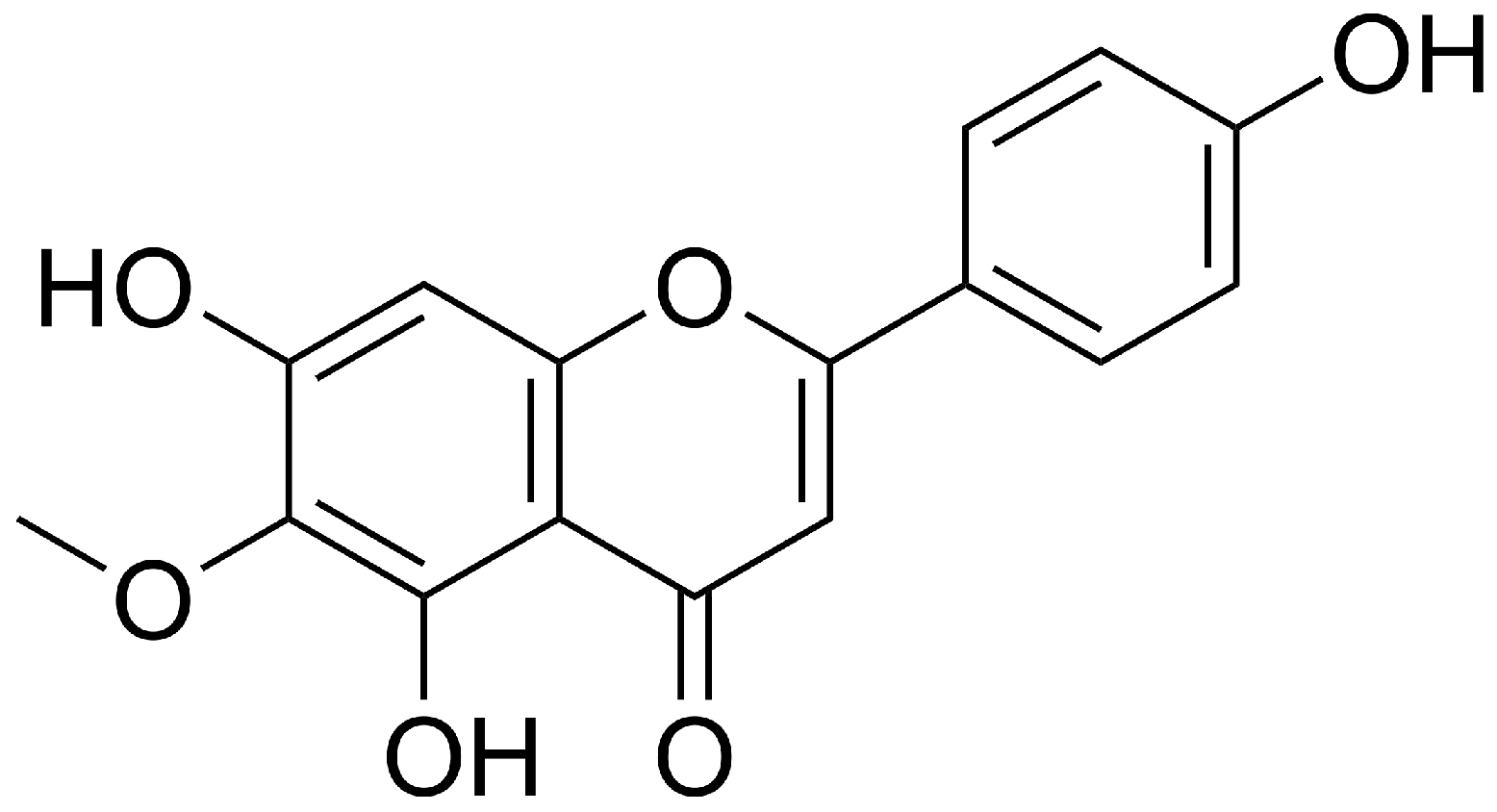
Hispidulin Protects C6 Astroglial Cells Against H2O2-Induced Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.3. Measurement of Cell Viability
2.4. Measurement of LDH
2.5. Measurement of Cellular ROS Production
2.6. Measurement of NO Production
2.7. Proinflammatory Cytokine Measurements
2.8. Western Blot Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
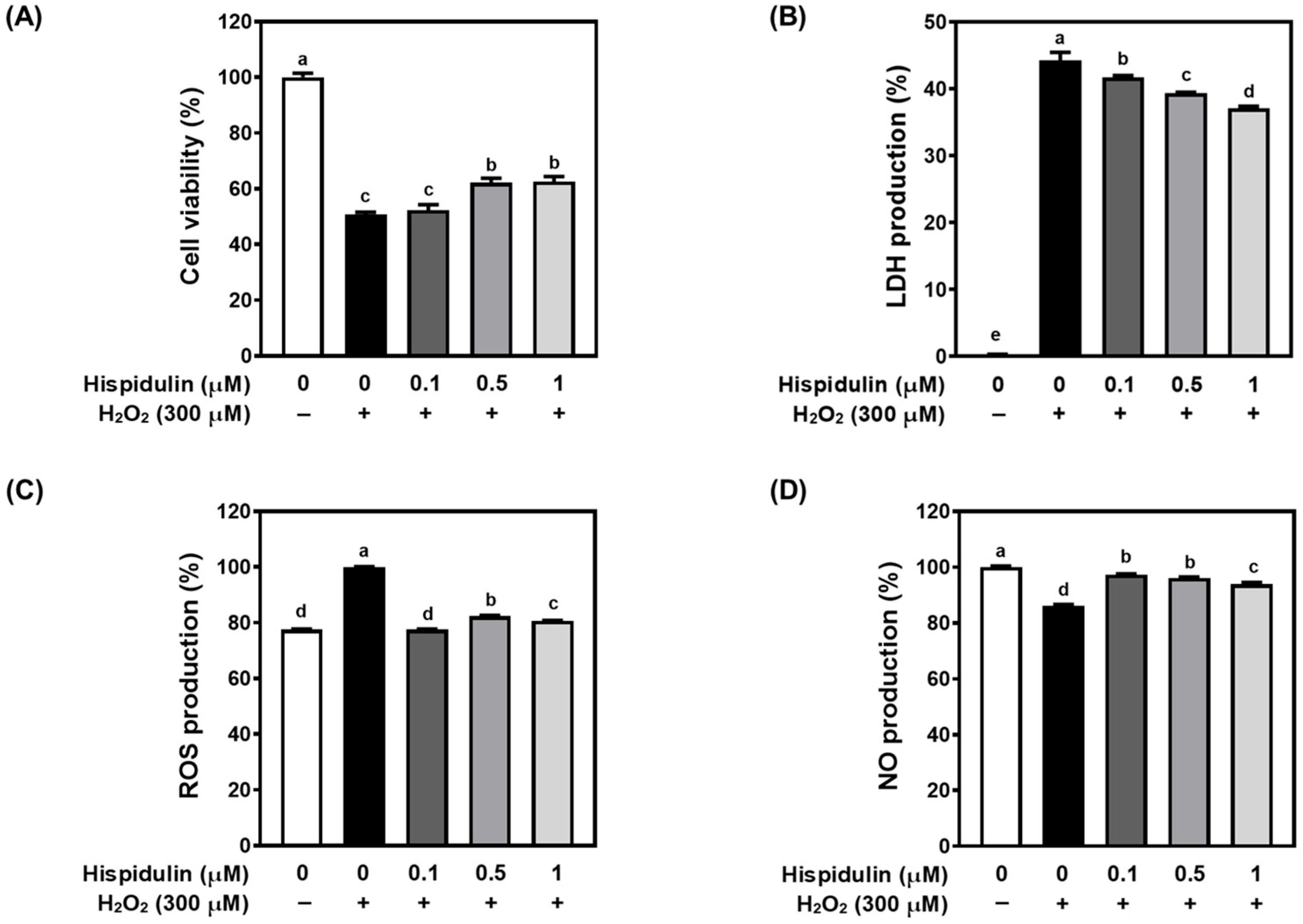
3.1. Hispidulin Protects C6 Astroglial Cells Against H2O2-Induced Cytotoxicity
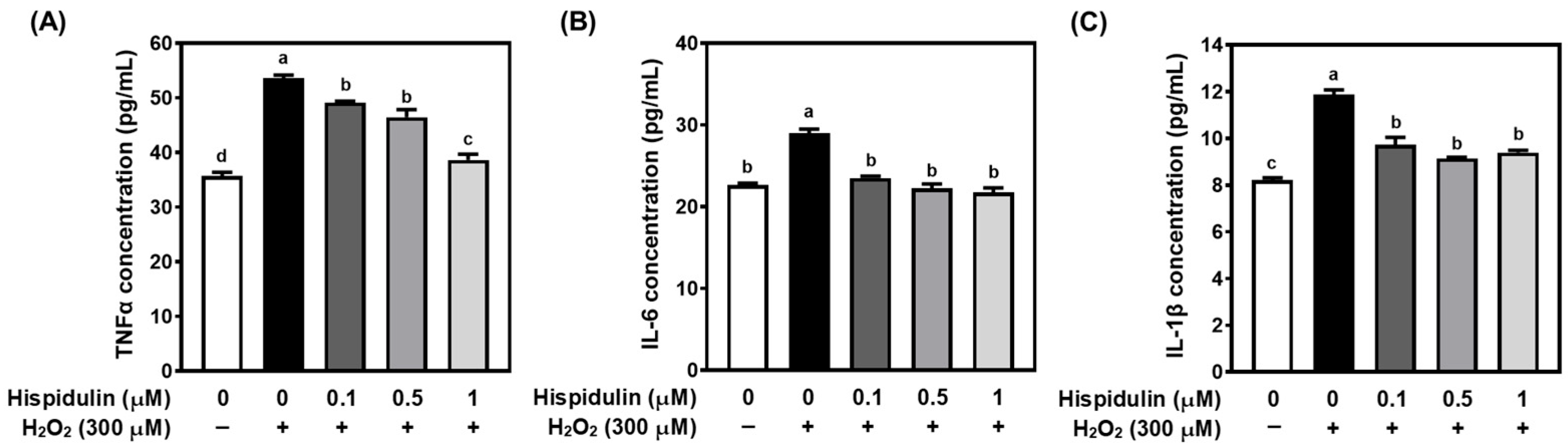
3.2. Hispidulin Inhibits Proinflammatory Cytokine Secretion in H2O2-Treated C6 Astroglial Cells
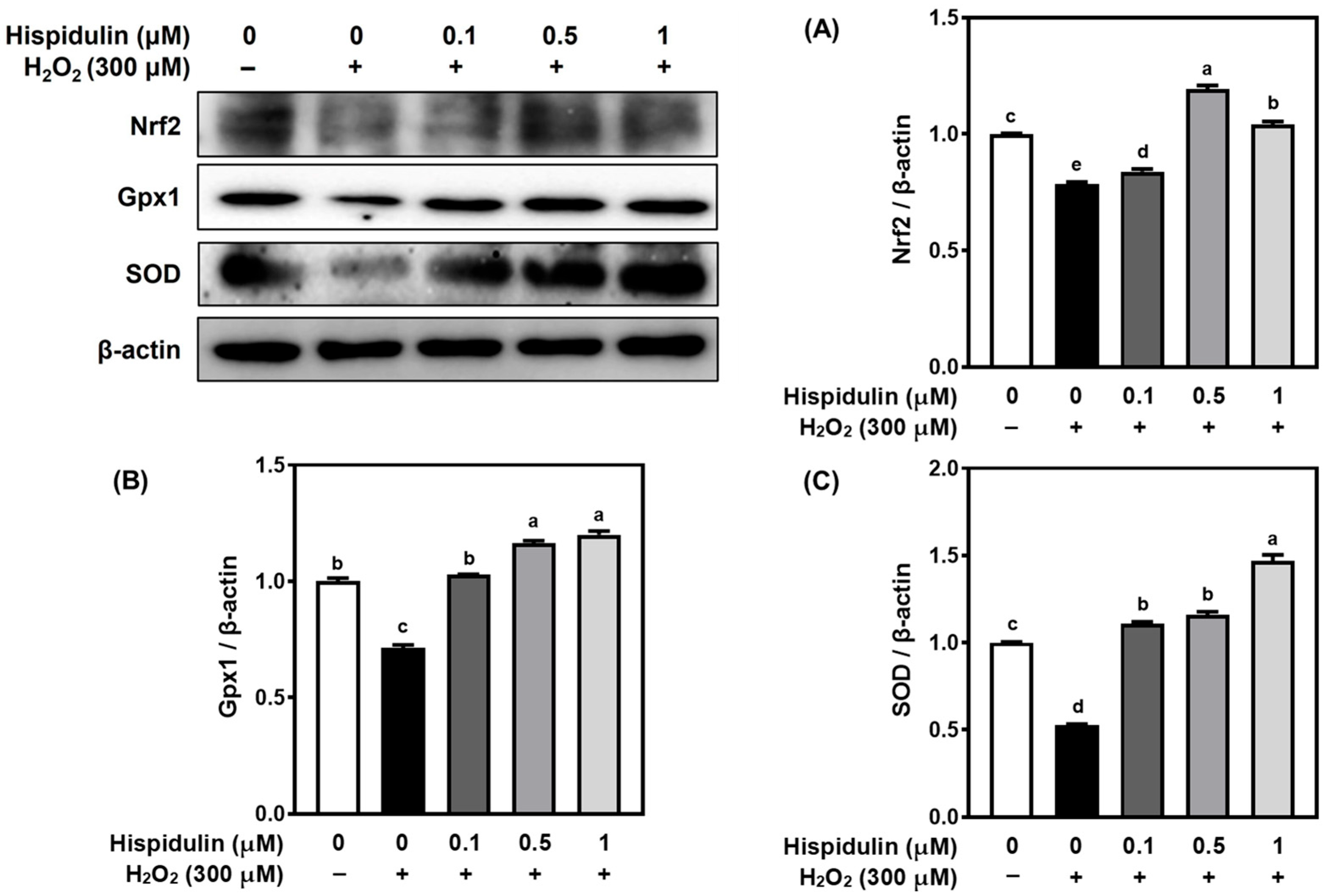
3.3. Hispidulin Increases the Expression of Nrf2 and Downstream Antioxidant Enzymes
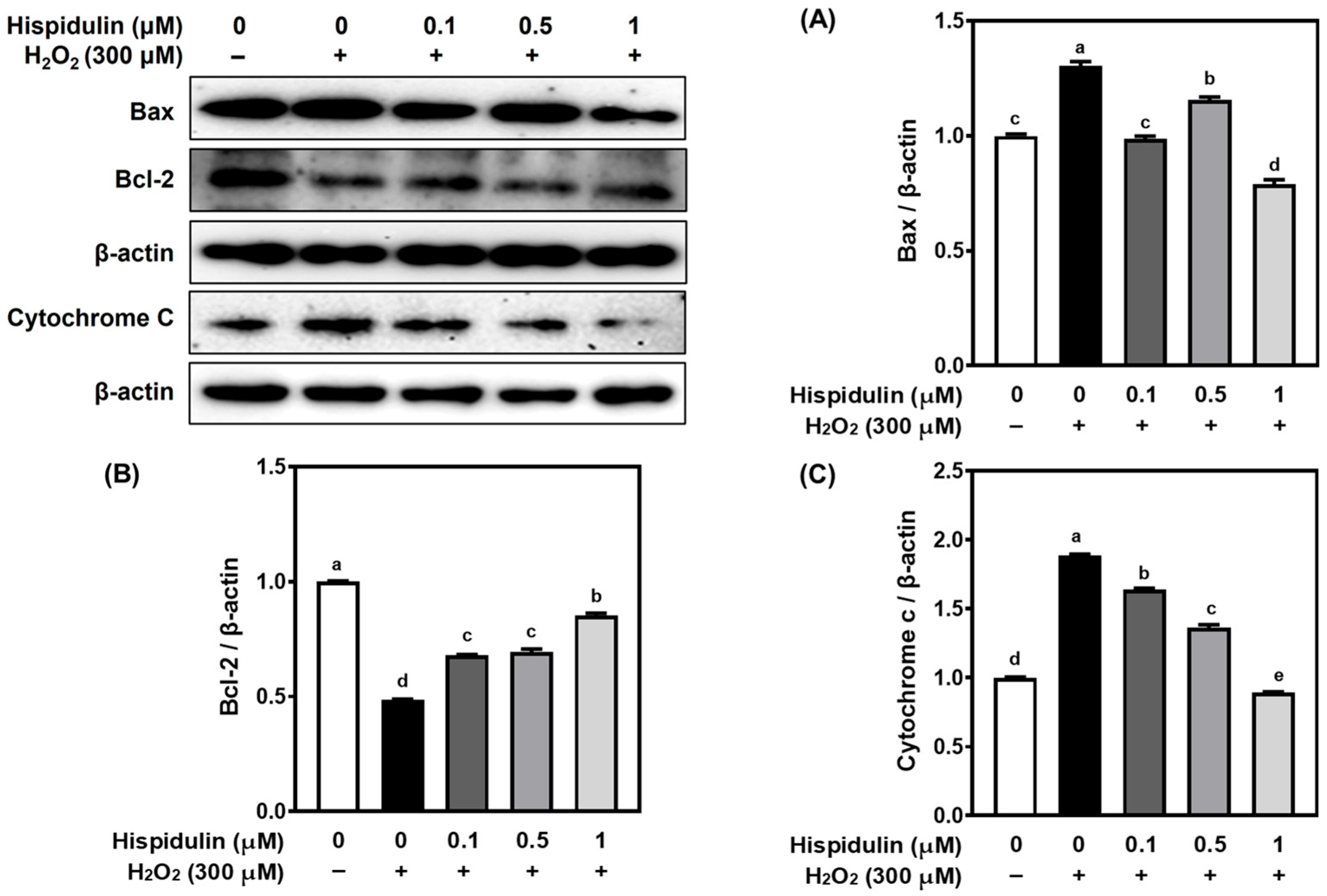
3.4. Hispidulin Modulates Apoptosis-Related Proteins in H2O2-Stimulated C6 Astroglial Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| ROS | Reactive Oxygen Species |
| Nrf2 | Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 |
| GPx1 | Glutathione Peroxidase 1 |
| SOD | Superoxide Dismutase |
| NF-κB | Nuclear Factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| NLRP3 | NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3 |
| AMPK | AMP-activated Protein Kinase |
| GSK3β | Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 beta |
| JAK/STAT | Janus Kinase/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| EDTA | Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen Peroxide |
| SNP | Sodium Pentacyanonitrosylferrate (III) dihydrate |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| DCF-DA | 2′,7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Difluoride |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation Assay |
| ECL | Enhanced Chemiluminescence |
