Author Contributions
This article is presented by the eight authors mentioned, each of whom were responsible for various aspects of the work. Conceptualization, B.Z. and Y.T.; methodology, B.Z. and Y.T.; software, Y.T., J.W.,Y.Z., and X.F.; validation, P.C., H.C., and F.L.; writing—original draft preparation, B.Z. and Y.T.; writing—review and editing, B.Z., Y.T., J.W., Y.Z., X.F., P.C., H.C., and F.L.; supervision, Y.T. and J.W.; project administration, B.Z.; funding acquisition, B.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Figure 1.
Finite element model of the transmission tower.
Figure 1.
Finite element model of the transmission tower.
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the five typical deformation conditions. (The red arrow represents the meanings of downward, inward, and outward).
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the five typical deformation conditions. (The red arrow represents the meanings of downward, inward, and outward).
Figure 3.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt deformation.
Figure 3.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt deformation.
Figure 4.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tilt deformation.
Figure 4.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tilt deformation.
Figure 5.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under compression deformation.
Figure 5.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under compression deformation.
Figure 6.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with compressive deformation.
Figure 6.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with compressive deformation.
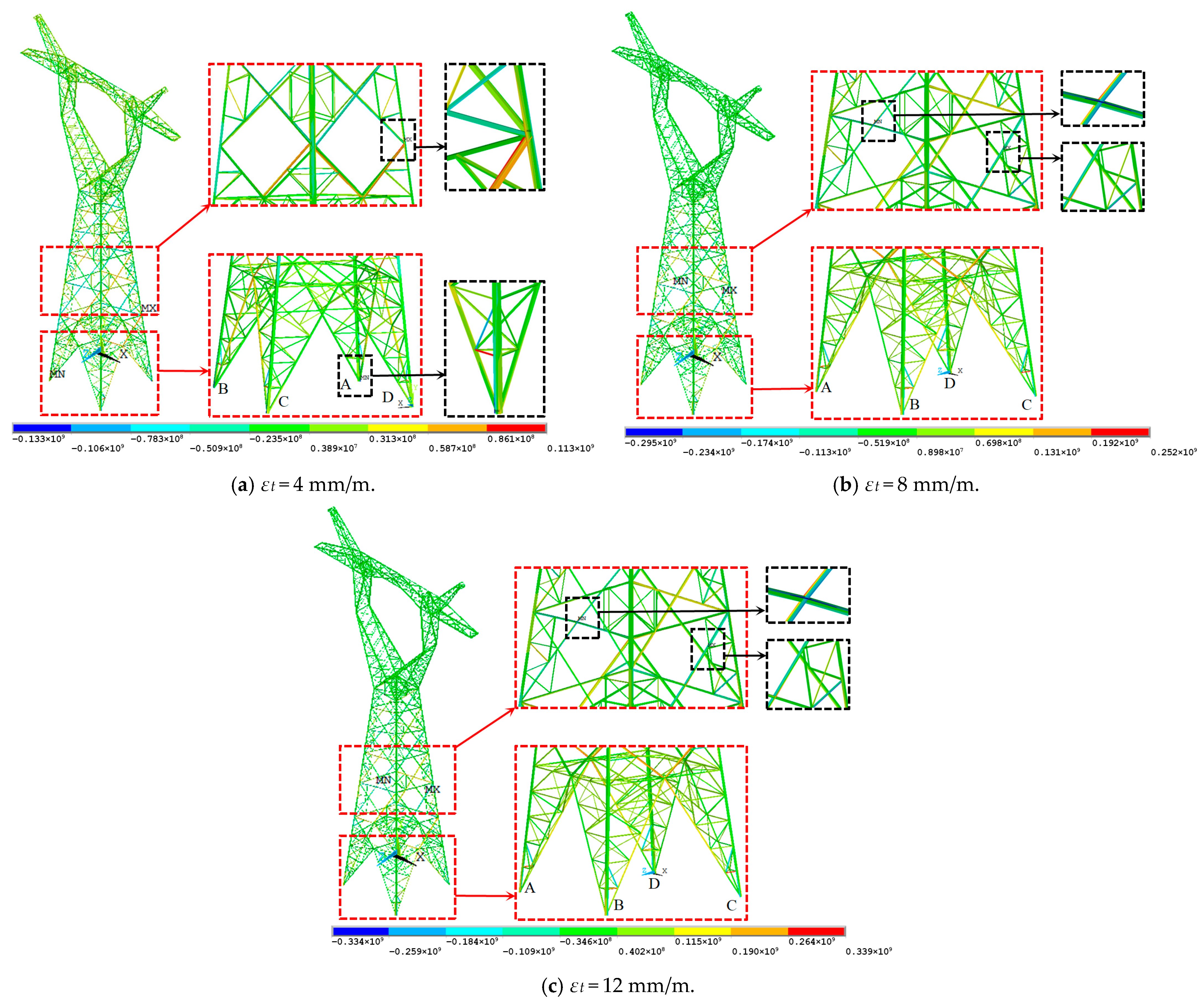
Figure 7.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tension deformation.
