Gut Microbiota of Peruvian Anchovy (Engraulis ringens) as a Novel Source of Lipase-Producing Bacteria with Biocatalytic Potential
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
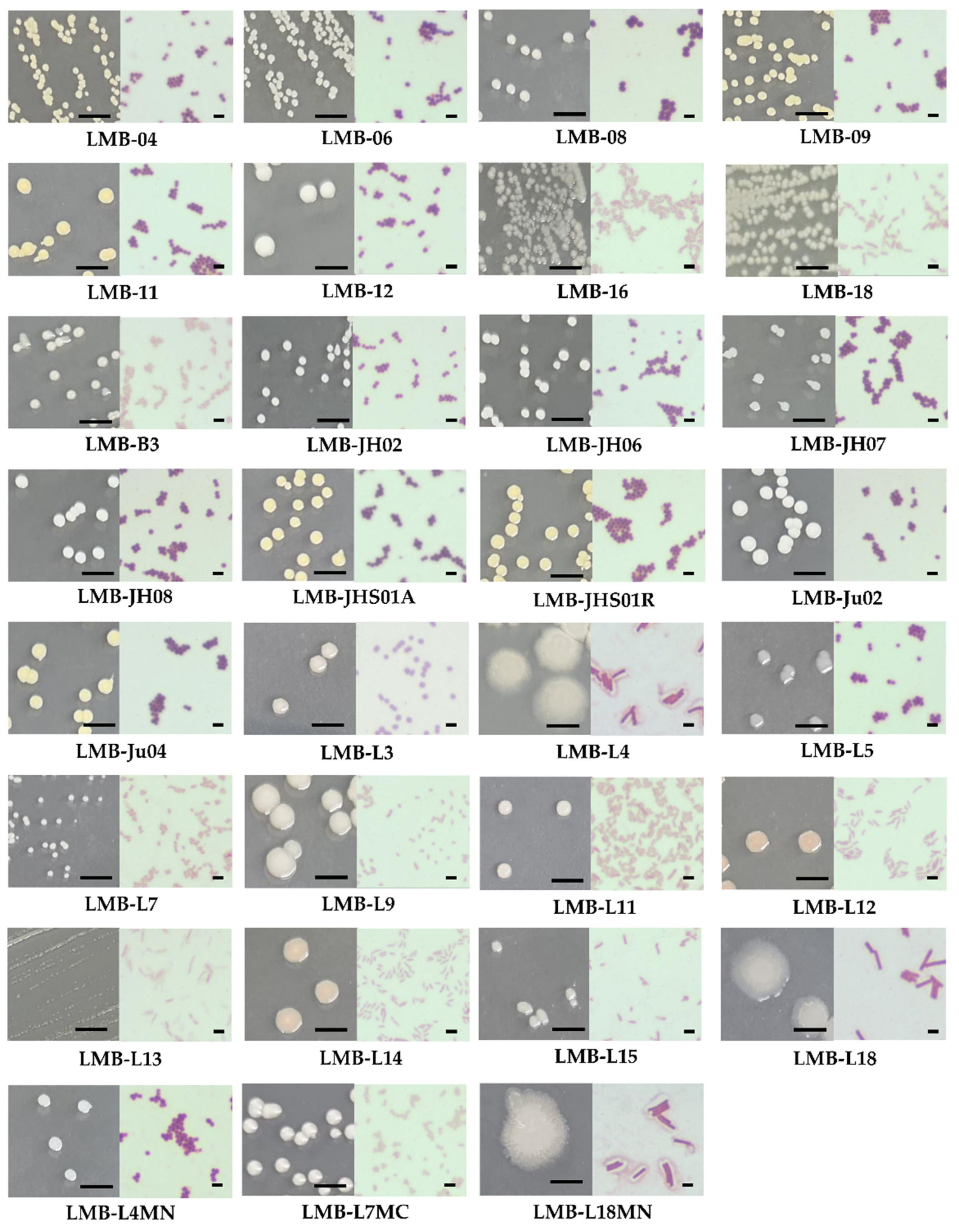
2.1. Isolation of Bacteria from Anchovy Guts
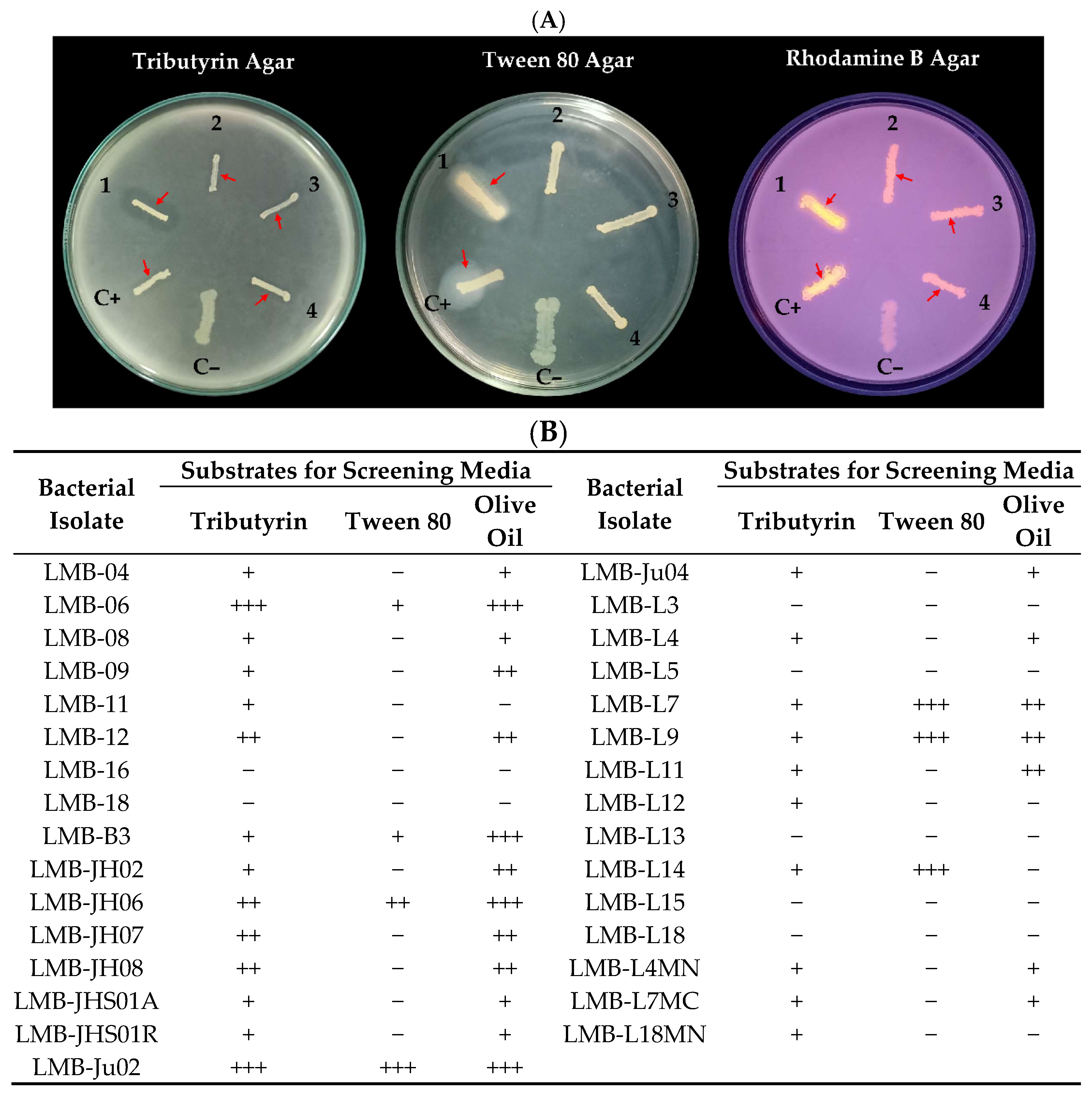
2.2. Screening of Lipase-Producing Bacterial Isolates
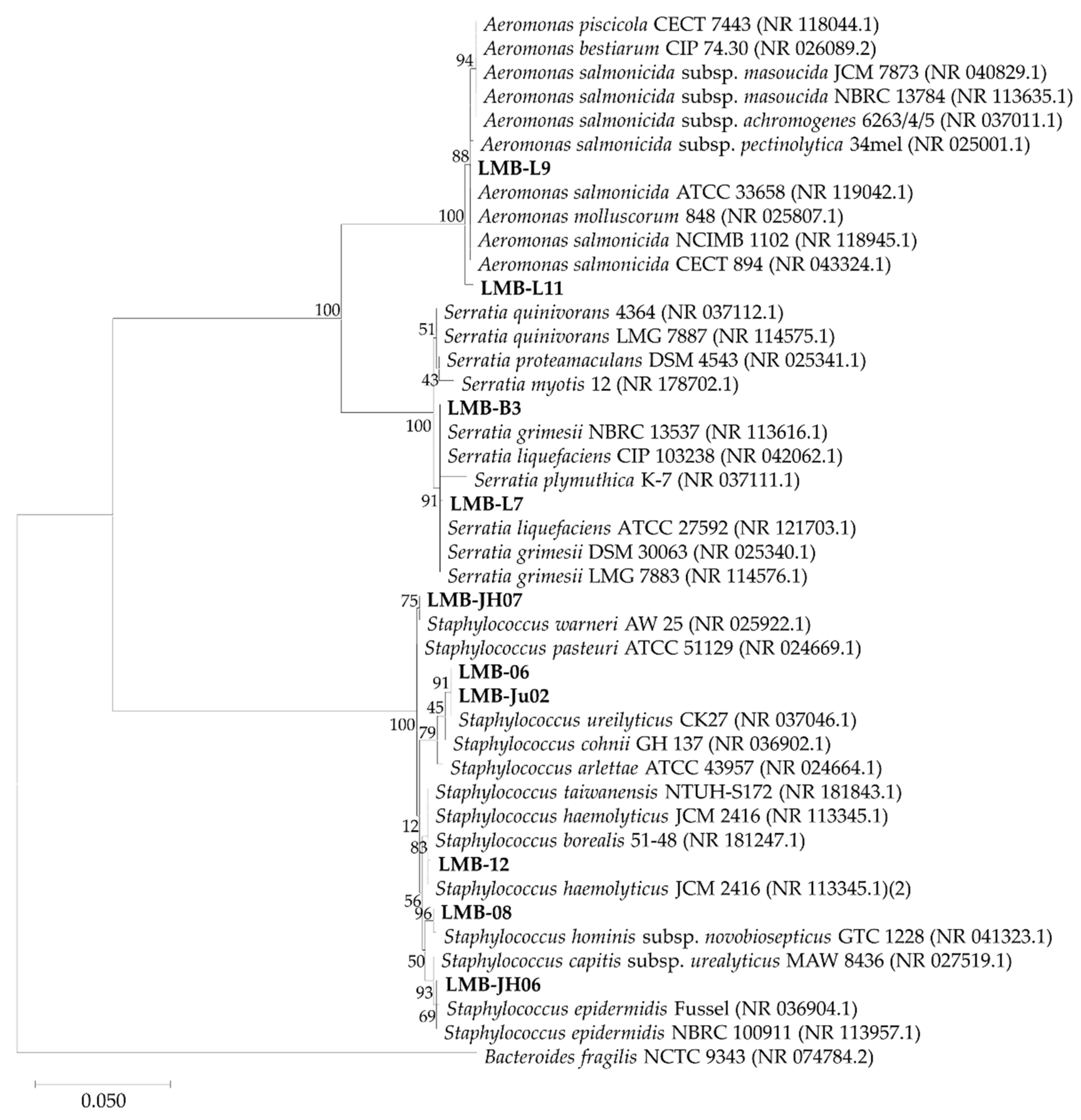
2.3. Molecular Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of Lipolytic Strains
2.4. Lipase Production
2.5. Determination of Soluble Protein Content
2.6. Determination of Lipase Activity
2.7. Effect of pH and Temperature on Lipase Activity
2.8. Effect of Different Ions, Solvents and Other Factors on Lipase Activity
2.9. Triglyceride Hydrolysis Assay
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Lipase-Producing Bacterial Strains from Anchovy Gut
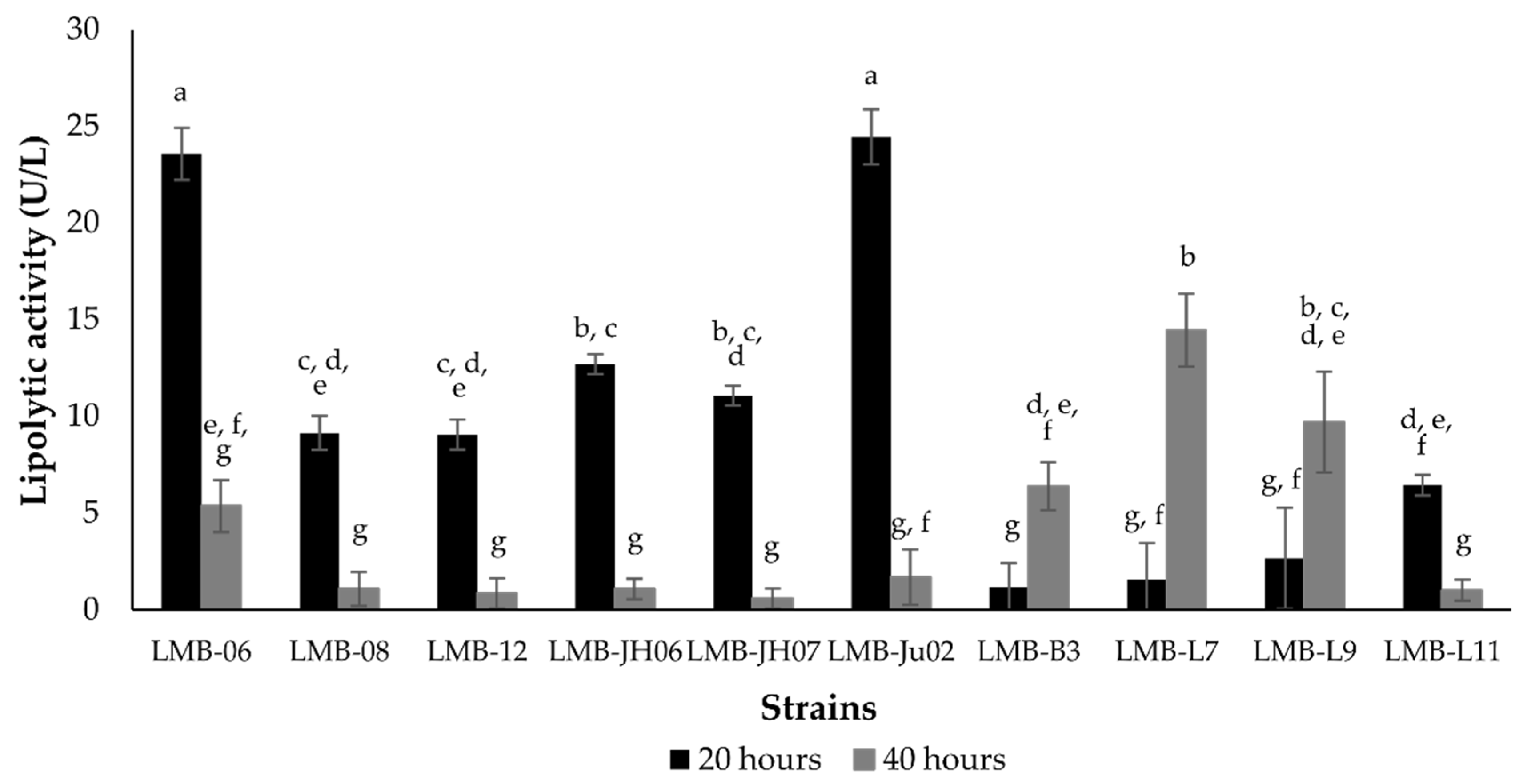
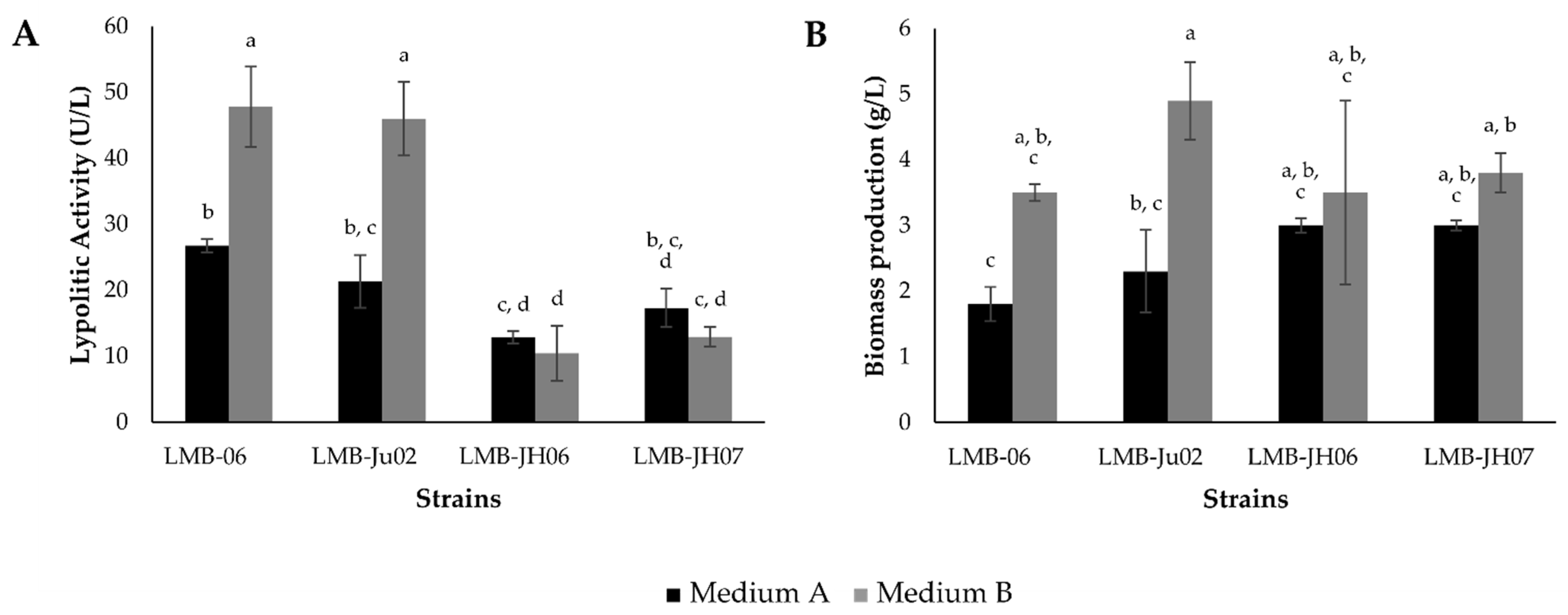
3.2. Yield and Productivity of Staphylococcus Lipases
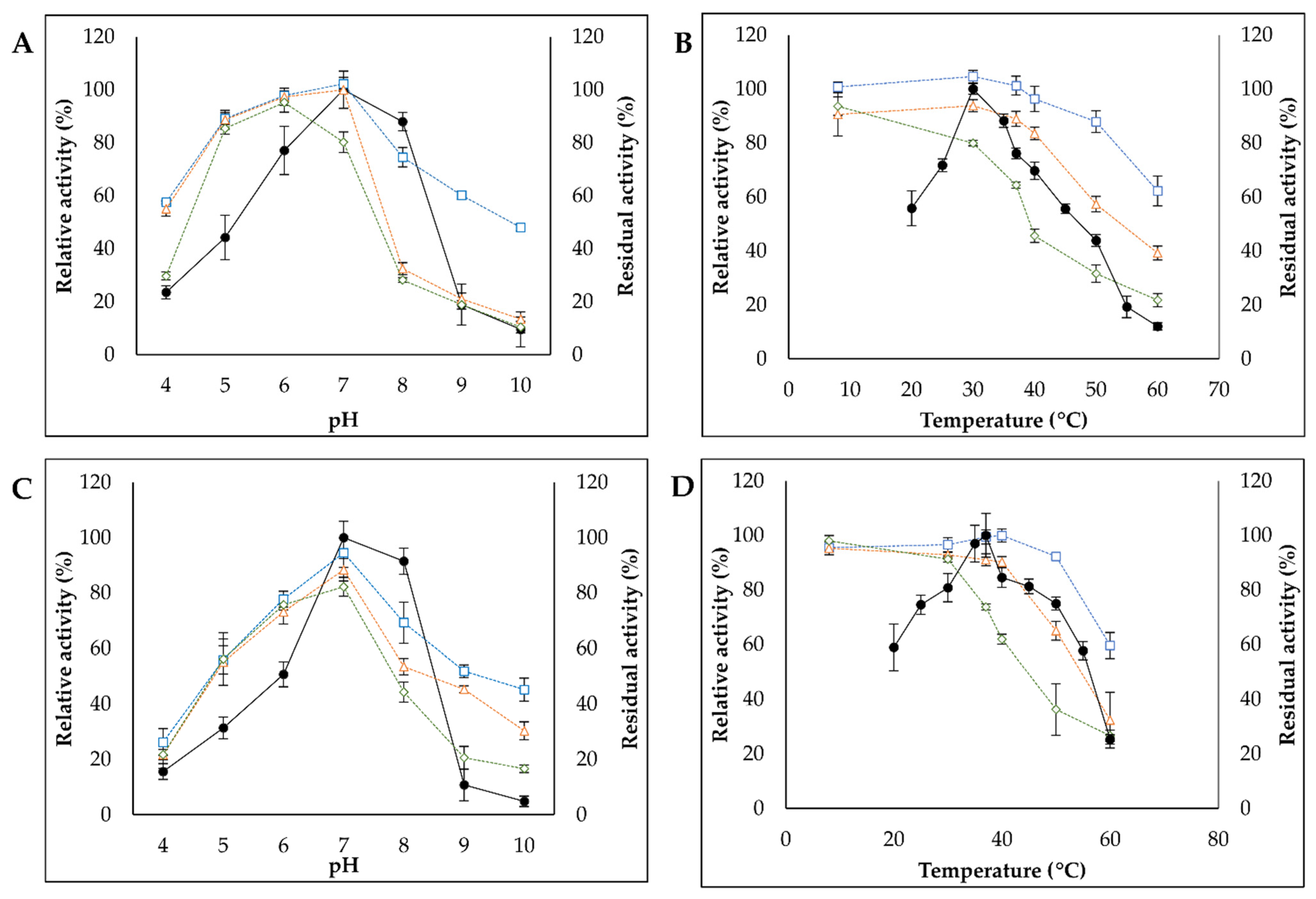
3.3. Partial Characterization of S. ureilitycus Secretomes
3.3.1. Effect of pH and Temperature on Enzymatic Activity and Stability
3.3.2. Effect of Metal Ions, Organic Solvents and Inhibitors on Enzymatic Activity and Stability
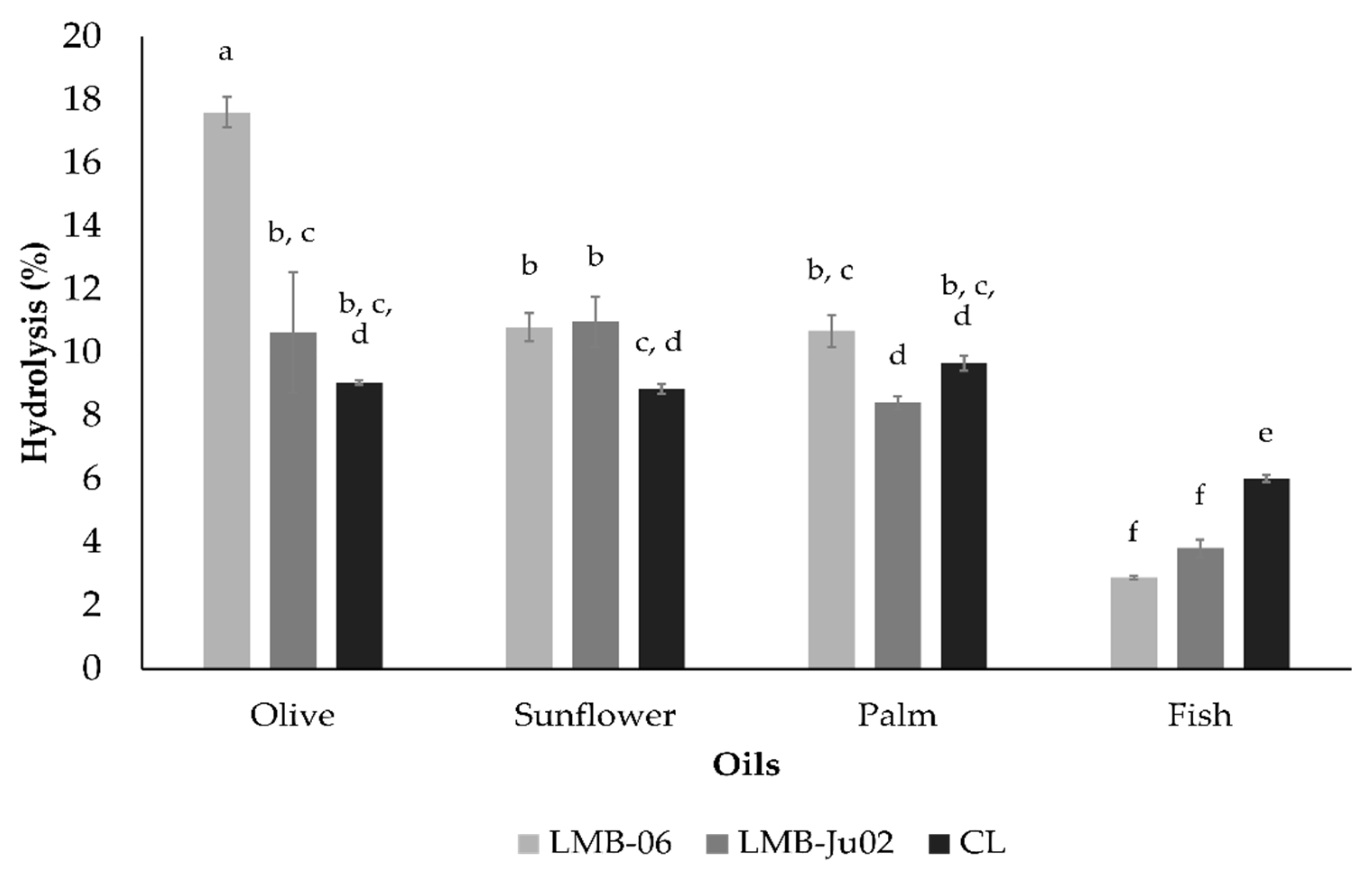
3.4. Enzymatic Hydrolysis of Triglycerides by Lipases from S. ureilyticus Secretomes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandra, P.; Enespa; Singh, R.; Arora, P.K. Microbial Lipases and Their Industrial Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Microb. Cell Fact. 2020, 19, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, A.; Guleria, S.; Sharma, R.; Gupta, R. The Lipases and Their Applications with Emphasis on Food Industry. In Microbial Biotechnology in Food and Health; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas-Godoy, L.; Gasteazoro, F.; Duquesne, S.; Bordes, F.; Marty, A.; Sandoval, G. Lipases: An Overview. In Lipases and Phospholipases; Sandoval, G., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1835, pp. 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Future Market Insights. Lipase Market Outlook (2025–2035): Global Industry Analysis and Opportunity Assessment. 2024. Available online: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/lipase-market (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Guerrand, D. Lipases Industrial Applications: Focus on Food and Agroindustries. OCL Oilseeds Fats Crops Lipids 2017, 24, D403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Khan, S.A.; Hamayun, M.; Lee, I.J. The Recent Advances in the Utility of Microbial Lipases: A Review. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Gudiukaite, R.; Gricajeva, A.; Sadauskas, M.; Malunavicius, V.; Kamyab, H.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, T.; Pant, D. Microbial Lipolytic Enzymes—Promising Energy-Efficient Biocatalysts in Bioremediation. Energy 2020, 192, 116674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Azeem, F.; Hussain, S.; Rasul, I.; Siddique, M.H.; Riaz, M.; Afzal, M.; Kouser, A.; Nadeem, H. Bacterial Lipases: A Review on Purification and Characterization. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 132, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, M.; Niehus, X.; Casas-Godoy, L.; Sandoval, G. Lipases as Biocatalyst for Biodiesel Production. In Lipases and Phospholipases; Sandoval, G., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; Volume 1835, pp. 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, S.; Puna, J.; Gomes, J. A Review on Bio-Based Catalysts (Immobilized Enzymes) Used for Biodiesel Production. Energies 2020, 13, 3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biermann, U.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Feussner, I.; Meier, M.A.; Metzger, J.O. Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives as Renewable Platform Molecules for the Chemical Industry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 20144–20165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambare, V.; Patankar, R.; Bhusare, B.; Christopher, L. Recent Advances in Feedstock and Lipase Research and Development towards Commercialization of Enzymatic Biodiesel. Processes 2021, 9, 1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, J.G.C.; Cardoso, F.V.; Santos, C.C.d.; Matias, R.R.; Machado, N.T.; Duvoisin Junior, S.; Albuquerque, P.M. Biocatalyzed Transesterification of Waste Cooking Oil for Biodiesel Production Using Lipase from the Amazonian Fungus Endomelanconiopsis endophytica. Energies 2023, 16, 6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.J.C.; de Carvalho, C.C.C.R. Marine Bioprospecting, Biocatalysis and Process Development. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzkar, N.; Sukhikh, S.; Babich, O. Study of Marine Microorganism Metabolites: New Resources for Bioactive Natural Products. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1285902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragozzino, C.; Casella, V.; Coppola, A.; Scarpato, S.; Buonocore, C.; Consiglio, A.; Palma Esposito, F.; Galasso, C.; Tedesco, P.; Della Sala, G.; et al. Last Decade Insights in Exploiting Marine Microorganisms as Sources of New Bioactive Natural Products. Mar. Drugs 2025, 23, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Sham, R.C.; Deng, Y.; Mao, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, T.; Leung, K.M.Y. Diversity of Gut Microbiomes in Marine Fishes Is Shaped by Host-Related Factors. Mol. Ecol. 2020, 29, 5019–5034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Shin, N.R.; Lee, J.B.; Kim, M.S.; Whon, T.W.; Hyun, D.W.; Yun, J.H.; Jung, M.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Bae, J.W. Host Habitat Is the Major Determinant of the Gut Microbiome of Fish. Microbiome 2021, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, A.K.; Ghosh, K.; Ringø, E. Enzyme-Producing Bacteria Isolated from Fish Gut: A Review. Aquac. Nutr. 2012, 18, 465–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, T.J.; Chowdhury, S.I.; Mozumder, H.A.; Chowdhury, M.N.A.; Ali, F.; Rahman, N.; Dey, S. Hydrolytic Exoenzymes Produced by Bacteria Isolated and Identified from the Gastrointestinal Tract of Bombay Duck. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapsari, R.T.; Susilowati, A.; Pangastuti, A. Isolation and Identification of Lipolytic Bacteria from the Digestive Tract of Eel (Anguilla bicolor bicolor). Int. J. Bonorowo Wetl. 2020, 10, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uniacke-Lowe, S.; Stanton, C.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. The Marine Fish Gut Microbiome as a Source of Novel Bacteriocins. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhayalan, A.; Jayanthi, K.; Manoharan, S.; Nadeem, A.; Govindasamy, B.; Pachiappan, P.; Vasudhevan, P. Fish Gut Symbiotic Bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis: RSM Optimization for Its Extracellular Lipase Enzyme Production, Lipase-Protein Purification, Characterization, and Docking Analysis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 301, 140428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinoza, P.; Bertrand, A. Revisiting Peruvian Anchovy (Engraulis ringens) Trophodynamics Provides a New Vision of the Humboldt Current System. Prog. Oceanogr. 2008, 79, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, L.M.; Wong, W.R.; Riener, R.M.; Schulze, C.J.; Linington, R.G. Examining the Fish Microbiome: Vertebrate-Derived Bacteria as an Environmental Niche for the Discovery of Unique Marine Natural Products. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coico, R. Gram Staining. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2006, 1, A.3C.1–A.3C.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilesanmi, O.I.; Adekunle, A.E.; Omolaiye, J.A.; Olorode, E.M.; Ogunkanmi, A.L. Isolation, Optimization and Molecular Characterization of Lipase Producing Bacteria from Contaminated Soil. Sci. Afr. 2020, 8, e00279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramnath, L.; Sithole, B.; Govinden, R. Identification of Lipolytic Enzymes Isolated from Bacteria Indigenous to Eucalyptus Wood Species for Application in the Pulping Industry. Biotechnol. Rep. 2017, 15, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerapagu, M.; Sankara Narayan, A.; Ponmurugan, K.; Jeya, K.R. Screening Selection Identification Production and Optimization of Bacterial Lipase from Oil Spilled Soil. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2013, 6, 62–67. [Google Scholar]
