Decision-Making for Product Form Image Based on ET-EEG Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- (2)
- The ET-EEG technique was used to collect behavioural, eye movement, and ERP data in the four conditions and to quantify the relationships among behavioural data, eye movement data, ERP data and image cognition.
- (3)
- The processing rules of user behaviour, visual perception and cognition during image decision-making were discussed in detail.
2. Product Image Evaluation Experiment
2.1. Construction of Kansei Image Space
2.2. Experimental Stimulus Collection and Image Semantic Evaluation
2.3. Experimental Design
2.3.1. Experimental Materials
2.3.2. Experimental Subjects
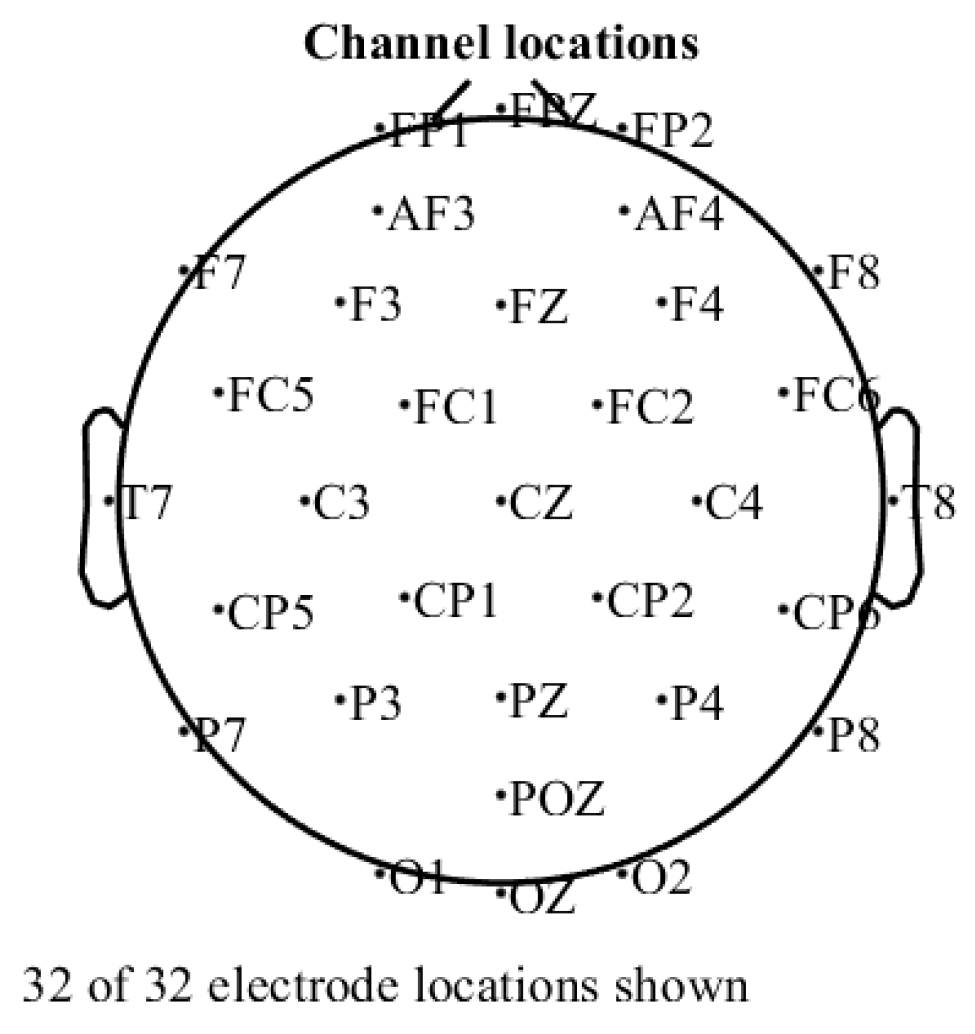
2.3.3. Experimental Equipment
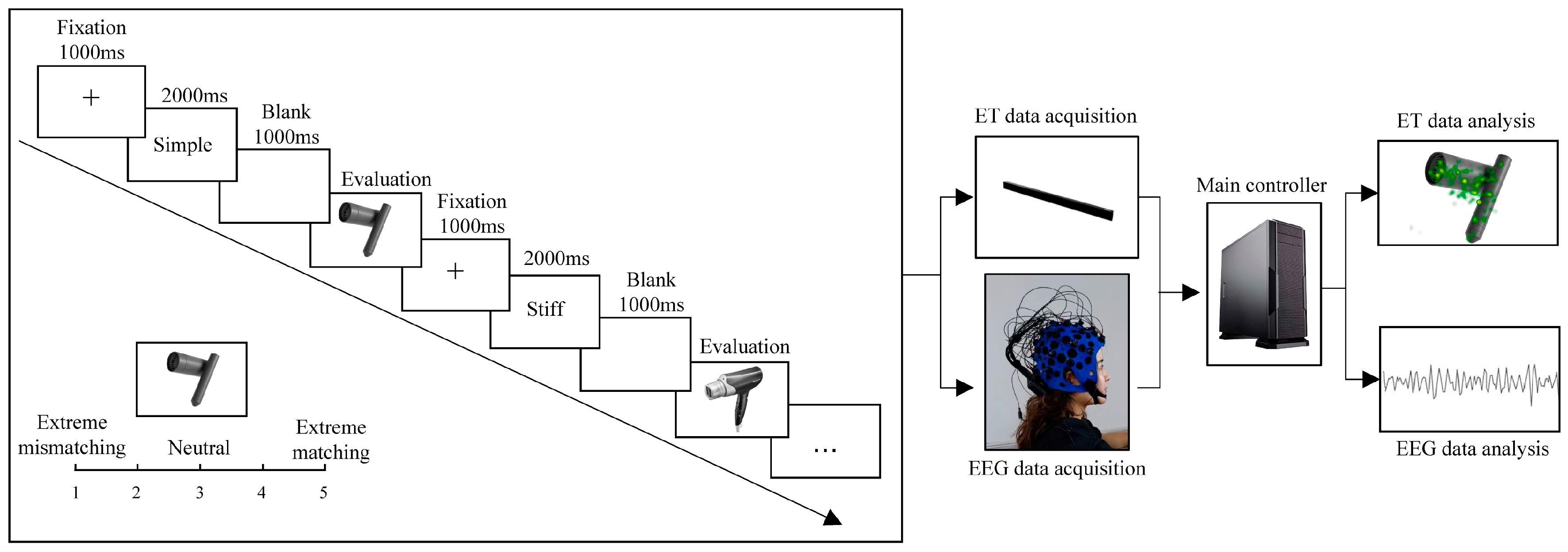
2.3.4. Experimental Process
3. Statistical Analysis
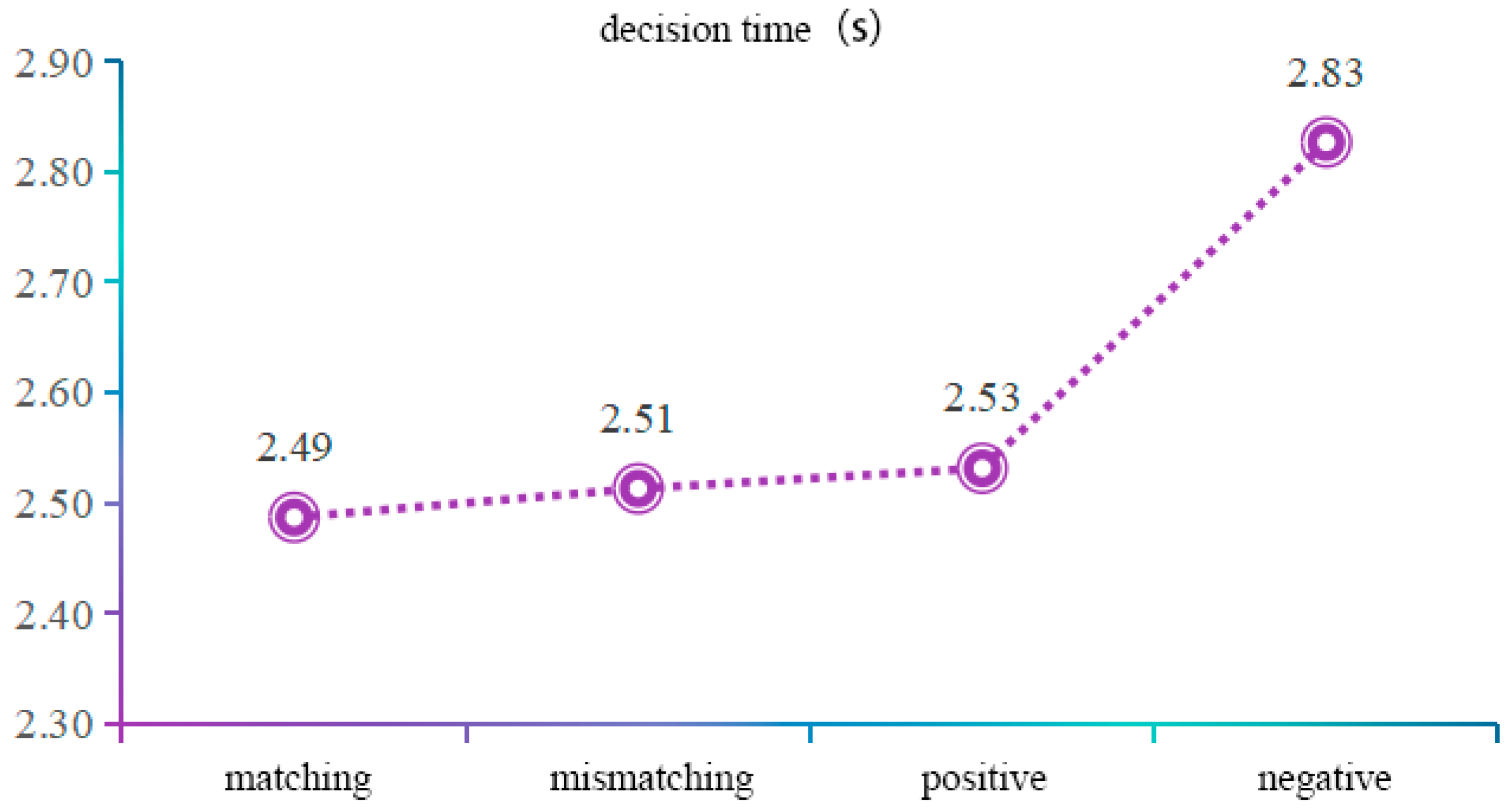
3.1. Behavioural Analysis
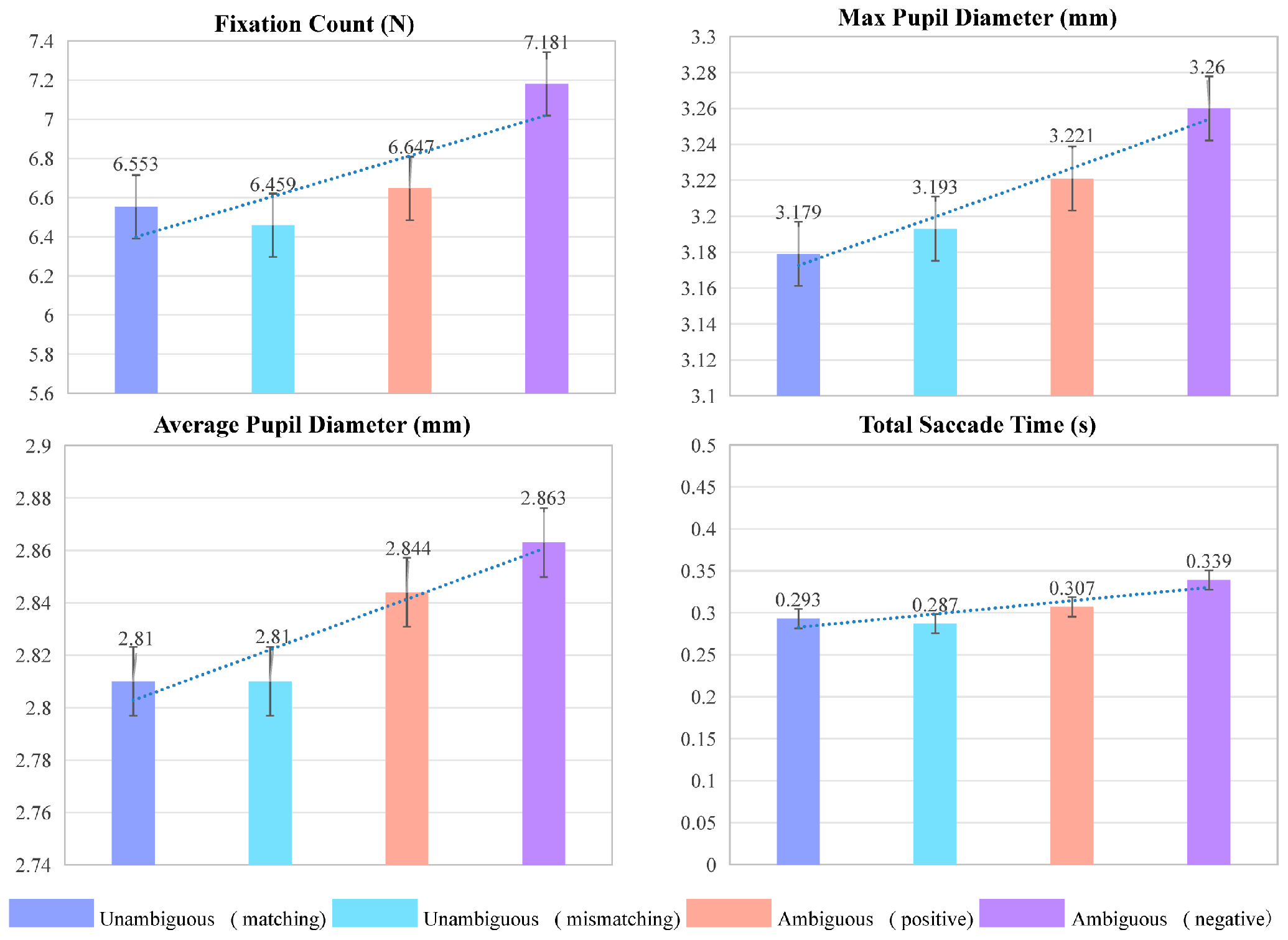
3.2. Eye Movement Feature Extraction
3.3. EEG Data Extraction
3.3.1. EEG Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
3.3.2. EEG Feature Analysis
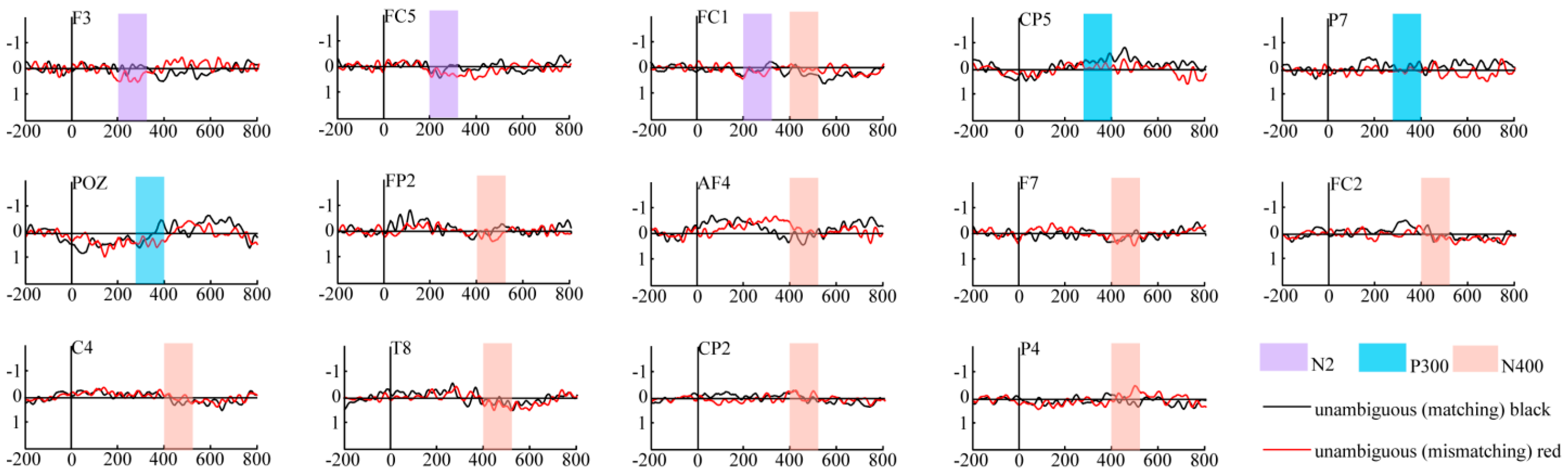
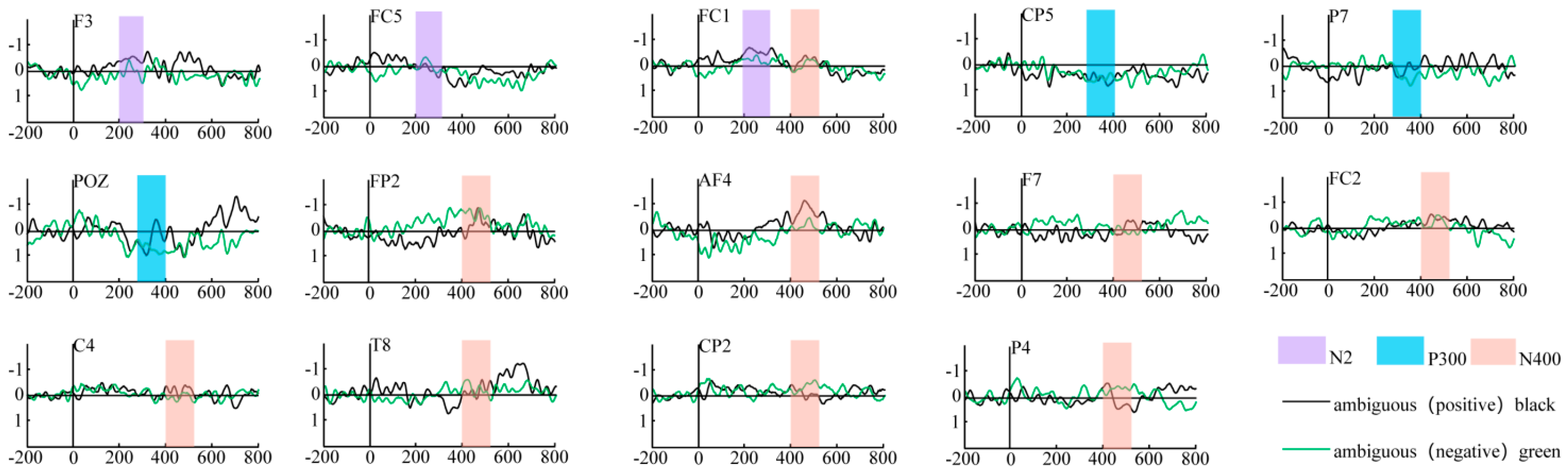
- N2 component analysis
- P300 component analysis
