Identification of Rubber Belt Damages Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of the Speed
3.2. Statistical Analysis
- Arithmetic mean for each strain gauge was calculated from 20 repetitions;
- Minimum and maximum values were pointed out;
- Mean square values Xms were calculated for each strain gauge;
- Standard deviations σ were considered;
- Kurtosis Xkurt was discussed.
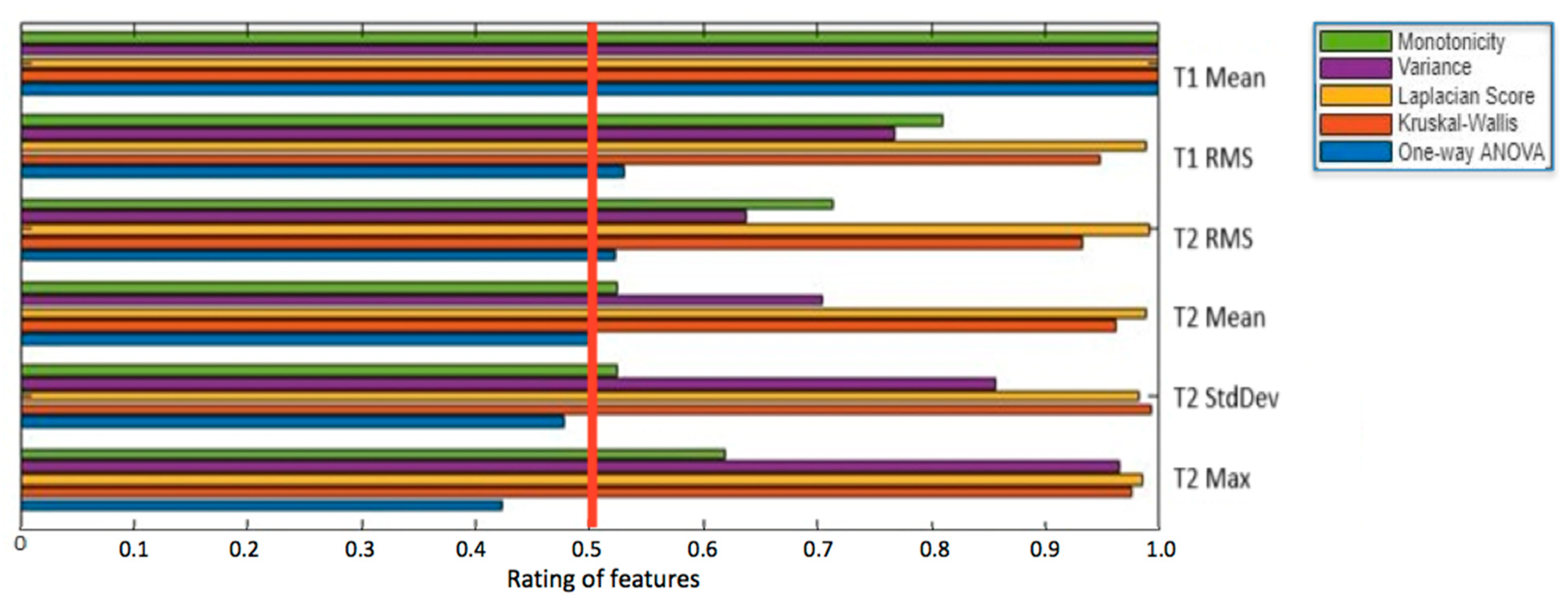
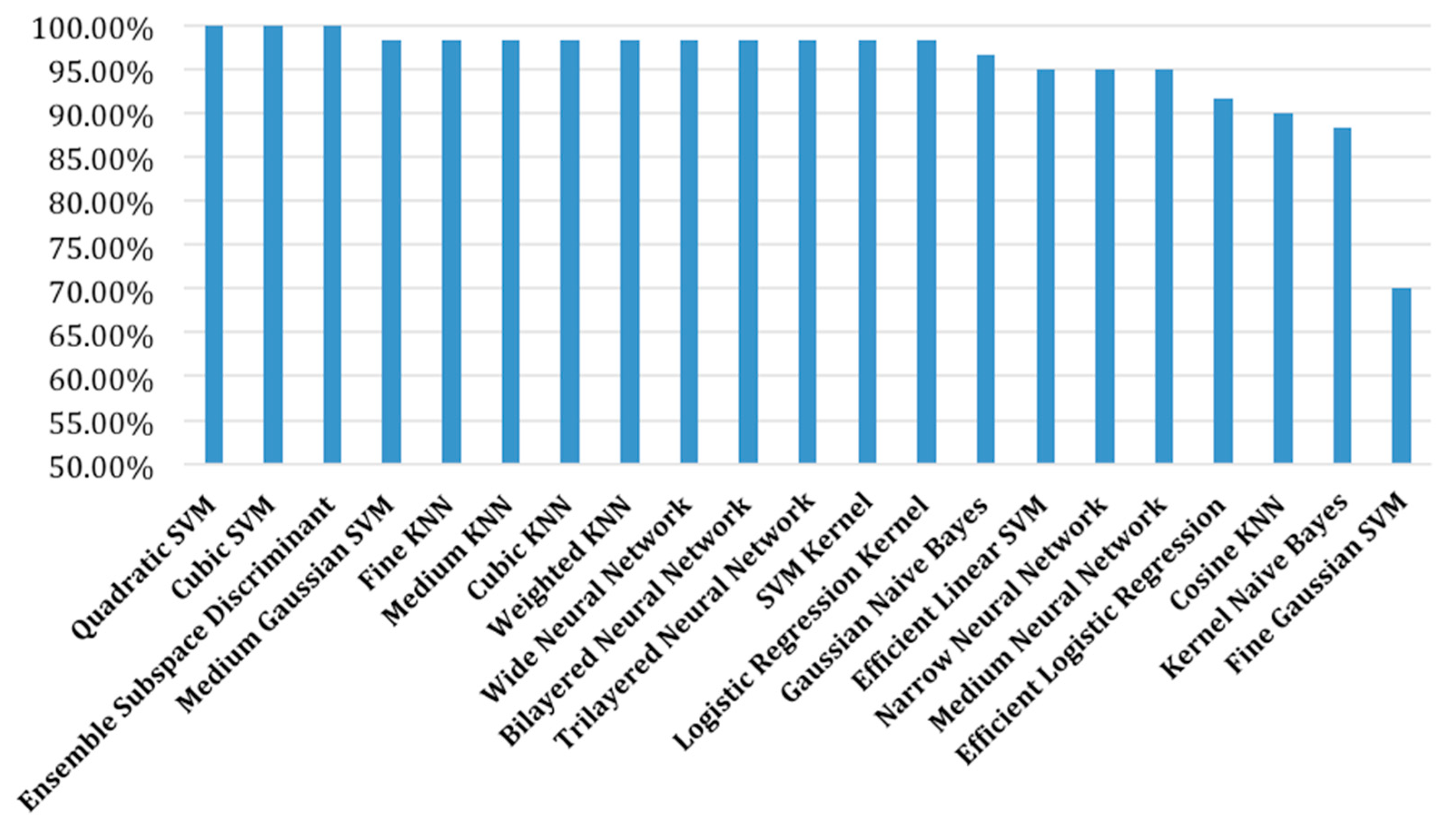
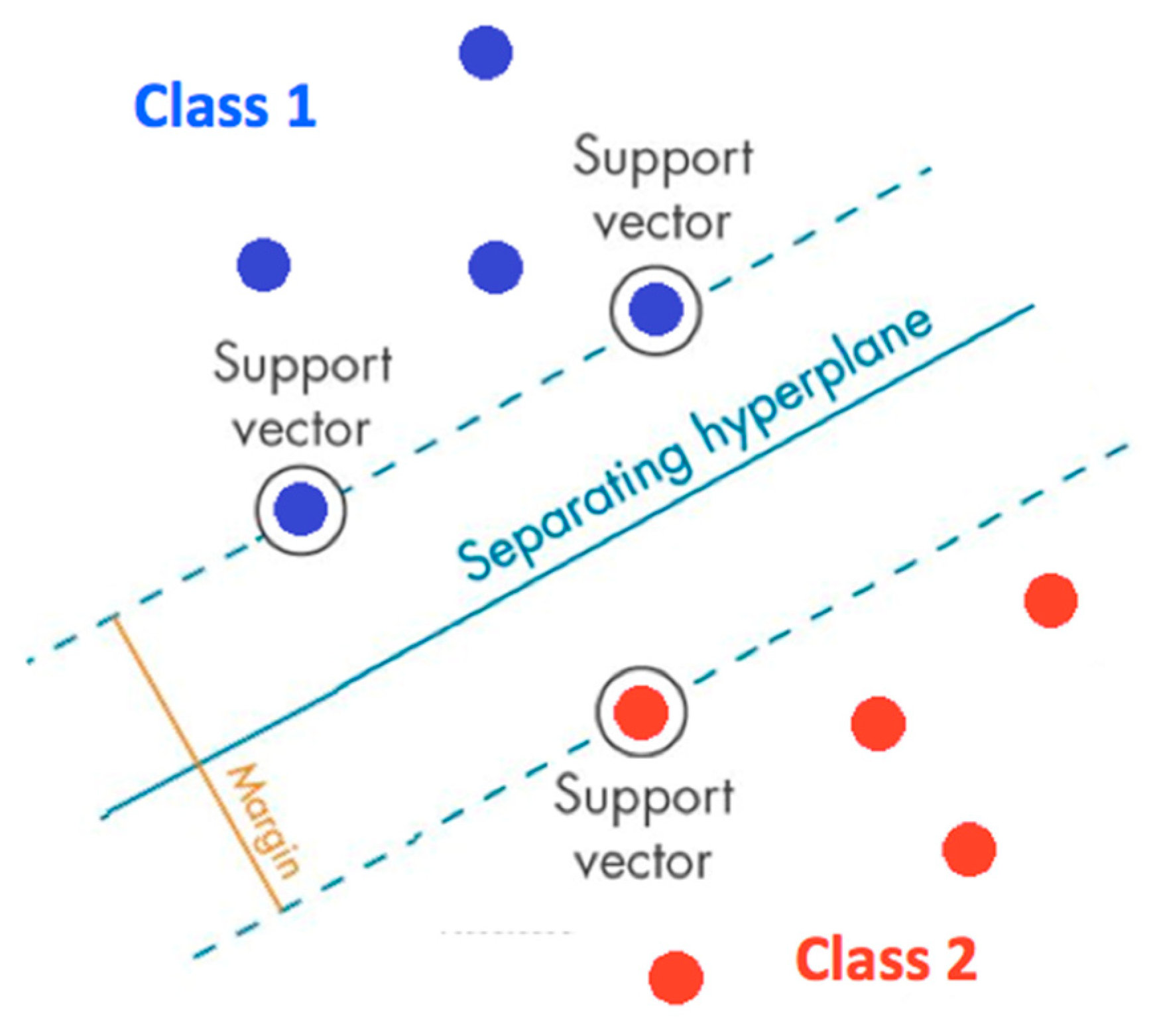
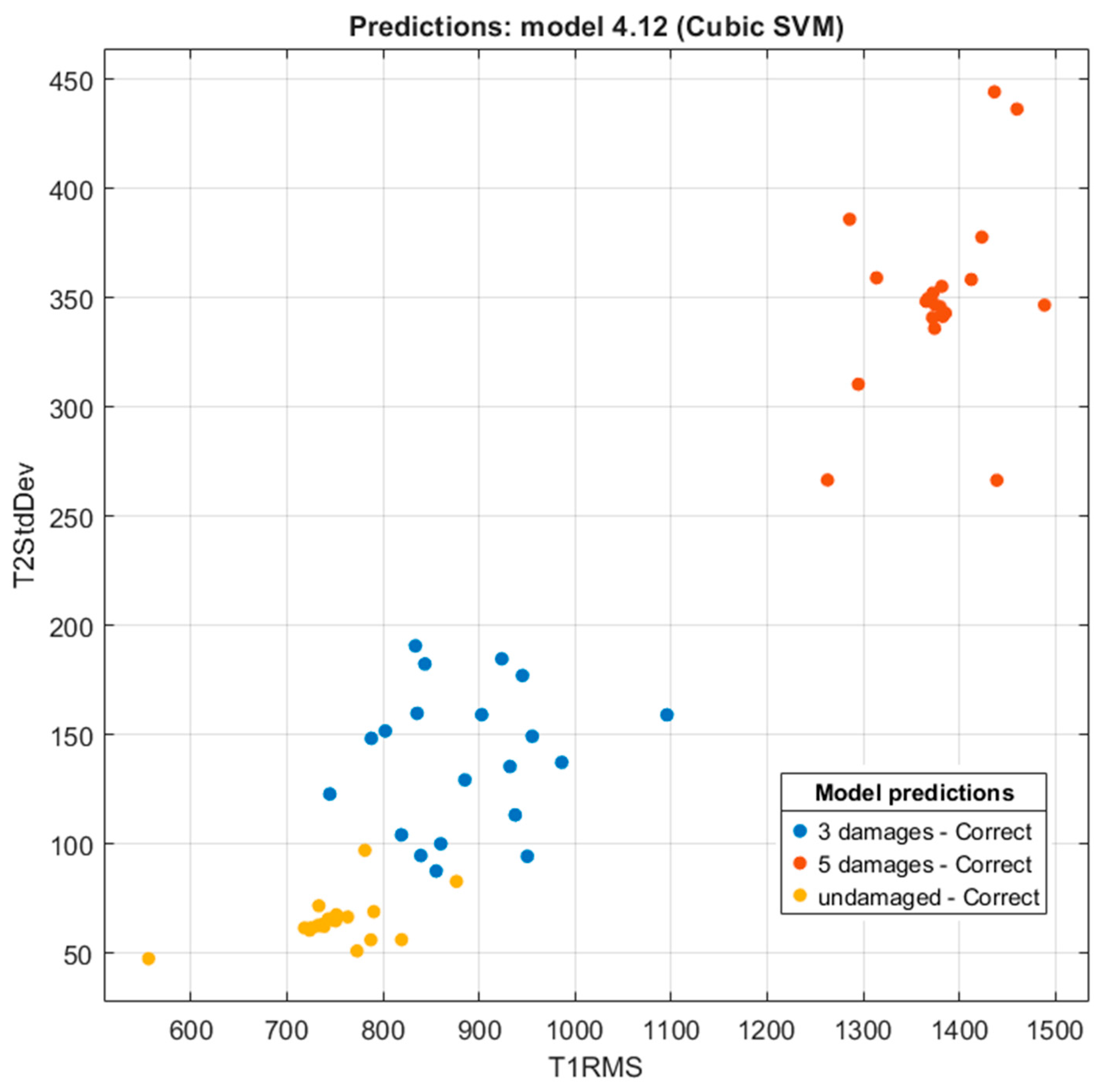
3.3. Tests of ML Algorithms
4. Conclusions
5. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mypati, O.; Mukherjee, A.; Mishra, D.; Pal, K.S.; Chakrabarti, P.P.; Pal, A. A critical review on applications of artificial intelligence in manufacturing. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 661–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortnowski, P.; Kawalec, W.; Król, R.; Ozdoba, M. Types and causes of damage to the conveyor belt—Review, classification and mutual relations. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2022, 140, 106520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowski, T.; Wodecki, J.; Zimroz, R.; Błażej, R.; Hardygóra, M. A Diagnostics of Conveyor Belt Splices. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuperl, U.; Stepien, K.; Munđar, G.; Kovačič, M. A Cloud-Based System for the Optical Monitoring of Tool Conditions during Milling through the Detection of Chip Surface Size and Identification of Cutting Force Trends. Processes 2022, 10, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Qiao, T.; Pang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Yan, G. Infrared spectrum analysis method for detection and early warning of longitudinal tear of mine conveyor belt. Measurement 2020, 165, 107856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hu, J.; Lin, K. Visual detection method based online lasers for the detection of longitudinal tears in conveyor belts. Measurement 2021, 183, 109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirjanów-Błażej, A.; Jurdziak, L.; Błażej, R.; Rzeszowska, A. Calibration procedure for ultrasonic sensors for precise thickness measurement. Measurement 2023, 214, 