- Esakkiraj, P.; Rajkumarbharathi, M.; Palavesam, A.; Immanuel, G. Lipase Production by Staphylococcus epidermidis CMST-Pi 1 Isolated from the Gut of Shrimp Penaeus indicus. Ann. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Link, A.J.; LaBaer, J. Trichloroacetic Acid (TCA) Precipitation of Proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Protoc. 2011, 2011, 993–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, R.; Singh, J.; Bharti, R.K.; Thakur, I.S. Isolation, Purification and Characterization of Lipase from Microbacterium sp. and Its Application in Biodiesel Production. Energy Procedia 2014, 54, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustranta, A. Use of Lipases in the Resolution of Racemic Ibuprofen. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1992, 38, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Hu, J.; Gui, X.; Wang, G.; Yan, Y. Enzymatic Enrichment of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Using Novel Lipase Preparations Modified by Combination of Immobilization and Fish Oil Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 7154–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho-Ruiz, M.D.L.A.; Mateos-Díaz, J.C.; Carrière, F.; Rodriguez, J.A. A Broad pH Range Indicator-Based Spectrophotometric Assay for True Lipases Using Tributyrin and Tricaprylin. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollof, J.; Hedstrom, S.A.; Nilsson-Ehle, P. The Tween 80 Reaction Does Not Correlate to Triglyceride Lipase Production of Staphylococcus Aureus. Apmis 1988, 96, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mates, A.; Sudakevitz, D. Production of Lipase by Staphylococcus aureus under Various Growth Conditions. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1973, 36, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boekema, B.K.H.L.; Beselin, A.; Breuer, M.; Hauer, B.; Koster, M.; Rosenau, F.; Jaeger, K.; Tommassen, J. Hexadecane and Tween 80 Stimulate Lipase Production in Burkholderia glumae by Different Mechanisms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, e00097-07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Z.D.; Xu, J.H.; Pan, J. Significant Improvement of Serratia marcescens Lipase Fermentation by Optimizing Medium, Induction, and Oxygen Supply. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 142, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarevúcka, M. Olive Oil as Inductor of Microbial Lipase. In Olive Oil—Constituents, Quality, Health Properties and Bioconversions; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2012; pp. 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciafardini, G.; Zullo, B.A. Virgin Olive Oil Yeasts: A Review. Food Microbiol. 2018, 70, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jammal, A.; Bariche, M.; Dohna, H.; Kambris, Z. Characterization of the Cultivable Gut Microflora in Wild-Caught Mediterranean Fish Species. Curr. Nutr. Food Sci. 2017, 13, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Yan, F.; Cui, Y.; Du, J.; Hu, G.; Zhai, W.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Fang, J.; Chen, L.; et al. A Symbiotic Bacterium of Antarctic Fish Reveals Environmental Adaptability Mechanisms and Biosynthetic Potential towards Antibacterial and Cytotoxic Activities. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1085063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parshukov, A.N.; Kashinskaya, E.N.; Simonov, E.P.; Hlunov, O.V.; Izvekova, G.I.; Andree, K.B.; Solovyev, M.M. Variations of the Intestinal Gut Microbiota of Farmed Rainbow Trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss (Walbaum), Depending on the Infection Status of the Fish. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 379–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawser, A.Q.M.R.; Foysal, M.J.; Chua, E.G.; Ali, M.H.; Mannan, A.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Paul, S.I.; Rahman, M.M.; Tay, A. Microbiome Data Reveal Significant Differences in the Bacterial Diversity in Freshwater Rohu (Labeo rohita) across the Supply Chain in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 75, 813–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueras, M.J.; Beaz-Hidalgo, R. Aeromonas: Introduction. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; Volume 1, pp. 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, G.D.; Balcázar, J.L. A Review on the Interactions between Gut Microbiota and Innate Immunity of Fish. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2008, 52, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillaspy, A.G.; Iandolo, J.J. Staphylococcus. In Encyclopedia of Food Microbiology; Batt, C.A., Tortorello, M.L., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2014; Volume 3, pp. 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Bulushi, I.M.; Poole, S.E.; Barlow, R.; Deeth, H.C.; Dykes, G.A. Speciation of Gram-Positive Bacteria in Fresh and Ambient-Stored Sub-Tropical Marine Fish. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 138, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askarian, F.; Zhou, Z.; Olsen, R.E.; Sperstad, S.; Ringø, E. Culturable Autochthonous Gut Bacteria in Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) Fed Diets with or without Chitin: Characterization by 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing, Ability to Produce Enzymes and in Vitro Growth Inhibition of Four Fish Pathogens. Aquaculture 2012, 326–329, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl, A.; Olsen, R.E.; Dimitroglou, A.; Foey, A.; Davies, S.; et al. Effect of Dietary Components on the Gut Microbiota of Aquatic Animals. A Never-Ending Story? Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esakkiraj, P.; Nawas, P.M.A.; Thomas, S.K.; Maruthiah, T.; Palavesam, A.; Immanuel, G. Solid-State Lipase Production by Staphylococcus cohnii AP-CMST Using Anchovy Processing Wastes. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 7, 637–644. [Google Scholar]
