Abstract
Voice assistants have become increasingly common in everyday devices such as smartphones and smart speakers. Improving their user experience (UX) is crucial to ensuring usability, acceptance, and long-term effectiveness. Heuristic evaluation is a widely used method for UX evaluation due to its efficiency in detecting problems quickly and at low cost. Nonetheless, existing usability/UX heuristics were not designed to address the specific challenges of voice-based interaction, which relies on spoken dialog and auditory feedback. To overcome this limitation, we developed HEUXIVA, a set of 13 heuristics specifically developed for evaluating UX with voice assistants. The proposal was created through a structured methodology and refined in two iterations. We validated HEUXIVA through heuristic evaluations, expert judgment, and user testing. The results offer preliminary but consistent evidence supporting the effectiveness of HEUXIVA in identifying UX issues specific to the voice assistant “Google Nest Mini”. Experts described the heuristics as clear, practical, and easy to use. They also highlighted their usefulness in evaluating interaction features and supporting the overall UX evaluation process. HEUXIVA therefore provides designers, researchers, and practitioners with a specialized tool to improve the quality of voice assistant interfaces and improve user satisfaction.
1. Introduction
As voice assistants become more common in smartphones, smart speakers, and other devices, understanding and improving user experience (UX) can significantly impact their use and effectiveness. UX evaluation can detect usability issues, identify user needs and preferences, and guide the design of more intuitive and effective voice interfaces. Heuristic evaluation is a widely used method for assessing UX with interfaces. It involves a group of UX/usability experts examining a system and evaluating whether its interface adheres to a set of principles known as heuristics [1]. This method is useful and effective for evaluating UX with voice assistants, as it allows for the quick and economical identification of usability problems. Nevertheless, it is crucial to have a set of heuristics that can detect specific issues related to these types of intelligent assistants, such as issues related to voice interaction, clarity and naturalness of the assistant’s responses, ease of use of voice commands, and the assistant’s ability to understand and effectively respond to user requests.
However, traditional UX/usability heuristics may not directly apply to voice interfaces, which rely on spoken language and audio feedback. Therefore, developing specialized heuristics adapted to the specific features and limitations of voice interaction can provide a more accurate and comprehensive evaluation for designers and researchers. For this reason, we proposed HEUXIVA: a set of 13 Heuristics for Evaluating User eXperience with Voice Assistants. The abbreviation HEUXIVA stands for Heuristics for Evaluating User eXperience with Voice Assistants. The acronym derives from the key concepts that define the purpose of the set: H for Heuristics, E for Evaluating, U for User, X for eXperience, V for Voice, and A for Assistants.
We used the methodology proposed by Quiñones et al. [2] to develop HEUXIVA. The proposed set was validated in two iterations through heuristic evaluation, user test, and expert judgments using Google Nest Mini. This allowed us to refine the proposed set and verify its effectiveness in detecting usability/UX problems related to voice assistants. Based on the results obtained, we conclude that, although preliminary, the findings indicate that HEUXIVA is a useful and reliable instrument for evaluating the user experience of voice assistants and that the research is progressing in a promising direction.
The article is organized as follows: Section 2 presents the background; Section 3 presentes the related work; Section 4 details the methodology applied to create HEUXIVA and explains the activities performed to develop, validate, and refine the set; Section 5 describes the validation process and its results; Section 6 presents HEUXIVA: a set of heuristics for evaluating user experience with voice assistants; Section 7 details the discussions; Section 8 presents the limitations of the study; and Section 9 discusses the conclusions and future work.
2. Background
The concepts of voice assistants, user experience and user experience evaluation are presented below. In addition, the related work is discussed.
2.1. Voice Assistants
Virtual assistants, including voice assistants and chatbots, are distinguished by their modes of interaction: voice and text, respectively [3]. These devices leverage artificial intelligence to perform various tasks based on user commands, such as sending emails, making phone calls, providing personalized recommendations, and controlling appliances [4,5,6]. In the literature, virtual assistants are referred to by several names, including Intelligent Personal Assistant (IPA) [4], Conversational Agents [7], and Virtual Personal Assistants (VPA) [8]. For the purposes of this study, the term IPA is used to denote these devices [9].
The characteristics of voice assistants vary depending on the device. Based on the literature review [9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18], we identified the following main features that describe these intelligent assistants:
- Effective Communication: The interaction between the user and the voice assistant is bidirectional, involving a continuous exchange of information and roles (sender and receiver) [13].
- Effective: Requests and responses are not restricted to a single topic and are coherent with the user’s environment [13,14].
- Activity Management: The voice assistant enables management actions, such as scheduling appointments, alarms, calls, sending messages, translations, among other tasks [14,18].
- Customizable: The device can be adapted according to the user’s preferences or needs, whether it be in language, voice of the assistant, voice commands for switches or smart plugs, news preferences, routines, among others [15,16].
- Multi-user: The device can recognize the voice of other people, making it usable by everyone present in the same location [17].
Additionally, we conducted a formal inspection to detect usability/UX issues with voice assistants (see Section 4.1). The results of this evaluation can be seen in Appendix D. As a result of this evaluation and considering the findings presented by [9,19,20,21], we consider the following features relevant when evaluating voice assistants:
- Security and Privacy: The device has a privacy policy that specifies what data they collect, why they collect it, and how the user can update, manage, export, and delete it.
- Multi-linkable: The device allows linking/integrating other devices and external services/apps and controlling their use, such as smart home devices (controlling lights, appliances, temperature, and air conditioning, etc.), music services, among others.
- Culturizable/Adaptable: The device recognizes/generates expressions and sets of words that cannot be deduced from the meanings of the words forming them, all according to the geographical location of the user.
- Voice Interface: The device provides the corresponding information through the voice interface.
- Guidance and Assistance: The device guides and assists the user with problems related to the use and installation/configuration of it.
2.2. User Experience
According to ISO 9241-10, the user experience (UX) is defined as “a person’s perceptions and responses that result from the use and/or anticipated use of a product, system or service” [22]. Several authors have proposed various attributes or factors to describe UX, such as Park et al. [23], Lykke et al. [24], and Morville [25]. To develop HEUXIVA, we selected the factors proposed by Morville [25], as they are concise and easy to consider for evaluating these devices:
- Useful: The product must be useful and satisfy a user’s need.
- Usable: The system must be easy to use and quick to learn.
- Desirable: The design elements should be attractive and interesting to the user to cause appreciation and emotion.
- Findable/locatable: Information should be navigable and easy to find within and outside a system.
- Credible: The image of the company or system must be trustworthy.
- Valuable: The system must provide added value or contribute to the user to satisfy his needs.
- Accessible: The system must be able to adapt to users with some type of disability.
2.3. User Experience Evaluation
UX evaluation methods provide information about a system interface and its users through several techniques, aiming to identify how users feel when interacting with software, devices, or applications. There are different evaluation methods, which can be classified into two main approaches: formative and summative [26,27]. Formative evaluations are conducted to improve the design of an interface, identify usability/UX problems, and detect elements that need improvement. Both qualitative and quantitative methods are used, such as usability inspections, usability tests, and heuristic evaluations [26,27]. On the other hand, summative evaluations are performed to measure whether a system meets expectations using quantitative and qualitative data, such as satisfaction surveys, performance metrics, and A/B tests [26,27]. To develop HEUXIVA, we used the following UX evaluation methods (throughout the stages of the applied methodology):
- Heuristic evaluation: A method in which a group of 3 to 5 evaluators analyze an interface, identifying positive and negative aspects according to a set of rules called heuristics [1].
- User testing (thinking aloud): A method involving representative users who navigate and interact with a system while performing predefined tasks, verbalizing their thoughts and actions aloud [28].
- Expert judgment: A method where UX experts and/or specialists apply their knowledge to review a system’s interface. They navigate the platform and identify elements that could improve or negatively affect the user experience [29,30].
3. Related Work
Langevin et al. [10] developed a set of usability heuristics to guide and evaluate the design of conversational agents, including both chatbots and voice assistants. They adapted Nielsen’s heuristics [31] and worked with experts to establish them. As a result, the authors proposed 11 heuristics, among which the “Context Prevention” and “Reliability” heuristics stand out as domain specific. Although this set includes voice assistants, it does not focus particularly on them, as chatbots are also considered (with a primary focus on evaluating mainly chatbots).
On the other hand, Sanchez-Adame et al. [11] created a set of 5 heuristics for chatbots. These devices, like voice assistants, use natural language processing to interact with users. The proposed heuristics are useful for evaluating chatbots but do not assess voice assistants. Moreover, they focus mainly on evaluating usability (efficiency, effectiveness, satisfaction) and not UX components.
Zwakman et al. [12] conducted research to verify if the System Usability Scale (SUS) [32] remains suitable for assessing usability aspects and end-user experiences. SUS was created to evaluate a system with an interface/GUI, and there are several differences between a voice-based environment and a GUI environment. The results indicated that using SUS might not be the best measure to evaluate the usability of smart assistants, as voice systems are interactive and more like human interaction. Additionally, SUS does not consider features unique to a voice environment, such as sound quality/clarity, ease of understanding, level of immersion, and speech monotony that may cause boredom. Based on the above, the authors adapted the 10 questions of SUS to evaluate voice assistants (VUS, [12,33]).
On the other hand, Cowan et al. [9] identified various problems related to the experiences of occasional users of Intelligent Personal Assistants (IPAs). Their research highlighted the following six main themes: (1) Challenges in supporting hands-free interaction; (2) Performance issues related to user accent and speech recognition overall; (3) Difficulties in integrating with third-party applications, platforms, and systems; (4) Social embarrassment as a barrier to using these devices in public settings; (5) The anthropomorphic nature of IPAs; and (6) Concerns regarding trust, data privacy, transparency, and ownership.
While there are interesting studies and sets of heuristics for evaluating aspects of smart assistants, none of them are directly focused on evaluating the UX with voice assistants. This reaffirms the need to create unique and specific heuristics for this domain that can effectively detect usability/UX problems, as these issues negatively affect users’ perception and interaction with these devices. Voice assistants have made the use of artificial intelligence more accessible, as users have been able to interact more intuitively with these devices. Given that HEUXIVA is a specific set for evaluating voice assistants, it will allow for establishing guidelines for the development and implementation of these technologies, making the interaction increasingly user-friendly.
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Methodology Applied for Developing HEUXIVA
The methodology proposed by Quiñones et al. [2] was used to develop the proposed set, since it establishes a methodical, iterative, and effective work plan using qualitative and quantitative methods. HEUXIVA was established and validated in two iterations through heuristic evaluations, expert judgments, and user testing (see Figure 1. Iterations are marked as “It. N”). In iteration 1, the eight stages of the methodology were conducted, and the first set of heuristics (HVA) was developed and validated. In iteration 2, the last three stages of the methodology were carried out to specify the final set of heuristics (HEUXIVA). Details of each iteration, including inputs, outputs, and activities performed, can be reviewed in Appendix A (iteration 1) and Appendix B (iteration 2). Appendix C presents the set of heuristics for voice assistants created in each iteration. Each set is abbreviated differently for each iteration: HVA (first version, iteration 1), HEUXIVA (second and final version, iteration 2). The iterations conducted are explained below.
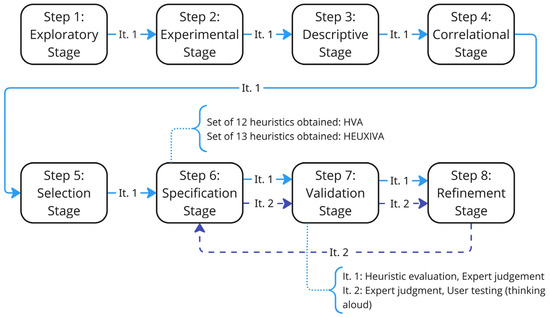
Figure 1.
Steps and iterations performed to develop HEUXIVA.
4.2. First Iteration: Development Process for HVA
In “Step 1: Exploratory Stage”, a literature review was conducted to obtain information on voice assistants and their features (see Section 2.1), user experience attributes (see Section 2.2), existing heuristic sets and related elements (see Section 2.3). To conduct this literature review, the digital databases Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar were considered. With the results obtained, the most relevant documents whose topics were related to the area were analyzed. Although there are several related studies to intelligent assistants, none establishes a specific set for voice assistants. For this reason, studies related to UX in the interaction with these devices and studies that are based on heuristics [10,11] and/or questionnaires of virtual and/or voice assistants [12,33] were selected.
In “Step 2: Experimental Stage”, a formal inspection of a Google Assistant device was performed. The objective was to familiarize the user with the device and detect problems that may negatively affect the user experience. Two researchers from the team used the device for 11 days. The first days were to get to know and adapt to the device, the following days the device was used fluently with the objective of finding possible usability/UX problems. During these days, a total of 13 problems were detected. Scores were assigned on a 4-level scale to the detected problems using the severity scale used in heuristic evaluations, where severity is understood as the level of seriousness of the identified problem [34] (for more details about the problems detected, see Appendix D). Most of the identified problems have a value less than or equal to 2, even so two were identified that stand out as catastrophic problems (with a score of 4). These are “P1: Device ignores user” and “P2: Difficulty initializing device”. The first can generate problems with the user regarding the correct functioning of the device and its value to the user; the second causes frustration in the user and the desire or need to use it is lost.
In “Step 3: Descriptive Stage”, the relevant information obtained from the previous stages was selected. For this, we prioritized the information collected on a 3-level scale (1 being: slightly relevant information and 3: very important information) [2] and this was later organized into 5 categories: information about voice assistants, features of voice assistants, usability/UX attributes, sets of existing heuristics and other related elements, and usability problems of voice assistants (detected in the experimental stage through formal inspection). Finally, according to the prioritization, the following information was selected to develop the heuristics (the details of the selected information can be seen in the Appendix E):
- 5 types of information of voice assistants: 3 definitions of voice assistant [4,7,8], need to create a UX evaluation method for voice assistants, taxonomy of voice assistants.
- 10 voice assistants’ features: effective communication, effective, activity management, customizable, multi-user, security and privacy, multi-linkable, culturizable/adaptable [9], voice interface, guidance and assistance.
- 3 usability attributes: effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction [35].
- 7 UX attributes: useful, desirable, usable, findable/locatable, credible, and valuable, and learning capacity [25,36].
- 5 sets of existing heuristics or related elements: Nielsen [31], Langevin et al. [10], Sanchez-Adame et al. [11], Zwakman et al. [12,33] (VUS), Nowacki and Gordeeva [37].
- Voice Assistant Usability Issues: formal inspection made in Stage 2, Infrequent Users’ Experiences of Intelligent Personal Assistants by Cowan [9].
While usability is conceptually part of UX, in this study we considered its attributes (effectiveness, efficiency, and satisfaction [35]) as a distinct group of evaluative dimensions. This decision was made to emphasize their relevance in the design and validation of the proposed heuristics. Separating these dimensions allowed us to ensure a balanced coverage of both functional quality (usability) and experiential quality (UX). This distinction also facilitated the mapping of heuristics to specific measurable criteria during the development process.
In “Step 4: Correlational Stage”, the correlation between voice assistant features, usability/UX attributes, heuristic sets, associated usability issues (detected in the experimental stage) and items from the Voice Usability Seal (VUS) questionnaire was performed. During this process, it was discovered that there is no heuristic that fully covers the usability/UX attributes related to the features, these are partially covered. However, there are several heuristics and information that allowed the new set to be generated (this correlation process can be seen in Appendix F).
In “Step 5: Selection Stage”, the existing heuristics were selected based on the information collected in Stage 4. The following actions were determined: adapt, keep or eliminate. 1 heuristic was kept, and 39 heuristics were adapted. Of these 40 heuristics, 12 were identified as useful, 11 as important and 17 as critical. A total of 11 heuristics were eliminated because they are not related to the topic of voice assistants or are fulfilled by another selected heuristic. Even though there are no heuristics that fully cover the characteristics of voice assistants, mixing several proposals and adding more complete specifications helped to generate the new set (details on the selection process can be seen in Appendix G).
In “Step 6: Specification Stage”, the preliminary set of heuristics for voice assistants was proposed (see Appendix C). This version contains 12 heuristics which were documented using the template proposed in the methodology [2] including the following information: ID, name, definition, covered voice assistant feature, covered usability/UX attribute, and related heuristics. In “Step 7: Validation Stage”, the first version of heuristics (HVA) was validated through heuristic evaluation and expert judgment. Details of these validations can be seen in more detail in Section 5.1 and Section 5.2, respectively. In “Step 8: Refinement Stage”, the heuristics were refined based on the feedback obtained in Stage 7 as follows (for more details on the refinement see Appendix H):
- 12 heuristics need to be refined mainly by improving their checklists and definition.
- A new heuristic needs to be added to cover the user response aspects.
- It was decided to carry out a second iteration repeating the last three steps of the methodology.
4.3. Second Iteration: Development Process for HEUXIVA
In the second iteration, the last three stages of the methodology were performed again, starting from “Step 6: Specification Stage”. In this step, a second version of the set of heuristics that evaluate voice assistants (HEUXIVA) was proposed. The refinement made in the first iteration was considered along with the information matched in “Step 4: Correlational Stage” in the first iteration (see Appendix C).
In “Step 7: Validation Stage”, the second version of the set of heuristics was validated through expert judgment and user testing. Details of the validations performed can be reviewed in Section 5.3 and Section 5.4, respectively. Finally, in “Step 8: Refinement Stage”, 10 heuristics were modified based on the expert judgment and user testing performed in Stage 7. The final version of HEUXIVA is presented in Section 6.
5. Results
5.1. Results Obtained in the Iteration 1: Validation Through Heuristic Evaluation
We conducted a heuristic evaluation to validate the effectiveness of the first version of the proposed heuristics (HVA). For this purpose, we defined a control group, composed of 3 evaluators who used the existing set of heuristics for “conversational agents” (CAH) [10]; and an experimental group, composed of 3 evaluators who used the new set of proposed heuristics in its first version: HVA. Both groups conducted the evaluation using Google’s voice assistant Nest Mini [38]. Each group was composed of evaluators with a similar level of experience in interacting with voice assistants and performing heuristic evaluations. All were computer engineers with formal training in UX research and professional experience ranging from three to five years in the field of UX. Their ages ranged from 30 to 35 years, and the group consisted of four men and two women.
To evaluate the effectiveness of HVA, we used the criteria defined in the methodology applied [2] (the explanation of the formulas and the calculation of each criterion applied to evaluate effectiveness can be found in Appendix I). The results obtained by the control and experimental groups were compared in terms of:
- Numbers of correct and incorrect associations of problems to heuristics
- Number of usability/UX problems identified
- Number of specific usability/UX problems identified
- Number of identified usability/UX problems that qualify as more severe (how catastrophic the usability/UX problem detected is)
- Number of identified usability/UX problems that qualify as more critical (how severe and frequent the problem detected is)
Table 1 shows the results obtained in the heuristic evaluations performed by the experimental and control groups. In addition, the effectiveness of HVA in terms of the five criteria is shown. As shown in Table 1, HVA performed better than CAH on two of the five criteria. HVA detected more usability/UX problems than CAH and detected more specific problems related to voice assistants (ESS1 > ESS2). However, CAH had a higher percentage of correct associations than HVA (CA1 < CA2), and CAH detected more severe (ESV1 < ESV2) and critical (ESC1 < ESC2) problems than HVA. The above indicates that HVA requires refinement in terms of its specification both to improve clarity and increase the number of correct associations of problems to heuristics, as well as to increase the number of severe and critical problems detected (related to voice assistants).

