Effect of Corn Straw Returning Under Different Irrigation Modes on Soil Organic Carbon and Active Organic Carbon in Semi-Arid Areas
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Experimental Area
2.2. Experimental Design and Agronomic Management
2.3. Soil Sample Collection and Preparation
2.4. Soil Analyses
2.5. Indicator Calculations
2.6. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Soil Organic Carbon Content
3.2. Soil Microbial Biomass Carbon
3.3. Soil Soluble Organic Carbon
3.4. Soil Easily Oxidizable Organic Carbon
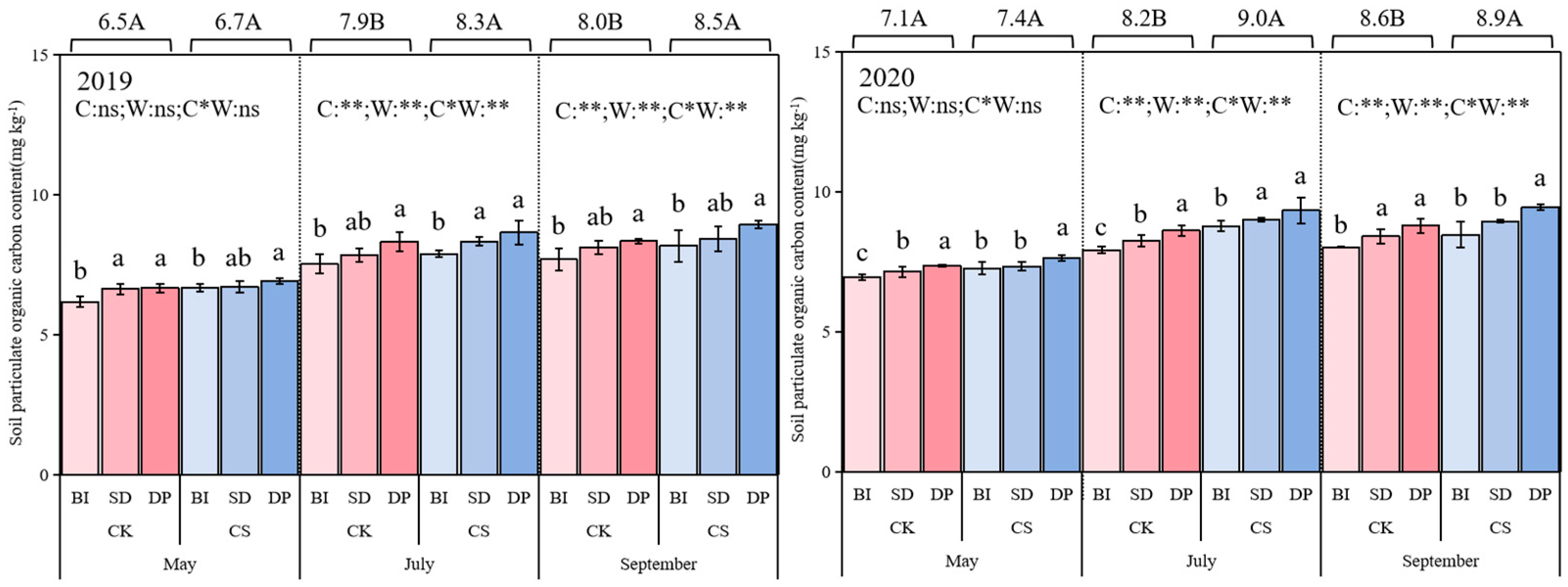
3.5. Soil Particulate Organic Carbon
3.6. Soil Carbon Storage Management Index and Oxidation Stability Coefficient
3.7. Soil Active Organic Carbon
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Straw Returning to the Field Under Different Irrigation Modes on Soil Organic Carbon
4.2. Different Straw Addition Methods Affect the Decomposition of Straw and Its Components
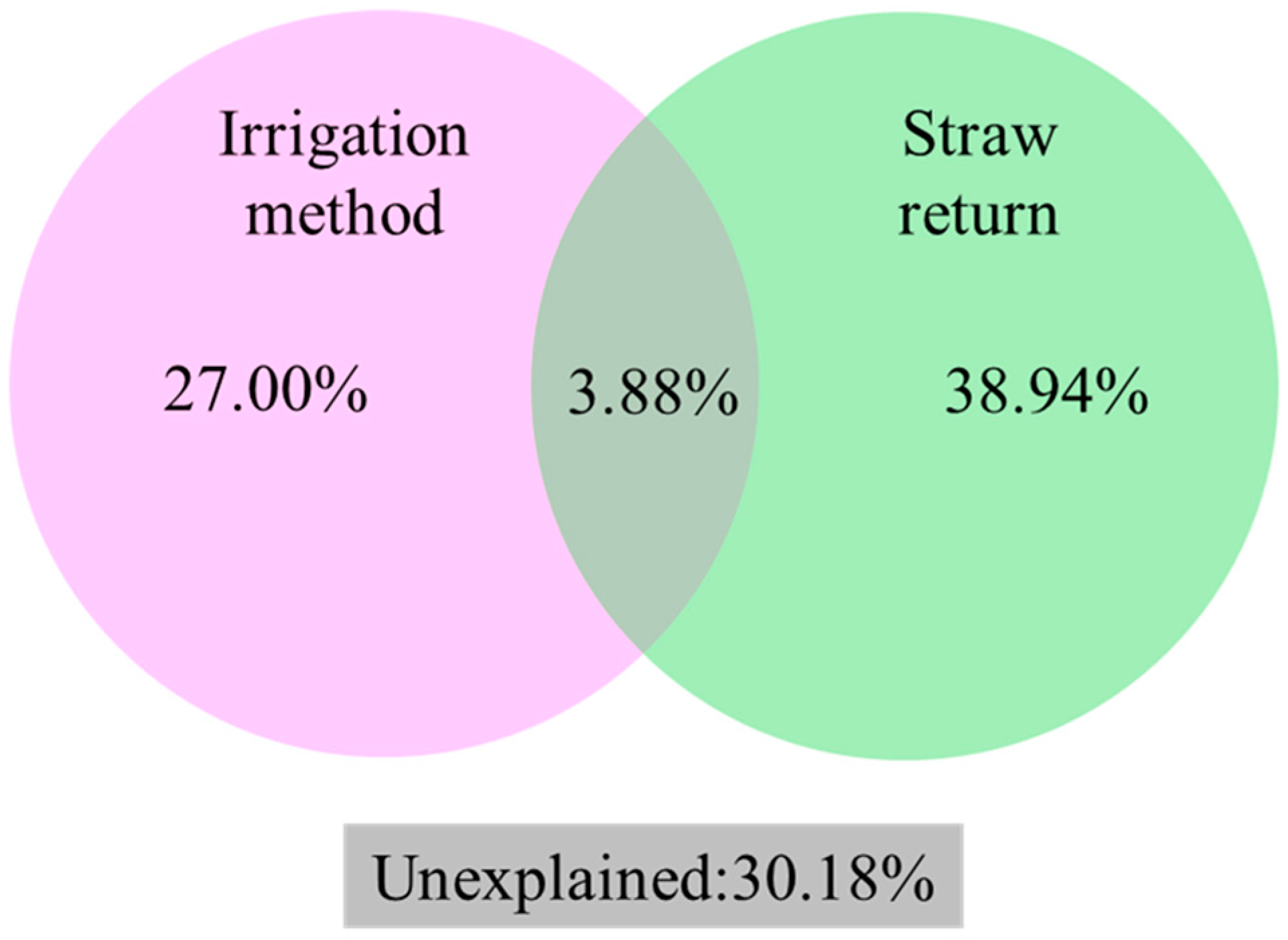
4.3. Impact of Straw Return on Soil Carbon Pool Management Index Under Different Irrigation Modes
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- As the growth period of corn advances, the combination of straw returning and drip irrigation provides sufficient carbon sources by accelerating straw decomposition, significantly increasing soil active organic carbon content, thereby enhancing soil active carbon storage and, ultimately, significantly increasing soil organic carbon (SOC) content. This indicates that the synergistic effect of straw returning and drip irrigation mode can help improve soil fertility and organic carbon levels and achieve soil fertilization.
- (2)
- From the perspective of soil carbon pool index, under the same straw treatment conditions, the Kos of shallow buried drip irrigation (SD) was significantly higher than that of flood irrigation (BI) and subsurface drip irrigation (DP), while the CPMI was lower than the latter two irrigation methods, indicating that SD treatment is beneficial for the accumulation of soil organic carbon and active organic carbon, while improving soil fertility.
- (3)
- In terms of soil active carbon content and soil carbon pool index, there was no significant difference between film mulching drip irrigation (DP) and shallow burying drip irrigation (SD), but the residual film produced by film mulching in DP treatment would cause a certain degree of soil pollution. Therefore, from the dual dimensions of enhancing soil active carbon pool and soil environmental sustainability, SD treatment has more significant comprehensive advantages.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Poeplau, C.; Begill, N.; Liang, Z.; Schiedung, M. Root litter quality drives the dynamic of native mineral-associated organic carbon in a temperate agricultural soil. Plant Soil 2023, 491, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, W.; Si, P.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B.; Yan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, E. Linkage between soil organic carbon and the utilization of soil microbial carbon under plastic film mulching in a semi-arid agroecosystem in China. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 65, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Min, F.; Yu, D.; Xin, Z.; Li, L.