Changes Induced in Seeds as a Result of Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment in Plasma Agriculture Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Bibliometric Evaluation of the Relationship Between Relevant Research Fields and Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment for Seeds
3. Non-Thermal Plasmas Used for the Treatment of Seeds
| NTP | Feed Gas | Treatment Time | Discharge Power/Power Density | Seed | Effects | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cold plasma | Nitrogen Helium Air Oxygen | 25 W | Mung bean |
| [48] | |
| LFGD | Air Air/oxygen | 60 W | Wheat |
| [49] | |
| RF plasma | Air | 120 s | 6.8–18 W | Pepper (Capsicum annuum, Roni-272) |
| [50] |
| FEDBD DBD | Helium Air | 15 min | Arabidopsis thaliana |
| [51] | |
| DBD | Air Argon | 3–81 min | Cotton |
| [33] | |
| RF low pressure | Nitrogen | 3–15 min | 10 W | Artichoke (Cynara cardunculus var. scolymus) |
| [52] |
| HV nano-second pulsed plasma | 1–5 shoots | Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) |
| [53] | ||
| q | Helium/air | 10–300 s | 30 W | Nasturtium (Tropaeolum majus) |
| [54] |
| DCSBD | Air | 30–300 s | 400 W 80 W/cm3 | Maize (Zea mays L. cv. Ronaldinio) |
| [13] |
| LPDBD | Ar/oxygen Ar/air | 90 s | 45 W | Wheat |
| [55] |
| FEDBD | Air | 15 min | Arabidopsis thaliana |
| [31] | |
| DBD | Air | 0.5–10 min | 2.5 W | Arabidopsis thaliana |
| [56] |
| Plasma jet | Argon | 1-10 min | Fenugreek |
| [57] | |
| DBD | Air | 30, 60, 180 s | Wheat |
| [58] | |
| Plasma jet | Air | 1–10 min | Tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) |
| [44] | |
| RF plasma | Argon | 1–15 min | Moringa oleifera |
| [59] | |
| AC corona | Air | Alfalfa |
| [60] | ||
| LPRF DBD Plasma jet | Argon Air Argon | 2 min 30–120 s 15 s/seed | 75, 100, 125, 150 W 75, 100, 125, 150 W 0.41, 0.51, 0.61, 0.72 W | Sunflower |
| [29] |
| DCSBD | Air Oxygen Nitrogen | 30–300 s | 400 W 80 W/cm3 | Pea (Pisum sativum L. cv. Prophet) |
| [61] |
| DBD | Air | 3-30 min | 3.05 W/cm2 | Radish |
| [30] |
| DBD | Argon | 10–60 s | 53.5 mW/cm3 | Wheat Barley |
| [32] |
| RF plasma | Argon | 1–20 min | Flax |
| [62] | |
| DBD | Argon Ar/oxygen | 10 min | Dehisced ginseng (Panax ginseng) |
| [8] | |
| RF plasma Afterglow | Oxygen | 5–30 s | 200, 600 W | Wheat (Triticum aestivum L. Apache and Bezostaya 1) |
| [63] |
| RF low pressure | Oxygen | 0.3–120 s | 50, 300 W | Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) |
| [64] |
| LPDBD | Argon/air | 3 min | Maize |
| [65] | |
| RF plasma | Argon | 3–4 min | Rice |
| [18] | |
| Plasma jet | Argon | 1–15 min | 1.2 W | Mung bean |