- N400 component analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Relationship Between Behavioural Data and Image Evaluation
4.2. Relationship Between Physiological Features and Image Evaluation
4.2.1. Relationship Between Eye Movement Indexes and Image Cognition
4.2.2. Relationship Between EEG Features and Image Cognition
4.3. Comprehensive Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ET-EEG | eye tracking–electroencephalography |
| ERPs | event-related potentials |
| EMM | explicit measurement method |
| EEG | electroencephalography |
| ET | eye tracking |
Appendix A
| Stimulus Number | Dull–Cute | Traditional–Fashionable | Stiff–Comfortable | Complicated–Simple |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.23 | −0.15 | −0.1 | 0.13 |
| 2 | 0.15 | 0.8 | −0.05 | 0.83 |
| 3 | 0.33 | −0.18 | 0.68 | 0.58 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.63 | 0.53 |
| 5 | 0.5 | −0.1 | 0.63 | 0.8 |
| 6 | 0.33 | 1.28 | −0.08 | −0.08 |
| 7 | 0.03 | 0.98 | 0.23 | 0.65 |
| 8 | −0.2 | −0.13 | 0.18 | 0.63 |
| 9 | 0.23 | 1.35 | 0.28 | 1.15 |
| 10 | −0.48 | 0.6 | −0.4 | −0.38 |
| 11 | 0.8 | 0.55 | 0.95 | 0.65 |
| 12 | 0.48 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| 13 | −0.2 | 0.13 | −0.2 | 0.3 |
| 14 | 0.8 | 0.63 | 0.6 | 0.4 |
| 15 | 0.03 | 0.23 | 0.28 | 0.73 |
| 16 | 0.33 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 1 |
