Automated Testing System for Environmentally Assisted Fatigue Crack Propagation with Compliance-Based Crack Monitoring
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
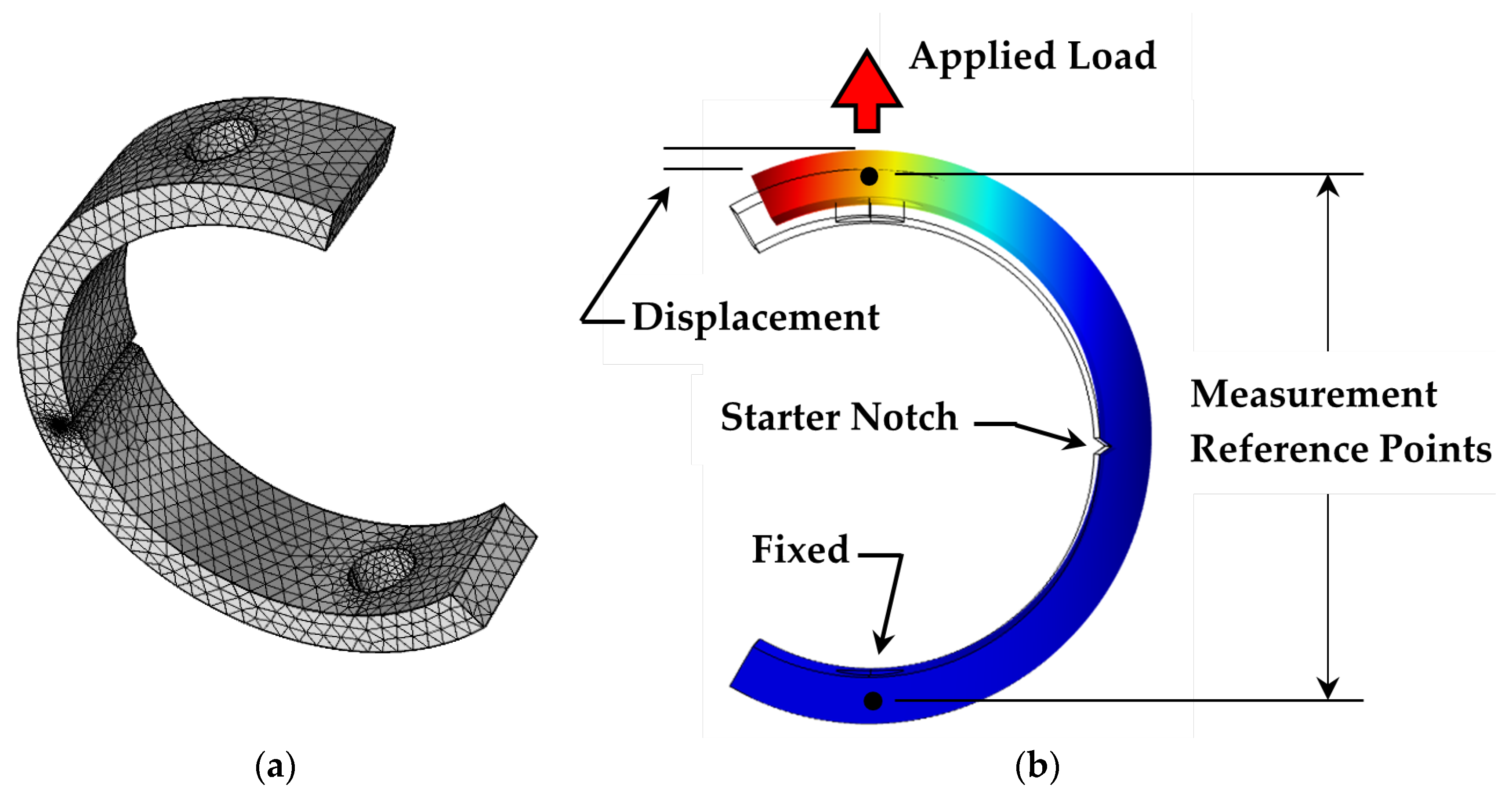
2. Materials and Methods