Table 1.
Effectiveness of HVA (first iteration).
5.2. Results Obtained in Iteration 1: Validation Through Expert Judgment
In addition to conducting a heuristic evaluation, in the first iteration we also conducted a survey with a group of three experts to evaluate HVA. These experts were those who participated as evaluators in the experimental group in the heuristic evaluation presented in Section 5.1. The survey was designed to obtain the evaluators’ perception of HVA along four dimensions: D1—Utility, D2—Clarity, D3—Ease of use, and D4—Need for a checklist. We used a five-point Likert-type scale (1 represents the worst rating and 5 the best for dimensions D1, D2, and D3. For dimension D4, a rating of 1 indicates a complete need for additional elements, while 5 signifies no need). Table 2 shows the average values obtained for each dimension per heuristic.

Table 2.
Average perception scores for HVA set in the four evaluated dimensions (first iteration).
Regarding dimension “D1—Utility”, the evaluators perceived all heuristics useful for evaluating voice assistants, except for the heuristic “HVA6: Consistent Voice Interface” (rated 3.3), indicating a need to review its utility by either improving its specification or removing it from the set. Nevertheless, all heuristics were perceived as clear by the evaluators (dimension “D2—Clarity”), with all ratings being 4.0 or higher. However, in terms of “dimension D3—Ease of use”, 6 out of the 12 heuristics were perceived by the evaluators as difficult to use in practice for detecting usability/UX issues in voice assistants (with ratings of 3.6 or lower), particularly the heuristics “HVA3: Brevity and Relevance of Information” and “HVA11: Reliability and Data Privacy” (both rated 2.6). This indicates a need to enhance the specification of these heuristics, either by adding more detail or improving their wording.
Finally, concerning dimension “D4—Need of additional elements”, the evaluators considered that 2 out of the 12 heuristics should incorporate additional information to improve their specification, the heuristics “HVA6: Consistent Voice Interface” and “HVA7: User Control and Freedom” (both rated 3.6). Both were perceived as useless and difficult to use, respectively, so their specifications could be significantly improved by incorporating additional elements. Based on the results obtained both from the heuristic evaluation and expert judgment, the heuristics were refined in the second iteration (step 6: specification stage).
5.3. Results Obtained in Iteration 2: Validation Through Expert Judgment
In the second iteration, we applied another survey to eight experts to validate the refined set of heuristics: HEUXIVA. We searched for experts through LinkedIn and contacted them via email. The experts had medium-to-high experience using heuristic sets and conducting heuristic evaluations. Specifically, three experts had high experience (more than 6 evaluations conducted); four experts had medium experience (4 to 5 evaluations), and one had low experience (3 evaluations conducted).
The survey had the same design as the one used in the first iteration (see Section 5.2), but this time it focused on evaluating the new heuristics proposal (HEUXIVA). The objective was to gather the evaluators’ perceptions of HEUXIVA along four dimensions: D1—Utility, D2—Clarity, D3—Ease of use, and D4—Need for a checklist. We used once again a five-point Likert-type scale (1 represents the worst rating and 5 the best for dimensions D1, D2, and D3. For dimension D4, a rating of 1 indicates a complete need for additional elements, while 5 signifies no need). Table 3 shows the average values obtained for each dimension per heuristic.

