Preliminary Proposal for Standardizing the Protocol for the Determination of Microplastics’ Influence on the CO2 and/or CH4 Emission in Agricultural Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Targeted Review of Methodologies
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Review of Approaches Used to Determine CO2 and/or CH4 Emissions in Agricultural Soils
3. Results
4. Discussion
4.1. Objectives of the Standardization of the Methodology
- (1)
- The identification of key types of added polymers specific to agricultural soils;
- (2)
- The determination of applied concentrations comparable to those actually detected in soil under natural conditions, also including the predicted future level of pollution;
- (3)
- The determination of uniform experimental conditions and the selection of a uniform method of CO2 and/or CH4 emission determination;
- (4)
- To ensure qualitative control of MP pollution from outside.
4.2. Determination of Types and Concentrations of MPs and Experimental Conditions
4.2.1. Sources of Contamination of Agricultural Soils with MPs
- (a)
- The application of sewage sludge;
- (b)
- The use of compost;
- (c)
- The use of controlled-release fertilizers (CRF), plant protection products using capsule suspension (CSPs), and seed film;
- (d)
- The application of mulch film.
- (a)
- Sewage sludge.
- (b)
- Compost utilization.
- -
- The extensive use of plastic products in poultry and livestock production (feed packaging bags, feed transportation pipelines, etc.);
- -
- The ingestion of MPs contaminated feed by livestock and poultry, which subsequently excrete MF in their feces;
- -
- MPs from the environment can penetrate manure during composting and transportation.
- (c)
- The use of controlled-release fertilizers (CRFs), plant protection products using capsule suspension (CSPs) and seed film coating.
- -
- For CSPs (Capsule Suspension Products): polyurethane (PU), polylactic acid (PLA), ethylcellulose (EC), and styrene-acrylate (SA) copolymers;
- -
- For CRFs: PE, PP, ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA), sulfur-coated (S-polymers), polycaprolactone (PCL), polylactic acid (PLA), and hydrogels polyacrylamide (PAM).
- (d)
- Application of mulching film.
4.2.2. Typical and Limit Concentrations of MPs in Soils
4.2.3. Determination of Incubation Time
4.2.4. Determination of Types and Concentrations of MPs
4.3. Prevention of External Contamination
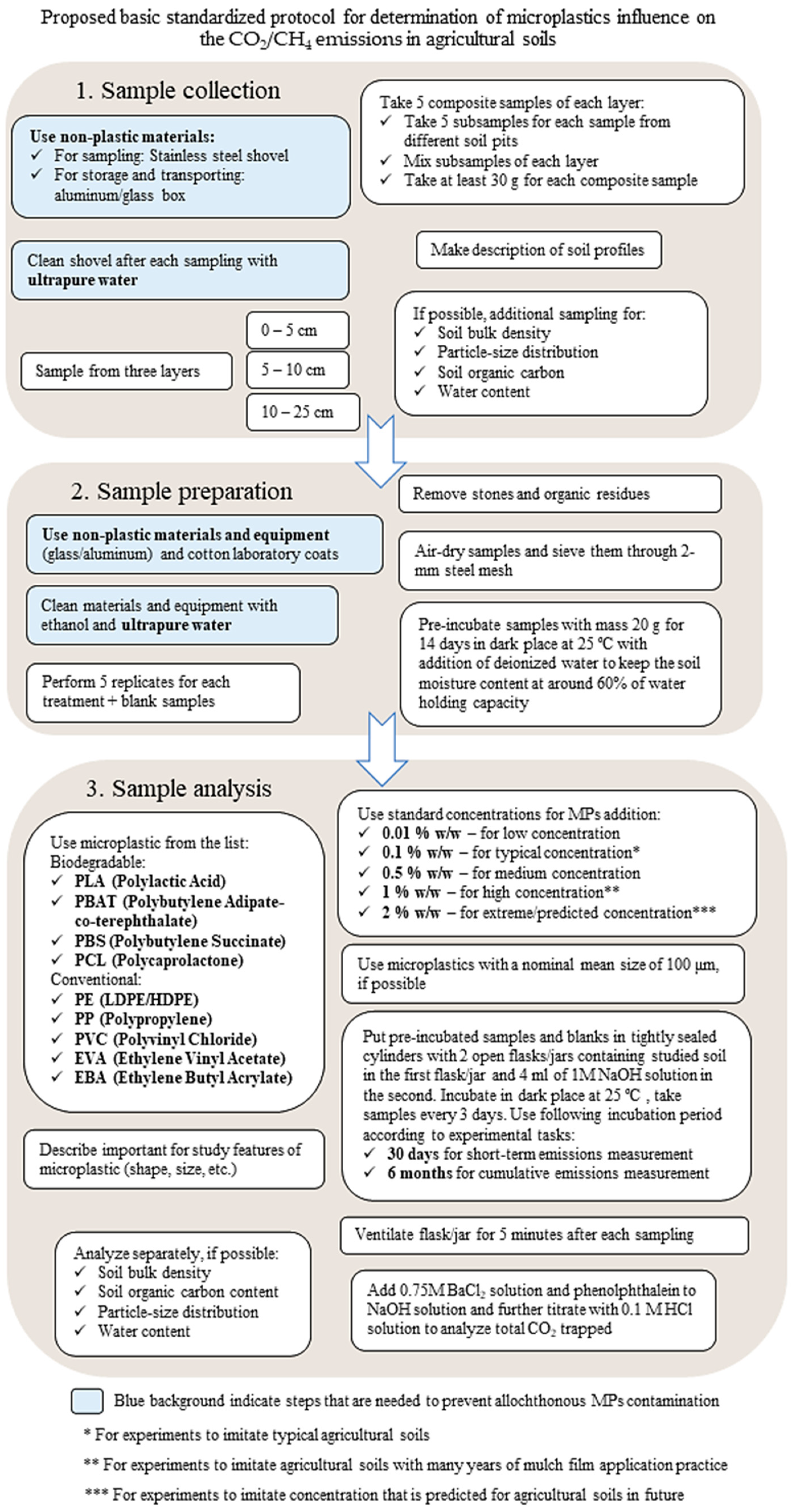
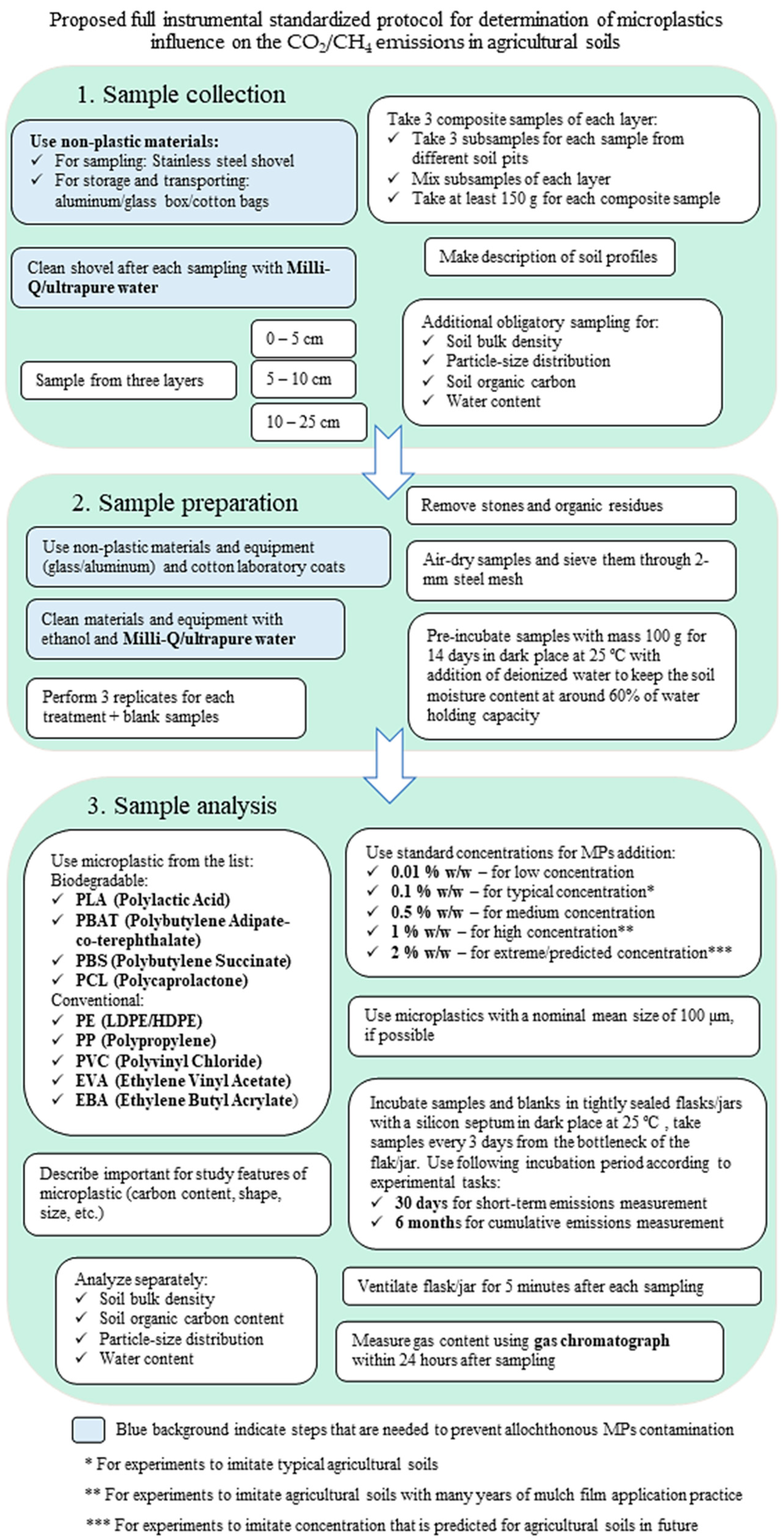
5. Conclusions
- Sample collection
- -
- Comply with external contamination control methods: use non-plastic materials for sample collection and transport (metal scoop, glass/metal boxes or for weight reduction and compactness cotton bags; rinse equipment with distilled water).
- Sample preparation
- -
- Observe methods to control external contamination (non-plastic laboratory equipment where possible, cotton lab coats, use distilled water to moisten soils).
- Sample analysis
- -
- -
- Adhere to current and/or predicted concentrations that are realistic for agricultural soils;
- -
- Use a temperature of 25 °C for the incubation of samples that is easily achievable, maintainable, and common in agricultural areas;
- -
- Adhere to a uniform duration of the experiment (30 days for short-term emissions measurement and 6 months for cumulative effect assessments);
- -
- Select a gas chromatography method for determining the results.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MPs | Microplastics |
| OC | Organic carbon |
| SOC | Soil organic carbon |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| DOM | Dissolved organic matter |
| CRFs | Controlled-release fertilizers |
