Hydration and Fluid Intake in Basketball Players During Training: Comparison of Different Age Categories
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Anthropometric Measurements
2.2.2. Hydration Status
2.2.3. Fluid Intake
2.3. Data Analysis
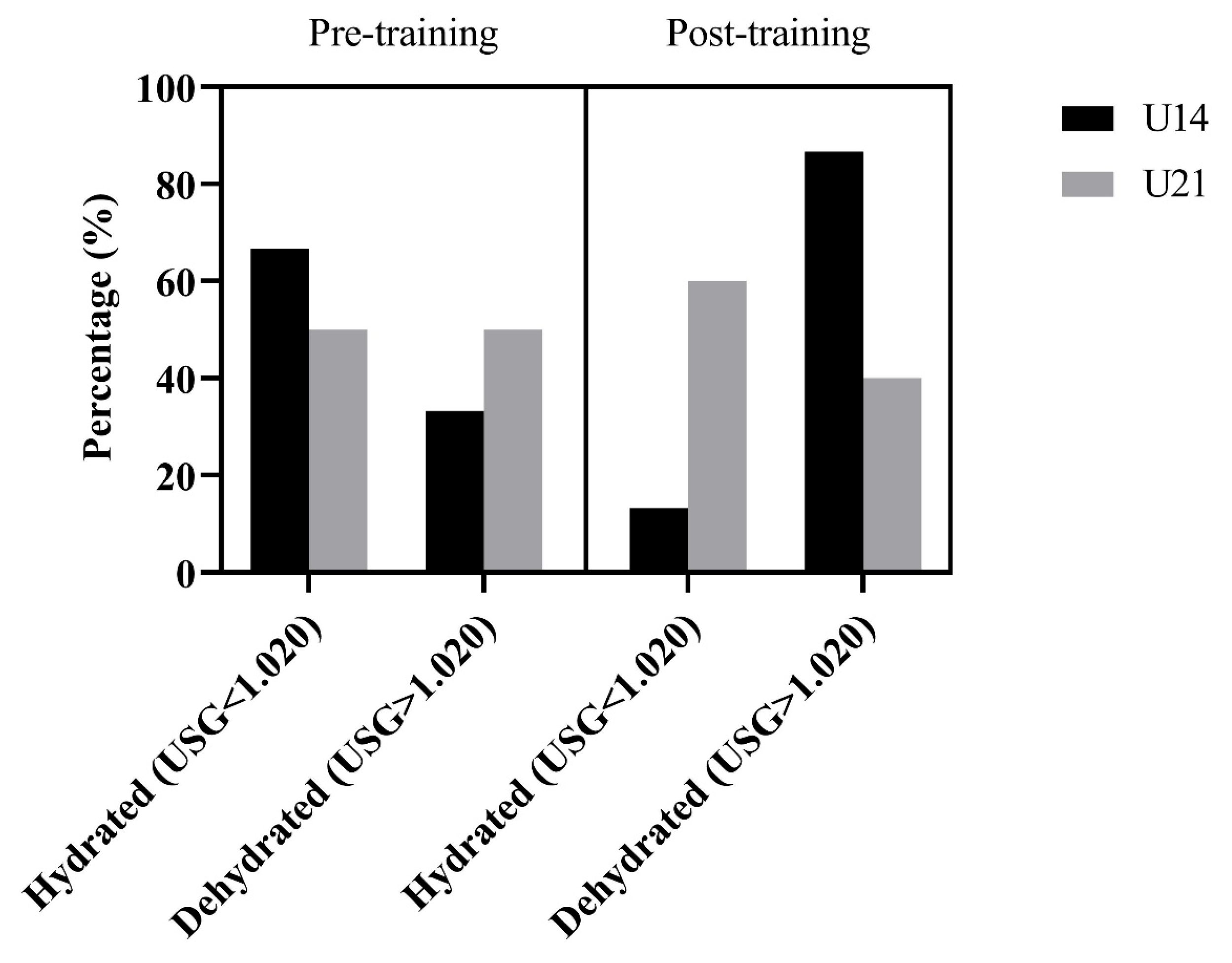
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Park, S.G.; Bae, Y.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, B.J. Effects of rehydration fluid temperature and composition on body weight retention upon voluntary drinking following exercise-induced dehydration. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2012, 6, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noakes, T. Fluid replacement during marathon running. Clin. J. Sport Med. 2003, 13, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noakes, T.D. Does dehydration impair exercise performance? Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittbrodt, M.T.; Millard-Stafford, M. Dehydration impairs cognitive performance: A meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2018, 50, 2360–2368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grandjean, A.C.; Grandjean, N.R. Dehydration and cognitive performance. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2007, 26, 549S–554S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al, V.M.; Martínez, J.; Cabrerizo, L.; Gargallo, M.; Lorenzo, H.; Quiles, J.; Planas, M.; Polanco, I.; Romero de Ávila, D.; Russolillo, J. Importance of water in the hydration of the Spanish population: FESNAD 2010 document. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Chishaki, T.; Umeda, T.; Takahashi, I.; Matsuzaka, M.; Iwane, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Ishibashi, G.; Ueno, Y.; Kashiwa, N.; Nakaji, S. Effects of dehydration on immune functions after a judo practice session. Luminescence 2013, 28, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, B.; Kons, R.L.; Detanico, D.; Šimenko, J. Acute Dehydration Impairs Performance and Physiological Responses in Highly Trained Judo Athletes. Biology 2022, 11, 872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barley, O.R.; Iredale, F.; Chapman, D.W.; Hopper, A.; Abbiss, C.R. Repeat Effort Performance Is Reduced 24 Hours After Acute Dehydration in Mixed Martial Arts Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2018, 32, 2555–2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.D.; Scott, D.M.; Brand, N.A.; Suh, H.-G.; Seal, A.D.; McDermott, B.P.; Ganio, M.S.; Kavouras, S.A. Mild hypohydration impairs cycle ergometry performance in the heat: A blinded study. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2019, 29, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casa, D.J.; Armstrong, L.E.; Hillman, S.K.; Montain, S.J.; Reiff, R.V.; Rich, B.S.; Roberts, W.O.; Stone, J.A. National Athletic Trainers’ Association position statement: Fluid replacement for athletes. J. Athl. Train. 2000, 35, 212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.C.; Park, K.J. The effect of rapid weight loss on sports injury in elite taekwondo athletes. Physician Sportsmed. 2023, 51, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.B.; Dougherty, K.A.; Chow, M.; Kenney, W.L. Progressive dehydration causes a progressive decline in basketball skill performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2007, 39, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMurray, R.; Williams, D.K.; Battaglini, C.L. The timing of fluid intake during an Olympic distance triathlon. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2006, 16, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, L.E. Rehydration during endurance exercise: Challenges, research, options, methods. Nutrients 2021, 13, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backhouse, S.H.; Biddle, S.J.; Williams, C. The influence of water ingestion during prolonged exercise on affect. Appetite 2007, 48, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, B.; Baydil, B.; Aydos, L. Weigh-in time affects hydration status and acute weight gain in combat sports: A comparison of judo and wrestling. Rev. De Artes Marciales Asiáticas 2021, 16, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlan, A.; Dascombe, B.; Reaburn, P. A comparison of the activity demands of elite and sub-elite Australian men’s basketball competition. J. Sports Sci. 2011, 29, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, S.E.; Carlson, J.S.; Jones, C.J.; McKenna, M.J. The physiological load imposed on basketball players during competition. J. Sports Sci. 1995, 13, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanović, E.; Stojiljković, N.; Scanlan, A.T.; Dalbo, V.J.; Berkelmans, D.M.; Milanović, Z. The activity demands and physiological responses encountered during basketball match-play: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 111–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouti, N.; Coso, J.D.; Estevez, E.; Mora-Rodriguez, R. Dehydration and sodium deficit during indoor practice in elite European male team players. