A Parallel Network for Continuous Motion Estimation of Finger Joint Angles with Surface Electromyographic Signals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
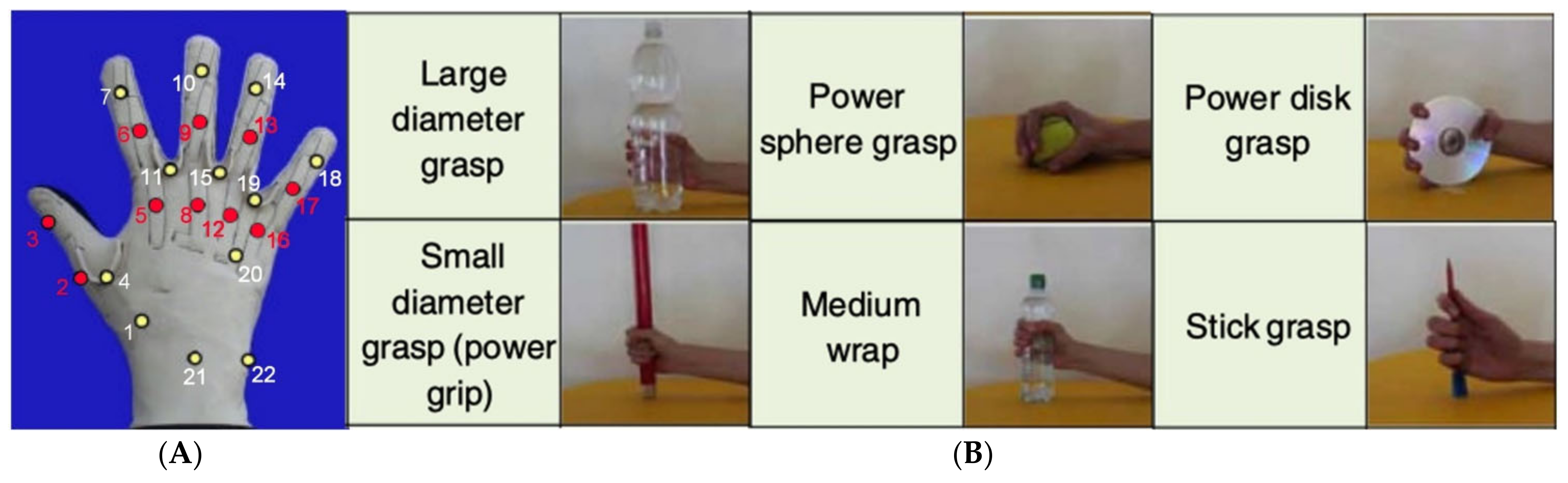
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Data Processing
2.2.1. Root Mean Square (RMS)
2.2.2. Peak Stress (PS)
2.2.3. Shake Expectation (SE)
2.2.4. Unbiased Standard Deviation (USTD)
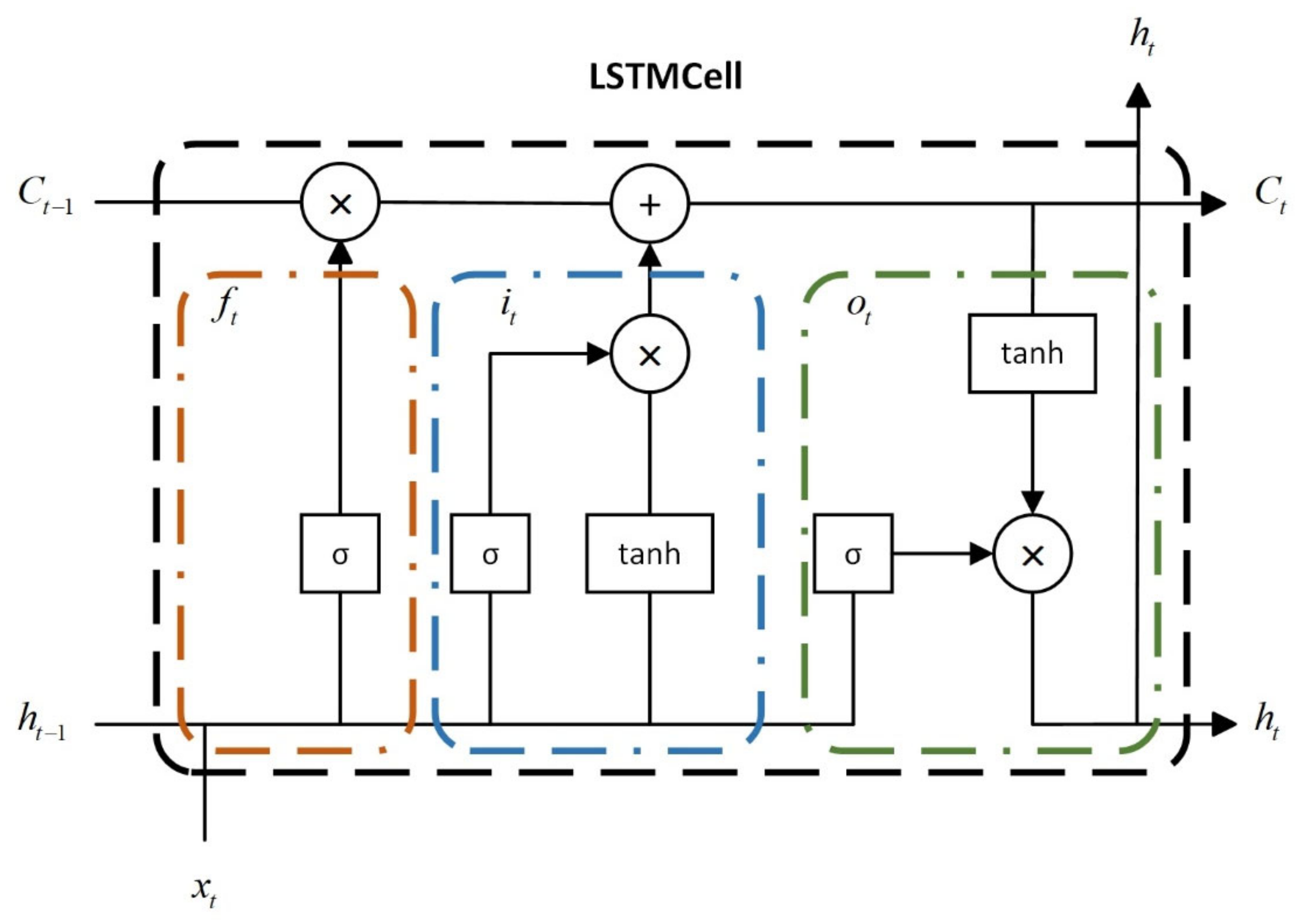
2.3. Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory Network
2.4. Temporal Convolutional Network
2.5. Parallel Network of CNN-Attention and BiLSTM
2.5.1. Multi-Scale Convolution
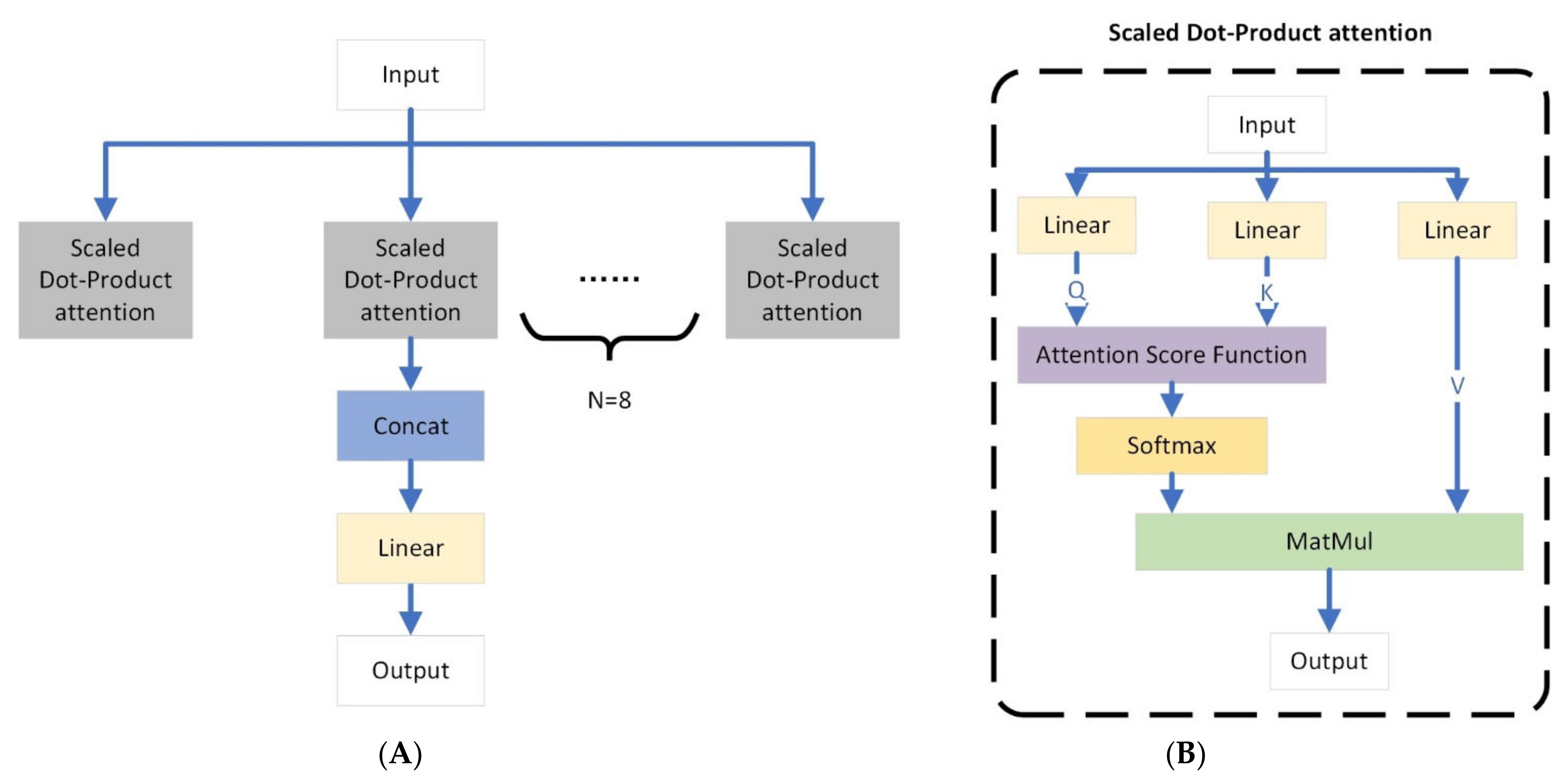
2.5.2. Multi-Head Attention Mechanism
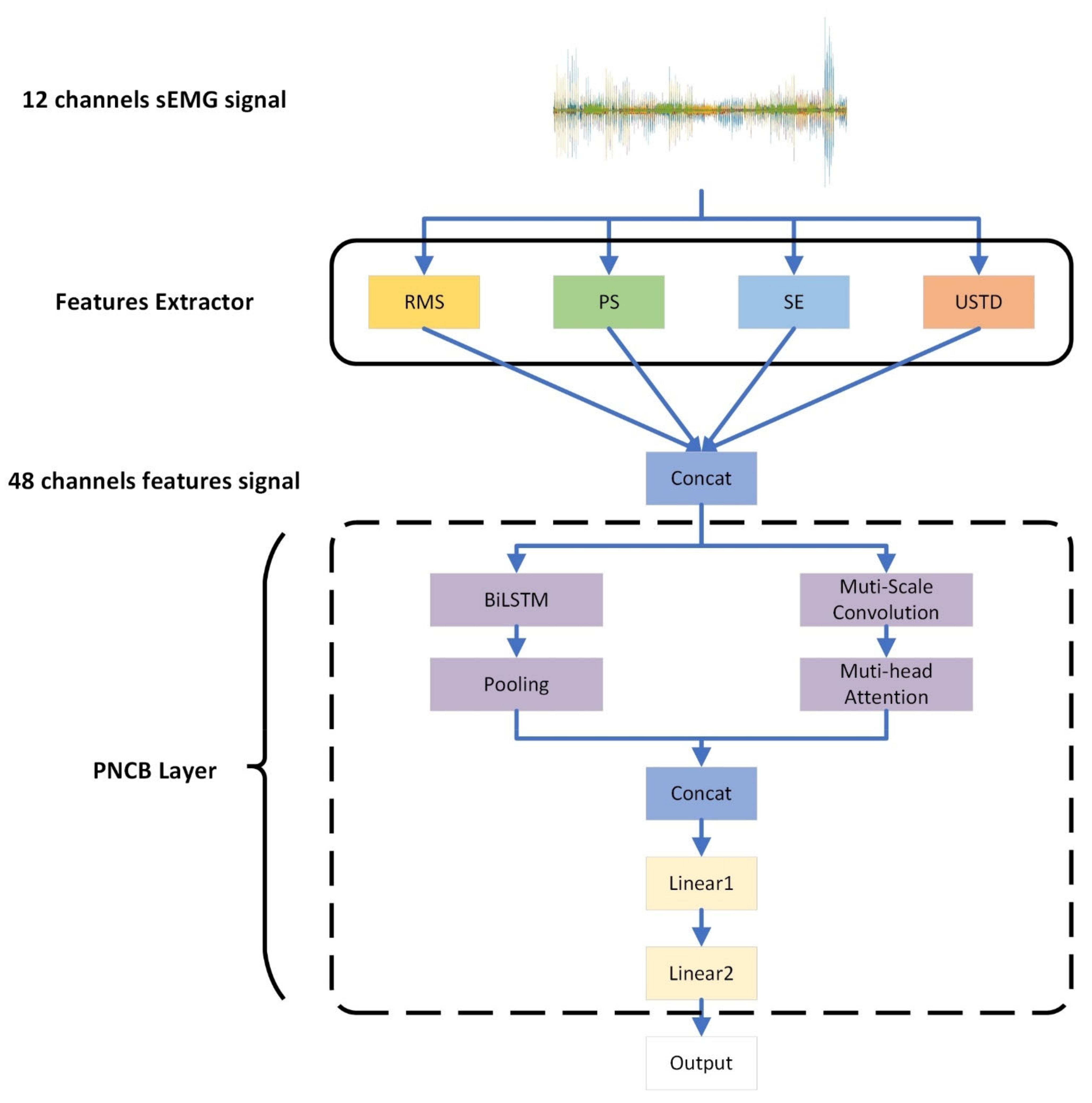
2.5.3. PNCB Model Structure
3. Result
3.1. Evaluation Metrics
3.2. Experimental Parameters and Statistical Analysis
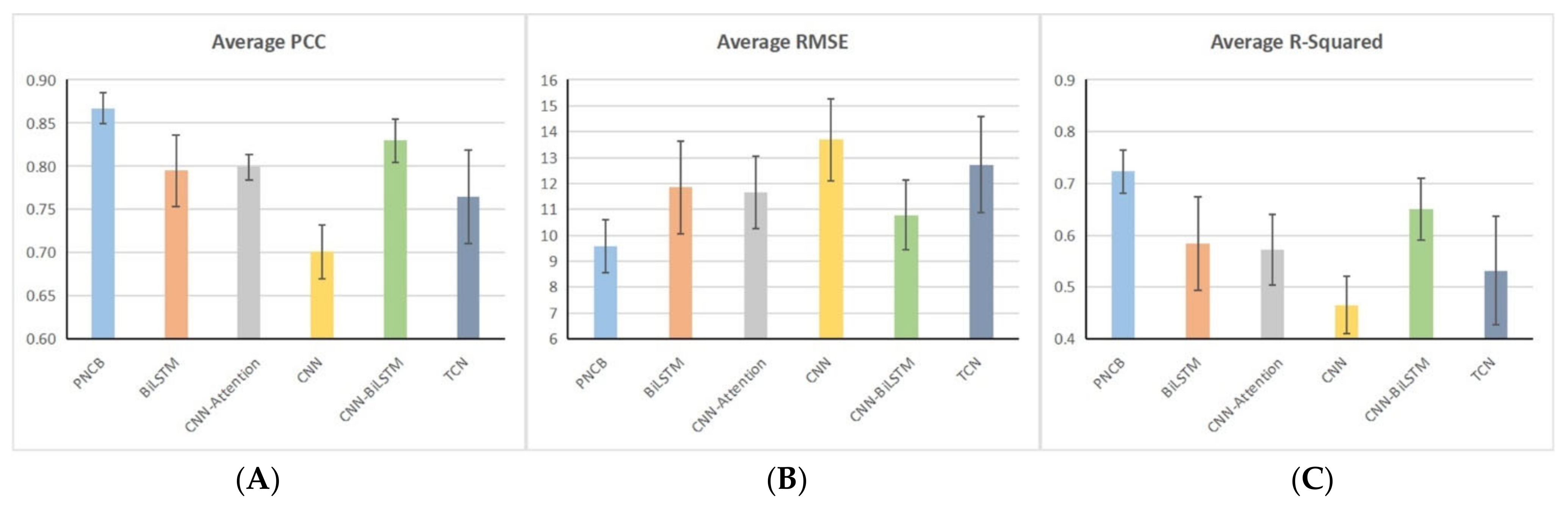
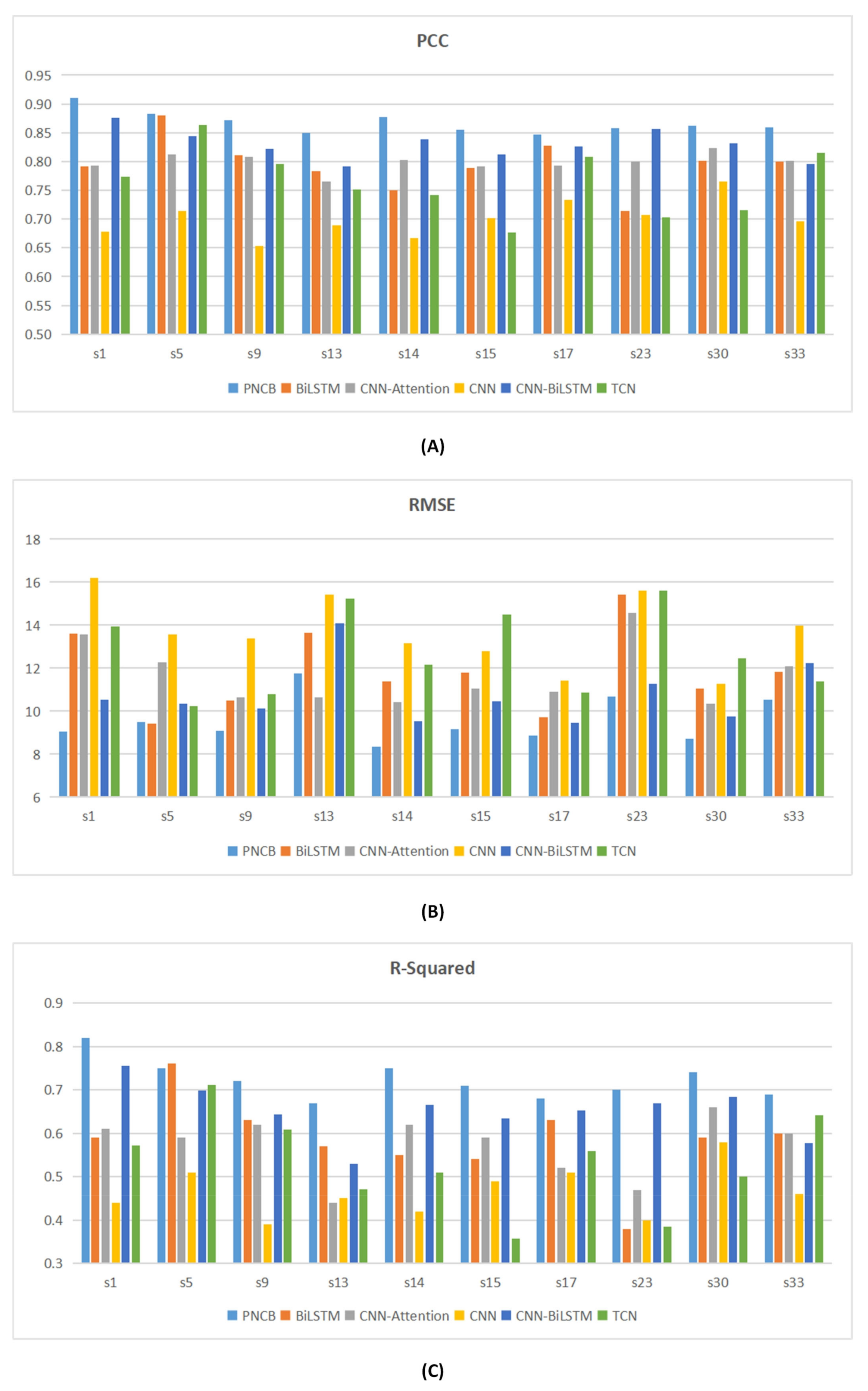
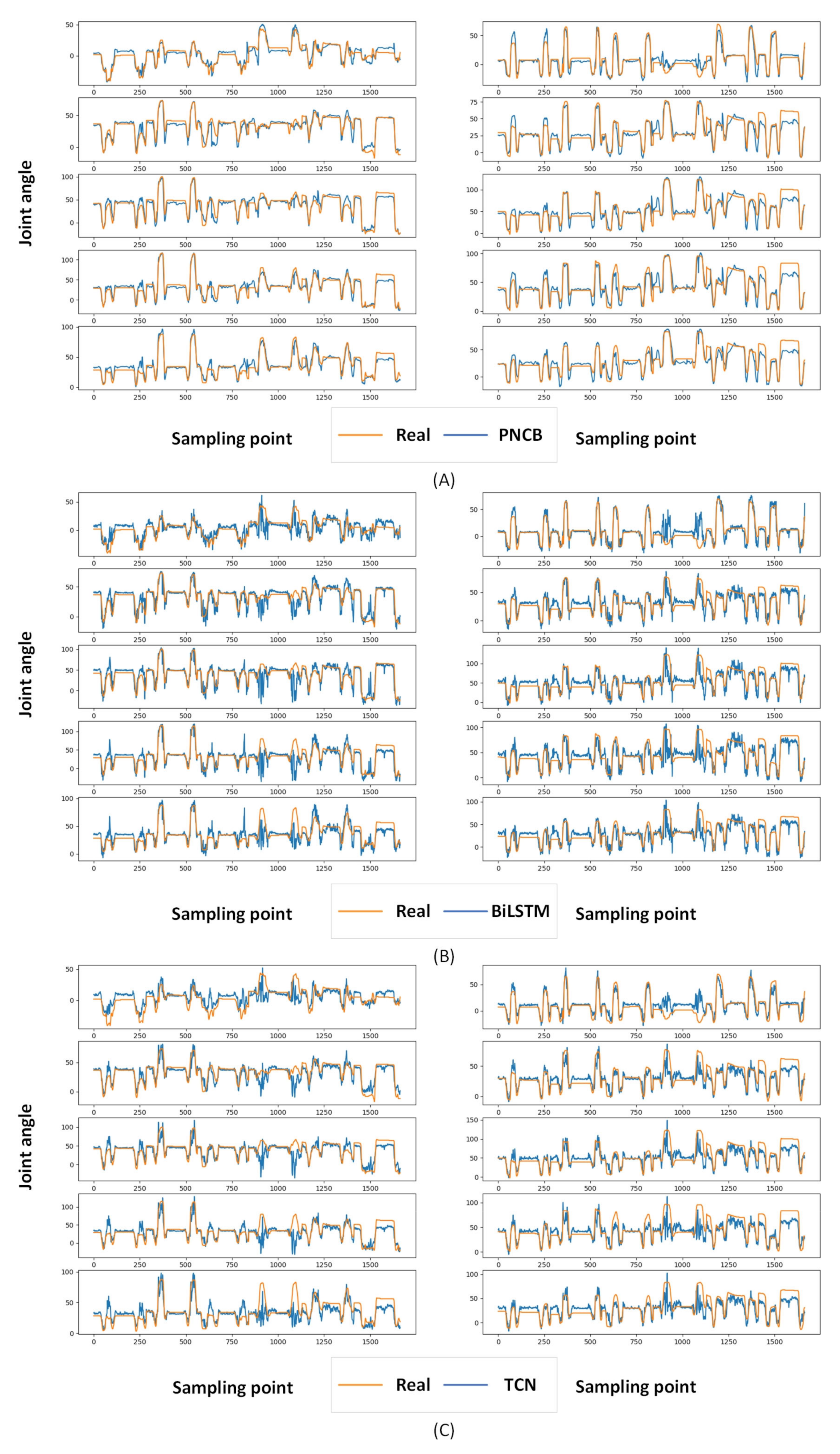