| CSPs | Capsule suspensions |
| LDPE | Low-density polyethylene |
| HDPE | High-density polyethylene |
| SW | Sewage sludge |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| PBAT | Polybutylene adipate terephthalate |
| PBS | Polybutylene succinate |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| HBC | Hydrochar |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PPC | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| EC | Ethylcellulose |
| SA | Copolymers (Styrene-Acrylate) |
| EVA | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate |
| EBA | Ethylene butyl acrylate |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone |
| PVA | Polybutylene succinate |
References
- Pilapitiya, P.G.C.N.T.; Ratnayake, A.S. The world of plastic waste: A review. Clean. Mater. 2024, 11, 100220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.C.; Olsen, Y.; Mitchell, R.P.; Davis, A.; Rowland, S.J. Lost at sea: Where is all the plastic? Science 2004, 304, 838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, S.; van Franeker, J.A. Quantitative overview of marine debris ingested by marine megafauna. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 151, 110858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meaza, I.; Toyoda, J.; Wise, J. Microplastics in Sea Turtles, Marine Mammals and Humans: A One Environmental Health Perspective. Front. Environ. Sci. 2021, 8, 575614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nosova, A.O.; Uspenskaya, M.V. Microplastics in soil: Impact on ecosystems, potential sources and analytical research methods (review). Yuzhno-Sib. Nauchn. Vestn. 2022, 4, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Liu, Y.F. The distribution of microplastics in soil aggregate fractions in southwestern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 642, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Lu, B.; Guo, W.S.; Tang, X.Y.; Wang, X.F.; Xue, Y.H.; Wang, L.; He, X. Distribution of microplastics in mulched soil in Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2021, 14, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corradini, F.; Meza, P.; Eguiluz, R.; Casado, F.; Huerta-Lwanga, E.; Geissen, V. Evidence of microplastic accumulation in agricultural soils from sewage sludge disposal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, C.J.; Lügger, K.; Heller, C. Mikroplastik in Auenböden der Boden—Dauerbeobachtung. Untersuchungen zur Raum-Zeitlichen Variabilität am Beispiel Hessens; Erich Schmidt Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rillig, M.C.; Ingraffia, R.; de Souza Machado, A.A.; Horton, A.A. Microplastic effects on carbon cycling processes in soils. PLoS Biol. 2021, 19, e3001130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balesdent, J.; Basile-Doelsch, I.; Brun, J.J.; Chéron, C.; Christensen, B.T.; Guenet, B.; Abiven, S. Atmosphere–soil carbon transfer as a function of soil depth. Nature 2018, 559, 599–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, G. Soil erosion affects variations of soil organic carbon and soil respiration along a slope in Northeast China. Ecol. Process. 2019, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyukin, N.Y.; Gutnikov, V.A. Dinamika sel’skokhozyaystvennykh resursov mira [Dynamics of world agricultural resources]. Gos. Upr. Elektron. Vestn. 2017, 64, 159–176. (In Russian) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.; Su, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, W.; Wu, D. Could soil microplastic pollution exacerbate climate change? A meta-analysis of greenhouse gas emissions and global warming potential. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 118945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafea, L.; Yap, J.; Beriot, N.; Felde, V.J.M.N.L.; Okoffo, E.D.; Enyoh, C.E.; Peth, S. Microplastics in agroecosystems: A review of effects on soil biota and key soil functions. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2022, 185, 5–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainberg, A.; Abakumov, E.; Nizamutdinov, T. Recent Insights into Microplastic Pollution and Its Effects on Soil Carbon: A Five-Year Ecosystem Review. Microplastics 2025, 4, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Xie, Y.; Wang, J.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, J.; Wei, H.; Ma, Y. Presence of different microplastics promotes greenhouse gas emissions and alters the microbial community composition of farmland soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 879, 162967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; Zhou, A.; Hua, Z.; Meng, H.; Zhu, F.; Li, S.; He, H. Microplastics alter soil carbon cycling: Effects on carbon storage, CO2 and CH4 emission and microbial community. Camb. Prism. Plast. 2024, 2, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socas-Hernández, C.; Miralles, P.; González-Sálamo, J.; Coscollà, C.; Hernández-Borges, J. Chapter 5—Sampling methods for microplastics determination in soil. In Microplastics in Agriculture and Food Science; Avino, P., Di Fiore, C., Farris, S., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2025; pp. 67–77. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, M.; Feng, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yao, H. Effects of microplastics on soil carbon dioxide emissions and the microbial functional genes involved in organic carbon decomposition in agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 80, 150714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barili, S.; Bernetti, A.; Sannino, C.; Montegiove, N.; Calzoni, E.; Cesaretti, A.; Gigliotti, G. Impact of PVC microplastics on soil chemical and microbiological parameters. Environ. Res. 2023, 229, 115891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rillig, M.C.; Hoffmann, M.; Lehmann, A.; Liang, Y.; Lück, M.; Augustin, J. Microplastic fibers affect dynamics and intensity of CO2 and N2O fluxes from soil differently. Microplast. Nanoplast. 2021, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Shi, J.; Yao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H. Comparative evaluation of the impacts of different microplastics on greenhouse gas emissions, microbial community structure, and ecosystem multifunctionality in paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 480, 135958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Gan, H.; Gao, M.; Zhou, B.; Xu, X.; Wang, X. Insights into effects of conventional and biodegradable microplastics on organic carbon decomposition in different soil aggregates. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 359, 124751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauscher, A.; Meyer, N.; Jakobs, A.; Bartnick, R.; Lueders, T.; Lehndorff, E. Biodegradable microplastic increases CO2 emission and alters microbial biomass and bacterial community composition in different soil types. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 182, 104714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Q.; Fan, P.; Xi, B.; Tan, W. Effects of microplastics on soil organic carbon and greenhouse gas emissions in the context of straw incorporation: A comparison with different types of soil. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Zhou, S.; Long, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, Z.; Xi, M.; Zheng, H. Long-term aged fibrous polypropylene microplastics promotes nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide, and methane emissions from a coastal wetland soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 896, 166332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Machado, A.A.; Lau, C.W.; Till, J.; Kloas, W.; Lehmann, A.; Becker, R.; Rillig, M.C. Impacts of Microplastics on the Soil Biophysical Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 9656–9665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, K.; Zheng, H.; Xi, M.; Jiang, Z. Effect of microplastics on soil greenhouse gas emissions: A global meta-analysis study. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 958, 178100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Tanentzap, A.J.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Xing, B.; Rillig, M.C.; Wang, J. Microplastics Generate Less Mineral Protection of Soil Carbon and More CO2 Emissions. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, 2409585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Tang, J.; Liu, X.; Liu, Q. Effects of microplastics on greenhouse gas emissions and the microbial community in fertilized soil. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 256, 113347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Ding, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Y.; Yao, H.; Ge, T. Microplastics shape microbial communities affecting soil organic matter decomposition in paddy soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 431, 128589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Wei, Z.; Agathokleous, E.; Zhang, B. Effect of microplastics on soil greenhouse gas emissions in agroecosystems: Does it depend upon microplastic shape and soil type? Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Zhao, C.; Dong, W.; Gong, W.; Dong, D. The impact of biodegradable plastics on methane and carbon dioxide emissions in soil ecosystems: A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy approach. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Yang, G.; Dou, P.; Qian, S.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Y.; Fanin, N. Microplastics negatively affect soil fauna but stimulate microbial activity: Insights from a field-based microplastic addition experiment. Proc. R. Soc. B 2020, 287, 20201268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimek, B.; Grzyb, D.; Łukiewicz, B.; Niklińska, M. Microplastics increase soil respiration rate, decrease soil mesofauna feeding activity and change enchytraeid body length distribution in three contrasting soils. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 201, 105463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakin, E.; Dilekoğlu, M.F.; Yanardağ, İ.H. Unseen threat: The devastating impact of microplastics on soil health in agricultural lands. Catena 2025, 253, 108904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozano, Y.M.; Aguilar-Trigueros, C.A.; Onandia, G.; Maaß, S.; Zhao, T.; Rillig, M.C. Effects of microplastics and drought on soil ecosystem functions and multifunctionality. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 58, 988–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Ji, Y.; Feng, Y.; Feng, Y.; Yang, Z. Influence of polyethylene terephthalate microplastic and biochar co-existence on paddy soil bacterial community structure and greenhouse gas emission. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 292 Pt B, 118386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S. Microplastic Pollution Promotes Soil Respiration: A Global-Scale Meta-Analysis (GCB Appendix Dataset). figshare Dataset. 2024. Available online: https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/_b_Microplastic_pollution_promotes_soil_respiration_a_global-scale_b_b_meta-analysis_b_GCB_Appendix_Dataset_/26124409/1?file=47299525 (accessed on 7 September 2025).
