The Influence of Personality Traits and Domain Knowledge on the Quality of Decision-Making in Engineering Design
Abstract
1. Introduction
- How do individual personality traits influence the quality and confidence of decisions made by engineering students?
- What is the impact of domain knowledge, both self-assessed and test-assessed, on decision-making quality and confidence?
- How do personality traits and domain knowledge interact to affect decision-making outcomes in engineering tasks?
2. Literature Review and Development of Hypotheses
2.1. Decision-Making in Engineering Design
2.2. Role of Personality Traits
2.3. Existing Methodologies in Quality Assessment
2.4. Impact of Knowledge on Decision-Making
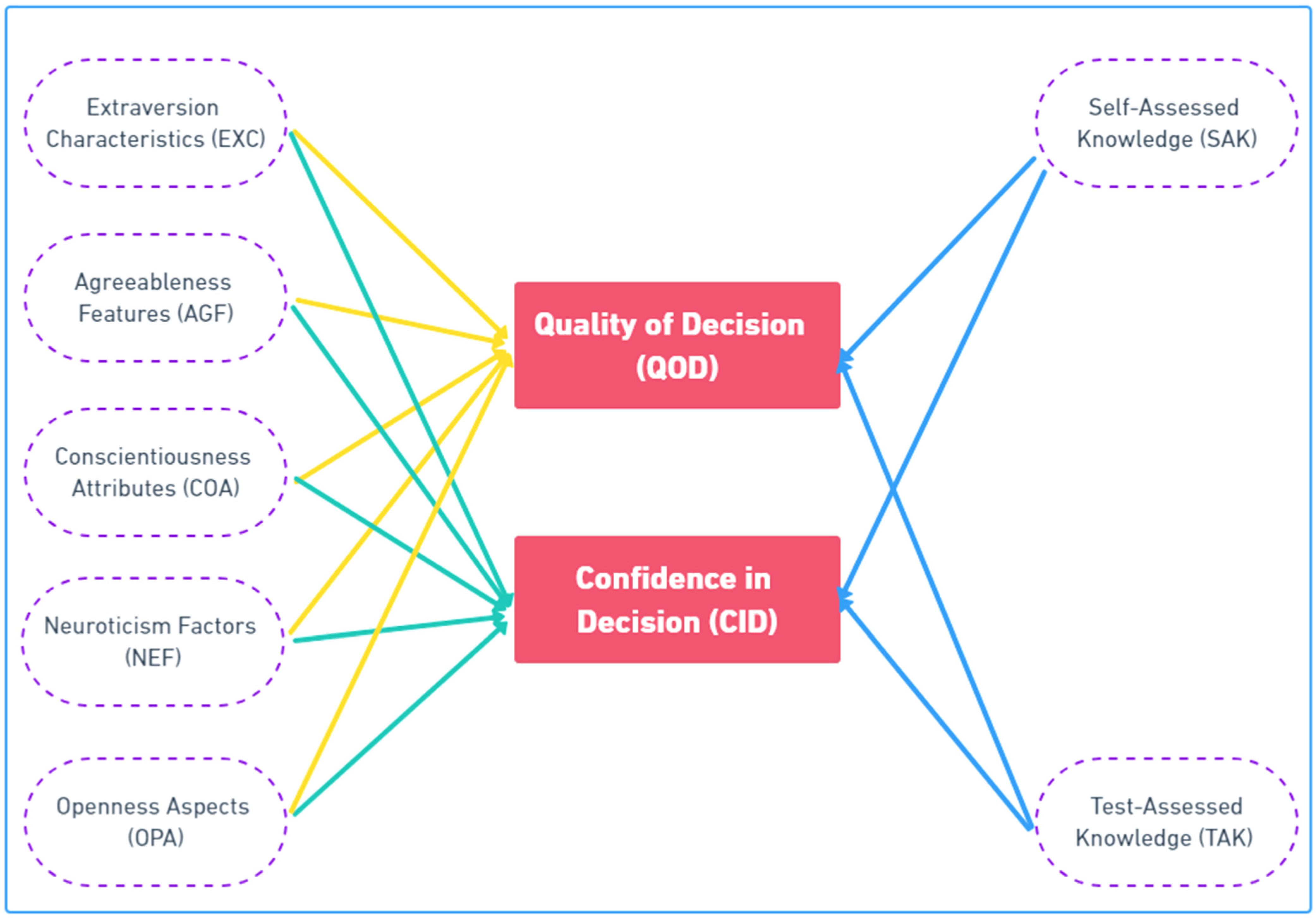
2.5. The Impact of the Big Five Personality Characteristics on Decision Quality and Confidence
