Abstract
This study addresses the challenge of cognitive waveform design for multiple-input–multiple-output (MIMO) radar systems operating in cluttered environments. It focuses on the key practical requirements for transmitting time-domain waveforms and proposes a novel approach. This method first determines the optimal frequency-domain waveform and then designs a time-domain waveform that closely approximates the frequency-domain solution. The primary objective is to enable MIMO radar systems to transmit orthogonal waveforms while accommodating various constraints. A frequency-domain waveform optimization model was initially developed using the principle of maximizing dual mutual information (DMI), and the energy spectral density (ESD) of the optimal waveform was derived using the water-filling method. Next, a time-domain waveform approximation model is constructed based on the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion, which incorporates constant modulus and peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) constraints. To minimize the performance degradation of the waveform, an improved adaptive gradient descent genetic algorithm (GD-AGA) was proposed to synthesize multichannel orthogonal time-domain waveforms for MIMO radars. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model for enhancing the performance of MIMO radar. Compared with traditional genetic algorithms (GA) and two enhanced GA alternatives, the proposed algorithm achieves a lower ESD loss and better orthogonal performance.
1. Introduction
To satisfy the requirements of radar systems that perform a variety of tasks in complex electromagnetic environments, researchers have proposed the concept of multiple-input–multiple-output (MIMO) radar [1] and cognitive radar (CR) [2].
Waveform design for cognitive radar has long been a research focus [3,4,5]. Waveform design is a constrained optimization problem that involves selecting the optimization criteria and constraints, which depends on the requirements of a specific task. Common optimization criteria include the signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio (SINR), mutual information (MI), and minimum mean square error (MMSE). Typical waveform constraints include the constant modulus, the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR), and energy constraints [6,7]. According to the definition of the waveform domain, cognitive waveform designs can generally be classified into two main categories: frequency-domain and time-domain optimal waveform designs. Frequency-domain waveform design primarily focuses on the energy spectrum distribution of the target and clutter. We obtained the energy spectral density (ESD) of the waveform by solving the energy constraint considering an optimal output criterion. Kay [8] originally utilized the water-filling method (WFM) from communication theory to design a waveform in a noisy environment and obtained an analytical expression for the optimal waveform by maximizing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) criterion under an energy constraint. C.Y. Chen [9] improved an iterative algorithm to jointly optimize the transmitted waveforms and receiving filters of the MIMO radar for the case of an extended target in clutter. However, the statistical characteristics of the clutter should be precisely known for this solution.
Waveform design under an energy constraint can be viewed as the optimal allocation of fixed resources. However, it is difficult to use the WFM to derive an analytical solution for the waveform when the model is complex. To solve this problem, the researchers in [10,11] applied the maximum marginal allocation (MMA) algorithm to appropriately obtain the optimal waveform in the frequency domain. Among them, Y. Cao et al. [10] applied MMA to obtain the optimal waveform with the joint optimization criteria of MI and SINR for cognitive radar that faced multiple tasks. F.M. Xin et al. [11] applied the MMA algorithm for cognitive radar with a dual mutual information (DMI) criterion, which is designed to maximize the MI between the received signal and the target impulse response and minimize the MI between the received signal and clutter impulse response. The MMA algorithm is essentially a dynamic programming technique that decomposes the optimization problem into multiple stages by discretizing the objective function. At each stage, fixed energy is allocated to the frequency bands such that the objective function is maximized. Through several stages, energy is optimally distributed among the frequency bands to obtain the optimal waveform so that it can effectively overcome the limitations of the WFM.
However, the frequency-domain waveform obtained using this approach cannot be directly applied to MIMO radar transmitters and instead requires additional synthesis of the time-domain waveform. To maximize the utilization of transmit power, constant modulus constraints are typically imposed on time-domain waveforms. Waveform design under a constant modulus constraint primarily involves optimizing the waveform phase. This is often achieved using the inverse Fourier transform to convert the time-domain waveform to the frequency domain, followed by windowing to reduce edge response mismatches. However, this results in significant distortions. To address this issue, Jackson et al. [12] introduced a constant phase method for optimizing the phase of constant-modulus waveforms by assuming a flat spectrum, which helps to reduce ESD losses. Nevertheless, the resulting waveform exhibited a significant error compared with the optimal waveform in the stopband. In another study conducted by Gong et al. [13], a constant modulus waveform optimization model was developed based on the minimum mean square error (MMSE) criterion with a phase recursive optimization method to approximate the ideal energy spectral density (ESD). Due to the limited number of phase optimizations, Liu et al. [14] employed genetic algorithms to improve the global search capabilities.