| [28] |
| DBD | Argon Nitrogen Oxygen Carbon dioxide | 1–5 min | 83.28 W upper electrode 5.28, 9.12, 12.86 W lower electrode | Beetroot (Beta vulgaris) |
| [38] |
| DBD | Air | 1–15 min | 5.3 W | Barley (Hordeum vulgare L. var. planet) |
| [40] |
| SCP DBD | Argon/air | 30–120 s | Rice (Oryza sativa var. Indica cv. KDML105) |
| [45] | |
| RF plasma | Air | 180 s | 50 W | Wheat |
| [17] |
| LFGD | Argon/air | 30–120 s | Maize (Zea mays L.) |
| [66] | |
| RF low pressure | Oxygen/water | 60 s | 10, 80 W | Bambara |
| [67] |
| Plasma jet | Argon | 30 s–30 min | Basil |
| [26] | |
| Plasma jet | Argon | 5–120 s | Spring wheat |
| [27] | |
| DCSBD Plasma jet | Air | 15–45 s | 400 W 30 W | Soybean |
| [34] |
| DBD Gliding arc (afterglow) | Air | 20 min | 1.06 W 4.23 W | Rice |
| [35] |
| DBD | Air | 2–15 min | 5–5.4 W | Melon |
| [36] |
| Cold plasma | 4 min | 100 W | S. leriifolia |
| [68] | |
| DBD | Air | 30–120 s | Brassica oleracea Lepidum sativum |
| [3] | |
| LPDBD | Air | 2–8 min | 10 W | Eggplant (Solanum melangena L.) |
| [69] |
| jet kINPen 11 | Argon | 10–20 s | Fenugreek |
| [70] | |
| DBD | Air | 20–100 s | Mung bean |
| [37] | |
| DBD | Air | 30–120 s | Alfalfa |
| [39] | |
| DBD | Air | 30–120 s | Fenugreek |
| [2] | |
| DBD | Argon | 30–420 s | 100 W | Iranian soybean cultivars |
| [41] |
| DCSBD | Nitrogen Air Oxygen | 30–120 s | 400 W | Soybean (Glycine max L.) |
| [71] |
| Cold plasma | Helium Oxygen Argon | 30–150 s | 100–500 W | Peanut |
| [72] |
| DBD | Ar | 60, 120 s | 80 W | Momordica charantia L. |
| [73] |
| RF plasma | Air | 15–90 min | 50 W | Maize Wheat Barley psyllium |
| [74] |
| RF plasma | He/air | 15 s | Rapeseed Brassica napus L. |
| [75] | |
| RF plasma | Air | 1–3 min | 0–100 W | Cowpea |
| [76] |
| DBD | Air | 6–10 min | Prosopis koelziana |
| [42] | |
| SCP DBD | Air Ar/air | 5–15 min | Chinese kale (Brasica oleracea var. alboglabra) |
| [11] |
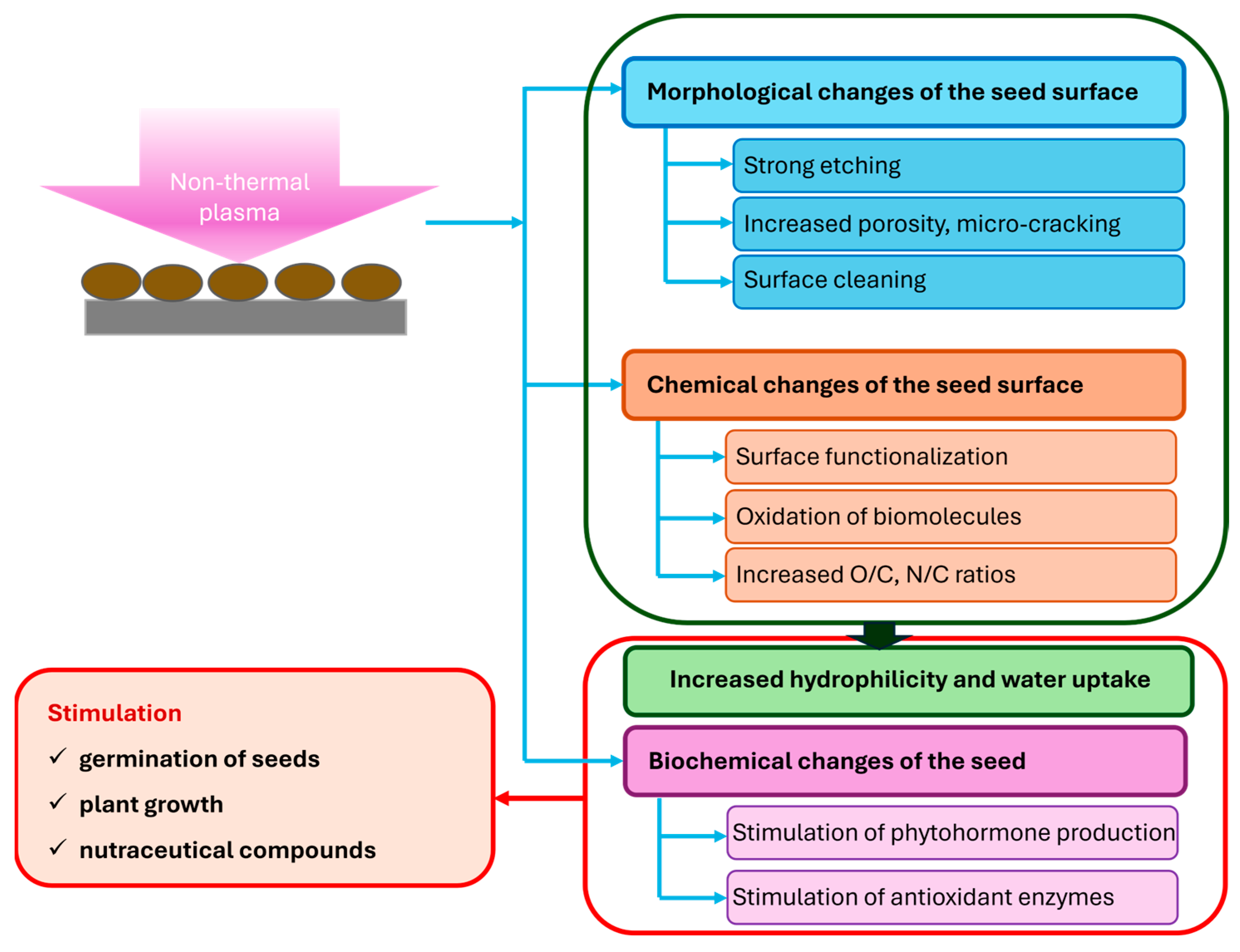
4. Modification of Seed Surfaces as a Result of NTP Treatment
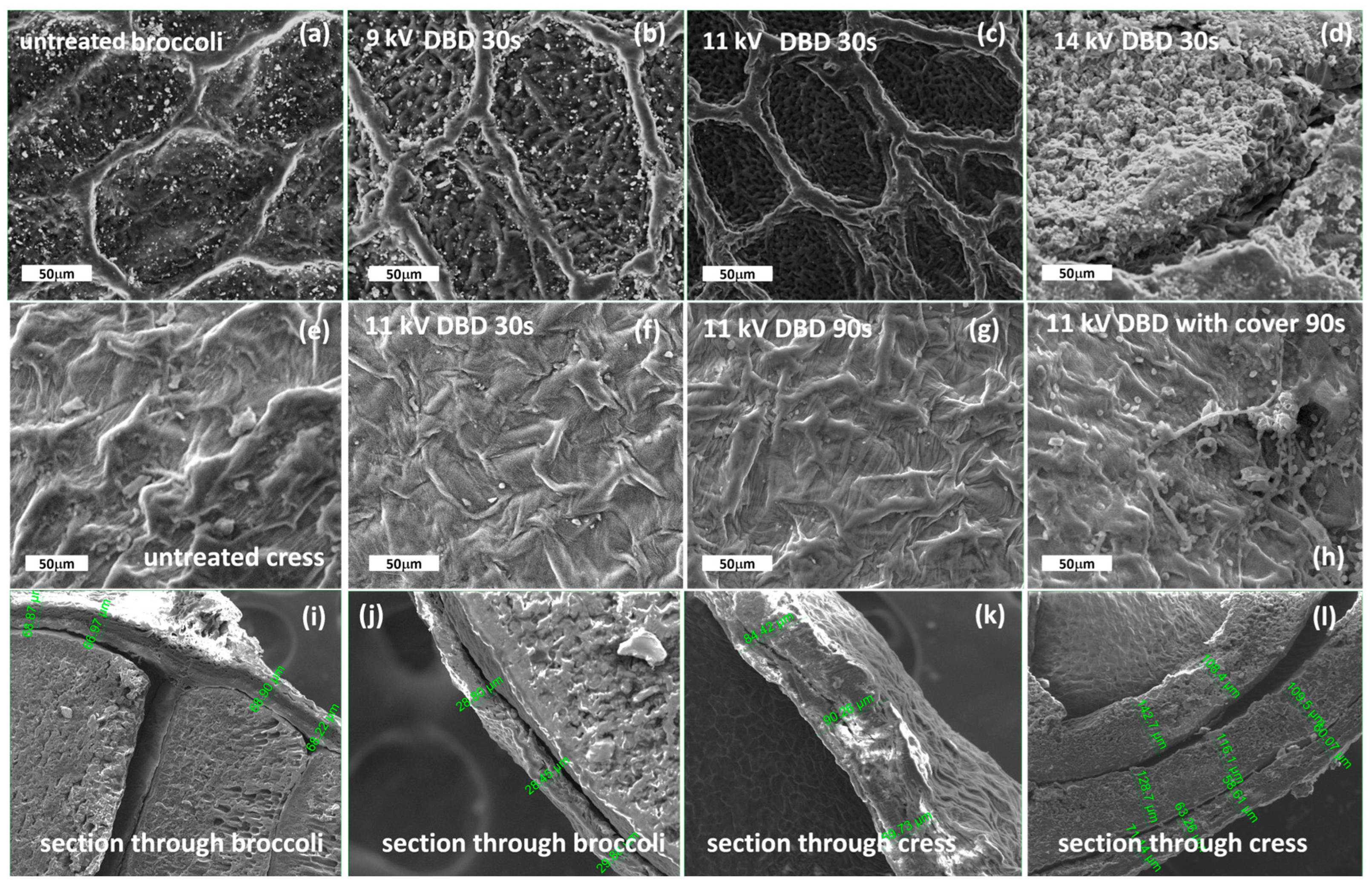
4.1. Morphological Changes Evidenced Using Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.2. Water Contact Angle of Seed Surfaces
4.3. Electrical Conductivity
4.4. Monitoring of Seed Chemistry
4.5. Modifications of Surface Chemistry Induced by NTP
4.6. Surface Decontamination of Seeds
- ➢
- Etching: Plasma removes contaminant layers through oxidative processes, breaking down organic and inorganic substances from the seed surface.
- ➢
- UV Sterilisation: UV radian emitted by the plasma destroys the genetic material of microorganisms, reducing the microbial load.
