Abstract
This paper investigated the tunnel slags generated from a specific tunnel project to systematically assess their environmental risk through phase composition, chemical composition, acidification potential, and heavy metal speciation. Leaching experiments were conducted under various influencing factors, including particle size, time, liquid-to-solid ratio, pH, temperature. The release concentration of heavy metals from the tunnel slag particles follows the following order: Zn > Cu > Cr. This is primarily attributed to the preferential release of Zn under acidic conditions due to its high acid-soluble state, while Cr, which is predominantly present in the residual state, exhibits very low mobility. Furthermore, decreased particle sizes, increased liquid-to-solid ratios, elevated leaching temperatures, extended leaching times, and lower pH values can effectively promote the dissolution of heavy metals from the tunnel slag. The cumulative leaching curves of Cr, Cu, and Zn from the three types of tunnel slags conform to the Elovich equation (R2 > 0.88), indicating that the release process of heavy metals is primarily controlled by diffusion mechanisms. The S- and Fe/Mg-rich characteristics of D3 confers a high acidification risk, accompanied by a rapid and persistent heavy metal release rate. In contrast, D2, which is influenced by the neutralizing effect of carbonate dissolution, releases heavy metals at a steady rate, while D1, which is dominated by inert minerals like quartz and muscovite, exhibits the slowest release rate. It is recommended that waste management engineering prioritize controlling S- and Fe/Mg-rich tunnel slags (D3) and mitigating risks of elements like Zn and Cu under acidic conditions. This study provides a scientific basis and technical support for the environmentally safe disposal and resource utilization of tunnel slag.
1. Introduction
With the rapid development of global transportation networks, highways and railways have become core components of infrastructure. Tunnel engineering, a critical aspect of mountain road construction, is widely employed in geologically complex regions such as plateaus, mid-altitude mountains, and hilly regions [1,2,3]. However, tunnel slag, which is generated during such projects, has considerable complex and is highly variable in composition. The current disposal method is mainly open stockpiling, resulting in low comprehensive utilization rates. The large-scale accumulation of tunnel slags not only consumes valuable land resources but also triggers environmental issues including water pollution, soil degradation, and ecosystem risks due to the leaching of heavy metals and other pollutants [4,5]. Therefore, the development of sustainable disposal and resource utilization of tunnel slags has emerged as a pressing challenge within the environmental and engineering fields.
Current research on tunnel slags primarily focuses on its resource utilization as an alternative material in civil engineering, especially in concrete and road construction [6,7,8,9]. Xiang et al. [10] found that the reduced sphericity of machine-made sand from tunnel slags increases the exothermic peak and cumulative heat in cement hydration, reduces the moisture signal of flocculated structures, and optimizes pore distribution along with hydration product homogeneity. Wang et al. [11] demonstrated that incorporating an appropriate amount of tunnel slag powder enhances concrete performance by improving slump, compressive strength, and toughness; refining the pore structure; and increasing the compactness of the interfacial transition zone. Additionally, the shrinkage deformation of tunnel slag concrete is observed to be lower than that of natural aggregate concrete and increases with higher stone powder content [12]. The addition of waste geotechnical fibers significantly improves the compactness and compressive and tensile strength of recycled fiber-reinforced tunnel slag concrete, optimizes the pore structure, and promotes the formation of a dense fiber–matrix interfacial transition zone [13]. The rough surface of tunnel slag particles enhances the interfacial bonding with cementitious materials, endowing 3D-printed concrete with favorable thixotropy, printing accuracy, and buildability when used as fine aggregates [14]. Moreover, the synergistic application of tunnel slags with other industrial solid wastes such as phosphogypsum and iron tailings can produce cement-stabilized base layers with good frost resistance, water stability, and delayed setting properties [15]. However, existing research predominantly focuses on the physical, mechanical, and engineering properties of tunnel slag, paying insufficient attention to its potential environmental risks.
