A Multi-Objective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm Incorporating Q-Learning Search for the Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problems with Multi-Type Automated Guided Vehicles
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Novel MILP model: A MILP model with the objective of minimizing makespan and TEC is developed to formulate the FJSP-MTA.
- (2)
- Novel algorithm framework: An efficient Q-HMOABC algorithm is designed to efficiently address the FJSP-MTA, and improved strategies are adopted in three ABC phases. Here, Q-HMOABC is formed by embedding the Q-learning RL method into the employed bee phase of the ABC algorithm.
- (3)
- Extensive experiments: Unconstrained benchmark functions and benchmark instances are conducted to test the performance of Q-HMOABC, where the statistical results illustrate the superiority of the proposed algorithm in solving the FJSP-MTA.
2. Literature Review
2.1. FJSP with AGV Transportation Resources
2.2. Solving Methods
3. Problem Description and Formulation
3.1. Problem Description
Assumptions
- Initial state constraint: All machines and AGVs are available at time 0, and all jobs can be processed at time 0.
- Each machine has a buffer zone that can be used to park AGVs and store jobs, and has sufficient buffering capacity.
- Each machine can process at most one operation at a time.
- Each AGV can transport at most one job or be empty at a time.
- The processing task of jobs cannot be interrupted as soon as it starts.
- The transportation task of jobs cannot be interrupted as soon as it starts.
- The loading and unloading time are excluded in the transportation time.
- The job does not return to the LU area once it has been completed.
- Machine and AGV breakdown during operation are not considered, with sufficient AGV battery power.
- The last operation of each job does not need to be transported after it is finished.
3.2. Formulation of MILP Model
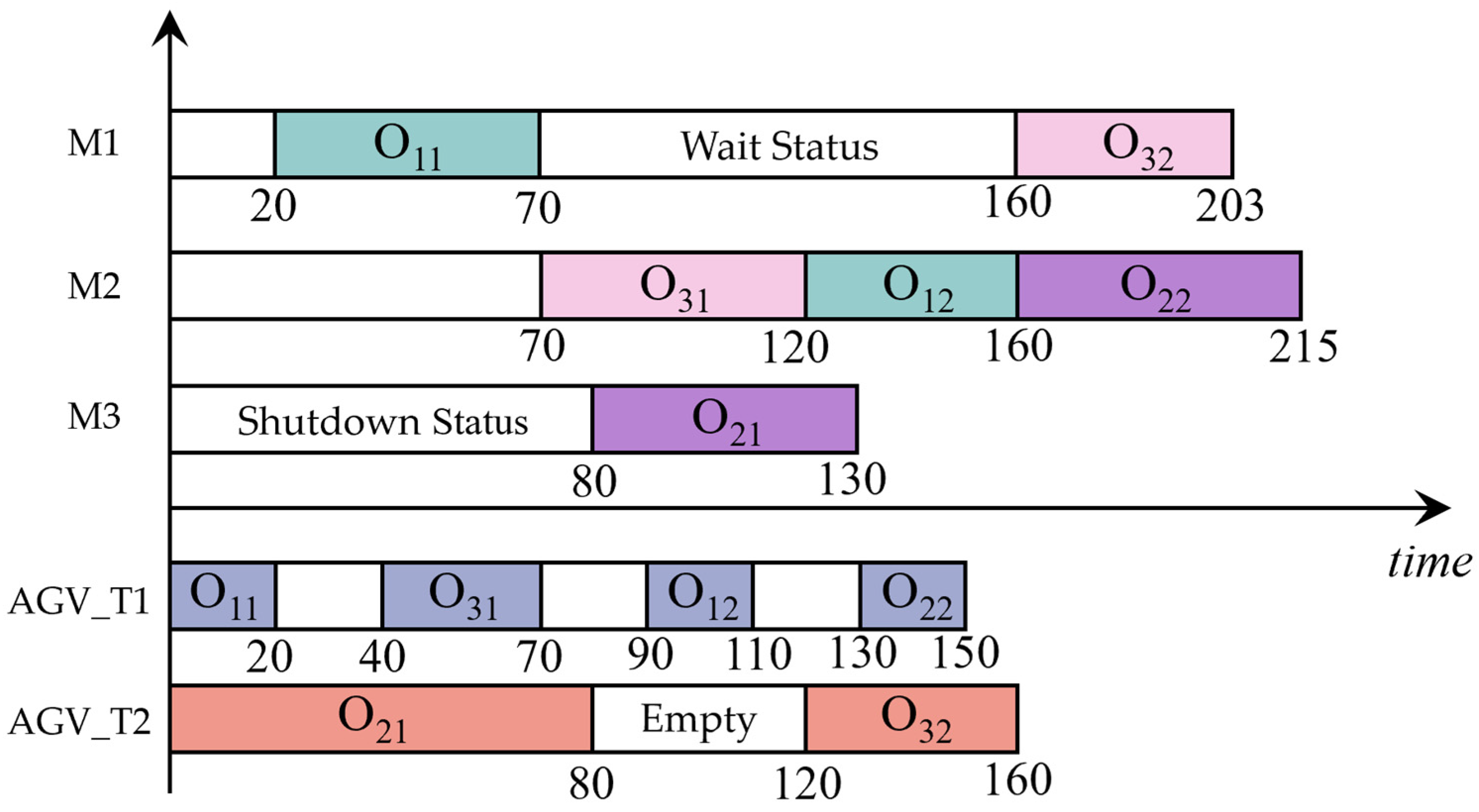
3.3. Example of FJSP-MTA
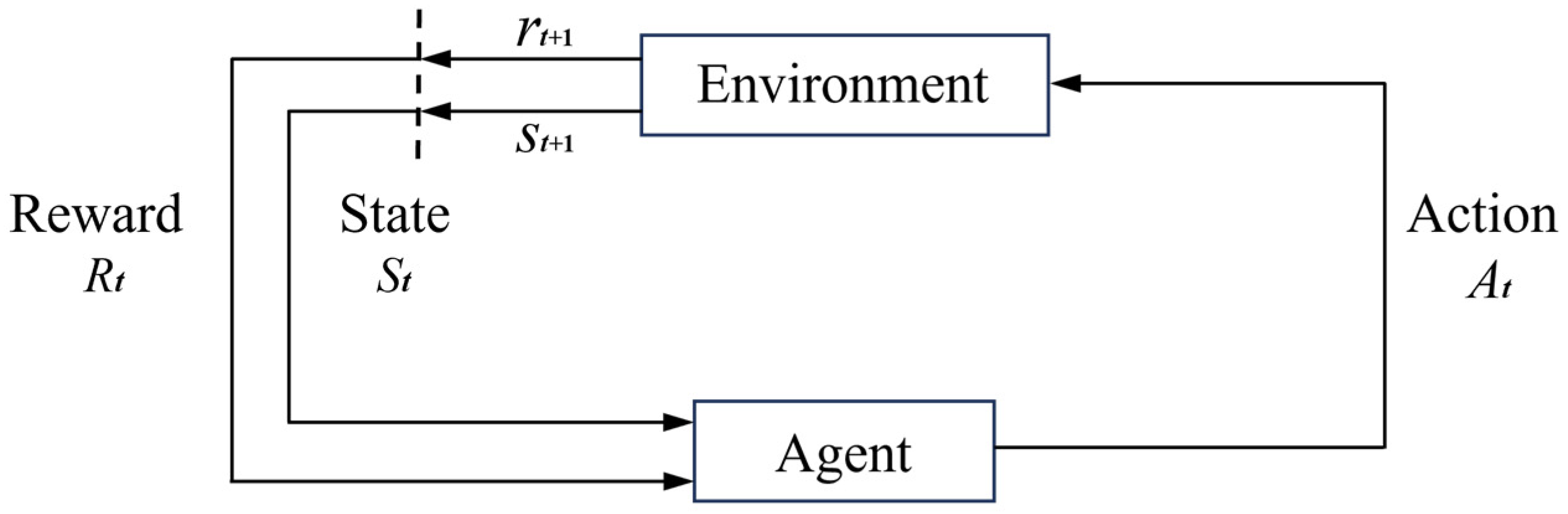
4. Q-Hybrid Multi Objective Artificial Bee Colony (Q-HMOABC)
4.1. Framework of the Q-HMOABC
| Algorithm 1: Q-HMOABC |
| Input: Job and AGV time, energy parameters, population size, learning rate, discount factor, exploring rate, restarting number, number of VNS; |
| Output: OS, MA, AD, Makespan, TEC; |
| 1 Initialize population by Tent chaotic map; |
| 2 Define fitness function ; |
| 3 Define Q-learning tuple with state , operator , |
| reward , Q-value ; |
| 4 ; |
| 5 while t < MaxIter do |
| 6 Perform fast non-dominated sorting on Pt, obtain fronts F1, …, Fk; |
| 7 for each employed bee do |
| 8 Select operator with probability , else random a; |
| 9 Generate candidate ; |
| 10 Evaluate ; |
| 11 if then |
| 12 ; |
| 13 Update ; |
| 14 for each onlooker bee do |
| 15 Select xk with probability ; |
| 16 Apply ; |
| 17 if then |
| 18 Update ; |
| 19 for each scout bee do |
| 20 if no improvement for LN iterations then |
| 21 Restart strategy ; |
| 22 Update Pareto archive |
| 23 if stopping criterion satisfied then |
| 24 return non-dominated set ; |
| 25 ; |
| 26 end while |
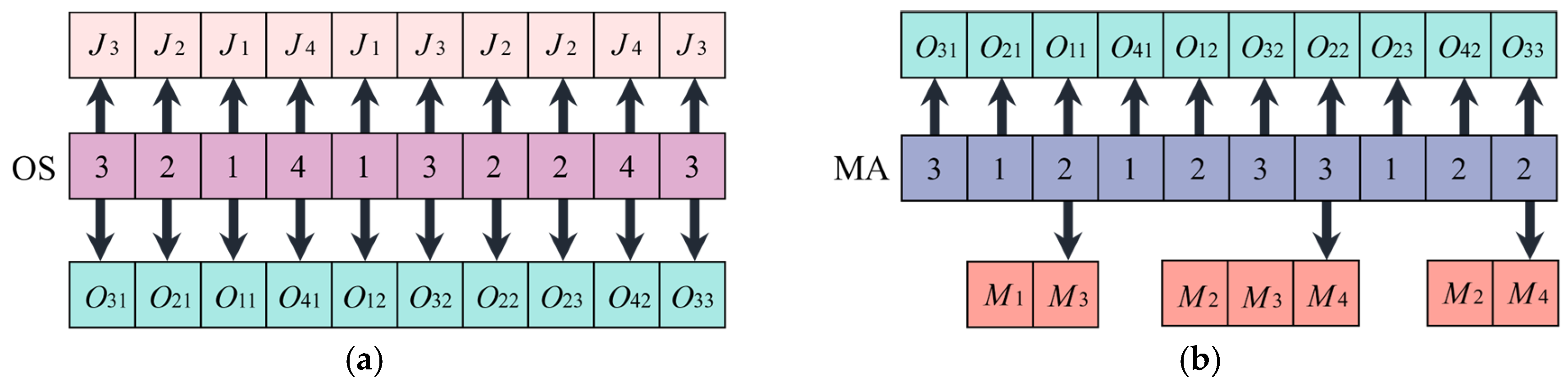
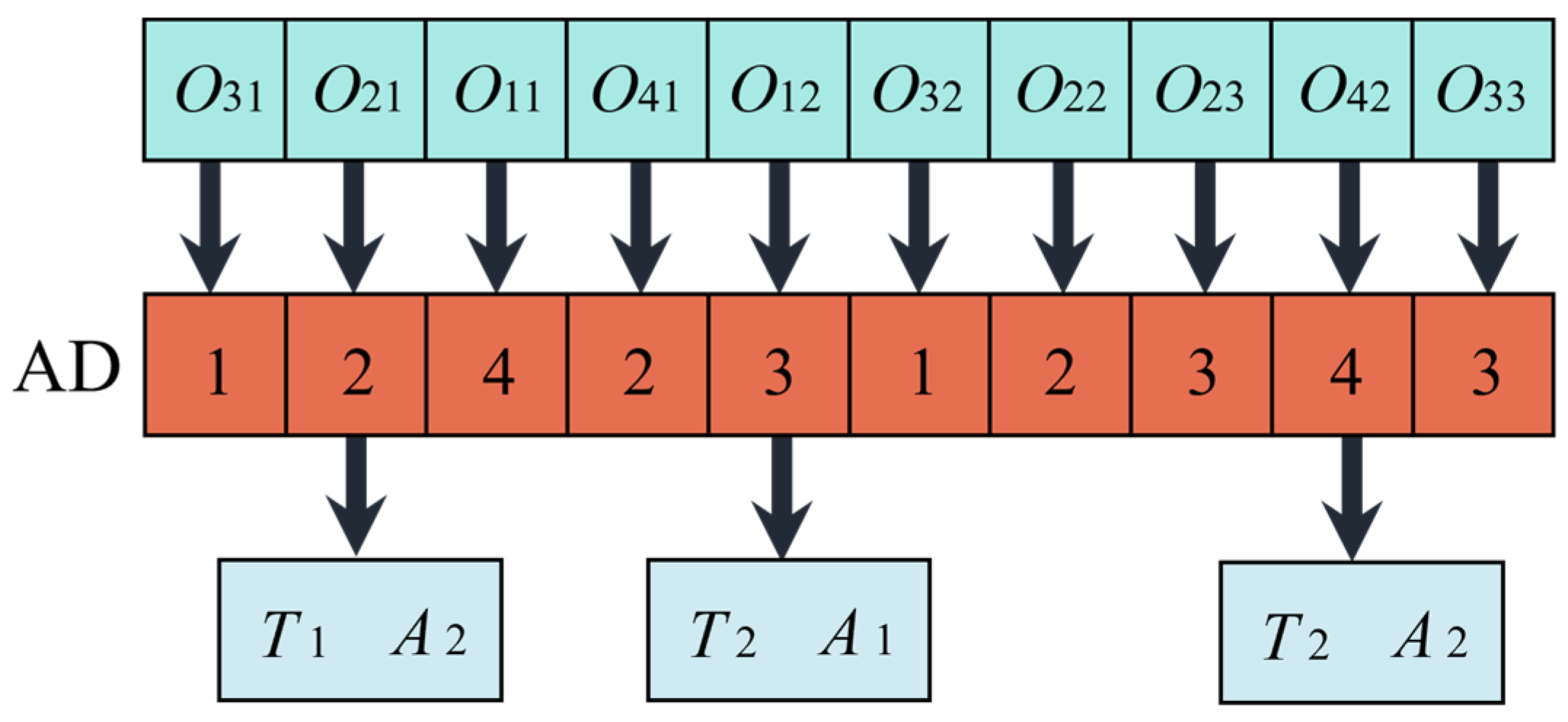
4.2. Solution Representation
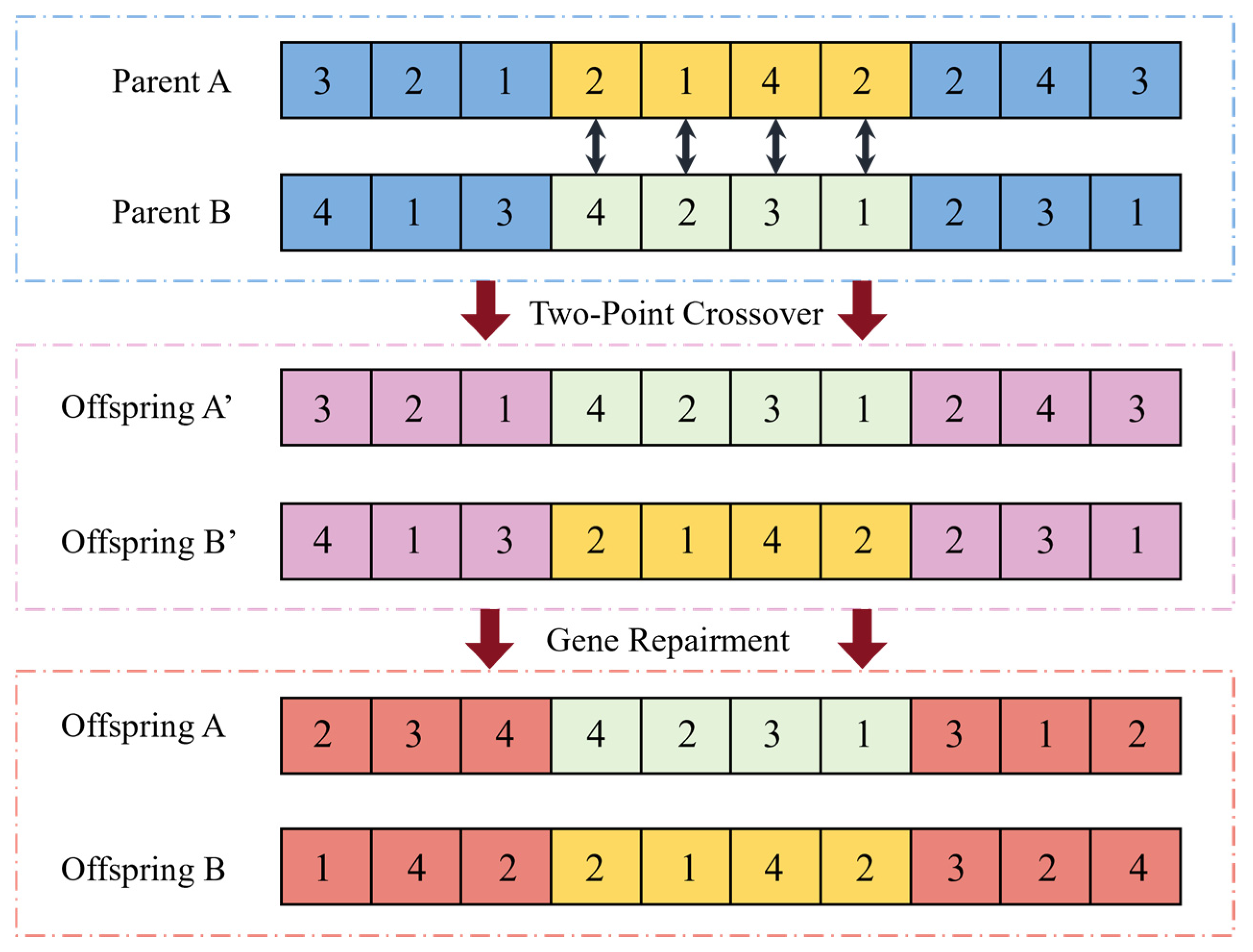
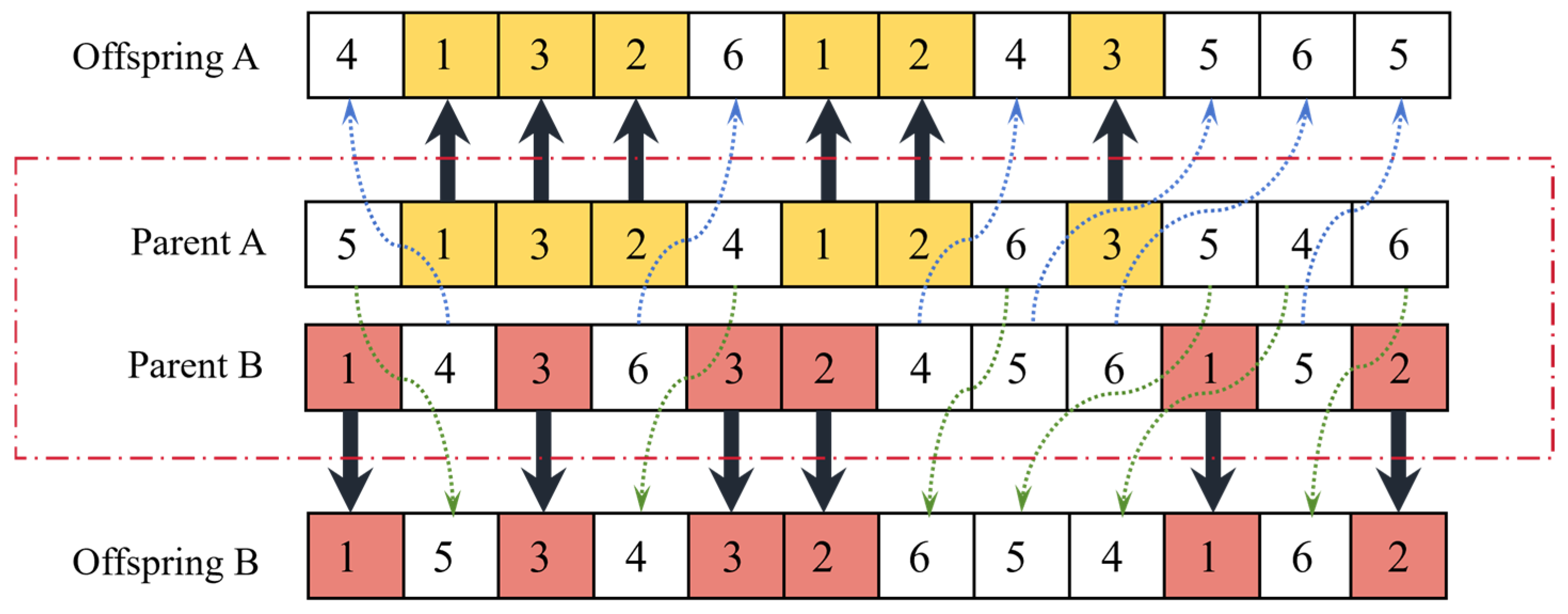
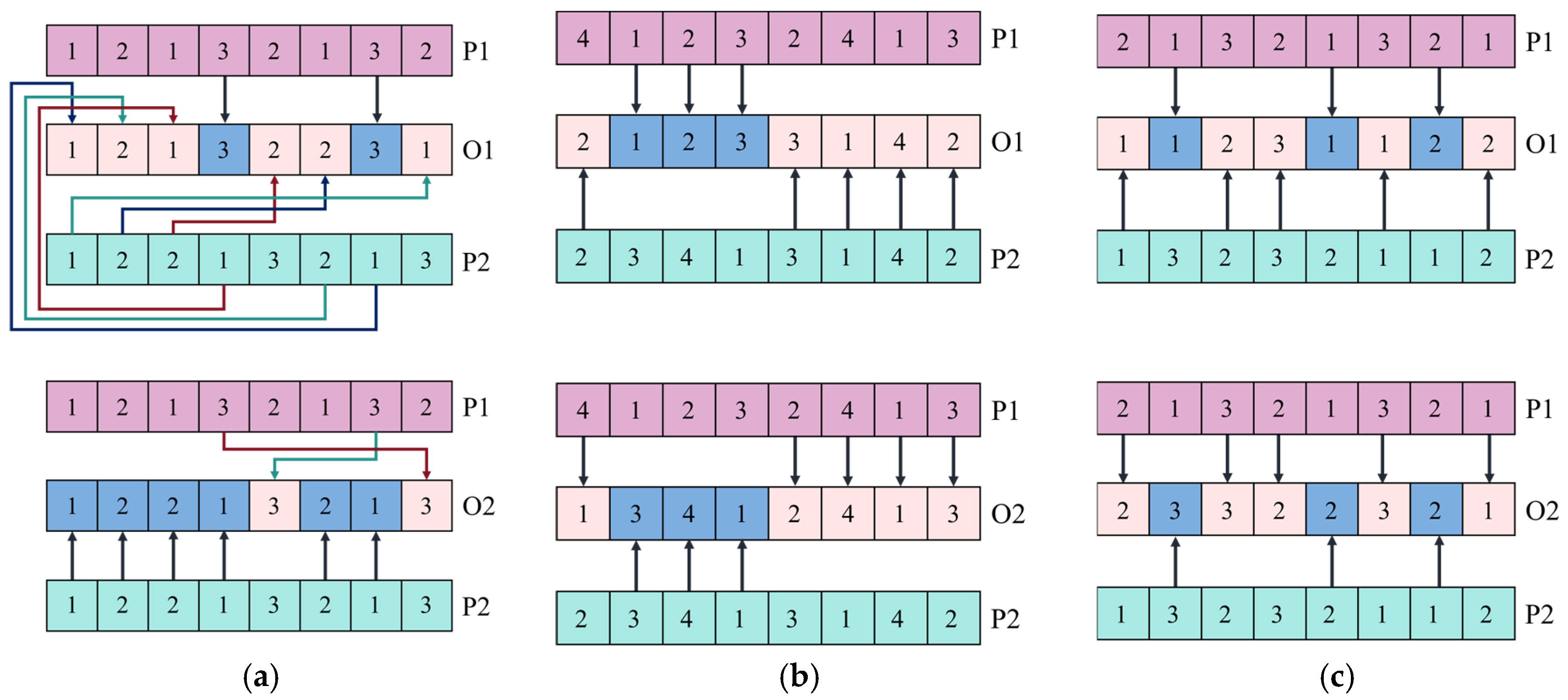
Crossover and Mutation
4.3. Population Initialization
4.4. Fast Nondominated Sorting Procedure