112744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmar, P.; Rzeszowska, A.; Burduk, A.; Jurdziak, L. Forecasting Conveyor Belt Performance in Future Using Pre-trained Models Based on Historical Failure Data. In Intelligent Systems in Production Engineering and Maintenance IV. ISPEM 2025. Lecture Notes in Mechanical Engineering; Burduk, A., Xavior, M.A., Machado, J., Butdee, S., Krot, K., Srikhumsuk, P., Lapczynska, D., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrejiova, M.; Grincova, A.; Marasova, D. Identification with machine learning techniques of a classification model for the degree of damage to rubber-textile conveyor belts with the aim to achieve sustainability. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2021, 127, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunckel, P.V.; Lobos, G.; Kristjanpoller, F.; Bustos, R.M.; Godoy, D. Methodology proposal for the development of failure prediction models applied to conveyor belts of mining material using machine learning. Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf. 2025, 256, 110709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, X.; Królczyk, G.; Sulowicz, M.; Glowacz, A.; Gardoni, P.; Li, Z. Damage Detection for Conveyor Belt Surface Based on Conditional Cycle Generative Adversarial Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorska, I.; Puchalski, A.; Bzinkowski, D. Localization of Conveyor Belt Damages Using a Deep Neural Network and a Hybrid Method for 1D Sequential Data Augmentation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 6784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, Y.; Gao, B.; Bai, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Zhou, L. Conveyor belt damage detection based on machine learning. J. Comput. Methods Sci. Eng. 2025, 25, 438–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rzeszowska, A.; Jurdziak, L.; Błażej, R. Feasibility Study of Neural Network-based Classification of Conveyor Belt Damage Using Partial DiagBelt Data. Civ. Environ. Eng. Rep. 2025, 35, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Tao, Q.; Wang, N.; Xiao, W.; Pan, C. YOLO-STOD: An industrial conveyor belt tear detection model based on Yolov5 algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Wang, G. Real-time conveyor belt damage detection method based on improved