Abstract
Generative steganography (GS) generates stego-media via secret messages, but existing GS only targets single-type multimedia data with poor universality. The generator and extractor sizes are highly coupled with resolution. Message mapping converts secret messages and noise, yet current GS schemes based on it use gridded data, failing to generate diverse multimedia universally. Inspired by implicit neural representation (INR), we propose generative implicit steganography via message mapping (GIS). We designed single-bit and multi-bit message mapping schemes in function domains. The scheme’s function generator eliminates the coupling between model and gridded data sizes, enabling diverse multimedia generation and breaking resolution limits. A dedicated point cloud extractor is trained for adaptability. Through a literature review, this scheme is the first to perform message mapping in the functional domain. During the experiment, taking images as an example, methods such as PSNR, StegExpose, and neural pruning were used to demonstrate that the generated image quality is almost indistinguishable from the real image. At the same time, the generated image is robust. The accuracy of message extraction can reach 96.88% when the embedding capacity is 1 bpp, 89.84% when the embedding capacity is 2 bpp, and 82.21% when the pruning rate is 0.3.
1. Introduction
Steganography is an information hiding technique in the field of secret communication, aimed at transmitting secret messages over public channels without being discovered. At present, research hotspots focus on steganography based on deep neural networks, which mostly use encoding and decoding structures. Generative steganography (GS) is a steganography technique that uses a generator as an encoder to directly generate stego-media.
At present, generative steganography can be divided into three categories based on different structures. The first category is synthesis-based generative steganography. One can use a generator to generate cover-media and embed a secret message, as shown in Figure 1a. Generators of this type usually use Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) [1,2] as the generative model, and diffusion models [3,4,5], flow models [6], VAE [7,8] and other generative models [9] are also used as generators. The second type is generative steganography based on message mapping, as shown in Figure 1b. One can map a secret message to the noise vector space through a mapping scheme and generate a stego-media from the mapped noise through a generator. Researchers [3,10,11,12] use message mapping to embed secret messages, which is also the most commonly used method in GS. The third type is generative steganography based on fixed message extractors, as shown in Figure 1c. This type of method no longer requires passing the message extractor, and various methods are adopted to fix or hide the message extractor, for example, by embedding fixed message positions [13] or directly modifying the stego-media by adding small perturbations to it [14].

Figure 1.
Generative steganography classification.
However, all the aforementioned methods share the following common issues: First, data is represented as gridded data, which restricts the methods to using single-type and fixed-size data, greatly limiting the flexibility and universality. Second, there is strong coupling between model size and data size, with the model size increasing exponentially as the resolution rises. Thirdly, the generative steganography scheme lacks robustness.
A newly developed implicit neural representation (INR) technology has addressed the issue of limited data representation and has become a trend in the development of data representation. INR is a form of continuous function that takes grid coordinates as input and outputs features. Inspired by INR, some researchers [15,16,17] have attempted to introduce INR into steganography. The adoption of INR expands the types of data usable for steganography and resolves the problem of a single data type in steganography. However, these efforts merely modify the data representation format—they still only adjust the parameter space and have not been applied to generative steganography.
The above problems still exist in generative steganography. So our goal is to construct a generative steganography scheme based on message mapping that can simultaneously address the generality of generators and extractors and improve robustness on this basis. To address the issue of generality, we use implicit neural representation to construct a cover independent function generator in generative steganography. Then, we perform message mapping in the function domain to satisfy the input of the function generator. Finally, we design a universal message extractor that matches the generator to handle various types of multimedia data. In addition, in the design of the scheme, we should also consider the actual deployment and real-world applications and make requirements for its efficiency and robustness.
To achieve the above goals, this paper proposes generative implicit steganography via message mapping (GIS). The scheme replaces the traditional generator with a function generator on the framework of message mapping-based generative steganography and designs a message mapping scheme in the noise space of the function generator. We design a message extractor specifically for point cloud data to replace traditional grid-based message extractors. Throughout the process, point cloud data is used as the actual processing object. The main contributions of this article are as follows:
- 1.
- This is the first time a function generator is used in message mapping-based generative steganography. It addresses the issue where the generator model size increases with data size, enables the representation of different types of multimedia data, and breaks through the resolution limitations of traditional gridded data.
- 2.
- Single-bit and multi-bit message mapping schemes are designed in the noise space of the function generator, with message embedding completed at the noise level of the generator.
- 3.
- A dedicated message extractor for point cloud data is designed, which avoids the strong coupling between extractor size and data size and improves the universality of the extractor.
The organizational structure of this paper is expanded through several logically coherent sections. The specific arrangements are as follows: First, in Section 1, the classification of generative steganography and the problems existing in the current field are summarized, and then the basic framework of this scheme is further introduced, and the core contributions of this research are clearly described. Then, Section 2 focuses on generative steganography and introduces three specific categories in detail. At the same time, it also explains the type of steganography based on implicit neural representation and its two classifications. On this basis, it points out the shortcomings in the current related research and this leads to the research idea of this paper. Then, Section 3 as the core content, comprehensively introduces the main process of the scheme proposed in this paper and clearly describes the specific details of the scheme from the key dimensions of data representation, message mapping scheme, function generator, and message extractor based on point cloud data. Next, Section 4 carries out systematic experimental analysis on the scheme, and quantifies the performance of the scheme from several important angles, such as visual security, message extraction accuracy, non detectability, robustness, efficiency, and super-resolution sampling, to verify the effectiveness of the scheme. Finally, Section 5 summarizes the methods proposed in this paper and their practical application effects and condenses the core results of this research.