4.5. Employed Bee Phase
| Algorithm 2: Employed Bee Phase with Q-learing |
| Input: Non-dominated archive Ω, Q-table Q, number of neighbourhood search LS, Learning rate, discount factor, exploration rate; |
| Output: Updated archive Ω; |
| 1 Let current solution be S (the employed bee’s incumbent); |
| 2 Set iteration counter ; |
| 3 while do |
| 4 Observe state ; |
| 5 Draw ; |
| 6 if then |
| 7 ; |
| 8 else |
| 9 Sample uniformly from action set; |
| 10 Generate neighbor ; |
| 11 Evaluate and ; |
| 12 if then |
| 13 ; ; UpdateArchive ; |
| 14 else if |
| 15 ; |
| 16 else |
| 17 ; UpdateArchive ; |
| 18 end if |
| 19 Observe ; |
| 20 ; |
| 21 ; |
| 22 end while |
4.5.1. The State Set
4.5.2. The Select Strategy
4.5.3. The Action Set
4.5.4. The Reward Set
4.6. Onlooker Bee Phase
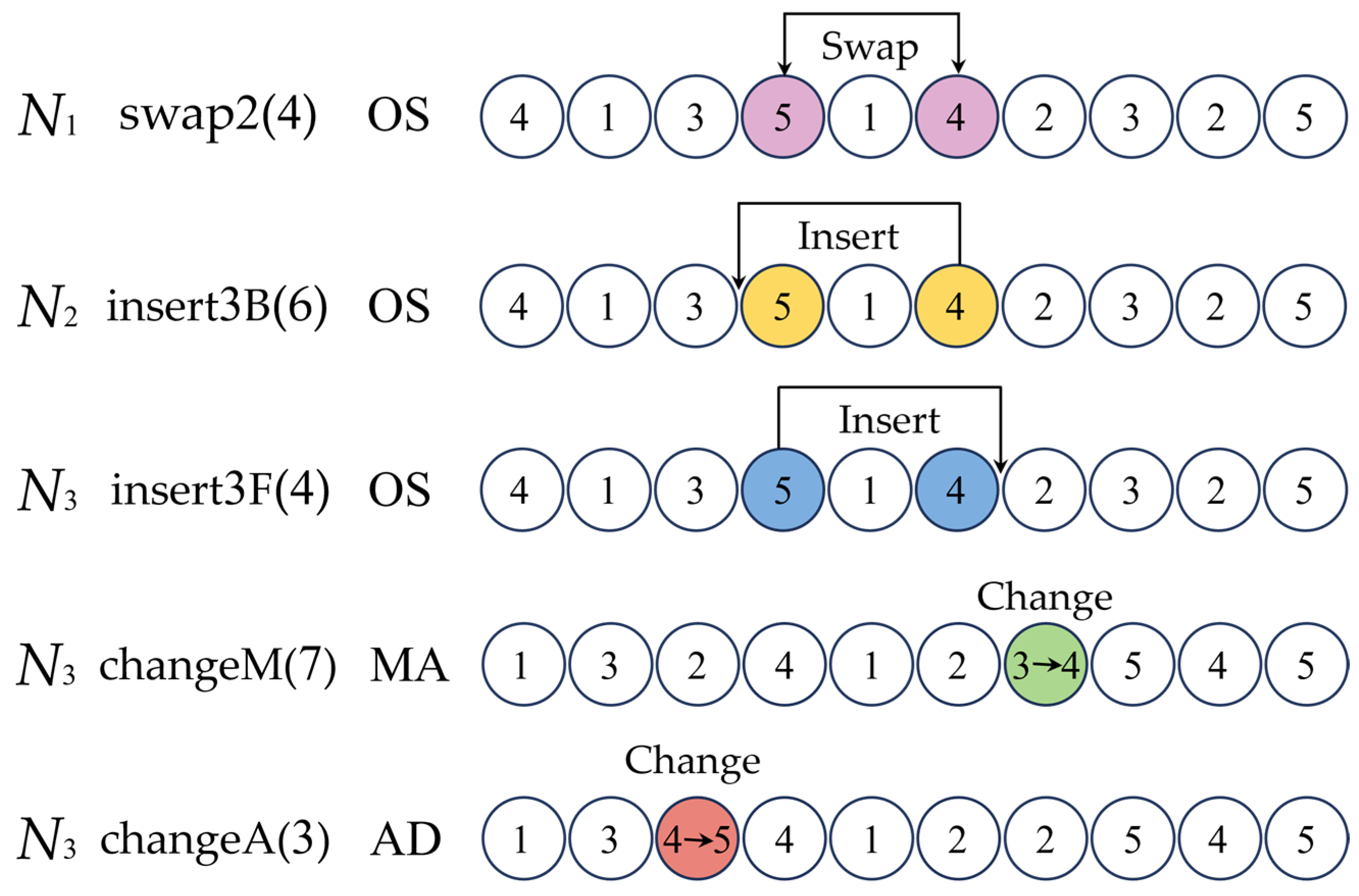
- N1: swap2(i): randomly select an integer i and swap the positions of the i-th operation and the (i + 2) th operation in the OS vector.
- N2: insert3B(i): randomly select an integer i and insert the i-th operation into the position of the (i − 3) th operation.
- N3: insert3F(i): randomly select an integer i and insert the i-th operation into the position of the (i + 3) th operation.
- N4: changeM(i): randomly select an integer i and change from the optional machine set.
- N5: changeA(i): randomly select an integer i and change from the optional AGV set.
4.7. Scout Bee Phase
5. Experimentation
5.1. Experimental Instances
5.2. Experimental Parameters
- (1)
- .
- (2)
- .
- (3)
- .
- (4)
- .
- (5)
- .
- (6)
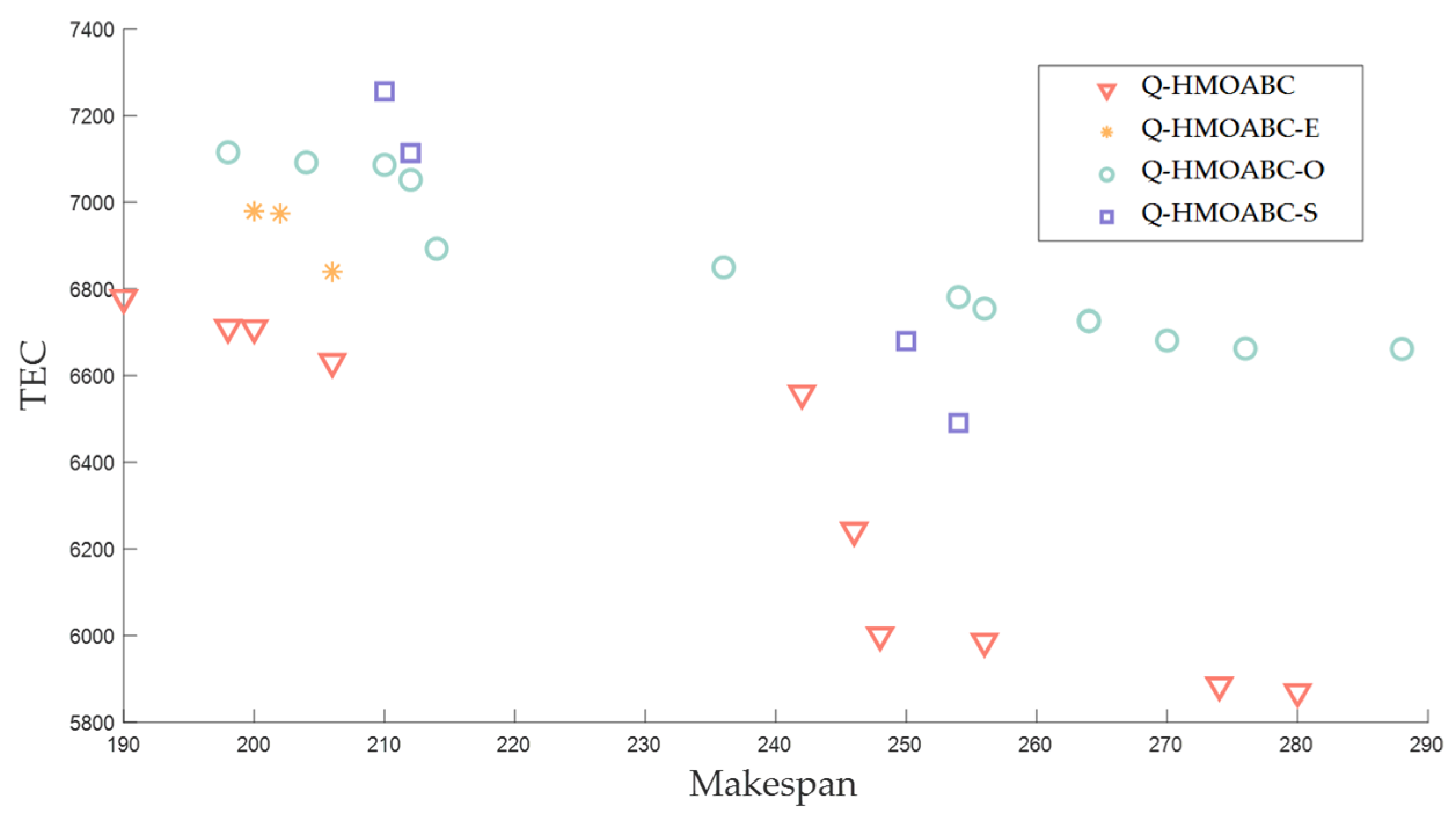
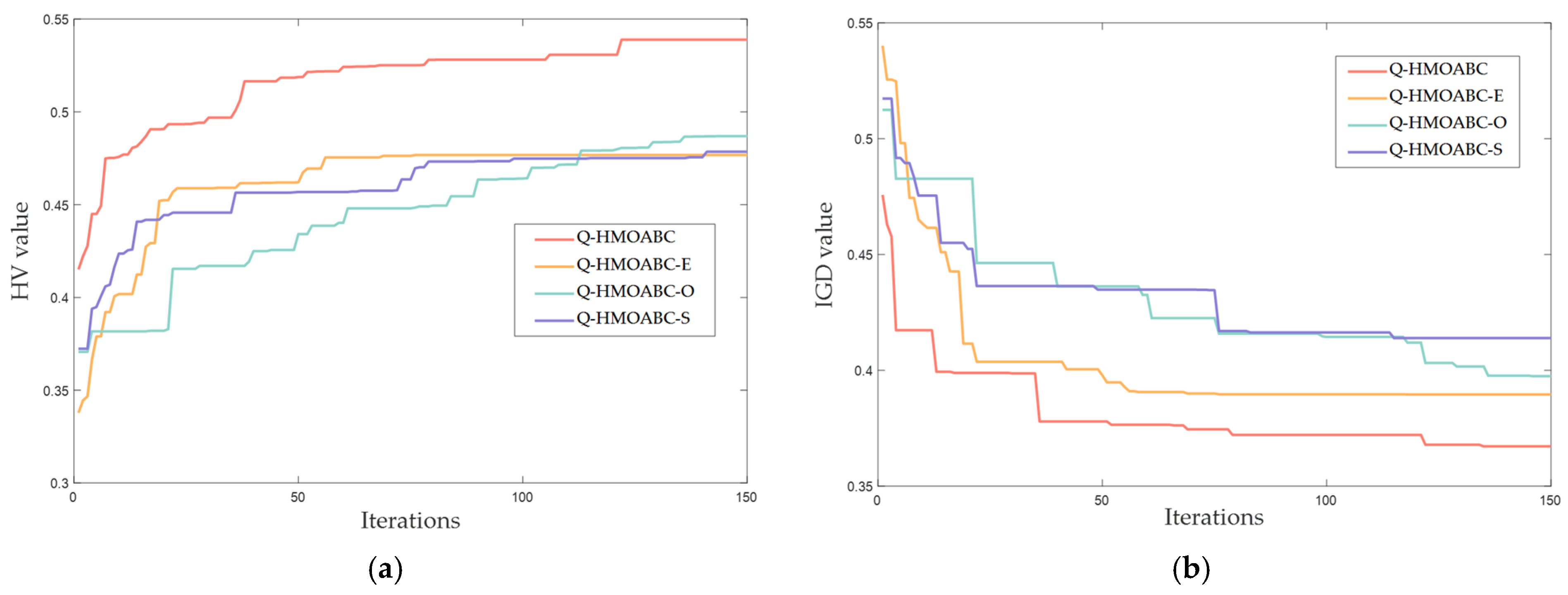
5.3. Effectiveness of Each Improvement of Q-HMOABC
5.3.1. Effectiveness of Q-HMOABC on Unconstrained Benchmark Functions
5.3.2. Effectiveness of Q-HMOABC on Benchmark Instances
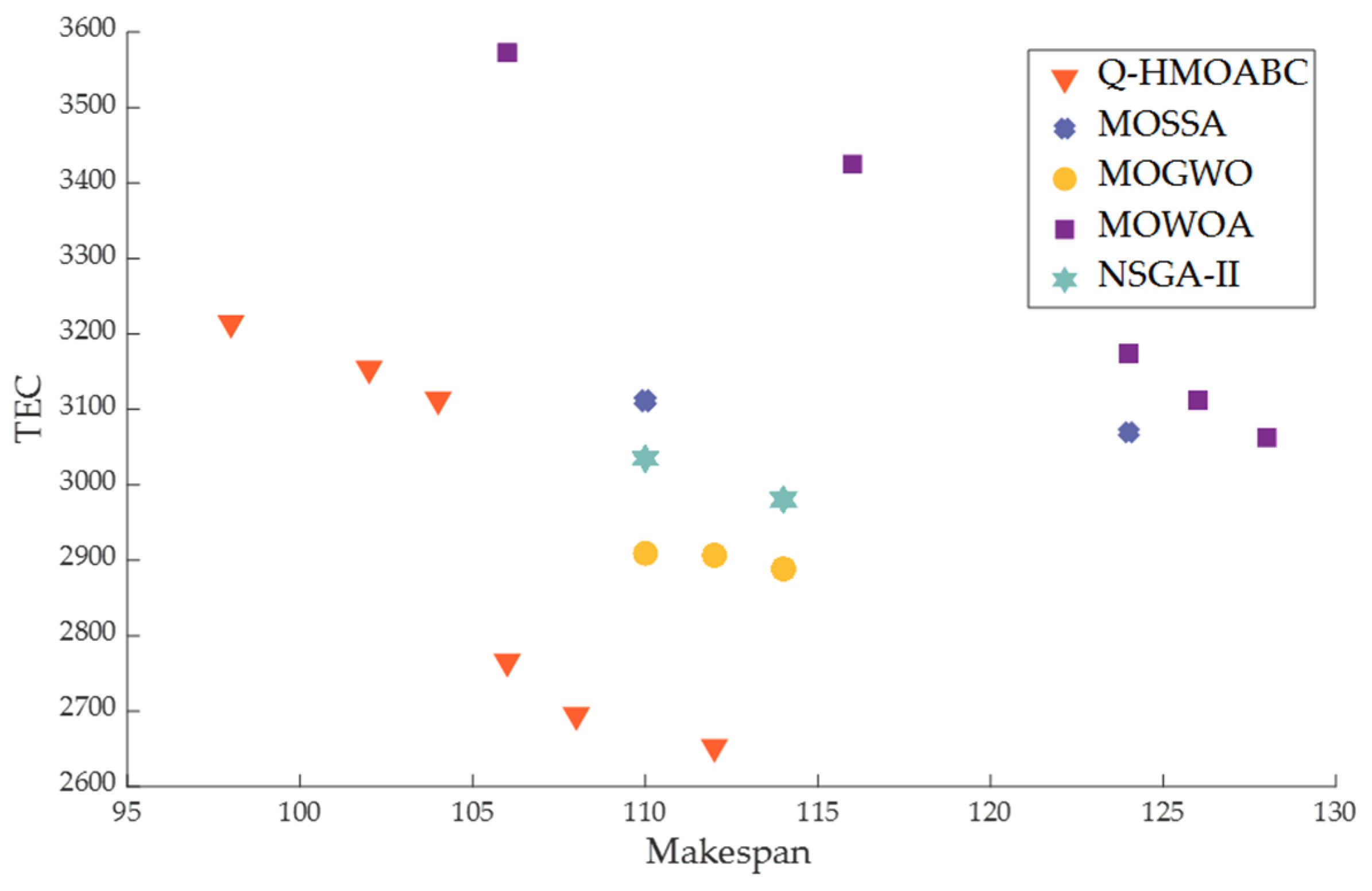
5.4. Comparison of Q-HMOABC with Other Algorithms
6. Discussion
7. Conclusions and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Notations
| Notations | Definitions |
| Parameter: | |
| I | Job set. (I = 1, 2, 3, …, n) |
| Ji | Operation set of job i. (Ji = 1, 2, 3, …, ni) |
| K | Machine set. (K = 1, 2, 3, …, m) |
| V | Total numbers of AGVs set. (V = 1, 2, 3, …, nV) |
| T | Total types of AGVs set. (T = 1, 2, 3, …, t) |
| Vt | Number of AGVs of type t. (t ∈ T) |
| i, i′ | Job indices. |
| j, j′ | Operation indices. |
| v, v′ | AGV indices, including all types of AGVs. |
| k, k′ | Machines indices. |
| Oi,j | The j-th operation of job i. |
| N | Total number of operations of all jobs. |
| n | Job number. |
| m | Machine number. |
| ni | Operation number of job i. |
| t | AGV type indices. |
| nV | Total number of AGVs of all types. |
| K(i,j) | Optional machine set for Oi,j. |
| PTi,j,k | Processing time of Oi,j on machine k. |
| TTk,k′,t | Transportation time of k and k′ type t AGV. |
| PPk | Processing power on machine k (k ∈ K). |
| Idle power of machine k (k ∈ K). | |
| The empty power of AGV t (t ∈ T). | |
| The load power of AGV t (t ∈ T). | |
| TEC | Total energy consumption in workshop. |
| MPEC | Machine processing energy consumption. |
| MIEC | Machine idle energy consumption. |
| ATEC | AGV total energy consumption. |
| M | A large positive number. |
| Decision variable: | |
| Cmax | Makespan |
| Xi,j,k,t,v | When Oi,j is processed on machine k and transported by AGV v of type t. (Xi,j,k,t,v = 0, 1). |
| YMi,j,i′,j′ | When Oi,j is processed before Oi′,j′ by the same machine. (YMi,j,i′,j′ = 0, 1). |