- ➢
- Introduction of Functional Groups: Plasma modifies the surface energy of seeds, creating hydrophilic groups (e.g., -OH, -COOH) that can reduce the adhesion of contaminants.
- ➢
- Chemical Remediation: Plasma can break down residual pesticides or fungicides on the seed surface, transforming them into less toxic compounds.
5. Physiological and Biochemical Changes in Seeds After NTP Treatment
5.1. Stimulation of Germination
5.2. Increase in Antioxidant Levels
5.3. NTP Treatment of Seeds and Growth Hormones
5.4. Activation of Enzymatic Metabolism
5.5. Impact on DNA: Damage or Adaptations
6. Challenges and Future Directions
- ➢
- Lack of parameter standardisation—a wide variety of plasma devices and configurations (DBD, plasma jet, corona discharge, etc.), each with specific parameters (voltage, frequency, exposure time, working gas). This makes it difficult to compare results and the reproducibility of treatments.
- ➢
- Irreproducible effects—due to the complexity of the interaction between plasma and the seed surface, the results can vary significantly depending on the plant species, variety, initial seed condition, and environmental conditions.
- ➢
- Lack of understanding of molecular mechanisms—although it is known that reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) play a key role, the exact mechanisms by which plasma influences gene expression, hormonal signalling, and secondary metabolism remain unclear.
- ➢
- Potential risk of phytotoxicity—prolonged treatments or those with non-optimised parameters can induce excessive oxidative stress, affecting seed viability and plant development.
- ➢
- Industrial scalability—large-scale application is still a challenge due to equipment costs, the need for real-time monitoring, and the lack of standardised protocols for different crops.
- ➢
- Lack of long-term studies—the effects of plasma treatment on future generations of plants and on the ecosystem are not sufficiently studied.Therefore, successfully integrating NTP treatments into agricultural practices requires an interdisciplinary framework, thus the need for collaboration between various scientific and technical fields to optimise each element in the operational chain. It is very important to correlate plasma parameters with the biological responses of the seeds to understand, optimise, and control the mechanisms of interactions. Such a framework would also allow the identification of critical thresholds from the perspective of the synergistic impact of plasma components on plant performance.