2. Related Work
The current research status of steganography is introduced from two categories: generative steganography and steganography based on an implicit neural network.
2.1. Generative Steganography
Generative steganography refers to using deep neural networks as generative models to directly generate stego-media driven by secret messages [18,19]. The advantage of this approach is that it avoids the problem of traditional embedded steganography leaving distorted evidence. According to the different technical frameworks used, generative steganography can be divided into the following three categories:
The first category is GS based on synthesis, as shown in Figure 1a. In this type of steganography, random noise is used as input to generate cover-media via a generator. Subsequently, the cover-media and secret message are synthesized by an encoder to obtain stego-media. The receiver recovers the secret message from stego-media using a message extractor. Such schemes typically adopt a GAN as the generative model. The initial introduction of a GAN into steganography mainly leverages their adversarial game strategy to generate realistic cover images for hiding secret information. Hu et al. [10] were the first to propose a carrier-free steganographic model based on a DCGAN, encoding secret messages into Gaussian noise vectors and achieving end-to-end steganography from noise encoding to image generation for the first time. A SGAN [20] used a DCGAN to generate cover-media suitable for steganography. Building on this, Shi et al. [21] replaced DCGANs with WGANs and proposed the SSGAN scheme, which enhanced the ability to resist GN-CNN detection. Cui et al. [22] utilized an MC-GAN [23] to generate images with complex foreground regions, employed LSBM [24] steganography for message embedding and finally stitched and synthesized the cover-media with the foreground image containing the hidden secret. Notably, the aforementioned schemes do not directly generate stego-media. Instead, they embed secret messages after generating cover-media, thus falling under the category of generative steganography in a broad sense.
The second type is GS based on message mapping, as shown in Figure 1b. This type of steganography first projects the secret message into the noise space through mapping rules or encoding. Then, it uses the noise mapped by the secret message to generate stego-media. The receiver uses a message extractor to extract noise from stego-media and then recovers the secret message through inverse mapping or decoding. Early mapping schemes were relatively direct, relying on a simple correspondence between noise and messages, with low embedding capacity and limited quality. In order to improve embedding capacity, Hu et al. [10] proposed mapping secret messages to the noise space of the generator and using block mapping to enhance embedding capacity. Kim et al. [3] proposed three message projection schemes to balance the relationship between message extraction accuracy, anti-analysis ability, and image quality, achieving 3 bpp embedding capacity while improving the accuracy of message extraction. With the increase in embedding capacity, higher requirements have been put forward for the consistency of hidden space distribution. Hidden vectors need to follow the statistical distribution of natural images, such as Gaussian distribution, and different distributions are easily detected by steganalysis. Yang et al. [25] first proposed the idea of implementing verifiable secure steganography based on generative artificial intelligence. It maps secret information that follows a uniform distribution to latent vectors that follow standard Gaussian distribution through inverse transformation sampling. It ensures that the statistical distribution of stego-images and real images is indistinguishable. This also provides a security assessment framework for subsequent research. In order to overcome the problem of maintaining distribution, VAE Stega [26] maps secret messages to the hidden space through a variational autoencoder and uses the encoder to learn the statistical distribution of natural text, balancing perceptual invisibility and statistical invisibility. Zhu et al. [27] proposed an adjustable message mapping scheme that keeps message mapping consistent with Gaussian noise distribution, significantly improving the anti-detection performance.
The third type is generative steganography based on fixed message extractors, as shown in Figure 1c. This type of steganography generates stego-media from random noise and uses a fixed message extractor to extract secret messages from them. The stego-media itself is trained by adding small perturbations to it until the extracted secret message is close enough to the real one. Liu et al. [13] used semantic image restoration technology and introduced Digital Cardan Grille (DCG) to determine the hidden position of messages, which is equivalent to fixing the message extractor and restoring the secret message at a fixed position. Subsequently, Kishore et al. [14] proposed fixed neural networks (FNNs), and the concept of fixed message extractors was formally introduced. Luo et al. [28] proposed a key-based FNNs based on FNNs, which solves the problem of unauthorized extraction in existing FNNs by controlling perturbation generation with keys. At the same time, it combines adaptive perturbation optimization strategies to improve the visual quality of stego-media. Li et al. [29] proposed Cover Separable Fixed Neural Network Steganography (Cs-FNNS), which eliminates the interference of cover-media on decoding and achieves strong anti-detection steganography through the “cover-perturbation separation” strategy and Steganographic Perturbation Search (SPS) algorithm. Cheng et al. [30] proposed Robust Fixed Neural Network Steganography (RFNNS) to address the issue of poor robustness in FNNs. By utilizing texture-aware localization techniques and a robust steganographic perturbation generation (RSPG) strategy, the robustness of the proposed approach was improved. Zhong et al. [15] applied it to generative steganography and proposed generative steganography based on a fixed message extractor.