2.6. Influence of Domain Knowledge on the Quality of Decision-Making and Confidence in Decision
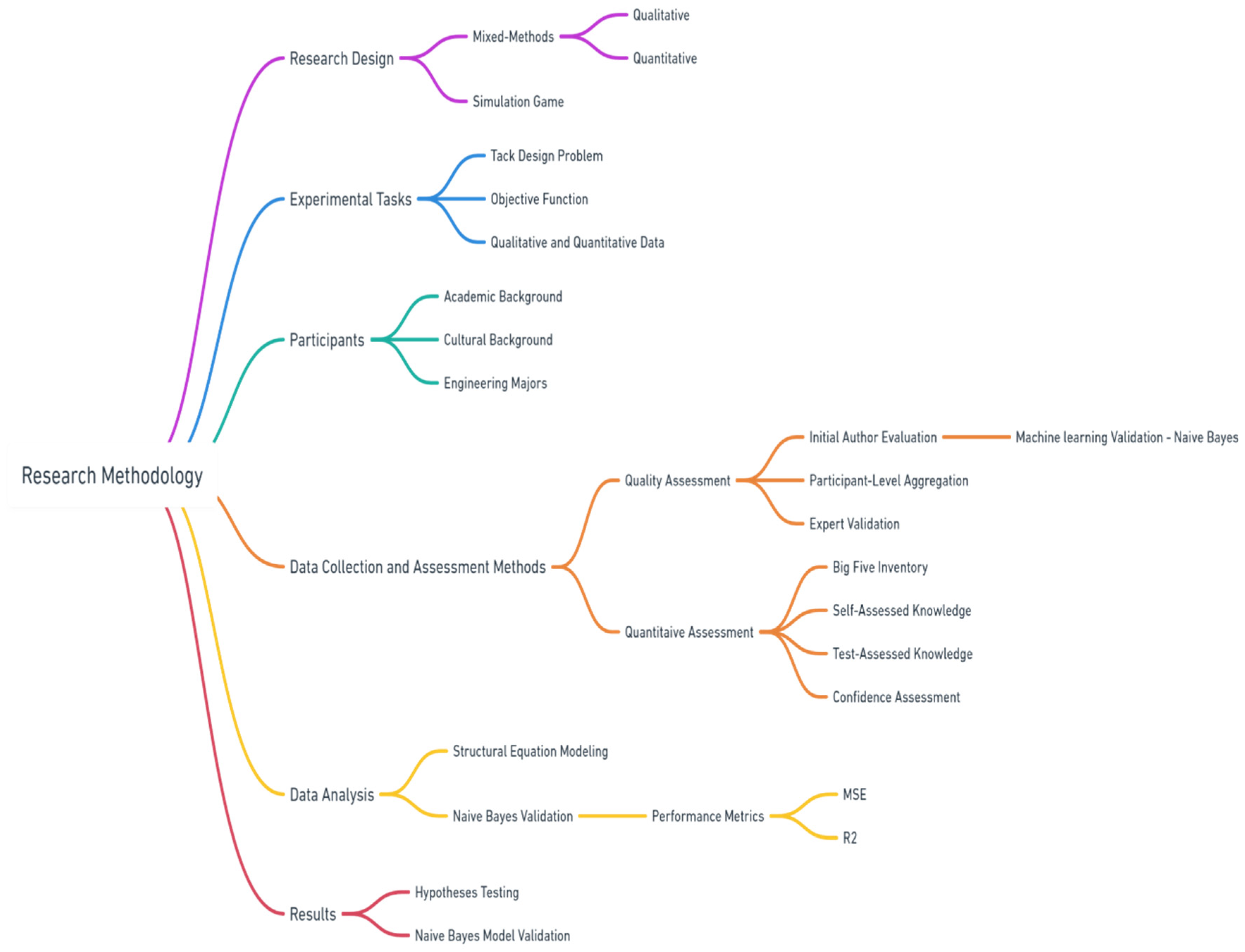
3. Research Methodology
3.1. Research Design
3.2. Experimental Tasks
3.3. Participants
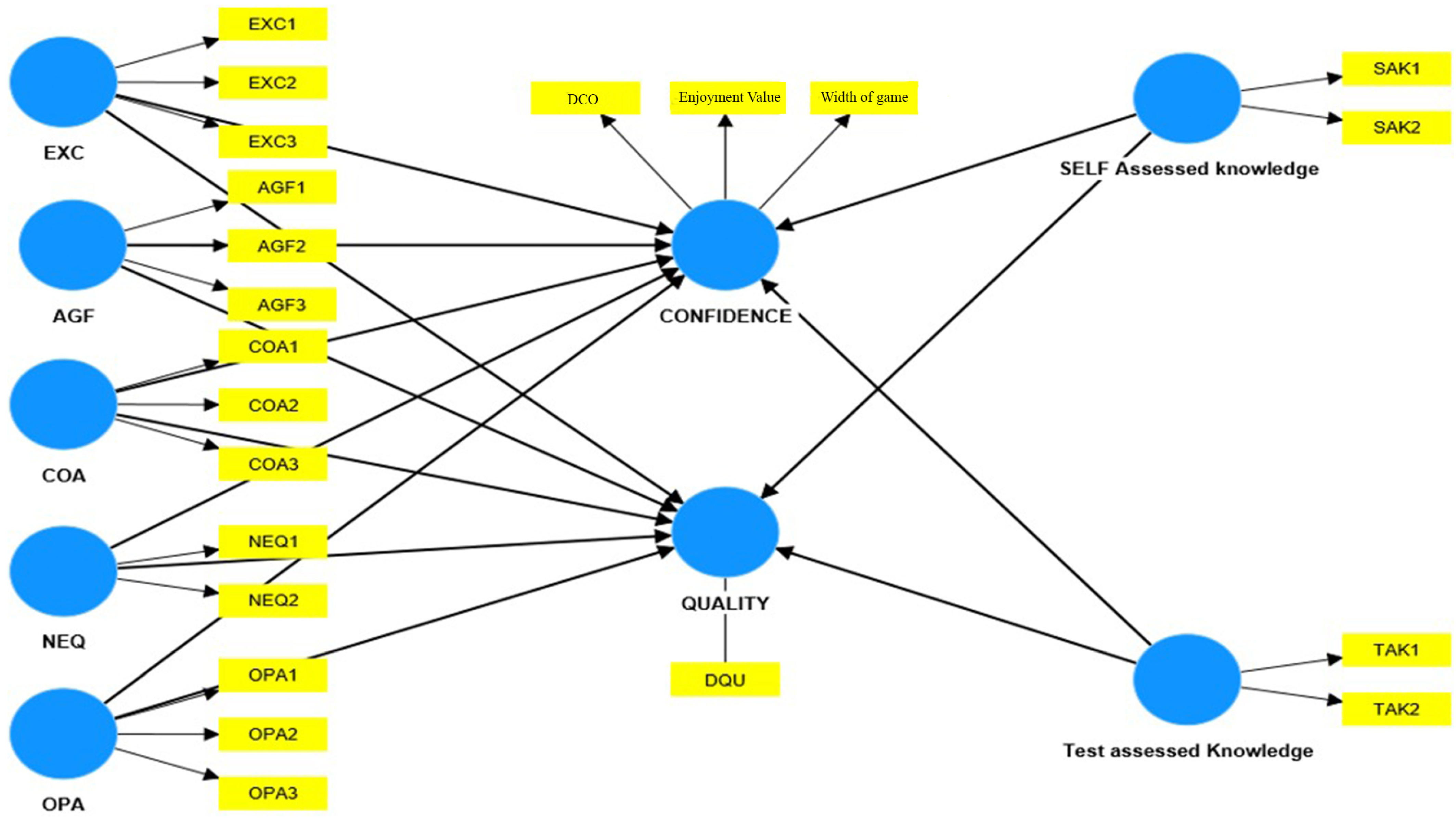
3.4. Quality Assessment Method
3.5. Data Collection and Assessment Methods
- Width of the track design;
- Enjoyment value associated with the track;
- Self-assessed confidence in each decision.
3.6. Data Analysis
4. The Results of Hypothesis Testing
4.1. Descriptive Analysis
- EXC1, EXC2, and EXC3 for Extraversion Characteristics;
- AGF1, AGF2, and AGF3 for Agreeableness Features;
- COA1, COA2, and COA3 for Conscientiousness Attributes;
- NEF1 and NEF2 for Neuroticism Factors;
- OPA1, OPA2, and OPA3 for Openness Aspects.