To ensure that the nonlinear radar amplifier operates at or near saturation and to avoid nonlinear distortion in the output waveform, it is often necessary to restrict the dynamic range of the waveform amplitude. Therefore, after obtaining the ideal ESD through the design of the frequency-domain waveform, a low peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) constraint should be considered when designing the time-domain waveform. In this scenario, the optimization involves the amplitude and phase variables of the signal. In this case, the methods implemented in Refs. [12,13] would no longer be applicable. Daoud et al. [15] utilized a genetic algorithm (GA) to address the PAPR limitations and improve waveform flexibility, but they faced the problem of “premature convergence”. To avoid this problem, D’Angelo and Palmieri [16] introduced the gradient descent (GD) algorithm, which provides strong local search performance and enhances overall convergence performance. In Ref. [17], a PAPR was included as one of the optimization criteria, and a cyclic optimization algorithm was employed to reduce the PAPR while maintaining orthogonality and a low sidelobe level. In Ref. [18], an AGA was applied to enhance the genetic algorithm (GA), allowing for the mutation and crossover intensities to be automatically adjusted based on the population state, thereby mitigating the risk of premature convergence. However, the selection of mapping functions lacks a systematically established optimal design principle and relies heavily on existing empirical knowledge.
Based on existing research works in Table 1, to take full advantage of MIMO radar waveform diversity and achieve a balance between target detection and parameter estimation performance through waveform design, this study establishes a frequency-domain waveform design model based on the DMI criterion. To this end, the optimal waveform ESD was obtained using the WFM. Based on this, a GD-AGA was proposed to synthesize a time-domain waveform to approximate the optimal ESD waveform. The proposed algorithm can employ waveform design under a constant modulus constraint and PAPR constraint and possesses lower ESD loss than the existing GA and some other improved GAs.

Table 1.
The related research chart.
The remainder of this study is organized as follows: Section 2 introduces the optimal waveform design model and the algorithm solution process in the frequency domain of the cognitive MIMO radar. Section 3 presents the optimal time-domain waveform model under constant modulus and PAPR constraints and the principle of the GD-AGA. Section 4 presents a comparative analysis of the simulation data. Finally, Section 5 summarizes the main results.
Description of operation symbols: denotes the Kronecker product operation, is the conjugate operation, is the conjugate transpose operation, is the transpose operation, represents the modulo value operation; signifies the convolution operation, and stands for the real and imaginary part operations, respectively.
2. Frequency-Domain Waveform Design
2.1. Development of an Optimization Model
The waveform design model for the cognitive radar is shown in Figure 1, where denotes a transmitted signal; , , and represent the target impulse response, the clutter impulse response, and the noise signal, respectively. In addition, all three signals possess Gaussian random processes with zero mean independent of each other, where signifies the signal scattered by the target, denotes the signal scattered by clutter, and represents the received signal. This model is often utilized in waveform design to maximize the SCNR and MI criteria. The SCNR and MI formulas are as follows:
where represents the bandwidth; is the target duration; , , and represent the target, clutter, and noise ESD, respectively; and signifies the individual transmit waveform ESD.

Figure 1.
Waveform design model for cognitive radar.
To enhance the target detection or parameter estimation performance of a radar system in a cluttered environment, maximizing the signal-to-clutter-plus-noise ratio (SCNR) or mutual information (MI) criterion is commonly used as an optimization criterion. In Ref. [11], using practical engineering scenarios, the influence of both the target and clutter on the received signal was considered. To maximize the DMI criterion, the mutual information between the received signal and target impulse response (TIR) is maximized, whereas the mutual information between the received signal and clutter impulse response (CIR) is minimized. Therefore,
If we compare Equations (1) and (2), we can see that the DMI criterion is different from the MI and SCNR criteria, and the molecular term is adjusted to . The target information is maximized, whereas the clutter interference is minimized by considering the spectral difference between the target and clutter. However, to improve the parameter estimation and target performance of the three criteria, further simulation comparison is required.