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NTP | Non-thermal plasma |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| DBD | Dielectric barrier discharge |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| DNA | Deoxyribonucleic acid |
| RF | radiofrequency |
| FEDBD | Floating electrode dielectric barrier discharge |
| HV | High voltage |
| DCSBD | Diffuse coplanar surface barrier discharge |
| LPRF | Low pressure radiofrequency |
| FTIR | Fourier transform infrared |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| LPDBD | Low pressure dielectric barrier discharge |
| SCP | Streamer corona plasma |
| RONS | Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RNS | Reactive nitrogen species |
| APPJ | Atmospheric pressure plasma jet |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy |
| WCA | Water contact angle |
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| POD | peroxidase |
| GA | Gibberellic acid |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| PAL | Phenylalanine ammonia-lyase |
| G-POX | Guaiacol peroxidase |
References
- Biruntha, M.; Menaka, C.; Yuvaraja, A.; Vanitha, C.; Ramjegathesh, R. Advancing seed quality through cold plasma technology: A sustainable approach for agricultural enhancement. Plant Sci. Today 2025, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motrescu, I.; Lungoci, C.; Ciolan, M.A.; Jitareanu, G. Non-thermal plasma (NTP) treatment of Trigonella foenum-graecum L. seeds stimulates the sprout growth and the production of nutraceutical compounds. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motrescu, I.; Ciolan, M.A.; Calistru, A.E.; Jitareanu, G. Germination and Growth Improvement of Some Micro-Greens under the Influence of Reactive Species Produced in a Non-Thermal Plasma (NTP). Agronomy 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerana, M.; Ketya, W.; Choi, E.H.; Park, G. Non-thermal plasma enhances growth and salinity tolerance of bok choy (Brassica rapa subsp. chinensis) in hydroponic culture. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1445791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Pangomm, K.; Veerana, M.; Mitra, S. Plant disease control by non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.A.N.; Rodrigues, S. Cold plasma technology for sustainable food production: Meeting the United Nations sustainable development goals. Sustain. Food Technol. 2025, 3, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppanova, L.; Medvecka, V.; Dylikova, J.; Hudecova, D.; Kalinakova, B.; Krystofova, S.; Zahoranova, A. Low-temperature plasma applications in chemical fungicide treatment reduction. Acta Chim. Slovaca 2020, 13, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, Y.Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Balaraju, K.; Mok, Y.S.; Yoo, S.J.; Jeon, Y. Enhancement of seed germination and microbial disinfection on ginseng by cold plasma treatment. J. Ginseng Res. 2021, 45, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.D.; Siliveru, K.; Zheng, Y. Emerging applications of cold plasma technology in cereal grains and products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 141, 104177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, F.; Bao, Y.; Ahmed, Z.; Huang, J.Y. Effect of high voltage atmospheric cold plasma on extraction of fenugreek galactomannan and its physicochemical properties. Food Res. Int. 2020, 138, 109776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannarat, S.; Homkanchan, S.; Puttha, J.; Srisonphan, S. Nonthermal plasma engineering for seed disinfection and germination using streamer corona and dielectric barrier discharges. Res. Eng. 2025, 26, 104884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerana, M.; Mumtaz, S.; Rana, J.N.; Javed, R.; Panngom, K.; Ahmed, B.; Akter, K.; Choi, E.H. Recent Advances in Non-Thermal Plasma for Seed Germination, Plant Growth, and Secondary Metabolite Synthesis: A Promising Frontier for Sustainable Agriculture. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2024, 44, 2263–2302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoranova, A.; Hoppanova, L.; Simoncicova, J.; Tucekova, Z.; Medvecka, V.; Hudecova, D.; Kalinakova, B.; Kovacik, D.; Cernak, M. Effect of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Maize Seeds: Enhancement of Seedlings Growth and Surface Microorganisms Inactivation. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2018, 38, 969–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavicek, P.; Stepanova, V.; Fleischer, M.; Kelar, J.; Tucekova, Z.K.; Jurmanova, J.; Pazderka, M.; Prasil, V.; Prasil, J. The Multi-Hollow Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge Usage for the Seeds’ Treatment Aimed to the Dustiness Decrease of Free-Floating Particles from Agrochemicals. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 1887–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šerá, B.; Scholtz, V.; Jirešová, J.; Khun, J.; Julák, J.; Šerý, M. Effects of Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment on Seed Germination and Early Growth of Leguminous Plants—A Review. Plants 2021, 10, 1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeysingha, D.N.; Dinesh, S.; Kottage, S.M.; Chen, L.; Roopesh, M.S.; Thilakarantha, M.S. Effects of cold plasma seed treatment on pea (Pisum sativum L.) plant performance under drought and well-watered conditions. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0322108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, M.; Ghomi, H.; Andreasen, C. Eco-friendly approach to improve traits of winter wheat by combining cold plasma treatments and carbonization of subtropical biomass waste. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 11218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, T.; Salim, M.; Afsheen, S.; Abrar, M.; Naseer, H.; Qureshi, M.T.; Hameed, R.S.A.; Mohamed, D.; Al Elaimi, M.; Soliman, M.S. Comparison of critical factor affecting the germination or rice seeds treated by LASER and plasma. Radiat. Eff. Defect. Sol. 2022, 177, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelar, A.; Singh, A.V.; Dietrich, P.; Maharjan, R.S.; Thissen, A.; Didwal, P.N.; Shinde, M.; Laux, P.; Luch, A.; Mathe, V.; et al. Emerging cold plasma treatment and machine learning prospects for seed priming: A step towards sustainable food production. RSC. Adv. 2022, 10467–10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, B.; Yu, N.