Table 3.
Average perception scores for HEUXIVA set in the four evaluated dimensions (second iteration).
As shown in Table 3, it is noticeable that most of the heuristics were well perceived by the experts in all four dimensions. Regarding dimension “D1—Utility”, 12 out of 13 heuristics received a rating above 4.3, indicating that they were perceived as very useful. Only the heuristic “HEUXIVA13: Guides and Documentation” received a “neutral” rating (3.8, “moderately useful”), suggesting that it could be refined to ensure it is considered useful for evaluating voice assistants. For the dimensions “D2—Clarity” and “D4—Need of additional elements”, all heuristics received ratings above 4.0, indicating that they were perceived as clear (easy to read) and do not require additional information for understanding and using them to detect usability/UX problems. Finally, concerning dimension “D3—Ease of Use”, 11 out of 13 heuristics were perceived as easy to use (with ratings above 4.0), except for the heuristics “HEUXIVA5: Information Accuracy” and “HEUXIVA7: Consistent Voice Interface”, which received a rating close to “neutral” (3.9), being perceived as “moderately easy to use”. This suggests that further improvements could be made to their specifications.
Compared to the results obtained in the expert judgment of the first iteration (see Section 5.2), we concluded that the specification of the heuristics has improved for all dimensions (see Table 4), particularly noting the positive enhancements in terms of “utility”, “ease of use”, and “need for additional elements” for the heuristics “HEUXIVA6: User Control and Freedom” and “HEUXIVA7: Consistent Voice Interface” (see Table 5).

Table 4.
Comparison of results obtained in the expert judgment in the first and second iteration.

Table 5.
Improvements in the perception of HEUXIVA6 and HEUXIVA7 in the expert judgment of iteration 2.
5.4. Results Obtained in Iteration 2: Validation Through User Testing
We conducted a user test to: (1) verify whether the most severe and critical problems identified by evaluators in the heuristic evaluation conducted in iteration 1 (see Section 5.1) are perceived in the same way by users; and (2) identify usability/UX issues that arise during user interaction with a voice assistant and verify if these issues are covered by HEUXIVA (i.e., to check if it is possible to identify these problems detected during a user test using HEUXIVA). The user test was a thinking aloud type, moderated by the authors and synchronous.
5.4.1. User Test Design
The user test consisted of three parts (pre-test, test, and post-test). The first part (or pre-test) included an individual questionnaire with demographic questions to understand the participant’s profile and their experience using voice assistants, as well as a confidentiality agreement. The second part (test) involved a scenario with 8 tasks that participants had to perform individually (see Table 6). Additionally, during the test, participants were required to verbally express their opinions, experiences, emotions, and comments about the tasks and the use of the voice assistant. Finally, the third part (post-test) included a questionnaire to evaluate the participants’ perceptions and experiences using the voice assistant. For the tests, the Google Nest Mini voice assistant was used.

Table 6.
Thinking aloud user test quantitative and qualitative results (second iteration).
5.4.2. Participant Selection
Twelve users participated in the test, aged between 22 and 28 years. Four of the participants had never used a voice assistant before (inexperienced users), four had used a voice assistant at least once (medium-experienced users), and four used them daily (highly experienced users). We decided to seek three different user profiles (inexperienced or novice, medium experienced, and highly experienced) to obtain representative results and visualize how users interact with this type of device.
5.4.3. Results Obtained
Based on verbal comments made by users during the execution of tasks and the responses provided by users in the post-test, several usability/UX issues were identified and documented. Table 6 shows the tasks performed by the users in the thinking-aloud test and their results. Based on the users’ performance of the tasks, 20 usability/UX problems were identified. We reviewed whether HEUXIVA allows the detection of the identified problems (P1 to P20), concluding that HEUXIVA covers all problems detected in the test (see Table 6, last column). This allows to determine that the proposed set is effective in detecting usability/UX issues related to voice assistants.
As shown in Table 6, users completed all tasks with average times ranging from 78 to 168 s, reflecting a good performance for simple actions and greater effort for complex tasks. The most expressed emotions (neutral, happiness, confusion, and irritation) suggest that positive experiences were linked to successful and fluent interactions, while negative emotions appeared when the assistant failed to interpret or execute commands correctly.
On the other hand, it can be observed that the problems detected during the user test were related to the following 8 heuristics: HEUXIVA1, HEUXIVA3, HEUXIVA4, HEUXIVA5, HEUXIVA6, HEUXIVA7, HEUXIVA10, and HEUXIVA12 (see Table 7). Of these 8 heuristics, 5 were proposed to identify specific usability/UX problems directly related to voice assistants (HEUXIVA3, HEUXIVA4, HEUXIVA5, HEUXIVA7, and HEUXIVA12). Based on the results obtained in the user test, it is possible to highlight the utility of the HEUXIVA set, as several specific usability/UX problems were identified while the users were using the voice assistant and completing the tasks (12 specific problems detected, see Table 7).

Table 7.
Problems detected in user testing and the related heuristics.
These findings offer preliminary but consistent evidence supporting the effectiveness of HEUXIVA in identifying UX issues specific to voice assistants.
6. HEUXIVA: Heuristics for Evaluating User eXperience with Voice Assistants
Based on the iterations and validation described in the previous sections, the HEUXIVA set was refined and improved. We proposed a total of 13 heuristics that can be used to evaluate the user experience of voice assistants. Of the proposed heuristics, 7 are new and are defined to detect specific problems of voice assistants (HEUXIVA3, HEUXIVA4, HEUXIVA5, HEUXIVA7, HEUXIVA8, HEUXIVA11, and HEUXIVA12). These heuristics are presented in Table 8, including: ID, name, description, the voice assistant features evaluated with the heuristic; and the UX attributes evaluated with the heuristic.

Table 8.
HEUXIVA: a set of Heuristics for Evaluating the User eXperience with Voice Assistants.
In addition, Appendix J presents each heuristic in detail using the template specified in the methodology applied [2]. Each heuristic is presented in a table containing: ID, name, definition, explanation, priority (how important the heuristic is: critical, important, or useful), usability and UX attributes evaluated with the heuristic, voice assistant features evaluated with the heuristic, set of heuristics related, a checklist, and a compliance example and non-compliance example.
A Supplementary Excel File (S1) is provided to support the practical application of HEUXIVA. This material includes five sheets: (1) a brief description of the 13 heuristics; (2) an extended description of each heuristic; (3) the corresponding checklist items for each one; (4) examples of usability/UX problems that can be identified using HEUXIVA and guidance on how to document them; and (5) a blank template for recording problems during heuristic evaluations. This resource aims to facilitate reproducibility and assist researchers and practitioners in applying the HEUXIVA.
7. Discussions
7.1. About the Results Obtained in Validation Stage (First and Second Iteration)
We performed four experiments to validate HEUXIVA, a heuristic evaluation and expert judgment in the first iteration, and another expert judgment and user testing in the second iteration. As shown in Table 1, the results from the first iteration demonstrate that the initial set of heuristics (HVA) achieved reasonable levels of effectiveness across the applied criteria. Although some variability was observed among evaluators, the findings show that the first version of heuristics permits to identify relevant usability/UX problems related to voice assistants. These early outcomes provided the empirical foundation for refining the heuristics into the final HEUXIVA set.
On the other hand, as shown in Table 4, the comparison of expert judgment results between the first and second iterations highlights the gradual refinement of HEUXIVA. Experts reported improvements in clarity, relevance, and applicability, particularly for those heuristics addressing user control and freedom, and consistent voice interface. The observed increase in agreement among evaluators suggests that the iterative process was effective in reducing ambiguity and improving the understanding of each heuristic’s purpose. Finally, the findings presented in Table 6 integrate quantitative and qualitative data from the thinking-aloud user test conducted during the second iteration. The results support the practical usefulness of HEUXIVA by demonstrating that the heuristics cover the types of usability/UX problems encountered by real users when interacting with voice assistants.
Although the current validations are preliminary, the results demonstrate good progress in the refinement of HEUXIVA through multiple iterations and experiments. The integration of expert and user perspectives provides evidence that the proposed set is useful and applicable for evaluating UX in voice assistants.
7.2. Comparative Analysis with Existing Heuristics and Evaluation Methods
To contextualize the contribution of HEUXIVA, Table 9 compares the proposed set with existing studies related to voice assistants’ evaluation, including the heuristics proposed by Langevin et al. [10] and Sánchez-Adame et al. [11], the Voice Usability Scale (VUS) proposed by Zwakman et al. [12], ergonomics criteria for voice user interface proposed by Nowacki and Gordeeva [37], and usability problems related to intelligent personal assistants (IPAs) identified by Cowan et al. [9]. While these previous studies represent important advances, most of them primarily address usability aspects and do not fully integrate user experience (UX) dimensions.

Table 9.
Comparison between studies related to voice assistants.
Existing sets of heuristics are focused on chatbots and conversational agents, rather than voice assistants specifically. The sets by Langevin et al. [10] and Sánchez-Adame et al. [11] adapt Nielsen’s general usability principles but overlook essential aspects of voice interaction. Cowan et al. [9] provides an empirical characterization of user challenges with IPAs, highlighting several usability/UX problems. However, their study focuses on describing user problems rather than translating them into heuristics. The ergonomic criteria by Nowacki and Gordeeva [37] provide valuable guidance for voice user interfaces (VUIs) but lack empirical validation. Finally, the Voice Usability Scale (VUS) by Zwakman et al. [12] offers a quantitative perspective on usability through a concise ten-item survey adapting SUS [32] but does not provide heuristics or focus on user experience.
In contrast, HEUXIVA integrates insights from these works while addressing their main gaps. It includes usability and UX perspectives, incorporates features unique to voice assistants (such as effective communication, voice interface, guidance and assistance, adaptation, among others), and introduces practical checklists to guide evaluations. Moreover, HEUXIVA was developed through a structured, iterative methodology that combines literature synthesis, heuristic evaluation, expert judgment, and user testing, resulting in a comprehensive set. Although the current validation of HEUXIVA is preliminary (limited to a single device and small participant samples) the comparative analysis indicates that HEUXIVA advances the evaluation of voice assistants by addressing specific interaction issues not captured by existing heuristic sets. This early validation nonetheless provides promising evidence of its potential to guide more comprehensive and context-aware UX evaluations in future studies.
7.3. Novel Contributions and Creation of New Heuristics
Of the HEUXIVA set, six heuristics were adapted from existing proposals (Nielsen [31], Langevin et al. [10], Sánchez-Adame et al. [11], Nowacki and Gordeeva [37]). This adaptation, however, was not a direct translation but part of a systematic integration process defined in the correlational and selection stages of the applied methodology. During these stages, each heuristic was evaluated for its relevance to voice-based interaction, its coverage of UX attributes, and its ability to identify usability/UX problems.
Through this process, we also defined new heuristics. Specifically, seven heuristics (HEUXIVA3, HEUXIVA4, HEUXIVA5, HEUXIVA7, HEUXIVA8, HEUXIVA11, and HEUXIVA12) are considered entirely novel, as the aspects they address were only partially covered by existing proposals. These heuristics go beyond traditional usability/UX principles by integrating elements that are unique to voice assistants, such as conversational fluidity, linguistic adaptability, information accuracy, personalization, privacy transparency, and reliability in autonomous interactions. HEUXIVA extends the conceptual and practical boundaries of prior heuristic sets, offering a more comprehensive instrument for evaluating user experience in voice assistants. Table 10 shows the origin of each HEUXIVA heuristic and its contribution to UX evaluation.

