Radiological Implications of Industrial Activities on Soil and Water: An Environmental Analytical Chemistry Perspective in Artisanal Gold-Mining Regions of Atiwa West
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
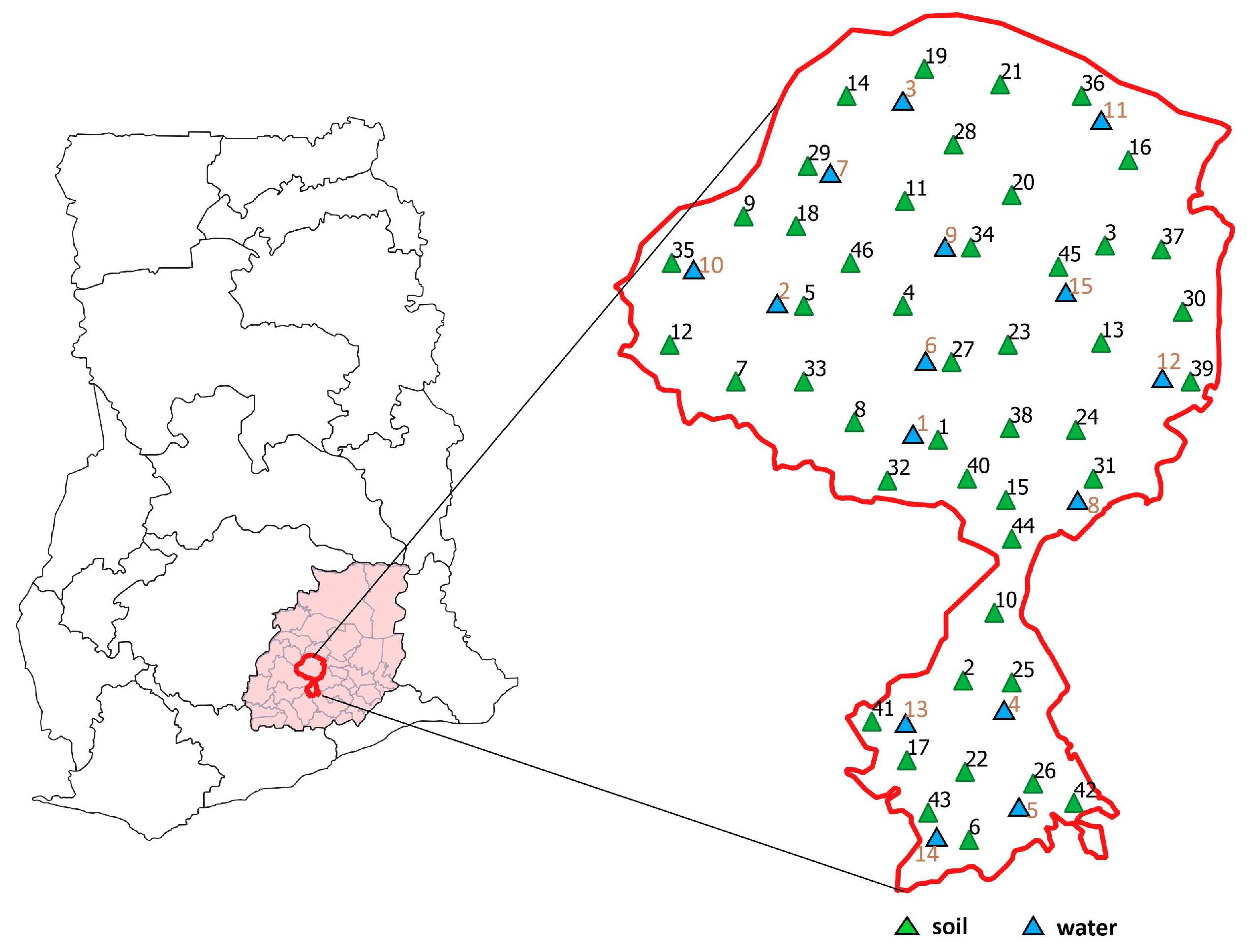
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Sample Preparation
2.4. Instrumental Analysis
2.5. Activity Concentration Measurement
2.6. Sediment–Water Distribution Coefficient
2.7. Assessment of Radiological Risk Parameters
2.7.1. Radium Equivalent Activity Index (Raeq)
2.7.2. Internal and External Hazard Indices
2.7.3. Absorbed Gamma Dose Rate (D)
2.7.4. Annual Effective Dose (AED)
2.7.5. Annual Gonadal Dose Equivalent (AGDE)
2.7.6. Excess Lifetime Cancer Risk (ELCR)
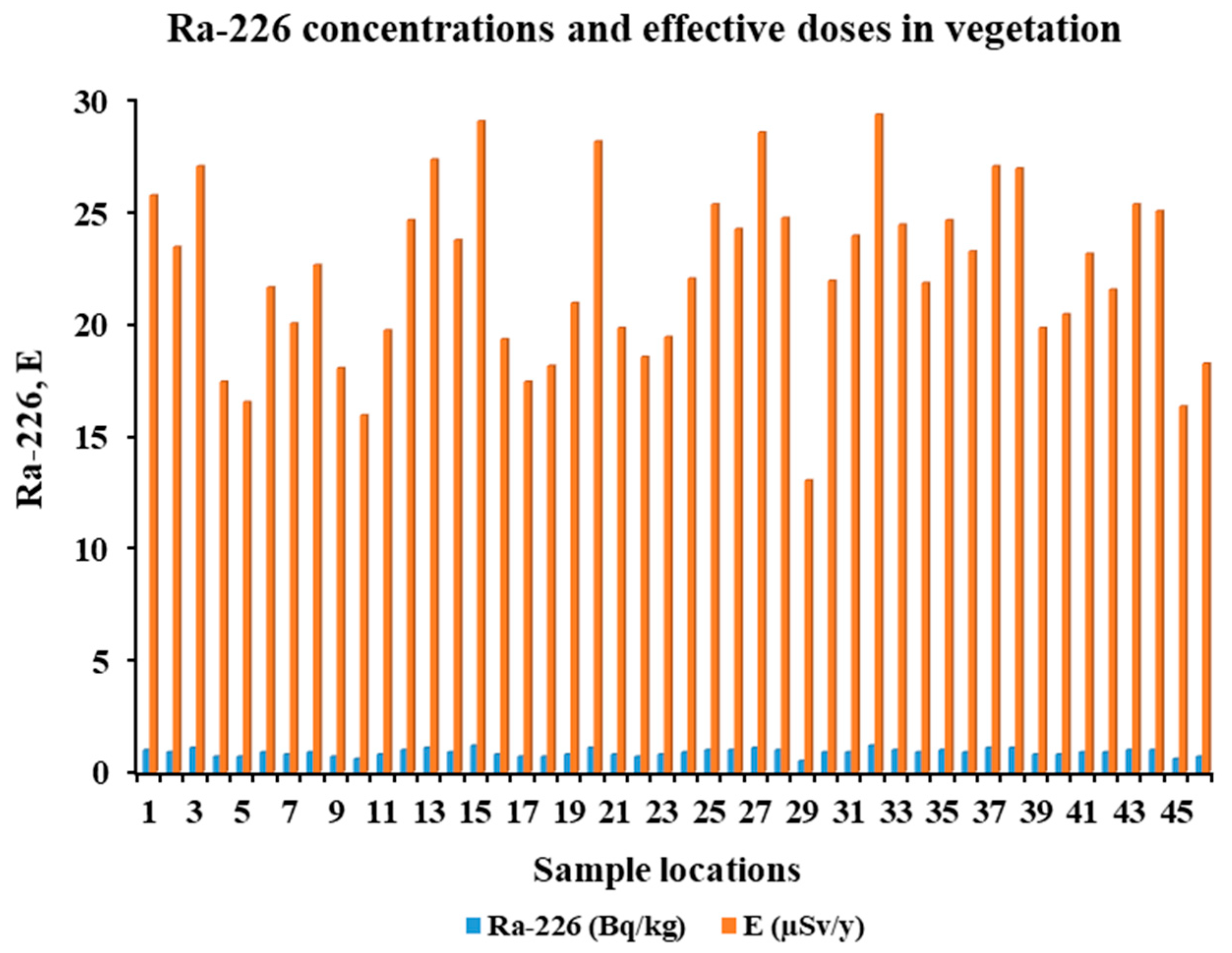
2.7.7. Estimation of Radium Uptake by Vegetables
2.7.8. Annual Effective Dose Due to Vegetable Consumption
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
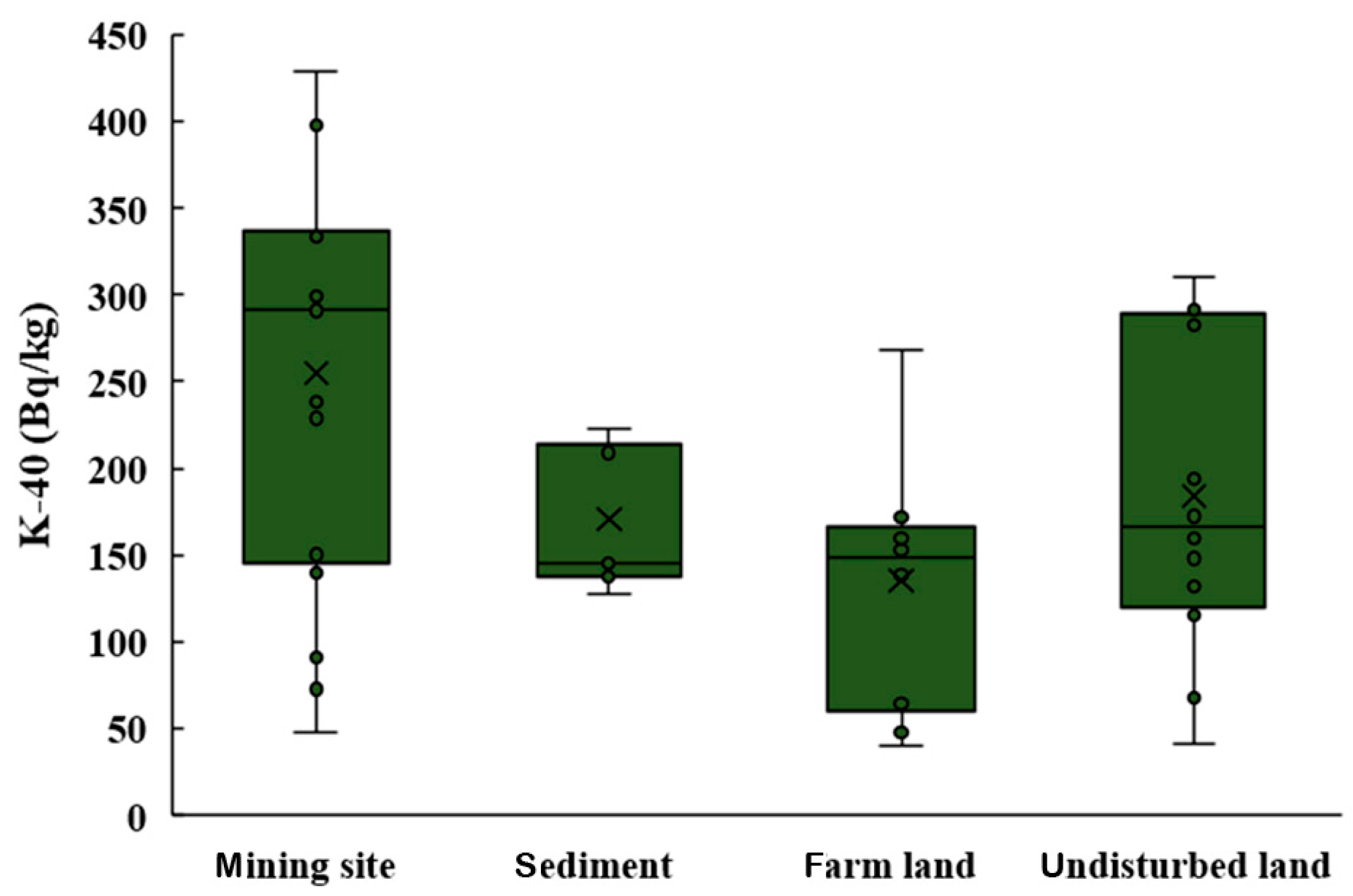
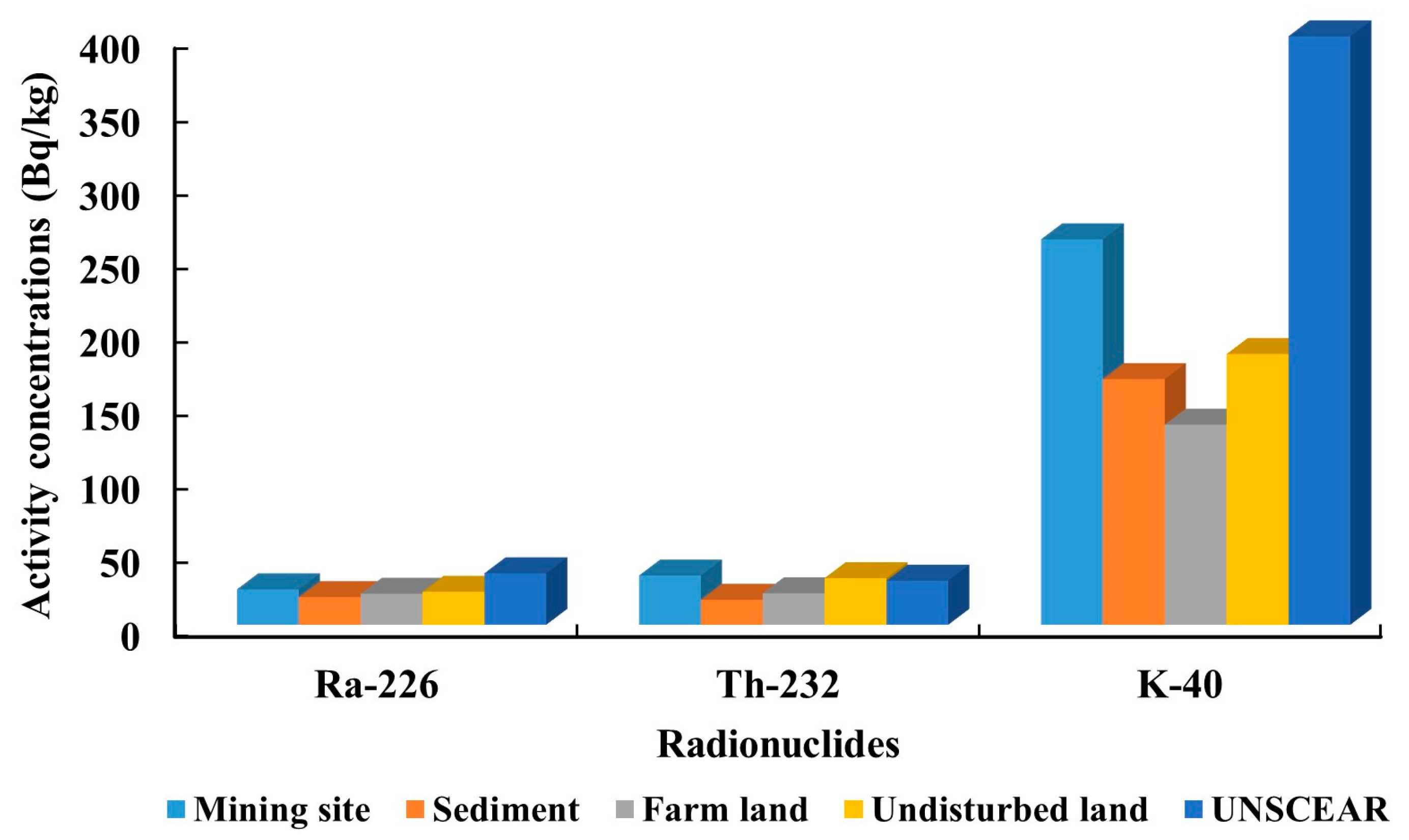
3.1. Activity Concentrations of Radionuclides in Soil and Sediment
Normality of Data
3.2. Activity Concentrations of Radionuclides in Water Samples
3.3. Relationships Between Measured Radionuclides
3.3.1. Activity Correlation and Ratios in Soil and Sediment
3.3.2. Pearson Correlation
3.3.3. Sediment–Water Distribution Coefficients (Kd)
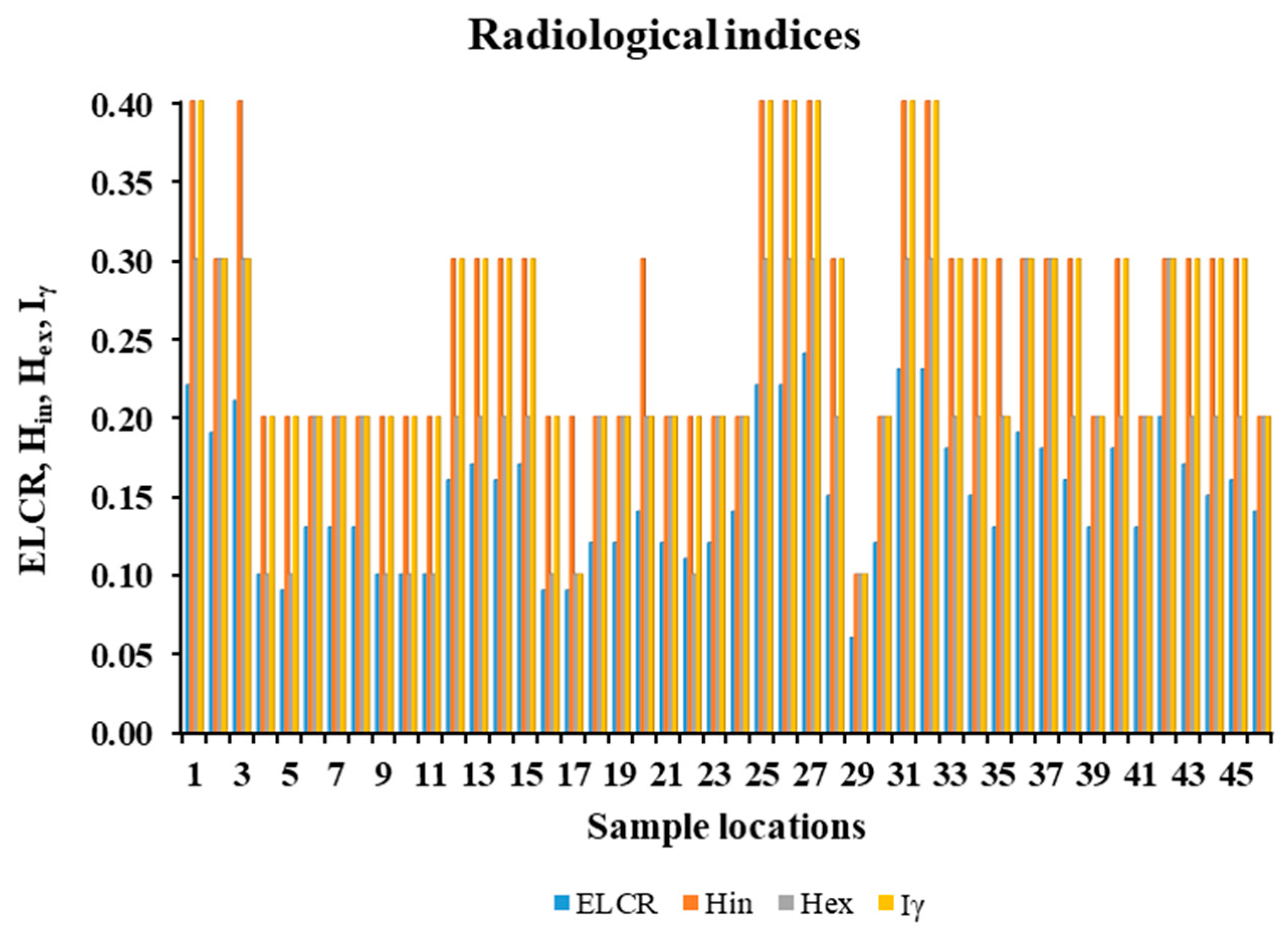
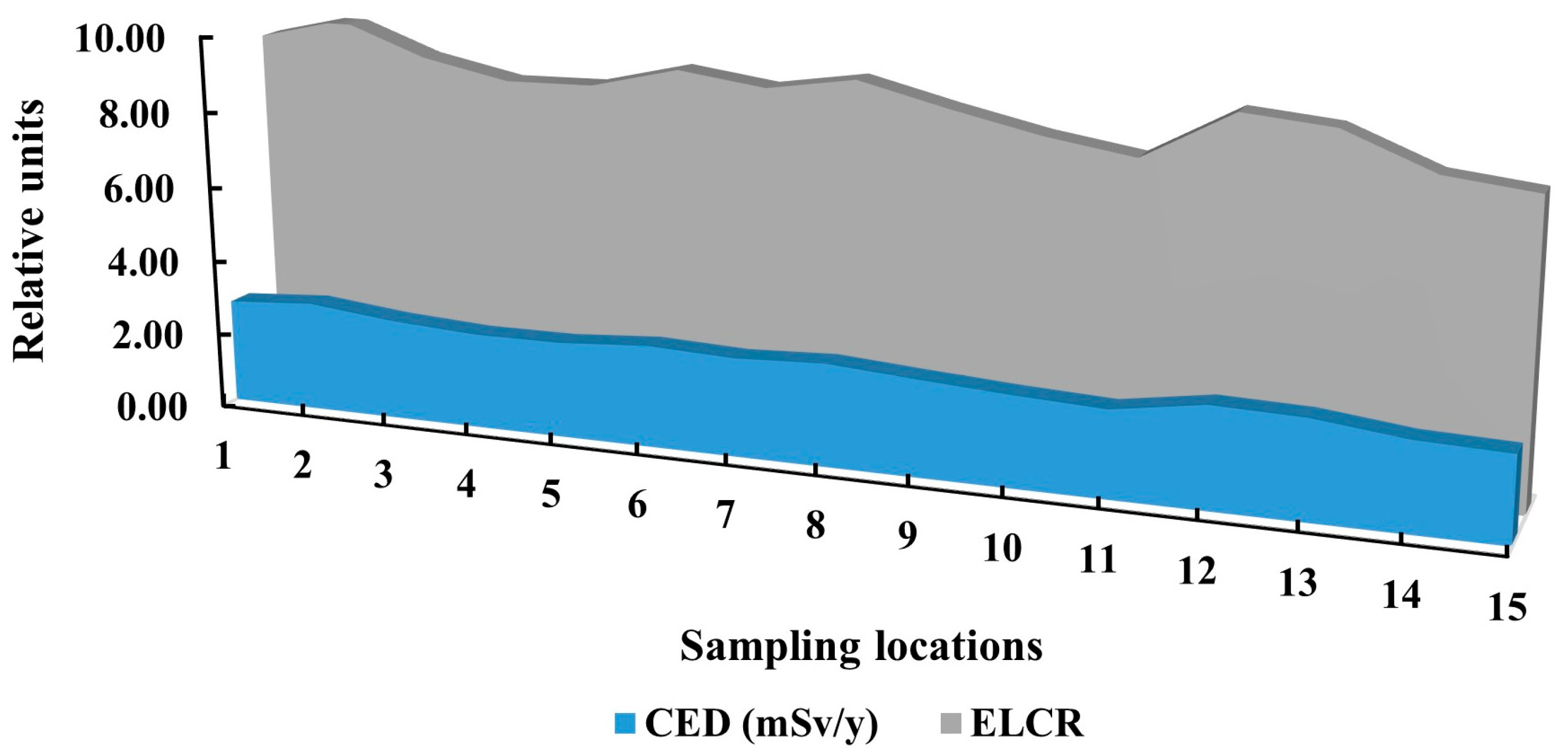
3.4. Radiological Risk Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Öge, T.O.; Özdemir, F.B.; Öge, M. Assessment of environmental radioactivity in soil samples from Bartın Province, Turkey. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2021, 328, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulkarim, M.S.; Umar, S.; Mohammed, A.; Modelu, D. Determination of radionuclides in soil samples taken from Gura Topp (Jos) using sodium iodide thallium detector NaI(Ti). Niger. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 26, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayeb, I.S.; Mustafa, M.B. Detection of natural radioactive materials in the soil of bauxite mining areas of Kuantan, Pahang, Malaysia. Int. J. Math. Phys. Sci. Res. 2016, 4, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Najam, L.A.; Younis, S.A. Assessment of natural radioactivity level in soil samples for selected regions in Nineveh Province (IRAQ). Int. J. Nov. Res. Phys. Chem. Math. 2015, 2, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sivakumar, S.