Figure 7.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tension deformation.
Figure 8.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tensile deformation.
Figure 8.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tensile deformation.
Figure 9.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt–compression deformation.
Figure 9.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt–compression deformation.
Figure 10.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tilt–compression deformation.
Figure 10.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tilt–compression deformation.
Figure 11.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt–tension deformation.
Figure 11.
The stress distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt–tension deformation.
Figure 12.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tilt–tension deformation.
Figure 12.
The fitting diagram of the maximum stress value of the member with tilt–tension deformation.
Figure 13.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt deformation.
Figure 13.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt deformation.
Figure 14.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the tilt deformation value.
Figure 14.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the tilt deformation value.
Figure 15.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under compression deformation.
Figure 15.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under compression deformation.
Figure 16.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the compression deformation value.
Figure 16.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the compression deformation value.
Figure 17.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tension deformation.
Figure 17.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tension deformation.
Figure 18.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the tension deformation value.
Figure 18.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the tension deformation value.
Figure 19.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt–compression deformation.
Figure 19.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of the transmission tower under tilt–compression deformation.
Figure 20.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the tilt–compression deformation value.
Figure 20.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with the tilt–compression deformation value.
Figure 21.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of transmission tower under tilt–tension deformation.
Figure 21.
The displacement distribution cloud plot of transmission tower under tilt–tension deformation.
Figure 22.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with tilt–tension deformation value.
Figure 22.
Correlations of Sx, Sy, Sz, and q with tilt–tension deformation value.
Figure 23.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and tilt deformation value.
Figure 23.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and tilt deformation value.
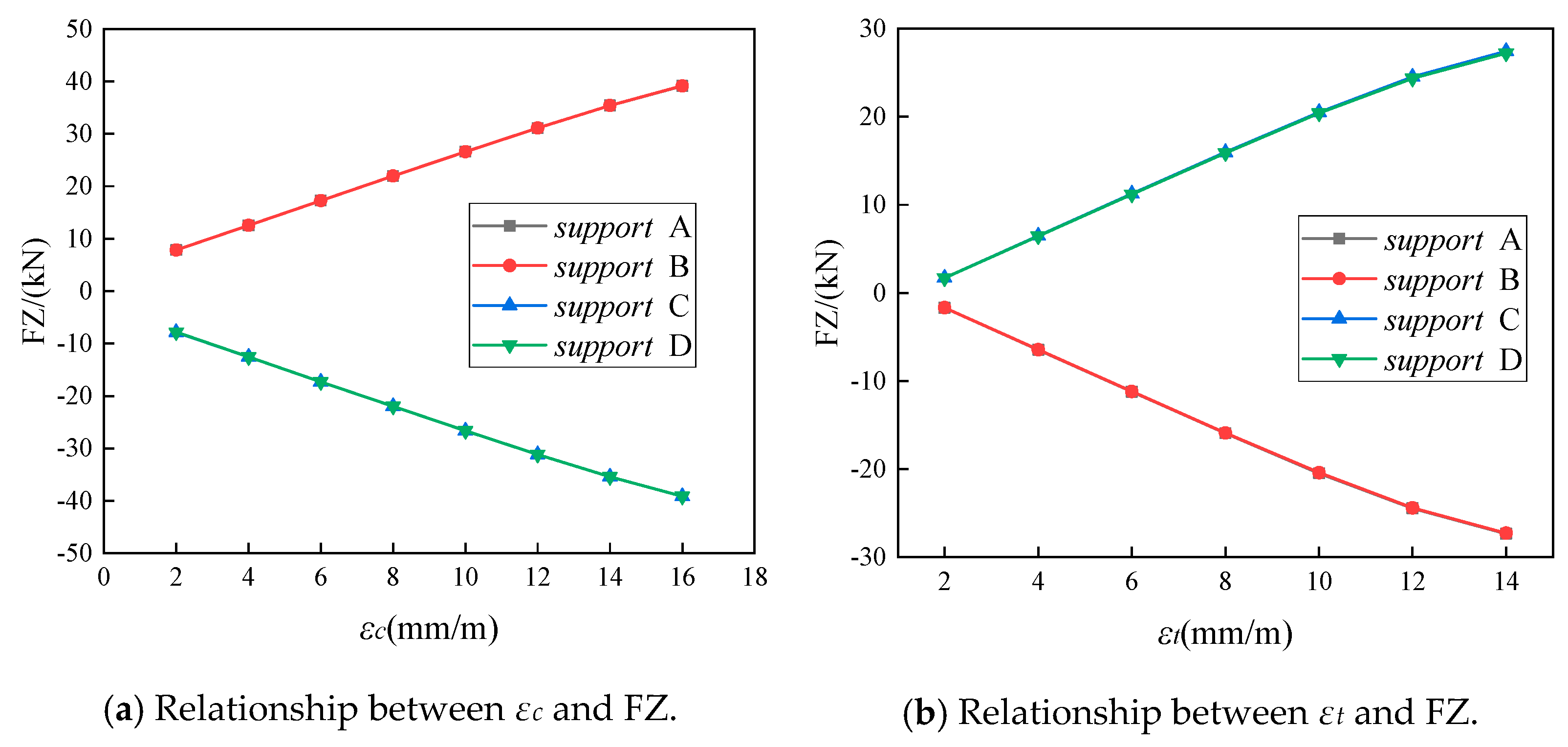
Figure 24.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and compression and tension deformation value.
Figure 24.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and compression and tension deformation value.
Figure 25.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and tilt–compression deformation value.
Figure 25.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and tilt–compression deformation value.
Figure 26.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and tilt–tension deformation value.
Figure 26.
Relationship curve between the support reaction force and tilt–tension deformation value.
Table 1.
Simulation scheme under individual deformation conditions.
Table 1.
Simulation scheme under individual deformation conditions.
| Scheme | Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Condition 3 |
|---|
| i (mm/m) | B (m) | UY (mm) | εc (mm/m) | B (m) | UZ (mm) | εt (mm/m) | B (m) | UZ (mm) |
|---|
| 1 | 3 | 8 | −24 | −2 | 8 | −16 | 2 | 8 | 16 |
| 2 | 6 | 8 | −48 | −4 | 8 | −32 | 4 | 8 | 32 |
| 3 | 10 | 8 | −80 | −6 | 8 | −48 | 6 | 8 | 48 |
| 4 | 15 | 8 | −120 | −8 | 8 | −64 | 8 | 8 | 64 |
| 5 | 20 | 8 | −160 | −10 | 8 | −80 | 10 | 8 | 80 |
| 6 | 25 | 8 | −200 | −12 | 8 | −96 | 12 | 8 | 96 |
| 7 | 30 | 8 | −240 | −14 | 8 | −112 | 14 | 8 | 112 |
| 8 | 35 | 8 | −280 | −16 | 8 | −128 | |
| 9 | 40 | 8 | −320 | |
| 10 | 50 | 8 | −400 |
| 11 | 60 | 8 | −480 |
Table 2.
Simulation scheme under combined deformation conditions.
Table 2.
Simulation scheme under combined deformation conditions.
| Scheme | Condition 4 | Condition 5 |
|---|
| i + εc (mm/m) | B (m) | UY (mm) | UZ (mm) | i + εc (mm/m) | B (m) | UY (mm) | UZ (mm) |
|---|
| 1 | 2 | 8 | −16 | −16 | 2 | 8 | −16 | −16 |
| 2 | 4 | 8 | −32 | −32 | 4 | 8 | −32 | −32 |
| 3 | 6 | 8 | −48 | −48 | 6 | 8 | −48 | −48 |
| 4 | 8 | 8 | −64 | −64 | 8 | 8 | −64 | −64 |
| 5 | 10 | 8 | −80 | −80 | 10 | 8 | −80 | −80 |
| 6 | 12 | 8 | −96 | −96 | 12 | 8 | −96 | −96 |
| 7 | 14 | 8 | −112 | −112 | | | | |
Table 3.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tilt deformation values.