References
- Valles, S.L.; Signh, S.K.; Campos-Campos, J.; Colmena, C.; Campo-Palacio, I.; Alvarez-Gamez, K.; Caballero, O.; Jorda, A. Functions of astrocytes under normal conditions and after a brain disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trofin, D.-M.; Sardaru, D.-P.; Trofin, D.; Onu, I.; Tutu, A.; Onu, A.; Onita, C.; Galaction, A.I.; Matei, D.V. Oxidative stress in brain function. Antioxidnats 2025, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qin, C.; Huang, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, K.; Xu, J.; Guo, G.; Tong, A.; Zhou, L. The role of astrocytes in oxidative stress of central nervous system: A mixed blessing. Cell Prolif. 2020, 53, e12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-E.; Leem, Y.-H.; Park, J.-S.; Kim, S.-E.; Kim, H.-S. Astrocytic Nrf2 mediates the neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of nootkatone in an MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Gasterich, N.; Clarner, T.; Voelz, C.; Behrens, V.; Beyer, C.; Fragoulis, A.; Zendedel, A. Astrocytic Nrf2 expression protects spinal cord from oxidative stress following spinal cord injury in a male mouse model. J. Neuroinflamm. 2022, 19, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandebura, A.N.; Paumier, A.; Onur, T.S.; Allen, N.J. Astrocyte contribution to dysfunction, risk and progression in neurodegenerative disorder. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2022, 24, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Patel, D.K. Medicinal importance, pharmacological activities, and analytical aspects of hispidulin: A concise report. J. Tradit. Complement. Med. 2017, 7, 360–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Zhao, F.; Yan, J.; Xia, Z.; Jiang, D.; Ma, P. Hispidulin: A promising flavonoid with diverse anti-cancer properties. Life Sci. 2020, 259, 118395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashaq, A.; Maqbool, M.F.; Maryam, A.; Khan, M.; Shakir, H.A.; Irfan, M.; Qazi, J.I.; Li, Y.; Ma, T. Hispidulin: A novel natural compound with therapeutic potential against human cancers. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 771–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, P.; Wu, T.; Yu, H.; Fang, K.; Ren, Z.; Tang, M. Hispidulin protects against focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 65, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, P.; Xie, J.; Qiu, S.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiu, X.; Li, L.; Tang, M. Hispidulin exhibits neuroprotective activities against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury through suppressing NLRP3-mediated pyroptosis. Life Sci. 2019, 232, 116599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-I.; Cheng, C.-I.; Kang, Y.-F.; Chang, P.-C.; Lin, I.-P.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Jhou, A.-J.; Lin, M.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lee, C.-H. Hispidulin inhibits neuroinflammation in lipopolysaccharide-activated BV2 microglia and attenuates the activation of Akt, NF-kB, and STAT3 pathway. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giakoumettis, D.; Kritis, A.; Foroglou, N. C6 cell line: The gold standard in glioma research. Hippokratia 2018, 22, 105–112. [Google Scholar]
- Quincozes-Santos, A.; Bobermin, L.D.; Latini, A.; Wajner, M.; Souza, D.O.; Goncalves, C.-A.; Gottfried, C. Reveratrol protects C6 astrocyte cell line against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress through heme oxygenase 1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e64372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.-O.; Jeong, J.-W.; Park, C.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.-Y.; Hwang, H.-J.; Cho, E.-J.; Choi, Y.H. Baicalein protects C6 glial cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis through regulation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polster, B.M.; Mark, K.A.; Arze, R.; Hudson, D. Calpain-independent intracellular protease activity is elevated in excitotoxic cortical neurons prior to delayed calcium deregulation and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Guo, Y.; Xu, Y. The biphasic effect of flavonoids on oxidative stress and cell proliferation. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Huang, K.; Ning, H. Hispidulin prevents sevoflurane-induced memory dysfunction in aged rats. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, J.M.; Schardien, K.; Wigdahl, B.; Nonnemacher, M.R. Roles of neuropathology-associated reactive astrocytes: A systemic review. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitazawa, M.; Cheng, D.; Tsukamoto, M.R.; Koike, M.A.; Wes, P.D.; Vasilevko, V.; Cribbs, D.H.; LaFerla, F.M. Blocking IL-1 signaling rescues cognition, attenuates tau pathology, and restores neuronal b-catenin pathway function in an Alzheimer’s disease model. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6539–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Ran, M.; Li, H.; Lin, Y.; Ma, K.; Yang, Y.; Fu, X.; Yang, S. New insight into neurological degeneration: Inflammatory cytokines and blood-brain barrier. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 1013933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruol, D.L. IL-6 regulation of synaptic function in the CNS. Neuropharmacology 2015, 96, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyra e Silva, N.M.; Gonçalves, R.A.; Pascoal, T.A.; Lima-Filho, R.A.S.; França Resende, E.P.; Vieira, E.L.M.; Teixeira, A.L.; de