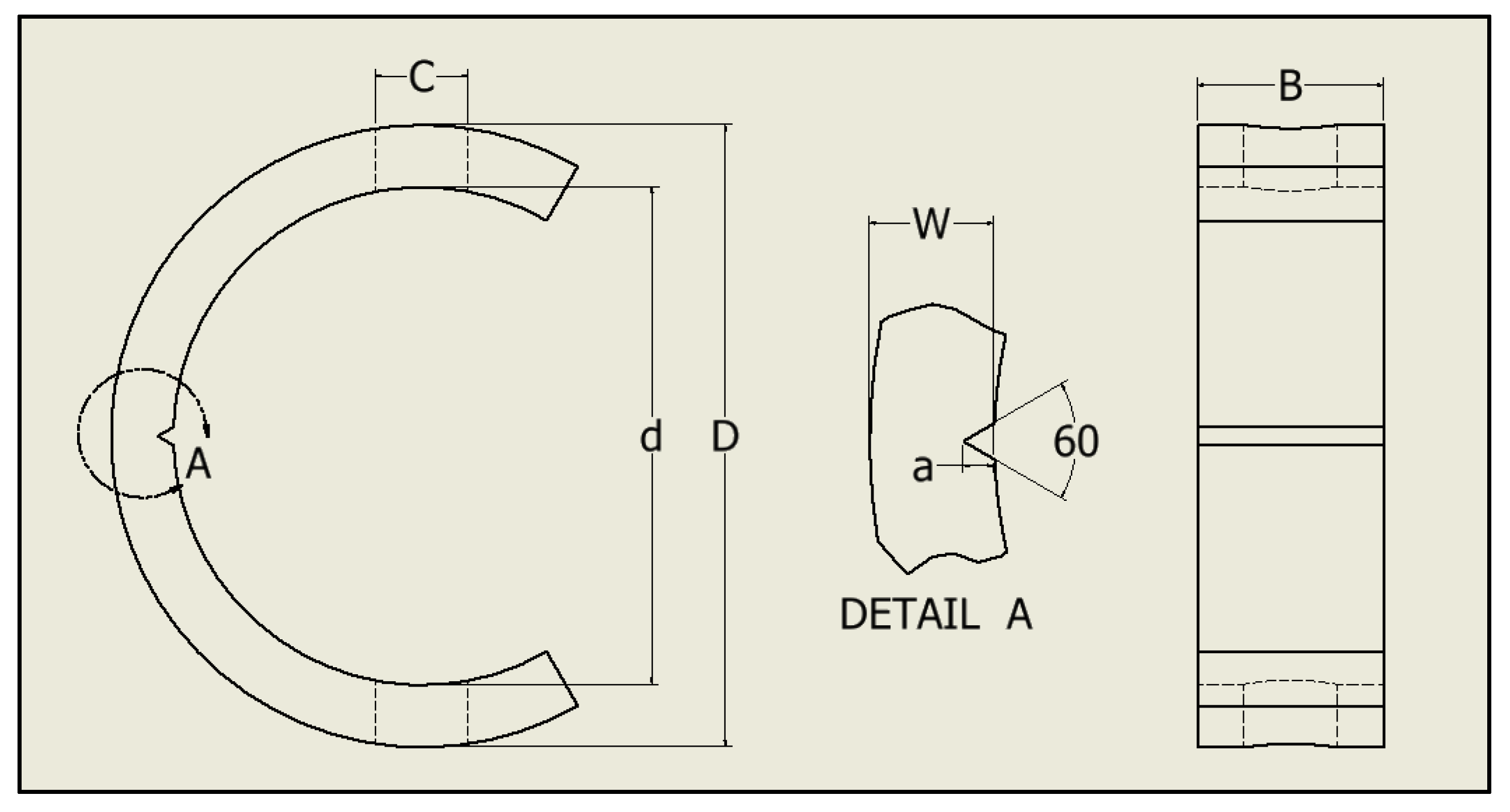
2.1. Sample Preparation
2.2. Test Environments and Exposure
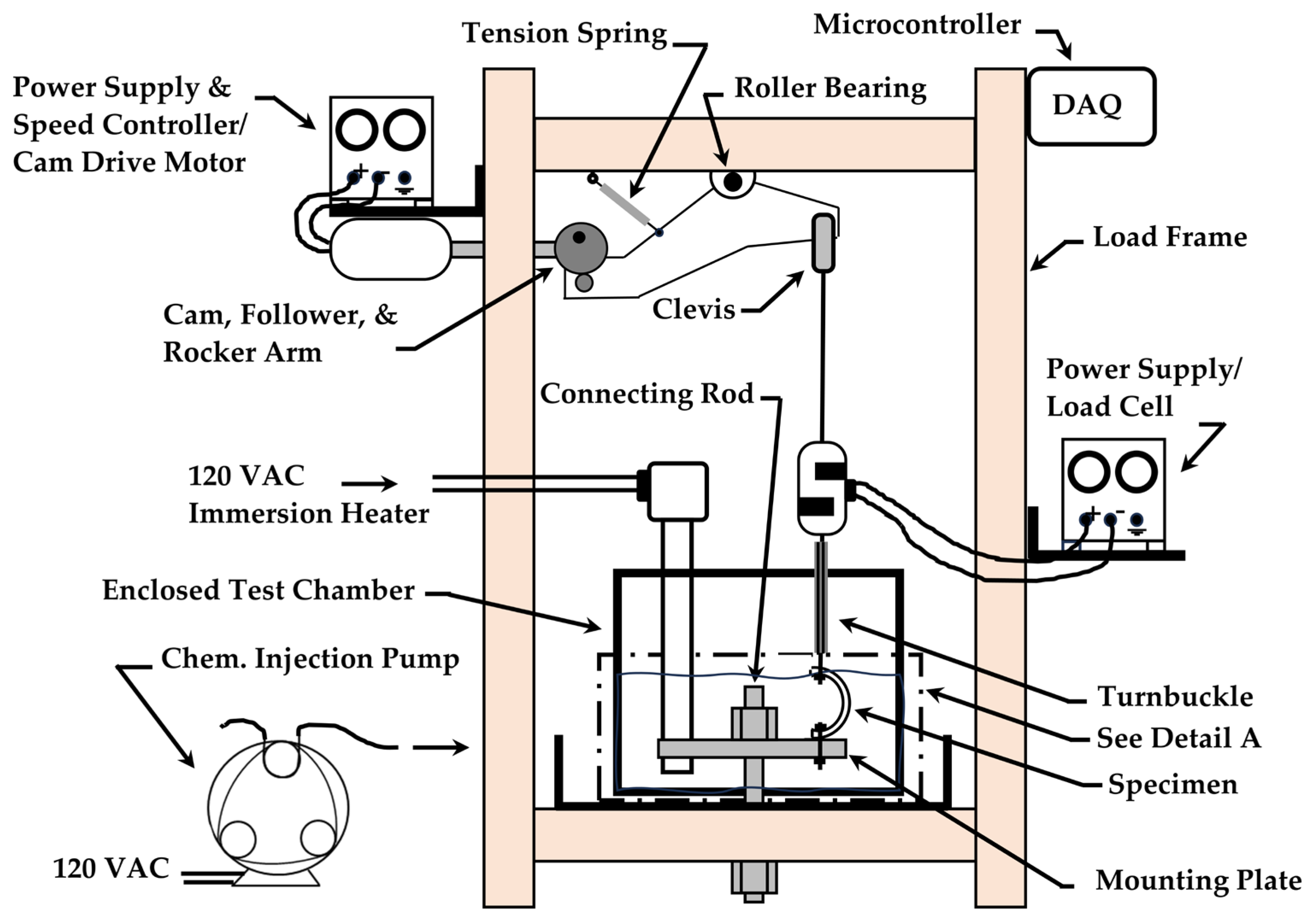
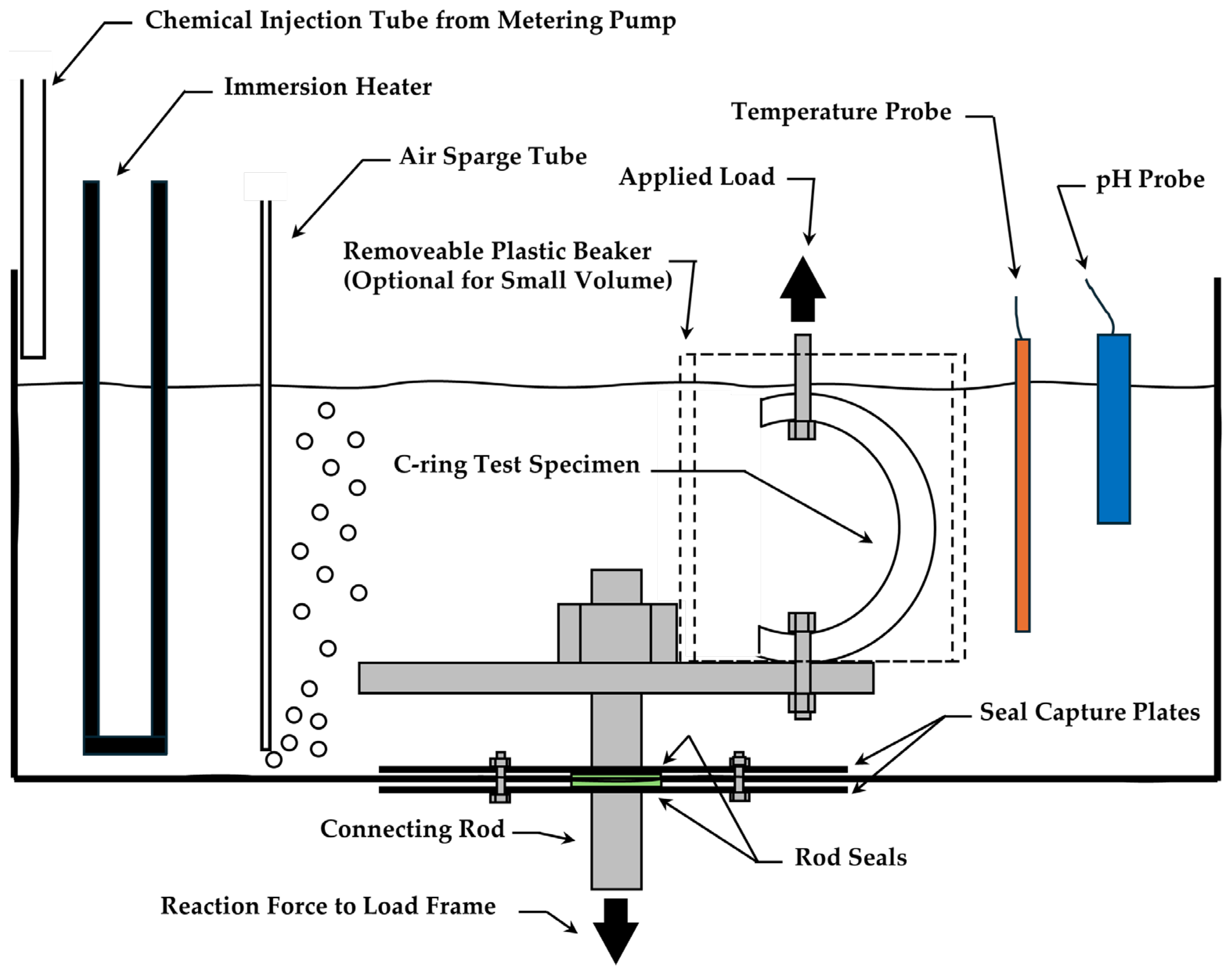
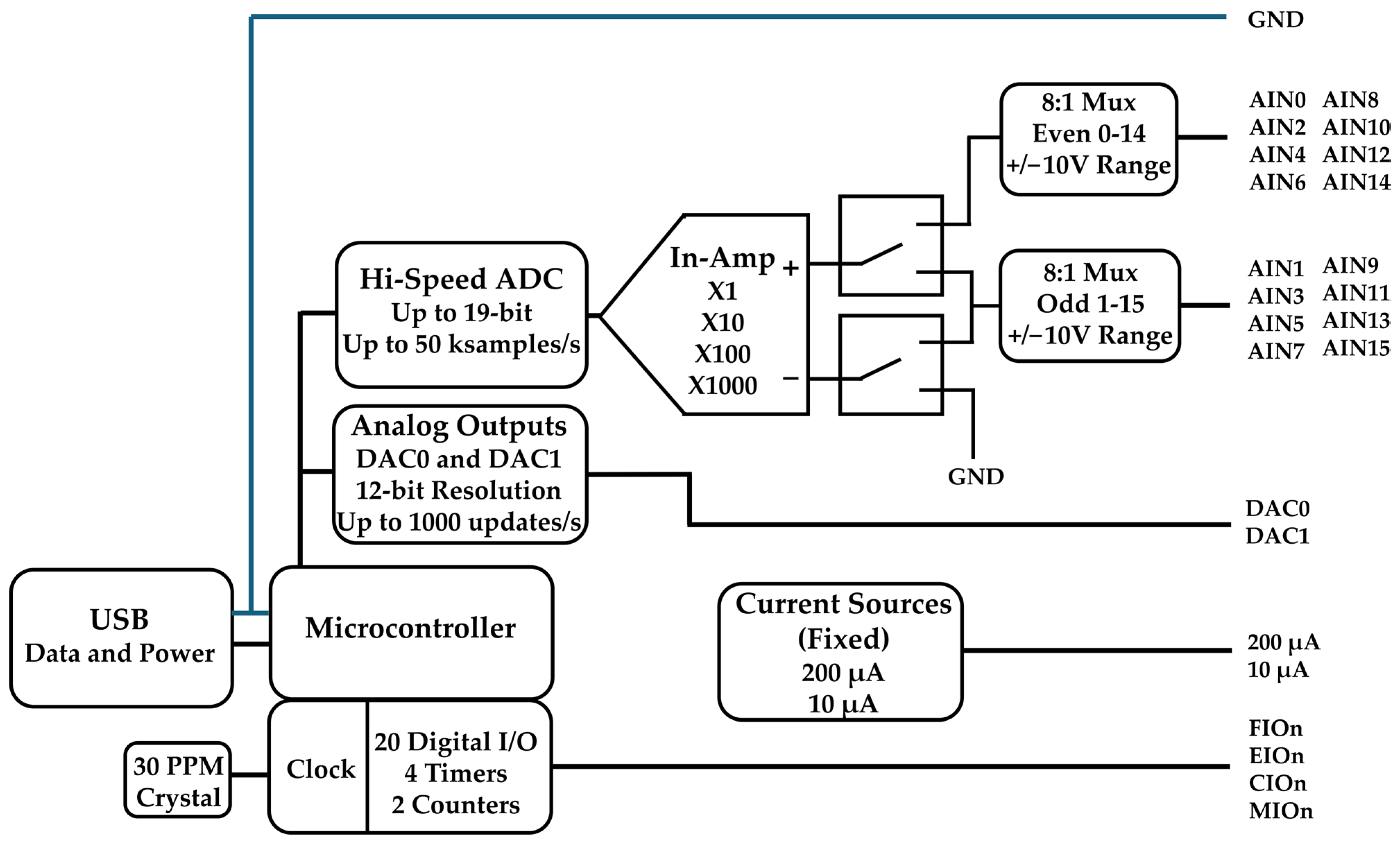
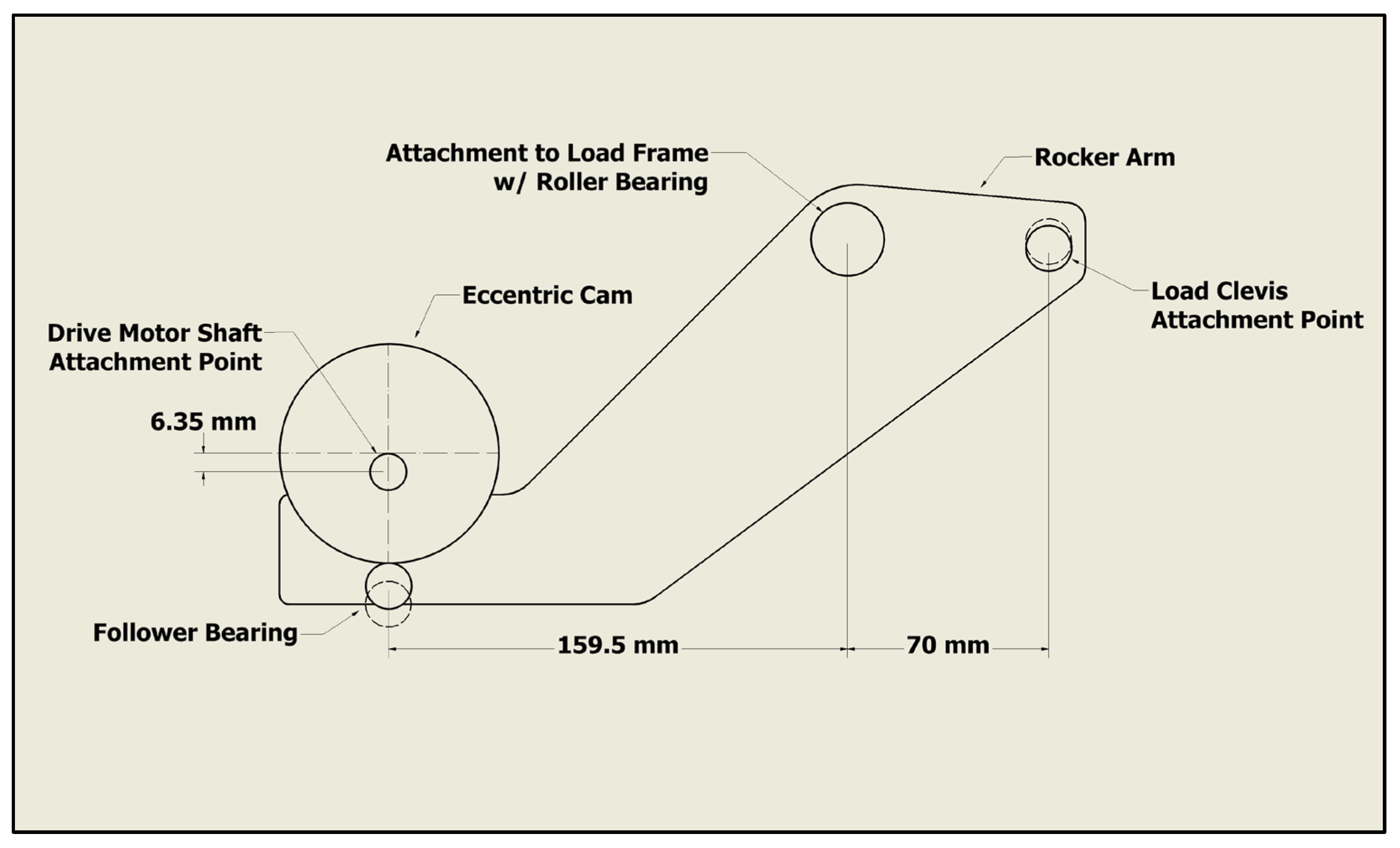