Table 10.
Origin of each HEUXIVA heuristic and its contribution to UX evaluation.
To ensure transparency of coverage and to avoid redundancy across heuristics, a matrix was developed linking each voice assistant feature with its corresponding HEUXIVA heuristic, checklist item, problem type, and representative example (see Appendix K). To prevent overlaps among heuristics, three rules were applied: (1) each voice assistant feature was mapped to a primary heuristic that best represents its evaluative focus; (2) checklist items covering similar UX aspects were grouped and assigned to the most specific heuristic; and (3) overlapping items were merged under the heuristic with the broader or more integrative scope.
8. Limitations
This study has several limitations; however, we believe it represents a valuable contribution toward advancing the evaluation of UX with voice assistants. First, the validation scope was narrow, as all experiments were conducted using Google Nest Mini. While this restricts generalization to other devices, it allowed to maintain experimental control and consistency across iterations. Focusing on a single device enabled a more precise identification of domain-specific UX issues, which can later be contrasted with other platforms in future research.
Second, the sample sizes were relatively small and homogeneous. The heuristic evaluation involved two independent groups of three experts each (HVA vs. CAH), which may not fully eliminate group-composition effects. However, this setup provided valuable initial evidence about the effectiveness and clarity of the proposed heuristics. A larger, cross-over design is recommended for future studies to enhance statistical robustness, but the current results already show consistent tendencies that support the validity of HEUXIVA.
Third, in the first iteration, the same specialists who conducted the heuristic evaluation also participated in the expert judgment survey. This overlap may introduce a degree of confirmation bias. Nevertheless, it also ensured continuity and a deep understanding of the heuristics under review, resulting in meaningful, expert-informed feedback that guided the refinement of the set. Future iterations will address this by engaging independent evaluators for each stage.
Finally, the user testing in the second iteration was limited to 12 participants aged 22–28, using a single device and eight scenarios. While this constitutes a limited sample, it provided an appropriate pilot exploration that successfully verified the applicability and coverage of HEUXIVA. Broader studies including diverse devices (e.g., Siri or Alexa), languages, and usage contexts are planned to expand the external validity of the results.
Overall, despite these limitations, the study presents a domain-specific heuristic set that fills a gap in the UX evaluation of voice assistants. The iterative process, combination of multiple validation methods, and findings demonstrate that HEUXIVA is both rigorous and promising, serving as a strong basis for future refinement and broader application.
9. Conclusions and Future Work
Voice assistants are designed to support users in their daily activities by performing tasks such as setting alarms, retrieving information, or managing smart devices through natural voice interaction. However, due to the diversity of existing platforms and their conversational limitations, they often present usability and UX issues that negatively affect user satisfaction and continued adoption. Establishing specific heuristics to evaluate the user experience with these devices is therefore essential to identify interaction problems and improve their overall quality.
In this study, we proposed HEUXIVA, a set of 13 heuristics specifically developed to evaluate the user experience of voice assistants. The heuristics were created through a structured, iterative methodology and validated through heuristic evaluation, expert judgment, and user testing. The results—although preliminary—suggest that HEUXIVA is a useful and reliable instrument for identifying usability and UX issues specific to voice assistants, indicating that this research is progressing in a promising direction.
As a limitation of this study, the experiments were conducted exclusively using the Google Nest Mini device, with small and homogeneous samples. These constraints provided control and consistency in early stages but also limit the generalizability of the findings. As future work, we plan to address these aspects through several actions: broaden the validation scope by including multiple platforms (e.g., Amazon Alexa and Apple Siri) and varied acoustic, linguistic, and environmental contexts; increase and diversify the participant samples, incorporating users from different age groups, linguistic backgrounds, and profiles to improve external validity; and separate evaluator roles by engaging independent expert groups for heuristic evaluation and for subsequent judgment or surveys, thereby reducing bias and improving result independence.
We expect that the proposed heuristic set will support researchers and industry practitioners in developing and refining new voice assistants, facilitating the detection of usability and UX problems and improving users’ overall interaction experience. By improving user experience, these systems can better ensure quality, satisfaction, and alignment with user expectations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app152011178/s1, Excel Sheet S1: (S1) HEUXIVA—Supplementary Material.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Q.; methodology, D.Q., S.C. and L.F.R.; validation, D.Q., J.R. and V.B.; formal analysis, D.Q., J.R. and V.B.; investigation, D.Q., J.R. and V.B.; resources, D.Q.; data curation, D.Q., C.S., J.R. and V.B.; writing—original draft preparation, D.Q., C.S., J.R., V.B. and L.F.R.; writing—review and editing, D.Q., S.C. and L.F.R.; visualization, D.Q., C.S. and L.F.R.; supervision, D.Q.; project administration, D.Q.; funding acquisition, D.Q. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Agencia Nacional de Investigación y Desarrollo (ANID), Chile, FONDECYT INICIACIÓN, Project No. 11190759.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards defined in the regulations of the Pontificia Universidad Católica de Valparaíso, Chile (protocol code BIOEPUCV-H 319-2019, date of approval: 14 October 2019), the Declaration of Bioethics and Human Rights of 2005 by UNESCO, and the ANID regulations for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data is contained within the article or Supplementary Material. The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all the participants (experts, users, evaluators, and researchers) who were involved in the experiments for this study. During the preparation of this work the authors used ChatGPT 4.0 and 5.0 to translate the text of the article into English. After using this tool, the authors reviewed and edited the content as needed and take full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Appendix A. Inputs, Outputs, and Activities for Each Step Performed in Iteration 1

Table A1.
Inputs, outputs, and activities for each step performed in iteration 1.
Table A1.
Inputs, outputs, and activities for each step performed in iteration 1.
| Step | Input | Output | Activities Performed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 1: Exploratory Stage | - | ① Information about voice assistant devices (three definitions, ten features, and the necessity and taxonomy of voice assistants); ② one proposal for usability attributes and one proposal for UX attributes; and ③ five sets of related heuristics | Conduct a literature review about voice assistants (definitions and features); usability/UX attributes; existing sets of usability/UX heuristics related, and other relevant information. |
| Step 2: Experimental Stage | ① Information about voice assistant devices; ② one proposal for usability attributes and one proposal for UX attributes; and ③ five sets of related heuristics | ④ Voice assistant usability issues | Conduct a formal inspection made by two researchers. Identify usability issues during the formal inspection of the device. |
| Step 3: Descriptive Stage | ① Information about voice assistant devices; ② one proposal for usability attributes and one proposal for UX attributes; and ③ five sets of related heuristics; ④ Voice assistant usability issues | ⑤ Selected information about voice assistants; ⑥ ten features of voice assistants; ⑦ three UX attributes from one proposal; ⑧ usability issues found; and ⑨ five selected sets of heuristics | Group all the information collected. Sort and prioritize the information using a three-level scale (3: highly important; 2: somewhat important; 1: not important). Select the relevant information to develop the set of heuristics. |
| Step 4: Correlational Stage | ⑤ Selected information about voice assistants; ⑥ ten features of voice assistants; ⑦ three UX attributes from one proposal; ⑧ usability issues found; and ⑨ five selected sets of heuristics | ⑩ Matched all features, attributes, existing heuristics, and other related elements together | Match the ten voice assistant features with the three UX attributes, and the five sets of heuristics [10,11,31,33,37]; and the usability issues. |
| Step 5: Selection Stage | ⑩ Matched features, attributes, existing heuristics, and other related elements | ⑪ Classified heuristics (1 heuristic to keep; 39 heuristics to adapt; and 11 heuristics to eliminate) | Review Nielsen heuristics [31], conversational agents heuristics [10], heuristics for evaluating chatbots [11], and the ergonomic criteria for voice user interfaces [37]. Determine what heuristics to: keep, adapt, and eliminate. |
| Step 6: Specification Stage | ⑩ Matched features, attributes, existing heuristics, and other related elements; ⑪ Classified heuristics (1 heuristic to keep; 39 heuristics to adapt; and 11 heuristics to eliminate) | ⑫ Set 12 of voice assistant heuristics, HVA (first iteration) | Specify 12 UX heuristics for voice assistants (HVA), including: id, name, definition, explanation, voice assistant feature, examples, UX attribute, and existing heuristics related. |
| Step 7: Validation Stage | ⑫ Set 12 of voice assistant heuristics, HVA (first iteration) | ⑬ Heuristic evaluation results: effectiveness of HVA; ⑭ Expert judgment results (survey) | Perform a heuristic evaluation with six evaluators (three evaluators for the control group, and three evaluators for the experimental group). Perform a survey for experts to review the heuristics. |
| Step 8: Refinement Stage | ⑬ Heuristic evaluation results: effectiveness of HVA; ⑭ Expert judgment results (survey) | ⑮ Refining document: (1) 12 heuristics to refine, 1 heuristic to add; (2) repeat steps 5–8 | Document the improvements to be performed in the specification of HVA. It is decided to repeat stages 5–8. |
Appendix B. Inputs, Outputs, and Activities for Each Step Performed in Iteration 2

Table A2.
Inputs, outputs, and activities for each step performed in iteration 2.
Table A2.
Inputs, outputs, and activities for each step performed in iteration 2.
| Step | Input | Output | Activities Performed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Step 6: Specification Stage | ⑮ Refining document: 12 heuristics to refine, 1 heuristic to add; ⑩ Matched features, attributes, existing heuristics, and other related elements; ⑫ Set 12 of voice assistant heuristics, HVA (first iteration) | ① Set 12 of voice assistant heuristics, HEUXIVA (second iteration) | Refine the specification of the 13 UX heuristics for voice assistants (HVA), including: id, name, definition, explanation, voice assistant feature, examples, UX attribute, and existing heuristics related. |
| Step 7: Validation Stage | ① Set 12 of voice assistant heuristics, HEUXIVA (second iteration) | ② Heuristic evaluation results: effectiveness of HEUXIVA; ③ Expert judgment results (survey); ④ User tests results | Perform a heuristic evaluation with X evaluators (X evaluators for the control group, and X evaluators for experimental group). Perform a survey for eight experts to review the heuristics. Perform a thinking-aloud test to evaluate a case study with twelve users. |
| Step 8: Refinement Stage | ① Set 12 of voice assistant heuristics, HEUXIVA (second iteration); ② Heuristic evaluation results: effectiveness of HEUXIVA; ③ Expert judgment results (survey); ④ User tests results | ⑤ Set of 13 voice assistant heuristics, HEUXIVA (second iteration) | Refine and improve the final specification of 13 UX heuristics for voice assistants (HEUXIVA). |
Appendix C. Set of Heuristics for Voice Assistants Developed at Each Iteration

Table A3.
Set of heuristics for voice assistants developed at each iteration.
Table A3.
Set of heuristics for voice assistants developed at each iteration.
| First Iteration (HVA) | Second Iteration (HEUXIVA) |
|---|---|
| HVA1: System Status Visibility | HEUXIVA1: System Status Visibility |
| HVA2: Feedback and Help Users Prevent Errors | HEUXIVA2: System Guidance and Capabilities |
| HVA3: Brevity and Relevance of Information | HEUXIVA3: Effective and Fluid Communication |
| HVA4: Natural Communication | HEUXIVA4: Environment Match Between Assistant and User Language |
| HVA5: Match Between the System and the Real World | HEUXIVA5: Information Accuracy |
| HVA6: Consistent Voice Interface | HEUXIVA6: User Control and Freedom |
| HVA7: User Control and Freedom | HEUXIVA7: Consistent Voice Interface |
| HVA8: Flexibility and Personalization | HEUXIVA8: Voice Shortcuts, Flexibility and Personalization |
| HVA9: Help Users Recognize, Diagnose, and Fix Errors | HEUXIVA9: Error Prevention |
| HVA10: System Guidance and Capabilities | HEUXIVA10: Help Users Recognize, Diagnose, and Fix Errors |
| HVA11: Reliability and Data Privacy | HEUXIVA11: Data Privacy |
| HVA12: Guides and Documentation | HEUXIVA12: Voice Assistant Reliability |
| HEUXIVA13: Guides and Documentation |
Appendix D. First Iteration, Step 2: “Experimental Stage”

