1. Introduction
Wrestling is one of the oldest and most complex sports, requiring a high degree of physical strength, endurance, explosiveness, technical mastery, and psychological resilience [
1]. Competitive matches are characterized by short but extremely intense episodes of exertion interspersed with brief pauses, which place substantial demands on anaerobic capacity, muscular strength, and rapid recovery ability [
2,
3]. Effective management of training load and recovery is crucial for maintaining peak performance and preventing overtraining in athletes [
4]. Previous studies have shown that even in elite athletes, such as Paralympic judokas, training cycles induce pronounced changes in performance and competitive readiness [
5]. This highlights the necessity of systematically monitoring physiological markers under different training regimes.
In this context, heart rate variability (HRV) has emerged as a valuable non-invasive biomarker for assessing the autonomic balance between the sympathetic and parasympathetic branches of the nervous system [
6,
7].
Despite the growing body of evidence on HRV applications in various sports, direct comparative data on different training paradigms (HIIT vs. volume-oriented programs) in elite wrestlers remain scarce. This gap highlights the novelty and necessity of the present study, which specifically addresses how these training modalities affect autonomic regulation and recovery dynamics in this population.
Dong [
8] emphasizes HRV as an indicator of autonomic regulation, reflecting the balance between sympathetic and parasympathetic activity, and highlights its usefulness for monitoring adaptation to training stress and optimizing the training process. Reductions in HRV have been associated with fatigue accumulation, diminished adaptation to exercise, and increased risk of overtraining [
9]. Conversely, the restoration of HRV to baseline levels after training is considered an indicator of adequate recovery and readiness for subsequent loads [
10]. Given the high demands of wrestling on explosive strength and short-term maximal endurance, HRV may represent a particularly useful tool for monitoring sport-specific adaptations in this discipline.
In wrestlers, Tian et al. [
11] used HRV to detect early signs of non-functional overreaching. The authors established HRV thresholds that allow for timely differentiation between functional and non-functional overload (e.g., rMSSD of about 82.76 ms (CI 77.75–87.78) for “normal adaptation” but 45.97 ms (CI 30.79–61.14) for adverse response, which allow for timely differentiation between functional and non-functional overload). These results highlight the importance of HRV as a tool for monitoring training load and recovery in wrestlers. Similarly, a study with adolescent judokas [
12] employing a dynamic tilt-test indicated that HRV adequately reflects adaptation to increased training load. Specifically, judokas showed higher values of RMSSD (49.3 ± 16.2 ms vs. 38.7 ± 14.5 ms in swimmers) and pNN50 (23.4 ± 11.8% vs. 16.1 ± 9.7%), reflecting more efficient parasympathetic adaptation.
Extending beyond combat sports, Santos-García et al. [
13] applied HRV monitoring in elite female soccer players. Their analysis revealed very strong positive correlations between rMSSD (4 h) and RHR (4 h), as well as strong positive correlations between short-term HRV indices (e.g., rMSSD 5 min vs. RHR (resting heart rate) 5 min; SDNN vs. RHR 5 min; rMSSD 5 min vs. SDNN).
In an Olympic context, Coyne et al. [
14] reported that HRV served as a sensitive tool for monitoring training load and recovery in an elite long jumper before and during the Rio 2016 Olympic Games. Decreases in HRV reflected elevated stress and the need for recovery.
Korobeynikov et al. [
15] investigated HRV differences in elite wrestlers, demonstrating that those with higher stress resilience exhibited higher HRV values and stronger parasympathetic tone.
A recent study [
16] investigated the dynamics of HRV (RMSSD, LF/HF, and others) in Greco-Roman wrestlers after a training break and resumption of practice, highlighting its relationship with physical condition and a specific wrestling fitness test (SWFT). Recovery through an 8-week re-training period shows that athletes manage to regain some of the lost performance, but do not fully reach the baseline levels observed before the break. This highlights that prolonged breaks lead to significant physiological and functional regressions that cannot be fully compensated even with intensive re-training. This evidence reinforces the role of HRV as a sensitive biomarker of training adaptation and recovery status.
The literature review further indicates that training modality can exert markedly different effects on autonomic regulation. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) often provokes more pronounced acute HRV changes, typically characterized by elevated sympathetic activation and temporary suppression of parasympathetic tone [
17]. Schneider et al. [
18] compared the effects of strength training (ST) and HIIT during an overload microcycle, reporting that HIIT induced stronger and faster HRV alterations, whereas ST led to more moderate, gradual adaptations. Consistent with this, Stöggl & Björklund [
19] showed that HIIT facilitated faster heart rate recovery (HRR) compared to traditional high-volume, low-intensity training programs. Although not a direct comparison between HIIT and volume programs, a six-week multicomponent training block in wrestlers [
20] demonstrated improvements in SWFT performance, underlining the impact of training structure on competitive readiness.
In the specific context of wrestling, where matches are brief yet extremely intense, the fine-tuning of training loads and recovery periods is crucial for achieving peak explosiveness and endurance at decisive moments. Plews et al. [
21] emphasized that HRV-based monitoring enables individualized training adjustments and optimizes athletic performance. Accordingly, in wrestling—where athletes are simultaneously exposed to strength, speed, and technical demands—systematic HRV monitoring may enhance adaptation and support optimal form before competition.
Volume-oriented programs, by their nature, may be expected to promote more gradual and stable autonomic adaptations. However, they also carry a higher risk of accumulated fatigue if applied over extended periods without adequate recovery strategies. Despite the considerable body of research, comparative data examining the effects of distinct training paradigms on both HRV dynamics and actual competitive outcomes in elite wrestlers remain scarce.
