Imidazoline-Based Fatty Acid Derivatives as Novel Shale Inhibitors for Water-Based Drilling Fluids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
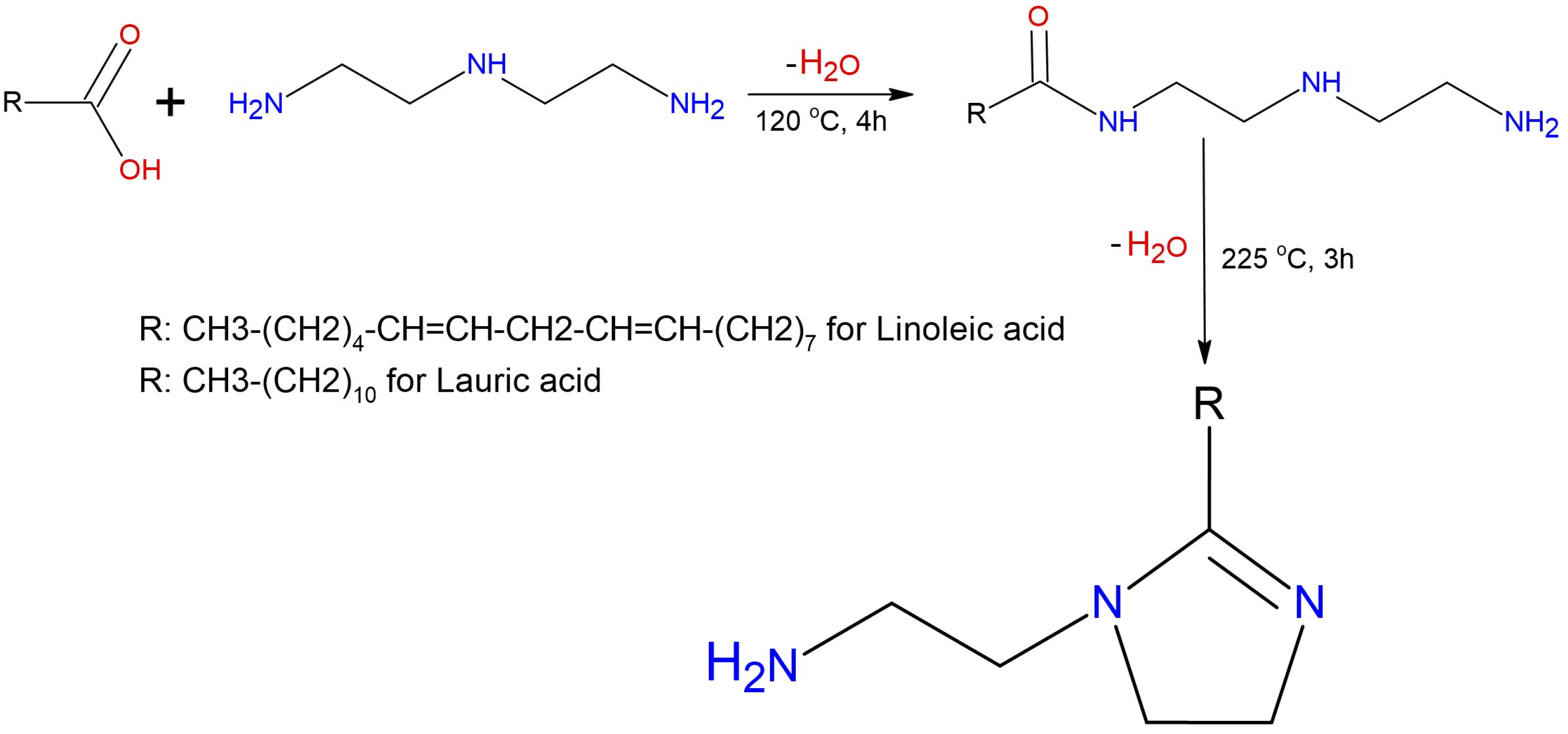
2.2. Synthesis of the Anti-Swelling Additive
2.3. Preparation of Water-Based Drilling Fluids
2.4. Characterization and Testing of the Anti-Swelling Additives
3. Results and Discussion
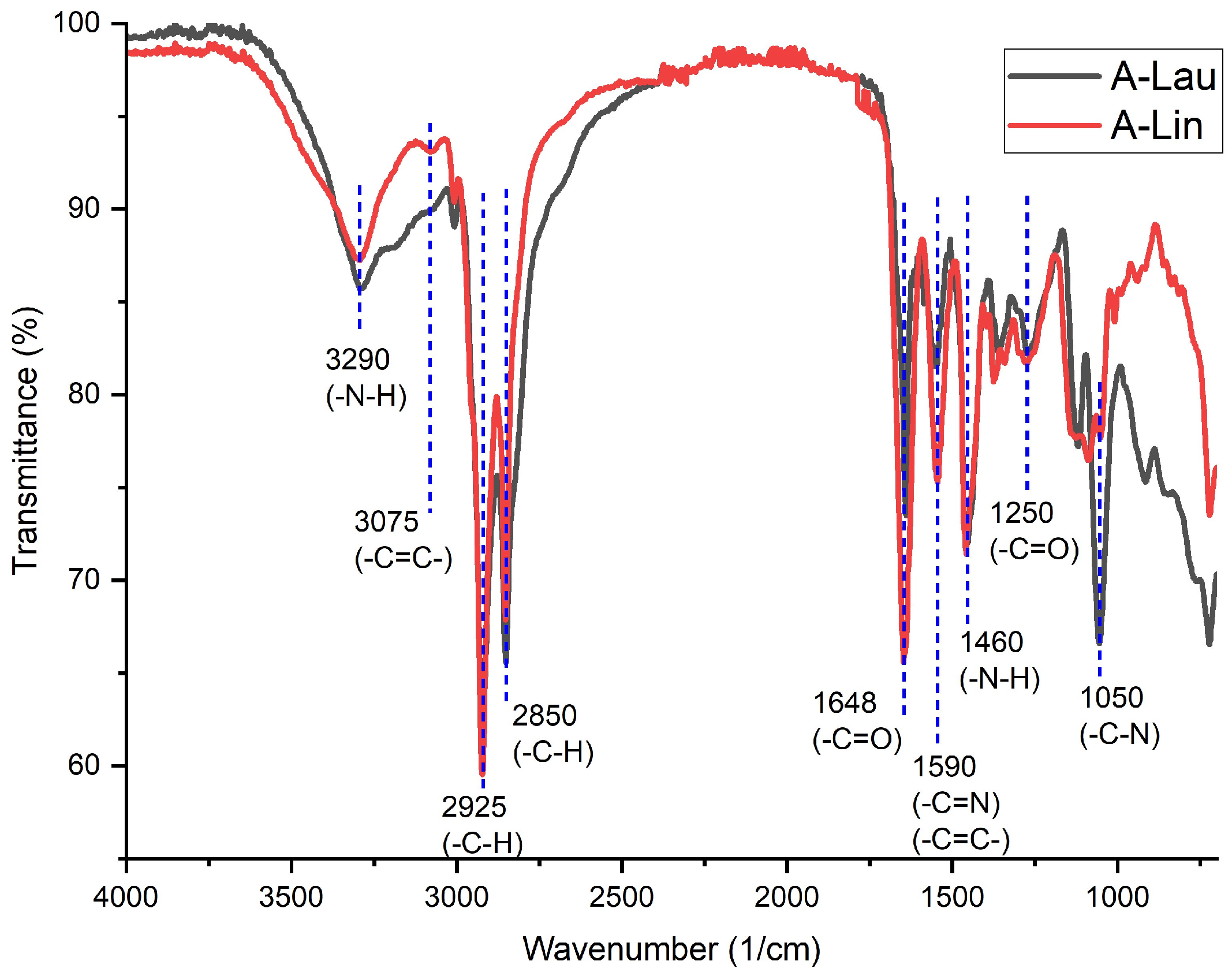
3.1. FTIR Spectral Analysis
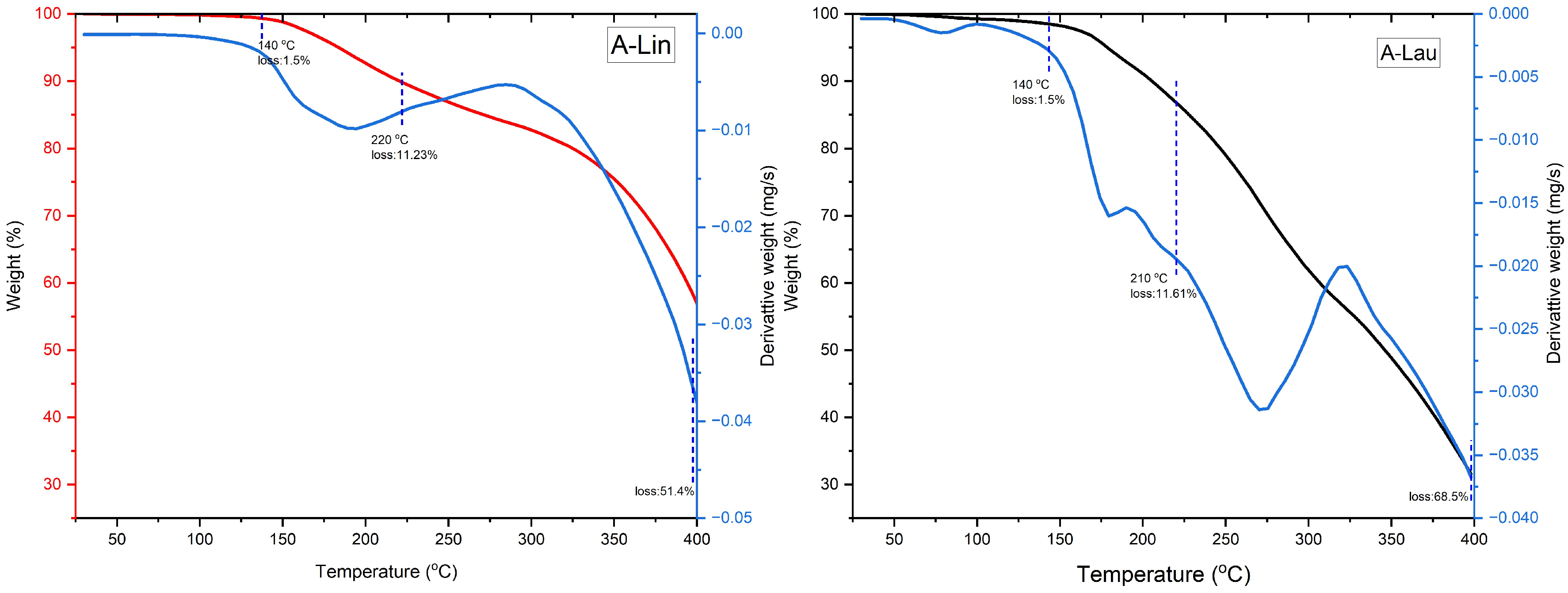
3.2. Thermal Stability Analysis (TGA-DTG)
3.3. XRD Analysis of the X Rosetti Shale
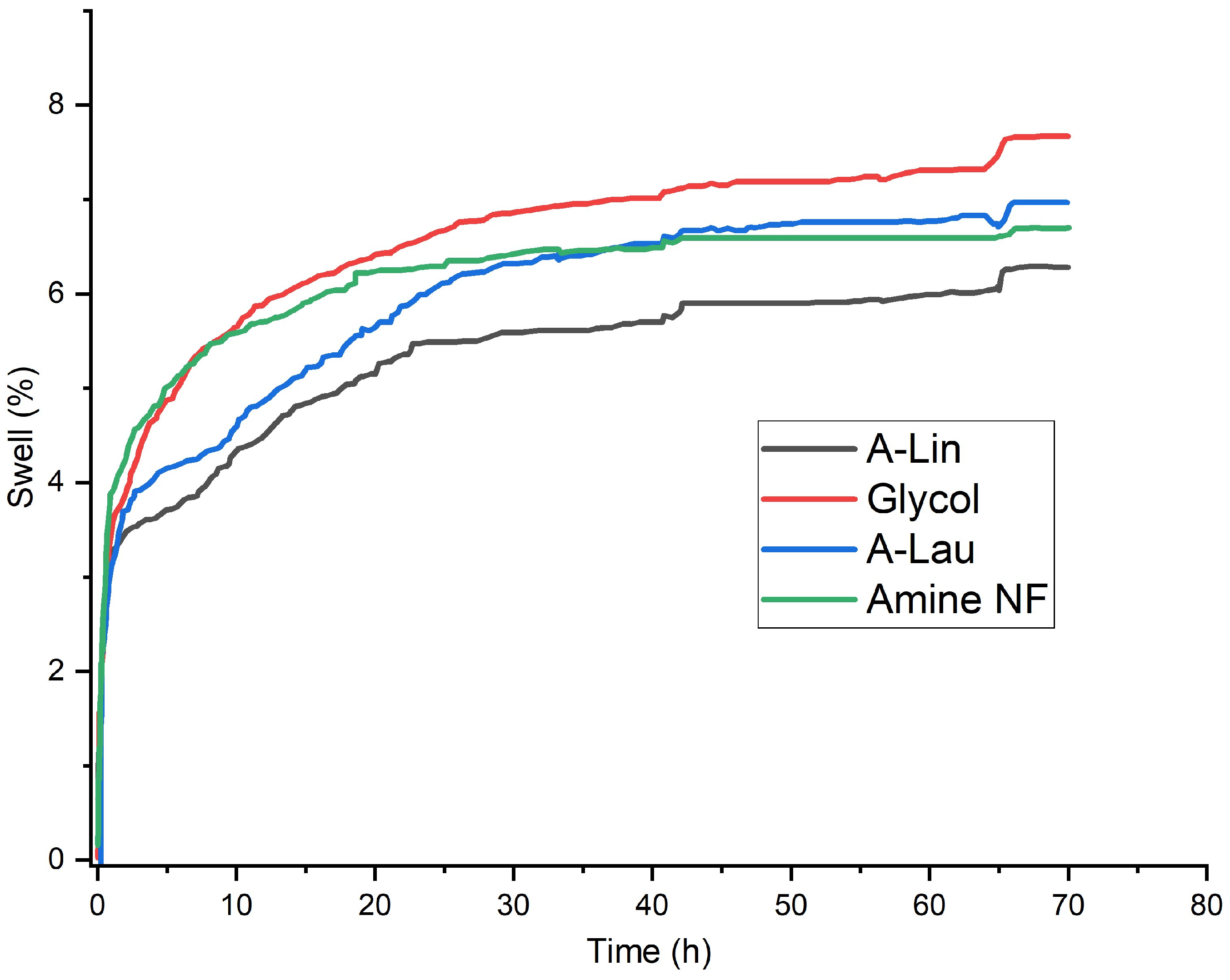
3.4. Analysis of Drilling Fluid Properties and Swelling Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Deville, J.P. Chapter 4—Drilling fluids. In Fluid Chemistry, Drilling and Completion; Wang, Q., Ed.; Gulf Professional Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2022; pp. 115–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendi, A.; Raja, M.; Vashisth, C.; Kaur, P.; Udayasri, A.; Mech, D.; Swamy, T.N.V.R.L.; Raghav, N. Drilling fluids: Score years of trends, innovations and implications in research. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 413, 125891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, H.; Mohammed, A.A.A.; Nasser, M.S.; Hussein, I.A.; El-Naas, M.H. Green drilling fluid additives for a sustainable hole-cleaning performance: A comprehensive review. Emergent Mater. 2024, 7, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Dong, T.; Yi, J.; Jiang, G. Development of Multiple Crosslinked Polymers and Its Application in Synthetic-Based Drilling Fluids. Gels 2024, 10, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, J.M.; Jones, M.; Shuchart, C.E.; Gerard, C. Oil-Based Muds for Reservoir Drilling: Their Performance and Cleanup Characteristics. SPE Drill. Complet. 