Table 3.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tilt deformation values.
| i (mm/m) | Member with Maximum Compressive Stress | Member with Maximum Tensile Stress |
|---|
| Number | Type | σc (MPa) | Number | Type | σt (MPa) |
|---|
| 3 | 6 | Q235 | 26.167 | 951 | Q235 | 15.884 |
| 6 | 6 | Q235 | 51.198 | 951 | Q235 | 35.639 |
| 10 | 6 | Q235 | 87.882 | 8 | Q235 | 68.998 |
| 15 | 6 | Q235 | 124.295 | 8 | Q235 | 105.127 |
| 20 | 6 | Q235 | 167.036 | 8 | Q235 | 147.729 |
| 25 | 6 | Q235 | 198.101 | 8 | Q235 | 178.035 |
| 30 | 6 | Q235 | 230.323 | 8 | Q235 | 209.172 |
| 35 | 6 | Q235 | 261.113 | 8 | Q235 | 240.365 |
| 40 | 6 | Q235 | 282.431 | 8 | Q235 | 260.846 |
| 50 | 6 | Q235 | 324.701 | 8 | Q235 | 302.136 |
| 60 | 6 | Q235 | 345.861 | 8 | Q235 | 322.753 |
Table 4.
Maximum stresses in structural members under compression deformation values.
Table 4.
Maximum stresses in structural members under compression deformation values.
| ɛc (mm/m) | Member with Maximum Compressive Stress | Member with Maximum Tensile Stress |
|---|
| Number | Type | σc (MPa) | Number | Type | σt (MPa) |
|---|
| 2 | 33 | Q235 | 54.485 | 8 | Q235 | 42.753 |
| 4 | 309 | Q235 | 103.507 | 8 | Q235 | 94.757 |
| 6 | 309 | Q235 | 154.813 | 8 | Q235 | 146.461 |
| 8 | 490 | Q235 | 227.958 | 8 | Q235 | 184.864 |
| 10 | 489 | Q235 | 300.631 | 323 | Q235 | 242.231 |
| 12 | 480 | Q235 | 335.852 | 323 | Q235 | 306.833 |
| 14 | 489 | Q235 | 401.372 | 323 | Q235 | 396.963 |
| 16 | 480 | Q235 | 431.985 | 323 | Q235 | 453.655 |
Table 5.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tension deformation values.
Table 5.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tension deformation values.
| ɛt (mm/m) | Member with Maximum Compressive Stress | Member with Maximum Tensile Stress |
|---|
| Number | Type | σc (MPa) | Number | Type | σt (MPa) |
|---|
| 2 | 8 | Q235 | 48.533 | 309 | Q235 | 36.081 |
| 4 | 8 | Q235 | 133.174 | 309 | Q235 | 113.482 |
| 6 | 329 | Q235 | 230.865 | 350 | Q235 | 151.987 |
| 8 | 330 | Q235 | 295.539 | 304 | Q235 | 251.768 |
| 10 | 330 | Q235 | 323.018 | 304 | Q235 | 294.965 |
| 12 | 330 | Q235 | 334.152 | 304 | Q235 | 338.835 |
| 14 | 385 | Q235 | 338.642 | 354 | Q235 | 347.589 |
Table 6.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tilt–compression deformation values.
Table 6.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tilt–compression deformation values.
| i + εc (mm/m) | Member with Maximum Compressive Stress | Member with Maximum Tensile Stress |
|---|
| Number | Type | σc (MPa) | Number | Type | σt (MPa) |
|---|
| 2 | 6 | Q235 | 83.694 | 951 | Q235 | 63.404 |
| 4 | 6 | Q235 | 157.882 | 951 | Q235 | 124.334 |
| 6 | 6 | Q235 | 231.903 | 951 | Q235 | 185.259 |
| 8 | 6 | Q235 | 304.126 | 951 | Q235 | 245.985 |
| 10 | 6 | Q235 | 363.762 | 951 | Q235 | 293.793 |
| 12 | 6 | Q235 | 420.651 | 951 | Q235 | 340.310 |
| 14 | 6 | Q235 | 462.679 | 951 | Q235 | 374.592 |
Table 7.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tilt–tension deformation values.
Table 7.