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Ravisankar, R.; Ravikumar, S.M.; Prince, J.; Jebakumar, P.; Vijayagopal, P.; Vijayalakshmi, I.; Jose, M.T. Measurement of natural radioactivity and evaluation of radiation hazards in coastal sediments of east coast of Tamilnadu using statistical approach. J. Taibah Univ. Sci. 2014, 8, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, A.A.; Tariq, S.; Din, K.U.; Manzoor, S.; Calligaris, C.; Waheed, A. Evaluation of excessive lifetime cancer risk due to natural radioactivity in the rivers sediments of Northern Pakistan. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademola, A.K.; Bello, A.K.; Adejumobi, A.C. Determination of natural radioactivity and hazard in soil samples in and around gold mining area in Itagunmodi, south-western, Nigeria. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocent, A.J.; Onimisi, M.Y.; Jonah, S.A. Evaluation of naturally occurring radionuclide materials in soil samples collected from some mining sites in Zamfara State, Nigeria. Br. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2013, 3, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzah, Z.; Rahman, S.A.A.; Saat, A. Measurement of 226Ra, 228Ra and 40K in soil in district of Kuala Krai using gamma spectrometry. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2011, 15, 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources, Effects, and Risks of Ionization Radiation; Report to the General Assembly 2000, with Annexes; UNSCEAR: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Shayeb, M.A.; Baloch, M.A. Distribution of natural radioactivity in soil and date palm-pits using high purity germanium radiation detectors and LB-alpha/beta gas flow counter in Saudi Arabia. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2020, 52, 1282–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, A.; Rajalakshmi, A.; Ravisankar, R.; Vijayagopal, P.; Venkatraman, B. Measurements of natural gamma radiations and effects of physico-chemical properties in soils of Yelagiri hills, Tamilnadu India with statistical approach. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 11, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taqi, A.H.; Shaker, A.M.; Battawy, A.A. Natural radioactivity assessment in soil samples from Kirkuk city of Iraq using HPGe detector. Int. J. Radiat. Res. 2018, 16, 455–463. Available online: http://ijrr.com/article-1-2398-en.html (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Yordanova, I.I.; Banov, M.D.; Misheva, L.G.; Staneva, D.N.; Bineva, T.K. Natural radioactivity in virgin soils and soils from some areas with closed uranium mining facilities in Bulgaria. Open Chem. 2015, 13, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpanowo, M.A.; Umaru, I.; Iyakwari, S. Assessment of radiological risk from the soils of artisanal mining areas of Anka, North West Nigeria. Afr. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 13, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaduzzaman, K.; Khandaker, M.U.; Amin, Y.M.; Bradley, D.A.; Mahat, R.H.; Nor, R.M. Soil-to-root vegetable transfer factors for 226Ra, 232Th, 40K, and 88Y in Malaysia. J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 135, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gao, B.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, G.; Wei, Q.; He, Y. Determination of radionuclide concentration and radiological hazard in soil and water near the uranium tailings reservoir in China. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2021, 33, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathuthu, M.; Uushona, V.; Indongo, V. Radiological safety of groundwater around a uranium mine in Namibia. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2021, 122, 102915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Joint Research Centre: EU Science Hub. Simplified Pathways of Natural Radionuclides. 2025. Available online: https://joint-research-centre.ec.europa.eu/sites/default/files/styles/oe_theme_medium_no_crop/public/2024-09/Simplified%20pathways%20of%20natural%20radionuclides.jpg?itok=Z0OhKE3a (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Ramadhany, M.F.; Wijaya, G.S.; Muharini, A. Assessment of natural radioactivity concentration and radiological risk in Tanjung Enim’s coal mine, South Sumatra Indonesia. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladan, S.C.; Mustapha, I.M.; Hassan, A.; Aliyu, M.S.; Tukur, S.R. Assessment of radioactivity concentration level in soil samples of some gold mining areas of Shiroro, Niger State, Nigeria. J. Radiat. Nucl. Appl. 2022, 7, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuangtakoun, S.; Hong, B.T.; Loat, B.V.; Cuong, P.V. Determination of natural radioactivity in soil samples around gold mining area in Khamkeut district, Bolikhamxay Province, Laos using gammarRay spectrometer with NaI (Tl) detector. VNU J. Sci. Math.-Phys. 2018, 34, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yachiso, G.; Chaubey, A.K.; Turi, B. Measurements of natural radioactivity levels in soil samples and hazards in Lega Dembi gold mining, East Guji, Oromia, Ethiopia. Res. Sq. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souffit, D.G.; Saïdou; Modibo, B.O.; Lepoire, D.; Tokonami, S. Risk assessment of exposure to natural radiation in soil using RESRAD-ONSITE and RESRAD-BIOTA in the cobalt-nickel bearing areas of Lomié in Eastern Cameroon. Radiation 2022, 2, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, E.S.; Maxwell, O.; Adewoyin, O.O.; Olawole, O.C.; Arijaje, T.E.; Embong, Z.; Saeed, M.A. Investigation of natural environmental radioactivity concentration in soil of coastaline area of Ado-Odo/Ota Nigeria and its radiological implications. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansah, K.J.; Dumakor-Dupey, N.K.; Kansake, B.A.; Assan, E.; Bekui, P. Socioeconomic and environmental assessment of informal artisanal and small-scale mining in Ghana. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 202, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galhardi, J.A.; García-Tenorio, R.; Bonotto, D.M.; Frances, I.D.; Motta, J.G. Natural radionuclides in plants, soils and sediments affected by U-rich coal mining activities in Brazil. J. Environ. Radioact. 2017, 177, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello, S.; Nasiru, R.; Garba, N.N.; Adeyemo, D.J. Annual effective dose associated with radon, gross alpha and gross beta radioactivity in drinking water from gold mining areas of Shanono and Bagwai, Kano state, Nigeria. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idriss, H.; Salih, I.; Alaamer, A.S.; Saleh, A.; Abdelgali, M.Y. Environmental-impact assessment of natural radioactivity around a traditional mining area in Al-Ibedia, Sudan. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2016, 70, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odumo, O.B.; Mustapha, A.O.; Patel, J.P.; Angeyo, H.K. Radiological survey and assessment of associated activity concentration of the naturally occurring radioactive materials (NORM) in the Migori artisanal gold mining belt of southern Nyanza, Kenya. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliyu, A.S.; Ibrahim, U.; Akpa, C.T.; Garba, N.N.; Ramli, A.T. Health and ecological hazards due to natural radioactivity in soil from mining areas of Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Isot. Environ. Health Stud. 2015, 51, 448–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Focus, E.; Rwiza, M.J.; Mohammed, N.K.; Banzi, F.P. The influence of gold mining on radioactivity of mining sites soil in Tanzania. EQA-Int. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 46, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barba-Lobo, A.; Gázquez, M.J.; Bolívar, J.P. A practical procedure to determine natural radionuclides in solid materials from mining. Minerals 2022, 12, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguelem, E.J.M.; Ndontchueng, M.M.; Motapon, O. Determination of 226Ra, 232Th, 40K, 235U and 238U activity concentration and public dose assessment in soil samples from bauxite core deposits in Western Cameroon. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adukpo, O.K.; Faanu, A.; Lawluvi, H.; Tettey-Larbi, L.; Emi-Reynolds, G.; Darko, E.O.; Kansaana, C.; Kpeglo, D.O.; Awudu, A.R.; Glover, E.T.; et al. Distribution and assessment of radionuclides in sediments, soil and water from the lower basin of river Pra in the Central and Western Regions of Ghana. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2015, 303, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyimah Ackah, E.; Ofosu, I.W.; Lutterodt, H.E.; Darko, G.; Kpeglo, D.O. Excess lifetime cancer risk and committed effective dose associated with dietary exposure to radioactivity of natural origin from mining areas. J. Consum. Prot. Food Saf. 2021, 16, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyi, I.; Oppon, O.C.; Glover, E.T.; Gbeddy, G.; Kokroko, W. Assessment of occupational radiation exposure in underground artisanal gold mines in Tongo, Upper East Region of Ghana. J. Environ. Radioact. 