4.2. The Assessment of Validity and Reliability
4.3. The Estimation Results of Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Contributions
5.2. Theoretical Implications
5.3. Implications for Practice
5.4. Limitations and Future Research
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Doellken, M.; Zimmerer, C.; Matthiesen, S. Challenges Faced by Design Engineers When Considering Manufacturing in Design–an Interview Study. Proc. Des. Soc. Des. Conf. 2020, 1, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, Z.; Nellippallil, A.B.; Wang, R.; Allen, J.K.; Wang, G.; Yan, Y.; Mistree, F. (Eds.) Foundations for Design Decision Support in Model-Based Complex Engineered Systems Realization. In Architecting A Knowledge-Based Platform for Design Engineering 4.0; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 23–46. ISBN 978-3-030-90521-7. [Google Scholar]
- Kolus, A.; Wells, R.; Neumann, P. Production quality and human factors engineering: A systematic review and theoretical framework. Appl. Ergon. 2018, 73, 55–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, W.P.; Kolus, A.; Wells, R.W. Human Factors in Production System Design and Quality Performance—A Systematic Review. IFAC-Papersonline 2016, 49, 1721–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Ye, G.; Chen, J.; Liao, P.-C. Editorial: Human decision-making behaviors in engineering and management: A neuropsychological perspective. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1062171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erjavec, J.; Popovič, A.; Trkman, P. The effect of personality traits and knowledge on the quality of decisions in supply chains. Econ. Res. Ekon. Istraž. 2019, 32, 2269–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oz, E.; Fedorowicz, J.; Stapleton, T. Improving quality, speed and confidence in decision-making: Measuring expert systems benefits. Inf. Manag. 1993, 24, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullman, D. Robust decision-making for engineering design. J. Eng. Des. 2001, 12, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Milisavljevic-Syed, J.; Guo, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, G. Knowledge-Based Design Guidance System for Cloud-Based Decision Support in the Design of Complex Engineered Systems. J. Mech. Des. 2021, 143, 072001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K.E.; Chen, W.; Schmidt, L.C. (Eds.) Decision Making in Engineering Design; ASME Press: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Miro, M.E.; Groves, D.G.; Tincher, B.; Syme, J.; Tanverakul, S.; Catt, D. Adaptive Water Management in the Face of Uncertainty: Integrating Machine Learning, Groundwater Modeling and Robust Decision Making. Clim. Risk Manag. 2021, 34, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, G.; Seepersad, C.C.; Allen, J.K.; Mistree, F. A Method for Interactive Decision-Making in Collaborative, Distributed Engineering Design. Int. J. Agil. Manuf. Syst. 2002, 5, 47–65. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, Z.; Nellippallil, A.B.; Yan, Y.; Wang, G.; Goh, C.H.; Allen, J.K.; Mistree, F. PDSIDES—A Knowledge-Based Platform for Decision Support in the Design of Engineering Systems. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. Eng. 2018, 18, 041001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnott, D.; Pervan, G. Design Science in Decision Support Systems Research: An Assessment using the Hevner, March, Park, and Ram Guidelines. J. Assoc. Inf. Syst. 2012, 13, 923–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazak, A.; Kratzwald, B. The Weighted Decision Matrix: Tracking Design Decisions in Service Compositions. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 7th International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing and Applications, Matsue, Japan, 17–19 November 2014; pp. 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Glasziou, P.; Vandenbroucke, J.; Chalmers, I. Assessing the quality of research. BMJ 2004, 328, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzog, V.; Suwelack, S. Data-Efficient Machine Learning on Three-Dimensional Engineering Data. J. Mech. Des. 2022, 144, 021709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cash, P.; Isaksson, O.; Maier, A.; Summers, J. Sampling in design research: Eight key considerations. Des. Stud. 2022, 78, 101077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltes, S.; Ralph, P. Sampling in software engineering research: A critical review and guidelines. Empir. Softw. Eng. 2022, 27, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palinkas, L.A.; Horwitz, S.M.; Green, C.A.; Wisdom, J.P.; Duan, N.; Hoagwood, K. Purposeful Sampling for Qualitative Data Collection and Analysis in Mixed Method Implementation Research. Adm. Policy Ment. Health Ment. Health Serv. Res. 2015, 42, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.P. Sampling Methods in Research Design. Headache J. Head Face Pain 2020, 60, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S.; McGowan, A.; Papalambros, P. Using qualitative research methods in engineering design research. In Proceedings of the DS 75-2: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED13), Design for Harmonies, Vol. 2: Design Theory and Research Methodology, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 19–22 August 2013; Design Society: Glasgow, UK, 2013; pp. 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Welsh, M.; Alhakim, A.; Ball, F.; Dunstan, J.; Begg, S. Do personality traits affect decision making ability: Can MBTI type predict biases? Aust. Pet. Prod. Explor. Assoc. J. 2011, 51, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, P.G.; de la Garza, J.M.; Vorster, M.C. Relationship between Personality Traits and Performance for Engineering and Architectural Professionals Providing Design Services. J. Manag. Eng. 2002, 18, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.; Little, P. Impacts of Organizational Culture and Personality Traits on Decision-making in Technical Organizations. Syst. Eng. 2008, 11, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mili, F.; Shen, W.; Martinez, I.; Noel, P.; Ram, M.; Zouras, E. Knowledge modeling for design decisions. Artif. Intell. Eng. 2001, 15, 153–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.B.; Elms, D.G. Engineering decisions: Information, knowledge and understanding. Struct. Saf. 2015, 52, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Törnroos, M.; Jokela, M.; Hakulinen, C. The relationship between personality and job satisfaction across occupations. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2019, 145, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, C.; de Grip, A.; Pfeifer, H. Do recruiters select workers with different personality traits for different tasks? A discrete choice experiment. Labour Econ. 2022, 78, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, P.J.; Parnell, G.S.; Henderson, D.L. Decision Making in Systems Engineering and Management; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; ISBN 978-1-119-90142-6. [Google Scholar]
- Simon, H.A. A Behavioral Model of Rational Choice. Q. J. Econ. 1955, 69, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinsey, M.J.; Gwynne, S.M.V.; Kuligowski, E.D.; Kinateder, M. Cognitive Biases Within Decision Making During Fire Evacuations. Fire Technol. 2019, 55, 465–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenhardt, K.M. Top management teams and the performance of entrepreneurial firms. Small Bus. Econ. 2013, 40, 805–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nutt, B. Linking FM practice and research. Facilities 1999, 17, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, J.; Zhao, L.; Milisavljevic-Syed, J.; Ming, Z. Integrating and navigating engineering design decision-related knowledge using decision knowledge graph. Adv. Eng. Inform. 2021, 50, 101366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shergadwala, M.; Bilionis, I.; Kannan, K.N.; Panchal, J.H. Quantifying the Impact of Domain Knowledge and Problem Framing on Sequential Decisions in Engineering Design. J. Mech. Des. 2018, 140, 101402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juanchich, M.; Dewberry, C.; Sirota, M.; Narendran, S. Cognitive Reflection Predicts Real-Life Decision Outcomes, but Not Over and Above Personality and Decision-Making Styles. J. Behav. Decis. Mak. 2016, 29, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, C.A.; Miller, S.R. Creativity in design teams: The influence of personality traits and risk attitudes on creative concept selection. Res. Eng. Des. 2016, 27, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F. Personality traits as predictor of cognitive biases: Moderating role of risk-attitude. Qual. Res. Financ. Mark. 2020, 12, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, K.W.; Thurasamy, R.; Al-Abrrow, H.; Alnoor, A.; Tiberius, V.; Abdullah, H.O.; Abbas, S. Influence of generational status on immigrants’ entrepreneurial intentions to start new ventures: A framework based on structural equation modeling and multicriteria decision-making. J. Entrep. Emerg. Econ. 2021, 15, 589–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glew, D.J.; O’Leary-Kelly, A.M.; Griffin, R.W.; Van Fleet, D.D. Participation in organizations: A preview of the issues and proposed framework for future analysis. J. Manag. 1995, 21, 395–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakasai, A.M.; Jan, M.T. The Impact of Big Five Personality Traits on Salespeople’s Performance: Exploring the Moderating Role of Culture. Arab. J. Bus. Manag. Rev. 2015, 4, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- De Mooij, M. Consumer Behavior and Culture: Consequences for Global Marketing and Advertising; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2019; ISBN 978-1-5264-7159-8. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, J.; Shirkey, G.; John, R.; Wu, S.R.; Park, H.; Shao, C. Applications of structural equation modeling (SEM) in ecological studies: An updated review. Ecol. Process. 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. On the Nature of Size Factors. Genetics 1918, 3, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. The Relative Importance of Heredity and Environment in Determining the Piebald Pattern of Guinea-Pigs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1920, 6, 320–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S. Correlation and causation. J. Agric. Res. 1921, 20, 557–580. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.-Y. Structural Equation Modeling: A Bayesian Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 978-0-470-02424-9. [Google Scholar]
- Neuberg, L.G. Causality: Models, Reasoning, And Inference, by Judea Pearl, Cambridge University Press, 2000. Econ. Theory 2003, 19, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naive Bayes Classifier in Machine Learning-Javatpoint. Available online: https://www.javatpoint.com/machine-learning-naive-bayes-classifier (accessed on 18 October 2023).