-N.; Zheng, W.; Zhang, L.-N.; Liu, Y.; Yu, J.-B.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; Park, G.; Sun, H.-N.; Kwon, T. Effect of non-thermal plasma (NTP) on common sunflower (Helianthus annus L.) seed growth via upregulation of antioxidant activity and energy metabolism-related gene expression. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 95, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Li, M.; Yang, T.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Wang, J.; Ma, M. Effect of cold plasma on physical-biochemical properties and nutritional components of soybean sprouts. Food Res. Int. 2022, 161, 111766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peťková, M.; Švubová, R.; Kyzek, S.; Medvecká, V.; Slováková, Ľ.; Ševčovičová, A.; Gálová, E. The Effects of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on Germination Parameters, Enzyme Activities and Induction of DNA Damage in Barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.; Hu, Z.; Ward, R.; Zhang, X.; Porter, A. Profiling and predicting the problem-solving patterns in China’s research systems: A methodology of intelligent bibliometrics and empirical insights. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2021, 2, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyack, K.W.; van Eck, N.J.; Colavizza, G.; Waltman, L. Characterizing in-text citations in scientific articles: A large-scale analysis. J. Informetr. 2018, 12, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafols, I.; Porter, A.L.; Leydesdorff, L. Science overlay maps: A new tool for research policy and library management. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Tec. 2010, 61, 1871–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almarashi, J.Q.M. Second grounded electrode non-equilibrium atmospheric pressure argon plasma jet impact on germination of basil (Ocimum basilicum) seeds. J. Taibah. Univ. Sci. 2023, 17, 2194847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldanov, B.B.; Ranzhurov, T.V. Influence of Nonthermal Plasma Jet on the Surface Properties of Wheat Seeds. High Energy Chem. 2023, 57, 527–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.Q.X.; Nguyen, L.N.; Nguyen, T.T.; Choi, E.H.; Nguyen, Q.L.; Kaushik, N.K.; Dao, N.T. Effects of Cold Plasma Treatment on Physical Modification and Endogenous Hormone Regulation in Enhancing Seed Germination and Radicle Growth of Mung Bean. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 10308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapirom, S.; Yu, L.D. Low-pressure and atmospheric plasma treatment of sunflower seeds. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 406, 126638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attri, P.; Ishikawa, K.; Okumura, T.; Koga, K.; Shiratani, M.; Mildaziene, V. Impact of seed color and storage time on the radish seed germination and sprout growth in plasma agriculture. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bafoil, M.; Le Ru, A.; Merhabi, N.; Eichwald, O.; Dunand, C.; Yousfi, M. New insights of low-temperature plasma effects on germination of three genotypes of Arabidopsis thaliana seeds under osmotic and saline stress. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 8649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, H.; Nishime, T.M.C.; Wannicke, N.; Mui, T.S.M.; Horn, S.; Quade, A.; Weltmann, K.D. A medium-scale volume dielectric barrier discharge system for short-term treatment of cereal seeds indicates improved germination performance with long-term effects. J. Appl. Phys. 2021, 129, 044904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groot, G.J.J.B.; Hundt, A.; Murphy, A.B.; Bange, M.P.; Mai-Prochnow, A. Cold plasma treatment for cotton seed germination improvement. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durcanyova, S.; Slovakova, L.; Klas, M.; Tomekova, J.; Durina, P.; Stupavska, M.; Kovacik, D.; Zahoranova, A. Efficacy Comparison of Three Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Sources for Soybean Seed Treatment: Plasma Characteristics, Seed Properties, Germination. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 1863–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Shaer, M.; Abdel-azim, M.; El-welily, H.; Hussein, Y.; Abdelghani, A.; Zaki, A.; Mobasher, M. Effects of DBD Direct Air Plasma and Gliding Arc Indirect Plasma Activated Mist on Germination, and Physiological Parameters of Rice Seed. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 1169–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chang, D.; Yang, K. Nanosecond Pulsed Atmospheric-Pressure Plasma Enhanced the Germination of Melon (Cucumis melo L.) Seeds. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, S.; Mishra, A.; Mishra, R.; Pandey, S.; Prakash, R. Transformative impact of atmospheric cold plasma on mung bean seeds: Unveiling surface characteristics, physicochemical alterations, and enhanced germination potential. AIP Adv. 2024, 14, 075215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohajer, M.H.; Khademi, A.; Rahmani, M.; Monfaredi, M.; Hamidi, A.; Mirjalili, M.H. Optimizing beet seed germination via dielectric barrier discharge plasma parameters. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motrescu, I.; Lungoci, C.; Calistru, A.E.; Luchian, C.E.; Gocan, T.M.; Rimbu, C.M.; Bulgariu, E.; Ciolan, M.A.; Jitareanu, G. Non-Thermal Plasma (NTP) Treatment of Alfalfa Seeds in Different Voltage Conditions Lead to Both Positive and Inhibitory Outcomes Related to Sprout Growth and Nutraceutical Properties. Plants 2024, 13, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perea-Brenes, A.; Gomez-Ramirez, A.; Lopez-Santos, C.; Oliva-Ramirez, M.; Molina, R.; Cotrino, J.; Garcia, J.L.; Cantos, M.; Gonzalez-Felipe, A.R. Comparative analysis of the germination of barley seeds subjected to drying, hydrogen peroxide, or oxidative air plasma treatments. Plasma Process Polym. 2022, 19, e2200035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayahi, K.; Sari, A.H.; Hamidi, A.; Nowruzi, B.; Hassani, F. Evaluating the impact of Cold plasma on Seedling Growth properties, seed germination, and soybean antioxidant enzyme activity. BMC Biotechnol. 