2001, 16, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ahmad, M.; Ganat, T. Development of a new formulation for enhancing the rheological and filtration characteristics of low-solids WBMs. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2021, 205, 108921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamrozik, A.; Protasova, E.; Gonet, A.; Bilstad, T.; Żurek, R. Characteristics of oil based muds and influence on the environment. AGH Drill. Oil Gas 2016, 33, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dye, W.; d’Augereau, K.; Hansen, N.; Otto, M.; Shoults, L.; Leaper, R.; Clapper, D.; Xiang, T. New Water-Based Mud Balances High-Performance Drilling and Environmental Compliance. SPE Drill. Complet. 2006, 21, 255–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khashay, M.; Zirak, M.; Sheng, J.J.; Ganat, T.; Esmaeilnezhad, E. Elevated temperature and pressure performance of water based drilling mud with green synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles and biodegradable polymer. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.E.; Nowrouzi, I.; Shahbazi, K.; Kamari, M.; Mohammadi, A.H.; Manshad, A.K. An investigation into shale swelling inhibition properties of dodecyltrimethylammonium chloride (DTAC) for water-based drilling fluids. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2023, 223, 211465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, A.; Arfaj, M.K.; Saleh, T.A. Advanced developments in shale inhibitors for oil production with low environmental footprints—A review. Fuel 2019, 247, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xia, C.; Liu, X. Water-based drilling fluids containing hydrophobic nanoparticles for minimizing shale hydration and formation damage. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Huang, P.; Wang, Q.; Han, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, F.; Pan, W.; Lv, K. Investigation of inhibition mechanism of three deep eutectic solvents as potential shale inhibitors in water-based drilling fluids. Fuel 2019, 244, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkes, C.D.; McLellan, P.; Maurer, W.; Ruan, C. Wellbore Instability in Shales: A Review of Fundamental Principles, Physico-Chemical Mechanisms in Mud-Shale Interaction and GRI-Funded Research; Gas Research Institute: Chicago, IL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, T.A. Advanced trends of shale inhibitors for enhanced properties of water-based drilling fluid. Upstream Oil Gas Technol. 2022, 8, 100069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Wang, L.; Guo, J.; Su, Q.; Zhuo, X. Effects of inhibitor KCl on shale expansibility and mechanical properties. Petroleum 2019, 5, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buslaev, G.; Lavrik, A. Comparative Study of Efficiency of Hydrate Inhibitors Based on Ammonium Salts and Polyvinylpyrrolidone. Int. J. Eng. 2026, 39, 898–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retnanto, A.; Yrac, R.; Shaikh, A.; Alagha, R.; Alsulaiti, F.; Chagouri, T. Experimental evaluation of corrosion inhibitors for completion fluids in the petroleum production systems. J. Pet. Explor. Prod. Technol. 