- John, O.P.; Naumann, L.P.; Soto, C.J. Paradigm shift to the integrative Big Five trait taxonomy: History, measurement, and conceptual issues. In Handbook of Personality: Theory and Research, 3rd ed.; The Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 114–158. ISBN 978-1-59385-836-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mooradian, T.A.; Swan, K.S. Personality-and-culture: The case of national extraversion and word-of-mouth. J. Bus. Res. 2006, 59, 778–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depue, R.A.; Collins, P.F. Neurobiology of the structure of personality: Dopamine, facilitation of incentive motivation, and extraversion. Behav. Brain Sci. 1999, 22, 491–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Clark, L.A. Chapter 29-Extraversion and Its Positive Emotional Core. In Handbook of Personality Psychology; Hogan, R., Johnson, J., Briggs, S., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1997; pp. 767–793. ISBN 978-0-12-134645-4. [Google Scholar]
- Judge, T.A.; Higgins, C.A.; Thoresen, C.J.; Barrick, M.R. The Big Five Personality Traits, General Mental Ability, and Career Success Across the Life Span. Pers. Psychol. 1999, 52, 621–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stavrova, O.; Evans, A.M.; van Beest, I. The Effects of Partner Extraversion and Agreeableness on Trust. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Bull. 2023, 49, 1028–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.C.; Varadarajan, P.R.; Dacin, P.A. Market Situation Interpretation and Response: The Role of Cognitive Style, Organizational Culture, and Information Use. J. Mark. 2003, 67, 63–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Furnham, A. Personality, self-esteem, and demographic predictions of happiness and depression. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2003, 34, 921–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutafi, J.; Furnham, A.; Paltiel, L. Why is Conscientiousness negatively correlated with intelligence? Personal. Individ. Differ. 2004, 37, 1013–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, C.; Gonzalez, R. Interaction with Others Increases Decision Confidence but Not Decision Quality: Evidence against Information Collection Views of Interactive Decision Making. Organ. Behav. Hum. Decis. Process. 1995, 61, 305–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenski, J.M.; Sobocko, K.; Whelan, A.D.C. Introversion, Solitude, and Subjective Well-Being. In The Handbook of Solitude; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 184–201. ISBN 978-1-118-42737-8. [Google Scholar]
- Canli, T.; Sivers, H.; Whitfield, S.L.; Gotlib, I.H.; Gabrieli, J.D.E. Amygdala Response to Happy Faces as a Function of Extraversion. Science 2002, 296, 2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, K.; Litov, L.; Yeung, B. Corporate Governance and Risk-Taking. J. Financ. 2008, 63, 1679–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziano, W.G.; Tobin, R.M. Agreeableness: Dimension of Personality or Social Desirability Artifact? J. Personal. 2002, 70, 695–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoncic, B.; Kregar, T.B.; Singh, G.; Denoble, A.F. The Big Five Personality–Entrepreneurship Relationship: Evidence from Slovenia. J. Small Bus. Manag. 2015, 53, 819–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Samroengraja, R. The Stationary Beer Game. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2000, 9, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, M.A.G.; van Tuijl, H.F.J.M.; Rutte, C.G.; Reymen, I.M.M.J. Personality and team performance: A meta-analysis. Eur. J. Personal. 2006, 20, 377–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, C.R.; Kaufmann, L.; Michel, A. Behavioral supply management: A taxonomy of judgment and decision-making biases. Int. J. Phys. Distrib. Logist. Manag. 