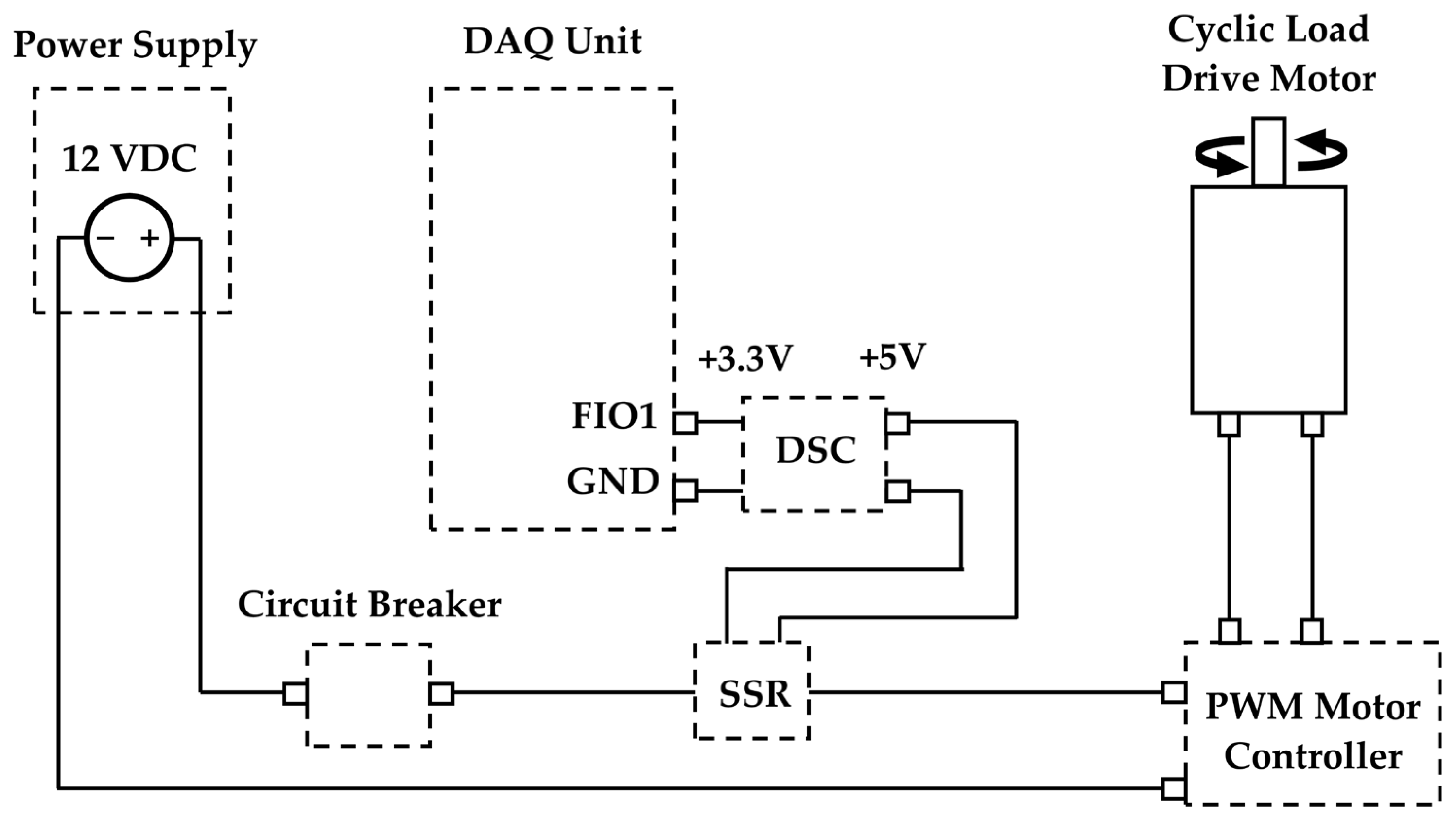
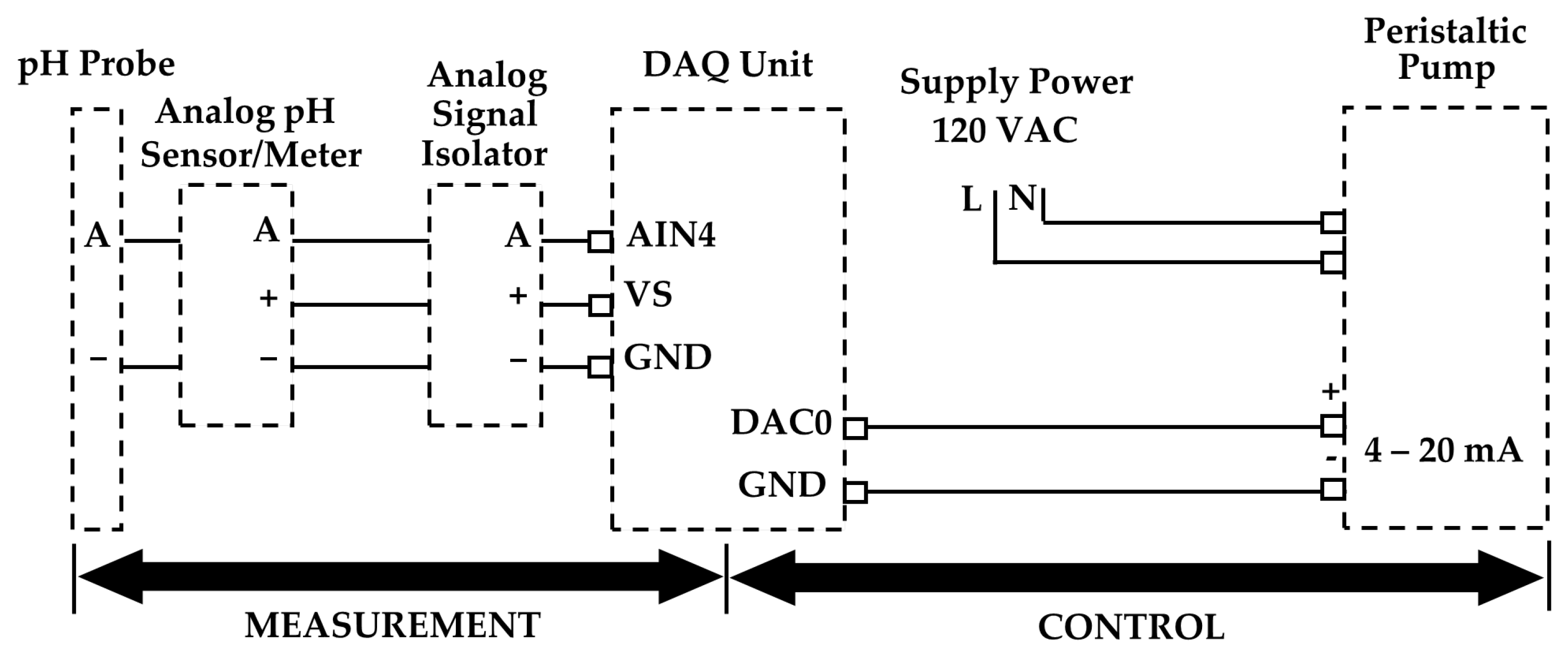
2.3. Test System and Instrumentation
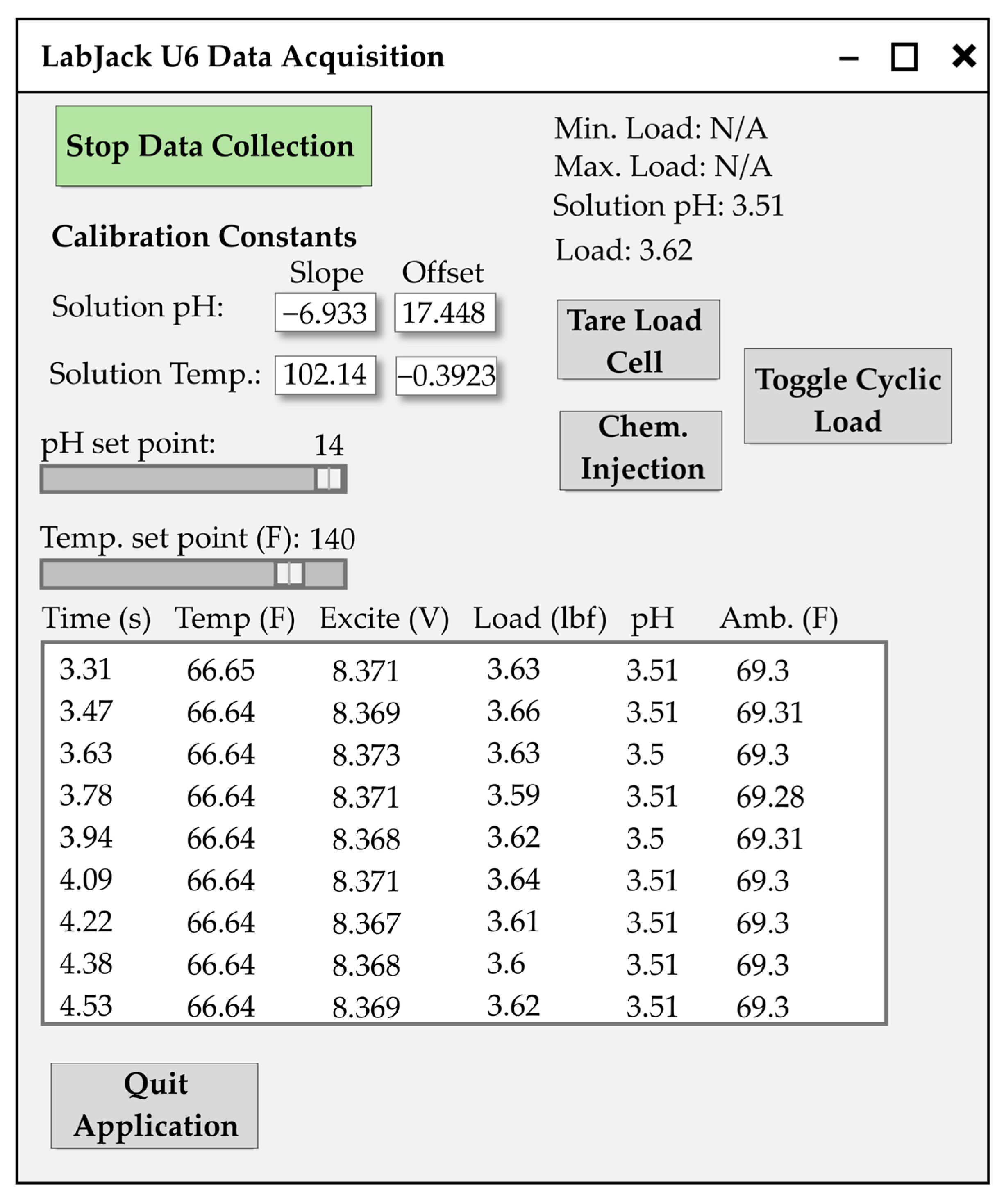
- Start/stop data collection toggle command button;
- pH and temperature calibration constant input fields;
- Tare load cell command button;
- Manual chemical injection command button;
- Temperature set point input slider;
- Visual streaming data collection window;
- Data collected is written to a text file;
- Quit application command button.