2024, 14, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, S.; Gilmore, T.; Twynam, A.J.; Patel, A.; Mason, S.; Kubala, G.; Vidick, B.; Parlar, M. Guidelines for Shale Inhibition During Openhole Gravel Packing with Water-Based Fluids. SPE Drill. Complet. 2008, 23, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavoh, C.B.; Md Yuha, Y.B.; Tay, W.H.; Ofei, T.N.; Lal, B.; Mukhtar, H. Experimental and modelling of the impact of quaternary ammonium salts/ionic liquid on the rheological and hydrate inhibition properties of xanthan gum water-based muds for drilling gas hydrate-bearing rocks. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2019, 183, 106468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, G.; Su, B.; Liu, X.; Hu, Y.; Huang, J.; Lu, Z. Research and Performance Evaluation of Environmentally Friendly Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells. Molecules 2024, 29, 5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J. Petroleum Engineer’s Guide to Oil Field Chemicals and Fluids; Gulf Professional Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.-C.; Xie, G.; Peng, N.-Y.; Zou, J.-G.; Xu, Y.; Deng, M.-Y.; Du, W.-C.; Xiao, Y.-R.; Huang, J.-J.; Luo, P.-Y. Synergistic inhibition of polyethylene glycol and potassium chloride in water-based drilling fluids. Pet. Sci. 2021, 18, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.K.; Lai, C.W.; Johan, M.R.; Gan, S.S.; Chua, W.W. Recent advances of modified polyacrylamide in drilling technology. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2022, 215, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sid, A.N.; Kouini, B.; Bezzekhami, M.A.; Toumi, S.; Ouchak, K.; Benfarhat, S.; Tahraoui, H.; Kebir, M.; Amrane, A.; Assadi, A.A.; et al. Optimization of Partially Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide (HPAM) Utilized in Water-Based Mud While Drilling. Processes 2023, 11, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Zhuang, G.-Z.; Li, X.-L. Advanced development of chemical inhibitors in water-based drilling fluids to improve shale stability: A review. Pet. Sci. 2025, 22, 1977–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zheng, X. Effective Modified Xanthan Gum Fluid Loss Agent for High-Temperature Water-Based Drilling Fluid and the Filtration Control Mechanism. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 23788–23801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; He, H.; Zhao, Y.; Rui, J.; Jiang, R.; Slaný, M.; Chen, G.; Gu, X. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Small-Molecule Ammonium as a Shale Hydration Inhibitor. Minerals 2024, 14, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, W.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.; Zhang, J.; Slaný, M. Synthesis, Property and Mechanism Analysis of a Novel Polyhydroxy Organic Amine Shale Hydration Inhibitor. Minerals 2020, 10, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barati, P.; Shahbazi, K.; Kamari, M.; Aghajafari, A. Shale hydration inhibition characteristics and mechanism of a new amine-based additive in water-based drilling fluids. Petroleum 2017, 3, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oseh, J.O.; Norddin, M.N.A.M.; Muhamad, H.N.; Ismail, I.; Gbadamosi, A.O.; Agi, A.; Ismail, A.R.; Blkoor, S.O. Influence