| YTt,v,i,j,i′,j′ | When Oi,j is transported before Oi′,j′ by AGV v of type t. (YTt,v, i,j, i′j′ = 0, 1) |
| Si,j | Start processing time of Oi,j. |
| SAi,j,t,v | Arrive time of AGV v of type t for transporting Oi,j. |
| EMk | End processing time for machine k. |
| EAt,v | End transporting time of AGV v of type t. |
References
- Mareddy, P.L.; Narapureddy, S.R.; Dwivedula, V.R.; Karanam, P.R. Development of scheduling methodology in a multi-machine flexible manufacturing system without tool delay employing flower pollination algorithm. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2022, 115, 105275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kacem, I.; Hammadi, S.; Borne, P. Approach by localization and multiobjective evolutionary optimization for flexible job-shop scheduling problems. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part C (Appl. Rev.) 2002, 32, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C. Research on flexible job shop scheduling under finite transportation conditions for digital twin workshop. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2021, 72, 102198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Lei, D.; Wang, L. A Bi-Population Evolutionary Algorithm With Feedback for Energy-Efficient Fuzzy Flexible Job Shop Scheduling. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2022, 52, 5295–5307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi-Mehrabad, M.; Dehnavi-Arani, S.; Evazabadian, F.; Mahmoodian, V. An Ant Colony Algorithm (ACA) for solving the new integrated model of job shop scheduling and conflict-free routing of AGVs. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2015, 86, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Bao, Q.; Zhang, H. Multi-objective green scheduling of integrated flexible job shop and automated guided vehicles. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 126, 106864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi-Javid, A.; Hooshangi-Tabrizi, P. Integrating employee timetabling with scheduling of machines and transporters in a job-shop environment: A mathematical formulation and an Anarchic Society Optimization algorithm. Comput. Oper. Res. 2017, 84, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.-V.; Singh, N.; Adan, I.; Martagan, T.; van de Sande, D. Scheduling heterogeneous multi-load AGVs with battery constraints. Comput. Oper. Res. 2021, 136, 105517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, X.; He, X.; Xiong, Z.; Wu, X. Multi-objective optimization for scheduling multi-load automated guided vehicles with consideration of energy consumption. Transp. Res. Part C Emerg. Technol. 2024, 161, 104548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, D.B.M.M.; Homayouni, S.M.; Fernandes, J.C. Energy-efficient job shop scheduling problem with transport resources considering speed adjustable resources. Int. J. Prod. Res. 2024, 62, 867–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Yu, H.; Gao, K.; Fu, Y.; Kim, J.H. A Q-learning based artificial bee colony algorithm for solving surgery scheduling problems with setup time. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2024, 90, 101686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajani, O.S.; Ivan, D.F.; Darlan, D.; Suganthan, P.N.; Gao, K.; Mallipeddi, R. Deep reinforcement learning as multiobjective optimization benchmarks: Problem formulation and performance assessment. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2024, 90, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Wang, L. A Cooperative Memetic Algorithm With Learning-Based Agent for Energy-Aware Distributed Hybrid Flow-Shop Scheduling. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2022, 26, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raman, N. Simultaneous scheduling of machines and material handling devices in automated manufacturing. In Proceedings of the Second ORSA/TIMS Conference on Flexible Manufacturing Systems: Operations Research Models and Applications, Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 12–15 August 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Bilge, U.; Ulusoy, G. A Time Window Approach to Simultaneous Scheduling of Machines and Material Handling System in an FMS. Oper. Res. 1995, 43, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, A. Transfer-robot task scheduling in flexible job shop. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1783–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Wang, L.; Zheng, J.; Chen, J.F.; Wang, X. A Learning-Based Multipopulation Evolutionary Optimization for Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem With Finite Transportation Resources. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2023, 27, 1590–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Cheng, W.; Zhang, B.; Zou, W.; Fang, W.; Duan, P. An Improved Genetic Algorithm for Solving the Multi-AGV Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem. Sensors 2023, 23, 3815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Cheng, W.; Meng, L.; Zhang, B.; Gao, K.; Zhang, C.; Duan, P. A dual population collaborative genetic algorithm for solving flexible job shop scheduling problem with AGV. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2024, 86, 101538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayouni, S.M.; Fontes, D.B.M.M. Production and transport scheduling in flexible job shop manufacturing systems. J. Glob. Optim. 2021, 79, 463–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayouni, S.M.; Fontes, D.B.M.M.; Gonçalves, J.F. A multistart biased random key genetic algorithm for the flexible job shop scheduling problem with transportation. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2023, 30, 688–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Luo, Q.; Wang, L.; Tang, H.; Li, Y. The Low-Carbon Scheduling Optimization of Integrated Multispeed Flexible Manufacturing and Multi-AGV Transportation. Processes 2022, 10, 1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Li, R.; Gong, W. Deep reinforcement learning-based memetic algorithm for energy-aware flexible job shop scheduling with multi-AGV. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 189, 109917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontes, D.B.M.M.; Homayouni, S.M. Joint production and transportation scheduling in flexible manufacturing systems. J. Glob. Optim. 2019, 74, 879–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, W. An improved genetic algorithm for the flexible job shop scheduling problem with multiple time constraints. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2020, 54, 100664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, S.; Burdette, J.E.; Cheng, X.; Kinghorn, A.D. Interaction of (+)-Strebloside and Its Derivatives with Na+/K+-ATPase and Other Targets. Molecules 2021, 26, 5675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, K.Z.; Suganthan, P.N.; Chua, T.J.; Chong, C.S.; Cai, T.X.; Pan, Q.K. A two-stage artificial bee colony algorithm scheduling flexible job-shop scheduling problem with new job insertion. Expert Syst. Appl. 2015, 42, 7652–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Wan, G.; Zeng, P. A heuristic-assisted deep reinforcement learning algorithm for flexible job shop scheduling with transport constraints. Complex Intell. Syst. 2025, 11, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Meng, L.; Zhang, B.; Gao, K.; Sang, H. Imitation Learning-Assisted Evolutionary Algorithm for Energy-Efficient Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem with Automated Guided Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liao, C.; Wang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Guo, S. A Reinforcement Learning-Artificial Bee Colony algorithm for Flexible Job-shop Scheduling Problem with Lot Streaming. Appl. Soft Comput. 2023, 146, 110658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. A Deep Reinforcement Learning Method Based on a Transformer Model for the Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problem. Electronics 2024, 13, 3696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-Q.; Wu, F.-C.; Qian, B.; Hu, R.; Wang, L.; Jin, H.-P. A Q-learning-based hyper-heuristic evolutionary algorithm for the distributed flexible job-shop scheduling problem with crane transportation. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 234, 121050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Anwer, N.; Eynard, B.; Shu, L.H.; Xiao, J. A novel digital twin-assisted prediction approach for optimum rescheduling in high-efficient flexible production workshops. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2023, 182, 109398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, B.; Gao, K.; Ren, Y.; Sang, H. MILP modeling and optimization of multi-objective flexible job shop scheduling problem with controllable processing times. Swarm Evol. Comput. 2023, 82, 101374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroussi, L.; Norre, S. Simultaneous scheduling of machines and vehicles for the flexible job shop problem. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Metaheuristics and Nature Inspired Computing, Djerba, Tunisia, 28–30 October 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Van Nostrand, R.C. Design of Experiments Using the Taguchi Approach: 16 Steps to Product and Process Improvement. Technometrics 2002, 44, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitzler, E.; Deb, K.; Thiele, L. Comparison of Multiobjective Evolutionary Algorithms: Empirical Results. Evol. Comput. 2000, 8, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Thiele, L.; Laumanns, M.; Zitzler, E. Scalable multi-objective optimization test problems. In Proceedings of the 2002 Congress on Evolutionary Computation. CEC’02 (Cat. No.02TH8600), Hilton, HI, USA, 12–17 May 2002; Volume 821, pp. 825–830. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, R.; Yan, L.; Gu, S. Research on joint scheduling of AGVs and machines in multi-objective flexible job shop based on ISSA. Robot. Intell. Autom. 2025, 45, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Yu, Z.; Niu, R.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Z. Research on Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Method for Agricultural Equipment Considering Multi-Resource Constraints. Agriculture 2025, 15, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Wei, M.; Gao, X. Modeling an Optimal Environmentally Friendly Energy-Saving Flexible Workshop. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Job | Operation | M1 | M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Job 1 | O1,1 | 50 | 62 | — |