2013, 126, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faanu, A.; Darko, E.O.; Ephraim, J.H. Determination of natural radioactivity and hazard in soil and rock samples in a mining area in Ghana. West Afr. J. Appl. Ecol. 2011, 19, 79–92. [Google Scholar]
- Faanu, A.; Kpeglo, D.O.; Sackey, M.; Darko, E.O.; Emi-Reynolds, G.; Lawluvi, H.; Awudu, R.; Adukpo, O.K.; Kansaana, C.; Ali, I.D.; et al. Natural and artificial radioactivity distribution in soil, rock and water of the Central Ashanti Gold Mine, Ghana. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 1593–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faanu, A.; Lawluvi, H.; Kpeglo, D.O.; Darko, E.O.; Emi-Reynolds, G.; Awudu, A.R.; Adukpo, O.K.; Kansaana, C.; Ali, I.D.; Agyeman, B.; et al. Assessment of natural and anthropogenic radioactivity levels in soils, rocks and water in the vicinity of Chirano Gold Mine in Ghana. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2014, 158, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faanu, A.; Adukpo, O.K.; Tettey-Larbi, L.; Lawluvi, H.; Kpeglo, D.O.; Darko, E.O.; Emi-Reynolds, G.; Awudu, R.A.; Kansaana, C.P.; Amoah, A.; et al. Natural radioactivity levels in soils, rocks, and water at a mining concession of Perseus gold mine and surrounding towns in Central Region of Ghana. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purwins, S. Bauxite mining at Atiwa Forest Reserve, Ghana: A political ecology of a conservation-exploitation conflict. GeoJournal 2020, 87, 1085–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Atiwa Fate Back in the Public Domain. Flowing Water or Bauxite Breakdown? IUCN: Gland, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Finance and Economic Planning (Ghana) (MOFEP). Programme-Based Budget Estimates for 2019, Atiwa West District Assembly. Ministry of Finance, Composite Budget for 2019–2022. 2019. Available online: https://mofep.gov.gh/sites/default/files/composite-budget/2019/ER/Atiwa-West.pdf (accessed on 23 July 2022).