Souza, L.C.; Peny, J.A.; Fortuna, J.T.S.; et al. Pro-inflammatory interleukin-6 signaling links cognitive impairments and peripheral metabolic alterations in Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatr. 2021, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Kensler, T.W.; Motohashi, H. The KEAP1-NRF2 system: A thiol-based sensor-effector apparatus for maintaining redox homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1169–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and oxidative stress: A general overview of mechanisms and implications in human disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jomova, K.; Alomar, S.Y.; Alwasel, S.H.; Nepovimova, E.; Kuca, K.; Valko, M. Several lines of antioxidant defense against oxidative stress: Antioxidant enzymes, nanomaterials with multiple enzyme-mimicking activities, and low-molecular-weight antioxidants. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 1323–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteras, N.; Blacker, T.S.; Zherebtsov, E.A.; Stelmashuk, O.A.; Zhang, Y.; Wigley, W.C.; Duchen, M.R.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Abramov, A.Y. Nrf2 regulates glucose uptake and metabolism in neurons and astrocytes. Redox. Biol. 2023, 62, 102672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zgorzynska, E.; Dziedzic, B.; Walczewska, A. An overview of the Nrf2/ARE pathway and its role in neurodegenerative disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dringen, R.; Arend, C. Glutathione metabolism of the brain-the role of astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 2025, 169, e70073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preet, G.; Hasan, A.H.; Ramlagan, P.; Fawdar, S.; Boulle, F.; Jaspars, M. Anti-neurodegenerating activity: Structure-activity relationship analysis of flavonoids. Molecules 2023, 28, 7188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patigo, A.; Hengphasatporn, K.; Cao, V.; Paunrat, W.; Vijara, N.; Chokmahasarn, T.; Maitarad, P.