2007, 37, 631–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highhouse, S.; Dalal, R.S.; Salas, E. Judgment and Decision Making at Work; Routledge: Abingdon, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-135-02195-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmot, M.P.; Ones, D.S. A century of research on conscientiousness at work. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 23004–23010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, M.-L.; Jiang, Z. Trait conscientiousness, thriving at work, career satisfaction and job satisfaction: Can supervisor support make a difference? Personal. Individ. Differ. 2021, 183, 111116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, J.F.; Moscoso, S.; Berges, A. Conscientiousness, Its Facets, and the Prediction of Job Performance Ratings: Evidence against the narrow measures. Int. J. Sel. Assess. 2013, 21, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodwell, J.; McWilliams, J.; Gulyas, A. The impact of characteristics of nurses’ relationships with their supervisor, engagement and trust, on performance behaviours and intent to quit. J. Adv. Nurs. 2017, 73, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, L.N.; Santoso, G.A.; Takwin, B.; Sunitiyoso, Y.; Abraham, J. Group decision quality, conscientiousness and competition. Cogent Psychol. 2021, 8, 1872907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosnowska, J.; Hofmans, J.; de Fruyt, F. Revisiting the neuroticism–performance link: A dynamic approach to individual differences. J. Occup. Organ. Psychol. 2020, 93, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debusscher, J.; Hofmans, J.; Fruyt, F.D. The Curvilinear Relationship between State Neuroticism and Momentary Task Performance. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e106989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzetti, G.; Chiesa, R.; Vignoli, M.; Depolo, M. The bad performance of neurotic employees: A matter of job satisfaction and workaholism. In Neuroticism: Characteristics, Impact on Job Performance and Health Outcomes; Psychology of emotions, motivations and actions; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 33–47. ISBN 978-1-63485-323-1. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, P.; Lei, Y.; Yan, F.; Yang, Z.; Yang, L.; Wang, L. Effects of acute stress on risky decision-making are related to neuroticism: An fMRI study of the Balloon Analogue Risk Task. J. Affect. Disord. 2023, 340, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Zhou, L.; Li, A.-M.; Hui, Q.-S.; Zhou, Y.-R.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Neuroticism and risk-taking: The role of competition with a former winner or loser. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2021, 179, 110917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T. The role of Neuroticism on psychological and physiological stress responses. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 2004, 40, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.-S.; Lau, X.-S.; Kung, Y.-T.; Kailsan, R.A. Openness to Experience Enhances Creativity: The Mediating Role of Intrinsic Motivation and the Creative Process Engagement. J. Creat. Behav. 2019, 53, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.M.; Zhou, J. When openness to experience and conscientiousness are related to creative behavior: An interactional approach. J. Appl. Psychol. 2001, 86, 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khindri, A.; Rangnekar, S. Can Adaptability Improve Openness to People’s Ideas? The Moderating Role of Work Experience. In Technology, Management and Business; Kumar Misra, R., Shrivastava, A., Sijoria, C., Eds.; Advanced Series in Management; Emerald Publishing Limited: Bingley, UK, 2023; Volume 31, pp. 143–156. ISBN 978-1-80455-519-4. [Google Scholar]