Therefore, the integration of HRV monitoring into the training process of wrestlers may provide valuable feedback on autonomic regulation, assist in precise load management, and mitigate the risk of overtraining. Based on these considerations, the present study aims to compare the effects of HIIT and volume-oriented training programs on both competitive performance and HRV dynamics in elite wrestlers.
Despite the growing interest in the applications of HRV in various sports, comparative data on different training paradigms in elite wrestlers remain scarce, especially regarding how high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and traditional volume-oriented programs differentially affect autonomic regulation and competitive readiness. To fill this gap, the present study aimed to compare the effects of HIIT and volume training on: (1) competitive performance, as assessed by official results and rankings from national championships; (2) dynamics of autonomic regulation, as assessed by HRV indices at three time points (pre-training, immediately post-training, and 2 h post-training); (3) acute and short-term adaptations in sympathetic and parasympathetic activity in response to the two training regimens; and (4) the relationship between HRV parameters and competitive performance, with the aim of assessing the potential of HRV as a tool for individualized training planning and prevention of overtraining.
3. Results
A total of 720 recordings (60 days × 12 athletes) were analyzed for each condition: pre-training, post-training, and 2 h recovery.
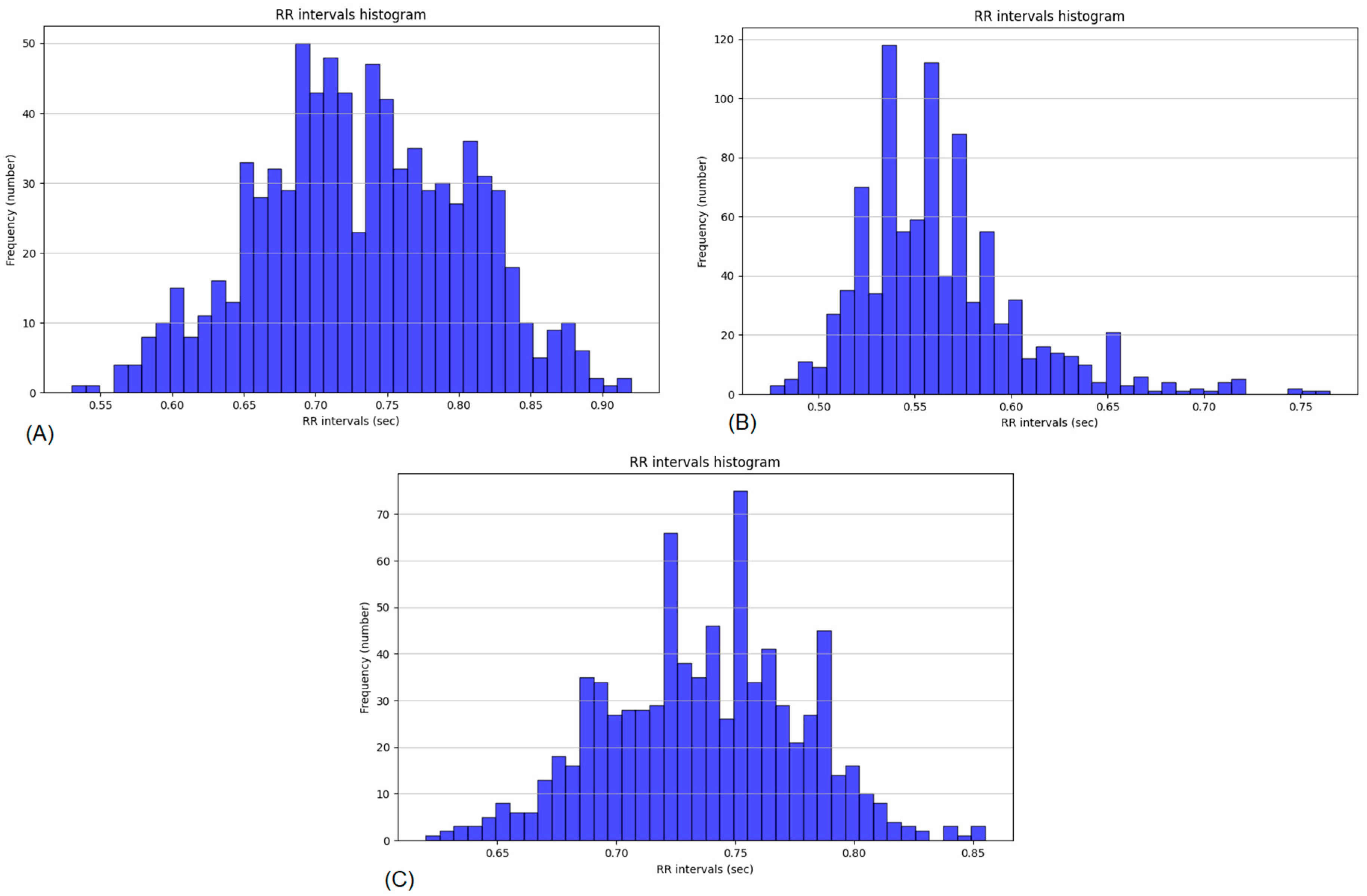
To illustrate the individual autonomic dynamics,
Figure 1 presents RR interval histograms of the same wrestler recorded before, immediately after, and 2 h after training. The distribution shifts towards shorter intervals immediately post-exercise, followed by partial restoration at 2 h, reflecting the acute sympathetic activation and subsequent parasympathetic recovery.