Studies on the leaching behavior of heavy metals have mainly concentrated on industrial slags and tailings, revealing differential release behaviors of elements like Cr, Cu, and Ni under various environments [16,17,18,19]. Metal-rich tailing leachate significantly impacts the quality of surface water and soil downstream of mining areas, posing a potential ecological risk to farmland soils irrigated with local surface water [20]. Among the environmental factors influencing heavy metal leaching, pH is widely recognized as a key controlling variable. As rainwater acidity increases (pH decreases), the leaching capacity of Mn, Sr, Pb, and U in uranium tailings enhances significantly [21]. Similarly, the leaching behavior of heavy metals (Cd, Ni, Cr, Pb, Cu, and Zn) from metallurgical slag is also highly dependent on the pH of the medium [22]. Moreover, different elements exhibit distinct release mechanisms: The release of Cu and Cd is primarily controlled by surface wash-off. That of Zn is initially dominated by diffusion and later by surface wash-off, while the leaching mechanisms of Pb and As vary with changing pH conditions [23]. In addition, the amount of heavy metals released is negatively correlated with the pH and the waste particle size but positively correlated with ambient temperature and Fe3+ concentration. Meanwhile, the presence of microorganisms can substantially accelerate heavy metal release [24]. Through geo-environmental simulation experiments, it is found that acid production from pyrite oxidation in tunnel slags is the primary driver of secondary pollution. The acidic environment can further promote the release of heavy metals like Cd, As, Mn, and Fe, and the release process may be accelerated under anaerobic conditions and photocatalytic systems [25]. This is mainly because Fe/Ti phases in the sulfide mineral matrix exhibit photochemical activity under light conditions, catalyzing sulfite oxidation and leading to highly acidic conditions, thereby increasing the leaching concentrations of Cd, As, Cr, Pb, and Mn [26]. However, heavy metals in metallurgical slags are often encapsulated or immobilized within the amorphous glass phase or crystalline matrix, while tailings frequently undergo screening, grinding, and even chemical modification during mineral processing, leading to alterations in physicochemical properties. In contrast, tunnel slags derive mainly from the mechanical excavation and crushing of geological strata, and its heavy metal release behavior is governed primarily by the composition of primary minerals, which is different from that of slags and tailings.
However, systematic assessments of the speciation and leaching kinetics of heavy metals in tunnel slags are still scarce, significantly limiting the accurate prediction of their environmental behavior and risk management. This work selected three typical tunnel slags produced in a tunnel project in western Sichuan as the research object. X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray fluorescence (XRF) spectroscopy, acid neutralization capacity (ANC) and net acid production (NAG) tests as well as an improved BCR sequential extraction method were used to analyze the phase composition, acidification potential, and heavy metal speciation. The leaching behavior of typical heavy metals under varying influencing factors (particle size, time, liquid-to-solid ratio, pH, and temperature) was systematically studied to unravel their release patterns and kinetic mechanisms. This work is expected to provide novel insights into the release kinetics of heavy metals from tunnel slag, offering a crucial theoretical basis and scientific support for its risk assessment, green disposal, and resource utilization.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
The raw material used in the test is the tunnel slags produced by a project in western Sichuan. To ensure the representativeness of the samples, approximately 5 t of freshly excavated slags was collected from the tunnel muck pile at the construction site. Large fragments were first mechanically crushed using a jaw crusher. The crushed materials were then homogenized and sieved to obtain the specific particle size for subsequent experiments. Three distinct types of samples were collected, which were light red tunnel slags (D1), gray tunnel slags (D2), and black tunnel slags (D3), as shown in Figure 1.

Figure 1.
Particle morphology of tunnel slag.
2.2. Characterization
The phase composition of the samples was identified using a D8 DISCOVER (Bruker AXS, Karlsruhe, Germany) diffractometer with Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5406 Å). The XRD patterns were collected in the 2θ range from 5° to 80° with a step size of 0.02° and a scanning speed of 6°/min under operating conditions of 40 kV and 40 mA. XRF spectroscopy was conducted to determine the chemical composition of the tunnel slag samples. The analysis was performed on a ZSX Primus II (Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan) spectrometer equipped with a Rh X-ray tube. All measurements were carried out under vacuum conditions with an accelerating voltage of 50 kV and a current of 60 mA. The concentrations of heavy metals in the leaching solutions were quantified using ICP-MS on an Agilent 7700x (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) instrument. The ICP-MS was operated with an RF power of 1550 W, a plasma argon flow rate of 1.0 L/min, and a sample uptake rate of 0.4 mL/min.
2.3. Acid Generation Potential of Tunnel Slag
A total of 1.0 g of the tunnel slag sample (200-mesh) was mixed with a 25.0 mL 0.2 mol/L HCl solution and heated at 85 °C for 4 h. After cooling naturally to room temperature, the solid residue was removed by filtration. The filtrate was then titrated with a 0.2 mol/L NaOH solution while using 1–2 drops of phenolphthalein as indicator. The volume of NaOH consumed at the endpoint was recorded. The acid neutralization capacity (ANC) was calculated according to Formula (1), where m represents the volume of NaOH consumed (mL) and w is the mass of the sample (g).