Table A4.
First iteration, Step 2 “Experimental stage”: List of usability/UX problems of the voice assistant found in formal inspection.
Table A4.
First iteration, Step 2 “Experimental stage”: List of usability/UX problems of the voice assistant found in formal inspection.
| ID | Problem | Occurrence Example | Explanation (Why It Affects the User) | Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Device ignores user | When making a request, action and/or question, the device will sometimes “wake up” (perform the listening action) and ignore the user without providing feedback as to why it will not perform the requested action. | When ignored, the user feels uncertain about what the problem is, and why it does not work. | 4 (catastrophic problem) |
| P2 | Difficulty initializing device | When connecting the device for the first time, the pairing process becomes difficult for the user because the device does not provide feedback until it is fully configured. Also, when reconnecting it to the same location, the device would present connection errors, and it must be manually reset. | When the device presents difficulties in initializing (user’s first impressions) it generates the person’s intention not to use it. | 4 (catastrophic problem) |
| P3 | Lack of manual or instructions | There is no guide to reset the device. | Without a complete user guide or manual, the person must manually search the Internet for external explanations. | 3 (major problem) |
| P4 | Device does not understand language and jargon | When the user expresses themself using language and technical terms, the device ends the conversation early and/or says, “I’m sorry, I didn’t understand”. | Since the device does not know the language of the place in which it is located, it causes the user to change the way they speak, in addition to not generating a fluid conversation. | 3 (major problem) |
| P5 | Device provides incoherent responses | When asking the device about certain topics (e.g., the user’s mood), it provides incoherent answers and changes the context of the conversation. | By providing incoherent and/or unrelated responses to the topic, the device generates uncertainty in the user about the device’s capabilities (the limits that the device has). | 3 (major problem) |
| P6 | The device does not recognize the user’s voice when in a noisy environment | When the device is in a noisy environment (e.g., television on), it does not distinguish the user’s voice despite having voice recognition. | If the user cannot be detected by the device, the user must increase the volume of their voice, raise the pitch and/or turn off the device that is providing noise near the device. | 3 (major problem) |
| P7 | Device does not provide useful information to user | When asking about the weather in the city of Punta Arenas, Chile, the device gives the weather in the city of Puntarenas, Costa Rica. | It is annoying for the user that it gives different results since it is supposed to know their location when connected to their home network and provide information accordingly. | 3 (major problem) |
| P8 | The device has limited memory | When you ask the device about a topic that was discussed less than 30 s ago, it does not remember what was discussed. | If the device does not remember what the user told it in the previous request, it gives the impression that the user is not being listened to and/or paid attention to. | 2 (minor problem) |
| P9 | The device does not have orientation on the volume up and down buttons | When trying to manually increase the volume of the device, the user becomes disoriented when trying to increase/decrease the volume. | The user may be confused as they must press the buttons at random to find out which button they wanted to select. | 2 (minor problem) |
| P10 | Device ends conversations prematurely | When interacting with the device, it stops talking after less than 1 s, causing the user to have to start the conversation again with the activation phrase. | As the device ends conversations at its discretion, it makes the user realize that they are talking to a machine/robot. | 2 (minor problem) |
| P11 | Inconsistent language | When the device is playing music on Spotify and the user disconnect it using his/her phone, the device displays a message in English despite being set to Spanish. | A message in another language causes confusion for the user because they may not understand what the device is communicating. | 2 (minor problem) |
| P12 | The device does not understand search requests | When the user asks the device to “Search Barso”, it responds “Sorry, I didn’t understand”, even though the device can perform Google searches. | By not understanding search queries, the user may become uncertain about whether the device works or can be useful. | 2 (minor problem) |
| P13 | Device does not manage voice pairings with external devices | The process of linking the device to external devices must be manual, using the mobile phone application (Google Home). | Since the action of managing links is not performed by voice, the user is forced to do them manually using the device’s mobile application. | 2 (minor problem) |
Appendix E. First Iteration, Step 3: “Descriptive Stage”

Table A5.
First iteration, Step 3 “Descriptive stage”: Relevance for voice assistant features, UX attributes, sets of existing heuristics, and related relevant elements.
Table A5.
First iteration, Step 3 “Descriptive stage”: Relevance for voice assistant features, UX attributes, sets of existing heuristics, and related relevant elements.
| Topic | Value According to Relevance | Explanation | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3: Highly Important | 2: Somewhat Important | 1: Not Important | ||
| Voice assistant information | Name and definition of voice assistant [4]; Name and definition of voice assistant [7]; Name and definition of voice assistant [8]; Need to create a UX evaluation method for voice assistants [12]. | Taxonomy of voice assistants [40] | - | The different definitions of voice assistants and the need to create a UX evaluation method for them were deemed highly relevant and their taxonomy was somewhat relevant. |
| Voice assistant features | Effective Communication; Effective; Activity Management; Customizable; Multi-user; Security and Privacy; Multi-linkable; Culturizable/adaptable; Voice Interface; Guidance and Assistance | - | - | All features were considered highly relevant. |
| UX attributes | Useful; Usable; Desirable; Findable/locatable; Credible; Valuable; Learning Capacity; Effectiveness; Efficiency; Satisfaction | - | Accessibility | Out of the three proposals for UX attributes collected in Stage 1, only Accessibility was not considered due to its complexity. |
| Sets of heuristics | 11 R. Langevin’s heuristics [10]; 10 Nielsen’s heuristics [31] | 5 L. M. Sanchez-Adame’s heuristics [11]; 8 C. Nowacki and A. Gordeeva’s heuristics [37] | - | Two sets of heuristics were deemed highly important, and 3 sets were considered somewhat relevant. |
| Usability/UX problems | Formal inspection by researchers (see Appendix D) | R. Cowan’s problems with the experience of people who use IPAs occasionally [9] | - | Two sets of usability/UX problems were considered relevant enough. |
| Other related elements | - | Zwakman’s VUS questionnaire [33] | - | One related element was selected. |
Appendix F. First Iteration, Step 4: “Correlational Stage”

Table A6.
First iteration, Step 4 “Correlational stage”: Match between the voice assistants features, usability/UX attributes, heuristics proposed by other authors, usability/UX problems detected, and related elements proposed by other authors.
Table A6.
First iteration, Step 4 “Correlational stage”: Match between the voice assistants features, usability/UX attributes, heuristics proposed by other authors, usability/UX problems detected, and related elements proposed by other authors.
| Feature | Usability/UX Attribute | Heuristic Related | Usability/UX Problems (Obtained from Formal Inspection and R. Cowan’s Problems [9] | VUS Items |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective communication | Effectiveness; Efficiency; Useful | H2: Context (partially covered feature) H3: Naturalness (partially covered feature) C1: Visibility of system status (slightly covered feature) C5: Error prevention (fully covered feature) C8: Aesthetic, minimalist and engaging design (partially covered feature) C9: Help users recognize, diagnose and recover from errors (fully covered feature) C10: Context preservation (partially covered feature) N1: Visibility of system status (slightly covered feature) N5: Error prevention (partially covered feature) N9: Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors (slightly covered feature) E1.2: Immediate feedback (partially covered feature) E5: Error management (slightly covered feature) E5.2: Quality of error messages (partially covered feature) E7.1: Short a long-term memory (partially covered feature) | P1: Device ignores user P5: Device provides incoherent responses P10: Device ends conversations prematurely P11: Inconsistent language | I1: I thought the response from the voice assistant was easy to understand |
| Effective | Effectiveness; Efficiency; Useful | H1: Complexity (slightly covered feature) H2: Context (slightly covered feature) C6: Help and guidance (partially covered feature) E5: Error management (slightly covered feature) | P7: Device does not provide useful information to user P8: The device has limited memory P12: The device does not understand search requests | I2: I thought the information provided by the voice assistant was not relevant to what I asked I10: I found the voice assistant difficult to use |
| Activity management | Useful; Credible; Valuable; Satisfaction; Learning capacity | C3: User control and freedom (slightly covered feature) C7: Flexibility and efficiency of use (partially covered feature) N3: User control and freedom (slightly covered feature) N7: Flexibility and efficiency of use (slightly covered feature) E2.1: Brevity (slightly covered feature) E2.2: Information density (slightly covered feature) E3.1: Explicit user action (partially covered feature) E3.2: User control (slightly covered feature) | P2: Device ignores user P3: Difficulty initializing device PP: Trust issues when assigning activities to the device | I5: I felt the voice assistant enabled me to successfully complete my tasks when I required help I7: The voice assistant had all the functions and capabilities that I expected it to have |
| Customizable | Satisfaction; Useful; Desirable | C7: Flexibility and efficiency of use (partially covered feature) N3: User control and freedom (slightly covered feature) N7: Flexibility and efficiency of use (slightly covered feature) E4.1: Flexibility (partially covered feature) E4.2: User’s experience level (partially covered feature) E7.2: Environment (partially covered feature) E8.2: Behavior (partially covered feature) | No associated problem found/detected | I6: I found it frustrating to use the voice assistant in a noisy and loud environment I8: I found it difficult to customize the voice assistant according to my needs and preferences |
| Multi-user | Effectiveness; Useful | H2: Context (slightly covered feature) C10: Context preservation (partially covered feature) E4.3: Multi-user (partially covered feature) | P6: The device does not recognize the user’s voice when in a noisy environment | An associated item was not found/detected |
| Security and privacy | Credible; Satisfaction; Findable/locatable | C11: Trustworthiness (partially covered feature) E8.2: Behavior (slightly covered feature) | PP: Trust, data privacy, transparency and data ownership issues | An associated item was not found/detected |
| Multi-linkable | Useful; Valuable; Effectiveness | C9: Help users recognize, diagnose and recover from errors (slightly covered feature) N9: Help users recognize, diagnose and recover from errors (slightly covered feature) | P13: Device does not manage voice pairings with external devices PP: Problems with integration with apps, platforms and systems | An associated item was not found/detected |
| Culturizable/adaptable | Efficiency; Satisfaction; Desirable | H2: Context (partially covered feature) H3: Naturalness (partially covered feature) C2: Match between system and the real world (partially covered feature) C4: Consistency and standards (partially covered feature) N2: Match between system and the real world (slightly covered feature) N4: Consistency and standards (partially covered feature) N8: Aesthetic and minimalist design (slightly covered feature E4: Adaptability (slightly covered feature) E4.1: Flexibility (partially covered feature) E4.3: Multi-user (partially covered feature) | P4: Device does not understand idioms and jargon | An associated item was not found/detected |
| Voice interface | Effectiveness; Efficiency; Useful | H3: Naturalness (partially covered feature) C1: Visibility of system status (slightly covered feature) C6: Help and guidance (partially covered feature) N1: Visibility of system status (partially covered feature) E6: Consistency (slightly covered feature) E6.2: External consistency E8.1: Identity | PP: Hands-free interaction support issues | An associated item was not found/detected |
| Guidance and assistance | Effectiveness; Useful; Valuable; Satisfaction; Findable/locatable | N10: Help and documentation (partially covered feature) | No associated problem found/detected | An associated item was not found/detected |
The letter “N” is used as ID to indicate the number of Nielsen’s heuristics [31], the letter “C” for R. Langevin’s heuristics [10], the letter “H” for L. M. Sanchez-Adame’s heuristics [11], the letter “E” for C. Nowacki and A. Gordeeva’s heuristics [37]; the letter “PP” for R. Cowan’s problems with the experience of people who use IPAs occasionally [9], and the letter “I” for Zwakman’s VUS questionnaire [33].
Appendix G. First Iteration, Step 5: “Selection Stage”