The comparison of the RR interval histograms before, immediately after, and 2 h post-training provides an individual-level perspective on fatigue and recovery dynamics. Prior to exercise, the distribution is centered at longer intervals with a relatively broad spread, reflecting a balanced autonomic tone. Immediately after training, the histogram shifts toward shorter intervals and becomes more asymmetric, indicating a pronounced sympathetic activation and acute fatigue. Two hours later, the distribution partially returns toward its baseline position, suggesting partial but not complete recovery of parasympathetic activity.
Table 2 presents the descriptive statistics (mean ± SD) and pairwise comparisons of HRV parameters (RMSSD, SDNN, LF, HF, LF/HF) measured before training, immediately after, and 2 h post-exercise in both the HIIT and Volume groups. The normality of the data for these parameters was checked by the Shapiro–Wilk test for each group and time point separately. The obtained
p-values did not show a significant deviation from the normal distribution (
p > 0.05), which allowed the application of parametric tests for statistical analysis. Since the study involved repeated measurements on the same participants (Pre, Post, 2 h), paired samples
t-test was applied to assess differences over time.
Analysis of HRV parameters revealed distinct responses in the two investigated training groups—HIIT and Volume:
The RMSSD demonstrated pronounced differences. In the HIIT group, RMSSD dropped markedly from 42.1 ms at baseline to 28.6 immediately after exercise (p < 0.001; d = 3.36). Although values partially recovered to 36.5 ms after two hours (p = 0.0013; d = 1.44), they remained significantly below baseline. In contrast, the Volume group exhibited only a moderate decrease, from 43.5 ms to 37.5 ms (p = 0.018; d = 0.45), followed by recovery to 40.8 ms, a level that did not significantly differ from pre-exercise (p = 0.072; d = 0.22). This suggests that HIIT caused a sharper parasympathetic withdrawal and incomplete recovery, while Volume training induced milder and more transient changes.
Similar trends were observed in the SDNN. In the HIIT group, SDNN fell from 138.3 ms to 95.8 ms (p < 0.001; d = 3.72), with partial recovery to 120.2 ms after two hours (p = 0.007; d = 1.61). The Volume group showed a smaller decline, from 140.2 ms to 118.4 ms (p = 0.020; d = 1.81), followed by recovery to 128.4 ± 10.4 ms, which was not significantly different from baseline (p = 0.061; d = 0.95). Thus, HIIT induced a stronger global HRV reduction, whereas Volume training promoted a more gradual return towards resting levels.
The HF component, reflecting parasympathetic modulation, was significantly suppressed in both groups, but to different extents. HIIT reduced HF power from 820.2 ms2 to 490.4 ms2 (p < 0.001), with partial recovery to 710.2 ms2 after two hours, still below baseline. The Volume group showed a smaller reduction, from 810.0 ms2 to 665.2 ms2, with recovery to 750.2 ms2, a value not significantly different from baseline (p = 0.091). These findings confirm that HIIT provoked a stronger parasympathetic withdrawal than Volume training.
Conversely, the LF component, representing mixed sympathetic–parasympathetic influences, increased more prominently in the HIIT group. LF rose from 1020.2 ms2 to 1450.3 ms2 immediately after training (p < 0.001), then declined to 1180.4 ms2 after two hours (p = 0.004 vs. baseline). The Volume group showed a more moderate elevation, from 980.1 ms2 to 1200.4 ms2, followed by partial normalization to 1080.4 ± 92.2 ms2.
The LF/HF ratio further emphasized the autonomic balance shift. In the HIIT group, values increased from 1.2 to 1.9 (p < 0.001), before partially recovering to 1.4 after two hours. In the Volume group, LF/HF rose from 1.3 to 1.6, and returned to 1.4, showing no significant difference from baseline (p = 0.084).
Application of the Bonferroni correction confirmed most of the significant differences in the HIIT group, where changes in RMSSD, SDNN, HF, LF and LF/HF remained statistically significant across all time comparisons (except Pre–2 h for LF/HF, p = 0.099). This indicates a clear and consistent effect of high-intensity exercise on autonomic regulation. In the Volume group, the initially reported significances were attenuated after adjustment, with no comparison reaching the strict Bonferroni threshold of p < 0.05, although some trends (e.g., LF and HF Post–2 h) retained moderate effects. This highlights that HIIT induces stronger and more robust changes in HRV, whereas in Volume the effects are more moderate and partially disappear under stricter statistical control.
Taken together, the results clearly demonstrate that HIIT elicited a greater effect on HRV parameters, characterized by a substantial withdrawal of parasympathetic activity, an increase in sympathetic dominance, and only partial recovery within two hours. Effect sizes (Cohen’s d) further support that these changes were more pronounced in the HIIT group compared to the Volume group.