The above three types of generative steganography all use generative models to construct stego-media. While Zhong [15] uses implicit data-oriented generators, most generative steganography uses explicit data-oriented generators. The type and size of media data are single and fixed, which is not universal.
2.2. Steganography Based on Implicit Neural Network
To address the issue of singularity in data representation, researchers have applied implicit neural representation to steganography schemes. Implicit neural representation is a technique for representing data as a continuous function. According to the application of implicit neural representation in steganography, it can be divided into two categories.
One type is steganography based on the redundancy characteristics of model parameters. Some researchers utilize the characteristic of parameter redundancy in neural network structures [31,32,33,34] to convert multimedia data into function data and construct stego-media by modifying (pruning or extending) the parameter redundancy of the function. Han et al. [31] implicitly represented video, audio, and 3D data, sampled the cover-media, and then performed steganography. However, this method only represented secret messages with implicit data and was essentially multimedia steganography. Liu et al. [35] first proposed the concept of implicit function steganography, which extends the function of secret messages through implicit representation to achieve message hiding. This method transforms the data format of secret messages into a unified function (model) format. Song et al. [36] represented multimedia as a network and scrambled it to form a large network for steganography. However, since the scrambled stego-network can only output noisy data, it has low concealment for steganography. Dong et al. [16] used the model pruning method in model compression technology to find redundant space and achieve implicit representation steganography after representing the image as implicit data. In addition, Dong et al. [17] proposed a multi-image steganography scheme based on implicit neural representation, which utilizes the redundancy of function parameters and employs amplitude-based weight selection and secret weight replacement methods to effectively hide and independently extract multiple secret images. The above method only changes the representation of data and is still multimedia steganography in essence.
Another type is generative implicit steganography. This method refers to using a generative model based on implicit neural representation as the generator [15,37] and implementing steganography by generating stego-function. Zhong et al. [15] used a function generator to construct function generative steganography, which generated an implicit neural representation vector using the generator and then performed steganography through data conversion. But its actual cover is still a two-dimensional image, which has not achieved complete universality. Zhong [37] constructed implicit representation generative steganography based on point cloud data, using a function generator as the generative model and a fixed message extractor to extract secret messages during the process. The above schemes are used to iterate and optimize cover-media to generate stego-media instead of directly generating stego-media [15,37].
Taking inspiration from the aforementioned techniques, the goal of this article is to construct a universal generative steganography scheme based on message mapping technology. In the scheme, a function generator is used as the generative model for steganography, eliminating the strong coupling between the generative model and data size and expanding the types of stego-media used for steganography. Simultaneously, we design single-bit and multi-bit mapping schemes in the noise space of the function domain, embedding the message mapping process into the noise level of the function generator. To match the generator, a message extractor specifically designed for point cloud data is designed to extract noise from point cloud data and recover secret messages through inverse mapping. The advantage of this approach is that the message extractor can receive data of different types and sizes. By using a function generator and a message extractor specifically designed for point cloud data, this type of steganography can unify the data format, efficiently generate stego-media, and construct a simple yet universal generative steganography scheme.
3. The Proposed Generative Implicit Steganography via Message Mapping
As illustrated in Figure 2, the proposed steganography framework consists of two phases. Firstly, we map the secret message to noise and then input it into a function generator to obtain a continuous function. We sample point cloud data from it as needed for transmission. After receiving the point cloud data sampled by the function, the receiver uses a message extractor specifically designed for the point cloud data to extract noise and recover the secret message through inverse mapping. In the scheme, we use point cloud data as the actual stego-media.
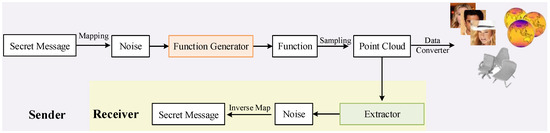
Figure 2.
The framework of scheme.
3.1. Data Representation
Currently, most multimedia data is represented explicitly, such as images represented as gridded data. Gridded data refers to the discrete pixelated representation of multimedia data. Its disadvantage is that the size of the data is closely related to the resolution. Another form of data representation is implicit representation. It mainly uses INR to parameterize multimedia data into continuous function data. This approach eliminates the strong coupling relationship between data size and resolution. The first step to transmit function data to gridded data is to obtain set pairs first, which is called point cloud data. Point cloud data is a collection of coordinates and features. It is a data representation form that falls between explicit and implicit data. Taking image I as an example, the image represented by gridded data consists of discrete pixels. Assuming each pixel is , the image can be represented as shown in Figure 3a. This is an explicit representation method. To perform parametric representation, we first need to convert explicit data into a collection representation of point cloud data. Assuming the coordinate values are and feature values are , the set composed of coordinates and features is the formal representation of the point cloud of image I, as shown in Figure 3b. Then, based on the implicit representation of input–output relationship constructor data from point cloud data, function data is determined by parameters : . Given the pixel position, the RGB coordinate values are obtained, as shown in Figure 3c. The three images below are three different representations of an image. Point cloud data serves as a bridge between implicit and explicit data, which can be obtained through sampling from function data or visualized as grid data through transformation.