In the present work, we aim to extend this criterion to MIMO radars. To this end, the centralized MIMO radar is assumed to have a uniform linear array structure, the number of transmitting array elements is considered to be , the distance between the transmitting antennas is taken as , the number of receiving array elements is denoted by , and the distance between the receiving antennas is taken as . Consequently, the transmitted waveform can be expressed as follows:
When the transmitted waveforms are orthogonal to one another, they create an omnidirectional low-gain wide beam in space. This allows the receiver to process the signals into multiple channels and achieve waveform diversity gain. This approach provides greater flexibility when it comes to designing waveform parameters and signal processing methods. At this point, the transmitted waveform satisfies the following orthogonal relationship:
We examine the presence of an extended target in the far-field region, where its TIR is equivalent to the superposition of multiple scatterers. It is assumed that when the target is located in the MIMO radar array element, the azimuth angle is . Therefore, the transmitted signal phase difference can be evaluated by , whereas the received signal phase difference can be calculated as , where represents the signal wavelength. The transmitted signal steering vector, , and the received signal steering vector, are provided by the following equation:
Let us define , , and as the target impulse response, clutter impulse response, and noise signal, respectively. Then, the vector expression, when the transmitted signal of the first array is scattered by the target and reaches the received array, is given by the following equation:
After matching the filtering process at the MIMO radar receiver and transforming it into the frequency domain, the output waveform is obtained as follows:
where . Combining Equations (7) and (2), the expression of the maximization DMI criterion for the waveform design based on the cognitive MIMO radar is derived as follows:
where , and denotes the transmission waveform of the fourth transmission array.
2.2. Application of the WFM
In the realm of cognitive waveform design constrained by energy limitations, recent studies have increasingly investigated the MMA and WFM algorithms as effective solutions.
The MMA algorithm utilizes a dynamic programming algorithm to optimally allocate waveform energy to a certain frequency band through the stage to achieve the optimal overall energy allocation effect. The accuracy and complexity of the algorithm are related to the minimum unit of energy allocation [11]. By constructing Lagrange multipliers, the WFM employs convex function characteristics to obtain the extreme point, and the solution result is represented by a waveform analytical formula. To solve the optimal waveform analytical equation and reduce the ESD loss of the subsequent time-domain waveform, we introduced the WFM algorithm solution process. For this purpose, the MMA algorithm was implemented to arrive at an appropriate solution. The details are provided here for brevity.
To facilitate the calculation, the signal bandwidth () was first discretized into sub-bands by defining as the spacing of each sub-band and E as the signal energy. Subsequently, the optimization model subjected to the energy constraint can be constructed as follows:
The objective function is convex, and the Lagrange multiplier can be constructed by simultaneously combining the objective function and constraints.
The partial derivative of the left and right ends with respect to , and the extreme point of the function obtained with the life partial derivative of 0 represents the optimal waveform ESD in the frequency domain, denoted as in the following form:
where the following conditions of , , and should be exactly met:
The optimal waveform ESD can be directly evaluated using the WFM, which provides a better performance improvement in terms of the synthesis of the subsequent MIMO radar time-domain waveform. Similarly, the established approach can be extended to maximize the SCNR and MI criteria, which are not explained here for the sake of brevity.
3. Time-Domain Waveform Design
3.1. Development of an Optimization Model
To allow for the characteristic of the high degree of freedom of MIMO radar to be fully utilized, in this section, the continuous phase-coded signal with phase uniformly distributed in is used to approach the optimal waveform ESD in the frequency domain (denoted as ESDopt) under the MMSE criterion. The optimization model is constructed as follows:
where and represent the transmitting array element, and represents the transmitting signal phase matrix. For the orthogonal constraints in the model, the penalty function method was effectively utilized to construct the regularization constant . Therefore, the objective function and constraint conditions can be combined as follows:
Let us define the fitness function of the algorithm using the following equation:
When the constant modulus constraint is relaxed to the low PAPR constraint, the main relations of the model can be expressed as follows:
In the case of , the PAPR constraint no longer plays a role; therefore, is typically performed. Similarly, the penalty function method was employed to deform the above equation, and the fitness function is constructed as follows:
3.2. Application of the GD-AGA
In this section, we introduce the process of solving the time domain orthogonal waveform using the GD-AGA. This algorithm enhances the local optimization performance by embedding the GD algorithm into the GA and adding an adaptive parameter tuning strategy to improve the influence of the parameters on the algorithm.
The GD algorithm requires the gradient of the objective function, which is detailed in the Appendix A.
The adaptive parameter adjustment strategy is as follows. When the fitness of an individual is less than the average fitness value, the individual’s performance is excellent, and the crossover and mutation probabilities should be appropriately adjusted according to its fitness value. In contrast, it adopts a crossover and mutation probability that is larger than those of the other individuals:
where and represent the initial crossover probability and initial mutation probability, respectively; denotes the larger fitness value in the crossover individual, signifies the average fitness value of the population, and represents the minimum fitness value of the population. It should be emphasized that the range values of all the constants , , , and are . To further improve the robustness of the GD-AGA, the random mutation factor is set in the kth iteration, where denotes the random value, and represents the maximum iteration number. The value of the mutant gene fragment was synchronously adjusted as follows:
The replacement strategy of worse individuals was adopted to accelerate the convergence of the algorithm. Based on the maximum and minimum fitness values ( and ) of individuals in the population, a limit was set, and all values greater than the limit value were replaced by the best individual in the population. In addition, the GD algorithm and mutation operation may cause the amplitude and phase variables to exceed their upper and lower limits during the execution. When a variable surpassed these bounds, it was adjusted to the nearest boundary value.