YOLO. Eng. Res. Express 2025, 7, 025513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhou, H.; Sun, K. Real-time damage detection network for mine conveyor belts based on knowledge distillation. Measurement 2025, 249, 116976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhou, M.; Hu, F.; Wen, Y. A framework integrating multispectral imaging and deep learning for accurate detection of conveyor belt surface damage. Measurement 2025, 256 (Part C), 118353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulcini, V.; Modoni, G. Machine learning-based digital twin of a conveyor belt for predictive maintenance. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 133, 6095–6110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujna, M.; Prístavka, M.; Lee, C.K.; Borusiewicz, A.; Samociuk, W.; Beloev, I.; Malaga-Toboła, U. Reducing the Probability of Failure in Manufacturing Equipment by Quantitative FTA Analysis. Agric. Eng. 2023, 27, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, B.; Zhao, X. Multi-objective predictive maintenance scheduling models integrating remaining useful life prediction and maintenance decisions. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2024, 197, 110581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzinkowski, D.; Rucki, M.; Chalko, L.; Kilikevicius, A.; Matijosius, J.; Cepova, L.; Ryba, T. Application of Machine Learning Algorithms in Real-Time Monitoring of Conveyor Belt Damage. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryba, T.; Rucki, M.; Siemiątkowski, Z. A Device for Strain Gauges Calibration. Polish Patent No. 245288, 21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Ryba, T.; Rucki, M.; Siemiątkowski, Z.; Bzinkowski, D.; Solecki, M. Design and calibration of the system supervising belt tension and wear in an industrial feeder. Facta Univ. Ser. Mech. Eng. 2022, 20, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzinkowski, D.; Ryba, T.; Siemiatkowski, Z.; Rucki, M. Real-time monitoring of the rubber belt tension in an industrial conveyor. Rep. Mech. Eng. 2022, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JCGM 100:2008; Evaluation of Measurement Data—Guide to the Expression of Uncertainty in Measurement. Bureau International des Poids et Mesures: Sèvres, France, 2008.