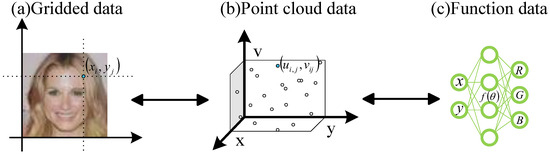
Figure 3.
Data representation.
Based on the characteristics of the three types of data mentioned above, this article uses a generative model based on INR as a generator to solve the problem of the close relationship between model size and grid data resolution. To make the message extractor universal, we design a point cloud message extractor. By extending the data types of steganography in this way, the universality of the generator and message extractor is enhanced.
3.2. Message Mapping
The purpose of the message mapping scheme is to extract secret messages accurately, so the simplest mapping method is selected in the design. The core of the mapping scheme design is the uniqueness of interval partition and the controllability of noise distribution. We design message mapping schemes in the functional domain. In order to achieve a higher message embedding rate, we design a multi-bit mapping scheme based on a single-bit mapping scheme.
3.2.1. Single-Bit Message Mapping
We call the single-bit mapping scheme , whose aim is to map the same message to a consistent value. When the secret message value is 0, the value of Z is also 0. When the secret message value is 1, the value of Z is or . The design of the mapping scheme is based on the uniqueness of the interval division and the controllability of the noise distribution. One can simply reverse map the obtained Z value to restore the 0 and 1 message values.
3.2.2. Multi-Bit Message Mapping
Our solution also achieves high-capacity embedding by designing a multi-bit mapping scheme, . When the hiding capacity is higher than 1 bpp, it is necessary to hide secret messages with more than 1 bit in a single signal. To achieve this, we use message grouping to implement multi-bit mapping. Firstly, group the secret messages into groups of two bits each, with four possible scenarios: 00, 01, 10, and 11. Map them to four different ranges of noise values, as shown in Figure 4. By hiding 2 bits in each bit to conceal the 2 bpp messages, the receiver can extract the noise and recover the secret message through inverse mapping.
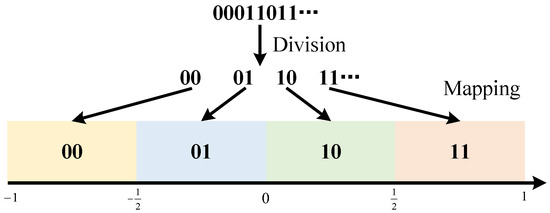
Figure 4.
Multi-bit message mapping.
3.3. Function Generator
Our goal is to apply INR to generative steganography, so we need a function generator that can continuously generate function instances. Many function generation models [38,39,40,41] provide ideas. Among them, we adopt the function generator proposed by Dopont [38], whose neural network architecture is shown in Figure 5. The input of the main network of the function generator is a 64-dimensional random noise vector, and the hidden layer consists of three fully connected layers with dimensions of 128. The hypernetwork module contains two hidden layers with dimensions of 256 and 512. The function representation module uses Fourier feature encoding to enhance the representation ability of high-dimensional coordinates in position encoding, with an encoding frequency of 128 and a standard deviation of 2.0.
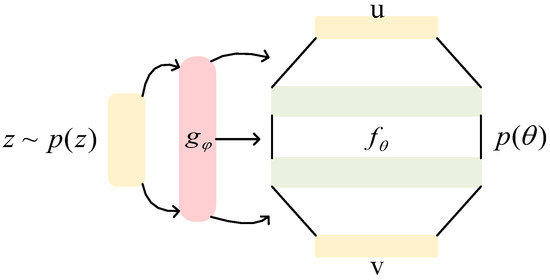
Figure 5.
The neural network construction of the function generator.
Our goal is to train generator to continuously generate functions . And what determines is its parameters , so our goal becomes obtaining from . By sampling z from and entering it into generator G, one can obtain a series of weights , among which . For the generated function, the input coordinate is u and the output feature is v.
To train the function generator, Dopont [38] proposed modeling by learning the function distribution and using the Generative Adversarial Stochastic Process (GASP). During the training process, a discriminator is introduced to input the generated point cloud and the real point cloud. The function generator is trained through an adversarial game process. Specifically, given latent vector z and coordinates , we generate features :
Here, represents random Fourier encoding, which is used to learn the high-frequency information of the function. We can evaluate the generator through a set of coordinates, , and a series of generated feature values, , to train the model.
In the discriminator, the GASP draws on the regularization equivalent penalty for point cloud data proposed by Mescheder [42]. After representing the image as point cloud data, for set , the penalty is defined as follows:
Here, D is the loss of the discriminator. In this process, we penalize the gradient of the discriminator through eigenvalues, and the training process eliminates the discretization of grid data and directly applies it to point cloud data types. The learning rate of the generator is , and the learning rate of the discriminator is . The current learning rate setting is a relatively balanced value that has been experimentally validated.
3.4. Point Cloud Message Extractor
This chapter will introduce the basic architecture, training parameters, and loss function definition of the point cloud message extractor.