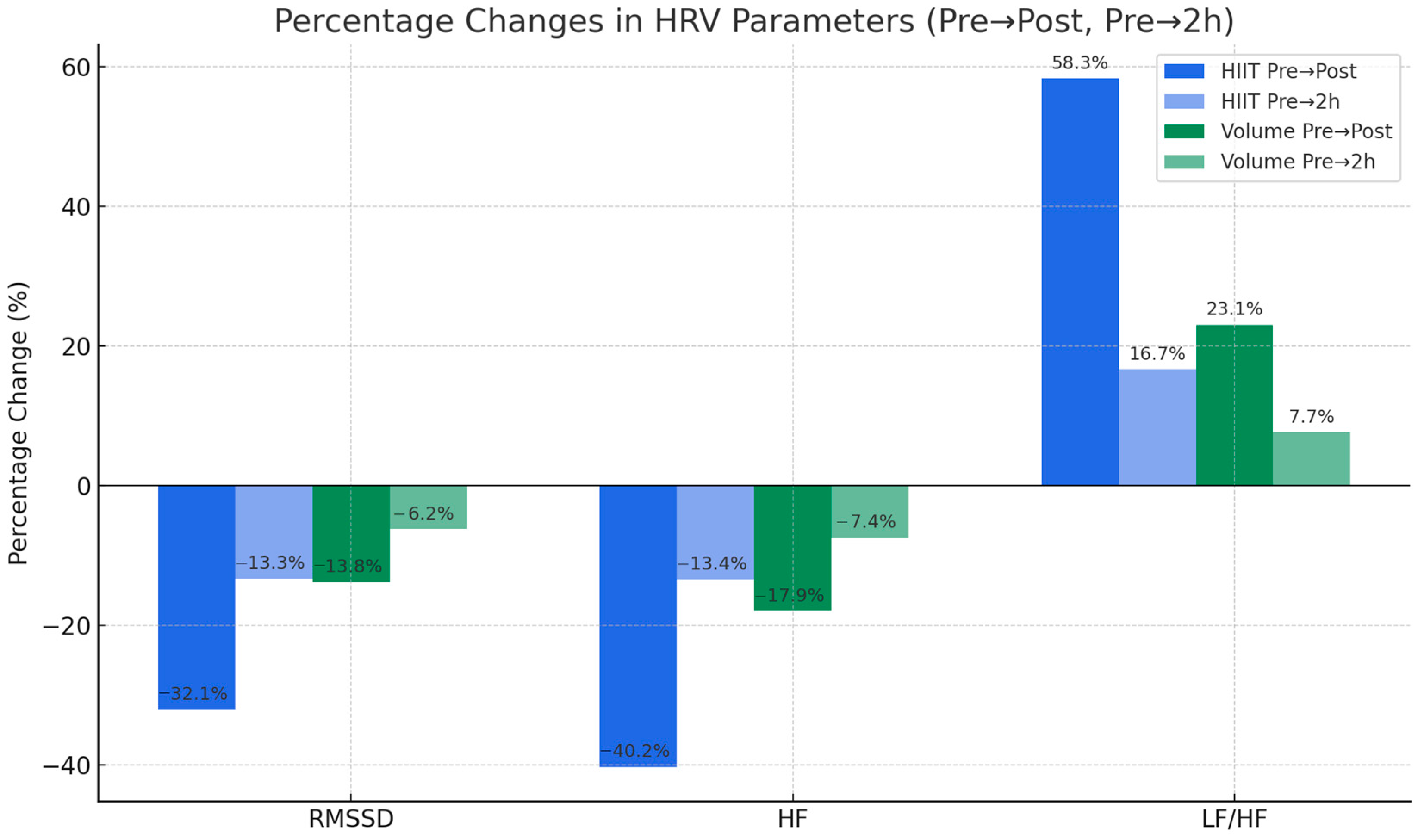
To further illustrate the differences between training modalities, percentage changes in key HRV parameters (RMSSD, HF, LF/HF) were calculated for both groups (HIIT and Volume) immediately after training and 2 h into recovery (
Figure 2).
The comparison of percentage changes in HRV parameters between the two groups revealed distinct patterns of autonomic modulation. In the HIIT group, RMSSD decreased by −32.0% immediately post-exercise and remained −13.3% below baseline after 2 h, while in the Volume group the reductions were smaller (−13.8% and −6.2%, respectively). Similarly, HF power in the HIIT group dropped by −40.2% post-exercise and recovered to −13.4% after 2 h, whereas the decreases in the Volume group were less pronounced (−17.9% and −7.4%). In contrast, the LF/HF ratio increased more markedly after HIIT (+58.3%) compared to Volume training (+23.1%), before partially normalizing at 2 h (+16.7% vs. +7.7%). These results confirm that HIIT acutely induces stronger vagal withdrawal and sympathovagal imbalance than Volume training, with only partial recovery within 2 h.
The results show that high-intensity interval training (HIIT) induces a sharper parasympathetic reduction and a stronger shift towards sympathetic dominance compared to traditional volume training. As a result, autonomic regulation is more severely impaired and recovery remains incomplete even two hours after the load. On the other hand, volume training leads to more moderate changes in cardiac autonomic regulation, with the autonomic balance being shifted to a lesser extent. The body demonstrates a faster and more complete recovery, with HRV parameters returning close to baseline levels within the same time window. Therefore, HIIT is more stressful for the autonomic nervous system and prolongs the recovery period, while volume training provides a smoother adaptation and more efficient recovery.
To test the effects of training program and time on HRV parameters, a two-factor Repeated Measures ANOVA (2 groups × 3 time points) was conducted, presented in
Table 3. For RMSSD, a significant effect of Group (F(1,4) = 4.40,
p = 0.044, ηp
2 = 0.524) and a significant interaction Group × Time (F(2,8) = 8.13,
p = 0.009, ηp
2 = 0.670) were found. Similar significant interactions were observed for HF (
p = 0.009) and LF/HF (
p = 0.012). This indicates that the dynamics of HRV in the two groups are different. The main effect of Time was not statistically significant for any of the parameters.
Interpretation with Holm correction. After applying Holm correction for multiple comparisons, some of the initially significant effects retained their statistical significance, while others dropped out. This highlights the importance of controlling for the risk of type I error in repeated testing.