Taking time-domain signal synthesis under a constant modulus constraint as an example, the GD algorithm and adaptive parameter tuning strategy were added to the GA, and the flowchart of the GD-AGA is provided in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1. Flowchart of the GD-AGA |
| Input:
, number of population individuals (), number of chromosomes (), , , , , , ,
and , , GD: step length , number of iterations Output: , , |
| Step 1: Running the GA: Initializing , and then calculating , , , and Step 2: a. Running the GD algorithm, for : Calculate the gradient ; Update ; Calculate ; Check the mutated crosses the boundary and replace it with the boundary edge value if it crosses the boundary. Terminate the algorithm after convergence. Update and . b. Roulette wheel algorithm Calculate the probability according to the individual fitness function. As a general rule, the smaller the probability, the better the performance. c. Adaptive crossover Update ; , update according to Equation (18), end; Update . d. Adaptive mutation , update and according to Equations (19) and (20); Check the mutated crosses the boundary and replace it with the boundary edge value if it crosses the boundary; end; Update . e. Replace the worst individual Update . Step 3: Evaluate the algorithm convergence and return to Step 2 in the lack of convergence. |
3.3. Analysis of Algorithm Complexity
In this study, the algorithm includes frequency- and time-domain waveform designs; thus, the complexity of the algorithm is decided by the two groups. In the frequency domain, because the FFT points are far larger than the MIMO radar array number, the algorithm complexity can be expressed as . In the time domain, the algorithm can be split into GD and AGA. Involving the FFT transformation and the gradient solution process, if we assume that the iteration of GD is , the algorithm complexity is . Assuming that the iteration of GA is , the population number is ; thus, the algorithm complexity is . Finally, the complexity of the algorithm is .
4. Simulation Analysis
To facilitate calculation and simulation, the units of the parameters were normalized and replaced by the value only. For this purpose, we set the MIMO radar transmitting array element as , receiving the array element number as , bandwidth as , FFT number as , the length of the extended target as 35 sampling points, the target and clutter relative to the radar angle as 30°, noise power as , and waveform energy as . In addition, the spacing of the transmitting and receiving array element was considered as half the wavelength.
4.1. Waveform Performance Analysis in the Frequency Domain
The extended target and clutter spectra are plotted in Figure 2 with the parameters set to the values given above, and the optimal waveform spectra obtained using the WFM and MMA approaches are shown in Figure 3.
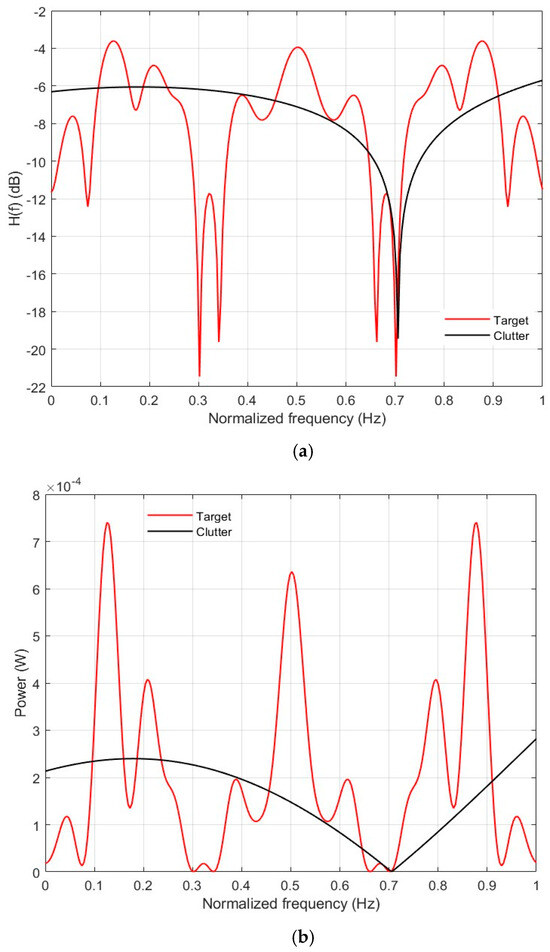
Figure 2.