- Amponsah, A.; Nasare, L.I.; Tom-Dery, D.; Baatuuwie, B.N. Land cover changes of Atiwa Range Forest Reserve, a biodiversity hotspot in Ghana. Trees For. People 2022, 9, 100301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Soil Sampling for Environmental Contaminants; IAEA-TECDOC-1415; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 2004; pp. 1–81. ISBN 92-0-111504-0. Available online: https://www.iaea.org/publications/7113/soil-sampling-for-environmental-contaminants (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- ISO 5667-3:2018; Water Quality—Sampling—Part 3: Preservation and Handling of Water Samples. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Method 903.1: Radium-226 in drinking water, radon emanation technique. In Methods for Chemical Analysis of Water and Wastes; EPA-600/4-79-020; U.S. EPA: Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). Measurement of Radionuclides in Food and the Environment; Technical Reports Series No. 295; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 18589-2:2015; Measurement of radioactivity in the environment—Soil—Part 2: Preparation of samples. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- Akuo-ko, E.O.; Adelikhah, M.; Amponsem, E.; Csordas, A.; Kovacs, T. Radiological assessment in beach sediment of coastline, Ghana. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orosun, M.M.; Usikalu, M.R.; Oyewumi, K.J.; Adagunodo, T.A. Natural radionuclides and radiological risk assessment of granite mining field in Asa, North-central Nigeria. MethodsX 2019, 6, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Recommendations of the International Commission on Radiological Protection. ICRP Publication 60. 1990. Available online: https://www.icrp.org/publication.asp?id=ICRPPublication60 (accessed on 3 September 2025).
- Beogo, C.E.; Cisse, O.I.; Zougmore, F. Assessment of radiological hazards from soil samples in the Northeastern area of Burkina Faso. SN Appl. Sci. 2022, 4, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atibu, E.K.; Arpagaus, P.; Mulaji, C.K.; Mpiana, P.T.; Poté, J.; Loizeau, J.-L.; Carvalho, F.P. High environmental radioactivity in artisanal and small-scale gold mining in Eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. Minerals 2022, 12, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources of Ionizing Radiation; UNSCEAR: Vienna, Austria, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, 4th ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2011; pp. 1–541.
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Recommendation of the International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP); Oxford Publication 60, Annals of the ICRP 210-3; Pergamon Press: New York, NY, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation; UNSCEAR: Vienna, Austria, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Idriss, H.; Salih, I.; Alaamer, A.S.; AL-Rajhi, M.A.; Osman, A.; Adreani, T.A.; Abdelgalil, M.Y.; Ali, N.Y. Health risk profile for terrestrial radionuclides in soil around artisanal gold mining area at Alsopag, Sudan. Acta Geophys. 2018, 66, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). International Basic Safety for Protection Against Ionizing Radiation and for the Safety of Radiation Sources; Safety Series No. 115; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA). The Environmental Behavior of Radium; Technical Report Series I 310; IAEA: Vienna, Austria, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Dina, N.T.; Das, S.C.; Kabir, M.Z.; Rasul, M.G.; Deeba, F.; Rajib, M.; Islam, M.S.; Hayder, A.; Ali, M.I. Natural radioactivity and its radiological implications from soils and rocks in Jaintiapur area, North-east Bangladesh. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2022, 331, 4457–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perevoshchikov, R.; Perminova, A.; Menshikova, E. Natural radionuclides in soils of natural-technogenic landscapes in the impact zone of potassium salt mining. Minerals 2022, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarrete, M.; Zúñiga, M.A.; Espinosa, G.; Golzarri, J.I. Radioactive contamination factor (RCF) obtained by comparing contaminant radioactivity (137Cs) with natural radioactivity (40K) in marine sediments taken up from Mexican sea waters. World J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 2014, 4, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lu, X.; Ding, X.; Feng, T. Natural radioactivity level in beach sand along the coast of Xiamen Island, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 91, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akuo-ko, E.O.; Adelikhah, M.; Amponsem, E.; Csordas, A.; Kovacs, T. Investigations of indoor radon levels and its mapping in the Greater Accra region, Ghana. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2023, 333, 2975–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, A.J.; Najam, L.A. Radium and uranium concentrations measurements in vegetable samples of Iraq. Detection 2015, 3, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking—Water Quality, 3rd ed.; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008.