Maximum stresses in structural members under tilt–tension deformation values.
| i + εt (mm/m) | Member with Maximum Compressive Stress | Member with Maximum Tensile Stress |
|---|
| Number | Type | σc (MPa) | Number | Type | σt (MPa) |
|---|
| 2 | 963 | Q235 | 80.914 | 8 | Q235 | 94.907 |
| 4 | 963 | Q235 | 140.268 | 8 | Q235 | 169.503. |
| 6 | 963 | Q235 | 199.515 | 8 | Q235 | 244.165 |
| 8 | 963 | Q235 | 258.609 | 8 | Q235 | 318.841 |
| 10 | 963 | Q235 | 317.392 | 8 | Q235 | 393.353 |
| 12 | 963 | Q235 | 375.448 | 8 | Q235 | 467.244 |
Table 8.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tilt deformation.
Table 8.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tilt deformation.
| i (mm/m)
| Sx (mm)
| Sy (mm)
| Sz (mm)
| S (mm)
| q (‰)
|
|---|
|
N.155
|
N.370
|
N.155
|
N.370
|
N.155
|
N.370
|
|---|
| 3 | 0.0138 | 0.0135 | −13.59 | −16.91 | 121.91 | 120.09 | 121.91 | 2.72 |
| 6 | 0.0269 | 0.0263 | −24.48 | −31.11 | 243.81 | 240.17 | 243.81 | 5.24 |
| 10 | 0.0443 | 0.0439 | −39.58 | −50.62 | 400.64 | 400.26 | 400.64 | 8.93 |
| 15 | 0.0663 | 0.0652 | −59.37 | −75.91 | 609.51 | 600.33 | 609.51 | 13.59 |
| 20 | 0.0922 | 0.0865 | −80.19 | −102.19 | 812.64 | 800.35 | 812.64 | 18.12 |
| 25 | 0.1152 | 0.1125 | −102.04 | −129.48 | 1015.19 | 999.76 | 1015.19 | 22.64 |
| 30 | 0.1381 | 0.1348 | −124.89 | −157.75 | 1217.41 | 1198.83 | 1217.41 | 27.15 |
| 35 | 0.1598 | 0.1588 | −148.76 | −186.98 | 1419.08 | 1397.34 | 1419.08 | 31.65 |
| 40 | 0.1842 | 0.1775 | −173.63 | −217.22 | 1620.18 | 1595.26 | 1620.18 | 36.13 |
| 50 | 0.2321 | 0.2318 | −226.35 | −280.56 | 2021.99 | 1990.64 | 2021.99 | 45.09 |
| 60 | 0.2762 | 0.2751 | −268.55 | −330.71 | 2423.39 | 2387.13 | 2423.39 | 54.05 |
Table 9.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under compression deformation.
Table 9.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under compression deformation.
| εc (mm/m) | Sx (10−4 mm) | Sy (mm) | Sz (mm) | S (mm) | q (‰) |
|---|
| N.155 | N.370 | N.155 | N.370 | N.155 | N.370 |
|---|
| 2 | −0.91 | 26.8 | −2.3248 | −2.3249 | −7.99575 | −7.99642 | −7.99575 | 0.178 |
| 4 | −9.76 | 41.3 | −1.6018 | −1.6019 | −15.99617 | −15.99683 | −15.99617 | 0.357 |
| 6 | −18.51 | 55.8 | −0.8986 | −0.8987 | −23.99661 | −23.99721 | −23.99661 | 0.535 |
| 8 | −27.32 | 70.4 | −0.2155 | −0.2154 | −31.99705 | −31.99762 | −31.99705 | 0.714 |
| 10 | −35.94 | 84.8 | 0.4474 | 0.4474 | −39.99752 | −39.99818 | −39.99752 | 0.892 |
| 12 | −44.63 | 99.4 | 1.0889 | 1.0889 | −47.99799 | −47.99863 | −47.99799 | 1.070 |
| 14 | −53.21 | 114.4 | 1.7066 | 1.7067 | −55.99848 | −55.99914 | −55.99848 | 1.245 |
| 16 | −61.32 | 128.8 | 2.2972 | 2.2973 | −63.99895 | −63.99972 | −63.99895 | 1.427 |
Table 10.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tension deformation.