(a) Extended target and clutter TIR spectrograms; (b) Extended target and clutter Power spectrum curve.

Figure 3.
(a) Analysis of the influence of the number of array elements on the waveform design; (b) Comparison of the waveforms generated by the WFM and MMA algorithms for various levels of P.
Figure 3a compares the influence of different transceiver elements on waveform design. Compared with the case of M = 2 and N = 4, the waveform energy of a single transmitting element is reduced when two new transmitting elements are added, and the output SCNR is reduced by 0.15 dB on average after 50 experiments. Reducing the receiving sensors by two results in a degradation in the quality of the received signal, resulting in no energy allocation on some frequency bands, and the output SCNR is reduced by 0.88 dB on average after 50 experiments.
Figure 3b shows the influence of different algorithms on the optimized waveform with M = 2 and N = 4 array elements. The WFM and MMA algorithms are capable of obtaining the optimal waveform through reasonable energy allocation in the frequency bands, and the allocation method depends on the optimization criterion; that is, under the criterion of maximizing the DMI, the waveform energy is allocated in the frequency band where the target TIR amplitude exceeds the clutter TIR. Conversely, no energy is allocated when the target TIR amplitude is lower than the clutter TIR. Owing to the different energy allocation criteria of the two algorithms, the obtained waveforms differed in terms of recognition performance. After 100 random simulations, the SCNR value of the waveform solved by the WFM is predicted to be 20.50 dB, whereas the SCNR value of the MMA algorithm is obtained as 20.35 dB. In this case, the performance of the WFM was better than that of the MMA algorithm.
To further compare the discrepancies of the designed waveforms based on various criteria, the optimal waveforms in the frequency domain were obtained using the WFM under three criteria—maximizing the DMI, MI, and SCNR—as shown in Figure 4. The shapes of the designed waveforms in the presence of the maximization SCNR and MI criteria were similar, and energy was consistently allocated in the frequency band corresponding to the higher target TIR. Additionally, the DMI criterion does not allocate more energy when the target TIR is lower than the cluttered TIR.
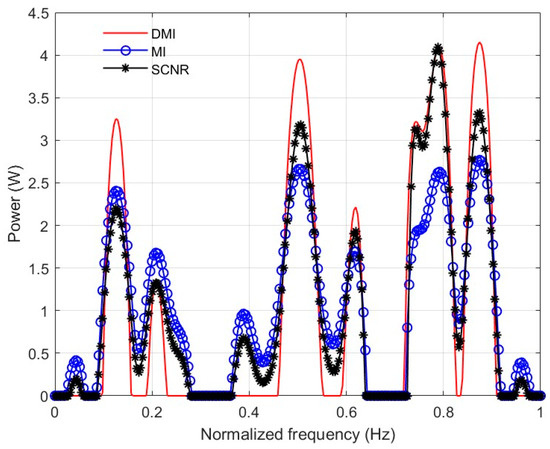
Figure 4.
Comparison of the predicted waveforms using various criteria.
The target detection and parameter estimation performance values of the design waveforms obtained after 100 random simulations, based on the three criteria, are listed in Table 2. The plotted results reveal that the detection performance and parameter estimation performance of the designed waveform using the DMI criterion are between the corresponding values of the maximization SCNR and MI criteria, and the waveform performance obtained by the solution is more balanced.

Table 2.
Performance comparison of the three employed criteria.
4.2. Performance Analysis of the GD-AGA
The GD parameters were set as follows: the step size () was set to 0.005, and the number of iterations () was set to 10. Additionally, the AGA factors were considered in the following form: the number of population individuals () was set to 100, the length of the signal number (T) was set to 200, the initial crossover probability () was set to 0.8, the initial mutation probability () was set to 0.1, and the parameters were set in the following order: , , , and .
The waveform obtained using the WFM, as shown in Figure 4, was substituted into Equation (14) as the ESDopt for evaluation. When the synthetic waveform closely matches the ESDopt, the algorithm’s performance improves, indicating that the synthetic waveform enhances the radar system’s effectiveness. Under the same parameter settings, for the GD-AGA proposed in the present study, the GA with the GD algorithm (GD-GA), GA with adaptive strategy (AGA), and general GA are reasonably compared. After the iterations of these algorithms, the fitness iteration curves of the various algorithms were appropriately evaluated, as shown in Figure 5. The corresponding optimal waveforms obtained after extracting the best individuals are shown in Figure 6.

Figure 5.
Comparison of the best fitness curves.