- Amin, S.A.; Ayoub, A.A.; Jassim, A.A. Radioactivity levels in some vegetables and herbs. Eng. Technol. J. 2018, 36, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation; UNSCEAR: Vienna, Austria, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Avwiri, G.O.; Osimobi, J.C.; Agbalagba, E.O. Evaluation of natural occurring radionuclide variation with lithology depth profile of Udi and Ezeagu local government areas of Enugu State, Nigeria. Int. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 2013, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Alvarado, J.A.C.; Balsiger, B.; Rollin, S.; Jakob, A.; Burger, M. Radioactive and chemical contamination of the water resources in the former uranium mining and milling sites of Mailuu Suu (Kyrgyzstan). J. Environ. Radioact. 2014, 138, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazemi, N.; Bajoga, A.D.; Bradley, D.A.; Regan, P.H.; Shams, H. Soil radioactivity levels, radiological maps, and risk assessment for the state of Kuwait. Chemosphere 2016, 154, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sureshgandhi, M.; Ravisankar, R.; Rajalakshmi, A.; Sivakumar, S.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Anand, D.P. Measurements of natural gamma radiation in beach sediments of north-east coast of Tamilnadu, India by gamma ray spectrometry with multivariate statistical approach. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2014, 7, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoo, F.; Darko, E.O.; Garavaglia, M.; Giovani, C.; Pividore, S.; Andam, A.B.; Amoako, J.K.; Adukpo, O.K.; Tandoh, J.B.; Inkoom, S. Public exposure to natural radioactivity and radon exhalation rate in construction materials used within Greater Accra Region of Ghana. Sci. Afr. 2018, 1, e00009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botwe, B.O.; Schirone, A.; Delbono, I.; Barsanti, M.; Delfanti, R.; Kelderman, P.; Nyarko, E.; Lens, P.N.L. Radioactivity concentrations and their radiological significance in sediments of the Tema Harbour, Greater Accra, Ghana. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2017, 10, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Review of Food Consumption Surveys, Recommendations; Africa, 102; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- International Commission on Radiological Protection (ICRP). Protection from Potential Exposures—Application to Selected Radiation Sources; ICRP Publication 76, Ann ICRP 27 (2); ICRP: Ottawa, ON, Canada, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zubair, M.; Shafiqullah. Measurement of natural radioactivity in several sandy-loamy soil samples from Sijua, Dhanbad, India. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, M.; Tripathi, P.; Choudary, I.; Mehra, R.; Kumar, A. Assessment of annual effective dose due to inhalation and ingestion of radon in water samples from some regions of Punjab, India. Int. J. Pure Appl. Phys. 2017, 13, 193–200. [Google Scholar]







| Ra-226 (Bq/kg) | Th-232 (Bq/kg) | K-40 (Bq/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mining sites | Mean | 24.1 ± 2.3 | 33.5 ± 2.5 | 262 ± 25 |
| Range | 12.9–29.1 | 10.8–44.0 | 48–429 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.5 | 8.8 | 115.1 | |
| Geometric mean | 23.8 | 31.9 | 225 | |
| Sediment | Mean | 18.8 | 17.0 | 167 |
| Range | 15.8–22.4 | 14.3–20.2 | 128–223 | |
| Standard deviation | 2.2 | 2.0 | 37.9 | |
| Geometric mean | 18.7 | 16.9 | 163 | |
| Farms | Mean | 21.1 | 21.4 | 136 |
| Range | 17.3–28.8 | 15.8–26.8 | 40–269 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.8 | 3.7 | 65.3 | |
| Geometric mean | 20.8 | 21.1 | 117 | |
| Undisturbed lands | Mean | 22.4 | 31.7 | 184 |
| Range | 16.2–26.8 | 25.9–38.8 | 41–310 | |
| Standard deviation | 3.2 | 3.9 | 87.8 | |
| Geometric mean | 22.2 | 31.4 | 159 |
| Ra-226 (Bq/L) | Ra-228 (Bq/L) | K-40 (Bq/L) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | 1.02 ± 0.2 | 4.53 ± 0.9 | 13.97 ± 3.2 |
| Minimum | 0.52 ± 0.2 | 3.92 ± 1.0 | 10.90 ± 3.1 |
| Maximum | 1.31 ± 0.2 | 5.12 ± 0.9 | 16.50 ± 3.2 |
| Median | 1.14 | 4.56 | 13.98 |
| Standard deviation | 0.27 | 0.31 | 1.73 |
| Geometric mean | 0.97 | 4.52 | 13.86 |
| Ra-226 | Th-232 | K-40 | Ra-226veg | Eveg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra-226 | 1.0 | ||||
| Th-232 | 0.7 | 1.0 | |||
| K-40 | 0.5 | 0.7 | 1.0 | ||
| Ra-226veg | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 1.0 | |
| Eveg | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akuo-ko, E.O.; Otoo, F.; Glover, E.T.; Amponsem, E.; Tettey-Larbi, L.; Ganbaatar, T.; Csordás, A.; Shahrokhi, A.; Kovács, T. Radiological Implications of Industrial Activities on Soil and Water: An Environmental Analytical Chemistry Perspective in Artisanal Gold-Mining Regions of Atiwa West. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189857
Akuo-ko EO, Otoo F, Glover ET, Amponsem E, Tettey-Larbi L, Ganbaatar T, Csordás A, Shahrokhi A, Kovács T. Radiological Implications of Industrial Activities on Soil and Water: An Environmental Analytical Chemistry Perspective in Artisanal Gold-Mining Regions of Atiwa West. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):9857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189857
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkuo-ko, Esther Osei, Francis Otoo, Eric Tetteh Glover, Eunice Amponsem, Lordford Tettey-Larbi, Tuvshinsaikhan Ganbaatar, Anita Csordás, Amin Shahrokhi, and Tibor Kovács. 2025. "Radiological Implications of Industrial Activities on Soil and Water: An Environmental Analytical Chemistry Perspective in Artisanal Gold-Mining Regions of Atiwa West" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 9857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189857
APA StyleAkuo-ko, E. O., Otoo, F., Glover, E. T., Amponsem, E., Tettey-Larbi, L., Ganbaatar, T., Csordás, A., Shahrokhi, A., & Kovács, T. (2025). Radiological Implications of Industrial Activities on Soil and Water: An Environmental Analytical Chemistry Perspective in Artisanal Gold-Mining Regions of Atiwa West. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 9857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15189857