Table A7.
First iteration, Step 5 “Selection stage”: Heuristics and principles selection process.
Table A7.
First iteration, Step 5 “Selection stage”: Heuristics and principles selection process.
| ID | Name | Action | References | Voice Assistant Feature Covered | Applicability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1 | Complexity | Adapt | [11] | Effectiveness | (1) Useful |
| H2 | Context | Adapt | [11] | Effective communication; Effectiveness; Multi-user; Culturizable/adaptable | (1) Useful |
| H3 | Naturalness | Adapt | [11] | Effective communication; Culturizable/adaptable; Voice interface | (2) Important |
| C1 | Visibility of system status | Adapt | [10] | Effective communication; Voice interface | (3) Critical |
| C2 | Match between system and the real world | Adapt | [10] | Culturizable/adaptable | (2) Important |
| C3 | User control and freedom | Adapt | [10] | Activity management | (3) Critical |
| C4 | Consistency and standards | Adapt | [10] | Culturizable/adaptable | (2) Important |
| C5 | Error prevention | Adapt | [10] | Effective communication | (3) Critical |
| C6 | Help and guidance | Adapt | [10] | Effectiveness; Voice interface | (3) Critical |
| C7 | Flexibility and efficiency of use | Adapt | [10] | Activity management; Customizable | (2) Important |
| C8 | Aesthetic, minimalist and engaging design | Adapt | [10] | Effective communication | (3) Critical |
| C9 | Help users recognize, diagnose and recover from errors | Adapt | [10] | Effective communication; Multi-linkable | (3) Critical |
| C10 | Context preservation | Adapt | [10] | Effective communication; Multi-user | (3) Critical |
| C11 | Trustworthiness | Adapt | [10] | Security and privacy | (3) Critical |
| N1 | Visibility of system status | Adapt | [31] | Effective communication; Voice interface | (2) Important |
| N3 | User control and freedom | Adapt | [31] | Activity management; Customizable | (3) Critical |
| N4 | Consistency and standards | Adapt | [31] | Culturizable/adaptable | (2) Important |
| N5 | Error prevention | Adapt | [31] | Effective communication | (2) Important |
| N6 | Recognition rather than recall | Adapt | [31] | Activity management | (1) Useful |
| N7 | Flexibility and efficiency of use | Adapt | [31] | Activity management; Customizable | (2) Important |
| N8 | Aesthetic and minimalist design | Adapt | [31] | Culturizable/adaptable | (1) Useful |
| N9 | Help users recognize, diagnose and recover from errors | Adapt | [31] | Effective communication; Multi-linkable | (2) Important |
| N10 | Help and documentation | Adapt | [31] | Guidance and assistance | (3) Critical |
| E1.2 | Immediate feedback | Adapt | [37] | Effective communication | (3) Critical |
| E2.1 | Brevity | Adapt | [37] | Activity management | (3) Critical |
| E2.2 | Information density | Adapt | [37] | Activity management | (3) Critical |
| E3.1 | Explicit user action | Adapt | [37] | Activity management | (3) Critical |
| E3.2 | User control | Adapt | [37] | Activity management | (3) Critical |
| E4 | Adaptability | Adapt | [37] | Culturizable/adaptable | (2) Important |
| E4.1 | Flexibility | Adapt | [37] | Customizable; Culturizable/adaptable | (1) Useful |
| E4.2 | User’s experience level | Adapt | [37] | Customizable | (1) Useful |
| E4.3 | Multi-user | Adapt | [37] | Multi-user; Culturizable/adaptable | (3) Critical |
| E5 | Error management | Adapt | [37] | Effective communication; Effectiveness | (1) Useful |
| E5.2 | Quality of error messages | Adapt | [37] | Effective communication | (1) Useful |
| E6 | Consistency | Adapt | [37] | Voice interface | (1) Useful |
| E6.2 | External consistency | Adapt | [37] | Voice interface | (1) Useful |
| E7.1 | Short a long-term memory | Adapt | [37] | Effective communication | (1) Useful |
| E7.2 | Environment | Adapt | [37] | Customizable | (2) Important |
| E8.1 | Identity | Adapt | [37] | Voice interface | (3) Critical |
| E8.2 | Behavior | Adapt | [37] | Customizable; Security and privacy | (1) Useful |
Appendix H. First Iteration, Step 8: “Refinement Stage”

Table A8.
First iteration, Step 8 “Refinement stage”: Refinement of the first set of heuristics HVA.
Table A8.
First iteration, Step 8 “Refinement stage”: Refinement of the first set of heuristics HVA.
| ID | Refinement Section | Description | Action | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HVA1 | Definition | Include “illumination aspects”. | Add | Heuristic evaluation |
| Reduction for better understanding. | Modify | Expert judgment | ||
| Checklist | Include the following elements:
| Add | Heuristic evaluation | |
| HVA2 | Name, Definition, Explanation | Modify to make them more comprehensible and representative. | Modify | Expert judgment |
| Checklist | Include the following elements:
| Add | Heuristic evaluation | |
| Remove the following item: The device warns of possible situations when carrying out a particular action. | Remove | Expert judgment | ||
| HVA3 | Definition, Explanation | Remove the description related to “short or minimal activation command”. | Remove | Expert judgment |
| Specification table | Include the concept of “coherence”. | Add | Expert judgment | |
| Review the ease of use of heuristic. | Analyze | Expert judgment | ||
| Checklist | Include the following elements:
| Add | Expert judgment | |
Remove the following elements:
| Remove | Expert judgment | ||
| HVA4 | Name, Definition | Modify to make them more comprehensible and representative. | Modify | Expert judgment |
| Specification table | Remove the concept of “coherence”. | Remove | Expert judgment | |
| Checklist | Include the following elements:
| Add | Heuristic evaluation | |
| HVA5 | Name, Explanation | Specify for better understanding. | Modify | Expert judgment |
| Definition | Include the concept of “idiolect”. | Add | Heuristic evaluation | |
| Checklist | Include the following element: The artifact recognizes the user’s particular way of speaking in requests. | Add | Heuristic evaluation | |
| Specification table | Analyze why HVA5 obtained 50% of correct associations. | Analyze | Heuristic evaluation | |
| HVA6 | Checklist | Include the following element: The device maintains its formal language even in error situations | Add | Expert judgment |
| Expand checklist listing. | Analyze, Add | Expert judgment | ||
| HVA8 | Name, Definition | Incorporate concepts: voice shortcut, customization/adaptation. | Add | Expert judgment |
| Checklist | Include the following elements:
| Add | Expert judgment | |
| HVA9 | Checklist | Include the following element: The device clearly indicates the possible causes of errors. | Add | Expert judgment |
| HVA10 | Checklist | Include the following elements:
| Add | Heuristic evaluation |
| HVA11 | Specification table | Review the ease of use of heuristic. | Analyze | Expert judgment |
Appendix I. Criteria Used to Evaluate the Effectiveness of a New Set of Usability/UX Heuristics (From [2,41])

Table A9.
Five criteria used to evaluate the effectiveness of a new set of usability/UX heuristics [2].
Table A9.
Five criteria used to evaluate the effectiveness of a new set of usability/UX heuristics [2].
| Criterion Description | Formula |
| where
|
|
|
| where
|
| where
|
| where
|
Appendix J. Full HEUXIVA Specification, Using the Template Proposed in the Methodology Applied

Table A10.
HEUXIVA 1: “System status visibility”.
Table A10.
HEUXIVA 1: “System status visibility”.
| ID | HEUXIVA1 |
|---|---|
| Name | System Status Visibility |
| Definition | The device must indicate to the user via voice, sound and/or illumination every action that is performed. |
| Explanation | The device must deliver communication sufficiently intuitive for the user through the intonation of the voice of the assistant, of emphasis at the beginning and end of the conversation giving way to the user to continue the dialog with the artifact. Likewise, to provide the user with the status of the system, the assistant must communicate every action performed, to be performed or being performed in the same context/situation or request. |
| Priority | (3) Critical |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Efficiency, Satisfaction UX: Useful, Valuable |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Effective conversation, Voice interface, Activity management |
| Set of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: Ok Google, play music Ok Google, play music Ok, playing *song name* on Spotify Ok, playing *song name* on Spotify*Music starts playing* |
Non-compliance: Ok Google, tell me about my reminders for today Ok Google, tell me about my reminders for today*Device lights turn on*  *Silence* *Silence* |

Table A11.
HEUXIVA 2: “System guidance and capabilities”.
Table A11.
HEUXIVA 2: “System guidance and capabilities”.
| ID | HEUXIVA2 |
|---|---|
| Name | System Guidance and Capabilities |
| Definition | The device must guide the user through dialog and activities using words that the user recognizes (and does not increase their cognitive ability). It should also clarify in a simple way its capabilities. |
| Explanation | The device must be capable of establishing a conversation with the user. Where it guides and orients the user throughout the dialog so that the device can function correctly, and the user does not get lost in the process. In turn, if the device does not have a feature and/or cannot carry out a user’s request, the device must explain in a simple way why it does not have and/or cannot execute the action in natural language. |
| Priority | (3) Critical |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Satisfaction UX: Useful, Desirable, Usable, Valuable |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Culturizable/adaptable, Voice interface, Effective communication, Activity management |
| Set of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Example | Compliance: Ok Google, read my email Ok Google, read my email My version does not allow me to perform this action, however, update 1.2 allows it My version does not allow me to perform this action, however, update 1.2 allows it |
Non-compliance: Ok Google, read my email Ok Google, read my email I’m sorry, I didn’t understand you I’m sorry, I didn’t understand you |

Table A12.
HEUXIVA 3: “Effective and fluid communication”.
Table A12.
HEUXIVA 3: “Effective and fluid communication”.
| ID | HEUXIVA3 |
|---|---|
| Name | Effective and Fluid Communication |
| Definition | The device must adapt to the context and situations that arise in the conversation, as well as remembering previous requests and conversations with the user. |
| Explanation | The device must communicate as effectively as possible with the user, respecting the context of the conversation and being prepared to pause, conversation fillers and interruptions, as well as failures in the dialog, detours, and in turn the device must be able to remember previous conversations with the user and/or requests from the user. |
| Priority | (3) Critical |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Efficiency UX: Useful, Usable |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Effective communication, Effective, Multi-user |
| Set of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: *User whispers*  It’s time to sleep It’s time to sleep*GA whispers*  I will play music to sleep, may you rest I will play music to sleep, may you rest |
| Non-compliance: *GA playing music*  OK Google, pause OK Google, pause According to the RAE, “pause” means brief interruption of an action or movement. According to the RAE, “pause” means brief interruption of an action or movement. |