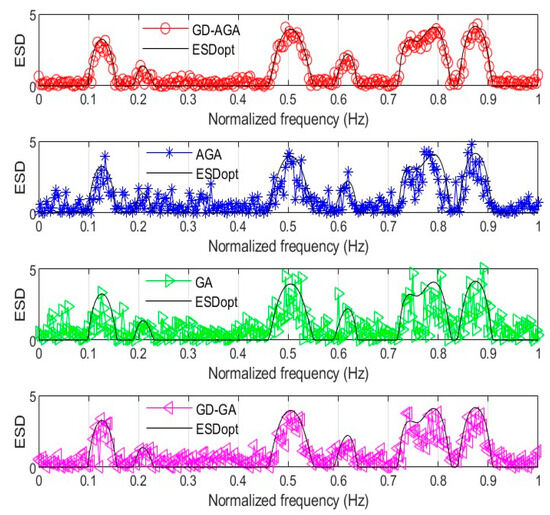
Figure 6.
Comparison of the optimal waveforms obtained from various approaches in the frequency domain.
From the perspective of convergence performance, the iterations of the GD-AGA, GD-GA, AGA, and GA tended to converge after 300, 150, 200, and 225 iterations, respectively. This clearly indicates that GD-AGA can overcome the “premature convergence” problem of the traditional GA. After the introduction of the GD algorithm, the GD-AGA and GD-GA had better convergence speeds in the early stages of operation, which reveals that the GD algorithm can improve the local convergence performance of the GA. From the output results, the GD-AGA exhibits better convergence performance and the best output waveform approximation effect among the four algorithms, which indicates the effectiveness of the improved GA strategy in the present work.
Because the heuristic algorithm has certain randomness, the results of each experiment are not the same. To comprehensively evaluate the influence of each parameter on the performance of the algorithm, the basic experimental parameters were set as follows: the number of iterations was set to 300, the initial crossover probability was set to 0.8, the initial mutation probability was set to 0.1, and the step size of the GD algorithm was set to 0.005. The factors and are used to represent the waveform approximation effect and quadrature performance, respectively, where smaller values of both represent better performances.
After 100 Monte Carlo stochastic simulation calculations, and of the waveforms obtained by the four algorithms for various parameter values are provided in Table 3. It is observed that for the improved GA strategy, the GD-GA or AGA can effectively reduce the discrepancy between the synthesized waveform and ESDopt; however, in terms of waveform orthogonality, the AGA demonstrates better performance compared with the GD-GA. When the GD algorithm and adaptive parameter tuning strategy are integrated into the GA, the proposed GD-AGA is superior to the other three algorithms in terms of both the waveform approximation effect and orthogonality.

Table 3.
Comparison of performance of various algorithms.
Considering that the regularization parameter has a weighted impact on and , the interval value was set to [0, 100], and the average value of 100 random simulation experiments is shown in Figure 7. The plotted results indicate that as the value of increases, the value of increases, which reveals that the waveform approximation effect is poor, and the value of decreases, which indicates better orthogonality among the waveforms. Consequently, a trade-off between the waveform approximation effect and orthogonality can be achieved by adjusting the tuning parameter value according to the actual requirements.
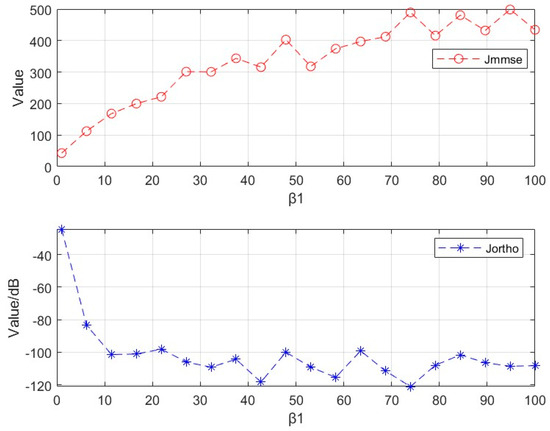
Figure 7.
Performance analysis of the algorithm in terms of .
4.3. Waveform Comparison in the Presence of Constant Modulus and PAPR Constraints
Using the GD-AGA, the time-domain waveforms obtained under the constant modulus and low PAPR constraints are illustrated in Figure 8. To this end, the waveform amplitude under the constant modulus constraint was normalized, the waveform amplitude in the presence of the low-PAPR constraint was randomly varied between 0 and 1, and the phase was distributed in the interval of .