Table 10.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tension deformation.
| εt (mm/m)
| Sx (10−4 mm)
| Sy (mm)
| Sz (mm)
| S (mm)
| q (‰)
|
|---|
|
N.155
|
N.370
|
N.155
|
N.370
|
N.155
|
N.370
|
|---|
| 2 | 17.1 | 16.8 | −3.8299 | −3.8312 | 8.00505 | 8.00521 | 8.00505 | 0.178 |
| 4 | 26.4 | 25.5 | −4.6119 | −4.6122 | 16.00543 | 16.00474 | 16.00543 | 0.357 |
| 6 | 35.2 | 34.9 | −5.4135 | −5.4137 | 24.00578 | 24.00509 | 24.00578 | 0.535 |
| 8 | 45.2 | 44.2 | −6.2339 | −6.2341 | 32.00612 | 32.00542 | 32.00612 | 0.714 |
| 10 | 54.7 | 53.7 | −7.0713 | −7.0716 | 40.00642 | 40.00571 | 40.00642 | 0.892 |
| 12 | 63.8 | 62.9 | −7.9184 | −7.9186 | 48.00665 | 48.00595 | 48.00665 | 1.070 |
| 14 | 72.9 | 71.9 | −8.7631 | −8.7632 | 56.00681 | 56.00615 | 56.00681 | 1.249 |
Table 11.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tilt–compression deformation.
Table 11.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tilt–compression deformation.
| i + εc (mm/m) | Sx (10−3 mm) | Sy (mm) | Sz (mm) | S (mm) | q (‰) |
|---|
| N.155 | N.370 | N.155 | N.370 | N.155 | N.370 |
|---|
| 2 | 10.41 | 8.29 | −10.822 | −13.212 | 89.1787 | 87.9145 | 89.1787 | 1.989 |
| 4 | 19.84 | 15.29 | −18.732 | −23.133 | 177.9141 | 175.4997 | 177.9141 | 3.968 |
| 6 | 29.27 | 22.31 | −26.843 | −33.434 | 266.3993 | 262.7785 | 266.3993 | 5.941 |
| 8 | 38.76 | 29.55 | −35.131 | −43.891 | 354.5725 | 349.7456 | 354.5725 | 7.908 |
| 10 | 48.67 | 37.61 | −43.614 | −54.531 | 442.4343 | 436.4017 | 442.4343 | 9.867 |
| 12 | 59.89 | 48.01 | −52.245 | −65.322 | 529.9849 | 522.7471 | 529.9849 | 11.819 |
| 14 | 71.21 | 59.79 | −61.032 | −76.251 | 617.2243 | 608.7817 | 617.2243 | 13.765 |
Table 12.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tilt–tension deformation.
Table 12.
Displacement of monitoring points and tower tilt angle under tilt–tension deformation.
| i + εt (mm/m) | Sx (10−3 mm) | Sy (mm) | Sz (mm) | S (mm) | q (‰) |
|---|
| N.155 | N.370 | N.155 | N.370 | N.155 | N.370 |
|---|
| 2 | 8.67 | 11.27 | −9.342 | −11.524 | 73.4124 | 72.2235 | 73.4124 | 1.637 |
| 4 | 16.72 | 21.41 | −15.745 | −20.124 | 147.5148 | 145.2145 | 147.5148 | 3.289 |
| 6 | 24.77 | 31.67 | −22.305 | −28.972 | 221.2448 | 217.5816 | 221.2448 | 4.934 |
| 8 | 33.01 | 42.03 | −29.085 | −37.986 | 295.6324 | 290.7298 | 295.6324 | 6.593 |
| 10 | 41.37 | 52.51 | −36.051 | −47.193 | 370.3418 | 364.1904 | 370.3418 | 8.259 |
| 12 | 49.87 | 63.12 | −43.207 | −56.596 | 445.3736 | 437.9641 | 445.3736 | 9.933 |
Table 13.
Y-direction support reaction forces FY under different ground tilt values.
Table 13.
Y-direction support reaction forces FY under different ground tilt values.
| i (mm/m)
|
Support A (kN)
|
Support B (kN)
|
Support C (kN)
|
Support D (kN)
|
|---|
| 3 | 27.228 | 27.373 | 31.035 | 30.911 |
| 6 | 25.323 | 25.607 | 32.933 | 32.683 |
| 10 | 22.783 | 23.253 | 35.465 | 35.046 |
| 15 | 19.606 | 20.311 | 38.631 | 38.011 |
| 20 | 16.429 | 17.369 | 41.794 | 40.956 |
| 25 | 13.912 | 15.147 | 44.183 | 43.258 |
| 30 | 11.859 | 13.351 | 46.169 | 45.17 |
| 35 | 11.141 | 12.393 | 47.201 | 45.811 |
| 40 | 10.847 | 12.073 | 47.543 | 46.066 |
| 50 | 10.609 | 12.041 | 47.692 | 46.216 |
| 60 | 10.266 | 11.905 | 47.831 | 46.429 |
Table 14.