3.4.1. Network Structure
Unlike the neat arrangement of gridded data, the representation of point cloud data involves the concept of latent distance [43]. It creates a more disordered spatial arrangement, as shown in Figure 6. Therefore, traditional grid-based convolution is no longer applicable. In this paper, a neural network based on point convolution is used as the framework of the message extractor. The network structure is shown in Figure 7. We defined four point convolutional layers and three fully connected layers. The design of downsampling layer by layer and increasing the feature dimension layer by layer preserves local information while extracting high-dimensional features. The numbers in the fully connected layer represent the input and output dimensions, and the output of the convolutional layer is flattened and the dimension is reduced layer by layer to finally output the feature vector of the specified dimension. The input of the model is different numbers of point cloud data, and the data size can be modified according to the image resolution to output noisy data. After calculation, the total number of parameters for the point cloud convolutional layer and fully connected layer is about 3.1 M. The overall structure adopts progressive downsampling to effectively extract multi-scale features, and BatchNorm is used to ensure high quality during the training process. Simultaneously, no Sigmoid output is suitable for continuous noise reconstruction.
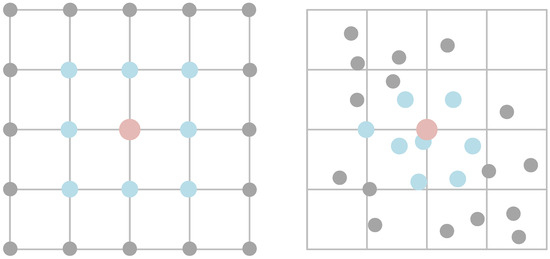
Figure 6.
Convolution neighborhood for regular convolutions and PointConv. Gray represents the overall area of the input feature map. Blue represents the area involved in the calculation. The red color represents the core point of convolution calculation.
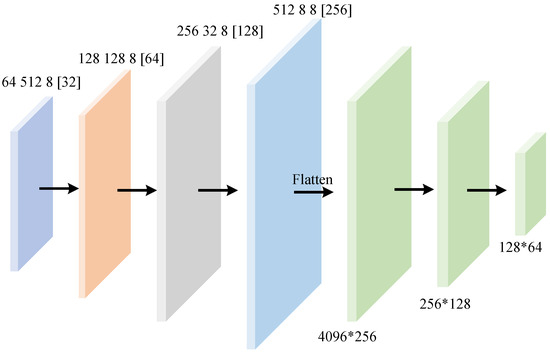
Figure 7.
Structure of point cloud message extractor.
3.4.2. Training
The message extractor is constructed based on point cloud convolution. During the training process, it has a batch processing capacity of 32, learning rate of 0.001 and regularization weight of 10.0. It randomly samples 1000 sets of data from the generated model as training samples and sets the epoch to 10,000 rounds. In each round of training, the average loss is calculated and compared with the previous training results to retain the best-performing model.
3.4.3. Loss Function
The message extraction task is not a discrete task, so the loss function in the training process needs to be adaptive to the continuous value output task. MSE has simple mathematical characteristics, low optimization difficulty and low computational cost, which is suitable for large-scale data training. In the process of training the message extractor, we use mean square error (MSE) to constrain the loss:
Here, is the feature value of the point cloud data converted from the real image, is the feature value of the point cloud data sampled from the function, and n is the number of samples.
4. Experiments and Analysis
In order to facilitate the visualization of experimental results, we use a data converter to visualize the generated data into two-dimensional images for analysis.
4.1. Evaluation Metrics
We evaluate its steganography ability from the perspectives of visual safety, message extraction accuracy, undetectability, robustness, and efficiency. At the same time, we evaluate its super-resolution sampling ability based on the characteristics of INR. To quantify the effectiveness of the evaluation plan, the following criteria are defined:
Message extraction accuracy (Acc):
where BER is the Bit Error Rate; XOR is the exclusive OR operation, used to calculate the number of erroneous bits; is the original secret message; is the extracted secret message; and is the length of the secret message.
4.2. Settings
Our experiments were conducted on NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4060 Ti graphics cards. The experimental environment has PyTorch version 2.5.1, TorchVision version 0.20.1, and CUDA version 12.1. The dataset is CelebA-HQ [44], and the image sizes were uniformly adjusted to before the experiment.
4.3. Visual Safety
We conducted experiments on the CelebA-HQ dataset [44] and randomly selected 6 out of 10,000 experimental results for display, as shown in Figure 8. The first row is stego-media generated by message mapping noise, the second row is cover-media generated by Gaussian noise, third row is the real image from the CelebA-HQ dataset [44] and the last line is the image generated by the StyleGAN2 [45]. It can be seen that the details of the stego-media generated by the noise generated from the message mapping scheme are clear and natural, the overall visual effect is smooth, and there is no obvious distortion, blur or abnormal texture. The stego-media and other images have excellent performance in structural background, color texture, style fidelity and so on, which are almost indistinguishable from the other two types of images.

Figure 8.
Visual safety.