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Pan, J. Mean residence times of active and slow soil organic carbon pools in croplands across China. Catena 2021, 202, 105271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Nan, S.; Yang, X.; Qin, Y.; Ma, T.; Li, X.; Yu, Y.; Bodner, G. Macroaggregation is promoted more effectively by organic than inorganic fertilizers in farmland ecosystems of China-A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 221, 105394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliessbach, A.; Hany, R.; Rentsch, D.; Frei, R.; Eyhorn, F. DOC trail: Soil organic matter quality and soil aggregate stability in organic and conventional soils. In Proceedings of the 13th International IFOAM Scientific Conference, vdf Hochschulverlag, Zürich, Switzerland, 28–31 August 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez, A.F.; Daroub, S.H.; Gerber, S.; Jennewein, S.P.; Singh, M.P. Water management effect on soil oxidation, greenhouse gas emissions, and nitrogen leaching in drained peat soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2021, 85, 814–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougherty, S.W.; Bauer, J.E.; Pohlman, J.W. Exudation rates and delta C-13 signatures of tree root soluble organic carbon in a riparian forest. Biogeochemistry 2018, 137, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, X.; Jin, L.; Su, X.; Li, C.; Kou, J. Effects of biological soil crusts on soil labile organic carbon of patchy alpine meadows in the Source Zone of the Yellow River, West China. Catena 2023, 220, 106715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, S.; Schindlbacher, A.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, H.; Ming, A.; Lu, L.; Li, Z. Topsoil organic carbon increases but its stability declines after five years of reduced throughfall. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 156, 108221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, T.; Liao, J.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Ni, J.; Li, Y.; Jin, L.; Ruan, H. Organic fertilization promotes the accumulation of soil particulate organic carbon in a 9-year plantation experiment. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 34, 4741–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, L.H.; Loss, A.; Canton, L.; Souza, M.; Ferreira, G.W.; Kurtz, C.; Brunetto, G.; Lourenzi, C.R.; Lovato, P.-E.; Comin, J.-J. Carbon and nitrogen content in granulometric fractions of organic matter in soil aggregates under no-tillage and conventional tillage planting systems for onions. Idesia 2018, 36, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ur Rehman, S.; Ijaz, S.S.; Raza, M.A.; Din, A.M.U.; Khan, K.S.; Fatima, S.; Raza, T.; Mehmood, S.; Saeed, A.; Ansar, M. Soil organic carbon sequestration and modeling under conservation tillage and cropping systems in a rainfed agriculture. Eur. J. Agron. 2023, 147, 126840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, F.; Chang, H. Duration of continuous cropping with straw return affects soil organic carbon. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 39, 1096–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.B.; Gardner, W.D.; Mishonov, A.V.; Richardson, M.J. Model-based remote sensing algorithms for particulate organic carbon (POC) in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 118, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, J.; Lehmann, J.; Rondon, M.; Goodale, C. Fate of soil-applied black carbon: Downward migration, leaching and soil respiration. Glob. Change Biol. 2010, 16, 1366–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruf, T.; Emmerling, C. Soil organic carbon allocation and dynamics under perennial energy crops and their feedbacks with soil microbial biomass and activity. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 36, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupwayi, N.Z.; Clayton, G.W.; O’dOnovan, J.T.; Harker, K.N.; Turkington, T.K.; Rice, W.A. Soil microbiological properties during decomposition of crop residues under conventional and zero tillage. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2004, 84, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooch, Y.; Ehsani, S.; Akbarinia, M. Stoichiometry of microbial indicators shows clearly more soil responses to land cover changes than absolute microbial activities. Ecol. Eng. 2019, 131, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Sahni, D.; Arora, S.; Sehgal, M.; Srivastava, D.; Singh, A. Soil microbial biomass C and microbial activity as influenced by pesticide use in Paddy. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Resource Management for Food Security and Rural Livelihoods, New Delhi, India, 10–13 February 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Wang, C.; Pan, T.; Zeng, C. Effects of rice straw incorporation on active soil organic carbon pools in a subtropical paddy field. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 152, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, H.; Bao, L.; Zhou, J. Crop yields and soil organic carbon fractions as influenced by straw incorporation in a rice–wheat cropping system in southeastern China. Indian Med. J. 2018, 112, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, G.; Lefroy, R.; Lisle, L. Soil carbon fractions based on their degree of oxidation, and the development of a carbon management index for agricultural systems. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1995, 46, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moharana, P.C.; Biswas, D.R.; Ghosh, A.; Sarkar, A.; Bhattacharyya, R.; Meena, M.D. Effects of crop residues composts on the fractions and forms of organic carbon and nitrogen in subtropical Indian conditions. Soil Res. 2019, 58, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, M.; Flessa, H.; Dreves, A.; Ludwig, B. Is thermal oxidation at different temperatures suitable to isolate soil organic carbon fractions with different turnover? J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2010, 173, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Yang, X.; Shi, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, H. Biochar and nitrogen fertilizer co-application changed SOC content and fraction composition in Huang-Huai-Hai plain, China. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Ge, T.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, R.; Peñuelas, J.; Li, Y.; Lynn, T.M.; Jones, D.L.; Wu, J.; Kuzyakov, Y. Paddy soils have a much higher microbial biomass content than upland soils: A review of the origin, mechanisms, and drivers. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 326, 107798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; He, S.; Xiao, L.; Li, L.; Liu, M. Effects of Drought on Dissolved Organic Carbon Content in Grassland and Forest Soils. Russ. J. Ecol. 2023, 54, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lu, X. Changes of soil labile organic carbon fractions and their relation to soil microbial characteristics in four typical wetlands of Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, Y.-P.; Deng, Q.; Jiang, J.; Cao, N.; Tang, X.; Zhang, D.; Yan, J. Soil acidification enhanced soil carbon sequestration through increased mineral protection. Plant Soil 2024, 503, 529–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Lv, X.; Cao, N.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, Y. Alterations of soil labile organic carbon fractions and biological properties under different residue-management methods with equivalent carbon input. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2020, 161, 103821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Nie, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Liu, W. Recovery efficiency and loss of 15N-labelled urea in a rice-soil system under water saving irrigation in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 222, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.; Yin, J.; Calabrese, S. Optimal drainage timing for mitigating methane emissions from rice paddy fields. Geoderma 2021, 394, 114986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, A.M.; O’Grady, D.; Leblanc, M.; Tweed, S.; Nelson, P.N.; Bird, M.I. Carbon Dioxide and Methane Emissions from a Wet-Dry Tropical Floodplain in Northern Australia. Wetlands 2014, 34, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haynes, R.J.; Swift, R.S. Stability of soil aggregates in relation to organic constituents and soil water content. J. Soil Sci. 1990, 41, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.L.; Reis, J.L.; Martins, O.C.; Castanheira, N.L.; Serralheiro, R.P. Comparative Assessment of Infiltration, Runoff and Erosion of Sprinkler Irrigated Soils. Biosyst. Eng. 2003, 86, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-X.; Feng, S.-Y.; Hou, X.-Y.; Kang, S.-Z.; Han, J.-J. Potato growth with and without plastic mulch in two typical regions of Northern China. Field Crops Res. 2009, 110, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhou, Y.; He, H. Effects of rehabilitation through afforestation on soil aggregate stability and aggregate-associated carbon after forest fires in subtropical China. Geoderma 2020, 376, 114548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, P.; Nie, T.; Zhang, Z.; Du, S. Straw return alleviates the greenhouse effect of paddy fields by increasing soil organic carbon sequestration under water-saving irrigation. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 287, 108434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Guo, Z. Straw application and soil organic carbon change: A meta-analysis. Soil Water Res. 2021, 16, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.L.; Bamberg, A.L.; Pereira, I.d.S.; Monteiro, A.B.; Potes, M.d.L.; de Lima, C.L.R. Water treatment residuals for ameliorating sandy soils: Implications in environmental, soil and plant growth parameters. Geoderma 2022, 407, 115537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seneviratne, S.I.; Viterbo, P.; Lüthi, D.; Schär, C. Inferring Changes in Terrestrial Water Storage Using ERA-40 Reanalysis Data: The Mississippi River Basin. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2039–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, K.; Huang, L.; Ji, Z.; Jiang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Responses of absolute and specific enzyme activity to consecutive application of composted sewage sludge in a Fluventic Ustochrept. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, J. Responses of soil organic carbon components and their sensitivity to karst rocky desertification control measures in Southwest China. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Han, X.; Wang, S.; Li, L.-J. Dynamics and composition of soil organic carbon in response to 15 years of straw return in a Mollisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 215, 105221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Xia, B. Response of microbial activity in the rhizosphere of maize seedlings (Zea mays L.) to pyrene contamination. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Yao, X.; Zeng, W.; Wang, W. Latitudinal and depth patterns of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in grasslands of an agro-pastoral ecotone. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 3833–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noori, Z.; Delavar, M.A.; Safari, Y.; Alavi-Siney, S.M. Reclamation of a calcium carbonate sodium soil with combined amendments: Interactive effects of chemical and organic materials on soil chemical properties. Arab J Geosci. 2021, 14, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dachraoui, M.; Sombrero, A. Soil organic carbon accumulation and carbon dioxide emissions during a 6-year research in irrigated continuous maize under two tillage systems in semiarid Mediterranean conditions. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2021, 19, e1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chi, F.Q.; Wei, D.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.M.; Guo, W.Y.; Xu, M. Effects of Different Organic Materials Returning to Field on the Content of Active Organic Carbon in Black Soil. Soybean Sci. 2016, 35, 975–980. [Google Scholar]
- Rühlmann, J.; Ruppel, S. Effects of organic amendments on soil carbon content and microbial biomass-results of the long-term box plot experiment in Grossbeeren. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2005, 51, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beare, M.H.; Wilson, P.E.; Fraser, P.M.; Butler, R.C. Management Effects on Barley Straw Decomposition, Nitrogen Release, and Crop Production. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.J.; Wu, X.H.; Jian, Y.; Yuan, H.Z.; Zhou, P.; Ge, T.D.; Tong, C.L.; Zou, D.S.; Wu, J.S. Carbon Dioxide Assimilation Potential, Functional Gene Amount and RubisCO Activity of Autotrophic Microorganisms in Agricultural Soils. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2014, 35, 1144–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.L.; Bettany, J.R. Influence of Freeze-Thaw and Flooding on the Loss of Soluble Organic Carbon and Carbon Dioxide from Soil. J. Environ. Qual. 1993, 22, 709–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Smith, P.; Li, L.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Shen, S.; Chen, X. Combined inorganic/organic fertilization enhances N efficiency and increases rice productivity through organic carbon accumulation in a rice paddy from the Tai Lake region, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 131, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.T.; He, X.H.; Xu, M.G.; Zhang, W.J.; Yang, X.Y.; Huang, S.M. Long-term fertilization increases soil organic carbon and alters its chemical composition in three wheat-maize cropping sites across central and south China. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 177, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Jin, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, Y.-Y.; Cui, N.; Wei, W. Effect of Different Irrigation Methods on Dissolved Organic Carbon and Microbial Biomass Carbon in the Greenhouse Soil. Agric. Sci. China 2010, 9, 1175–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zen, Q.C.; Li, X.; Dong, Y.H.; Li, Y.Y. Soil microbial biomass nitrogen and carbon, water soluble nitrogen and carbon under different arbors forests on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2015, 35, 3598–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aminiyan, M.M.; Sinegani, A.A.S.; Sheklabadi, M. The effect of zeolite and some plant residues on soil organic carbon changes in density and soluble fractions: Incubation research. Agric. Adv. 2016, 5, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, W.; Bano, R.; Khatak, B.U.; Hussain, I.; Yousaf, M.; David, J. Temperature Sensitivity and Soil Organic Carbon Pools Decomposition under Different Moisture Regimes: Effect on Total Microbial and Enzymatic Activity. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 43, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaver, G.R.; Giblin, A.E.; Nadelhoffer, K.J.; Thieler, K.K.; Downs, M.R.; Laundre, J.A.; Rastetter, E.B. Carbon turnover in Alaskan tundra soils: Effects of organic matter quality, temperature, moisture and fertilizer. J. Ecol. 2010, 94, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Gu, J.; Yang, J. Effects of long-term straw returning on rice yield and soil properties and bacterial community in a rice-wheat rotation system. Field Crops Res. 2023, 291, 108800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badri, D.V.; Vivanco, J.M. Regulation and function of root exudates. Plant Cell Environ. 2010, 32, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Ayantobo, O.O.; Wang, Z. Effects of macro-plastics on soil hydrothermal environment, cotton yield, and fiber quality under mulched drip irrigation in the arid region of Northwest China. Field Crops Res. 2023, 302, 109060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Song, D.; Pu, X.; Dang, P.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H. Effect of different straw returning measures on resource use efficiency and spring maize yield under a plastic film mulch system. Eur. J. Agron. 