Table A13.
HEUXIVA 4: “Environment match between assistant and user language”.
Table A13.
HEUXIVA 4: “Environment match between assistant and user language”.
| ID | HEUXIVA4 |
|---|---|
| Name | Environment Match Between Assistant and User Language |
| Definition | The device must understand the user’s particular way of speaking, in addition to interacting in their language; with words, phrases and concepts familiar to the user. |
| Explanation | The device must be verbally adapted to the geographical location in which it is located, giving way to conversations using the language and concepts or expressions that the user uses daily. |
| Priority | (2) Important |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness UX: Useful, Valuable, Desirable |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Culturizable/adaptable, Multi-user, Voice interface |
| Set of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: Ok Google. How are you? Ok Google. How are you? I feel very well I feel very well*2 s later*  Ok Google, reproduce música Ok Google, reproduce música Reproduciendo *name of song* en Spotify. Reproduciendo *name of song* en Spotify. |
| Non-compliance: *User speaking English*  Ok Google, What time is it? Ok Google, What time is it?*GA answer in Spanish*  Son las 8 de la mañana Son las 8 de la mañana |

Table A14.
HEUXIVA5: “Information Accuracy”.
Table A14.
HEUXIVA5: “Information Accuracy”.
| ID | HEUXIVA5 |
|---|---|
| Name | Information Accuracy |
| Definition | The responses delivered by the device must be relevant, brief and according to what is requested by the user. Similarly, the device must provide truthful information during interaction with the user. |
| Explanation | For actions/requests to be more efficient and effective, the device’s responses must be coherent and truthful, that is, the information provided must be logical, realistic and true. In turn, to capture the user’s attention, the responses must be brief and contain the most essential and/or important part of what is requested. |
| Priority | (3) Critical |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Efficiency, Satisfaction UX: Useful, Valuable |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Effective conversation, Effective, Voice interface |
| Set of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: Ok, Google, when did World War II start? Ok, Google, when did World War II start? The Second World War began on 1 September, 1939. The Second World War began on 1 September, 1939. |
Non-compliance: Ok Google, what is the temperature? Ok Google, what is the temperature? The current temperature in Valparaíso is 11 °C, for tomorrow a temperature of 16° is expected with a maximum of 15° and a minimum of 7° and a probability of rain of 20%. The current temperature in Valparaíso is 11 °C, for tomorrow a temperature of 16° is expected with a maximum of 15° and a minimum of 7° and a probability of rain of 20%. |

Table A15.
HEUXIVA6: “User control and freedom”.
Table A15.
HEUXIVA6: “User control and freedom”.
| ID | HEUXIVA6 |
|---|---|
| Name | User Control and Freedom |
| Definition | The device allows the user to perform, redo, and undo actions or requests. |
| Explanation | The device allows actions requested by the user and at their request. Sometimes redo and undo these requests when the user deems it. |
| Priority | (3) Critical |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Satisfaction UX: Credible, Valuable, Learning capacity, Useful |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Activity management, Effective communication, Customizable |
| Set of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: Ok Google, delete my 7 p.m. alarm Ok Google, delete my 7 p.m. alarm Ok, alarm deleted Ok, alarm deleted |
Non-compliance: Ok Google, delete my 7 p.m. alarm Ok Google, delete my 7 p.m. alarm I can’t delete the alarm I can’t delete the alarm |

Table A16.
HEUXIVA7: “Consistent voice interface”.
Table A16.
HEUXIVA7: “Consistent voice interface”.
| ID | HEUXIVA7 |
|---|---|
| Name | Consistent Voice Interface |
| Definition | The device must be able to provide the information through voice and being consistent in its personality. |
| Explanation | The device should be able to provide information and/or answers ideally through the voice interface and, in turn, in the interaction with the user, the device should follow standards in the user’s personality, that is, have a consistent voice/tone, language style and sounds, so as not to confuse the user. |
| Priority | (2) Important |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Satisfaction UX: Credible, Desirable, Useful, Valuable |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Effective conversation, Voice interface, Culturizable/adaptable, Activity management |
| Set of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: *It is 1:00 p.m. on 28 July.  Ok Google, read my reminders Ok Google, read my reminders Today you have 2 reminders, one at 2:30 p.m. “Take pills” and another at 6:00 p.m. “Walk”. Do you want me to mention the week’s reminders? Today you have 2 reminders, one at 2:30 p.m. “Take pills” and another at 6:00 p.m. “Walk”. Do you want me to mention the week’s reminders? |
| Non-compliance: *GA is playing music on Spotify*  Ok Google, how are you? Ok Google, how are you?*GA indicates in a feminine voice*  I feel great today. I feel great today.*User unlinks the GA connection with Spotify* *GA indicates in masculine voice*  Error when playing Spotify Error when playing Spotify |

Table A17.
HEUXIVA 8: “Voice shortcuts, flexibility and personalization”.
Table A17.
HEUXIVA 8: “Voice shortcuts, flexibility and personalization”.
| ID | HEUXIVA8 |
|---|---|
| Name | Voice Shortcuts, Flexibility and Personalization |
| Definition | The device must answer depending on the environment in which the user is located, providing shortcuts according to the context, allowing customization and adapting according to the needs of the user. |
| Explanation | The device must have flexibility to adapt to the needs and capabilities of users, this being the type of user (novice, expert), physical environments and aspects of device customization. In addition to providing voice shortcuts to perform an action more quickly. |
| Priority | (2) Important |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Efficiency, Satisfaction UX: Usable, Learning capacity |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Customizable, Multi-user, Multi-linkable |
| Sets of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Example | Compliance: Ok Google, music. Ok Google, music. Ok, reproducing *song name* on Spotify Ok, reproducing *song name* on Spotify(The user can say “music” instead of “play music”) |
Non-compliance: Ok Google, music. Ok Google, music. I’m sorry, I didn’t understand. I’m sorry, I didn’t understand. |

Table A18.
HEUXIVA 9: “Error prevention”.
Table A18.
HEUXIVA 9: “Error prevention”.
| ID | HEUXIVA9 |
|---|---|
| Name | Error Prevention |
| Definition | The device must provide the necessary information to warn the user when an error is about to occur. |
| Explanation | When the user requests an action that could change the context of the interaction and/or an error is about to be triggered, the system must warn the user, communicating the consequences of the action that is about to be performed. |
| Priority | (2) Important |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Efficiency UX: Useful |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Effective Conversation, Voice interface |
| Sets of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: Ok Google, play music Ok Google, play music Ok, playing music Ok, playing music Ok Google, call mom Ok Google, call mom When calling, the music will stop, do you still want to call? When calling, the music will stop, do you still want to call? |
Non-compliance: Ok Google, read me today’s news Ok Google, read me today’s news Here you have today’s news Here you have today’s news*Reads the news*  Ok Google, I want to watch a Youtube video Ok Google, I want to watch a Youtube video Ok, playing recommended videos on Youtube Ok, playing recommended videos on Youtube*Stops reading the news* |

Table A19.
HEUXIVA 10: “Help users recognize, diagnose, and fix errors”.
Table A19.
HEUXIVA 10: “Help users recognize, diagnose, and fix errors”.
| ID | HEUXIVA10 |
|---|---|
| Name | Help Users Recognize, Diagnose, and Fix Errors |
| Definition | Error messages should be expressed in simple language (not codes), accurately indicate the problem, and constructively suggest a solution that mostly uses voice commands or actions. |
| Explanation | At the time of an error or problem occurring during interaction with the device, that is, while the user is using the device, it manifests and implies the error in a language understandable to it and provides an appropriate solution and help, all this preferably through the voice interface. |
| Priority | (3) Critical |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Efficiency UX: Valuable, Useful |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Culturizable/adaptable, Voice interface, Multi-linkable |
| Sets of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: Ok Google, call Fernanda O. Ok Google, call Fernanda O. I’m sorry, I can’t do that. To make a call you must first link the device with Google’s Duo App. I’m sorry, I can’t do that. To make a call you must first link the device with Google’s Duo App. |
| Non-compliance: *There’s an alarm programmed for the next day and 9 p.m.*  Ok Google, create a new alarm for tomorrow at 9 p.m. Ok Google, create a new alarm for tomorrow at 9 p.m. Sorry, I didn’t understand Sorry, I didn’t understand |

Table A20.
HEUXIVA 11: “Data privacy”.
Table A20.
HEUXIVA 11: “Data privacy”.
| ID | HEUXIVA11 |
|---|---|
| Name | Data Privacy |
| Definition | The device must inform the user about the privacy and use of personal data. Likewise, it must grant the possibility of rejecting the collection and analysis of their data, thus being transparent and truthful with the user. |
| Explanation | The device must request the user’s permission for the use of the data that will be collected over time, and the user must have the possibility to reject this option. |
| Priority | (3) Critical |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Satisfaction UX: Valuable, Credible |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Security and privacy, Activity management |
| Sets of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: *Initializing the device for the first time*  Hello, our conversations help me improve, do you allow me to collect data? Hello, our conversations help me improve, do you allow me to collect data? No thanks No thanks Okay, the data from our conversations will not be collected. Okay, the data from our conversations will not be collected. |
| Non-compliance: *Initializing the device for the first time*  Hello, our conversations help me improve, do you allow me to collect data? Hello, our conversations help me improve, do you allow me to collect data? No thanks No thanks If you do not accept, I will not be able to function properly If you do not accept, I will not be able to function properly |

Table A21.
HEUXIVA 12: “Voice assistant reliability”.
Table A21.
HEUXIVA 12: “Voice assistant reliability”.
| ID | HEUXIVA12 |
|---|---|
| Name | Voice Assistant Reliability |
| Definition | Reliability must be transmitted through the behavior of the device both in interaction with the user and when the user is inactive. |
| Explanation | The device must communicate to the user how active listening works to generate more trust between the user and the device. In turn, this should be activated only by using the activation command. |
| Priority | (3) Important |
| UX/Usability attribute | UX: Valuable, Credible |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Customizable, Security and privacy |
| Sets of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: Ok Google, call Daniela Ok Google, call Daniela Ok, calling Daniela Ok, calling Daniela |
Non-compliance: *Talking to another person in the environment* *Talking to another person in the environment**GA device activates*  Calling Daniela Calling Daniela |

Table A22.
HEUXIVA13: “Guides and documentation”.
Table A22.
HEUXIVA13: “Guides and documentation”.
| ID | HEUXIVA13 |
|---|---|
| Name | Guides and Documentation |
| Definition | The device must provide simple and comprehensive physical or electronic documentation of the internal and external workings of the device, either through a request from the user or external search. |
| Explanation | The device must be provided with a user manual/guide for easy first use and installation/reinstallation to a new location for novice and/or first-time users. This being through the voice assistant (preset explained/described installation instructions before connecting it to the WIFI). This should contain all the information and usage examples necessary for the user to interact with the device properly. The appliance must provide internal, external information (device buttons/its operation) and of configuration about it. |
| Priority | (2) Important |
| UX/Usability attribute | Usability: Effectiveness, Satisfaction UX: Findable/locatable, Valuable, Usable |
| Voice Assistant Feature | Guidance and assistance |
| Sets of heuristics related |
|
| Checklist |
|
| Examples | Compliance: The device has a physical instruction manual and an online one on its website. |
| Non-compliance: The device has no information on basic functions. |
Appendix K. Coverage Matrix Linking Voice Assistant Features, Heuristics, Checklist Items, and Problem Types