| O1,2 | — | 40 | 55 | |
| Job 2 | O2,1 | 55 | 47 | 50 |
| O2,2 | 65 | 55 | — | |
| Job 3 | O3,1 | 75 | 50 | 43 |
| O3,2 | 43 | — | 52 |
| AGV_T1 | M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 | AGV_T2 | M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | 0 | 20 | 30 | 40 | M0 | 0 | 40 | 60 | 80 |
| M1 | 20 | 0 | 20 | 30 | M1 | 40 | 0 | 40 | 60 |
| M2 | 30 | 20 | 0 | 20 | M2 | 60 | 40 | 0 | 40 |
| M3 | 40 | 30 | 20 | 0 | M3 | 80 | 60 | 40 | 0 |
| Test | Parameter | Mean of IGD | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ps | α | γ | ε | N | LS | ||
| 1 | 40 | 0.05 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 20 | 5 | 0.38786 |
| 2 | 40 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 30 | 10 | 0.37171 |
| 3 | 40 | 0.15 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 40 | 15 | 0.36829 |
| 4 | 60 | 0.05 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 30 | 15 | 0.36577 |
| 5 | 60 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 40 | 5 | 0.37891 |
| 6 | 60 | 0.15 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 20 | 10 | 0.37141 |
| 7 | 80 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 40 | 10 | 0.37171 |
| 8 | 80 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 20 | 15 | 0.36714 |
| 9 | 80 | 0.15 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 30 | 5 | 0.38339 |
| 10 | 40 | 0.05 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 30 | 10 | 0.37181 |
| 11 | 40 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.3 | 40 | 15 | 0.36324 |
| 12 | 40 | 0.15 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 20 | 5 | 0.38538 |
| 13 | 60 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 0.7 | 20 | 15 | 0.36154 |
| 14 | 60 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.3 | 30 | 5 | 0.38859 |
| 15 | 60 | 0.15 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 40 | 10 | 0.36797 |
| 16 | 80 | 0.05 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 40 | 5 | 0.38515 |
| 17 | 80 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 20 | 10 | 0.36261 |
| 18 | 80 | 0.15 | 0.8 | 0.3 | 30 | 15 | 0.36585 |
| Functions | Statistics | Q-HMOABC-E | Q-HMOABC-O | Q-HMOABC-S | Q-HMOABC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZDT3 | Mean | 0.02087 | 0.03223 | 0.01979 | 0.01547 |
| Max | 0.02621 | 0.03745 | 0.02295 | 0.01612 | |
| Min | 0.01594 | 0.02643 | 0.01625 | 0.01487 | |
| Std | 1.742 × 10−3 | 1.834 × 10−3 | 1.177 × 10−3 | 2.135 × 10−4 | |
| ZDT4 | Mean | 0.5258 | 1.7716 | 2.4999 | 7.327 × 10−3 |
| Max | 0.5822 | 1.8409 | 2.8305 | 7.605 × 10−3 | |
| Min | 0.4710 | 1.6812 | 2.1164 | 7.018 × 10−3 | |
| Std | 0.0305 | 0.0437 | 0.1956 | 1.751 × 10−4 | |
| ZDT6 | Mean | 2.935 × 10−3 | 2.972 × 10−3 | 0.01029 | 2.025 × 10−3 |
| Max | 3.054 × 10−3 | 3.103 × 10−3 | 0.01530 | 2.827 × 10−3 | |
| Min | 2.861 × 10−3 | 2.823 × 10−3 | 8.154 × 10−3 | 1.495 × 10−3 | |
| Std | 5.217 × 10−5 | 8.499 × 10−5 | 1.983 × 10−3 | 2.317 × 10−5 | |
| DTLZ2 | Mean | 0.09558 | 0.05251 | 0.05147 | 0.04958 |
| Max | 0.12074 | 0.06307 | 0.05866 | 0.05940 | |
| Min | 0.06182 | 0.04730 | 0.04327 | 0.04129 | |
| Std | 0.01614 | 4.965 × 10−3 | 4.086 × 10−3 | 5.203 × 10−3 | |
| DTLZ5 | Mean | 0.02981 | 0.01431 | 0.01112 | 8.064 × 10−3 |