2022, 134, 126461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitkenhead, J.A.; McDowell, W.H. Soil C:N ratio as a predictor of annual riverine DOC flux at local and global scales. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2000, 14, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.S. Local Coexistence of Deciduous-Forest Groundlayer Species Growing in Different Seasons. Ecology 1985, 66, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, X.; Gu, X.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Extreme drought slightly decreased soil labile organic C and N contents and altered microbial community structure in a subtropical evergreen forest. For. Ecol. Manag. 2018, 429, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Bai, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Cui, Y.; Hu, S.; Jonathan, M.A.; Dong, L.; Yu, X. Soil microbial trait-based strategies drive the storage and stability of the soil carbon pool in Robinia pseudoacacia plantations. Catena 2023, 222, 106894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, X.; Meng, Y.; Li, X.; Quan, X.; Shan, J.; Zhao, W.; Wang, H. Comparing the Effects of Biochar and Straw Amendment on Soil Carbon Pools and Bacterial Community Structure in Degraded Soil. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 751–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.P.; Wang, J.J.; Li, L.J. Responses of labile organic carbon components to different fertilization practices in white soil. Univ. Glasg. 2015, 34, 3734. [Google Scholar]
- Chaganti, V.N.; Ganjegunte, G.; Somenahally, A.; Hargrove, W.L.; Ulery, A.; Enciso, J.M.; Flynn, R. Response of soil organic carbon and soil health indicators to treated wastewater irrigation in bioenergy sorghum production on an arid soil. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2197–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, H.; Huang, C.; Ju, X. Effects of nitrogen management and straw return on soil organic carbon sequestration and aggregate-associated carbon. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2018, 69, 913–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.H.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yu, N.; Wand, W.C. Effect of irrigation methods on mineralization of soil organic nitrogen in protected field. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2009, 46, 869–877. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, K.; Ghoshal, N.; Singh, S. Soil carbon dioxide flux, carbon sequestration and crop productivity in a tropical dryland agroecosystem: Influence of organic inputs of varying resource quality. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2009, 42, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, P.; Peng, C.; Wang, J.; He, H.; Zhang, X. Long-term manure amendments enhance neutral sugar accumulation in bulk soil and particulate organic matter in a Mollisol. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 78, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
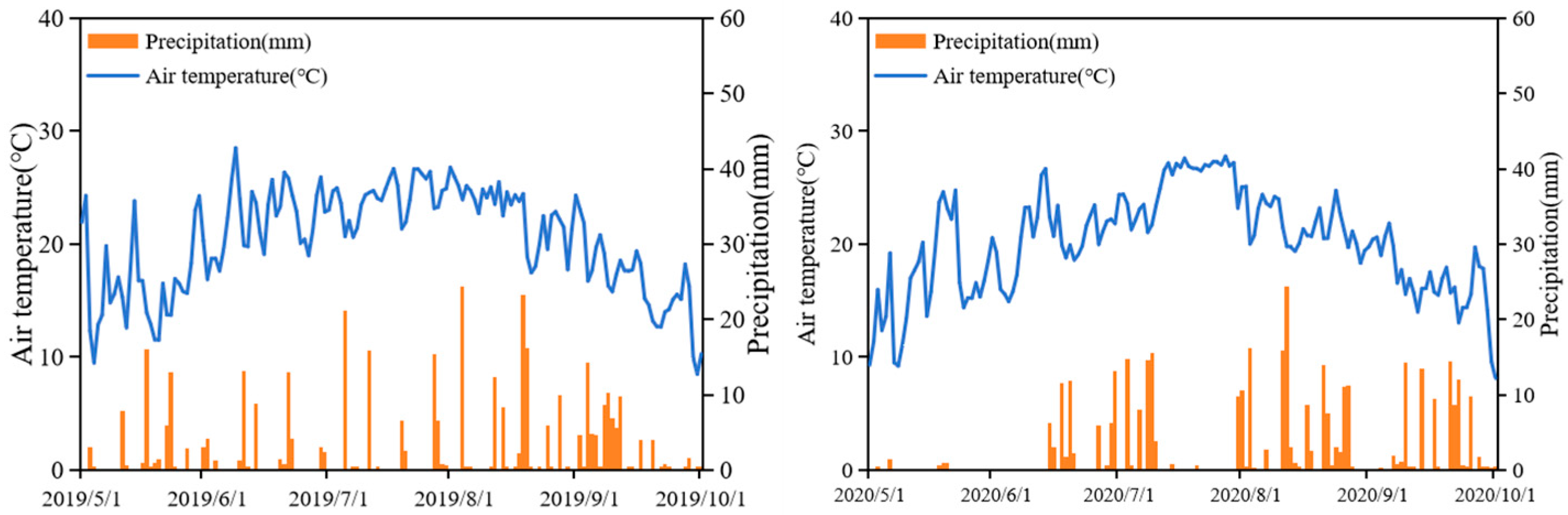

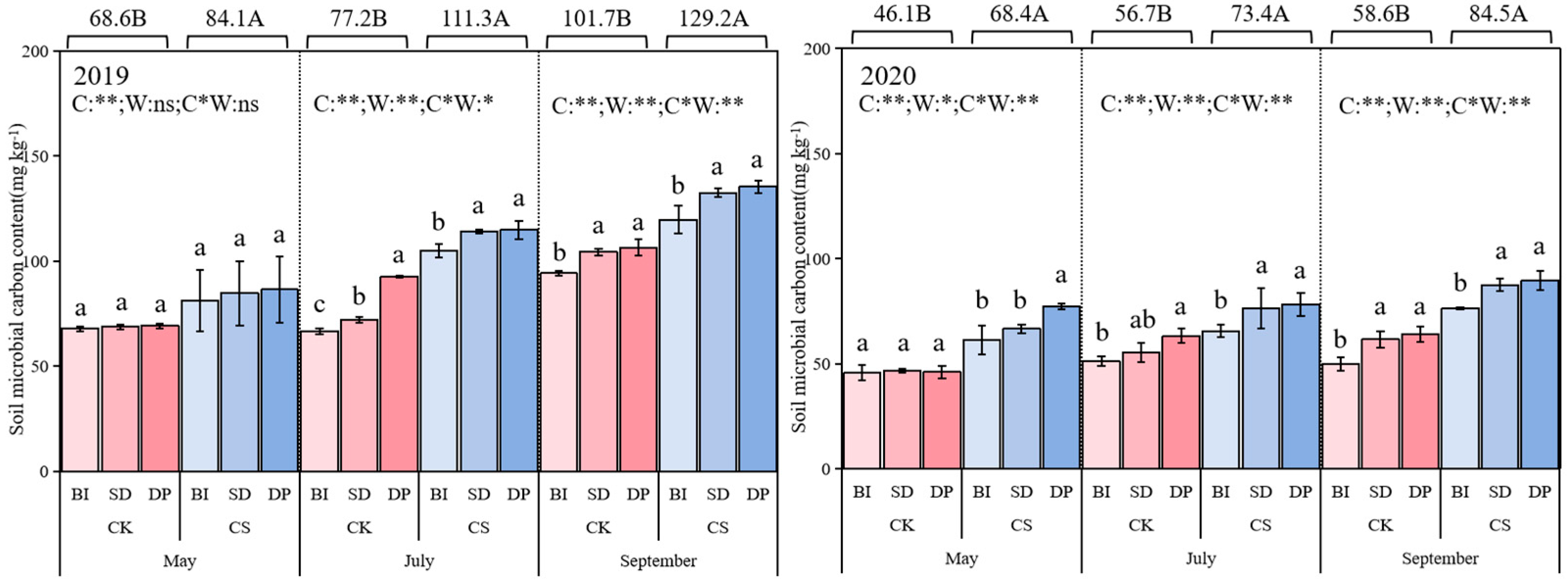
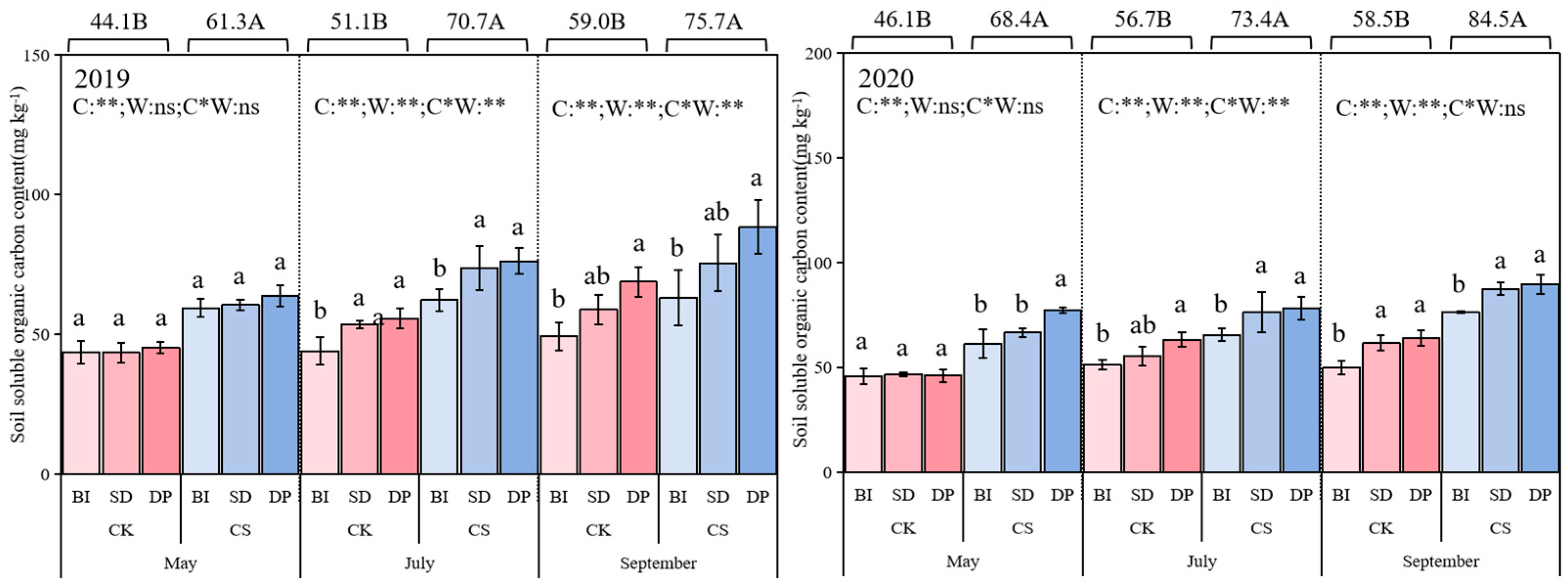
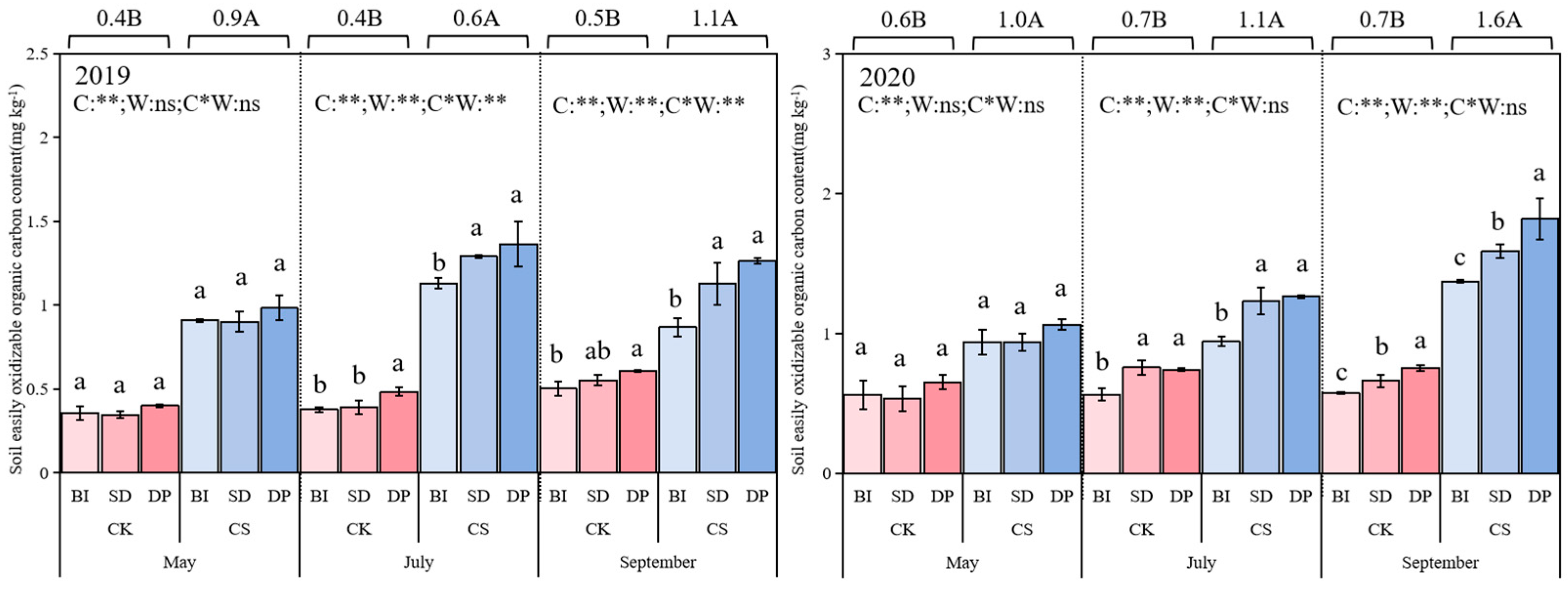
| Treatment | CPMI (%) | CPI | AI | A | Stable Organic Carbon (g/kg) | Kos | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | ||