| 17 | 0.5 | 0.63 | 0.45 | 0.45 |
| 18 | 0.73 | 1 | 0.78 | 1.05 |
| 19 | −0.15 | 1.05 | −0.13 | 1.28 |
| 20 | 0.38 | 1.15 | −0.1 | 1.08 |
| 21 | 0.43 | −0.28 | 0.65 | 0.6 |
| 22 | 0.25 | 0.8 | 0.13 | 0.08 |
| 23 | 0.83 | 1.1 | 0.75 | 0.95 |
| 24 | −0.05 | 0.25 | −0.05 | −0.43 |
| 25 | −0.13 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.05 |
| 26 | 0.83 | 0.15 | 0.88 | 0.75 |
| 27 | −0.1 | −0.13 | 0.08 | 0.25 |
| 28 | 0.8 | 1 | 0.55 | 1.1 |
| 29 | 0.03 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.78 |
| 30 | 0.85 | 0.6 | 0.98 | 0.95 |
| 31 | −0.1 | −0.38 | 0.28 | 0.43 |
| 32 | 0.78 | 1.1 | 0.33 | 1.15 |
| 33 | 0.75 | 1.15 | 0.75 | 1.25 |
| 34 | 0.5 | 0.75 | 0.53 | 0.38 |
| 35 | 0.13 | 0.63 | 0.15 | −0.38 |
| 36 | 0.93 | 1.1 | 0.73 | 1.05 |
| 37 | −0.3 | 0.08 | −0.23 | −0.35 |
| 38 | 0.28 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| 39 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.33 | 0.03 |
| 40 | 0.28 | 0.4 | 0.15 | 0.65 |
| 41 | −0.23 | −0.45 | −0.55 | −0.6 |
| 42 | 0.13 | −0.23 | 0.33 | 0.65 |
| 43 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| 44 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0 | −0.15 |
| 45 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.58 |