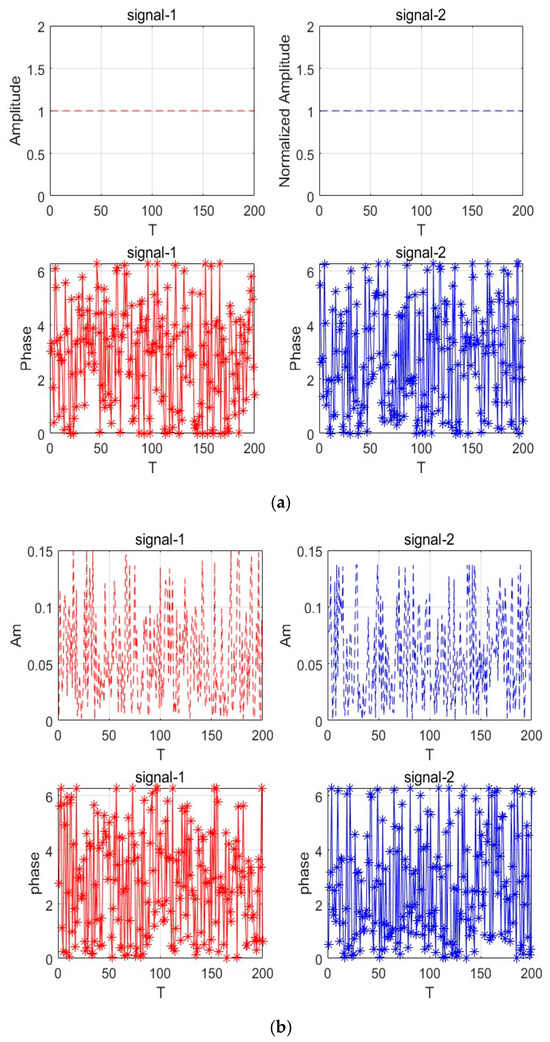
Figure 8.
(a) Constant envelope time-domain waveform based on the GD-AGA; (b) time-domain waveforms under PAPR constraints based on the GD-AGA.
The same parameter settings used in Section 3.2 were adopted; the number of iterations was set to 300, the initial crossover probability was set to 0.8, the initial mutation probability was set to 0.1, the step size of the GD algorithm was 0.005, and was used. On this basis, the performance values under different PAPR constraint values were extracted through 100 Monte Carlo stochastic simulations, and they are presented in Table 4. The results revealed that the waveform performance under the PAPR constraint varied only slightly as the value of increased. However, owing to the increase in the number of optimization variables, the waveform approximation and orthogonality performance exhibited a remarkable reduction compared with the values under the constant modulus constraint outlined in Table 3.

Table 4.
Comparison between the results of the PAPR and the constant envelope.
5. Conclusions and Future Prospects
To enhance the performance of MIMO radar in order to detect targets amidst clutter, we methodically designed specific orthogonal time-domain waveforms that can be practically transmitted via the application end. For this purpose, this study adopts a strategy in which the orthogonal time-domain waveform for a cognitive MIMO radar is designed using a frequency domain method followed by a time domain approach. First, in the frequency domain, the optimal waveform ESD curve was effectively extracted using the WFM via maximizing the DMI criterion and energy constraints. Compared with the MMA algorithm, the WFM scheme provides an analytical expression for the optimal waveform. The optimal waveform recognition and parameter estimation performances fell between the SCNR and MI criteria. Next, in the time domain, the adaptive parameter tuning and gradient descent principle were introduced into the GA, and accordingly, the GD-AGA was proposed. Under the MMSE criterion and orthogonal constraints, time-domain waveforms that satisfied the constant modulus and low PAPR constraints were appropriately synthesized to approximate the optimal waveform ESD. The simulation results demonstrate that the proposed model effectively enhances the target detection performance in cluttered environments for MIMO radar systems. The orthogonal time-domain waveforms of the designed MIMO radar satisfy the constant modulus and low PAPR constraints, and the proposed algorithm demonstrates better convergence performance compared with the traditional GA and improved GAs.
Future research directions could include exploring polarimetric radar [19] and other radars, and multi-objective optimization design could be performed under the condition that the requirements of multiple tasks such as communication, radar detection, and interference suppression are met. In addition, in future work, we will extend upon the development of worst-case robust waveform design under parameter uncertainty.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.S., Y.Z. and J.L.; Methodology, T.S., Y.Z. and J.L.; Software, T.S.; Validation, T.S. and Y.Z.; Formal analysis, T.S.; Investigation, T.S. and Y.Z.; Resources, J.L., Y.Z., K.L. and P.W.; Data Curation, T.S.; Writing—original draft, T.S.; Writing—review and editing, Y.Z., T.S., K.L. and P.W.; Visualization, T.S.; Supervision, J.L. and Y.Z.; Funding acquisition, K.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no.62473373).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author and the first author.