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Shigeta, Y.; Boonyasuppayakorn, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, in vitro, in silico, and SAR studies of flavone analogs towards anti-dengue activity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiebig, C.; Keiner, S.; Ebert, B.; Schaffner, I.; Jagasia, R.; Lie, D.C.; Beckervordersandforth, R. Mitochondrial dysfunction in astrocytes impairs the generation of reactive astrocytes and enhances neuronal cell death in the cortex upon photothrombotic lesion. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Wei, S.; Nguyen, T.H.; Jo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Park, W.; Gariani, K.; Oh, C.-M.; Kim, H.H.; Ha, K.-T.; et al. Mitochondria-associated programmed cell death as a therapeutic target for age-related disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1595–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Nedergaard, M. Physiology of astrolia. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 239–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkhratsky, A.; Butt, A.; Li, B.; Illes, P.; Zorec, R.; Semyanov, A.; Tang, Y.; Sofroniew, M.V. Astrocytes in human central nervous system disease: A frontier for new therapies. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parenti, I.; Rabaneda, L.G.; Schoen, H.; Novarino, G. Neurodevelopmental disorders: From genetics to functional pathways. Trends Neurosci. 2020, 43, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.-Y.; Huang, Q.-Y.; Zhu, M.-Z.; Ren, J.; Cao, X.; Xiong, W.-C.; Xiao, X.-D.; Zhu, X.