| 46 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.55 |
| 47 | 0 | 0.65 | −0.08 | 0.58 |
| 48 | −0.38 | −0.53 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| 49 | 0.68 | 0.43 | 0.2 | 0.53 |
| 50 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.7 | 0.85 |
References
- Zhang, B.C.; Guo, W.M.; Wang, Y.Q.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Xu, J. Research on passenger visual image for train interior design. J. Mech. Eng. 2016, 52, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.J.; Pan, Y.H. Review of theory, key technologies and its application of perceptual image in product design. Chin. J. Mech. Eng. 2007, 43, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.H. Design Method of Interior Color of Subway Vehicle Based on NCS and Perceptual Image. Mech. Des. Res. 2021, 3, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Q.; Lin, L.; Milekic, S. Affective Image Classification Based on User Eye Movement and EEG Experience Information. Interact. Comput. 2018, 30, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, M.; Li, P.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, X.X. Product color emotional design method based on CNT-GAT and EGT-GA. Packaging Engineering. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2025, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.S.; Feng, H.B.; Du, X.B.; Nie, R.; Lin, Y.; Ma, C.; Zhang, L. EEG-Based Evaluation of Aesthetic Experience Using BiLSTM Network. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2024, 40, 8166–8179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.L.; Gu, C.R.; Fu, M.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y. A novel feature fusion network for multimodal emotion recognition from EEG and eye movement signals. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1234162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.H.; Xing, Z.M.; Wang, Y.R.; Fang, S.; Gao, X.; Dong, X. Research on Emotion Recognition Method of Cerebral Blood Oxygen Signal Based on CNN-Transformer Network. Sensors 2023, 23, 8643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Li, C.Y.; Huang, Z.G.; Romanoor, N.H. Research on gap between consumer demand and product design supply of new Chinese-style clothing products. J. Text. Res. 2021, 42, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Liu, Y.L.; Sun, L. An Intelligent Generative Design Method for Product Styling Driven by Visual Perception Data. J. Comput.-Aided Des. Comput. Grap 2025, 1–19. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/urlid/11.2925.tp.20250214.1634.037 (accessed on 8 October 2025).