- Zhang, J.; Ding, W.; Wang, S.; Ha, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, W.; Zhao, M.; Zou, G.; Chen, Y. Pollution characteristics of microplastics in greenhouse soil profiles with the long-term application of organic compost. Resour. Environ. Sustain. 2024, 17, 100165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmi, A.; Al-Khaldy, A.; AlOlayan, M. Sewage sludge land application: Balancing act between agronomic benefits and environmental concerns. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, X.; Ding, W.; Wang, X.; Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Zou, G.; Chen, Y. Long-term application of organic compost is the primary contributor to microplastic pollution of soils in a wheat–maize rotation. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 866, 161123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, N.; Ding, W.; Han, B.; Zhao, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Cao, B.; Zou, G.; Chen, Y. Microplastic pollution and the related ecological risks of organic composts from different raw materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 458, 131911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertahi, S.; Ilsouk, M.; Zeroual, Y.; Oukarroum, A.; Barakat, A. Recent trends in organic coating based on biopolymers and biomass for controlled and slow release fertilizers. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 341–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jia, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, J. Agricultural plastic mulching as a source of microplastics in the terrestrial environment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Wu, J.; Xiong, H.; Zeb, A.; Yang, T.; Su, X.; Su, L.; Liu, W. Effects of microplastics derived from polymer-coated fertilizer on maize growth, rhizosphere, and soil properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 318, 128571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumi, N.; Kusube, T.; Nagao, S.; Okochi, H. The role of coated fertilizer used in paddy fields as a source of microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 161, 111727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Min, W.; Flury, M.; Gunina, A.; Lv, J.; Li, Q.; Jiang, R. Impact of long-term conventional and biodegradable film mulching on microplastic abundance, soil structure and organic carbon in a cotton field. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 356, 124367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, X.; Neal, A.L.; Crawford, J.W.; Mooney, S.J.; Bacq-Labreuil, A. Evolution of the transport properties of soil aggregates and their relationship with soil organic carbon following land use changes. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, B.; Zhang, P.; Jia, Z. Is biodegradable film an alternative to polyethylene plastic film for improving maize productivity in rainfed agricultural areas?—Evidence from field experiments. Agric. Water Manag. 2022, 272, 107868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Železnikar, Š.; Noč, M.; Zupanc, V.; Lwanga, E.H.; Drobne, D.; Pintar, M. Impact of conventional and biobased microplastics from mulch films on soil bulk density, hydraulic conductivity and water retention in two different soil types under wetting−drying cycles. Results Eng. 2025, 25, 104455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin-LaHue, D.; Ghimire, S.; Yu, Y.; Scheenstra, E.J.; Miles, C.A.; Flury, M. In-field degradation of soil-biodegradable plastic mulch films in a Mediterranean climate. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Rillig, M.C.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Liu, Y.; Yao, B.; Li, Y. Global Responses of Soil Carbon Dynamics to Microplastic Exposure: A Data Synthesis of Laboratory Studies. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 5821–5831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, C.; Xie, B. Microplastics and Soil Greenhouse Gas Emissions: A Critical Reflection on Meta-Analyses. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 18927–18935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Type of MPs | Soil Description | Concentration, % w/w | Incubation Time | Method of GHG Detection | Results of Experiments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FPP | Coastal wetland | 0.2, 2 | 60 days | Gas chromatography | Elevation in emissions | [27] |
| PET, PVC | Albic Luvisol | 0.4 | 40 days | FTIR spectroscopy and special flow systems | Elevation in emissions | [22] |
| LDPE, PBAT | Sandy loam, cropland | 0.1, 1 | NS | Gas chromatography | LDPE—no effect, PBAT—elevation of emissions | [25] |
| PLA, PP, LDPE | Surface soils from a rice-paddy field | 0.5, 1, 1.5 | 41 days | Gas chromatography | Reduction in emissions | [23] |
| PBC | Topsoil, agricultural site | 0.021 | 360 days | Closed chamber titration | Reduction in emissions in short-term | [21] |
| PE, PVC, PBAT, PLA | Surface silty soils | NS | 21 days | Fluorescence excitation–emission matrix spectroscopy, ultrahigh-resolution FTIR mass spectrometry | Elevation in emissions | [30] |
| PE | Chernozems, Ferrasols, Luvisols | NS | 56 days | Gas chromatography | Elevation in emissions in Ferrasols, No effect in Chernozems and Luvisols | [33] |
| LDPE | Loamy sand soils | NS | 287 days | Fluorescence measurement of hydrolytic enzymes, involved in carbon cycling | Elevation in emissions | [35] |
| PE | NS | 0.8 | 15 weeks | Closed chamber titration | Elevation in emissions | [36] |
| PE | Topsoil from greenhouses | NS | 90 days | Closed chamber titration | Reduction in emissions | [37] |
| PET | NS | 0.4–7 | 60 days | Infrared gas analyzer | Neutral | [38] |
| PET | Alluvial paddy soils | 0.2 | 60–120 days | Gas chromatography | Reduction in emissions | [39] |
| Conventional and biodegradable | Various | Various | >30 days | NS | Elevation in emissions | [40] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vainberg, A.; Kushnov, I.; Abakumov, E.; Polyakov, V. Preliminary Proposal for Standardizing the Protocol for the Determination of Microplastics’ Influence on the CO2 and/or CH4 Emission in Agricultural Soils. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011025
Vainberg A, Kushnov I, Abakumov E, Polyakov V. Preliminary Proposal for Standardizing the Protocol for the Determination of Microplastics’ Influence on the CO2 and/or CH4 Emission in Agricultural Soils. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011025
Chicago/Turabian StyleVainberg, Anastasia, Ivan Kushnov, Evgeny Abakumov, and Vyacheslav Polyakov. 2025. "Preliminary Proposal for Standardizing the Protocol for the Determination of Microplastics’ Influence on the CO2 and/or CH4 Emission in Agricultural Soils" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011025
APA StyleVainberg, A., Kushnov, I., Abakumov, E., & Polyakov, V. (2025). Preliminary Proposal for Standardizing the Protocol for the Determination of Microplastics’ Influence on the CO2 and/or CH4 Emission in Agricultural Soils. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11025. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011025