For RMSSD, significance was retained only for the Group × Time interaction, indicating that the differences between groups were mostly manifested in temporal dynamics, rather than as a stable effect of group or time alone.
For HF, both the group effect and the interaction remained significant after Holm correction. This confirms that parasympathetic activity is lower in HIIT compared to Volume and that the two groups differ in the way HRV changes over time.
For LF/HF, significant group and interaction effects were also retained, clearly indicating that HIIT leads to a more pronounced sympathetic dominance and a different temporal trajectory compared to Volume.
The effects for SDNN and LF lost significance after Holm correction, meaning that the initially reported differences may be due to multiple comparisons and should be interpreted with caution.
Table 4 summarizes the results of the athletes in the HIIT and Volume training groups, expressed as the number of points earned by each athlete during a control competition. Points for Bulgarian national wrestling competitions are determined according to the international wrestling rules [
24] established by United World Wrestling (UWW): points in wrestling are awarded based on the type and effectiveness of the action. Takedowns are worth between 2 and 5 points depending on the amplitude and control: 5 points are awarded for a high-amplitude throw that puts the opponent directly in a dangerous position (on his back), 4 points for a throw with an amplitude that does not lead to a dangerous position, and 2 points for a takedown with a lower amplitude or a transition to control from a standing position. Turns/Exposing the opponent are awarded 2 points when the opponent is turned so that his shoulders are facing the mat at an angle of ≤90°. A step out results in 1 point awarded to the opponent if the wrestler completely leaves the mat area. Penalties for passivity result in 1 point for the active wrestler, along with a warning for the passive one. Violations (penalties) can add 1 or 2 points to the opponent, depending on their severity. Technical superiority ends the match when a point difference of 10 in freestyle or 8 in Greco-Roman wrestling is reached.
These data illustrate how the observed physiological changes also affect actual athletic performance, allowing a comparison between the two approaches under practical load conditions.
The results of the Shapiro–Wilk test showed for the HIIT group: W = 0.894, p = 0.133; for the volume group: W = 0.908, p = 0.204. For both groups p > 0.05, therefore, there were no statistically significant deviations from normality and it can be assumed that the results were normally distributed.
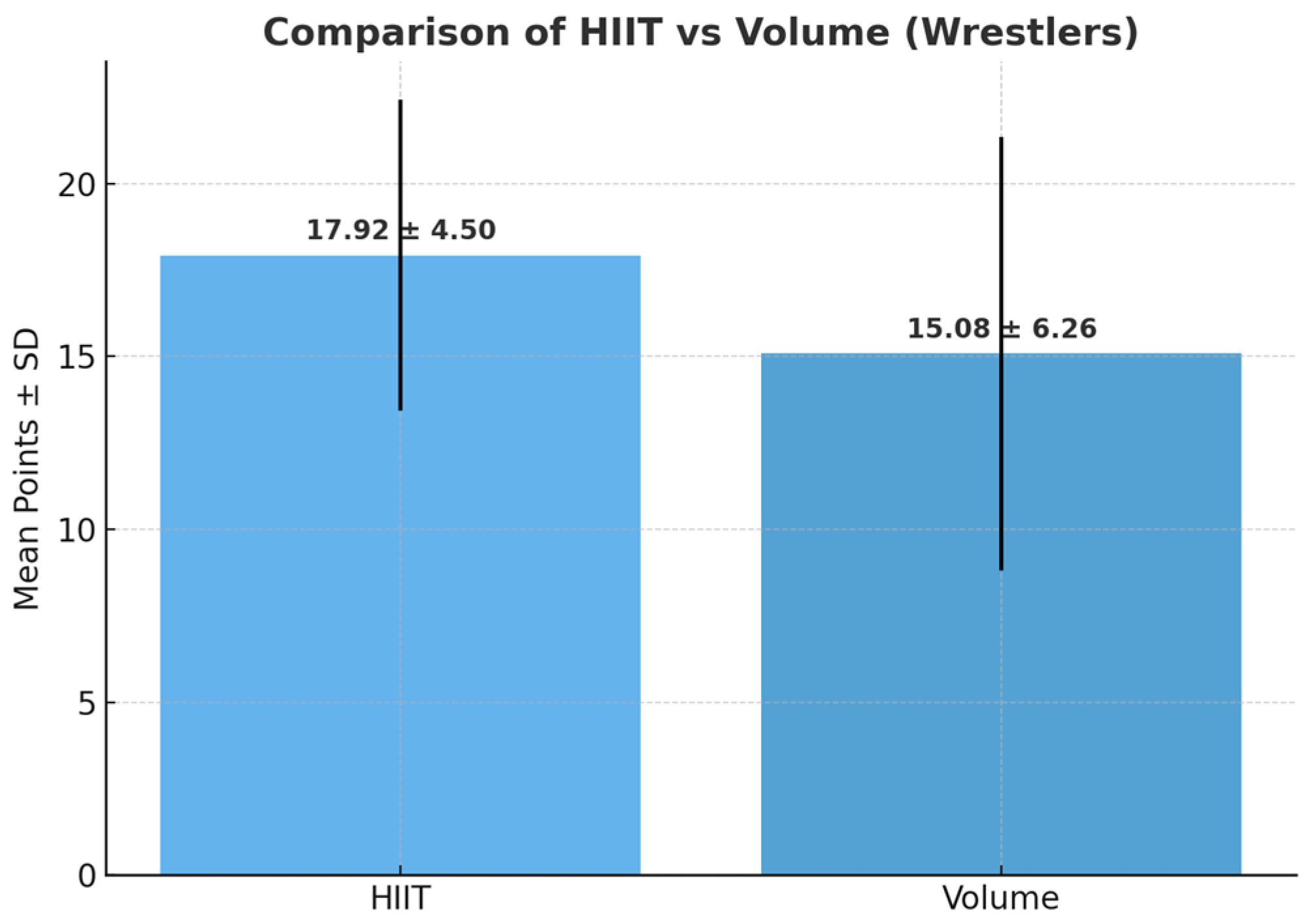
The analysis of the competition scores revealed higher mean values in the high-intensity interval training (HIIT) group (
Figure 3) compared to the Volume training group. The mean value for the HIIT group was 17.92 ± 4.50, while for the volume group it was 15.08 ± 6.26.