2.4. Compliance Calibration and Validation Technique
2.5. Test Procedure
3. Results and Discussion
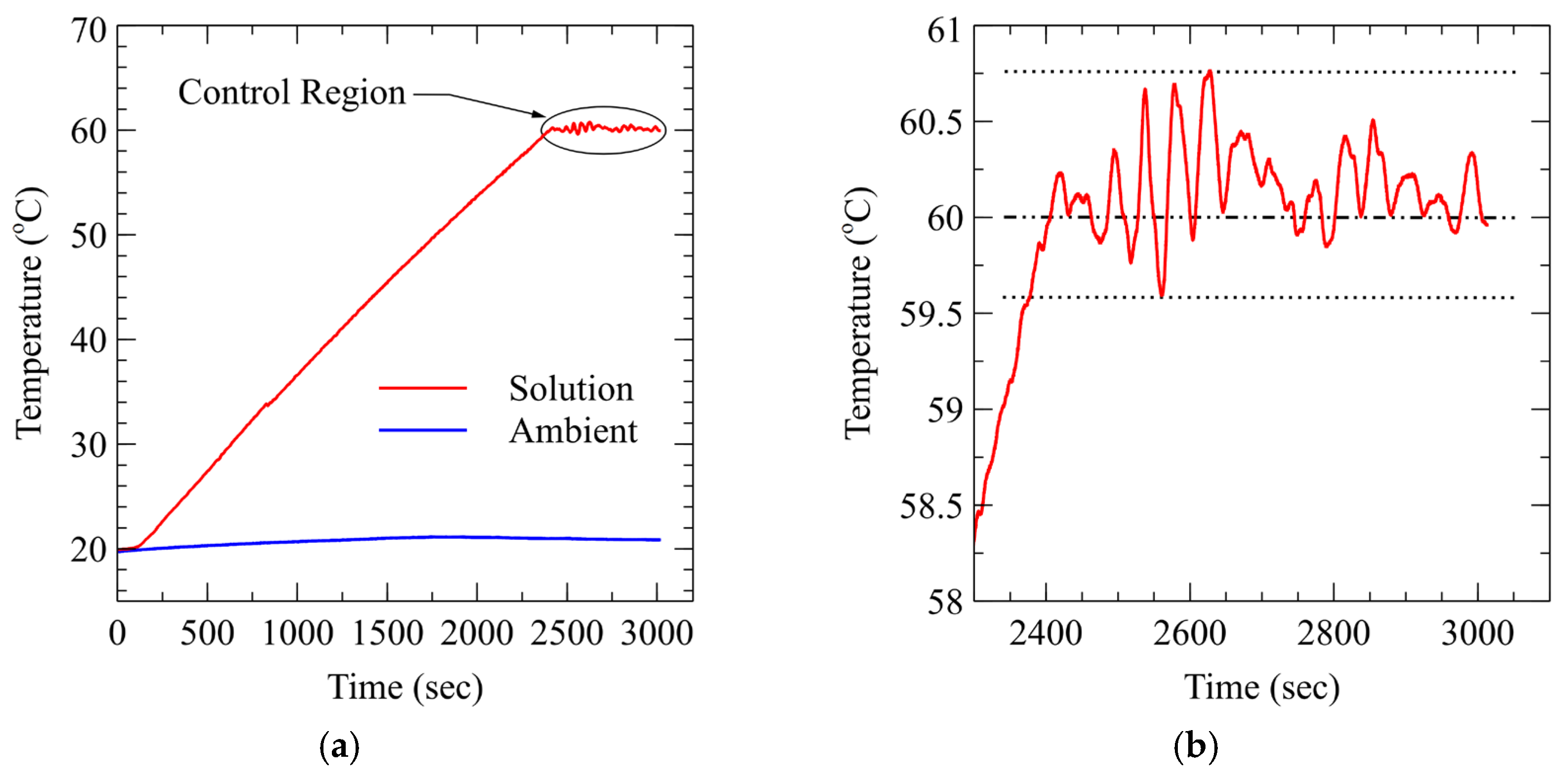
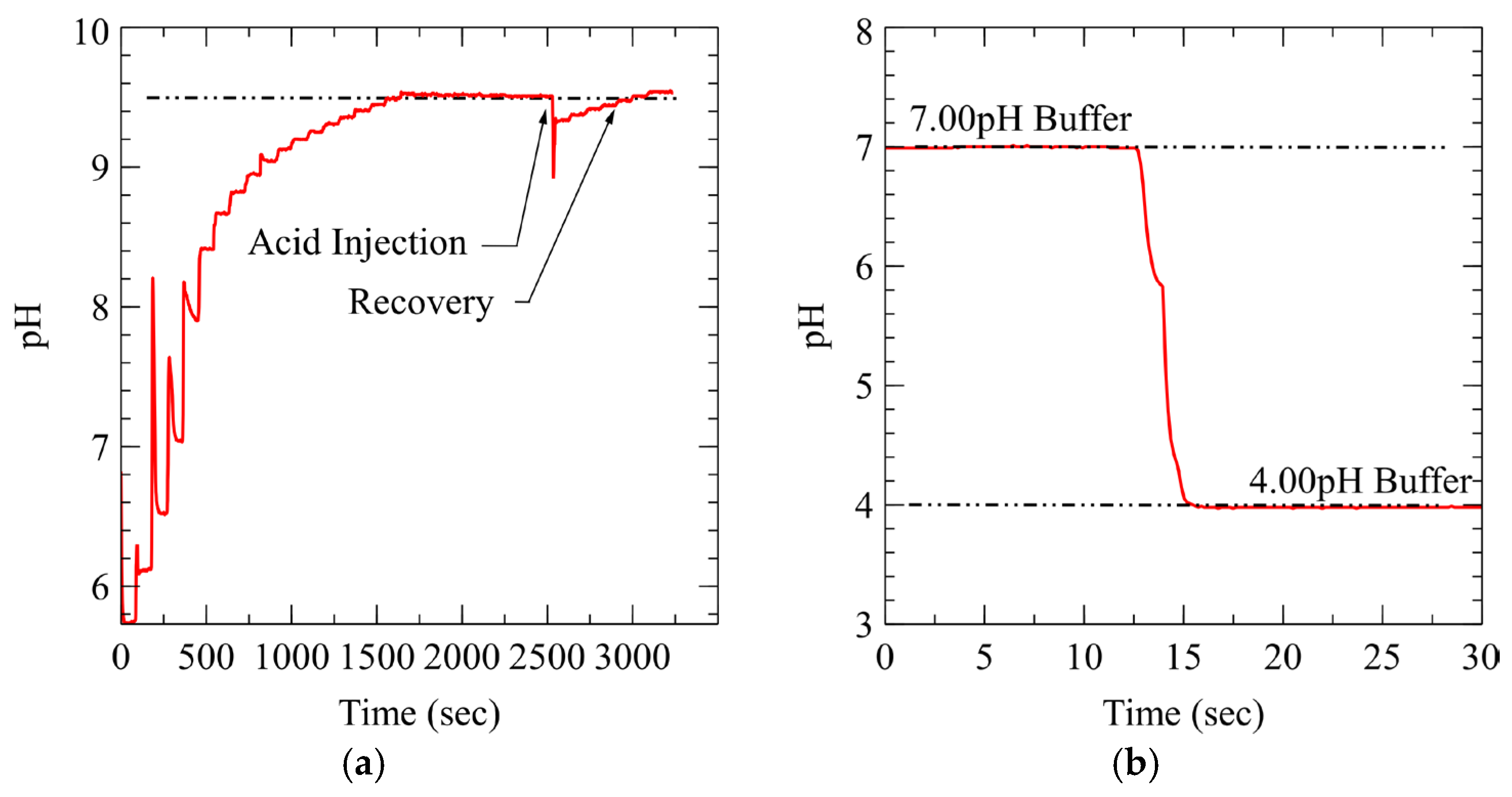