-H. An improved ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous quantitation of cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1563, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustapha, S.; Magaji, R.A.; Magaji, M.G.; Gaya, I.B.; Umar, B.; Yusha’u, Y.; Daku, A.B.; Chiroma, S.M.; Jaafar, A.; Mehat, M.Z.; et al. Neuroprotective roles of flavonoid “hispidulin” in the central nervous system: A review. Iron J. Basic Med. Sci. 2024, 27, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, A.; Singh, L.; Dalal, D. Neuroprotective potential of hispidulin and diosmin: A review of molecular mechanisms. Metab. Brain Dis. 2025, 40, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Luo, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X. An improved ultra-high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method determining hispidulin and homoplantaginin in rat plasma and associated pharmacokinetic studies. Acta Chromatogr. 2023, 35, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.-H.; Pang, Q.; Kim, B.; Cho, E.J. Hispidulin Protects C6 Astroglial Cells Against H2O2-Induced Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011069
Kim J-H, Pang Q, Kim B, Cho EJ. Hispidulin Protects C6 Astroglial Cells Against H2O2-Induced Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011069
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Ji-Hyun, Qiqi Pang, Bohkyung Kim, and Eun Ju Cho. 2025. "Hispidulin Protects C6 Astroglial Cells Against H2O2-Induced Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011069
APA StyleKim, J.-H., Pang, Q., Kim, B., & Cho, E. J. (2025). Hispidulin Protects C6 Astroglial Cells Against H2O2-Induced Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Apoptosis. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11069. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011069