- Daroonpunt, R.; Saeng-in, P.; Tanasupawat, S. Identification and Lipolytic Activity of Bacillus and Staphylococcus Strains from Shrimp Paste (Ka-Pi). J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 9, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobarak-Qamsari, E.; Kasra-Kermanshahi, R.; Moosavi-Nejad, Z. Isolation and Identification of a Novel, Lipase-Producing Bacterium, Pseudomonas aeruginosa KM110. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2011, 3, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida, A.F.; Tauk-Tornisielo, S.M.; Carmona, E.C. Acid Lipase from Candida viswanathii: Production, Biochemical Properties, and Potential Application. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 435818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; Ramteke, P.W.; Kumar, P.A. Studies on the Enhanced Production of Extracellular Lipase by Staphylococcus epidermidis. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 52, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaei-Nouroozi, A.; Rezaei, S.; Khoshnevis, N.; Doosti, M.; Hajihoseini, R.; Khoshayand, M.R.; Faramarzi, M.A. Medium-Based Optimization of an Organic Solvent-Tolerant Extracellular Lipase from the Isolated Halophilic Alkalibacillus salilacus. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 933–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkan, H.; Baysal, Z.; Uyar, F.; Dogru, M. Production of Lipase by a Newly Isolated Bacillus coagulans under Solid-State Fermentation Using Melon Wastes. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2007, 136, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenstein, R.; Götz, F. Staphylococcal Lipases: Biochemical and Molecular Characterization. Biochimie 2000, 82, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, P.K. Staphylococcus lipolyticus sp. nov., a New Cold-Adapted Lipase Producing Marine Species. Ann. Microbiol. 2013, 63, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, M.; Garlapati, V.K. Production and Characterization of a Halo-, Solvent-, Thermo-Tolerant Alkaline Lipase by Staphylococcus arlettae JPBW-1, Isolated from Rock Salt Mine. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 171, 1429–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W. Characterization of Lipases from Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis Isolated from Human Facial Sebaceous Skin. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 22, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, R.C.; Fernandez-Lafuente, R. Lipase from Rhizomucor miehei as a Biocatalyst in Fats and Oils Modification. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2010, 66, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Ma, M.; Zeng, Z.; Yu, P.; Gong, D.; Deng, S. Production, Purification and Biochemical Characterisation of a Novel Lipase from a Newly Identified Lipolytic Bacterium Staphylococcus caprae NCU S6. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2021, 36, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambourova, M.; Kirilova, N.; Mandeva, R.; Derekova, A. Purification and Properties of Thermostable Lipase from a Thermophilic Bacillus stearothermophilus MC 7. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2003, 22, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherif, S.; Mnif, S.; Hadrich, F.; Abdelkafi, S.; Sayadi, S. A Newly High Alkaline Lipase: An Ideal Choice for Application in Detergent Formulations. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, V.M.G.; Krieger, N.; Mitchell, D.A.; Baratti, J.C.; Filippis, I.D.; Fontana, J.D. Evaluation of the Potential for Use in Biocatalysis of a Lipase from a Wild Strain of Bacillus megaterium. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2004, 31, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dhar, K.; Kanwar, S.S.; Arora, P.K. Lipase Catalysis in Organic Solvents: Advantages and Applications. Biol. Proced. Online 2016, 18, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Fernández, J.; Benaiges, M.D.; Valero, F. Rhizopus oryzae Lipase, a Promising Industrial Enzyme: Biochemical Characteristics, Production and Biocatalytic Applications. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Lv, F.; Bie, X.; Liu, S.; Ding, Z.; Xu, W. A Newly Isolated Organic Solvent Tolerant Staphylococcus saprophyticus M36 Produced Organic Solvent-Stable Lipase. Curr. Microbiol. 2006, 53, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugihara, A.; Ueshima, M.; Shimada, Y.; Tsunasawa, S.; Tominaga, Y. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Thermostable Lipase from Pseudomonas cepacia. J. Biochem. 1992, 112, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, Y.; Aono, R.; Doukyu, N. Purification, Characterization, and Molecular Cloning of Organic-Solvent-Tolerant Cholesterol Esterase from Cyclohexane-Tolerant Burkholderia cepacia Strain ST-200. Extremophiles 2006, 10, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hun, C.J.; Rahman, R.N.Z.A.; Salleh, A.B.; Basri, M. A Newly Isolated Organic Solvent Tolerant Bacillus sphaericus 205y Producing Organic Solvent-Stable Lipase. Biochem. Eng. J. 2003, 15, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jia, W.; Duan, M.; Lin, H.; Huang, J.; Li, X.; Shu, Z. Enhancement of Hydrogen Peroxide Tolerance of Lipase LipA from Bacillus subtilis Using Semi-Rational Design. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020, 159, 107590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsavova, J.; Misurcova, L.; Ambrozova, J.; Vicha, R.; Mlcek, J. Fatty Acids Composition of Vegetable Oils and Its Contribution to Dietary Energy Intake and Dependence of Cardiovascular Mortality on Dietary Intake of Fatty Acids. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12871–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, A.Q.; da Silva, V.A., Jr.; Góes, A.J.S.; Silva, M.S.; de Oliveira, G.G.; Bastos, I.V.G.A.; Alves, A.J. The Fatty Acid Composition of Vegetable Oils and Their Potential Use in Wound Care. Adv. Skin Wound Care 2019, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Codex Alimentarius Commission. Standard for Fish Oils (CXS 329-2017). Available online: https://www.fao.org/fao-who-codexalimentarius/sh-proxy/es/?lnk=1&url=https%253A%252F%252Fworkspace.fao.org%252Fsites%252Fcodex%252FStandards%252FCXS%2B329-2017%252FCXS_329e.pdf (accessed on 15 September 2025).