In our study, the HIIT group showed higher mean scores on the competition than the volume training group (17.92 vs. 15.08), with a medium effect size (Cohen’s d = 0.52) but the difference did not reach statistical significance (p = 0.218). This suggests a potential practical advantage of HIIT, but interpretation should be cautious. Several confounding factors may have influenced the results, including the lack of pre-measured individual training output, as well as the failure to include psychophysiological factors such as mood, anxiety, sleep, and diet. Furthermore, training activity outside the study was not strictly controlled, which may increase the variability of the results. Due to these limitations, we cannot definitively attribute the observed mean difference solely to the type of training. Future studies with tighter controls on training process and lifestyle are needed to confirm the potential advantage of HIIT.
The lack of statistical significance may also be due to the limited sample size, which limits the generalizability of the current results. This highlights the need for future studies with larger cohorts to confirm the observed practical benefit of HIIT.
Linear regression analysis was performed to investigate the relationship between HRV parameters and competition results. In the analysis of the competitors from the HIIT group, clear relationships were found between HRV parameters and competition scores. Parasympathetic markers showed positive correlations: RMSSD (Pre r = 0.42, Post r = 0.61, 2 h r = 0.55), SDNN (Pre r = 0.39, Post r = 0.48, 2 h r = 0.50) and HF (Pre r = 0.46, Post r = 0.63, 2 h r = 0.59). This means that higher parasympathetic activity and greater heart rate variability are associated with better performance on the mat. On the other hand, sympathetic parameters showed an inverse relationship: LF (Pre r = −0.28, Post r = −0.32, 2 h r = −0.35) and especially LF/HF (Pre r = −0.51, Post r = −0.67, 2 h r = −0.61), indicating that sympathetic dominance is associated with lower competitive results. The strongest relationships were reported for HF_Post (r = 0.63) and LF/HF_Post (r = −0.67), which emphasizes the importance of the acute post-training autonomic response as a predictor of athletic performance. In the Volume group, weaker and less consistent relationships were obtained between HRV parameters and competitive results compared to the HIIT group. This can be explained as follows: volume training loads the sympathetic more moderately, maintains more stable parasympathetic activity and does not cause such sharp fluctuations in autonomic balance. RMSSD and HF remained positively but less strongly correlated with competition scores (r = 0.26 and 0.40), while LF and LF/HF did not show a clear negative correlation, as with HIIT.
Practically, this suggests that the Volume group produces more sustained but less acute adaptations, which is beneficial for long-term conditioning and recovery, but is not as strong a predictor of immediate competition performance. In the context of wrestlers, where explosive actions and rapid autonomic reactivity are required, the HIIT group appears to be better for immediate competition preparation, as the stronger correlations between HRV (especially HF_Post and LF/HF_Post) and scores indicate that the autonomic nervous system response after training is directly related to performance on the mat.
A post hoc power analysis was conducted based on the observed effect sizes (ηp2) and the available sample size (n = 12 per group). The analysis showed that large effects such as HF (ηp2 ≈ 0.90) and LF/HF (ηp2 ≈ 0.90) achieved high statistical power (>0.80), whereas moderate effects such as RMSSD (ηp2 ≈ 0.52) and SDNN (ηp2 ≈ 0.42) yielded only moderate power (≈0.40–0.60). This indicates that the current study was well powered to detect large group differences, but underpowered for medium or small effects, which may explain some of the non-significant findings.
To facilitate practical interpretation, the following framework can be provided for coaches and practitioners. A reduction in RMSSD or HF generally indicates decreased parasympathetic (vagal) activity, often reflecting acute fatigue or stress from high-intensity exercise. An increase in LF or LF/HF ratio may signal heightened sympathetic activation, associated with greater physiological strain or incomplete recovery. Conversely, a return of RMSSD and HF to baseline levels suggests adequate recovery and readiness for subsequent training. Such HRV trends can guide individualized adjustments of training load, intensity, and recovery periods in wrestlers, enabling optimization of performance while minimizing overtraining risk.
4. Discussion
The present study compared the effects of a 3-month high-intensity interval training program and a traditional volume-oriented training approach on competitive performance and HRV dynamics in elite wrestlers. Both training paradigms led to improvements in competition outcomes; however, the HIIT group demonstrated a higher mean competition score.
The higher competition scores in the HIIT group suggest that the acute autonomic profile induced by this training type may translate into improved readiness for high-intensity, intermittent efforts characteristic of wrestling bouts.
Our findings support the use of HRV monitoring as a sensitive, non-invasive tool to guide training load adjustments and recovery strategies in elite combat athletes. By tracking daily and post-session HRV trends, coaches can better individualize periodization, avoiding overreaching while maximizing competitive readiness.