A 2.5 g tunnel slag sample (200-mesh) was added to a 250 mL 150 g/L H2O2 solution and left to react at room temperature for 24 h. After the reaction, the conical flask was transferred to a constant-temperature water bath and heated for 1 h to completely decompose residual H2O2. After cooling naturally to room temperature, the supernatant was titrated with 0.1 mol/L NaOH until the pH value reached 7.0. Net acid production (NAG) was calculated using Formula (2), where m is the volume of NaOH consumed (mL) and w is the mass of the sample (g).
2.4. Heavy Metal Speciation and Leaching in Tunnel Slag
The improved BCR method was used to analyze the proportion of acid-soluble, -reducible, -oxidizable, and residual states of heavy metals [27]. According to the “Solid waste-Extraction procedure for leaching toxicity-Sulphuric acid & nitric acid method” (H/T 299-2007), the water content of the sample was first determined, and then the sample was crushed and passed through a 9.5 mm sieve [28]. Then 500 g of the test sample was placed in a 2 L wide-mouth bottle, and deionized water was added to achieve a liquid-to-solid ratio of 10:1 (L/S, L/kg) after accounting for the water content. The mixture was oscillated at 23 °C for 18 h (frequency: 120 r/min; amplitude: 40 mm). After oscillation, the leachate was filtered and collected for subsequent analysis.
The three types of tunnel slags were crushed and sieved into particle size fractions of 0.15–0.3 mm, 0.3–0.6 mm, 0.6–1.18 mm, and 1.18–2.36 mm. For each leaching experiment, a 10 g sample was placed in a 250 mL wide-mouth bottle under different times, liquid-to-solid ratios, pH values, and temperatures. All bottles were placed in a constant-temperature oscillator at 30 °C and shaken at 120 r/min for 8 h, followed by standing for 16 h. The leaching solution was filtered through a 0.45 μm membrane, and the concentrations of heavy metal elements were measured via ICP-MS.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. XRD and XRF
As shown in Figure 2, the three types of tunnel slags exhibit good crystallinity, with the phase compositions mainly consisting of quartz, calcite, biotite, actinolite, and muscovite. Notably, compared to D1, D2 and D3 show higher diffraction peak intensities for actinolite, suggesting that they may undergone more intense metamorphism. Additionally, the biotite content in D3 is significantly higher than that in D1 and D2, indicating that the tunnel slag particles primarily originated from Fe/Mg-rich metamorphic rocks. The relative enrichment of dark minerals such as biotite and actinolite in D2 and D3 contributes to their gray-to-black appearance.
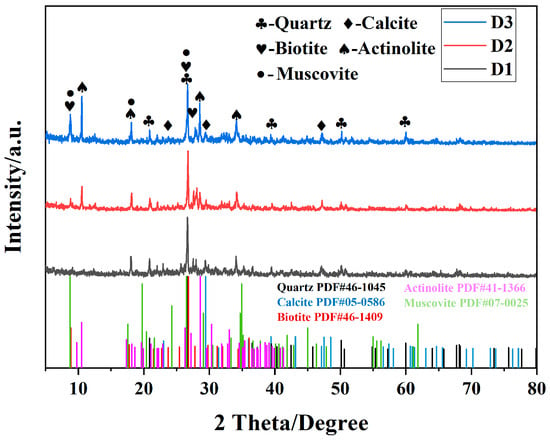
Figure 2.
Phase composition of tunnel slags.
XRF analysis revealed significant differences in chemical composition of the samples (Table 1). The combined SiO2 and Al2O3 content in D1 accounts for 82.85% of the total, which is highly consistent with the XRD results showing a silicate mineral-dominated phase (quartz, muscovite). D2 exhibits distinct calcium and iron enrichment, with a combined CaO (17.66%) and Fe2O3 (13.83%) content totaling 31.49%, while the combined SiO2 and Al2O3 content is 57.98%, aligning with its phase composition that is rich in calcite and actinolite. The high Al2O3 and Fe2O3 content in D3 further confirms its biotite-rich characteristic. Meanwhile, the sum of SiO2, Al2O3, Fe2O3, CaO, and K2O in D3 accounts for 93.6%, with the CaO content reaching 7.99%, indicating the presence of Ca-rich minerals (such as calcite) alongside the predominant aluminum–iron minerals. Meanwhile, the pollution load index (PLI) of characteristic heavy metals (Zn, Cu, and Cr) in three types of tunnel slag (D1, D2, and D3) is evaluated. The PLI values are 0.078, 0.28, and 0.34, respectively, all of which are significantly below the risk threshold of 1, indicating that the heavy metal pollution load in the tunnel slag studied is very low, with concentrations at natural background levels.