3.1. System Performance and Control Stability
3.1.1. Temperature Control Loop
3.1.2. pH Control Loop
3.2. Load Measurement and Signal Quality
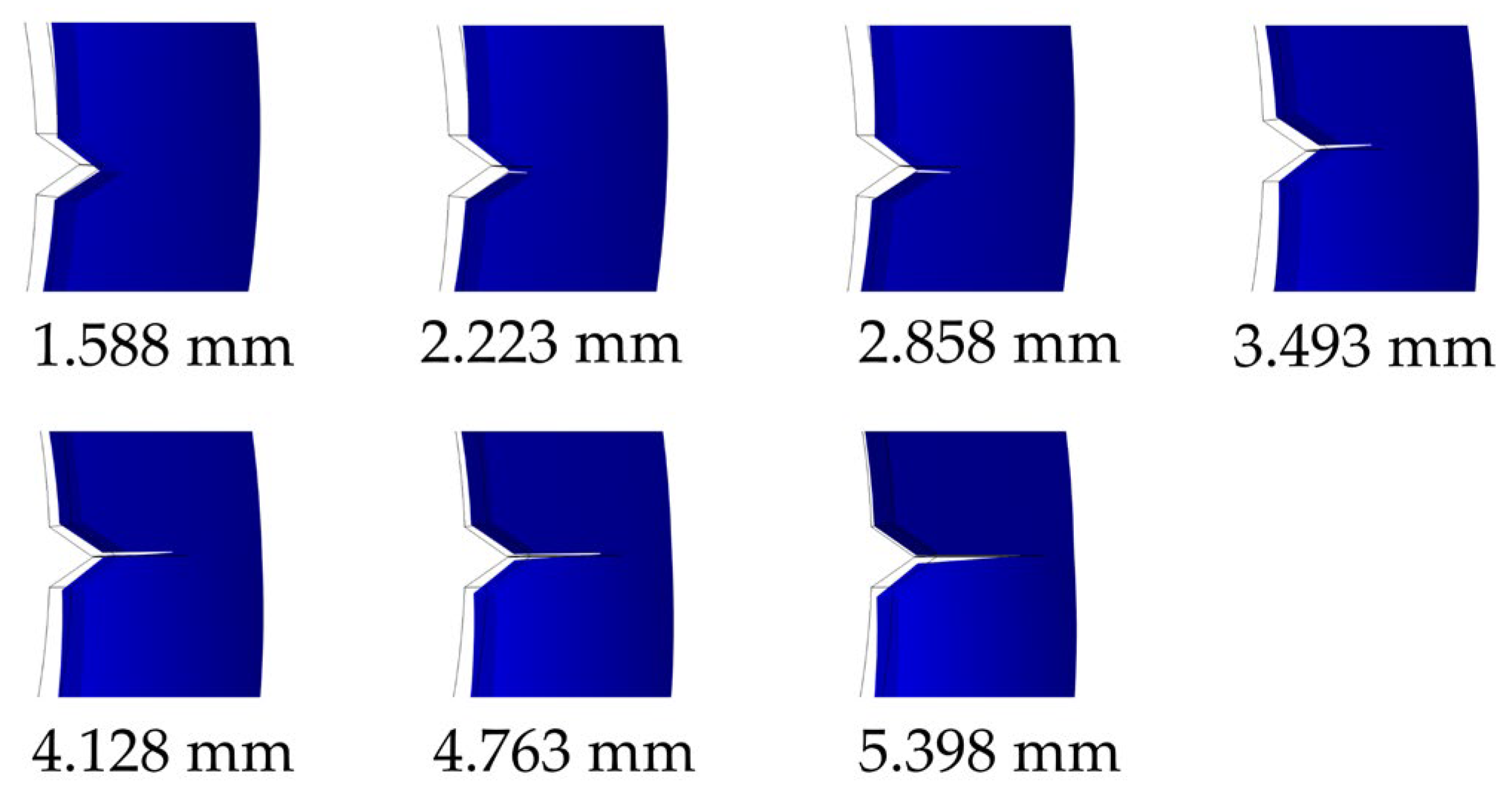