4.1. Interpretation and Implications
It should be acknowledged that, although significant Group × Time interactions were detected, the analytical approach cannot fully disentangle whether the observed differences arise from the training modality itself, the temporal dynamics, or their interaction.
The obtained HRV results demonstrate that the type of training load (intensity vs. volume) exerts a markedly different influence on the autonomic regulation of athletes. HIIT was associated with a sharp decrease in parasympathetic markers (RMSSD, HF) and a significant increase in sympathetic predominance (LF, LF/HF). This profile reflects an acute stress response of the autonomic nervous system, which is characterized by heightened arousal, accelerated recovery demands, and incomplete normalization even two hours after training. Such changes are typical of maximal exertion and point to a greater physiological cost of HIIT sessions.
From a training perspective, this means that HIIT imposes a strong recovery requirement on athletes, and frequent application without adequate recovery could lead to cumulative fatigue, autonomic imbalance, and an increased risk of overreaching or overtraining. At the same time, the pronounced sympathetic activation may be useful as a specific preparatory stimulus when the goal is to simulate the high arousal and stress typical of competition conditions. In this sense, HIIT is suitable in the final phases of preparation, but requires careful scheduling and sufficient recovery time to avoid performance deterioration.
The Volume training group exhibited a different pattern—milder reductions in parasympathetic activity, moderate sympathetic activation, and recovery of HRV parameters to values close to baseline within two hours. This indicates that volume-based sessions are less taxing on autonomic balance and allow for quicker return to homeostasis. Such a training load may be more appropriate in the general preparation phase, where the aim is to build aerobic capacity and endurance without excessively stressing the recovery systems. Moreover, the more balanced autonomic response after Volume training suggests that athletes would maintain a higher readiness for daily training and lower risk of maladaptation.
In terms of competitive readiness, the observed results imply that athletes who predominantly perform HIIT sessions may require longer recovery windows before entering competition, as their autonomic system needs more time to reestablish parasympathetic dominance. Conversely, athletes undergoing Volume training demonstrate faster autonomic recovery, which may support more frequent participation in preparatory sessions without impairing readiness.
4.2. Regarding Competitive Outcomes
Our results showed that athletes following the HIIT protocol achieved higher mean competitive scores (17.9 ± 4.5) compared to those in the volume-based training group (15.1 ± 6.3). Despite this trend, statistical analysis did not reveal a significant difference (p = 0.216). This may be attributed to the relatively small sample size (n = 12 per group) and variations in individual adaptation among athletes. The difference between the HIIT and Volume groups was therefore not statistically significant at the conventional level of p = 0.05. This indicates that, with the current data, it cannot be stated with high confidence that HIIT leads to superior outcomes compared to endurance-based training, although mean values favored the HIIT group. Moreover, the relatively small sample size and the absence of a priori power analysis limit the confidence in interpreting non-significant findings, which should therefore be considered preliminary.
4.3. Consistent Findings from the Literature
Numerous studies confirm the superiority of HIIT over traditional volume-based training with respect to aerobic capacity and cardiorespiratory adaptation. Milanović et al. [
25] conducted a systematic review showing that HIIT induces greater improvements in VO
2 max compared to moderate-intensity continuous exercise. Songsorn et al. [
26] reported significant increases in time-domain HRV markers (SDNN, RMSSD) following a six-week whole-body HIIT program in previously inactive adults, accompanied by a reduction in resting heart rate. Similarly, Benavides Roca et al. [
27] demonstrated that HIIT elicited a significantly greater acute reduction in HRV (SDNN decreased by 26.1 ms) compared to resistance training (−11.6 ms), reflecting a more pronounced autonomic disturbance. A recent systematic review by Grässler et al. ([
28] further emphasized that higher intensity and frequency of training are more likely to improve resting HRV in young and middle-aged healthy adults.
4.4. Contrasting Evidence
However, there are also studies indicating that both training approaches may yield comparable outcomes. Helgerud et al. [
29] found that both HIIT and higher-volume training improved aerobic capacity, though the magnitude of effects varied depending on the athletes’ baseline fitness. Other studies in wrestling and combat sports suggest that volume-based training is important for building a foundation of endurance, whereas HIIT is more effective for optimizing peak performance. For example, a multicomponent program [
20] implemented in elite wrestlers resulted in significant improvements in competition outcomes after six weeks. A systematic review [
30] also confirmed that HIIT provides superior improvements in aerobic and anaerobic performance in Olympic combat sports compared to alternative methods.
4.5. Interpretation of Findings
In this context, our results align with the trend suggesting that HIIT may confer a performance advantage, even if this was not statistically significant within the present sample. This highlights the necessity for larger-scale studies encompassing diverse age groups, training backgrounds, and longer intervention periods to establish the robustness of these effects.
An additional aspect of our findings concerns the relationship between HRV dynamics and competitive performance. While the HIIT group exhibited a sharper acute decline in parasympathetic activity (lower RMSSD and HF values immediately post-exercise) and a stronger increase in LF/HF, it was this group that ultimately achieved higher competitive scores. This suggests that greater variability in autonomic responses, along with partial but incomplete recovery within two hours, may serve as indicators of adaptive processes that, over time, promote enhanced endurance and efficiency in competition. In contrast, the volume-based group displayed more moderate HRV changes and a faster return to baseline, yet this did not translate into the same competitive advantage. Thus, our analysis indicates that higher-intensity training, while more physiologically stressful in the short term, may create more favorable conditions for achieving superior performance in the sporting context.