Table 1.
Chemical composition of tunnel slags (wt%).
3.2. Acid Generation Potential
The initial pH values of the leachates from all three tunnel slags are greater than seven, indicating a neutral to weakly alkaline initial leaching environment (Figure 3). However, comparative analysis of ANC and NAG revealed significant differences in acidification potential. The NAG value for D1 far exceeds its ANC, indicating that acid production from sulfide oxidation vastly outweighs the neutralization capacity of its carbonate minerals. Thus, D1 poses a very high acidification risk upon long-term exposure to oxidizing environments. The ANC and NAG values for D2 are roughly equal, as its abundant calcite and other carbonate minerals can buffer the acid production process from sulfides. D3 has the highest ANC, slightly exceeding its NAG, suggesting an ability to neutralize acid. However, Fe/Mg-rich minerals like biotite might promote a sharp increase in the initial acid production rate during sulfide oxidation. In contrast, the dissolution and neutralization process of carbonate minerals is relatively slower, potentially leading to localized acidification.
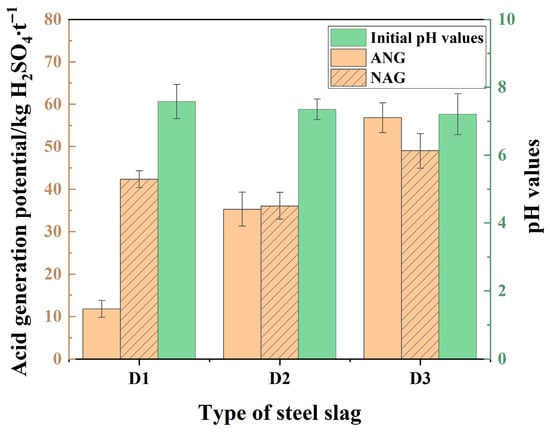
Figure 3.
Acid generation potential of tunnel slags.
3.3. Speciation of Cr, Cu, and Zn
As shown in Figure 4, the speciation of key heavy metals (Cr, Cu, and Zn) in the tunnel slags was analyzed using an improved BCR sequential extraction method. In all three types of slags, Cr is primarily in the residual state, indicating that it is mainly encapsulated in silicate mineral lattices or present in insoluble primary minerals, thereby exhibiting very low environmental mobility under natural conditions. Notably, the residual state of Cr in D2 reaches approximately 83%, which can be attributed to the strong immobilization effect of Ca/Fe-rich minerals (calcite and actinolite). The acid-soluble states of Cr in both D1 and D3 exceed 9%, indicating a relatively higher potential release risk. Particularly, the sum of the acid-soluble and -reducible states of Cr in D1 reaches 28%, meaning that Cr in these states is relatively easily released and mobilized under acidic or reducing environments. Although Cu is also primarily present in the residual state, the proportion of non-residual states is significantly higher than that of Cr, indicating relatively lower stability. Specifically, the oxidizable state of Cu in D1 accounts for about 20%, suggesting considerable association with organic matter or sulfides, thereby posing a release risk under oxidizing conditions. In both D2 and D3, the acid-soluble states of Cu exceed 20%, accompanied by a considerable proportion in the reducible states, indicating that Cu in D2 and D3 is largely associated with carbonate minerals (e.g., calcite) and Fe/Mg oxides and rendering it highly sensitive to decreasing pH values. Zn is mainly in the residual state in the tunnel slags, indicating high stability. However, the acid-soluble state of Zn is relatively high in all three types of tunnel slag, suggesting the presence of substantial Zn in adsorbed states or associated carbonates. Consequently, Zn has a high potential for preferential release and migration when environmental pH decreases.
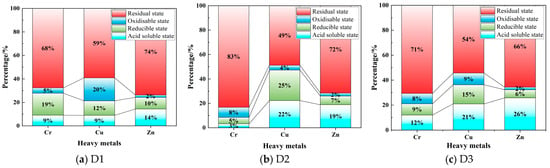
Figure 4.
Speciation of Cr, Cu, and Zn in tunnel slags.