4.4. Message Extractor Accuracy
We define the number of secret messages embedded per pixel as the embedding capacity, measured in bpp. To illustrate the impact of training epochs on the accuracy of the extractor, we set the learning rate to 0.001 and the message embedding capacity from 1 bpp to 2 bpp. Figure 9 shows the accuracy curves of message extraction under different training epochs. As the training epochs increase, the acc also increases. When the message embedding capacity is 64 bits, the accuracy of message extraction is 96.88%. The smaller the payload, the higher the extraction accuracy. Table 1 shows a comparison between our proposal and other proposals. It can be seen from the results that when the capacity is 1 bpp, the accuracy is at an excellent level compared with other methods under the same conditions, slightly lower than that of the GSN and diffusion stego, but still has a good performance. When the capacity is increased to 2 bpp, the accuracy rate decreases, but the overall accuracy rate can still maintain a certain level, indicating that our steganography scheme has corresponding performance under different capacity requirements.
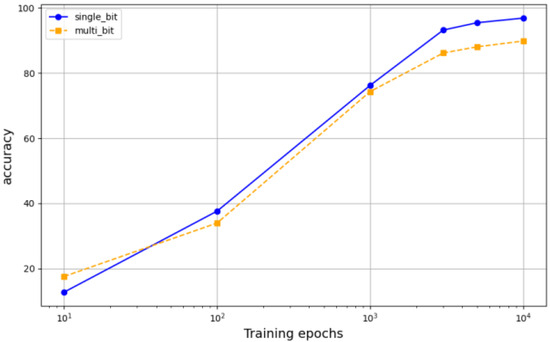
Figure 9.
Accuracy of different training epochs.

Table 1.
Comparison of message extraction accuracy among different schemes.
4.5. Undetectability
To evaluate its undetectability, we chose the open-source steganalysis tool StegExpose [48]. The results are shown in Table 2. W establish a stego-media dataset with a size of 10,000 and an image resolution of as the analysis object. The detection rate is 6.24%. Sample pair is a steganalysis method based on sample pair analysis, where values closer to 0 indicate a lower likelihood of steganography embedding. RS analysis is a steganalysis method based on Regular Singular analysis. The closer it is to 0, the better. Fusion (mean) is the average result obtained by integrating multiple analysis methods. In summary, the values of all indicators are close to 0, indicating that no obvious steganographic embedding traces were detected in the analyzed data.

Table 2.
Results of StegExpose.
To further detect the invisibility of the scheme, we use KS (the Kolmogoro–Smirnov test) and T test to statistically analyze the noise and random Gaussian noise after message mapping. It can be seen from Figure 10 that there are some differences in the distribution of the two noises, but the frequencies of some intervals are close. Through experiments, the KS test statistics of the two are 0.1562, and the p value is 0.3438. The statistic of the t test was 0.1807, and the p value was 0.8569. It can be seen from the results of the two tests that at the 5% significance level, the assumption that “two distributions are the same” cannot be rejected, which proves that the distribution difference between the mapped noise and random Gaussian noise is not statistically significant, which further proves the invisibility of the scheme.
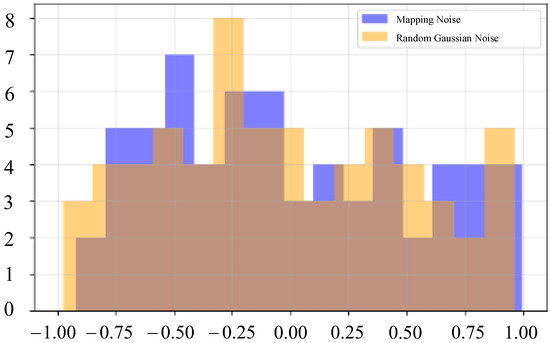
Figure 10.
Noise distribution comparison.
4.6. Robustness
We use continuous point cloud data so the traditional method of evaluating robustness based on gridded data is no longer applicable. We adopt unstructured pruning techniques to evaluate its robustness. Figure 11 presents a visual display of point cloud data at different pruning rates. The first column shows the image without pruning, followed by images from left to right with pruning rates of 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, and 0.8. It can be seen from the results that when the pruning rate is low (such as 0.01 or 0.05), the visual quality of the image almost does not decline, and the details of the face are still clear, and the overall integrity can be maintained. This shows that the model can retain the key information better when pruning at a small scale and has less impact on the image quality. With the increase in pruning rate, the image shows obvious degradation, which means that too high a pruning rate has a greater impact on the stego-media. The acc for images with different pruning rates is shown in Table 3. It can be seen from the results that with the increasing pruning rate, the accuracy of message extraction shows a downward trend. When the pruning rate was low, although the extraction accuracy decreased to some extent, it still remained at a high level. When the pruning rate reaches 0.1, the message extraction accuracy can still reach 87.50%, which proves that the scheme has good robustness.

Figure 11.
Visualization image after unstructured pruning.

Table 3.
Acc under different pruning rates.
4.7. Efficiency
When the message embedding amount is 1 bpp, the training time for the model to generate 10,000 epochs is 24 h. When the sample size is 1000 and the batch processing amount is 32, the training time for the message extractor is 120 h. As shown in Figure 12, the time required for the generator to generate data of different resolutions after training is almost the same. The efficiency of the extractor in extracting noise from images of different resolutions is also basically the same. The time cost of message extraction and stego-media generation is controllable. However, in high-resolution scenes, the time cost of both will increase significantly, especially the generation time of stego-media, which may have a certain impact on the practicability of steganography schemes in high-resolution image scenes (such as application scenarios with high real-time requirements).