| Max | 0.04205 | 0.02774 | 0.01896 | 8.237 × 10−3 | |
| Min | 0.02578 | 8.161 × 10−3 | 7.817 × 10−3 | 7.147 × 10−3 | |
| Std | 4.415 × 10−3 | 5.341 × 10−3 | 3.055 × 10−3 | 2.769 × 10−4 |
| Functions | Statistics | Q-HMOABC-E | Q-HMOABC-O | Q-HMOABC-S | Q-HMOABC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZDT3 | Mean | 1.735 × 10−3 | 2.616 × 10−3 | 1.297 × 10−3 | 1.033 × 10−3 |
| Max | 2.031 × 10−3 | 2.913 × 10−3 | 1.443 × 10−3 | 1.276 × 10−3 | |
| Min | 1.596 × 10−3 | 2.205 × 10−3 | 1.139 × 10−3 | 9.409 × 10−4 | |
| Std | 1.182 × 10−4 | 1.934 × 10−4 | 8.306 × 10−5 | 9.178 × 10−5 | |
| ZDT4 | Mean | 0.06360 | 0.2121 | 0.3029 | 9.217 × 10−5 |
| Max | 0.09144 | 0.3513 | 0.4501 | 1.153 × 10−4 | |
| Min | 0.04801 | 0.1247 | 0.1773 | 8.592 × 10−5 | |
| Std | 9.866 × 10−3 | 0.05507 | 0.06845 | 8.024 × 10−6 | |
| ZDT6 | Mean | 0.07706 | 0.09419 | 0.07757 | 5.227 × 10−4 |
| Max | 0.1043 | 0.1358 | 0.1132 | 7.905 × 10−4 | |
| Min | 0.05942 | 0.06703 | 0.06419 | 4.143 × 10−4 | |
| Std | 9.816 × 10−3 | 0.01625 | 0.01352 | 1.030 × 10−4 | |
| DTLZ2 | Mean | 9.264 × 10−3 | 2.215 × 10−3 | 1.810 × 10−3 | 1.614 × 10−3 |
| Max | 0.01294 | 2.971 × 10−3 | 1.945 × 10−3 | 1.803 × 10−3 | |
| Min | 6.671 × 10−3 | 1.523 × 10−3 | 1.662 × 10−3 | 1.425 × 10−3 | |
| Std | 1.529 × 10−3 | 3.581 × 10−4 | 6.794 × 10−5 | 9.725 × 10−5 | |
| DTLZ5 | Mean | 2.832 × 10−3 | 1.340 × 10−3 | 1.207 × 10−3 | 3.538 × 10−4 |
| Max | 3.281 × 10−3 | 1.736 × 10−3 | 1.553 × 10−3 | 3.910 × 10−4 | |
| Min | 2.394 × 10−3 | 1.039 × 10−3 | 9.835 × 10−4 | 2.968 × 10−4 | |
| Std | 2.018 × 10−4 | 1.909 × 10−4 | 1.431 × 10−4 | 2.164 × 10−5 |
| Instances | Q-HMOABC-E | Q-HMOABC-O | Q-HMOABC-S | Q-HMOABC | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best | Mean | Best | Mean | Best | Mean | Best | Mean | |
| BU01 | 0.5237 | 0.5092 | 0.5004 | 0.4922 | 0.5214 | 0.5059 | 0.5593 | 0.5471 |
| BU02 | 0.4674 | 0.4555 | 0.4528 | 0.4423 | 0.4702 | 0.4605 | 0.5012 | 0.4947 |
| BU04 | 0.5587 | 0.5332 | 0.5574 | 0.5134 | 0.5647 | 0.5273 | 0.6283 | 0.5921 |
| BU05 | 0.5129 | 0.5075 | 0.5310 | 0.5103 | 0.5382 | 0.5178 | 0.5599 | 0.5422 |
| BU07 | 0.5096 | 0.4885 | 0.5127 | 0.4787 | 0.5209 | 0.5067 | 0.5556 | 0.5384 |
| BU08 | 0.4828 | 0.4504 | 0.4614 | 0.4264 | 0.4837 | 0.4427 | 0.4967 | 0.4788 |
| BU09 | 0.5114 | 0.5070 | 0.5216 | 0.5051 | 0.5492 | 0.5229 | 0.5655 | 0.5486 |
| DN01 | 0.4831 | 0.4620 | 0.4437 | 0.4275 | 0.4756 | 0.4633 | 0.4969 | 0.4828 |
| DN02 | 0.4523 | 0.4406 | 0.4114 | 0.3958 | 0.4419 | 0.4293 | 0.4889 | 0.4617 |
| DN03 | 0.4590 | 0.4484 | 0.4540 | 0.4107 | 0.4527 | 0.4309 | 0.4930 | 0.4766 |
| DN04 | 0.5084 | 0.4872 | 0.4506 | 0.4258 | 0.4830 | 0.4602 | 0.5050 | 0.4796 |
| DN05 | 0.5056 | 0.4796 | 0.4836 | 0.4493 | 0.5020 | 0.4706 | 0.5207 | 0.5036 |
| DN06 | 0.4602 | 0.4375 | 0.4410 | 0.4112 | 0.4763 | 0.4468 | 0.4864 | 0.4654 |
| DN07 | 0.5008 | 0.4845 | 0.4568 | 0.4399 | 0.5074 | 0.4836 | 0.5190 | 0.4992 |
| DN08 | 0.4724 | 0.4594 | 0.4674 | 0.4321 | 0.4727 | 0.4584 | 0.4921 | 0.4838 |
| DN09 | 0.5078 | 0.4906 | 0.4871 | 0.4544 | 0.4901 | 0.4807 | 0.5186 | 0.5101 |
| DN10 | 0.4273 | 0.4178 | 0.3895 | 0.3804 | 0.4269 | 0.4003 | 0.4785 | 0.4537 |
| Instances | HV | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q-HMOABC | MOSSA | MOGWO | MOWOA | NSGA-II | |
| BU01 | 0.5051 | 0.3921 | 0.4245 | 0.4027 | 0.4525 |
| BU02 | 0.5021 | 0.4013 | 0.4148 | 0.4046 | 0.4526 |
| BU04 | 0.6063 | 0.4519 | 0.5024 | 0.4494 | 0.5423 |
| BU05 | 0.5526 | 0.4332 | 0.4673 | 0.4390 | 0.5031 |