3.4. Influencing Factors of Leaching Concentration of Cr, Cu, and Zn
3.4.1. Particle Size
The influence of particle size on the leaching concentration of Cr, Cu, and Zn under acidic conditions (pH = 3, L/S = 10:1, and 30 °C) is shown in Figure 5. For all three tunnel slag, the leaching concentrations of Cr, Cu, and Zn decrease significantly with the increase in particle size, which is primarily because larger particle sizes result in a smaller specific surface area, greatly reducing the solid–liquid contact interface and thus slowing the diffusion and dissolution of heavy metal ions from the mineral matrix into the solution. The order of the elemental release concentration is consistently Zn > Cu > Cr. The high proportion of acid-soluble states in Zn facilitates its easy release under acidic conditions, leading to elevated leaching concentrations. In contrast, the release of Cu is dependent on the dissolution of carbonate or sulfide inclusions, while the high residual state of Cr results in the lowest release concentration. Furthermore, under the condition of acidic leaching, the heavy metal leaching concentrations follow the order D3 > D2 > D1, which is highly consistent with the mineral composition and heavy metal speciation. The high acid-soluble fraction of heavy metals in D3 particles, combined with their biotite-rich mineral characteristics, accelerates the oxidation and dissolution of sulfides and other materials, promoting heavy metal release. The Ca-rich characteristics of D2 facilitate rapid dissolution of calcite under acidic conditions, releasing adsorbed heavy metals. Conversely, D1, which is composed mainly of silicate minerals such as quartz and muscovite, exhibits good acid erosion resistance, significantly inhibiting heavy metal dissolution.
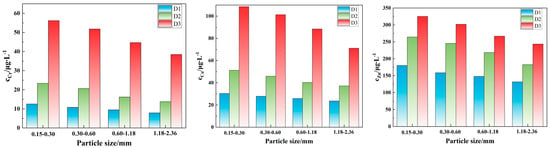
Figure 5.
Effect of particle size on the leaching concentration of Cr, Cu, and Zn in tunnel slags.
3.4.2. Leaching Time
As shown in Figure 6, under fixed conditions (particle size: 0.3–0.6 mm, pH = 3.0, and 30 °C), the cumulative leaching amounts of Cr, Cu, and Zn from the three types of tunnel slags gradually increase with extended leaching time. Within the initial 12 h, the leaching concentrations of heavy metals increase sharply, primarily due to the rapid desorption or dissolution of the acid-soluble and partially reducible states under strong acid conditions. As the immersion time extends further, the release rate decreases significantly, mainly because the release of stable heavy metal states likely requires the destruction of mineral lattices and the acid corrosion process of silicates such as biotite and actinolite is slow. The time-dependent leaching behavior underscores an initial fast phase controlled by surface reactions, followed by slow diffusion which is limited release from the mineral matrix.
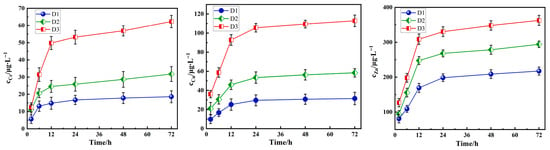
Figure 6.
Effect of leaching time on the leaching concentration of Cr, Cu, and Zn in tunnel slags.
3.4.3. Liquid-to-Solid Ratio
Under fixed acidic leaching conditions (particle size: 0.3–0.6 mm, pH = 3.0, and 30 °C), the order of the heavy metal release concentration remained as Zn > Cu > Cr under different L/S ratios, reaffirming that Zn is most sensitive to acidic environments due to its high acid-soluble state, while Cr is most difficult to release due to its high residual state (Figure 7). The cumulative leaching amounts of Cr, Cu, and Zn gradually increased with increasing L/S ratios. A high L/S ratio significantly reduces the concentration gradient of heavy metals in the solution, enhances the ion diffusion rate at the solid–liquid interface, and accelerates the desorption of acid-soluble metals and the dissolution of carbonate phases. Conversely, a low L/S ratio inhibits mass transfer efficiency and dissolution rates within the solution, thereby weakening the dissolution of internal carbonate minerals and the desorption of adsorbed heavy metals.
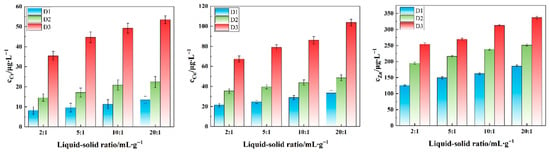
Figure 7.
Effect of the liquid-to-solid ratio on the leaching concentration of Cr, Cu, and Zn in tunnel slags.