of (3–Aminopropyl) triethoxysilane on entrapped polypropylene at nanosilica composite for shale swelling and hydration inhibition. J. Pet. Sci. Eng. 2020, 194, 107560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xian, S.; Chen, S.; Lian, Y.; Du, W.; Song, Z.; Chen, G. Preparation and Evaluation of Ammonium Adipate Solutions as Inhibitors of Shale Rock Swelling. Minerals 2021, 11, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, G.; Su, B.; Huang, J. Preparation and Mechanism of Shale Inhibitor TIL-NH2 for Shale Gas Horizontal Wells. Molecules 2024, 29, 3403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; Qiu, Z.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, J.; Huang, W. Study of 4, 4′-methylenebis-cyclohexanamine as a high temperature-resistant shale inhibitor. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 7585–7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isac-García, J.; Dobado, J.A.; Calvo-Flores, F.G.; Martínez-García, H. Chapter 4—Basic Laboratory Operations. In Experimental Organic Chemistry; Isac-García, J., Dobado, J.A., Calvo-Flores, F.G., Martínez-García, H., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; pp. 71–144. [Google Scholar]
- Wongwanichkangwarn, I.; Limtrakul, S.; Vatanatham, T.; Ramachandran, P.A. Amidation Reaction System: Kinetic Studies and Improvement by Product Removal. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 30451–30464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- API RP 13B-1; Recommended Practice for Field Testing Water-Based Drilling Fluids. American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2000.