- Lazzarotti, V.; Bengtsson, L.; Manzini, R.; Pellegrini, L.; Rippa, P. Openness and innovation performance: An empirical analysis of openness determinants and performance mediators. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 2017, 20, 463–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitamurto, T.; Holland, D.; Hussain, S. Three layers of openness in design: Examining the open paradigm in design research. In Proceedings of the DS 75-1: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Engineering Design (ICED13), Design for Harmonies, Vol. 1: Design Processes, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 19–22 August 2013; Design Society: Glasgow, UK, 2013; pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Edvardsson, I.; Sigurðardóttir, Á. Decision making in organisations: A comparison between the private and public sector. Icel. Rev. Polit. Adm. 2010, 6, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Othman, R.; El Othman, R.; Hallit, R.; Obeid, S.; Hallit, S. Personality traits, emotional intelligence and decision-making styles in Lebanese universities medical students. BMC Psychol. 2020, 8, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzioni, A. Mixed Scanning Model of Decision Making in Organizations. In Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance; Farazmand, A., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–5. ISBN 978-3-319-31816-5. [Google Scholar]
- Dietrich, C. Decision Making: Factors that Influence Decision Making, Heuristics Used, and Decision Outcomes. Inq. J. 2010, 2, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sundstroem, A. Self-Assessment of Knowledge and Abilities. A Literature Study. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Self-assessment-of-knowledge-and-abilities-%3A-A-Sundstr%C3%B6m/9fb7cd4ee4fa51ba18a2017e2f789e4f36ceee95 (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- National Research Council. Theoretical Foundations for Decision Making in Engineering Design; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed-Kristensen, S.; Hacker, P.; Wallace, K. The role of knowledge and experience in engineering design. In Proceedings of the DS 35: Proceedings ICED 05, the 15th International Conference on Engineering Design, Melbourne, Australia, 15–18 August 2005; Design Society: Glasgow, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, S.S.; Powell, D.; Cornett, D. Chapter 9-Engineous: A Unified Method for Design Automation, Optimization, and Integration. In Artificial Intelligence in Engineering Design; Tong, C., Sriram, D., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992; pp. 235–254. ISBN 978-0-12-660563-1. [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer, N.; Becker, K.; Sutton, M. Engineering Design Thinking: High School Students’ Performance and Knowledge. J. Eng. Educ. 2015, 104, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snibsøer, A.K.; Ciliska, D.; Yost, J.; Graverholt, B.; Nortvedt, M.W.; Riise, T.; Espehaug, B. Self-reported and objectively assessed knowledge of evidence-based practice terminology among healthcare students: A cross-sectional study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Kotzebue, L. Beliefs, Self-reported or Performance-Assessed TPACK: What Can Predict the Quality of Technology-Enhanced Biology Lesson Plans? J. Sci. Educ. Technol. 2022, 31, 570–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, A.; Huang, S. Simulation Games in Engineering Education: A State-of-the-Art Review. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2011, 19, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Designing a Frictional Roller Coaster with Math and Physics!-Activity. Available online: https://www.teachengineering.org/activities/view/ind-1996-frictional-roller-coaster-design-project-calculus (accessed on 10 September 2019).