3.4.4. pH Value
As shown in Figure 8, under fixed conditions (particle size: 0.3–0.6 mm, L/S = 10:1, 30 °C), the leaching amounts of Cr, Cu, and Zn from the three tunnel slags gradually decrease as the pH increases (pH = 3.00, 5.00, 7.00, and 9.00). Under acidic conditions, highly reactive acid-soluble heavy metals rapidly dissociate, and the dissolution of carbonate minerals further facilitates metal release. As the pH value rises to neutral and alkaline ranges, the solubility of heavy metal hydrolysis products decreases significantly, and the enhanced negative surface charge of the tunnel slags promotes re-adsorption of heavy metal ions, thereby further suppressing their dissolution.
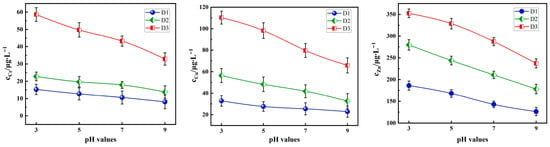
Figure 8.
Effect of the pH value on the leaching concentration of Cr, Cu, and Zn in tunnel slags.
3.4.5. Temperature
Under fixed conditions (particle size: 0.3–0.6 mm, pH = 3.0, and L/S = 10:1), the leaching amounts of Cr, Cu, and Zn from the three types of tunnel slags show an increasing trend with rising temperatures (Figure 9). An increase in temperature raises the solubility product constants of numerous heavy metal salts, thereby reducing their precipitation tendency and favoring the dissolution and stabilization of metal ions in the aqueous phase. Simultaneously, an elevated temperature significantly accelerates the corrosion reaction rate of minerals, promoting the release of occluded heavy metals. Additionally, higher temperatures also reduce solution viscosity and increase the ion diffusion coefficient, thereby accelerating the migration rate of heavy metal ions from the solid surface or pores into the solution.
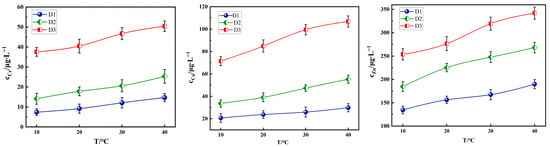
Figure 9.
Effect of temperature on the leaching concentration of Cr, Cu and Zn in tunnel slags.
In summary, the leaching behavior of heavy metals from tunnel slags is significantly influenced by multiple factors, including particle size, leaching time, L/S ratio, pH value, and temperature. A reduction in particle size increases the specific surface area, enhancing solid–liquid contact efficiency and thereby promoting the diffusion of ions and interfacial chemical reactions. A prolonged leaching time facilitates the release of metals in acid-soluble and -reducible states and progressively activates the dissolution of silicate minerals. An increased L/S ratio reduces the concentration gradient of metal ions in the solution, improves mass transfer efficiency, and accelerates desorption from surfaces as well as the decomposition of mineral phases. A lower pH environment strongly promotes the dissolution of acid-sensitive phases such as carbonates and sulfides, thereby releasing associated heavy metals. An elevated temperature can increase reaction rate constants and improve ion diffusion capacity, resulting in greater leaching extents. Therefore, the release of heavy metals from tunnel slags is cooperatively controlled by a combination of surface reactions, diffusion kinetics, and mineral dissolution processes. At the same time, the maximum leaching concentrations of Cr, Cu, and Zn in the three types of tunnel slags are significantly lower than the intervention values specified in the “Soil Environmental Quality Agricultural Land Soil Pollution Risk Control Standard” (GB 15618-2018) [29] and the “Soil Environmental Quality Development Land Soil Pollution Risk Control Standard” (GB 36600-2018) [30]. Furthermore, the leaching concentrations observed in this study under the most unfavorable conditions remain much lower than those reported for the Dexing copper mine tailings [31]. It is indicated that the release of heavy metals in the tunnel slags studied does not pose a significant pollution risk to the surrounding soil under the tested leaching conditions.
3.5. Release Kinetics of Cr, Cu, and Zn
Under acidic leaching conditions (pH = 3, L/S = 10:1, and 30 °C), the time-dependent cumulative leaching amounts of Cr, Cu, and Zn from the tunnel slags conform to the Elovich equation (R2 > 0.88), indicating that the release process of heavy metals is primarily controlled by diffusion mechanisms (Figure 10 and Table 2). The initial release rate (α) and sustained release capacity (β) for the three heavy metals in different tunnel slags follow the order Zn > Cu > Cr, which is correlated strongly with the proportion of the acid-soluble fraction in their speciation. The S- and Fe/Mg-rich characteristics of D3 promote accelerated sulfide oxidation under acidic conditions, leading to a high α and strong β for heavy metals, particularly for Zn and Cu. The rapid dissolution of carbonate minerals in D2 releases adsorbed and bound heavy metals, resulting in a relatively fast α. D1, with its high content of inert silicate minerals (quartz and muscovite) and residual state of heavy metals, exhibits the lowest α and the weakest β, corresponding to the mildest leaching behavior.