Acknowledgments
We thank the editor and the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments, which helped to improve our work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| MIMO | multiple-input–multiple-output |
| DMI | dual mutual information |
| ESD | energy spectral density |
| MMSE | minimum mean square error |
| PAPR | peak-to-average power ratio |
| GD-AGA | gradient descent genetic algorithm |
| GA | genetic algorithm |
| CR | cognitive radar |
| SINR | signal-to-interference-plus-noise ratio |
| SCNR | signal-to-clutter-plus-noise ratio |
| MI | mutual information |
| WFM | water-filling method |
| MMA | maximum marginal allocation |
| SNR | signal-to-noise ratio |
| TIR | target impulse response |
| CIR | clutter impulse response |
Appendix A
The GD-AGA algorithm enhances the local optimization performance by embedding the GD algorithm into the GA algorithm and adding an adaptive parameter tuning strategy to improve the influence of parameters on the algorithm. The synthetic MIMO radar-transmitted signal is first expressed as follows:
Let us now represent the point DFT transformation of the signal by . Therefore, the fitness fractions in Equations (15) and (17) can be expressed as follows:
The GD algorithm computes the gradient of the objective function, such that the objective function tends to converge in the gradient descent direction. The gradient of the magnitude and phase with respect to is calculated as follows:
Because the value of for the phase gradient is zero, when is satisfied, the amplitude gradient can be derived as follows:
where denotes the corresponding symbol of the peak signal amplitude. can be obtained separately by determining the magnitude and phase gradient:
References
- Fishler, E.; Haimovich, A.; Blum, R.; Chizhik, D.; Cimini, L.; Valenzuela, R. MIMO radar: An idea whose time has come. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radar Conference, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 29 April 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haykin, S. Cognitive radar: A way of the future. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2006, 23, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.; Lu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, G. Waveform Design of Cognitive MIMO Radar with Multiple Targets and Multiple Criterias. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Conference on Information Science, Electrical, and Automation Engineering, ISEAE 2024, Wuhan, China, 19–21 April 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, X.; Yang, J.; Cui, G. Cognitive Radar Subpulses Waveform Design via Online Greedy Search. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2025, 73, 1122–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Shen, T.; Peng, P. Joint Waveform Design of Cognitive MIMO Radar for Multi-Target Detection. Int. J. Pattern Recognit. Artif. Intell. 2025, 39, 2550015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, P.; He, H.; Li, J. Optimization of the receive filter and transmit sequence for active sensing. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2012, 60, 1730–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, H.; Stoica, P. Waveform Design for Active Sensing Systems: A Computational Approach. Ph.D. Thesis, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, S.M. Optimal signal design for detection of gaussian point targets in stationary gaussian clutter/reverberation. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2007, 1, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Vaidyanathan, P.P. MIMO radar waveform optimization with prior information of the extended target and clutter. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2009, 57, 3533–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Li, M.; Qu, S. Waveform design of cognitive radar based on joint criteria. Syst. Eng. 2022, 44, 3364–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.M.; Wang, J.K.; Wang, B.; Li, M.M. Adaptive radar waveform design based on dual mutual information criterion. J. Northeast. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2019, 40, 1690–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.; Kay, S.; Vankayalapati, N. Iterative method for nonlinear FM synthesis of radar signals. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2010, 46, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Meng, H.; Wei, Y.; Wang, X. Phase-modulated waveform design for extended target detection in the presence of clutter. Sensors 2011, 11, 7162–7177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; He, Z.; Zeng, J.; Liu, B. Polyphase orthogonal code design for MIMO radar systems. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Radar, Shanghai, China, 16–19 October 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoud, O.; Damati, A.; Alsawalmeh, W. Enhancing the MIMO-OFDM radar systems performance using GA. In Proceedings of the International Multi-Conference on Systems, Signals & Devices, Amman, Jordan, 27–30 June 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, G.; Palmieri, F. GGA: A modified genetic algorithm with gradient-based local search for solving constrained optimization problems. Inf. Sci. 2021, 547, 136–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xia, X.-G.; Kong, L. IRCI free range reconstruction for SAR imaging with arbitrary length OFDM pulse. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2014, 62, 4748–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, F.; Chen, Z.; Feng, X.; He, C.; Xu, J. Optimal design of anti-interrupted sampling repeater jamming waveform for missile-borne radar based on an improved genetic algorithm. IET Signal Process. 2021, 15, 622–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Cheng, X.; Huang, H.; Ciuonzo, D.; Shankar, B.; Ottersten, B. Constant-modulus waveform design with polarization-adaptive power allocation in polarimetric radar. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2023, 71, 2146–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).