- Ryba, T.; Bzinkowski, D.; Siemiątkowski, Z.; Rucki, M.; Stawarz, S.; Caban, J.; Samociuk, W. Monitoring of Rubber Belt Material Performance and Damage. Materials 2024, 17, 765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Yue, Q.; Zhou, Q. Study on Visual Detection Method of Multi-scale Damage to Conveyor Belt Under Complex Background. J. Fail. Anal. Prev. 2024, 24, 896–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyerer, J.; Richter, M.; Nagel, M. Pattern Recognition: Introduction, Features, Classifiers and Principles; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, W.P.; Sturdivant, R.X. Probability and Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences with Modeling Using R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Nowakowski, M. The ANOVA method as a popular research tool. Stud. I Pr. WNEiZ 2019, 55, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Support Vector Machines for Binary Classification. Available online: https://uk.mathworks.com/help/stats/support-vector-machines-for-binary-classification.html (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Verma, R.N.; Deo, R.; Srivastava, R.; Subbarao, N.; Singh, G.P. A new fuzzy support vector machine with pinball loss. Discov Artif Intell 2023, 3, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhi, T.M.; Srinivasan, K. A Duo Autoencoder-SVM based Approach for Secure Performance Monitoring of Industrial Conveyor Belt System. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2023, 177, 108359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Liang, H. A multi-class support vector machine real-time detection system for surface damage of conveyor belts based on visual saliency. Measurement 2019, 146, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fu, S.; Liu, F.; Cheng, X. Intelligent fault diagnosis of belt conveyor rollers using a polar KNN algorithm with audio features. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 168, 109101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco-Loera, F.; Alcaraz-Mejia, M.; Chavez-Hurtado, J.L. An Interpretable Hybrid Fault Prediction Framework Using XGBoost and a Probabilistic Graphical Model for Predictive Maintenance: A Case Study in Textile Manufacturing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryba, T.; Bzinkowski, D.; Rucki, M. Method and device for supervision of the tension and wear of the conveyor rubber belts. Polish Patent Application No. P.447569, 22 January 2024. [Google Scholar]