3.3. Compliance Calibration and Validation
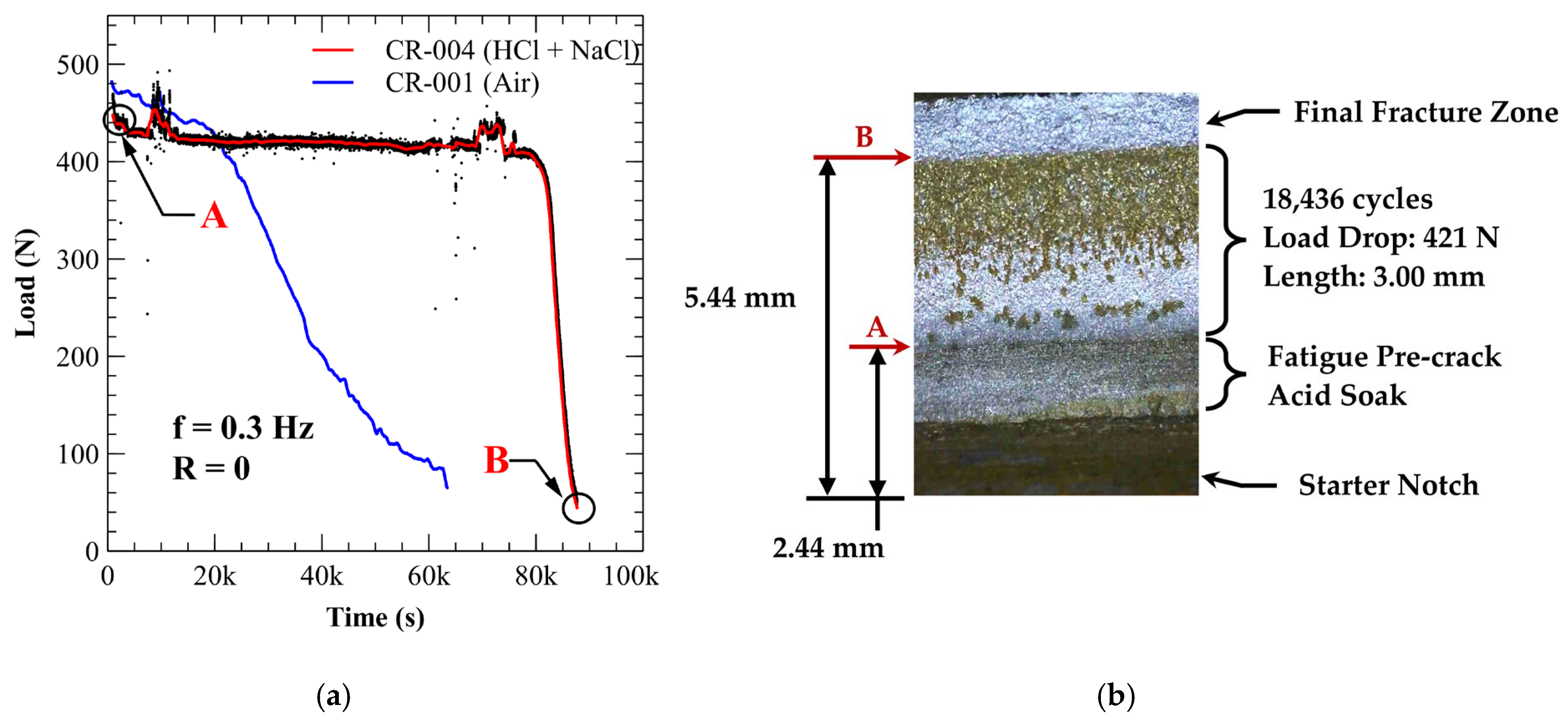
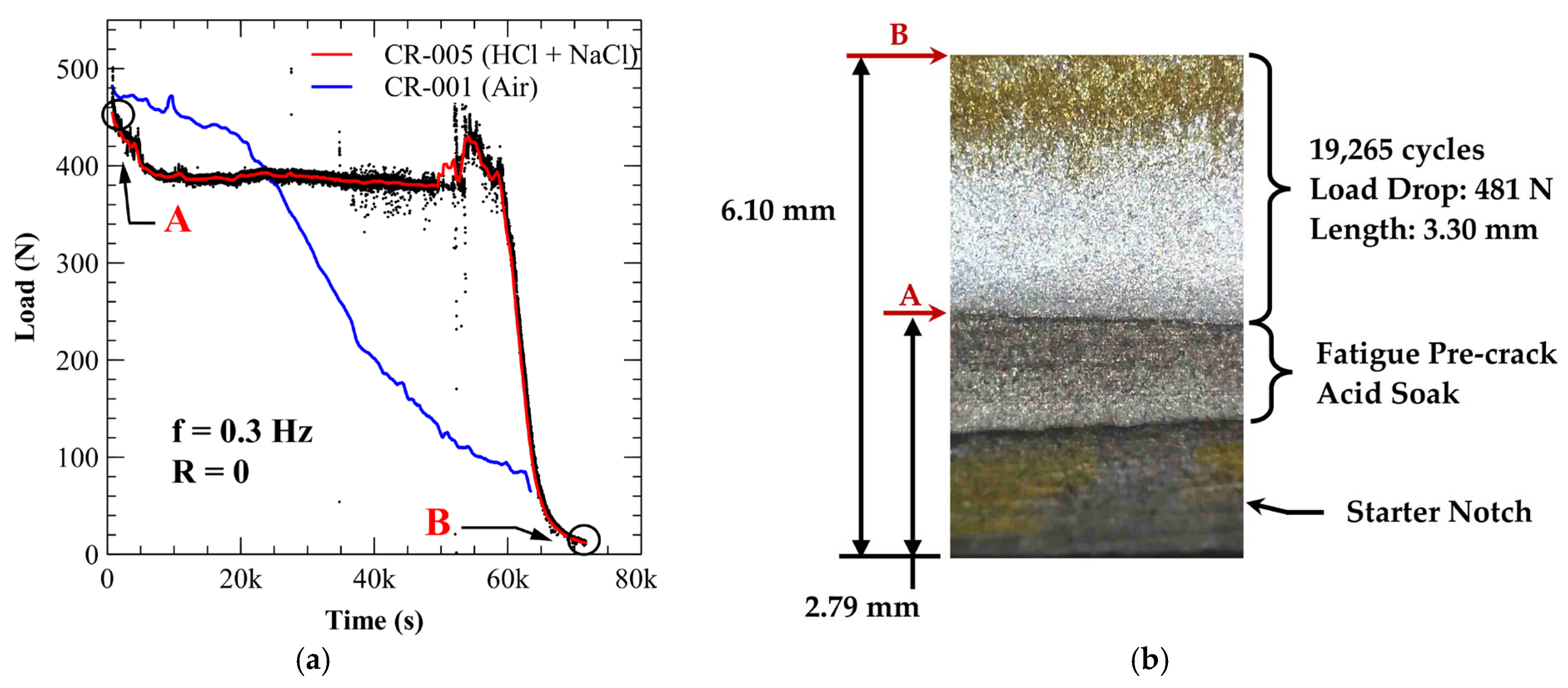
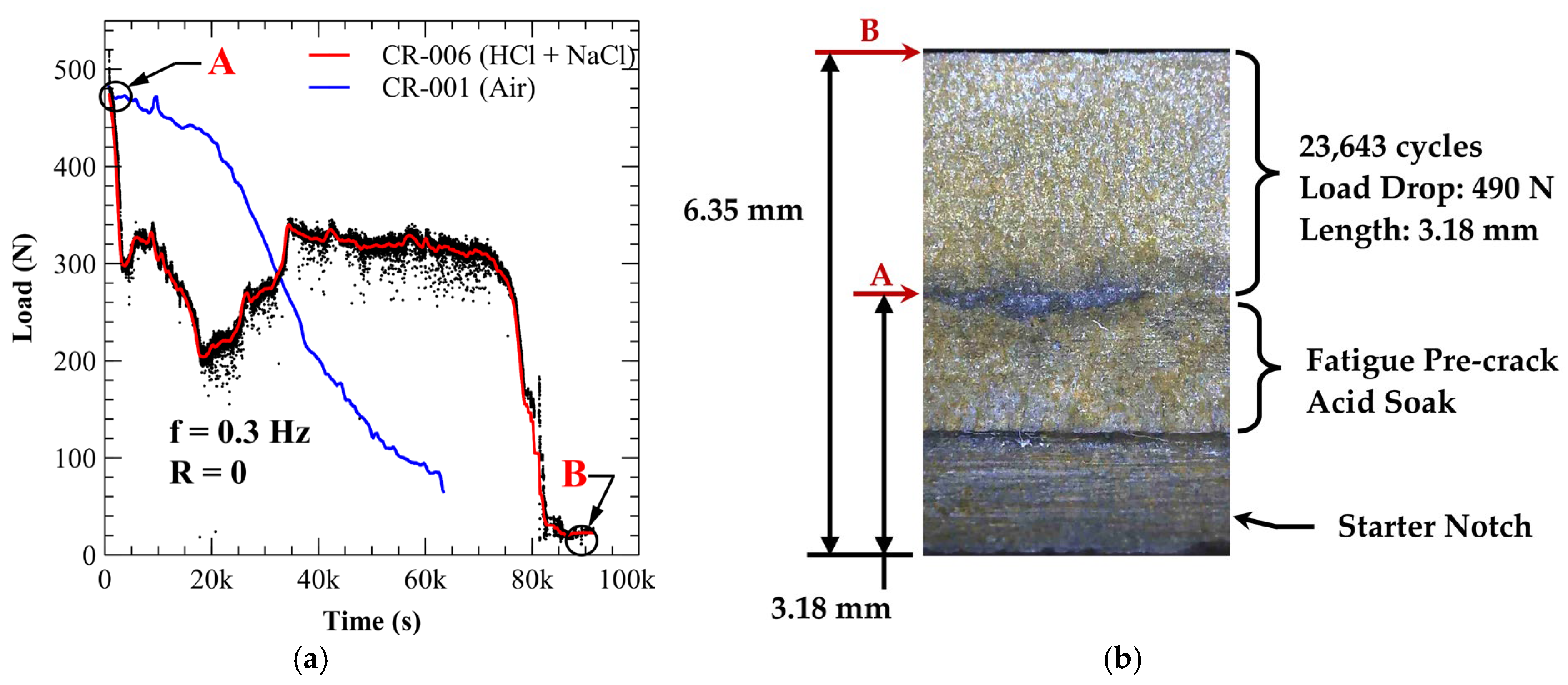
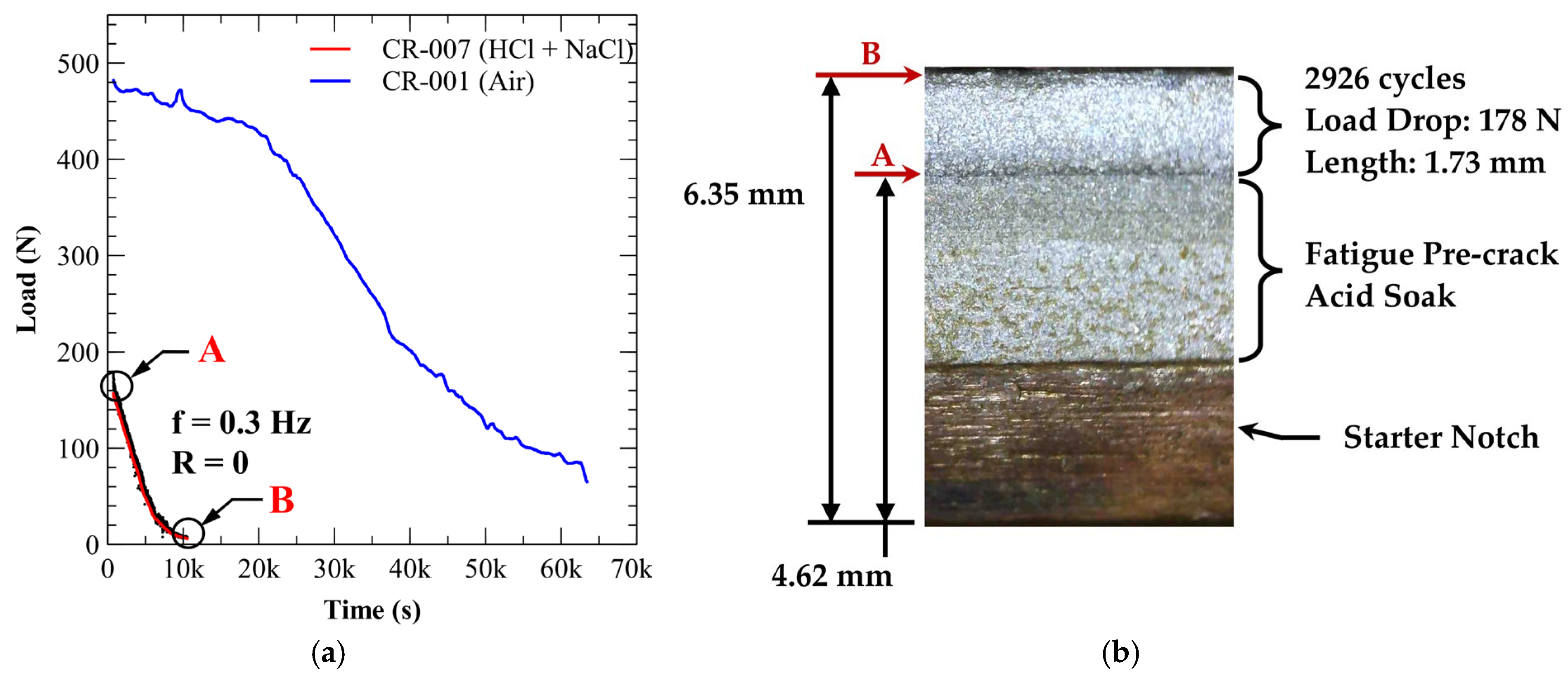