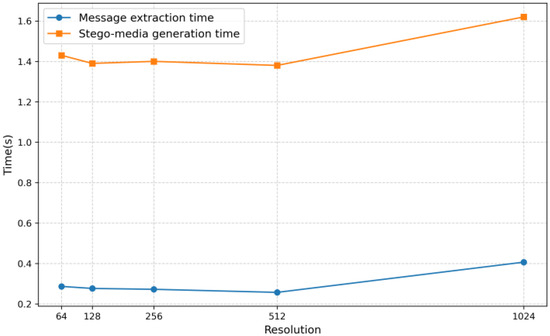
Figure 12.
Efficiency of generator and extractor.
4.8. Super-Resolution
Figure 13 shows the stego-media obtained from the super-resolution sampling of the model when the training dataset is resolution. The image resolutions from left to right are 64, 128, 256, 512, and 1024. In order to facilitate viewing, all images have been adjusted to resolution. This article uses INR instead of traditional gridded data, which enables images not to be limited by resolution. It has high flexibility and universality ability for processing image data of different resolutions.

Figure 13.
Super resolution.
To make the difference more apparent, we enlarged a small resolution image and compared it. The left image in Figure 14 shows the reconstruction secret message with a resolution of adjusted to , while the right image shows the reconstruction secret message with a resolution of directly sampled. The left image appears more blurry compared to the right image, indicating the effectiveness of super-resolution sampling.

Figure 14.
Comparison of different resolutions.
5. Conclusions
This article is the first to implement secret message mapping in the noise level of the functional domain. We construct generative implicit steganography via message mapping (GIS). This approach innovates the feature that message mapping-based GS can only act on gridded data. We introduce a function generator to eliminate the strong coupling relationship between model size and data size. The versatility of point cloud data enables it to handle a variety of different types of data. At the same time, by designing a point cloud message extractor, the model size of the extractor is not limited by data resolution and can receive multimedia data of different sizes. The experiments show that our scheme can achieve 96.88% message extraction accuracy when the embedding capacity is 1 bpp. When the pruning rate is 0.3, the message extraction accuracy can still reach 82.21%, which has good robustness. It also has advantages in the quality of the stego-media. In the future, we will consider applying implicit neural representation technology to generative steganography for data with a time axis such as video and audio to construct a completely universal implicit representation generative steganography scheme.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and M.Z.; methodology, Y.Z. and J.L.; software, Y.K.; validation, P.L. and Y.Z.; formal analysis, Y.Z.; investigation, J.L.; resources, M.Z.; data curation, Y.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.L.; visualization, P.L.; supervision, Y.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study did not involve humans or animals.
Informed Consent Statement
This study did not involve humans.
Data Availability Statement
Due to the involvement of subsequent research, the data provided in this study can be provided at the request of the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| GS | Generative Steganography |
| GAN | Generative Adversarial Network |
| INR | Implicit Neural Representation |
| GIS | Generative Implicit Steganography |
References
- Goodfellow, I.J.; Pouget-Abadie, J.; Mirza, M.; Xu, B.; Warde-Farley, D.; Ozair, S.; Courville, A.C.; Bengio, Y. Generative adversarial networks. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Computing Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT), Kharagpur, India, 6–8 July 2021; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hayes, J.; Danezis, G. Generating steganographic images via adversarial training. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; pp. 1954–1963. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.; Shin, C.; Choi, J.; Jung, D.; Yoon, S. Diffusion-Stego: Training-free Diffusion Generative Steganography via Message Projection. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.18726. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2006.11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, P.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Z.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, S. Generative Steganography Diffusion. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.03472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Dhariwal, P. Glow: Generative Flow with Invertible 1 × 1 Convolutions. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1807.03039. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Welling, M. Auto-Encoding Variational Bayes. arXiv 2013, arXiv:1312.6114. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, K.; Chen, K.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N. Provably secure generative steganography based on autoregressive model. In Proceedings of the Digital Forensics and Watermarking, Jeju Island, Republic of Korea, 22–24 October 2018; Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; Volume 11378, pp. 55–68. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, H.; Chen, D.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N. When Provably Secure Steganography Meets Generative Models. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.03732v2. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, D.; Wang, L.; Jiang, W.; Zheng, S.; Li, B. A novel image steganography method via deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 38303–38314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, H.; Harit, R.; Chen, X.; Sun, X. Coverless image steganography without embedding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Cloud Computing and Security, Geneva, Switzerland, 22–27 March 2015; pp. 123–132. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.L.; Yi, C.; Xiao, M.S. Coverless information hiding based on bag-of-words model of image. J. Appl. Sci. 2016, 34, 527–536. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Z.; Ke, Y.; Lei, Y.-Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X. Digital cardan grille: A modern approach for information hiding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence, Shanghai, China, 13–15 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Kishore, V.; Chen, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Weinberger, K.Q.; Weinberger. Fixed neural network steganography: Train the images, not the network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations, Virtually, 25–29 April 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, J.; Luo, P.; Ke, Y.; Cai, S. INR-Based Generative Steganography by Point Cloud Representation. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2410.11673. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, W.; Pan, X.; Ke, Y. Implicit neural representation steganography by neuron pruning. Multim. Syst. 2024, 30, 266. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Sun, W.; Pan, X.; Ke, Y. StegaINR4MIH: Steganography by implicit neural representation for multi-image hiding. J. Electron. Imaging 2024, 33, 063017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ming, Z.; Jun, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ke, Y. Coverless information hiding based on generative adversarial networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1712.06951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, J.; Schaefer, G.; Fang, H. Image Disentanglement Autoencoder for Steganography Without Embedding. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 19–24 June 2022; pp. 2303–2312. [Google Scholar]