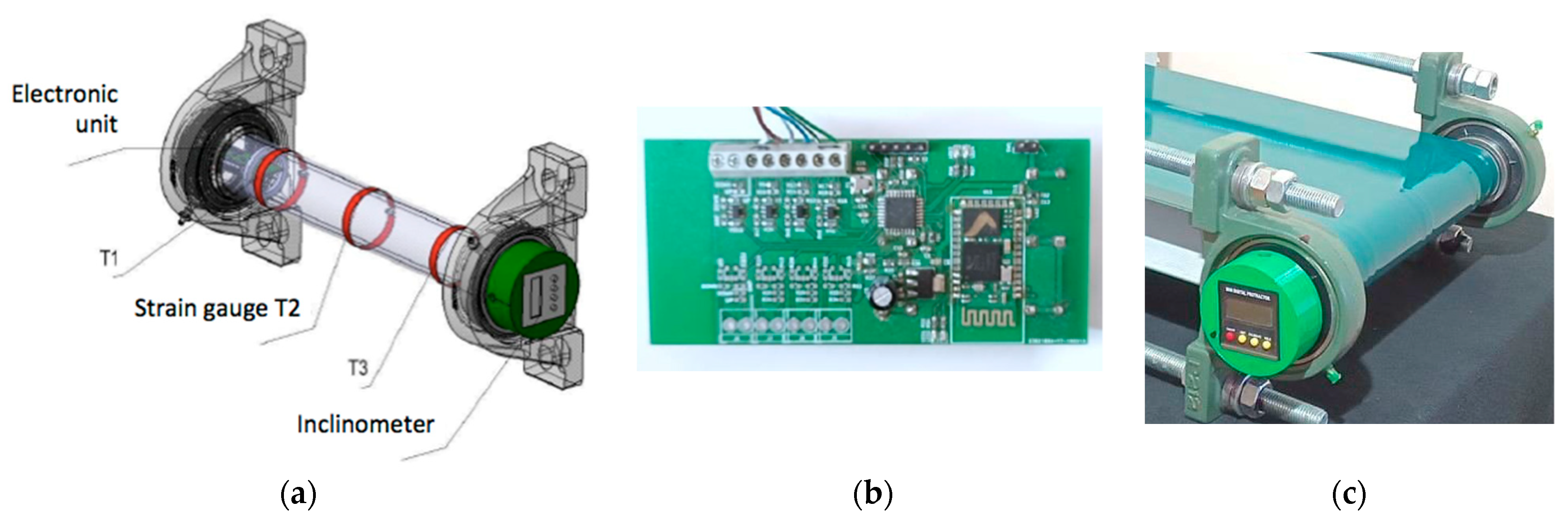

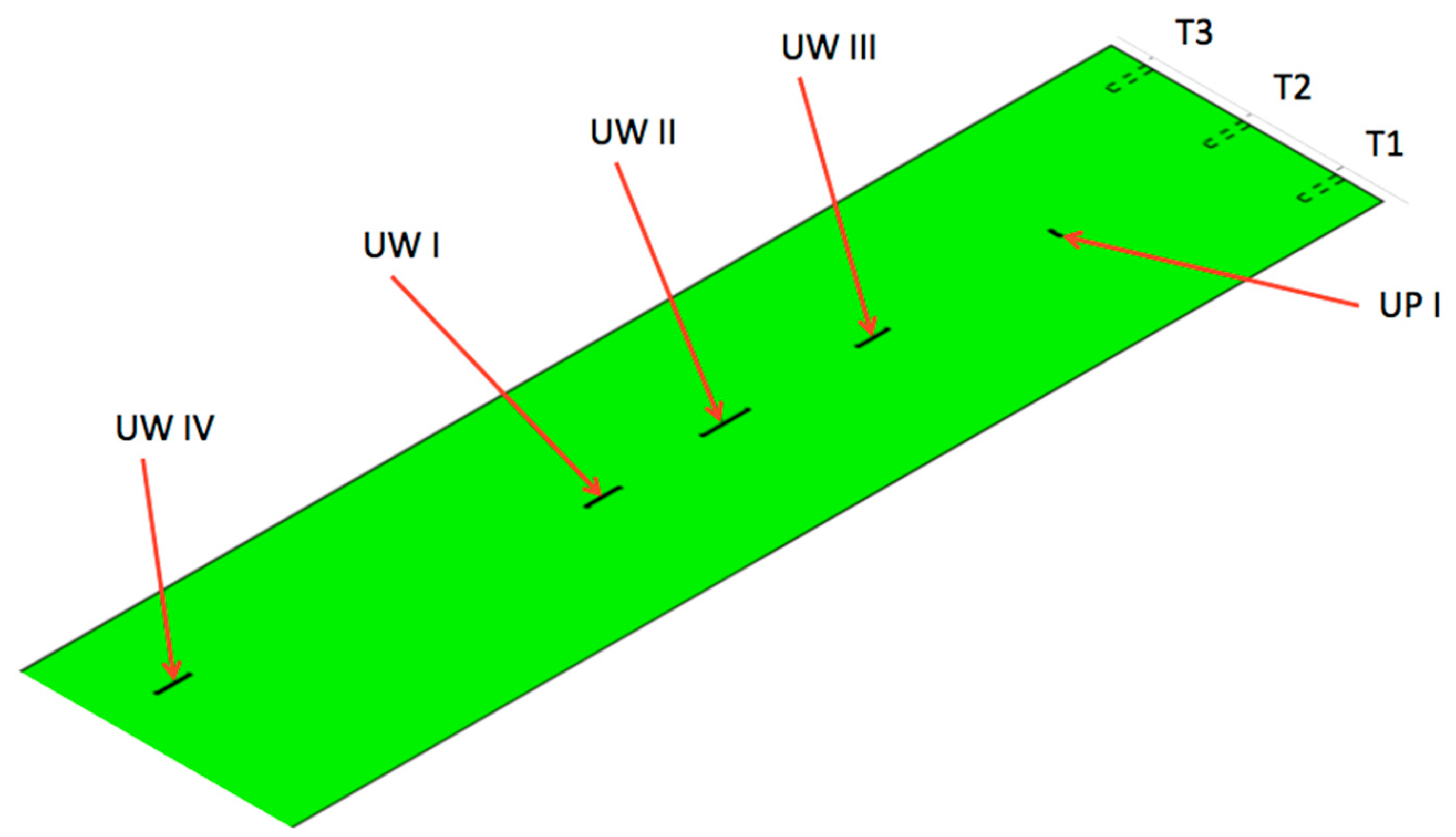
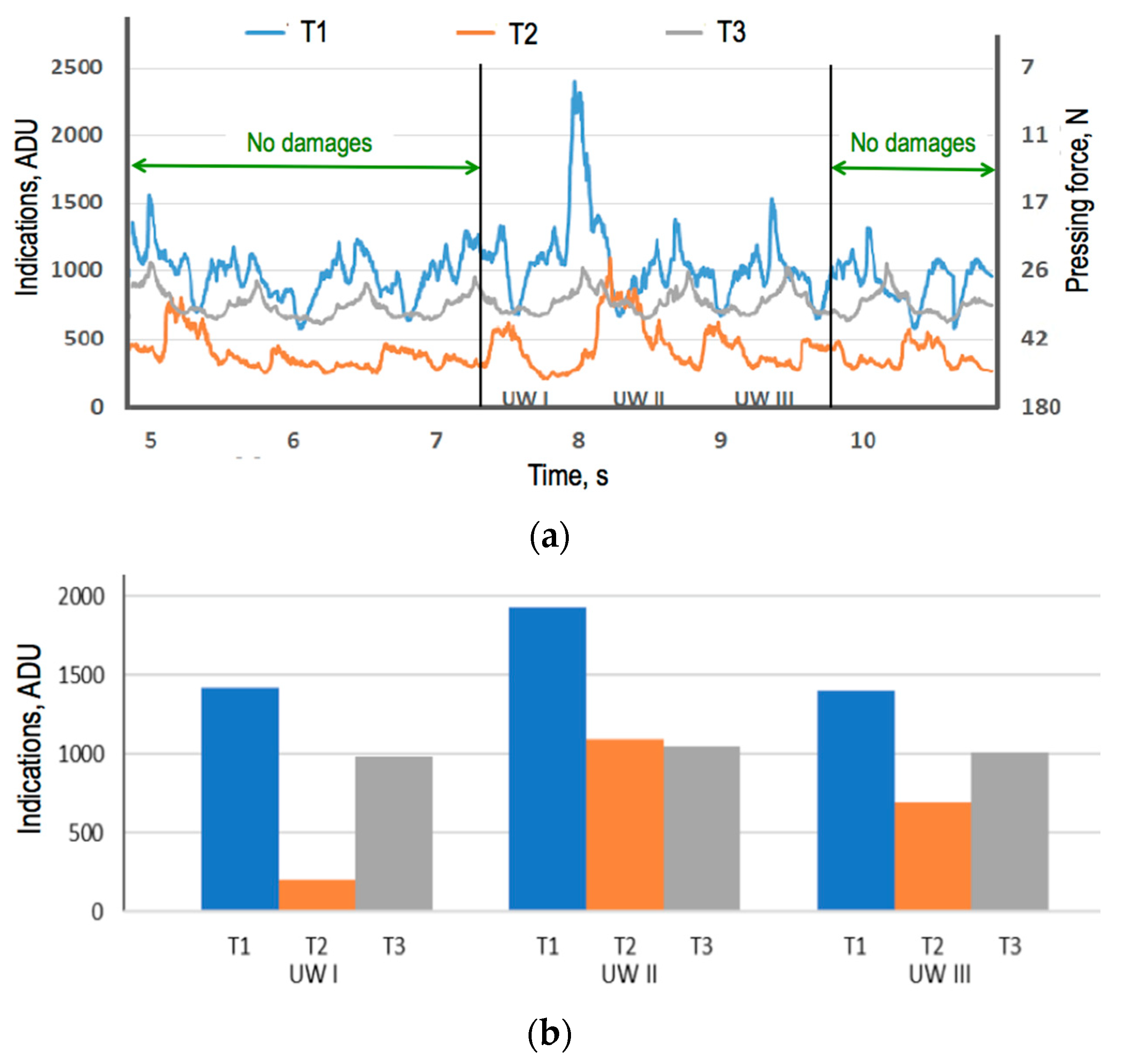
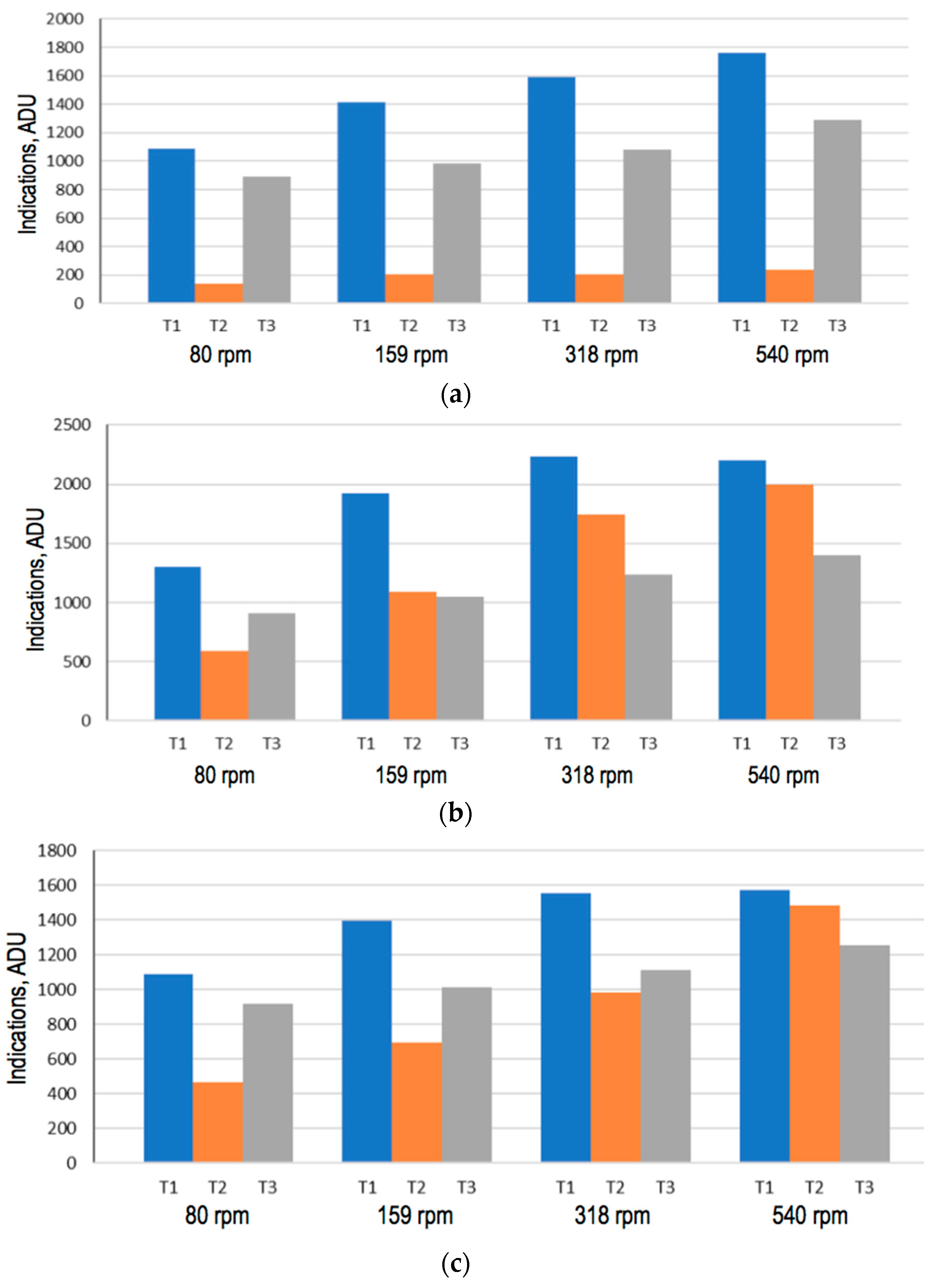

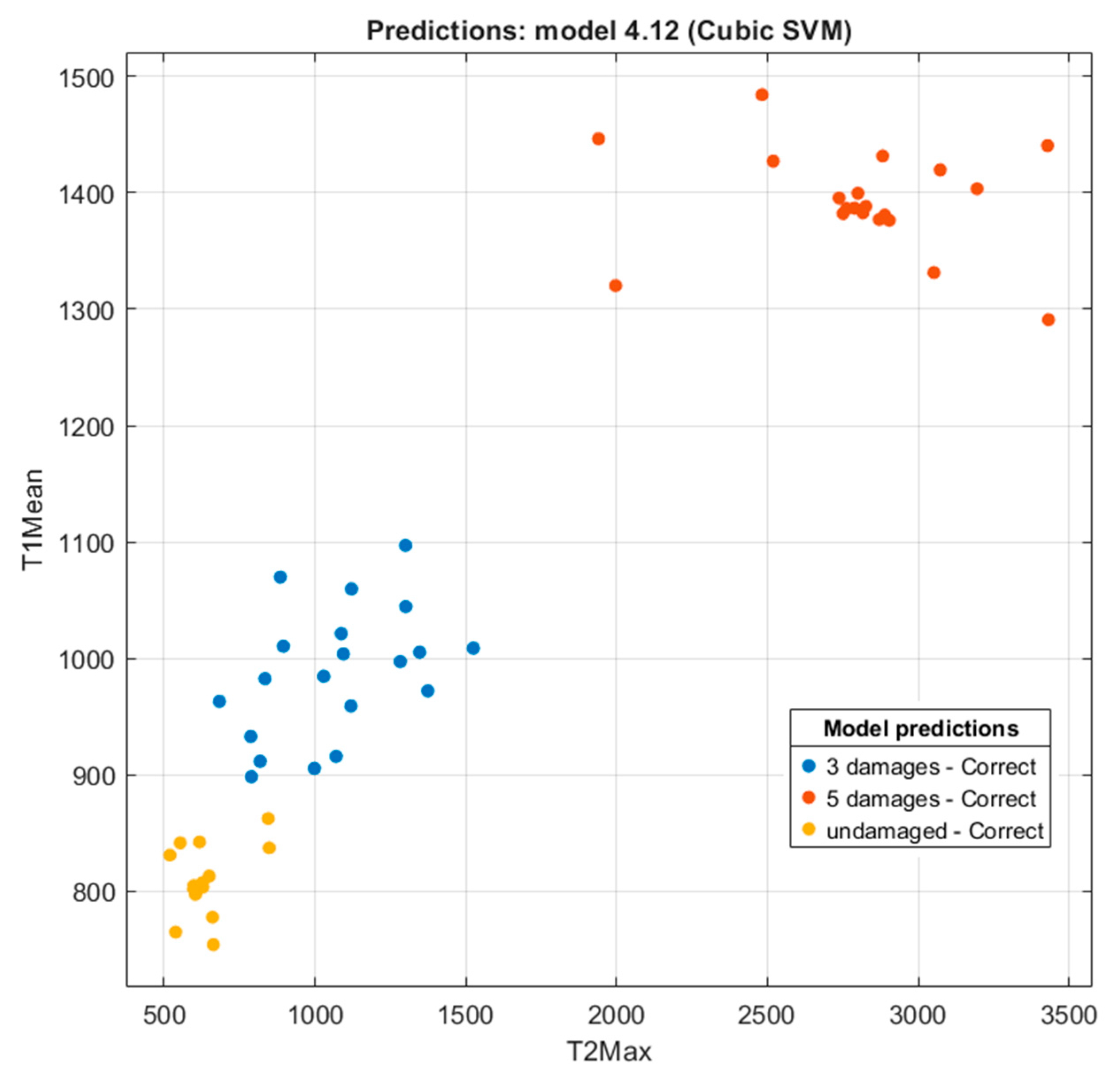
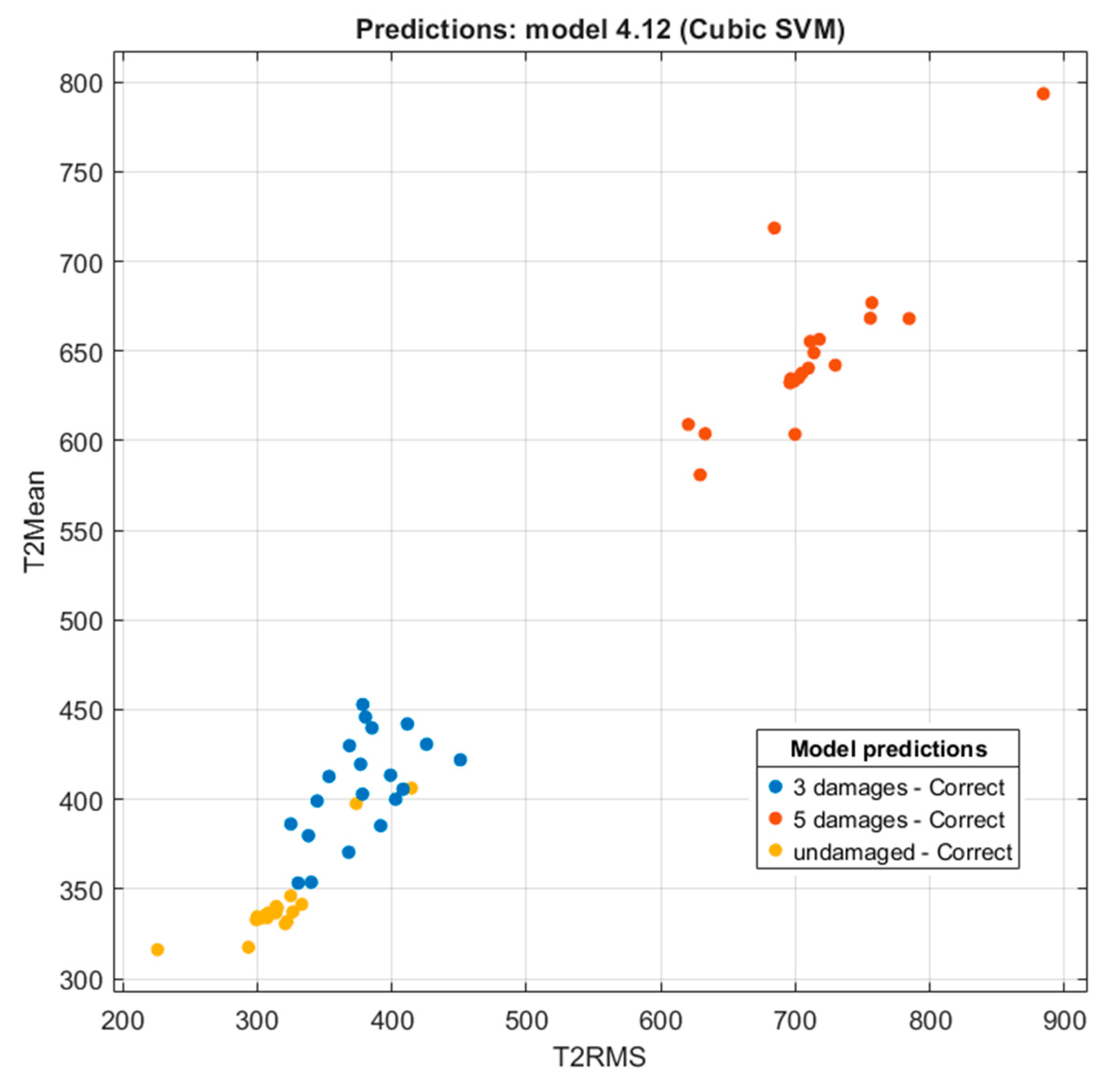
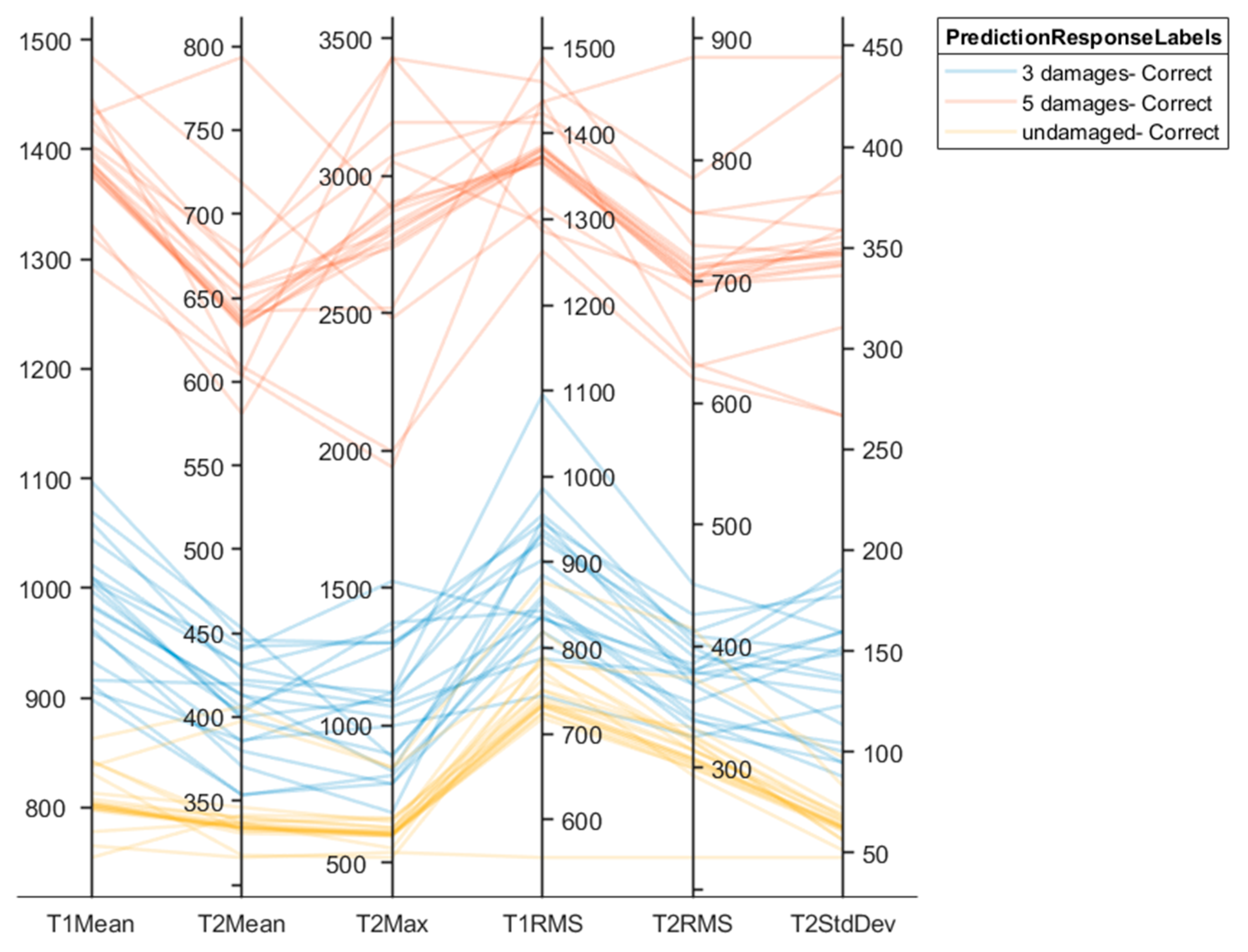
| No. | Pulley Rotational Speed n, rpm | Belt Linear Speed V, m/s |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 80 | 0.25 |
| 2 | 159 | 0.50 |
| 3 | 318 | 1.00 |
| 4 | 520 | 1.60 |
| Stage of Experiment | Damage Denotation | Direction | Length, mm | Depth | Position |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | UW I | Longitudinal | 50 | Crosscut | 170 mm from the belt edge |
| UW II | Longitudinal | 70 | Crosscut | 175 mm from the belt edge | |
| UW III | Longitudinal | 45 | 1.0 | 175 mm from the belt edge | |
| 2 | UW IV | Longitudinal | 50 | 1.5 | 115 mm from the belt edge |
| UP I | Transverse | 10 | Crosscut | 170–180 mm from the belt edge |
| Statistics | Strain Gauge | Belt with no Damage | Belt with 3 Damages | Belt with 5 Damages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | T1 | 807.4 | 987.4 | 1392.4 |
| T2 | 340.9 | 407.3 | 648.8 | |
| T3 | 729.8 | 767.3 | 862.7 | |
| Min | T1 | 473.0 | 485.0 | 664.0 |