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2010, 10, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, T. Fluid replacement requirements for child athletes. Sports Med. 2011, 41, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenney, W.L.; Chiu, P. Influence of age on thirst and fluid intake. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2001, 33, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Or, O.; Dotan, R.; Inbar, O.; Rotshtein, A.; Zonder, H. Voluntary hypohydration in 10-to 12-year-old boys. J. Appl. Physiol. 1980, 48, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Kuwahara, T.; Araki, T. Maturation-and aging-related changes in heat loss effector function. J. Physiol. Anthropol. Appl. Hum. Sci. 2004, 23, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, Y.; Shibasaki, M. Regional differences in age-related decrements of the cutaneous vascular and sweating responses to passive heating. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. Occup. Physiol. 1996, 74, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larose, J.; Wright, H.E.; Stapleton, J.; Sigal, R.J.; Boulay, P.; Hardcastle, S.; Kenny, G.P. Whole body heat loss is reduced in older males during short bouts of intermittent exercise. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R619–R629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, J.R.; Anderson, S. The aging kidney: Physiological changes. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2010, 17, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, P.A.; Rolls, B.J.; Ledingham, J.G.G.; Forsling, M.L.; Morton, J.J.; Crowe, M.J.; Wollner, L. Reduced thirst after water deprivation in healthy elderly men. N. Engl. J. Med. 1984, 311, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thigpen, L.K.; Green, J.M.; O’Neal, E.K. Hydration profile and sweat loss perception of male and female division II basketball players during practice. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 3425–3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, B. Hydration status and fluid intake of young athletes from different sports during training. Turk. J. Sport Exerc. 2021, 23, 165–170. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.-G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y. Statistical notes for clinical researchers: Sample size calculation 1. comparison of two independent sample means. Restor. Dent. Endod. 2016, 41, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauter, S.; Simenko, J. Morphological Asymmetries Profile and the Difference between Low- and High-Performing Road Cyclists Using 3D Scanning. Biology 2021, 10, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubac, D.; Marusic, U.; Karninčič, H. Hydration Status Assessment Techniques and Their Applicability Among Olympic Combat Sports Athletes: Literature Review. Strength Cond. J. 2016, 38, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardenaar, F.; Ortega-Santos, C.P.; Vento, K.; Olzinski, S.; Olig, J.; Kavouras, S.; Johnston, C. Reliability of 3 Urine Specific Gravity Meters for Measuring Brix and Urine Solutions at Different Temperatures. J. Athl. Train. 2021, 56, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casa, D.J.; Clarkson, P.M.; Roberts, W.O. American College of Sports Medicine roundtable on hydration and physical activity: Consensus statements. Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2005, 4, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, P.; Pandey, C.M.; Singh, U.; Gupta, A.; Sahu, C.; Keshri, A. Descriptive statistics and normality tests for statistical data. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaoutis, G.; Kavouras, S.A.; Kotsis, Y.P.; Tsekouras, Y.E.; Makrillos, M.; Bardis, C.N. Ad libitum fluid intake does not prevent dehydration in suboptimally hydrated young soccer players during a training session of a summer camp. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2013, 23, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshayes, T.A.; Jeker, D.; Goulet, E.D. Impact of pre-exercise hypohydration on aerobic exercise performance, peak oxygen consumption and oxygen consumption at lactate threshold: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2020, 50, 581–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devlin, L.H.; Fraser, S.F.; Barras, N.S.; Hawley, J.A. Moderate levels of hypohydration impairs bowling accuracy but not bowling velocity in skilled cricket players. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2001, 4, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, K.A.; Baker, L.B.; Chow, M.; Kenney, W.L. Two percent dehydration impairs and six percent carbohydrate drink improves boys basketball skills. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2006, 38, 1650–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horswill, C.A.; Passe, D.H.; Stofan, J.R.; Horn, M.K.; Murray, R. Adequacy of fluid ingestion in adolescents and adults during moderate-intensity exercise. Pediatr. Exerc. Sci. 2005, 17, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Brown, A.M.; De Félix-Dávila, R.A. Hydration status in adolescent judo athletes before and after training in the heat. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2012, 7, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenleaf, J.E.; Sargent, F. Voluntary dehydration in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1965, 20, 719–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pediatrics, A.A.O. Climatic heat stress and the exercising child and adolescent. American Academy of Pediatrics. Comm. Sports Med. Fitness. Pediatr. 2000, 106, 158–159. [Google Scholar]
- Osterberg, K.L.; Horswill, C.A.; Baker, L.B. Pregame Urine Specific Gravity and Fluid Intake by National Basketball Association Players During Competition. J. Athl. Train. 2009, 44, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubac, D.; Cular, D.; Marusic, U. Reliability of urinary dehydration markers in elite youth boxers. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, B.P.; Anderson, S.A.; Armstrong, L.E.; Casa, D.J.; Cheuvront, S.N.; Cooper, L.; Kenney, W.L.; O’Connor, F.G.; Roberts, W.O. National athletic trainers’ association position statement: Fluid replacement for the physically active. J. Athl. Train. 2017, 52, 877–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variables | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U21 | U14 | U21 | U14 | p | d | |
| Age (years) | 21.3 ± 1.2 | 13.0 ± 0.0 | - | - | - | - |
| Height (m) | 1.82 ± 0.10 | 1.69 ± 0.10 | 1.79–1.86 | 1.66–1.74 | <0.001 | 0.280 |
| Body weight (kg) | 80.7 ± 13.2 | 63.4 ± 14.2 | 76.5–84.9 | 58.1–68.7 | <0.001 | 0.280 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.4 ± 4.5 | 21.8 ± 3.3 | 22.8–26.0 | 20.6–23.1 | 0.016 | 0.251 |
| Fat percentage (%) | 14.5 ± 6.4 | 16.1 ± 4.6 | 12.4–16.5 | 14.5–17.9 | 0.224 | 0.244 |
| Sport experience (years) | 9.6 ± 2.2 | 4.1 ± 1.1 | 8.9–10.3 | 3.6–4.5 | <0.001 | 0.418 |
| Group | Mean ± SD | 95% CI | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| USG Pre-Training | USG Post-Training | USG Pre-Training | USG Post-Training | p (Holm Corrected) | |
| U14 | 1.020 ± 0.007 | 1.024 ± 0.006 | 1.018–1.023 | 1.024–1.026 | 0.03 |
| U21 | 1.020 ± 0.005 | 1.016 ± 0.008 * | 1.019–1.022 | 1.013–1.019 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kaplan, A.; Ceylan, B.; Baydil, B.; Šimenko, J. Hydration and Fluid Intake in Basketball Players During Training: Comparison of Different Age Categories. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910304
Kaplan A, Ceylan B, Baydil B, Šimenko J. Hydration and Fluid Intake in Basketball Players During Training: Comparison of Different Age Categories. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910304
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaplan, Abdurrahim, Bayram Ceylan, Bilgehan Baydil, and Jožef Šimenko. 2025. "Hydration and Fluid Intake in Basketball Players During Training: Comparison of Different Age Categories" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910304
APA StyleKaplan, A., Ceylan, B., Baydil, B., & Šimenko, J. (2025). Hydration and Fluid Intake in Basketball Players During Training: Comparison of Different Age Categories. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10304. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910304