- Stephens, M.; Gomez-Nava, S.; Churan, M. AADE-09-NTCE-11-04: Laboratory Methods to Assess Shale Reactivity with Drilling Fluids. In Proceedings of the AADE National Technical Conference and Exhibition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 21–23 April 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.Y.; Jiang, Z.N.; Li, Y.R.; Dong, C.F.; Liu, H.F.; Zhang, G.A. A new exceptional imidazoline derivative corrosion inhibitor for carbon steel in supercritical CO2 environment. Corros. Sci. 2025, 245, 112663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, B.M.; Salih, N.; Salimon, J. Optimization of the chemoenzymatic mono-epoxidation of linoleic acid using D-optimal design. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2014, 18, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazorenko, G.; Kasprzhitskii, A.; Yavna, V. Synthesis and structural characterization of betaine- and imidazoline-based organoclays. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 692, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muktiarti, N.; Ditama, I.; Soegijono, B. Characterization of imidazoline derivates synthesized from soybean oil fatty acids as corrosion inhibitors on mild steel. AIP Conf. Proc. 2020, 2242, 020023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Liu, K.; Zhao, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ge, H. Inhibition Performance and Mechanism of Poly(Citric Acid–Glutamic Acid) on Carbon Steel Corrosion in Simulated Seawater. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzakowska, M.; Sztanke, M.; Rzymowska, J.; Sztanke, K. Thermal Decomposition Path—Studied by the Simultaneous Thermogravimetry Coupled with Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry—Of Imidazoline/Dimethyl Succinate Hybrids and Their Biological Characterization. Materials 2023, 16, 4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guan, C.; Zhang, A.; Chen, D.; Qing, Z. Thermal stabilities and the thermal degradation kinetics of polyimides. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2004, 84, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharya, A.; Sachan, H.K.; Tiwari, S.K.; Singhal, S.; Singh, P.C.; Rai, S.; Kumar, S.; Mehta, M.; Gautam, P.K.R. New occurrence of albitite from Nubra valley, Ladakh: Characterization from mineralogy and whole rock geochemistry. Curr. Sci. 2016, 111, 1531–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Hu, Y.; He, J.; Tian, M.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Q.; Chen, S.; Chen, D.; Chen, P.; et al. Novel Insights into the Hydroxylation Behaviors of α-Quartz (101) Surface and its Effects on the Adsorption of Sodium Oleate. Minerals 2019, 9, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Xu, C.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, N. Study on preparation and structure of chrysanthemum-shaped micron calcium carbonate based on inverse microemulsion. Micro Nano Lett. 2020, 15, 1151–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczmarek, S.E.; Gregg, J.M.; Bish, D.L.; Machel, H.G.; Fouke, B.W. Dolomite, very high-magnesium calcite, and microbes—Implications for the microbial model of dolomitization. In Characterization and Modeling of Carbonates–Mountjoy Symposium 1; Society for Sedimentary Geology: Tulsa, OK, USA, 2017; Volume 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jaroudi, S.S.; Ul-Hamid, A.; Mohammed, A.-R.I.; Saner, S. Use of X-ray powder diffraction for quantitative analysis of carbonate rock reservoir samples. Powder Technol. 2007, 175, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, G.; Damian, F.; Szakács, Z.; Iepure, G.; Aştefanei, D. Mineralogical and Physico-Chemical Characterization of the Oraşu-Nou (Romania) Bentonite Resources. Minerals 2021, 11, 938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borralleras, P.; Segura, I.; Aranda, M.A.G.; Aguado, A. Influence of experimental procedure on d-spacing measurement by XRD of montmorillonite clay pastes containing PCE-based superplasticizer. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 116, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Mei, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.-b. Characteristics of clay minerals in sediments of Hemudu area, Zhejiang, China in Holocene and their environmental significance. China Geol. 2019, 2, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belachew, N.; Hinsene, H. Preparation of cationic surfactant-modified kaolin for enhanced adsorption of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanad, M.M.S.; Rashad, M.M. Cost-effective integrated strategy for the fabrication of hard-magnet barium hexaferrite powders from low-grade barite ore. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 991–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Carrasco, S.; Valverde, J.M. In situ XRD analysis of dolomite calcination under CO2 in a humid environment. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 6502–6516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidian, M.; Godinez, L.J.; Prasad, M. Effect of clay and organic matter on nitrogen adsorption specific surface area and cation exchange capacity in shales (mudrocks). J. Nat. Gas Sci. Eng. 2016, 33, 1095–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.H.; Reddy, P.S.; Mohanty, B.; Reddy, K.R. Combined effect of mineralogical and chemical parameters on swelling behaviour of expansive soils. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagoz, E.; Mengen, A.E. Shale Characterization Methods Using XRD, CEC, and LSM: Experimental Findings. Pet. Petrochem. Eng. J. 2024, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Khan, R.; Murtaza, M.; Abdulraheem, A.; Kamal, M.S.; Mahmoud, M. Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids as Clay Swelling Inhibitors: Mechanism, Performance Evaluation, and Effect of Different Anions. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 26682–26696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Sun, J.; Xiu, Z.; Huang, X.; Lv, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Dong, X. Preparation and Performance Evaluation of Ionic Liquid Copolymer Shale Inhibitor for Drilling Fluid Gel System. Gels 2024, 10, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Products | WBM 1 (Amine NF) | WBM 2 (Glycol) | WBM 3 (A-Lau) | WBM 4 (A-Lin) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water (mL) | 917 | 917 | 917 | 917 |
| Caustic soda (g) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Sodium carbonate (g) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| Potassium chloride (g) | 70 | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| Defoamer (mL) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Bactericide (mL) | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Amine NF (g) | 20 | – | – | – |
| Glycol (g) | – | 20 | – | – |
| A-Lau (g) | – | – | 20 | – |
| A-Lin (g) | – | – | – | 20 |
| PAC LV (g) | 10 | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| Xanthan gum (g) | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Barite (g) | 202 | 202 | 202 | 202 |
| Parameters | WBM 1 Amine NF | WBM 2 Glycol | WBM 3 A-Lau | WBM 4 A-Lin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mud weight (g/cm3) | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 | 1.20 |
| pH | 9.20 | 9.45 | 10.23 | 9.72 |
| Fann 600 rpm @ 49 °C | 60 | 56 | 60 | 47 |
| Fann 300 rpm @ 49 °C | 41 | 40 | 38 | 33 |
| Fann 200 rpm @ 49 °C | 30 | 33 | 29 | 27 |
| Fann 100 rpm @ 49 °C | 21 | 22 | 19 | 19 |
| Fann 6 rpm @ 49 °C | 6 | 5 | 5 | 6 |
| Fann 3 rpm @ 49 °C | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5 |
| Gels 10″/10′ | 5/6 | 5/6 | 4/5 | 5/6 |
| Plastic Viscosity (cP) | 19 | 16 | 22 | 14 |
| Yield Point (lb/100 ft2) | 22 | 24 | 16 | 19 |
| API Filtrate (mL) | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.4 | 8.4 |
| Mud Cake (mm) | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Bicarbonate (mg/L) | 122 | 122 | 244 | 122 |
| Carbonate (mg/L) | 600 | 720 | 720 | 720 |
| Hydroxyl (mg/L) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Calcium (mg/L) | 160 | 160 | 160 | 160 |
| Chlorides (mg/L) | 33,000 | 33,000 | 33,000 | 33,000 |
| Magnesium (mg/L) | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 |
| Lubricity coefficient | 0.195 | 0.192 | 0.154 | 0.148 |
| Swell % | 6.7 | 7.7 | 7.0 | 6.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stan, I.G.; Tudose, M.; Prundurel, A.P.; Branoiu, G.; Dumitrache, L.; Suditu, S.; Stoica, D.B.; Zaharia, E.; Doukeh, R. Imidazoline-Based Fatty Acid Derivatives as Novel Shale Inhibitors for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011050
Stan IG, Tudose M, Prundurel AP, Branoiu G, Dumitrache L, Suditu S, Stoica DB, Zaharia E, Doukeh R. Imidazoline-Based Fatty Acid Derivatives as Novel Shale Inhibitors for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011050
Chicago/Turabian StyleStan, Ioana Gabriela, Mihail Tudose, Alina Petronela Prundurel, Gheorghe Branoiu, Liviu Dumitrache, Silvian Suditu, Doru Bogdan Stoica, Emil Zaharia, and Rami Doukeh. 2025. "Imidazoline-Based Fatty Acid Derivatives as Novel Shale Inhibitors for Water-Based Drilling Fluids" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011050
APA StyleStan, I. G., Tudose, M., Prundurel, A. P., Branoiu, G., Dumitrache, L., Suditu, S., Stoica, D. B., Zaharia, E., & Doukeh, R. (2025). Imidazoline-Based Fatty Acid Derivatives as Novel Shale Inhibitors for Water-Based Drilling Fluids. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11050. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011050