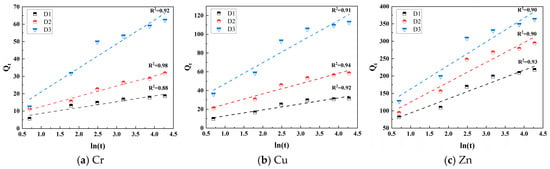
Figure 10.
Release kinetics of Cr, Cu, and Zn in tunnel slag.

Table 2.
Elovich equation fitting parameters for the release kinetics of Cr, Cu, and Zn in tunnel slag.
4. Conclusions
Based on a systematic investigation of the phase composition, chemical composition, heavy metal speciation, and heavy metal release behavior of tunnel slags, this work reveals distinct environmental risks among different types of slags. The silicate-rich slag D1, primarily composed of quartz and muscovite, presents a high stable heavy metal state, with the residual and reducible fractions accounting for over 85% of the Cr. It also shows the lowest leaching concentration, with Cr release measuring only 18.6 μg/L under specific conditions (0.3–0.6 mm particle size, pH 3.0, 30 °C, and 72 h). In contrast, the S- and Fe/Mg-rich slag D3, abundant in biotite and sulfides, exhibits the most rapid and persistent release, reaching a Cr leaching concentration of 62.3 μg/L under the same conditions. The Ca/Fe-rich slag D2, containing high contents of calcite and actinolite, displays a rapid yet steady release pattern dominated by carbonate dissolution. Furthermore, factors including decreased particle sizes, increased liquid-to-solid ratios, elevated leaching temperatures, extended leaching times, and decreased pH values all enhanced the release of heavy metals from the tunnel slag particles. The leaching behaviors and kinetic parameters identified in this work provide a scientific basis for developing targeted management and utilization strategies for different types of tunnel slags. For example, exposure of S- and Fe/Mg-rich slag (D3) to oxygen and rainwater should be minimized to effectively suppress acidification and rapid release of heavy metals. Such slag is not suitable for large-scale open-air stockpiling or direct resource utilization. Ca-rich slag (D2) may be considered for use in controlled scenarios where pH remains stable in the neutral to alkaline range. However, should significant acidification occur in the surrounding environment, the release of heavy metals must be promptly monitored. In contrast, low-risk Si-rich tunnel slag (D1), which exhibits the lowest heavy metal leaching concentrations and the highest environmental stability, is an ideal candidate for large-scale resource utilization, such as in concrete aggregates or road construction materials. In summary, this work not only elucidates the key mechanisms of heavy metal release from tunnel slags but also offers technical guidance and theoretical support for their safe disposal and resource utilization. Future research should extend beyond laboratory-scale experiments to include field monitoring of slag stockpiles and the development of more sophisticated risk prediction models in order to quantitatively assess the long-term ecological risks under real-world exposure pathways.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, X.W. and L.Z.; methodology, X.Z. and Y.W.; validation, X.W.; investigation, Y.W. and G.L.; writing—original draft preparation, X.Z. and G.L.; writing—review and editing, T.W. and L.Z.; supervision, T.W. and C.Y.; project administration, L.Z. and C.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2023YFB3711400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (52178265).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
Authors Guanghua Lu and Changsheng Yue were employed by the company Central Research Institute of Building and Construction Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Fu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, L.; Xie, Y. Evaluating the feasibility of slag from slurry shield tunnels as a growth medium for landscaping. J. Air. Waste. Manag. 2022, 72, 455–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnuaim, A.; Abbas, Y.; Khan, M. Sustainable application of processed TBM excavated rock material as green structural concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 274, 121245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yao, Y.; Huang, C. Utilization of tunnel waste slag for cement-stabilized base layers in highway engineering. Materials 2024, 17, 4525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Yin, Y.; Mi, W.; Chen, R.; Lin, X. Assessing performance, economic costs and environmental benefits of high-performance ecological geopolymer concrete incorporating excavated rock and soil from tunnelling, fly ash and slag as reclaimed raw materials. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 110351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Z. Study on key technologies of green and efficient utilization of huge abandoned slag of railway tunnel. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2022, 16, 1649–1656. [Google Scholar]