2024, 24, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahabi, Z.M.; Nasibi, F.; Noori, H. Cold plasma technology as a pre-treatment for seed priming enhances germination and reduces salinity stress in Prosopis koelziana. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 26250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mildaziene, V.; Ivankov, A.; Sera, B.; Baniulis, D. Biochemical and Physiological Plant Processes Affected by Seed Treatment with Non-Thermal Plasma. Plants 2022, 11, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.; Adhikari, M.; Ghimire, B.; Adhikari, B.C.; Park, G.; Choi, E.H. Cold plasma seed priming modulates growth, redox homeostasis and stress response by inducing reactive species in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum). Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2020, 156, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rongsangchaicharean, T.; Srisonphan, S.; Onwimol, D. Responses of Rice Seed Quality to Large-Scale Atmospheric Nonthermal Plasmas. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2022, 42, 1127–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stryczewska, H.D.; Boiko, O. Applications of Plasma Produced with Electrical Discharges in Gases for Agriculture and Biomedicine. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravash, N.; Hesari, J.; Feizollahi, E.; Dhaliwal, H.K.; Roopesh, M.S. Valorization of Cold Plasma Technologies for Eliminating Biological and Chemical Food Hazards. Food Eng. Rev. 2024, 16, 22–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Yang, S.; Bazaka, K.; Ostrikov, K.K. Effects of Atmospheric-Pressure N2, He, Air, and O2 Microplasmas on Mung Bean Seed Germination and Seedling Growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 1, 32603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, N.C.; Hasan, M.M.; Talukder, M.R.; Hossain, M.D.; Chowdhury, A.N. Prospective Applications of Low Frequency Glow Discharge Plasmas on Enhanced Germination, Growth and Yield of Wheat. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2018, 38, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapira, Y.; Multanen, V.; Whyman, G.; Bormashenko, Y.; Chaniel, G.; Barkay, Z.; Bormashenko, E. Plasma Treatment Switches the Regime of Wetting and Floating of Pepper Seeds. Colloid. Surface B 2017, 157, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafoil, M.; Jemmat, A.; Martinez, Y.; Merbahi, N.; Eichwald, O.; Dunand, C.; Yousif, M. Effect of low temperature plasmas and plasma activated waters on Arabidiopsis thaliana germination and growth. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.I.; Mohsenimehr, S.; Hadian, J.; Ghorbanpour, M.; Shokri, B. Physico-chemical induced modification of seed germination and early development in artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) using low energy plasma technology. Phys. Plasmas 2018, 25, 013525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.H.; Ki, S.H.; Kang, M.H.; Choi, J.S.; Park, Y.; Oh, J.; Kim, S.B.; Yoo, S.J.; Choi, E.H.; Park, G. Characterization of Physical and Biochemical Changes in Plasma Treated Spinach Seed During Germination. J. Phys. D. Appl. Phys. 2018, 51, 145205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, R.; Lopez-Santos, C.; Gomez-Ramirez, A.; Vilchez, A.; Espinos, J.P.; Gonzalez-Felipe, A.R. Influence of irrigation conditions in the germination of plasma treated Nasturtium seeds. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Sajub, S.A.; Rahi, M.S.; Tahura, S.; Roy, N.C.; Parvez, S.; Reza, M.A.; Talukder, M.R.; Kabir, A.H. Mechanisms and Signaling Associated with LPDBD Plasma Mediated Growth Improvement in Wheat. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Ding, H.; Ma, R.; Jiao, Z. Research on the Physio-Biochemical Mechanism of Non-Thermal Plasma-Regulated Seed Germination and Early Seedling Development in Arabidopsis. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 01322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhlalmawla, S.A.; Mohamed, A.A.H.; Almarashi, J.Q.M.; Boutraa, T. The impact of cold atmospheric pressure plasma jet on seed germination and seedling growth of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum). Plasma Sci. Technol. 2019, 21, 105503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Los, A.; Ziuzina, D.; Boehm, D.; Cullen, P.J.; Bourke, P. Investigation of mechanisms involved in germination enhancement of wheat (Triticum aestivum) by cold plasma: Effects on seed surface chemistry and characteristics. Plasma Process Polym. 2019, 16, 1800148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, N. Effect of RF plasma on Moringa seeds germination and growth. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2020, 14, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, X.; Song, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Ding, C.; Chen, H. Spectral characteristics on increasing hydrophilicity of Alfalfa seeds treated with alternating current corona discharge field. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 5, 118350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svubova, R.; Kyzek, S.; Medvecka, V.; Slavakova, L.; Galova, E.; Zahoranova, A. Novel insight at the Effect of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma on the Activity of Enzymes Essential for the Germination of Pea (Pisum sativum L. cv Prophet) Seeds. Plasma Process Polym. 2020, 40, 1221–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauwe, R.; Roulard, R.; Ramos, M.; Thiombiano, B.; Mesnard, F.; Gontier, E.; Jamali, A. Etching of the seed cuticle by cold plasma shortens imbibitional leakage in Linum usitatissimum L. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 167, 113536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staric, P.; Mlakar, S.G.; Junkar, I. Response of Two Different Wheat Varieties to Glow and Afterglow Oxygen Plasma. Plants 2021, 10, 1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holc, M.; Gselman, P.; Primc, G.; Vesel, A.; Mozetic, M.; Recek, N. Wettability and Water Uptake Improvement in Plasma-Treated Alfalfa Seeds. Agriculture 2022, 12, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.F.; Sohan, M.S.R.; Hasan, M.; Miah, M.M.; Sajib, S.A.; Karmakar, S.; Khalid-Bin-Ferdaus, K.M.; Kabir, A.H.; Rashid, M.M.; Talukder, M.R.; et al. Enhancement of Seed Germination Rate and Growth of Maize (Zea mays L.) Through LPDBD Ar/Air Plasma. J. Soil. Sci. Plant. Nutr. 2022, 22, 1778–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohan, M.S.R.; Hasan, M.; Hossain, M.F.; Sajub, S.A.; Khalid-Bin-Ferdaus, K.M.; Kabir, A.H.; Rashid, M.M.; Talukder, M.R.; Elseehy, M.M.; El-Shehawi, A.; et al. Low-frequency glow discharge (LFGD) plasma treatment enhances maize (Zea mays L.) seed germination, agronomic traits, enzymatic activities, and nutritional properties. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2022, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Siow, K.S.; Wee, M.F.M.R.; Patra, A. A study to examine the ageing behaviour of cold plasma-treated agricultural seeds. Sci. Rep. 2022, 13, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodsimaab, S.P.; Hagh, Z.G.; Makarian, H.; Gholipoor, M. Deciphering morphological and biochemical responses of Salvia leriifolia to seed cold plasma treatment, priming, and foliar spraying with nano-salicylic acid. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 18672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.; Rashid, M.M.; Alam, M.S.; Talukder, M.R. Enhancement of Growth, Enzymes, Nutrition and Yield of Eggplant: Combined Effects of Plasma Treatments. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2023, 43, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guragain, R.P.; Kierzkowska-Pawlak, H.; Fronczak, M.; Kedzierska-Sar, A.; Subedi, D.P.; Tyczkowski, J. Germination improvement of fenugreek seeds with cold plasma: Exploring long-lasting effects of surface modification. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 324, 112619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomekova, J.; Svubova, R.; Slovakova, L.; Holubova-Cerevkova, L.; Kyzek, S.; Galova, E.; Zahoranova, A. Interaction of Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma with Soybean Seeds: Effect on Germination and DNA, Seed Surface Characteristics and Plasma Diagnostics. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2024, 44, 487–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yao, Q.; Li, X.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, X. Study of the Effects of Plasma Pretreatment on the Microstructure of Peanuts. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 7752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddighinia, F.S.; Iranbaksh, A.; Ardebeili, Z.O.; Satari, T.N.; Soleimanpour, S. Seed Priming with Cold Plasma and Multi-walled Carbon Nanotubes Modified Growth, Tissue Differentiation, Anatomy, and Yield in Bitter Melon (Momordica charantia). J. Plant Growth Reg. 2020, 39, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, M.; Coad, B.R. Plasma glows and shifting water flows: Measuring the changes of water transport phenomena in seeds after plasma treatment. Food Chem. 2025, 479, 143733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Dong, Y. Seed priming with cold plasma mitigated the negative influence of drought stress on growth and yield of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Ind. Crops Prod. 2025, 228, 120899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saudy, H.S.; Hamed, M.F.; El-Mageed, T.A.A.; El-Bordeny, N.E.; Madkour, M.A.; Shokry, M.H.; Gouda, G.F.; Jaremko, M.; Emwas, A.H.; Elgendy, A.T. Utilization of plasma as an ameliorator for forage productivity and in vitro traits of cowpea cultivated in salty soil. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 20322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriruksa, C.; Sawangrat, C.; Sansongsiri, S.; Boonyawan, D.; Thanapornpoonpong, S. Influence of Seed Coat Integrity on the Response of Pepper Seeds to Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma Treatment. Plants 2025, 14, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, A.; Essumang, D.; Hummerick, M.; Johnson, C.; Kruger, M.; Massa, G.; Engeling, K. Reviewing Plasma Seed Treatments for Advancing Agriculture Applications on Earth and Into the Final Frontier. Grav. Space Res. 2021, 9, 133–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Qu, G.; Wang, T.; Sun, Q.; Ling, D.; Hu, S. Enhancement of germination and seedling growth of wheat seed using dielectric barrier discharge plasma with various gas sources. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2017, 37, 1105–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, K.B.; Cherif, M.M.; Assaid, I.; Elfalleh, W.; Khezami, L.; Ghorbal, A.; Assadi, A.A. Exploring Cold plasma technology: Enhancements in Carob seed germination, phytochemical Composition, and antioxidant activity. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalwa, C.; Thakur, A.K.; Vikam, A.; Rane, R.; Vaid, A. Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment and Priming in Bell Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Int. J. Biores. Manag. 2017, 8, 535–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randeniya, L.K.; de Groot, G.J.J.B. Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment of Agricultural Seeds for Stimulation of Germination, Removal of Surface Contamination and Other Benefits: A Review. Plasma Process Polym. 2015, 12, 608–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, B.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Chen, S.; Hunag, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, X. Involvement of reactive oxygen species in endosperm cap weakening and embryo elongation growth during lettuce seed germination. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 3189–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekarun, J.; Watthanaphanit, A. In-situ treatment of tomato and rice seeds in-liquid to promote seed germination and seedling growth. Plasma Process Polym. 2022, 19, e202100238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalachova, T.; Jindrichova, B.; Pospichalova, R.; Fujera, J.; Artemenko, A.; Janick, J.; Antonova, A.; Kylian, O.; Prukner, V.; Burketova, L.; et al. Plasma Treatment Modifies Element Distribution in Seed Coating and Affects Further Germination and Plant Growth through Interaction with Soil Microbiome. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 72, 5609–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Effect of Cold Plasma Treatment on Cooking, Thermomechanical and Surface Structural Properties of Chinese Milled Rice. Food Bioprocess. Tech. 2021, 14, 866–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motrescu, I.; Ogino, A.; Tanaka, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Kodani, S.; Kawagishi, H.; Popa, G.; Nagatsu, M. Effects of Nitrogen and Oxygen Radicals on Low-Temperature Bio-Molecule Processing. Jap. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 50, 08JF07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravlje, J.; Regvar, M.; Vogel-Mikuš, K. Development of Cold Plasma Technologies for Surface Decontamination of Seed Fungal Pathogens: Present Status and Perspectives. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.; Jiafeng, J.; Jiangang, L.; Minchong, S.; Xin, H.; Hanliang, S.; Yuanhua, D. Effects of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean. Sci. Rep. 2014, 31, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Liang, F.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, L.; Shu, J.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, H.; Qin, X.; Shao, C.; Feng, J.; et al. Stimulating Effect of Low-Temperature Plasma (LTP) on the Germination Rate and Vigor of Alfalfa Seed (Medicago Sativa L.). In Computer and Computing Technologies in Agriculture IX, Proceedings of the CCTA 2015. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology, Beijing, China, 27–30 September 2015; Li, D., Li, Z., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; p. 479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Guo, H.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Shao, H.; Zong, J. Cold plasma treatment improves seed germination and accelerates the establishment of centipedegrass. Crop Sci. 2021, 61, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayasi, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Kusano, S.; Kumagai, S.; Ito, T. Non-thermal atmospheric-pressure plasma exposure as a practical method for improvement of Brassica juncea seed germination. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 392, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socco, S.; Bovee, R.C.; Palczewski, M.B.; Hickok, J.R.; Thomas, D.D. Epigenetics: The third pillar of nitric oxide signaling. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 121, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasempour, M.; Iranbakhsh, A.; Ebadi, M.; Ardebili, Z.O. Seed priming with cold plasma improved seedling performance, secondary metabolism, and expression of deacetylvindoline O-acetyltransferase gene in Catharanthus roseus. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 2020, 60, e201900159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priatama, R.A.; Pervitasari, A.N.; Park, S.; Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.K. Current Advancements in the Molecular Mechanism of Plasma Treatment for Seed Germination and Plant Growth. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeber, K.; Nakabayashi, K.; Miatton, E.; Leubner-Metzger, G.; Soppe, W.J.J. Molecular mechanisms of seed dormancy. Plant Cell Environ. 2012, 35, 1769–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waskow, A.; Howling, A.; Furno, I. Advantages and Limitations of Surface Analysis Techniques on Plasma-Treated Arabidopsis thaliana Seeds. Front. Mat. 2021, 8, 642099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.; Chen, Z. The pivotal role of abscisic acid signaling during transision from seed maturation to germination. Plant Cell Rep. 2017, 36, 689–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Kishor, R.; Singh, V.; Sing, V.; Prasad, P.; Aulakh, N.S.; Kumar, T.; Kumar, B. Radio-frequency (RF) room temperature plasma treatment of sweer basil seeds (Ocimum basilicum L.) for germination potential enhancement by immaculation. J. Appl. Res. Med. Aromat. Plants 2021, 26, 100350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajan, A.; Boopathy, B.; Radhakrishnan, M.; Rao, L.; Schluter, O.K.; Tiwari, B.K. Plasma processing: A sustainable technology in agri-food processing. Sustain. Food Technol. 2023, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzek, S.; Holubova, L.; Medvecka, V.; Tomekova, J. Cold Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Can Induce Adaptive Response in Pea Seeds. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2019, 39, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Ono, R.; Nakano, R.; Shiratani, M.; Tashiro, K.; Kuhara, S.; Yasuda, K.; Hagiwara, H. DNA Microarray Analysis of Plant Seeds Irradiated by Active Oxygen Species in Oxygen Plasma. Plasma Med. 2016, 6, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, J.J.; Jo, J.O.; Huynh, D.L.; Mongre, R.K.; Ghosh, M.; Singh, A.K.; Lee, S.B.; Mok, Y.S.; Hyuk, P.; Jeong, D.K. Growth-inducing effects of argon plasma on soybean sprouts via the regulation of demethylation levels of energy metabolism-related genes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saravana Kumar, R.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Cheng, H.; Sun, L.; He, S.; Hao, F. Redox Components: Key Regulators of Epigenetic Modifications in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luchian, C.E.; Lungoci, C.; Ciolan, M.-A.; Rimbu, C.-M.; Miron, L.D.; Motrescu, I. Changes Induced in Seeds as a Result of Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment in Plasma Agriculture Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910366
Luchian CE, Lungoci C, Ciolan M-A, Rimbu C-M, Miron LD, Motrescu I. Changes Induced in Seeds as a Result of Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment in Plasma Agriculture Applications. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(19):10366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910366
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuchian, Camelia Elena, Constantin Lungoci, Mihai-Alexandru Ciolan, Cristina-Mihaela Rimbu, Liviu Dan Miron, and Iuliana Motrescu. 2025. "Changes Induced in Seeds as a Result of Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment in Plasma Agriculture Applications" Applied Sciences 15, no. 19: 10366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910366
APA StyleLuchian, C. E., Lungoci, C., Ciolan, M.-A., Rimbu, C.-M., Miron, L. D., & Motrescu, I. (2025). Changes Induced in Seeds as a Result of Non-Thermal Plasma Treatment in Plasma Agriculture Applications. Applied Sciences, 15(19), 10366. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151910366