| BU07 | 0.5217 | 0.4214 | 0.4374 | 0.4051 | 0.4643 |
| BU08 | 0.5507 | 0.4535 | 0.4716 | 0.4429 | 0.5053 |
| BU09 | 0.5425 | 0.4281 | 0.4449 | 0.4298 | 0.4979 |
| DN01 | 0.5182 | 0.4626 | 0.4769 | 0.4533 | 0.4739 |
| DN02 | 0.4741 | 0.4021 | 0.4223 | 0.4090 | 0.4284 |
| DN03 | 0.4704 | 0.3934 | 0.4321 | 0.4017 | 0.4710 |
| DN04 | 0.5242 | 0.4116 | 0.4703 | 0.4126 | 0.4916 |
| DN05 | 0.5192 | 0.4354 | 0.4667 | 0.4306 | 0.4632 |
| DN06 | 0.4665 | 0.3935 | 0.4294 | 0.3927 | 0.4225 |
| DN07 | 0.4841 | 0.4098 | 0.4384 | 0.4124 | 0.4324 |
| DN08 | 0.4360 | 0.3751 | 0.4026 | 0.3891 | 0.4104 |
| DN09 | 0.4906 | 0.4123 | 0.4378 | 0.3996 | 0.4449 |
| DN10 | 0.4635 | 0.3886 | 0.4100 | 0.3875 | 0.4064 |
| Mean Runtime(s) | 714.6 | 811.7 | 761.2 | 774.3 | 730.5 |
| Instances | IGD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q-HMOABC | MOSSA | MOGWO | MOWOA | NSGA-II | |
| BU01 | 0.3857 | 0.4912 | 0.4537 | 0.4861 | 0.4255 |
| BU02 | 0.3863 | 0.4809 | 0.4716 | 0.4781 | 0.4176 |
| BU04 | 0.2801 | 0.4189 | 0.3655 | 0.4228 | 0.3281 |
| BU05 | 0.3476 | 0.4477 | 0.4064 | 0.4410 | 0.3744 |
| BU07 | 0.3600 | 0.4568 | 0.4302 | 0.4656 | 0.4031 |
| BU08 | 0.3318 | 0.4183 | 0.4019 | 0.4271 | 0.3701 |
| BU09 | 0.3400 | 0.4441 | 0.4213 | 0.4422 | 0.3743 |
| DN01 | 0.3609 | 0.4120 | 0.3973 | 0.4250 | 0.3953 |
| DN02 | 0.4340 | 0.4935 | 0.4675 | 0.4951 | 0.4573 |
| DN03 | 0.4195 | 0.4879 | 0.4601 | 0.4774 | 0.4394 |
| DN04 | 0.3485 | 0.4587 | 0.3959 | 0.4574 | 0.3782 |
| DN05 | 0.3566 | 0.4434 | 0.4010 | 0.4448 | 0.4072 |
| DN06 | 0.4494 | 0.4967 | 0.4637 | 0.4987 | 0.4679 |
| DN07 | 0.4109 | 0.4705 | 0.4494 | 0.4651 | 0.4442 |
| DN08 | 0.4423 | 0.5008 | 0.4818 | 0.5020 | 0.4703 |
| DN09 | 0.4059 | 0.4729 | 0.4556 | 0.4729 | 0.4358 |
| DN10 | 0.4327 | 0.4957 | 0.4663 | 0.4921 | 0.4737 |
| Mean Runtime(s) | 638.4 | 733.9 | 682.0 | 706.2 | 661.5 |
| Algorithms | HV | IGD |
|---|---|---|
| Q-HMOABC vs. MOSSA | 0.010 | 0.007 |
| Q-HMOABC vs. MOGWO | 0.006 | 0.010 |
| Q-HMOABC vs. MOWOA | 0.008 | 0.006 |
| Q-HMOABC vs. NSGA-II | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, S.; Zhang, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z. A Multi-Objective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm Incorporating Q-Learning Search for the Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problems with Multi-Type Automated Guided Vehicles. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010948
Ge S, Zhang H, Xu Z, Yang Z. A Multi-Objective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm Incorporating Q-Learning Search for the Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problems with Multi-Type Automated Guided Vehicles. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010948
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Shihong, Hao Zhang, Zhigang Xu, and Zhiqi Yang. 2025. "A Multi-Objective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm Incorporating Q-Learning Search for the Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problems with Multi-Type Automated Guided Vehicles" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010948
APA StyleGe, S., Zhang, H., Xu, Z., & Yang, Z. (2025). A Multi-Objective Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm Incorporating Q-Learning Search for the Flexible Job Shop Scheduling Problems with Multi-Type Automated Guided Vehicles. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10948. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010948