The sharper reductions in RMSSD and HF and the increase in LF/HF following HIIT are consistent with an acute sympathetic predominance. This response is largely driven by higher catecholamine release (adrenaline and noradrenaline), which accelerates cardiac rhythm, increases myocardial contractility, and elevates vascular tone. At the metabolic level, HIIT provokes greater lactate accumulation due to intensified anaerobic glycolysis, creating a larger oxygen debt and stimulating compensatory hyperventilation. The combination of elevated metabolic acidosis, increased body temperature, and heightened neuromuscular demand further augments sympathetic outflow and delays full vagal reactivation. These mechanisms explain the pronounced reductions in parasympathetic markers (RMSSD, HF) and the sustained elevation of the LF/HF ratio observed two hours post-exercise.
In contrast, the more moderate responses observed in the Volume group suggest a predominance of aerobic metabolism, characterized by steady-state oxidative phosphorylation and lower reliance on glycolytic pathways. This metabolic profile reduces lactate accumulation and catecholamine release, limiting the degree of autonomic perturbation. Consequently, parasympathetic reactivation occurs more rapidly, reflected in the faster normalization of RMSSD and HF values. These differences illustrate two complementary adaptive strategies: HIIT provides a strong but transient stress stimulus that can enhance tolerance to acute competitive demands, while volume training promotes gradual autonomic adaptation, supporting long-term recovery stability and aerobic conditioning.
While exploratory correlations were examined between HRV indices and competition results, the study design did not include a formal regression model. Future work with larger samples is required to confirm the extent to which HRV dynamics can predict competitive success in wrestlers.
4.6. Future Work
Although the study design focused on a 3-month intervention, the HRV (heart rate variability) recordings presented here specifically addressed acute responses to individual training sessions. Chronic adaptations over the entire intervention period were beyond the scope of the current measurements but could be explored in future analyses by averaging HRV across multiple sessions or examining longitudinal trends.
Longer-term measurements (e.g., up to 24 h after exercise) would provide a more complete picture of recovery processes. In our study, the 2 h time window was chosen because this is the period during which the most pronounced acute cardiovegetative changes occur after exercise. Future studies should include longer-term time points to assess the full dynamics of recovery processes.
The inclusion of additional objective tests of physical fitness (e.g., wrestling-specific tests of strength, power, or endurance) would enrich the assessment of the training effect. In future studies, we plan to combine competitive results with standardized physical fitness tests to achieve a more complete assessment.
The authors plan to extend the present research by validating a specially developed IoT-based photoplethysmography (PPG) device [
31], designed for real-time monitoring during sports activities. This device will integrate signal acquisition, feature extraction, and HRV-based analysis to provide athletes and coaches with immediate feedback regarding training intensity and recovery dynamics. The proposed system builds upon our previous experience in PPG and ECG analysis [
32,
33,
34].
By combining wearable sensor technology with advanced signal processing, the system aims to enhance personalized training strategies, prevent overtraining, and support medical decision-making in sports physiology. This approach is fully aligned with the scope of biomedical monitoring, digital health, and performance assessment in sports science.
4.7. Limitations
The sample size (n = 12) was not determined a priori by a power calculation, but was limited by the number of elite athletes available. This is a methodological limitation that should be considered when interpreting the results.
Furthermore, the small sample size (n = 12 per group) is a major limitation of the present study, which limits the statistical power of the analyses and may explain the lack of statistical significance in some comparisons, despite the medium to large effect sizes. Therefore, our findings should be approached with caution and confirmation should be sought in larger cohorts of elite wrestlers.
The study focused on male elite wrestlers, which may affect the generalizability of the findings to other combat sports or female athletes. Additionally, the HRV measurements were restricted to pre-training, immediate post-training, and 2 h recovery windows; more frequent sampling could provide deeper insights into recovery kinetics. Future research should investigate the long-term effects of alternating HIIT and volume-oriented cycles within a single competitive season.
Mood/anxiety, sleep, diet and lifestyle may influence the performance of the athletes. These factors were not assessed as part of the protocol and this is a limitation of the study.
The number of matches conducted was not equal among all competitors, which is a limitation. However, using results from a control competition conducted according to the rules of a national championship provides a high degree of validity, as the results reflect real competition conditions and workload faced by the athletes. All participants competed under the same rules and regulations, which minimizes the influence of external factors. In future studies, it would be useful to consider standardizing the number of matches or additional indicators for comparability of competition workload.
It should be borne in mind that performance in official tournaments can be influenced by external factors such as the level of opponents, referee decisions or the current psychological state of the competitors. This undoubtedly represents a limitation.
The results obtained support the use of HRV monitoring as a sensitive, non-invasive tool to guide training load adjustments and recovery strategies in elite combat athletes.
4.8. Practical Applications
Individualized training load prescription: HRV monitoring before and after training sessions can help coaches fine-tune the intensity and volume of workouts, preventing overreaching while maximizing readiness for competition.
Competition preparation: HIIT appears to induce a physiological state favorable for explosive and high-intensity actions, potentially improving match performance in combat sports.
Recovery management: Tracking HRV during the post-training recovery window provides insights into autonomic restoration, allowing the adjustment of recovery modalities such as active recovery, stretching, or hydrotherapy.
Early detection of maladaptation: Declines in baseline HRV or delayed post-training recovery trends may signal the need to reduce training load or modify training structure.
Applicability to other combat sports: While this study focuses on wrestling, the principles of HRV-guided training may extend to sports like judo, boxing, taekwondo, and MMA, where intermittent high-intensity efforts are decisive.