- Taqa, A.A.; Al-Ansari, M.; Taha, R.; Senouci, A.; Al-Zubi, G.M.; Mohsen, M.O. Performance of concrete mixes containing TBM slag as partial coarse aggregate replacements. Materials 2021, 14, 6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Qiu, W.; Liu, D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, R. Experimental study on the properties of mortar and concrete made with tunnel slag machine-made Sand. Materials 2022, 15, 4817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Z.; Lü, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Xu, K. Study on mechanical property and breakage behavior of tunnel slag containing weak rocks as road construction material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhu, Z.; Pu, S.; Wan, Y.; Huo, W.; Peng, Y. Preparation and engineering properties of alkali-activated filling grouts for shield tunnel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 314, 125620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Hu, D.; Yang, G.; Chen, J.; Xu, W.; Li, H. Influence law and control mechanism of manufactured sand particles derived from tunnel slag on cement hydration. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 92, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Meng, F.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Shi, J. Effect of stone powder content on the mechanical properties and microstructure of tunnel slag aggregate-based concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 388, 131692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Y.; Meng, F.; Jiang, J.; Sui, S. Study of hydration and hardening behavior of stone powder-modified concrete made with tunnel slag aggregate. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2025, 150, 4001–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Du, C.; Yi, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, C. Microstructural and mechanical evolution of recycled fiber-reinforced tunnel slag concrete under wet-dry cycles. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2025, 43, 101905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, C.; Guo, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.; Ma, G.; Wang, Q. Spray-based 3D printed tunnel slag concrete: Evaluation for printability and mechanical performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 467, 140392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, C.; Shi, W.; Wang, N.; Xue, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Meng, X. Laboratory investigation of solid wastes combined with tunnel slag in cement stabilized base of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamila, M.; Anna, K. The importance of time and other determinants in the assessment of heavy metals release during solid waste management. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, Q.; Qin, L.; Chen, W.; Han, J. Effects of pressurized pretreatment combined with fly ash stabilization on heavy metal leaching in municipal solid waste incineration fly ash. Fuel 2026, 403, 136126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahkarami, E.; Ghasemi, M.; Mohebbi-Poorkani, A. Assessment of kinetic models for oxidative leaching of copper and zinc from converter furnace dust: A sustainable approach to metal recovery. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 378, 134512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.; Zha, X.; Dong, L.; Dassekpo, J.-B.M.; Xiao, J. Calcium dissolution-induced porosity increase in cement-solidified MSWIFA: Implications for heavy metal leaching behavior. Process Saf. Environ. 2025, 201, 107493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Sun, Z.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Leaching of heavy metals from abandoned mine tailings brought by precipitation and the associated environmental impact. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 695, 133893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Sun, H.J.; Peng, T.J.; Duan, T. Transport and transformation of uraniumand heavy metals from uranium tailings under simulated rain at different pH. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 495–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Król, A.; Mizerna, K.; Bożym, M. An assessment of pH-dependent release and mobility of heavy metals from metallurgical slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Yu, D.; Hao, W.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Potential risk, leaching behavior and mechanism of heavy metals from mine tailings under acid rain. Chemosphere 2024, 350, 140995. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.B.; Chen, D.N.; Lin, H. The behavior of heavy metal release from sulfide waste rock under microbial action and different environmental factors. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 75293–75306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Ren, Y.; Qu, G.; Li, J.; Jin, C.; Liu, Y.; Kuang, L. Synergistic mechanism of physical chemistry and acid bacteria: Product evolution of sulphides during tunnel mining. Geol. J. 2024, 59, 2304–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Xue, S.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Analysis of heavy metal pollution sources caused by sulfide minerals in tunnel waste under photocatalytic oxidation conditions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2025, 32, 11550–11561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauret, G.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- H/T 299; Solid Waste Leaching Toxicity Leaching Method Sulfuric Acid Nitric Acid Method. The State Environmental Protection Administration: Beijng, China, 2007.
- GB 15618; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment and State Administration for Maket Regulation: Beijng, China, 2018.
- GB 36600; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Development Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment and State Administration for Maket Regulation: Beijng, China, 2018.
- Guo, Y.-G.; Huang, P.; Zhang, W.-G.; Yuan, X.-W.; Fan, F.-X.; Wang, H.-L.; Liu, J.-S.; Wang, Z.-H. Leaching of heavy metals from Dexing copper mine tailings pond. Trans. Nonferr. Metal. Soc. 2013, 23, 3068–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).