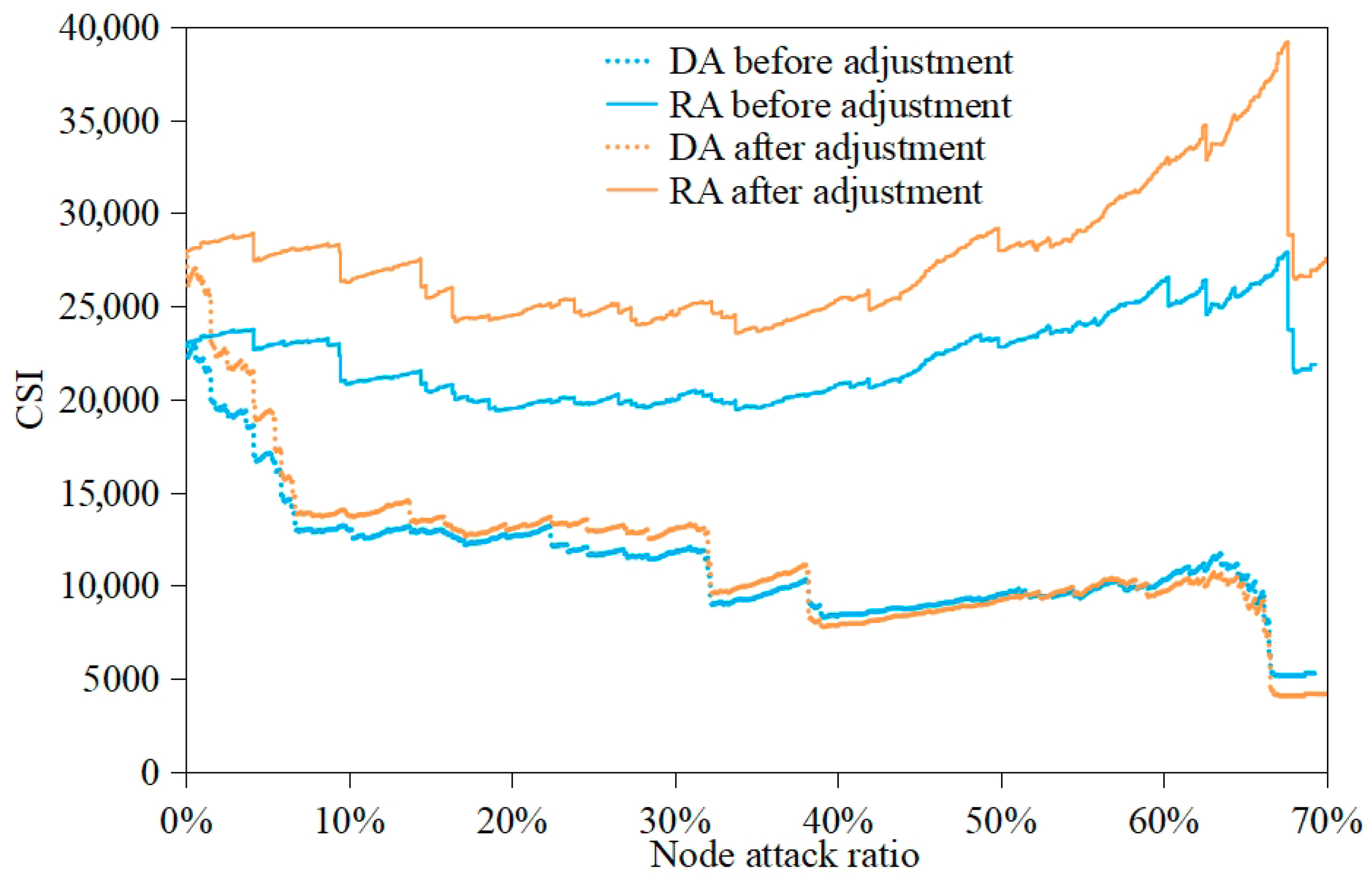
| CSI | Max | 22,997.7 | 27,891.7 | 22,912.9 | 23,863.2 | 38,346.3 | 38,908.8 |
| Min | 5169.7 | 19,409.0 | 5992.6 | 18,645.8 | 9752.0 | 32,016.9 | |
| Mean | 11,224.6 | 22,100.1 | 9951.1 | 21,027.3 | 15,679.5 | 34,632.5 | |
| Risk scenario | r1 | r2 | r1 | r2 | r1 | r2 | |
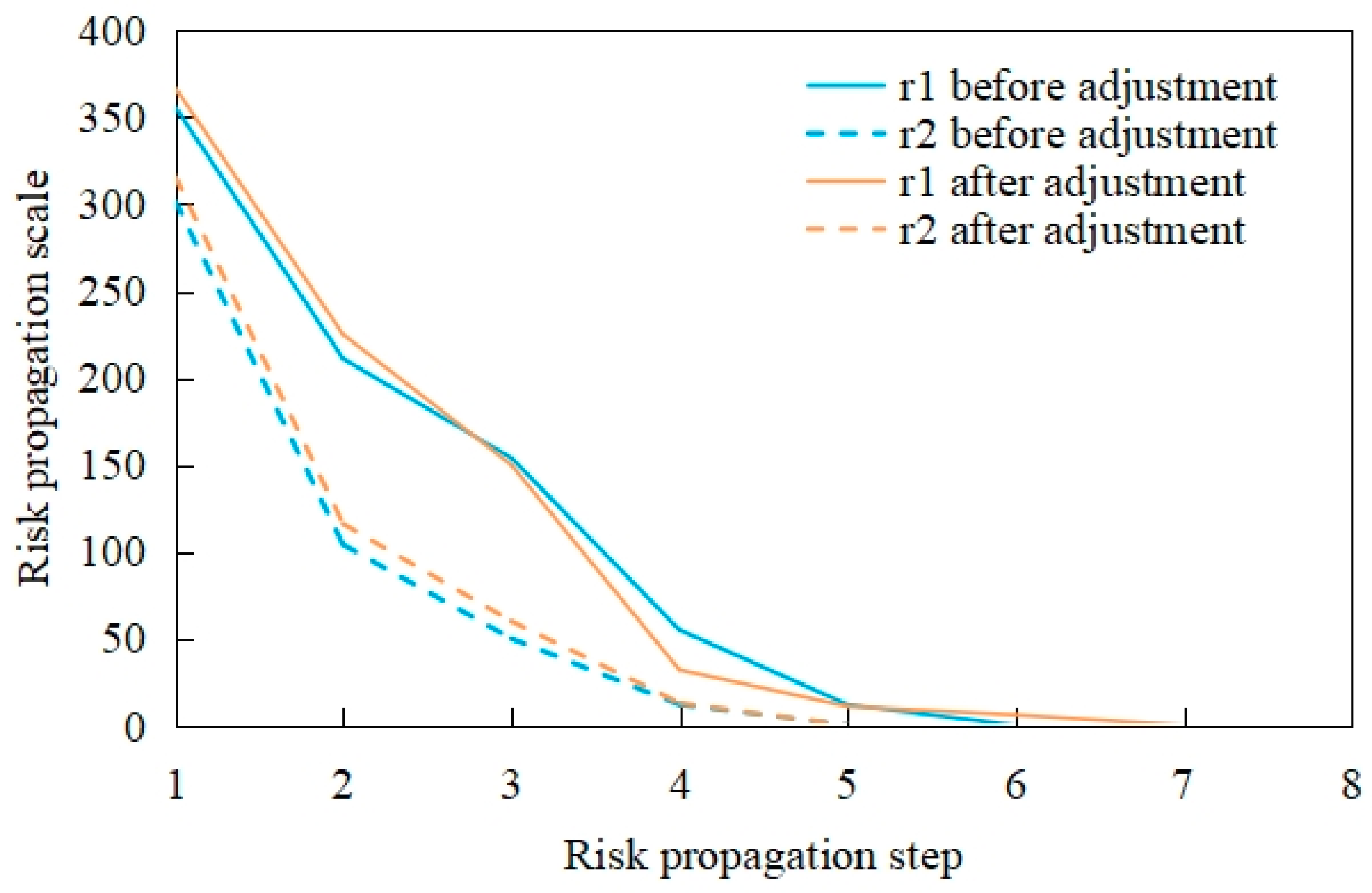
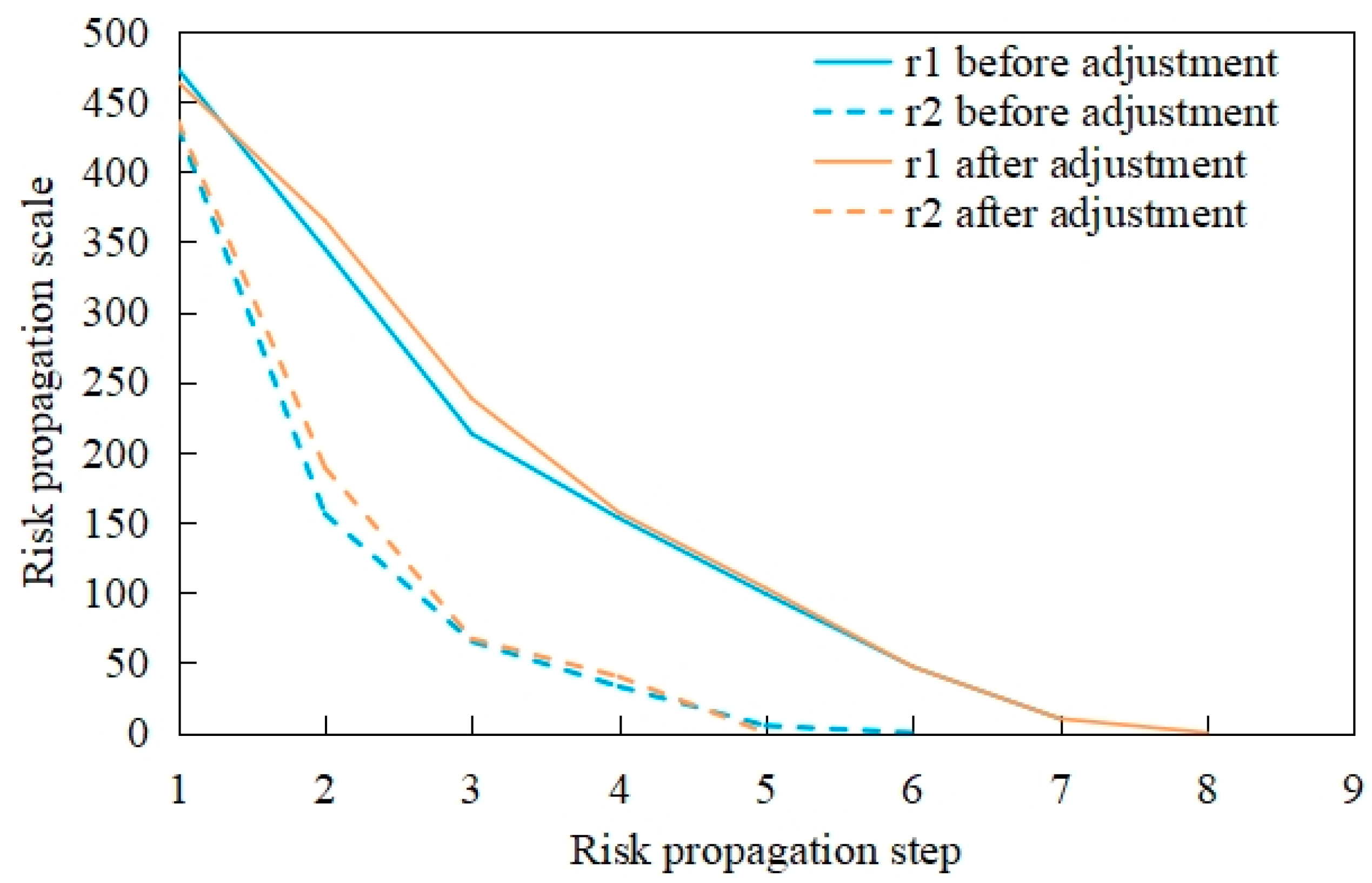
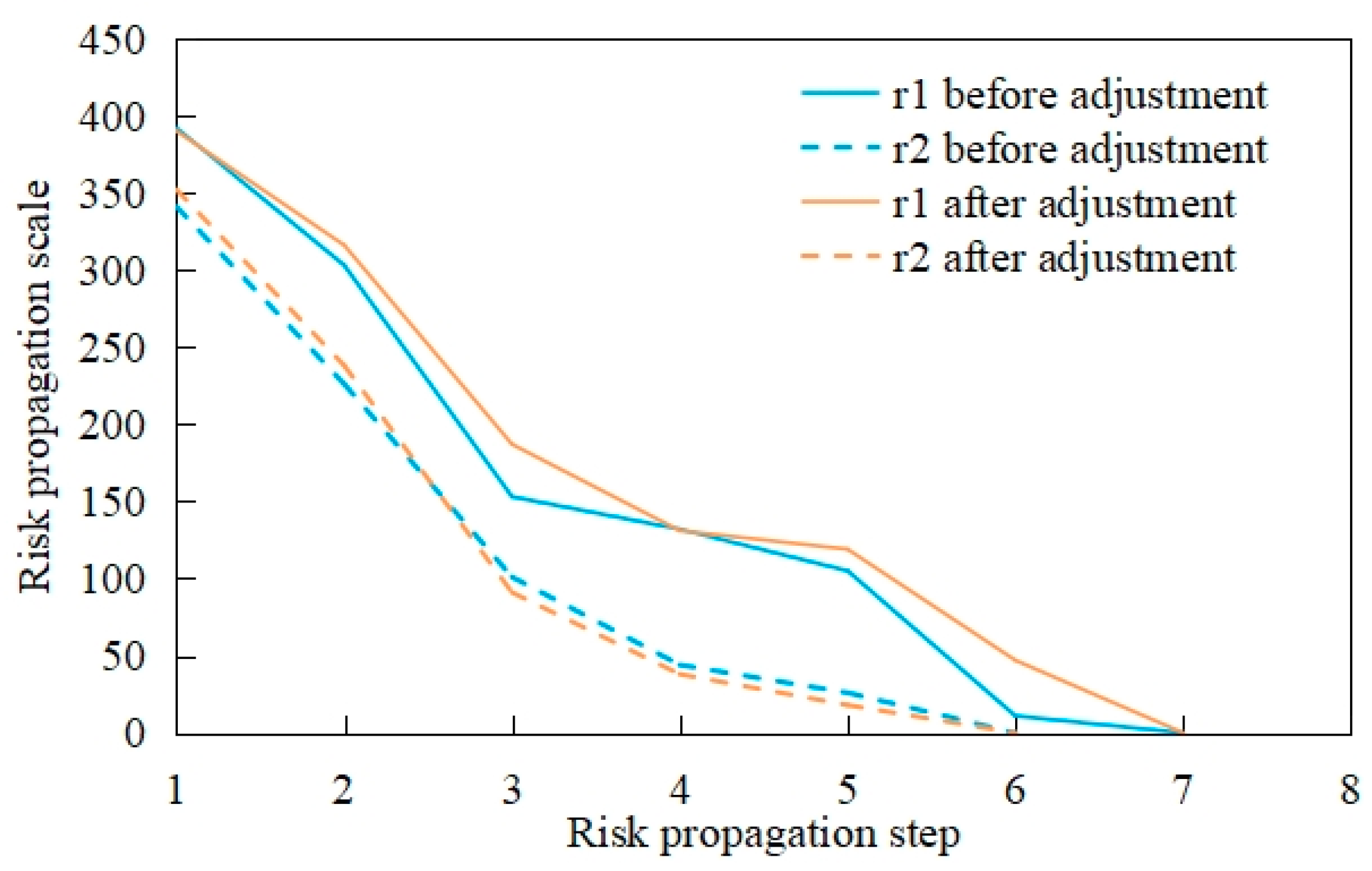
| CFS | Max-failed nodes | 11 | 8 | 23 | 13 | 17 | 10 |
| Mean-failed nodes | 4.28 | 3.56 | 7.52 | 3.80 | 6.81 | 4.95 | |
| Failure step | 6 | 5 | 8 | 6 | 7 | 6 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, X.; Li, Z. Digital-Driven New Quality Productivity and Its Impact on Supply Chain Resilience: A Complex Network Approach Integrating the Hadamard Product. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11193. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011193
Kang X, Li Z. Digital-Driven New Quality Productivity and Its Impact on Supply Chain Resilience: A Complex Network Approach Integrating the Hadamard Product. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11193. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011193
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Xi, and Zhanfeng Li. 2025. "Digital-Driven New Quality Productivity and Its Impact on Supply Chain Resilience: A Complex Network Approach Integrating the Hadamard Product" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11193. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011193
APA StyleKang, X., & Li, Z. (2025). Digital-Driven New Quality Productivity and Its Impact on Supply Chain Resilience: A Complex Network Approach Integrating the Hadamard Product. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11193. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011193