| T2 | 209.0 | 144.0 | 198.0 | |
| T3 | 552.0 | 598.0 | 592.0 | |
| Max | T1 | 1511.0 | 2594.0 | 3398.0 |
| T2 | 848.0 | 1525.0 | 3432.0 | |
| T3 | 1147.0 | 1411.0 | 1603.0 | |
| Mean square Xms | T1 | 748.2 | 886.8 | 1378.7 |
| T2 | 315.7 | 378.0 | 711.8 | |
| T3 | 666.4 | 679.4 | 842.7 | |
| Std. dev. σ | T1 | 166.0 | 207.3 | 325.5 |
| T2 | 64.7 | 139.1 | 350.7 | |
| T3 | 100.2 | 95.8 | 141.1 | |
| Kurtosis Xkurt | T1 | –0.6 | 1.7 | 2.4 |
| T2 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 10.4 | |
| T3 | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.6 |
| Algorithm | Classification Accuracy | Number of Erroneously Classified Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Quadratic SVM | 100.00% | 0 |
| Cubic SVM | 100.00% | 0 |
| Ensemble Subspace Discriminant | 100.00% | 0 |
| Linear SVM | 98.33% | 1 |
| Medium Gaussian SVM | 98.33% | 1 |
| Fine KNN | 98.33% | 1 |
| Medium KNN | 98.33% | 1 |
| Cubic KNN | 98.33% | 1 |
| Weighted KNN | 98.33% | 1 |
| Wide Neural Network | 98.33% | 1 |
| Bilayered Neural Network | 98.33% | 1 |
| Trilayered Neural Network | 98.33% | 1 |
| SVM Kernel | 98.33% | 1 |
| Logistic Regression Kernel | 98.33% | 1 |
| Gaussian Naive Bayes | 96.67% | 2 |
| Efficient Linear SVM | 95.00% | 3 |
| Narrow Neural Network | 95.00% | 3 |
| Medium Neural Network | 95.00% | 3 |
| Efficient Logistic Regression | 91.67% | 5 |
| Cosine KNN | 90.00% | 6 |
| Kernel Naive Bayes | 88.33% | 7 |
| Fine Gaussian SVM | 70.00% | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rucki, M.; Kilikevicius, A.; Bzinkowski, D.; Ryba, T. Identification of Rubber Belt Damages Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10449. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910449
Rucki M, Kilikevicius A, Bzinkowski D, Ryba T. Identification of Rubber Belt Damages Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10449. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910449
Chicago/Turabian StyleRucki, Miroslaw, Arturas Kilikevicius, Damian Bzinkowski, and Tomasz Ryba. 2025. "Identification of Rubber Belt Damages Using Machine Learning Algorithms" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10449. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910449
APA StyleRucki, M., Kilikevicius, A., Bzinkowski, D., & Ryba, T. (2025). Identification of Rubber Belt Damages Using Machine Learning Algorithms. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10449. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910449