- Noble, H.; Heale, R. Triangulation in research, with examples. Evid. Based Nurs. 2019, 22, 67–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonsen, K.; Jehn, K.A. Using triangulation to validate themes in qualitative studies. Qual. Res. Organ. Manag. Int. J. 2009, 4, 123–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.d.S.; Ribeiro, M.C.; de Queiroga, D.E.U.; da Silva, I.A.P.; Ferreira, S.M.S. The use of multiple triangulations as a validation strategy in a qualitative study. Cienc. Saude Coletiva 2020, 25, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.J.; John, O.P. Short and extra-short forms of the Big Five Inventory–2: The BFI-2-S and BFI-2-XS. J. Res. Personal. 2017, 68, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, S.L. The Growth of Structural Equation Modeling: 1994-2001. Struct. Equ. Model. Multidiscip. J. 2003, 10, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blumer, A.; Ehrenfeucht, A.; Haussler, D.; Warmuth, M.K. Occam’s Razor. Inf. Process. Lett. 1987, 24, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, M.R.A.; Sami, W.; Sidek, M.H.M. Discriminant Validity Assessment: Use of Fornell & Larcker criterion versus HTMT Criterion. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2017, 890, 012163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F., Jr.; Hult, G.T.M.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M.; Danks, N.P.; Ray, S. (Eds.) Evaluation of Reflective Measurement Models. In Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM) Using R: A Workbook; Classroom Companion: Business; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 75–90. ISBN 978-3-030-80519-7. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error: Algebra and Statistics. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 382–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vert, A.M. The Interactive Effects of Expertise, Extraversion, and Agreeableness on Influence and Decision Quality in Groups; The University of Oklahoma: Norman, OK, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wilmot, M.P.; Ones, D.S. Agreeableness and Its Consequences: A Quantitative Review of Meta-Analytic Findings. Personal. Soc. Psychol. Rev. 2022, 26, 242–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haro, J.M.D.; Vena, J. Exploring the relationship between personality traits and innovative behaviour: A mixed-methods approach. Int. J. Organ. Anal. 2024; ahead-of-print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrick, M.R.; Mount, M.K. The Big Five Personality Dimensions and Job Performance: A Meta-Analysis. Pers. Psychol. 1991, 44, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tett, R.P.; Burnett, D.D. A personality trait-based interactionist model of job performance. J. Appl. Psychol. 2003, 88, 500–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, J.F. The five factor model of personality and job performance in the European Community. J. Appl. Psychol. 1997, 82, 30–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, F.L.; Hunter, J.E. The validity and utility of selection methods in personnel psychology: Practical and theoretical implications of 85 years of research findings. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 124, 262–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judge, T.A.; Ilies, R. Relationship of personality to performance motivation: A meta-analytic review. J. Appl. Psychol. 2002, 87, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endler, N.S.; Magnusson, D. Toward an interactional psychology of personality. Psychol. Bull. 1976, 83, 956–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

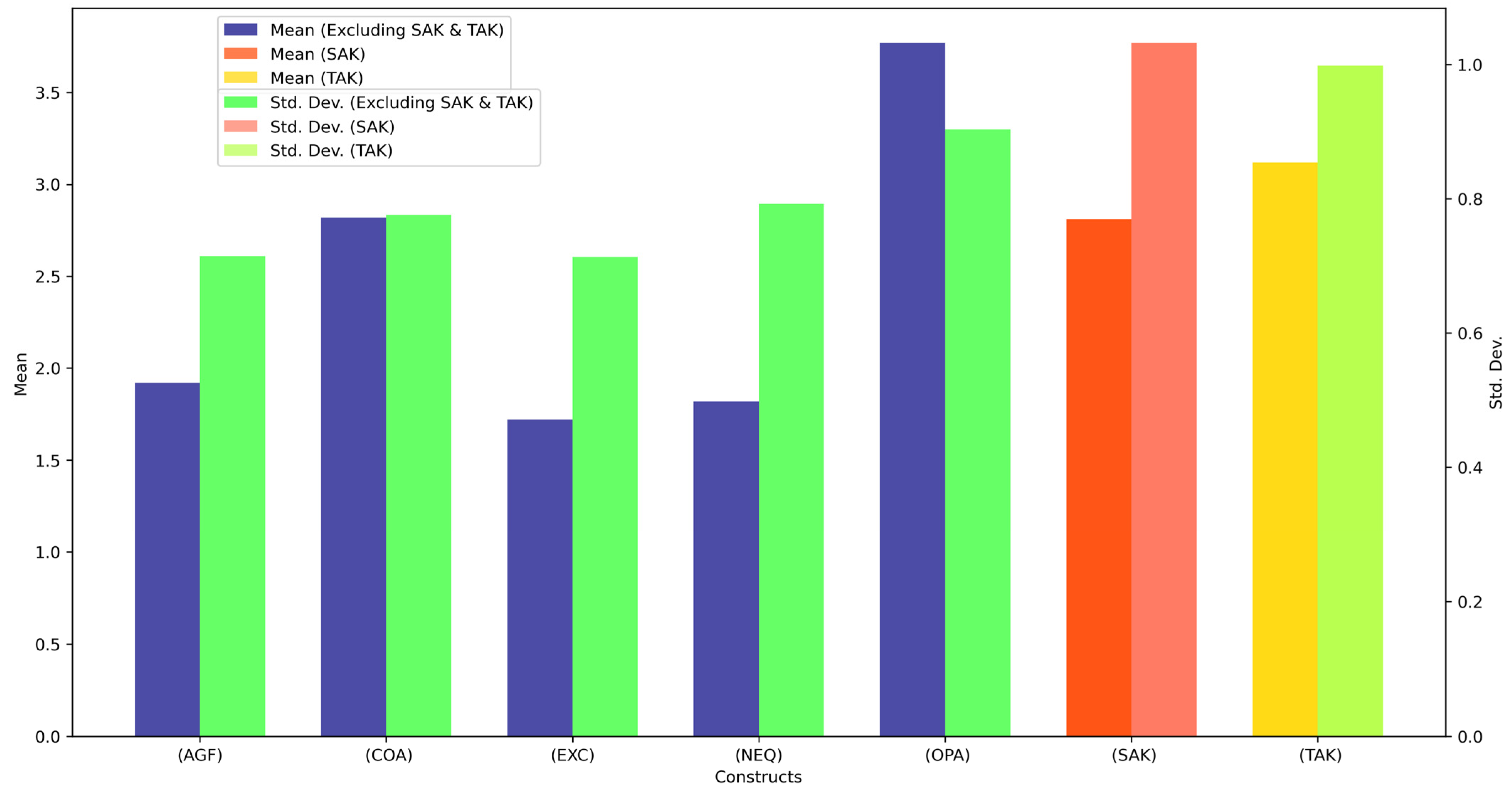
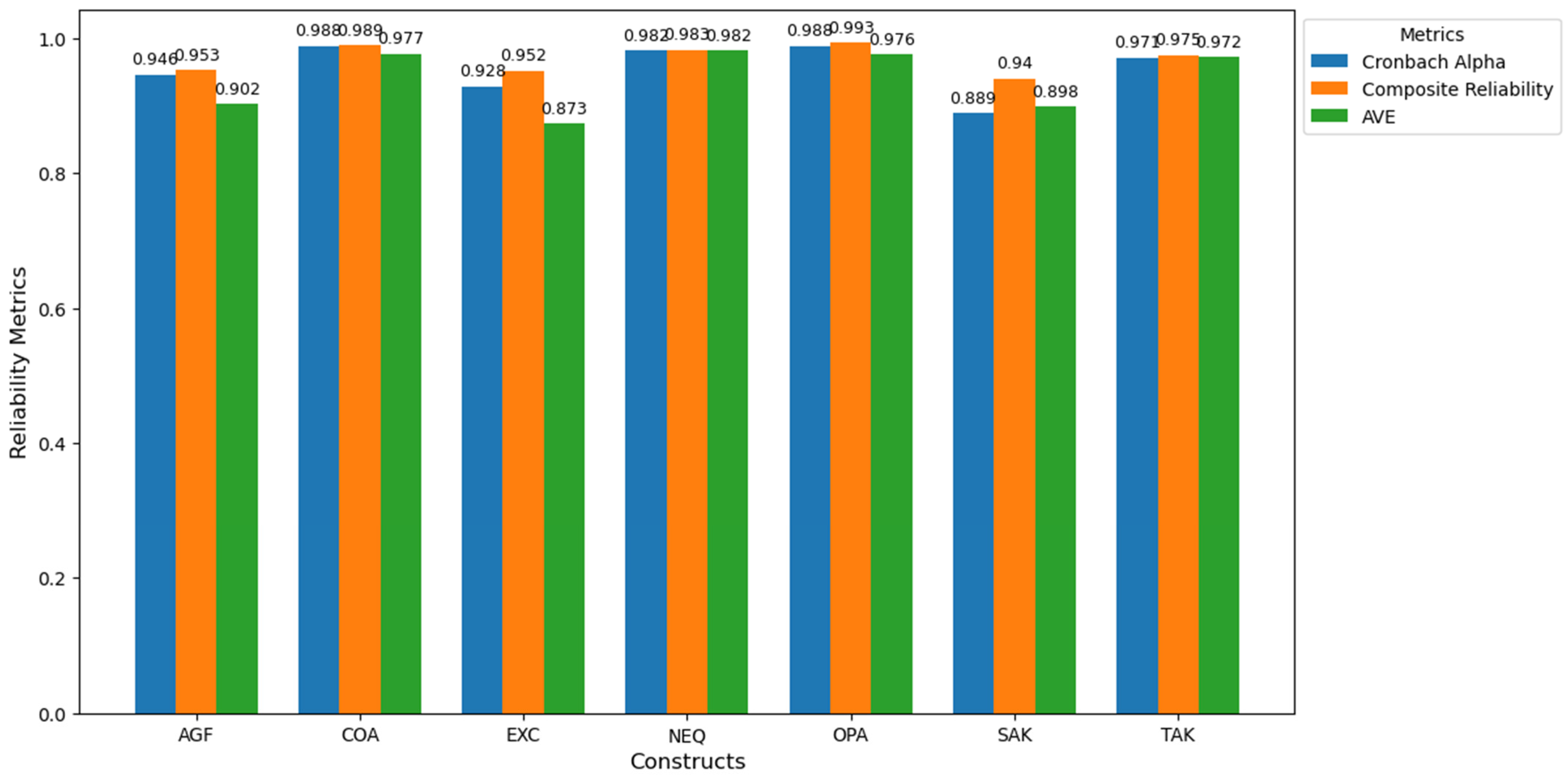
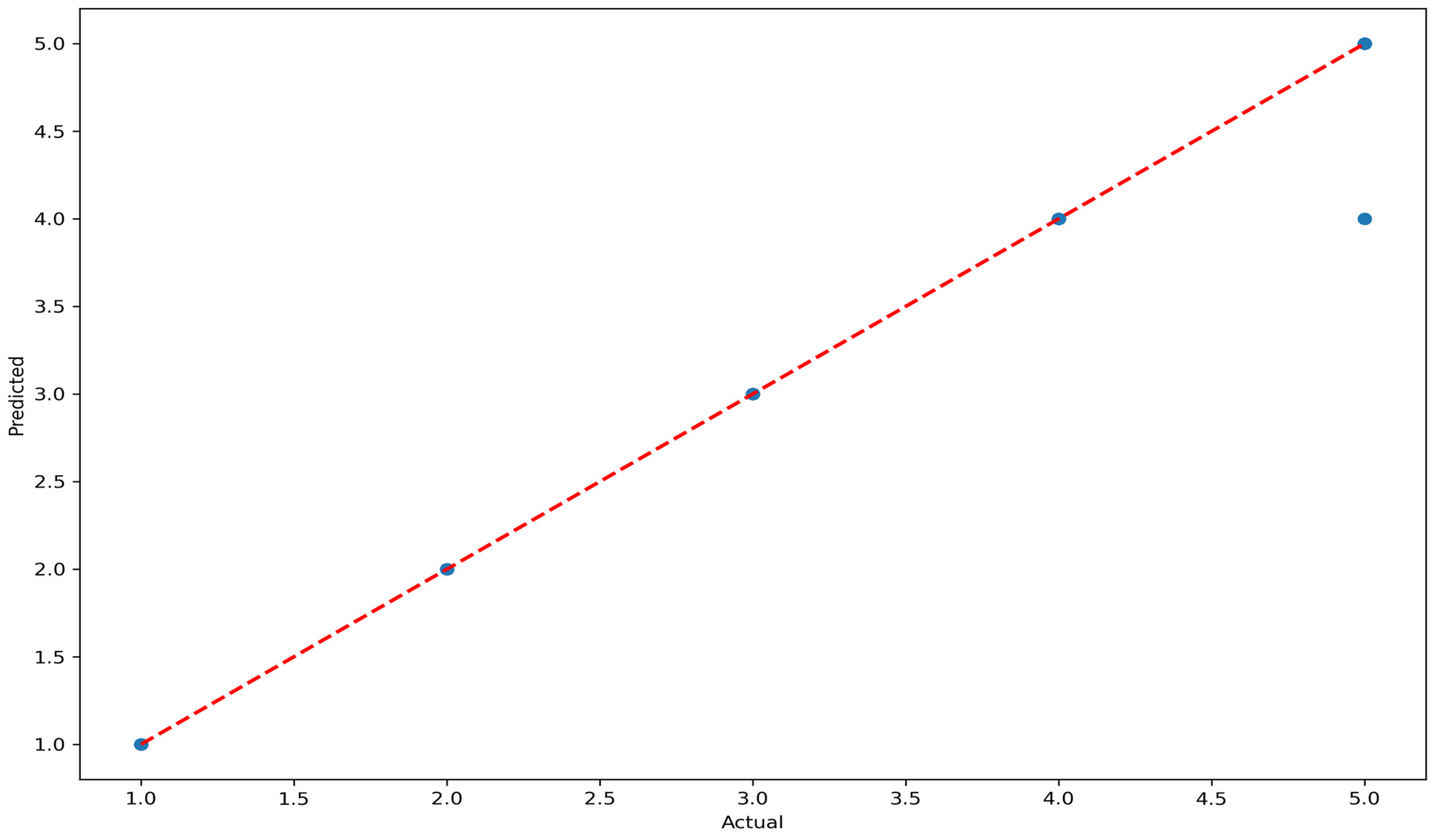

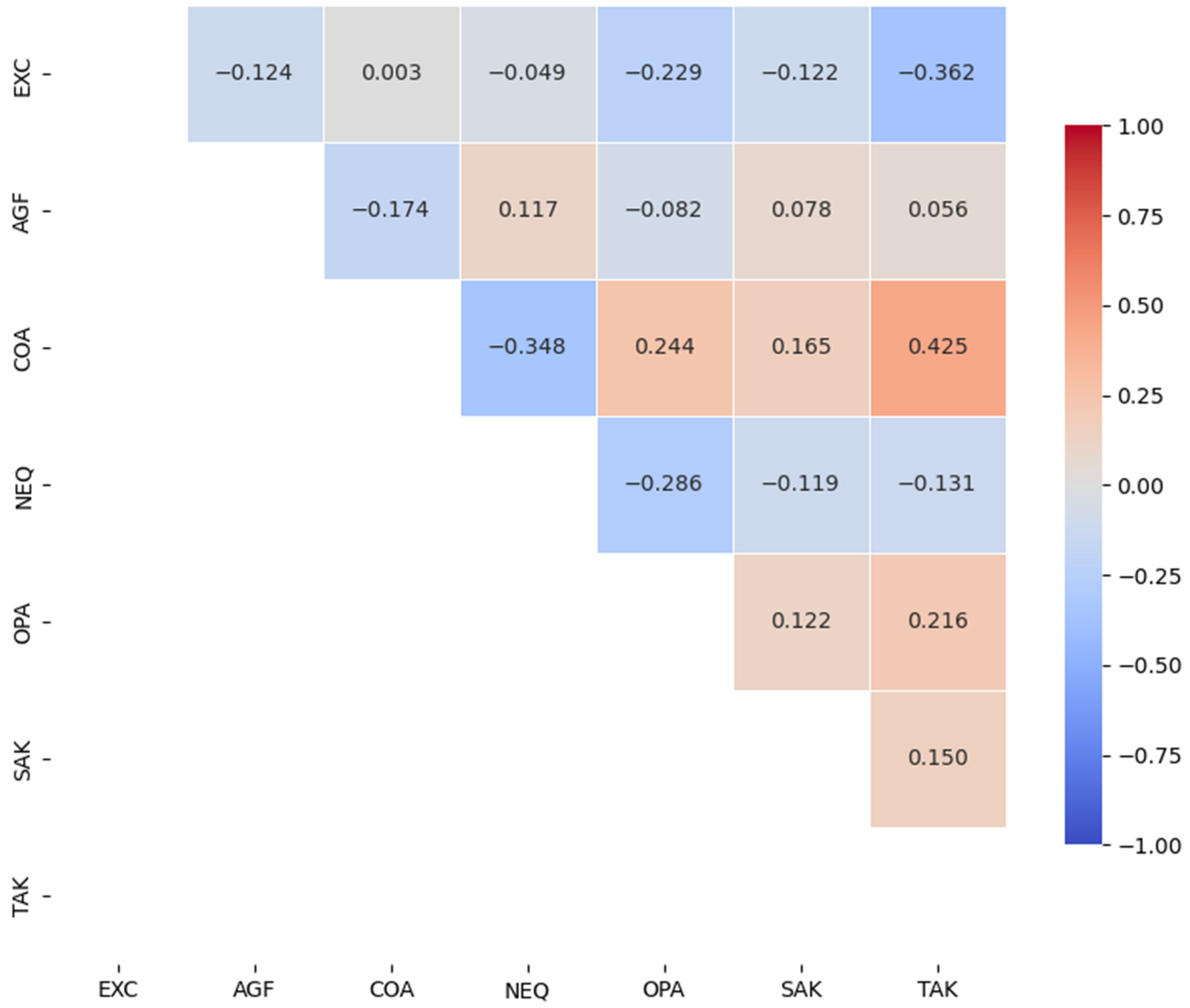
| Construct | Indicator | Mean | Std. Dev. | Loading |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extraversion Characteristics (EXC) | EXC1 | 1.69 | 0.701 | 0.963 * |