Z-direction support reaction forces FZ under different ground compression and tension values.
Table 14.
Z-direction support reaction forces FZ under different ground compression and tension values.
| εc/εt (mm/m) | Support A | Support B | Support C | Support D |
|---|
| FZ (kN) | FZ (kN) | FZ (kN) | FZ (kN) |
|---|
| 2 | −7.825 | 1.702 | −7.823 | 1.684 | 7.824 | −1.701 | 7.824 | −1.686 |
| 4 | −12.569 | 6.473 | −12.562 | 6.441 | 12.567 | −6.469 | 12.565 | −6.445 |
| 6 | −17.293 | 11.232 | −17.283 | 11.182 | 17.289 | −11.225 | 17.287 | −11.188 |
| 8 | −21.987 | 15.944 | −21.976 | 15.871 | 21.982 | −15.932 | 21.981 | −15.883 |
| 10 | −26.629 | 20.496 | −26.619 | 20.389 | 26.623 | −20.472 | 26.626 | −20.412 |
| 12 | −31.163 | 24.501 | −31.154 | 24.343 | 31.155 | −24.452 | 31.162 | −24.392 |
| 14 | −35.434 | 27.414 | −35.429 | 27.195 | 35.425 | −27.334 | 35.438 | −27.275 |
| 16 | −39.169 | | −39.168 | | 39.161 | | 39.177 | |
Table 15.
Y- and Z-direction support reaction forces FY and FZ under different ground tilt–compression.
Table 15.
Y- and Z-direction support reaction forces FY and FZ under different ground tilt–compression.
| i + εc (mm/m) | Support A (kN) | Support B (kN) | Support C (kN) | Support D (kN) |
|---|
| FY | FZ | FY | FZ | FY | FZ | FY | FZ |
|---|
| 2 | 27.802 | −7.824 | 28.031 | −7.822 | 30.331 | 7.816 | 30.384 | 7.828 |
| 4 | 26.468 | −12.564 | 26.942 | −12.551 | 31.505 | 12.547 | 31.631 | 12.568 |
| 6 | 25.131 | −17.28 | 25.872 | −17.259 | 32.662 | 17.253 | 32.879 | 17.289 |
| 8 | 23.793 | −21.963 | 24.822 | −21.935 | 33.801 | 21.926 | 34.131 | 21.973 |
| 10 | 22.453 | −26.593 | 23.788 | −26.559 | 34.923 | 26.544 | 35.383 | 26.608 |
| 12 | 21.111 | −31.116 | 22.769 | −31.077 | 36.031 | 31.055 | 36.636 | 31.139 |
| 14 | 19.768 | −35.383 | 21.759 | −35.339 | 37.131 | 35.309 | 37.889 | 35.413 |
Table 16.
Y- and Z-direction support reaction forces FY and FZ under different ground tilt–tension.
Table 16.
Y- and Z-direction support reaction forces FY and FZ under different ground tilt–tension.
| i + εt (mm/m) | Support A (kN) | Support B (kN) | Support C (kN) | Support D (kN) |
|---|
| FY | FZ | FY | FZ | FY | FZ | FY | FZ |
|---|
| 2 | 27.913 | 1.703 | 28.211 | 1.688 | 30.462 | −1.707 | 30.269 | −1.683 |
| 4 | 26.672 | 6.478 | 26.972 | 6.451 | 31.784 | −6.486 | 31.419 | −6.443 |
| 6 | 25.411 | 11.247 | 25.745 | 11.203 | 33.102 | −11.258 | 32.666 | −11.192 |
| 8 | 24.129 | 15.972 | 24.422 | 15.907 | 34.414 | −15.983 | 33.781 | −15.895 |
| 10 | 22.826 | 20.538 | 23.108 | 20.442 | 35.719 | −20.543 | 34.995 | −20.437 |
| 12 | 21.506 | 24.526 | 21.811 | 24.377 | 37.006 | −24.507 | 36.225 | −24.396 |