3.3. Experimental Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xiong, D.; Zhang, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y. Deep Learning for EMG-based Human-Machine Interaction: A Review. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2021, 8, 512–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benalcázar, M.E.; González, J.; Jaramillo-Yánez, A.; Anchundia, C.E.; Zambrano, P.; Segura, M. A Model for Real-Time Hand Gesture Recognition Using Electromyography (EMG), Covariances and Feed-Forward Artificial Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE ANDESCON, Quito, Ecuador, 13–16 October 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, K.E.; Nichols, K.A.; Okamura, A.M. Toward human-robot collaboration in surgery: Performance assessment of human and robotic agents in an inclusion segmentation task. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Stockholm, Sweden, 16–21 May 2016; pp. 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakonen, M.; Piitulainen, H.; Visala, A. Current state of digital signal processing in myoelectric interfaces and related applications. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2015, 18, 334–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artemiadis, P. EMG-based Robot Control Interfaces: Past, Present and Future. Adv. Robot. Autom. 2012, 1, e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Bi, S.; Zhang, G.; Cao, G. High-Density Surface EMG-Based Gesture Recognition Using a 3D Convolutional Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Lee, S.W. Movement intention decoding based on deep learning for multiuser myoelectric interfaces. In Proceedings of the 2016 4th International Winter Conference on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwon, Republic of Korea, 22–24 February 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, L.; Guan, C. A review on EMG-based motor intention prediction of continuous human upper limb motion for human-robot collaboration. Biomed. Signal Process. Control. 2019, 51, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liu, L.; Clancy, E.A. Influence of Joint Angle on EMG-Torque Model During Constant-Posture, Torque-Varying Contractions. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Buchanan, T.S. Prediction of joint moments using a neural network model of muscle activations from EMG signals. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2002, 10, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, S.; Ma, K.; Huang, S.; Li, G.; Cai, S.; Xie, L. A Continuous Estimation Model of Upper Limb Joint Angles by Using Surface Electromyography and Deep Learning Method. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 174940–174950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, A.; Panwar, M.; Biswas, D.; Acharyya, A. MyoNet: A Transfer-Learning-Based LRCN for Lower Limb Movement Recognition and Knee Joint Angle Prediction for Remote Monitoring of Rehabilitation Progress From sEMG. IEEE J. Transl. Eng. Health Med. 2020, 8, 2100310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, C.; Chen, W. Cross-Comparison of EMG-to-Force Methods for Multi-DoF Finger Force Prediction Using One-DoF Training. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 13958–13968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Guo, W.; Zhang, H.; Samuel, O.W.; Ji, X.; Xu, L.; Li, G. A Novel and Efficient Feature Extraction Method for Deep Learning Based Continuous Estimation. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7341–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, X.; Jandaghi, E.; Zeng, W.; Zhou, M.; Yuan, C. Dynamics Learning-Based Fault Isolation for A Soft Trunk Robot. In Proceedings of the 2023 American Control Conference (ACC), San Diego, CA, USA, 31 May–2 June 2023; pp. 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandaghi, E.; Chen, X.; Yuan, C. Motion Dynamics Modeling and Fault Detection of a Soft Trunk Robot. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics (AIM), Seattle, WA, USA, 28–30 June 2023; pp. 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodaghi, M.; Hosseini, M.; Gottumukkala, R. A Multimodal Intermediate Fusion Network with Manifold Learning for Stress Detection. arXiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, M.; Muller, H. The Ninapro database: A resource for sEMG naturally controlled robotic hand prosthetics. In Proceedings of the 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Milan, Italy, 25–29 August 2015; pp. 7151–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, G.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Choi, Y. EMG-Based Continuous Control Scheme with Simple Classifier for Electric-Powered Wheelchair. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 3695–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siami-Namini, S.; Tavakoli, N.; Namin, A.S. The Performance of LSTM and BiLSTM in Forecasting Time Series. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Big Data (Big Data), Los Angeles, CA, USA, 9–12 December 2019; pp. 3285–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Meng, Y.; Qiu, X.; Yu, Z.; Wu, X. Sentiment Analysis of Comment Texts Based on BiLSTM. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 51522–51532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Lin, C.; Samuel, O.W.; Guo, W.; Zhang, H.; Greenwald, S.; Xu, L.; Li, G. A Bi-Directional LSTM Network for Estimating Continuous Upper Limb Movement from Surface Electromyography. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2021, 6, 7217–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Kolter, J.Z.; Koltun, V. An Empirical Evaluation of Generic Convolutional and Recurrent Networks for Sequence Modeling. arXiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanghieri, M.; Benatti, S.; Conti, F.; Burrello, A.; Benini, L. Temporal Variability Analysis in sEMG Hand Grasp Recognition using Temporal Convolutional Networks. In Proceedings of the 2020 2nd IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Circuits and Systems (AICAS), Genova, Italy, 31 August–2 September 2020; pp. 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Gao, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, Q.; Pang, F. Distributed Attention-Based Temporal Convolutional Network for Remaining Useful Life Prediction. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 9594–9602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Yap, P.T.; Shen, D. Multi-task learning for segmentation and classification of tumors in 3D automated breast ultrasound images. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 70, 101918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention Is All You Need. arXiv 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization. arXiv 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, G.K.; Castellini, C.; Hahne, J.M.; Farina, D.; Dosen, S. A Classification Method for Myoelectric Control of Hand Prostheses Inspired by Muscle Coordination. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 1745–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, C.; Zhou, S. A Parallel Network for Continuous Motion Estimation of Finger Joint Angles with Surface Electromyographic Signals. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011078
Lin C, Zhou S. A Parallel Network for Continuous Motion Estimation of Finger Joint Angles with Surface Electromyographic Signals. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011078
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Chuang, and Shengshuo Zhou. 2025. "A Parallel Network for Continuous Motion Estimation of Finger Joint Angles with Surface Electromyographic Signals" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011078
APA StyleLin, C., & Zhou, S. (2025). A Parallel Network for Continuous Motion Estimation of Finger Joint Angles with Surface Electromyographic Signals. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11078. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011078