- Volkhonskiy, D.; Nazarov, I.; Borisenko, B.; Burnaev, E. Steganographic Generative Adversarial Networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Vision, Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 26–28 April 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Dong, J.; Wang, W.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, X. SSGAN: Secure Steganography Based on Generative Adversarial Networks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1707.01613. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, Z. Image steganography based on foreground object generation by generative adversarial networks in mobile edge computing with internet of things. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 90815–90824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Yoo, Y.J.; Kwak, N. MC-GAN: Multi-conditional generative adversarial network for image synthesis. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.01123. [Google Scholar]
- Mielikainen, J. LSB Matching revisited. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2006, 13, 285–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, K.; Zeng, K.; Zhang, W.; Yu, N. Provably Secure Robust Image Steganography. IEEE Trans. Multim. 2024, 26, 5040–5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Huang, Y. VAE-Stega: Linguistic Steganography Based on Variational Auto-Encoder. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2021, 16, 880–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L.; Xie, X.; Zhou, Y. Plug-and-Hide: Provable and Adjustable Diffusion Generative Steganography. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.04878. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Li, S.; Li, G.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, X. Securing Fixed Neural Network Steganography. In Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 29 October–3 November 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Li, S.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, X. Cover-separable Fixed Neural Network Steganography via Deep Generative Models. In Proceedings of the 32nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM’24), Melbourne, Australia, 28 October–1 November 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; Yin, Z.; Zhang, X. RFNNS: Robust Fixed Neural Network Steganography with Popular Deep Generative Models. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2505.04116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Mao, H.; Dally, W.J. Deep Compression: Compressing Deep Neural Network with Pruning, Trained Quantization and Huffman Coding. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1510.00149. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Sun, M.; Zhou, T.; Huang, G.; Darrell, T. Rethinking the Value of Network Pruning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.05270. [Google Scholar]
- Frankle, J.; Dziugaite, G.K.; Roy, D.M.; Carbin, M. Pruning Neural Networks at Initialization: Why are We Missing the Mark? arXiv 2020, arXiv:2009.08576. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.J. DDMI: Domain-Agnostic Latent Diffusion Models for Synthesizing High-Quality Implicit Neural Representations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.12517. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Luo, P.; Ke, Y. Hiding Functions within Functions: Steganography by Implicit Neural Representations. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.04743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Yang, S.; Yoo, C.D.; Kim, J. Implicit Steganography Beyond the Constraints of Modality. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Krakow, Poland, 30 September–5 October 2023; pp. 289–304. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Liu, J.; Ke, Y.; Liu, M. Image steganography based on generative implicit neural representation. J. Electron. Imaging 2024, 33, 063043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, E.; Teh, Y.W.; Doucet, A. Generative Models as Distributions of Functions. In Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, Virtually, 13–15 April 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, P.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Luo, G.; Qian, Z.; Zhou, Q. Generative Steganography Network. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (MM’22), Lisbon, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 1621–1629. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, P.; Abnar, S.; Gu, J.; Schwing, A.; Susskind, J.M.; Bautista, M.A. Diffusion Probabilistic Fields. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.00165. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Collins, K.M.; Tenenbaum, J.B.; Sitzmann, V. Learning Signal-Agnostic Manifolds of Neural Fields. In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems, Online, 6–14 December 2021; pp. 8320–8331. [Google Scholar]
- Mescheder, L.; Geiger, A.; Nowozin, S. Which Training Methods for GANs do actually Converge? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Stockholm, Sweden, 10–15 July 2018; pp. 3481–3490. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, W.; Qi, Z.A.; Li, F. PointConv: Deep Convolutional Networks on 3D Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 16–20 June 2019; pp. 9621–9630. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Aila, T.; Laine, S.; Lehtinen, J. Progressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability, and Variation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), Vancouver Convention Center, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Karras, T.; Laine, S.; Aittala, M.; Hellsten, J.; Lehtinen, J.; Aila, T. Analyzing and Improving the Image Quality of StyleGAN. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Online, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 8110–8119. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Guo, Q.; Cheung, K.C.; See, S.; Wan, R. CopyRNeRF: Protecting the CopyRight of Neural Radiance Fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Q.; Luo, Z.; Cheung, K.C.; See, S.; Wan, R. Protecting NeRFs’ Copyright via Plug-and-Play Watermarking Base Model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, B. StegExpose—A Tool for Detecting LSB Steganography. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1410.6656. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).