- Dyer, J.M.; Stymne, S.; Green, A.G.; Carlsson, A.S. High-value oils from plants. Plant J. 2008, 54, 640–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, G.P.R.; Correia, T.B.A.; Reis, W.S.M.; Bredda, E.H.; Da Rós, P.C.M.; Pereira, E.B. Enzymatic hydrolysis of waste cooking oil by lipase catalysis: Simplex mixture design optimization. Catal. Lett. 2023, 153, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kanwar, S.S. Organic solvent tolerant lipases and applications. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 625258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Bacterial Isolate | Identity | Accession N° |
|---|---|---|
| LMB-L7 | Serratia sp. | PQ967986 |
| LMB-B3 | Serratia sp. | PQ967987 |
| LMB-L9 | Aeromonas sp. | PQ967984 |
| LMB-L11 | Aeromonas sp. | PQ967985 |
| LMB-12 | Staphylococcus haemolyticus | PQ967991 |
| LMB-Ju02 | Staphylococcus ureilyticus | PQ967989 |
| LMB-06 | Staphylococcus ureilyticus | PQ967988 |
| LMB-08 | Staphylococcus hominis subsp. novobiosepticus | PQ967990 |
| LMB-JH06 | Staphylococcus epidermidis | PQ967992 |
| LMB-JH07 | Staphylococcus warneri | PQ967993 |
| Strain | Medium A | Medium B | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SA a | YE/X b | ΓX c | ΓV d | SA a | YE/X b | ΓX c | ΓV d | |
| S. ureilyticus LMB-Ju02 | 238.0 ± 15.5 | 14.9 ± 2.3 | 7.5 × 10−1 ± 1.2 × 10−1 | 1.3 ± 5 × 10−2 | 166.4 ± 38.3 | 13.5 ± 1.2 | 6.7 × 10−1 ± 9 × 10−2 | 2.4 ± 3.1 × 10−1 |
| S. ureilyticus LMB-06 | 457.8 ± 122.7 | 9.2 ± 3.1 | 4.6 × 10−1 ± 1.5 × 10−1 | 1.1 ± 1.9 × 10−1 | 159.0 ± 26.0 | 9.5 ± 0.3 | 4.7 × 10−1 ± 8 × 10−2 | 2.3 ± 2.7 × 10−1 |
| S. epidermidis LMB-JH06 | 231.2 ± 35.7 | 4.3 ± 1.6 | 2.2 ×10−1 ± 8.1 × 10−2 | 0.6 ± 4.6 × 10−2 | 39.0 ± 15.8 | 2.9 ± 0.4 | 1.5 × 10−1 ± 8.3 × 10−2 | 0.5 ± 2.1 × 10−1 |
| S. warneri LMB-JH07 | 556.4 ± 179.1 | 5.8 ± 1.0 | 2.9 × 10−1 ± 4.9 × 10−2 | 0.9 ± 1.4 × 10−1 | 45.9 ± 5.3 | 3.4 ± 0.5 | 1.7 × 10−1 ± 2.3 × 10−2 | 0.6 ± 7.2 × 10−2 |
| Oil Type | Density (g/mL) | Acid Value (mgKOH/g) | %FFA | Saponification Value (mgKOH/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Olive | 0.877 | 0.449 | 0.244 | 184.026 |
| Sunflower | 0.892 | 0.449 | 0.193 | 232.713 |
| Palm | 0.873 | 0.524 | 0.203 | 257.618 |
| Anchovy | 0.853 | 2.380 | 1.457 | 229.130 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huarcaya, M.; Barrientos, A.; Benites Pariente, J.S.; Gutierrez Mesias, L.G.; Samolski, I.; Ludeña, Y.; Villena, G.K. Gut Microbiota of Peruvian Anchovy (Engraulis ringens) as a Novel Source of Lipase-Producing Bacteria with Biocatalytic Potential. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10930. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010930
Huarcaya M, Barrientos A, Benites Pariente JS, Gutierrez Mesias LG, Samolski I, Ludeña Y, Villena GK. Gut Microbiota of Peruvian Anchovy (Engraulis ringens) as a Novel Source of Lipase-Producing Bacteria with Biocatalytic Potential. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(20):10930. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010930
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuarcaya, Margaret, Antony Barrientos, Jhonathan S. Benites Pariente, Luis Gabriel Gutierrez Mesias, Ilanit Samolski, Yvette Ludeña, and Gretty K. Villena. 2025. "Gut Microbiota of Peruvian Anchovy (Engraulis ringens) as a Novel Source of Lipase-Producing Bacteria with Biocatalytic Potential" Applied Sciences 15, no. 20: 10930. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010930
APA StyleHuarcaya, M., Barrientos, A., Benites Pariente, J. S., Gutierrez Mesias, L. G., Samolski, I., Ludeña, Y., & Villena, G. K. (2025). Gut Microbiota of Peruvian Anchovy (Engraulis ringens) as a Novel Source of Lipase-Producing Bacteria with Biocatalytic Potential. Applied Sciences, 15(20), 10930. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152010930