| CK | BI | 68.8 ± 7.2 Bb | 77.6 ± 8.2 Bb | 1.1 ± 0.0 Ba | 1.1 ± 0.0 Bb | 0.7 ± 0.1 Bb | 0.7 ± 0.0 Bb | 0.02 ± 0 Bb | 0.03 ± 0 Bb | 16.4 ± 0.5 Aa | 16.2 ± 0.2 Ab | 42.0 ± 2.2 Ab | 37.0 ± 2.2 Ab |
| q | 60.8 ± 1.3 Bb | 62.0 ± 1.3 Bc | 1.1 ± 0.0 Ba | 1.1 ± 0 Bab | 0.6 ± 0.0 Bb | 0.6 ± 0.0 Bc | 0.02 ± 0 Bb | 0.02 ± 0 Bc | 16.5 ± 0.3 Aa | 16.8 ± 0.03 Aa | 47.3 ± 0.5 Aa | 47.5 ± 0.6 Aa | |
| DP | 85.3 ± 4.8 Ba | 94.0 ± 4.3 Ba | 1.1 ± 0.0 Ba | 1.1 ± 0.0 Ba | 0.8 ± 0.1 Ba | 0.9 ± 0.0 Ba | 0.03 ± 0 Ba | 0.03 ± 0 Ba | 16.4 ± 0.1 Aa | 17.0 ± 0.2 Aa | 33.9 ± 1.2 Ac | 32.0 ± 1.2 Ab | |
| CS | BI | 207.4 ± 6.2 Ab | 298.9 ± 9.1 Ab | 1.1 ± 0.0 Ac | 1.123 ± 0.0 Ab | 1.9 ± 0.1 Aa | 2.7 ± 0.1 Aa | 0.07 ± 0 Aa | 0.10 ± 0.1 Aa | 15.8 ± 0.1 Ab | 16.2 ± 0.3 Aa | 14.0 ± 0.3 Ba | 10.2 ± 0.2 Bb |
| SD | 238.9 ± 2.1 Aab | 254.4 ± 2.4 Ab | 1.1 ± 0.0 Ab | 1.2 ± 0.02 Aab | 2.2 ± 0.03 Aa | 2.2 ± 0.0 Ab | 0.08 ± 0 Aa | 0.08 ± 0.1 Ab | 16.0 ± 0.1 Bb | 16.8 ± 0.2 Aa | 12.4 ± 0.1 Ba | 12.2 ± 0.2 Ba | |
| DP | 252.9 ± 27.1 Aa | 352.9 ± 38.5 Aa | 1.1 ± 0.0 Aa | 1.2 ± 0.0 Aa | 2.2 ± 0.2 Aa | 3.0 ± 0.2 Aa | 0.08 ± 0.0 Aa | 0.11 ± 0.01 Aa | 16.7 ± 0.2 Ba | 16.9 ± 0.1 Ba | 12.3 ± 0.8 Ba | 9.2 ± 0.56 Bb | |
| ANOVA | |||||||||||||
| W | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | ** | * | * | |
| C | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| W × C | ** | ** | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Treatment | DOC/SOC (%) | SCE | POC/SOC (%) | qMBC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CK | BI | 0.28 ± 0.00 Bb | 3.01 ± 0.11 Bb | 45.0 ± 1.0 Ba | 0.49 ± 0.01 Bc |
| SD | 0.31 ± 0.01 Bb | 2.47 ± 0.08 Bc | 45.5 ± 0.2 Ba | 0.54 ± 0.01 Bb | |
| DP | 0.33 ± 0.01 Ba | 3.66 ± 0.04 Ba | 46.3 ± 0.4 Ba | 0.58 ± 0.01 Ba | |
| CS | BI | 0.39 ± 0.01 Ac | 6.7 ± 0.17 Ab | 46.7 ± 0.8 Ab | 0.60 ± 0.01 Ab |
| SD | 0.43 ± 0.00 Ab | 6.6 ± 0.07 Ab | 48.3 ± 0.5 Aab | 0.67 ± 0.02 Aab | |
| DP | 0.47 ± 0.00 Aa | 7.9 ± 0.31 Aa | 50.0 ± 0.2 Aa | 0.70 ± 0.02 Aa | |
| ANOVA | |||||
| W | ** | * | ** | ** | |
| C | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| W × C | ** | ** | ns | ns | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, W.; Wu, J.; Ma, X.; Duo, X.; Gu, Y. Effect of Corn Straw Returning Under Different Irrigation Modes on Soil Organic Carbon and Active Organic Carbon in Semi-Arid Areas. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011006
Cheng W, Wu J, Ma X, Duo X, Gu Y. Effect of Corn Straw Returning Under Different Irrigation Modes on Soil Organic Carbon and Active Organic Carbon in Semi-Arid Areas. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011006
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Wei, Jinggui Wu, Xiaochi Ma, Xinqu Duo, and Yue Gu. 2025. "Effect of Corn Straw Returning Under Different Irrigation Modes on Soil Organic Carbon and Active Organic Carbon in Semi-Arid Areas" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011006
APA StyleCheng, W., Wu, J., Ma, X., Duo, X., & Gu, Y. (2025). Effect of Corn Straw Returning Under Different Irrigation Modes on Soil Organic Carbon and Active Organic Carbon in Semi-Arid Areas. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 11006. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152011006