Table A23.
Coverage matrix for HEUXIVA heuristics.
Table A23.
Coverage matrix for HEUXIVA heuristics.
| Voice Assistant Feature | HEUXIVA Heuristic | Checklist Item (Example) | Problem Type (UX Aspect) | Example (Compliance/Non-Compliance) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effective communication | HEUXIVA1, HEUXIVA2, HEUXIVA3, HEUXIVA5, HEUXIVA6, HEUXIVA7, HEUXIVA9 | (HEUXIVA1) The device has lighting signals when it interacts with the user. | Lack of system feedback | ✅ The device lights up and says “I’m listening”. ❌ No response after the “wake” word. |
| (HEUXIVA6) The artifact executes the user’s requests. | Lack of control | ✅ “Stop music”. Command immediately halts playback. ❌ Must wait for assistant to finish speaking. | ||
| (HEUXIVA9) The device rephrases unclear input for confirmation. | Ambiguous input handling | ✅ “Did you mean alarm for 7 AM or 7 PM?”/❌ Executes wrong command without clarifying. | ||
| Effective | HEUXIVA3, HEUXIVA5 | (HEUXIVA3) The device provides a continuous conversation option and maintains context between consecutive interactions. | Context loss | ✅ Understands follow-up question: “And what about tomorrow?”/❌ Requires repeating full command each time. |
| Activity management | HEUXIVA1, HEUXIVA2, HEUXIVA6, HEUXIVA7, HEUXIVA11 | (HEUXIVA2) The devices allow users to perform and manage functional tasks (such as scheduling appointments or setting alarms) through voice commands. | Task management and functionality coverage | ✅ The assistant successfully schedules a meeting or sends a message via voice command./❌ The assistant fails to complete management actions or requires manual confirmation on a secondary device. |
| Customizable | HEUXIVA6, HEUXIVA8, HEUXIVA12 | (HEUXIVA12) The device performs tasks accurately even under varying conditions (e.g., background noise). | Performance | ✅ Recognizes commands in noisy environments./❌ Fails to respond when music is playing. |
| Multi-user | HEUXIVA3, HEUXIVA4, HEUXIVA8 | (HEUXIVA4) The device recognizes and differentiate the voices of multiple users, allowing everyone in the same environment to interact with the assistant naturally. | Multi-user inclusiveness | ✅ The assistant identifies different household members and adapts responses (e.g., personalized calendar or music)./❌ Only responds to the registered user’s voice, ignoring others in the same space. |
| Security and privacy | HEUXIVA11, HEUXIVA12 | (HEUXIVA11) The device requests authorization for the use of the data collected during the dialog. | Transparency issue | ✅ “Do you agree to save this recording?”/❌ Stores voice data automatically. |
| Multi-linkable | HEUXIVA8, HEUXIVA10 | (HEUXIVA8) The device allows linking or integrating external services and smart devices (e.g., music apps, lighting, appliances, temperature control) and enables their management through voice commands. | Integration | ✅ The assistant connects to Spotify and smart lights, allowing full control by voice./❌ Integration with external apps or devices fails or requires manual configuration. |
| Culturizable/adaptable | HEUXIVA2, HEUXIVA4, HEUXIVA7, HEUXIVA10 | (HEUXIVA10) The device suggests possible solutions or recovery options. | Lack of recovery adaptation | ✅ “Try saying the command again”./❌ Offers no instruction to fix issue. |
| Voice interface | HEUXIVA1, HEUXIVA2, HEUXIVA4, HEUXIVA5, HEUXIVA7, HEUXIVA9, HEUXIVA10 | (HEUXIVA5) The response of the device is coherent and cohesive with the user request. | Irrelevant or excessive information | ✅ Gives only relevant weather data./❌ Reads the entire Wikipedia page. |
| (HEUXIVA7) The device uses a consistent tone, vocabulary, and personality across interactions. | Inconsistent persona | ✅ Maintains friendly tone and terminology./❌ Changes voice or phrasing randomly. | ||
| Guidance and assistance | HEUXIVA13 | (HEUXIVA13) The device provides access to guides or helps resources through voice. | Lack of support resources | ✅ “You can say ‘Help’ to learn available commands”./❌ No help option available. |
“The ✅ symbol shows an example of compliance of each heuristic; while the ❌ symbol shows an example of a non-compliance”.
References
- Nielsen, J.; Molich, R. Heuristic evaluation of user interfaces. In Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems Empowering People—CHI ’90, Seattle, WA, USA, 1–5 April 1990; pp. 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, D.; Rusu, C.; Rusu, V. A methodology to develop usability/user experience heuristics. Comput. Stand. Interfaces 2018, 59, 109–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzepka, C.; Berger, B.; Hess, T. Voice assistant vs. Chatbot–examining the fit between conversational agents’ interaction modalities and information search tasks. Inf. Syst. Front. 2022, 24, 839–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Casal, J.; Saleem, K.; Denisov, V. Intelligent personal assistants based on internet of things approaches. IEEE Syst. J. 2016, 12, 1793–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.; Rodrigues, J.J.P.C.; Silva, B.M.C.; Casal, J.; Saleem, K.; Denisov, V. An IoT-based mobile gateway for intelligent personal assistants on mobile health environments. J. Netw. Comput. Appl. 2016, 71, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Yang, H. Understanding adoption of intelligent personal assistants: A parasocial relationship perspective. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2018, 118, 618–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aymerich-Franch, L.; Ferrer, I. Investigating the use of speech-based conversational agents for life coaching. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud. 2022, 159, 102745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massai, L.; Nesi, P.; Pantaleo, G. PAVAL: A location-aware virtual personal assistant for retrieving geolocated points of interest and location-based services. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2019, 77, 70–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, B.R.; Pantidi, N.; Coyle, D.; Morrissey, K.; Clarke, P.; Al-Shehri, S.; Earley, D.; Bandeira, N. “What can i help you with?” infrequent users’ experiences of intelligent personal assistants. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services, Vienna, Austria, 4–7 September 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Langevin, R.; Lordon, R.J.; Avrahami, T.; Cowan, B.R.; Hirsch, T.; Hsieh, G. Heuristic evaluation of conversational agents. In Proceedings of the 2021 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Virtual, 8–13 May 2021; pp. 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Adame, L.M.; Mendoza, S.; Urquiza, J.; Rodríguez, J.; Meneses-Viveros, A. Towards a set of heuristics for evaluating chatbots. IEEE Lat. Am. Trans. 2021, 19, 2037–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwakman, D.S.; Pal, D.; Triyason, T.; Vanijja, V. Usability of voice-based intelligent personal assistants. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence (ICTC), Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 21–23 October 2020; pp. 652–657. [Google Scholar]
- Google Actions on Google Glossary (Dialogflow). 2024. Available online: https://developers.google.com/assistant/df-asdk/glossary (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Google Nest Explore What You Can Do with Google Nest and Home Devices. 2025. Available online: https://support.google.com/googlenest/answer/7130274 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Google Nest Customize Smart Plug or Smart Switch Voice Commands with Device Type. 2025. Available online: https://support.google.com/googlenest/answer/9921419 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Google Nest Customize Your News Experience. 2025. Available online: https://support.google.com/googlenest/answer/7551674 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Google Nest Guests and Your Google Connected Home Devices. 2025. Available online: https://support.google.com/googlenest/answer/7177221 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- García, N.H.; Martínez, I.L.; Gutiérrez, M.S.; Veracruzana, X. Development of new commands for Google Assistant using Dialogflow, Firebase and NodeMCU (ESP8266) as an intermediary. Abstr. Appl. 2020, 29, 74–87. [Google Scholar]
- Google Nest FAQs on Privacy: Google Nest. 2025. Available online: https://support.google.com/googlenest/answer/9415830 (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Google Assistant What It Can Do—Get Started. 2025. Available online: https://assistant.google.com/learn/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Google Assistant Control Smart Home Devices with Google Assistant. 2025. Available online: https://support.google.com/assistant/answer/7314909? (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- ISO 9241-210:2019; Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction—Part 210: Human-Centred Design for Interactive Systems. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- Park, J.; Han, S.H.; Kim, H.K.; Cho, Y.; Park, W. Developing elements of user experience for mobile phones and services: Survey, interview, and observation approaches. Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf. Serv. Ind. 2013, 23, 279–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lykke, M.; Jantzen, C. User experience dimensions: A systematic approach to experiential qualities for evaluating information interaction in museums. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM on Conference on Human Information Interaction and Retrieval, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 13–17 March 2016; pp. 81–90. [Google Scholar]
- Morville, P. User Experience Design. Semantic Studios. 2004. Available online: https://semanticstudios.com/user_experience_design/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Lewis, J.R. Usability: Lessons Learned. and Yet to Be Learned. Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact. 2014, 30, 663–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendrick, A. Formative vs. Summative Evaluations. Nielsen Norman Group. 2019. Available online: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/formative-vs-summative-evaluations/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Nielsen, J. Thinking Aloud: The #1 Usability Tool. Nielsen Norman Group. 2012. Available online: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/thinking-aloud-the-1-usability-tool/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Experience Research Society UX Expert Evaluation. 2024. Available online: https://experienceresearchsociety.org/ux-methods/ux-expert-evaluation/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Harley, A. UX Expert Reviews. Nielsen Norman Group. 2018. Available online: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/ux-expert-reviews/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Nielsen, J. 10 Usability Heuristics for User Interface Design. Nielsen Norman Group. 2024. Available online: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/ten-usability-heuristics/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Brooke, J. SUS-A quick and dirty usability scale. Usability Eval. Ind. 1996, 189, 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Zwakman, D.S.; Pal, D.; Triyason, T.; Arpnikanondt, C. Voice usability scale: Measuring the user experience with voice assistants. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Symposium on Smart Electronic Systems (iSES) (Formerly iNiS), Chennai, India, 14–16 December 2020; pp. 308–311. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, J. Severity Ratings for Usability Problems. Nielsen Norman Group. 1994. Available online: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/how-to-rate-the-severity-of-usability-problems/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- ISO 9241-11:2018; Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction—Part 11: Usability: Definitions and Concepts. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63500.html (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Nielsen, J. Usability 101: Introduction to Usability. Nielsen Norman Group. 2012. Available online: https://www.nngroup.com/articles/usability-101-introduction-to-usability/ (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Nowacki, C.; Gordeeva, A.; Lizé, A.-H. Improving the usability of voice user interfaces: A new set of ergonomic criteria. In Proceedings of the Design, User Experience, and Usability. Design for Contemporary Interactive Environments: 9th International Conference, DUXU 2020, Held as Part of the 22nd HCI International Conference, HCII 2020, Copenhagen, Denmark, 19–24 July 2020; Proceedings, Part I. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 117–133. [Google Scholar]
- Google Store Nest Mini—Overview. 2025. Available online: https://store.google.com/us/product/google_nest_mini?hl=en-US (accessed on 15 January 2025).
- Scapin, D.L.; Bastien, J.M.C. Ergonomic criteria for evaluating the ergonomic quality of interactive systems. Behav. Inf. Technol. 1997, 16, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barcelos Silva, A.; Gomes, M.M.; da Costa, C.A.; da Rosa Righi, R.; Barbosa, J.L.V.; Pessin, G.; De Doncker, G.; Federizzi, G. Intelligent personal assistants: A systematic literature review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2020, 147, 113193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiñones, D.; Ojeda, C.; Herrera, R.F.; Rojas, L.F. UXH-GEDAPP: A set of user experience heuristics for evaluating generative design applications. Inf. Softw. Technol. 2024, 168, 107408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).