- Yang, D.M.; Zhang, X.T.; Zhang, J.N.; Wang, Z.; Dong, X. Intelligent Design Method of Urban Rail Transit Vehicle Modeling Integrating Regional Culture. Mach. Des. Res. 2025, 41, 21–27+34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.T.; Su, P.F.; Su, S.F. Fusion of Cognitive Information: Evaluation and Evolution Method of Product Image Form. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021, 2021, 5524093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.S.; Xu, X.Q.; Chen, G.Q.; Sun, L.; Wu, J. Image prediction model of electric vehicle based on neural network. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 27, 1135–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Zhou, Z.; He, M.; Tang, C. Solution to Resolve Cognitive Ambiguity in Interactive Customization of Product Shape. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2020, 13, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgianni, Y.; Maccioni, L. Review of the use of neurophysiological and biometric measures in experimental design research. Artif. Intell. Eng. Design. Anal. Manuf. 2020, 34, 248–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Cao, Y.; Qu, Q.; Duffy, V.G. An exploratory study using electroencephalography (EEG) to measure the smartphone user experience in the short term. Int. J. Hum.–Comput. Interact. 2020, 36, 1008–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.L.; Luo, Y.J. Research status of brain mechanism of visual motion perception. Adv. Psychol. Sci. 2003, 11, 132–135. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.H.; Lu, Y.N. Can pupil size be measured to assess design products? Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2014, 44, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Gou, B.C.; Chu, J.J.; Yang, Y. Way of getting user requirements based on eye tracking technology. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2015, 51, 233–237. [Google Scholar]
- Qu, Q.X.; Guo, F. Can eye movements be effectively measured to assess product design?: Gender differences should be considered. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2019, 72, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.T.; Deng, W.D. Cognitive Differences of Product Image Sketches Based on Sketch Eye Tracking. J. Comput.-Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 2019, 31, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.N.; Lin, Z.; Pan, M.J.; Chen, X. An emotion recognition model based on long short-term memory networks and EEG signals and its application in parametric design. J. Mech. Med. Biol. 2023, 23, 2340096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, D.; Sofya, K. EEG correlates of perceived food product similarity in a cross-modal taste-visual task. Food Qual. Prefer. 2020, 85, 103980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Kang, Y.Y.; Guo, X.; Li, P.; He, H. The effect analysis of shape design of different charging piles based on Human physiological characteristics using the MF-DFA. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Zeng, J.; Chen, C.; Wang, Q. Investigation on Effect of Appearance Characteristics on Product Identity Based on EEG. J. Tongji Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2020, 48, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Gil, J.M.; Virgili-Goma, J.; Gil, R.; Guilera, T.; Batalla, I.; Soler-González, J.; García, R. Method for improving EEG based emotion recognition by combining it with synchronized biometric and eye tracking technologies in a non-invasive and low cost way. Front. Comput. Neurosci 2016, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Qi, J.; Hu, J.; Hao, S. A new approach for product evaluation based on integration of EEG and eye-tracking. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2022, 52, 101601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.W.; Yu, S.H.; Ma, N.; Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; He, J. Prediction of product design decision Making: An investigation of eye movements and EEG features. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2020, 45, 101095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Li, M.M.; Hu, M.C.; Li, F.; Lin, B. Distinguishing and quantifying the visual aesthetics of a product: An integrated approach of eye-tracking and EEG. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2019, 71, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.Q.; Lin, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, L.; Guo, Z. Research on the construction method of kansei image prediction model based on cognition of EEG and ET. Int. J. Interact. Des. Manuf. 2020, 2, 565–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, Z.A. Research on Product Preference Image Measurement Based on the Visual Neurocognitive Mechanism. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 2020, 1006, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Xu, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, X.C. The Effect of Congenital Blindness on Color Cognition: An ERP Study. Stud. Psychol. Behav. 2022, 20, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Ren, M.M.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhong, Y. The impact of feedback on self-deception: Evidence from ERP. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2022, 54, 481–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Chen, C.; Tang, Z.C. Study of Electroencephalography Cognitive Model of Product Image. J. Mech. Eng. 2018, 54, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shi, X.K.; Li, W.N.; Hu, Y. Influence of cognitive control based on different conflict levels on the expression of gender stereotypes. Acta Psychol. Sin. 2022, 54, 628–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.N.; Liu, Y.L.; Shi, R.; Li, X.; Tang, Z. Product Image Modeling Design Method for Cross-cultural Fusion. Packag. Eng. 2019, 40, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.N.; Lin, L.; Yang, M.Q.; Zhang, Y. Product image extraction model construction based on multi-modal implicit measurement of unconsciousness. Comput. Integr. Manuf. Syst. 2022, 28, 1150–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Xue, C.Q.; Gedeon, T.; Hu, H.; Li, J. Visual search on information features on digital task monitoring interface. J. Southeast Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 48, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.M.; Guo, F.; Ren, Z.G.; Duffy, V.G. A visual and neural evaluation of the affective impression on humanoid robot appearances in free viewing. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2022, 88, 103159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorin, H.; Patel, J.; Qiu, Q.Y.; Merians, A.; Adamovich, S.; Fluet, G. A Review of the Use of Gaze and Pupil Metrics to Assess Mental Workload in Gamified and Simulated Sensorimotor Tasks. Sensors 2024, 24, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, R.R.; Bradley, M.M.; Lang, P.J. Emotional imagery and pupil diameter. Psychophysiology 2018, 55, e13050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buter, R.; Soberanis-Mukul, R.D.; Shanka, R.; Puentes, P.R.; Ghazi, A.; Wu, J.Y.; Unberath, M. Cognitive effort detection for tele-robotic surgery via personalized pupil response modeling. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2024, 19, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Luo, Y.Y. Research on Consumer Privacy Paradox Behavior from the Perspective of Self-perception Theory: Evidence from ERPs. Nankai Bus. Rev. 2021, 24, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, H.P.; Cao, D.; LI, Y.J. Electroencephalogram characteristics under successful cognitive reappraisal in emotion regulation. J. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 37, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.W.; Zhao, X.H.; Huang, L.H.; Rong, J. Influence Mechanism of Bridge Sign Complexity on Cognitive Characteristics of Drivers’ Electroencephalogram. J. Southwest Jiaotong Univ. 2021, 56, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, B.; Du, B.X.; Chen, S.H.; Li, Y.; He, W.; Luo, W. Moral judgment modulates fairness consideration in the early outcome evaluation stage. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2020, 65, 1985–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, H.Y.; Xue, C.Q.; Shao, J. Match judgments of semantic word-product image based on event-related potential. J. Southeast Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 44, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.H.; Yang, L.Z. An ERP Study on the Process of Conflict Emotion Control. Psychol. Sci. 2008, 31, 1365–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
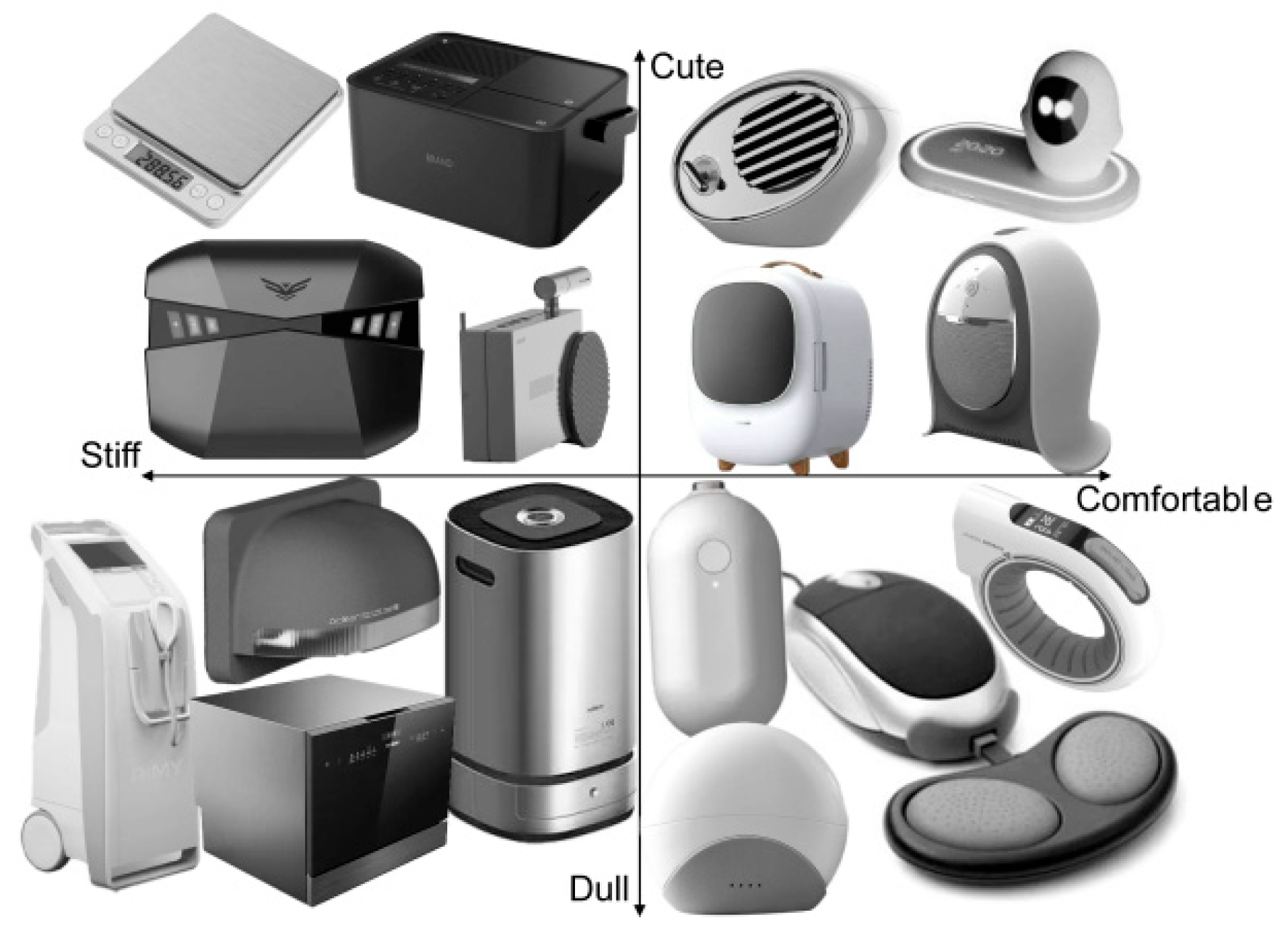
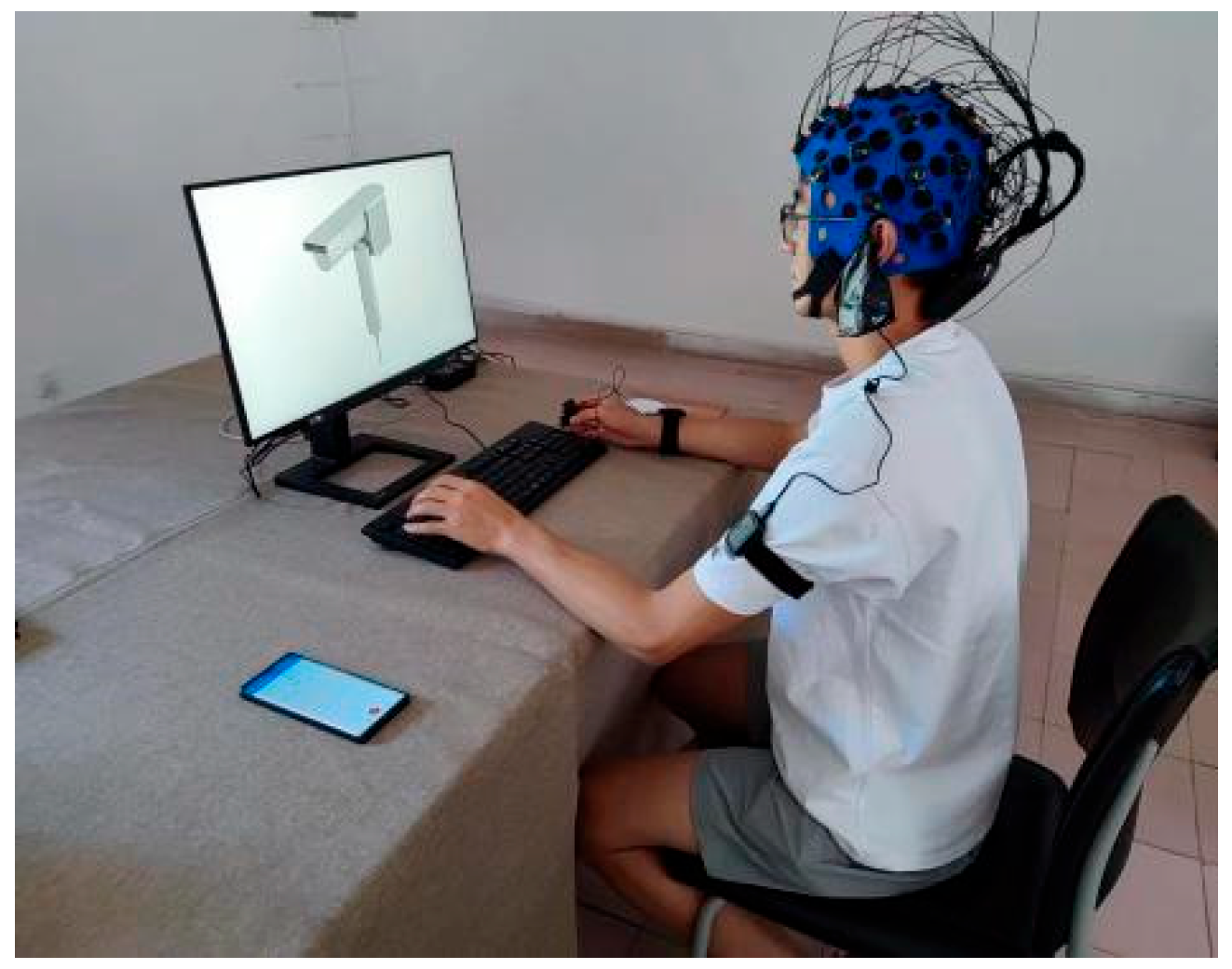



| Cluster | Adjectives | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | cute | slick | fresh | |||||
| 2 | fashionable | technological | art | cool | exquisite | strong | textured | fluent |
| 3 | comfortable | sober | elegant | traditional | secure | environmental | handsome | |
| 4 | simple | convenient | ||||||
| Stimulus Number | Dull–Cute | Traditional–Fashionable | Stiff–Comfortable | Complicated–Simple |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | −0.23 | −0.15 | −0.1 | 0.13 |
| 2 | 0.15 | 0.8 | −0.05 | 0.83 |
| 3 | 0.33 | −0.18 | 0.68 | 0.58 |
| 4 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.63 | 0.53 |
| 5 | 0.5 | −0.1 | 0.63 | 0.8 |
| 6 | 0.33 | 1.28 | −0.08 | −0.08 |
| … | … | … | … | … |
| 43 | 0.95 | 0.55 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| 44 | 0.05 | 0.4 | 0 | −0.15 |
| 45 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.58 |
| 46 | 0.28 | 0.45 | 0.28 | 0.55 |
| 47 | 0 | 0.65 | −0.08 | 0.58 |
| 48 | −0.38 | −0.53 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| 49 | 0.68 | 0.43 | 0.2 | 0.53 |
| 50 | 0.75 | 0.93 | 0.7 | 0.85 |
| Eye Movement Index | F | p |
|---|---|---|
| Average pupil diameter (mm) | 2.449 | 0 |
| Maximum pupil diameter (mm) | 1.813 | 0.015 |
| Total saccade time (s) | 1.548 | 0.056 |
| Fixation count (N) | 1.598 | 0.044 |
| ERP Component | Time Window (ms) | Electrode | F | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N2 | 200–300 | F3 | 3.931 | 0.022 |
| FC5 | 3.587 | 0.031 | ||
| FC1 | 6.058 | 0.003 | ||
| P300 | 300–400 | CP5 | 8.401 | 0 |
| P7 | 3.317 | 0.04 | ||
| POZ | 3.094 | 0.049 | ||
| N400 | 400–500 | FP2 | 3.481 | 0.034 |
| AF4 | 4.406 | 0.014 | ||
| F7 | 3.845 | 0.024 | ||
| FC1 | 4.287 | 0.016 | ||
| FC2 | 5.587 | 0.005 | ||
| C4 | 4.088 | 0.019 | ||
| T8 | 6.728 | 0.002 | ||
| CP2 | 5.149 | 0.007 | ||
| P4 | 6.42 | 0.002 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, S.; Qiu, K. Decision-Making for Product Form Image Based on ET-EEG Technology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10979. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010979
Shi H, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Liu S, Qiu K. Decision-Making for Product Form Image Based on ET-EEG Technology. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10979. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010979
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Huaixi, Shutao Zhang, Qinwei Zhang, Shifeng Liu, and Kai Qiu. 2025. "Decision-Making for Product Form Image Based on ET-EEG Technology" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10979. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010979
APA StyleShi, H., Zhang, S., Zhang, Q., Liu, S., & Qiu, K. (2025). Decision-Making for Product Form Image Based on ET-EEG Technology. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10979. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010979