| EXC2 | 1.73 | 0.688 | 0.940 * | |
| EXC3 | 1.73 | 0.751 | 0.899 * | |
| Agreeableness Features (AGFs) | AGF1 | 1.91 | 0.733 | 0.931 * |
| AGF2 | 1.93 | 0.720 | 0.956 * | |
| AGF3 | 1.93 | 0.688 | 0.963 * | |
| Conscientiousness Attributes (COAs) | COA1 | 2.82 | 0.777 | 0.988 * |
| COA2 | 2.84 | 0.737 | 0.995 * | |
| COA3 | 2.80 | 0.815 | 0.983 * | |
| Neuroticism Factors (NEFs) | NEF1 | 1.82 | 0.806 | 0.991 * |
| NEF2 | 1.82 | 0.777 | 0.991 * | |
| Openness Aspects (OPAs) | OPA1 | 3.76 | 0.883 | 0.994 * |
| OPA2 | 3.76 | 0.933 | 0.986 * | |
| OPA3 | 3.80 | 0.894 | 0.984 * | |
| Self-Assessed Knowledge (SAK) | SAK1 | 2.84 | 1.021 | 0.962 * |
| SAK2 | 2.78 | 1.042 | 0.933 * | |
| Test-Assessed Knowledge (TAK) | TAK1 | 3.11 | 1.005 | 0.985 * |
| TAK2 | 3.13 | 0.991 | 0.987 * |
| Construct. | Cronbach’s Alpha | Composite Reliability | Average Variance Extracted (AVE) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Extraversion Characteristics (EXCs) | 0.928 | 0.952 | 0.873 |
| Agreeableness Features (AGFs) | 0.946 | 0.953 | 0.902 |
| Conscientiousness Attributes (COAs) | 0.988 | 0.989 | 0.977 |
| Neuroticism Factors (NEFs) | 0.982 | 0.983 | 0.982 |
| Openness Aspects (OPAs) | 0.988 | 0.993 | 0.976 |
| Self-Assessed Knowledge (SAK) | 0.889 | 0.940 | 0.898 |
| Test-Assessed Knowledge (TAK) | 0.971 | 0.975 | 0.972 |
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Nested Cross-Validation Score (Mean ) | 0.688 |
| Mean Squared Error (MSE) | 0.015 |
| R-squared () | 0.989 |
| Construct | EXC | AGF | COA | NEF | OPA | SAK | TAK |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXC | 0.934 | −0.124 | 0.003 | −0.049 | −0.229 | −0.122 | −0.362 |
| AGF | 0.950 | −0.174 | 0.117 | −0.082 | 0.078 | 0.056 | |
| COA | 0.988 | −0.348 | 0.244 | 0.165 | 0.425 | ||
| NEF | 0.991 | −0.286 | −0.119 | −0.131 | |||
| OPA | 0.988 | 0.122 | 0.216 | ||||
| SAK | 0.948 | 0.150 | |||||
| TAK | 0.986 |
| Criterion | Indicators | Path Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quality | EXC | 0.628 | 0.090 | |
| AGF | ||||
| COA | 0.118 | |||
| NEF | 0.075 | |||
| OPA | 0.168 | |||
| SAK | (ns) | 0.002 | ||
| TAK | 0.122 | |||
| Confidence | EXC | 0.333 | (ns) | 0.000 |
| AGF | 0.061 | |||
| COA | (ns) | 0.000 | ||
| NEF | 0.048 | |||
| OPA | 0.066 | |||
| SAK | (ns) | 0.001 | ||
| TAK | 0.100 |
| Hypotheses | Results | Hypotheses | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| (H1a) For QOD by EXC | ✔ | (H4b) For CID by NEF | ✘ |
| (H1b) For CID by EXC | ✘ | (H5a) For QOD by OPA | ✔ |
| (H2a) For QOD by AGF | ✔ | (H5b) For CID by OPA | ✘ |
| (H2b) For CID by AGF | ✘ | (H6a) For QOD by SAK | ✘ |
| (H3a) For QOD by COA | ✔ | (H6b) For QOD by TAK | ✔ |
| (H3b) For CID by COA | ✘ | (H7a) For CID by SAK | ✘ |
| (H4a) For QOD by NEF | ✔ | (H7b) For CID by TAK | ✔ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmad, M.; Wang, G. The Influence of Personality Traits and Domain Knowledge on the Quality of Decision-Making in Engineering Design. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020518
Ahmad M, Wang G. The Influence of Personality Traits and Domain Knowledge on the Quality of Decision-Making in Engineering Design. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(2):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020518
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmad, Muhammad, and Guoxin Wang. 2025. "The Influence of Personality Traits and Domain Knowledge on the Quality of Decision-Making in Engineering Design" Applied Sciences 15, no. 2: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020518
APA StyleAhmad, M., & Wang, G. (2025). The Influence of Personality Traits and Domain Knowledge on the Quality of Decision-Making in Engineering Design. Applied Sciences, 15(2), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15020518