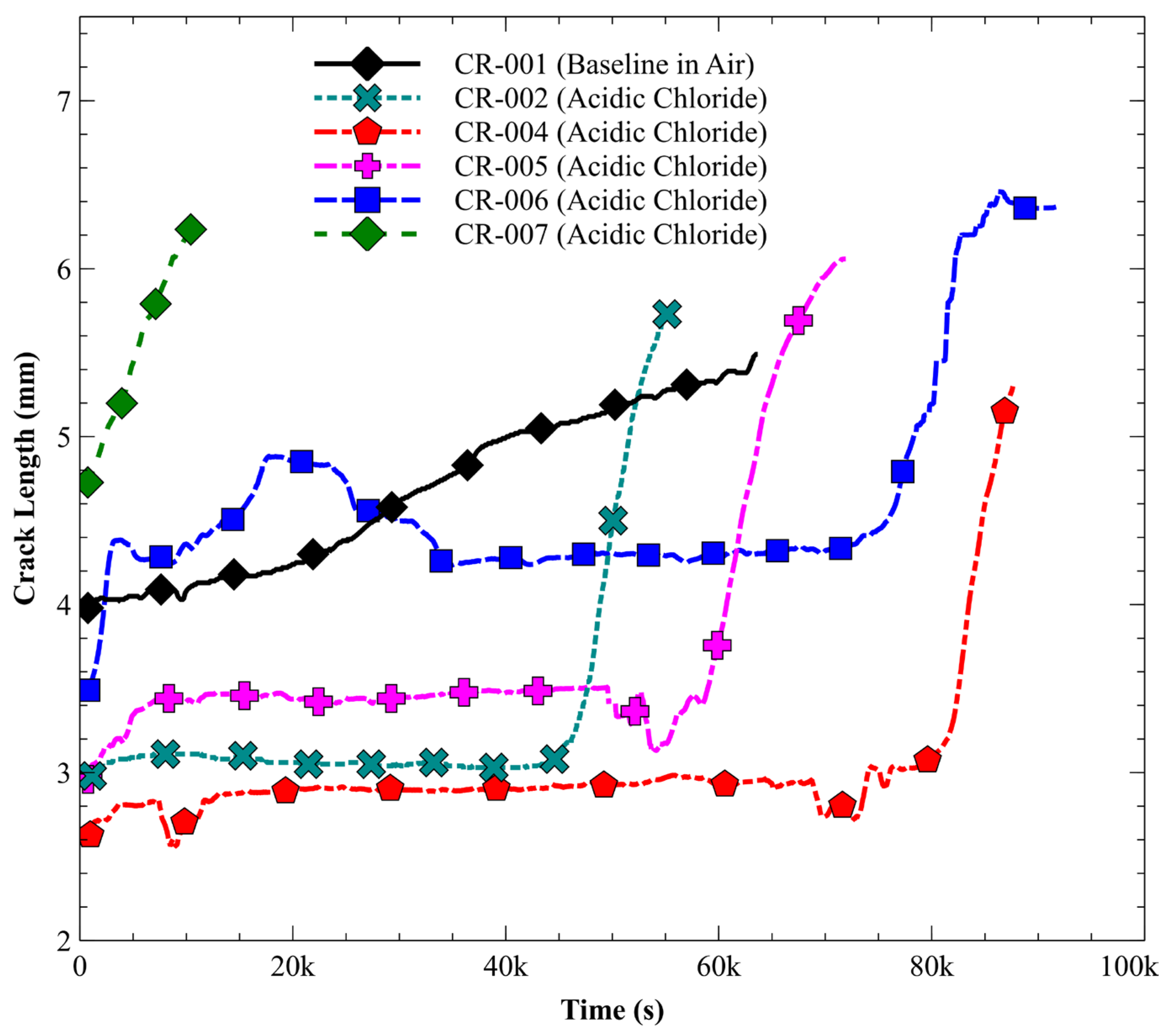
3.4. Environmentally Assisted Fatigue Crack Growth
3.4.1. A210-A1 Carbon Steel (Acidic Chloride Exposure)
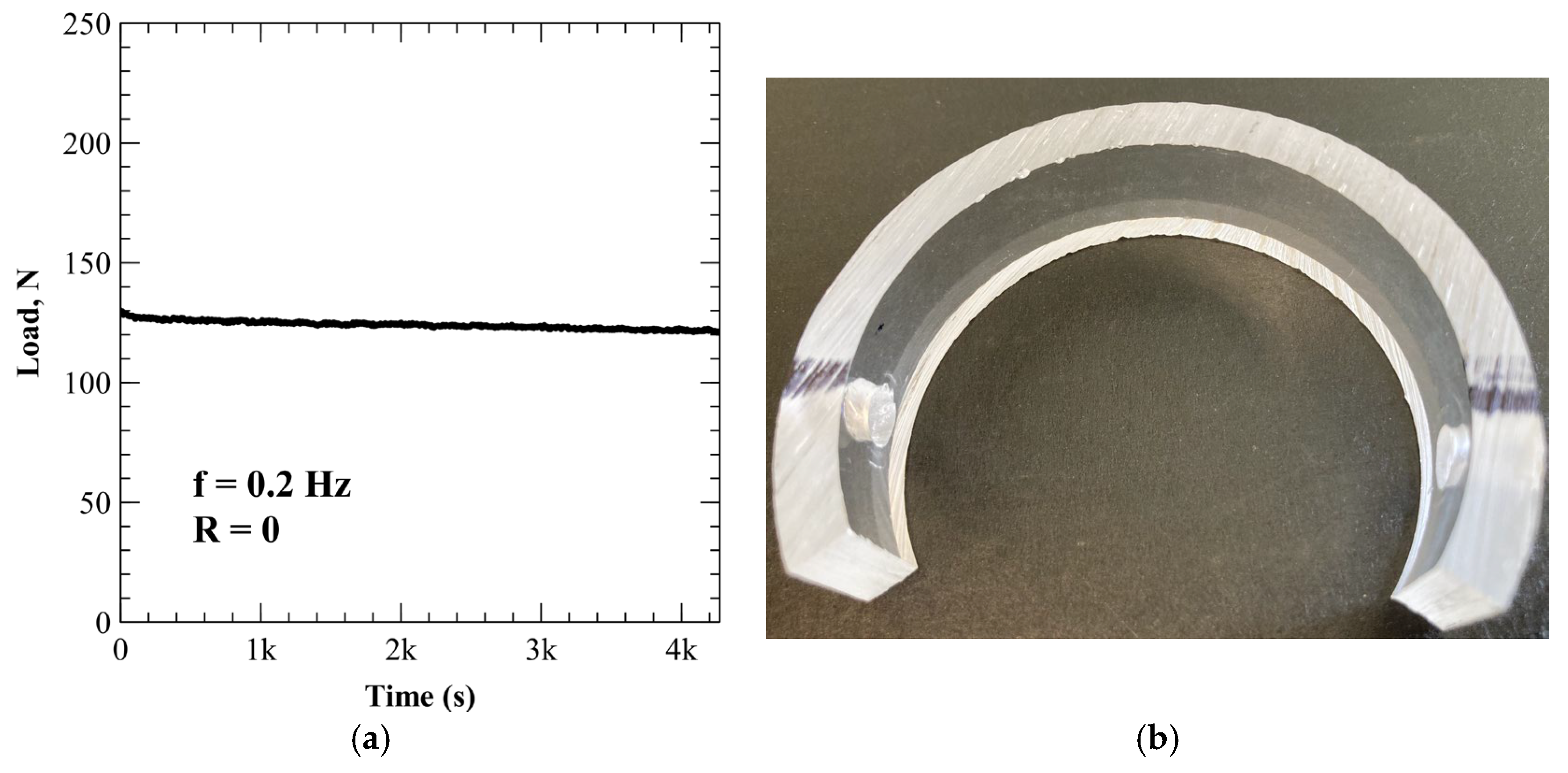
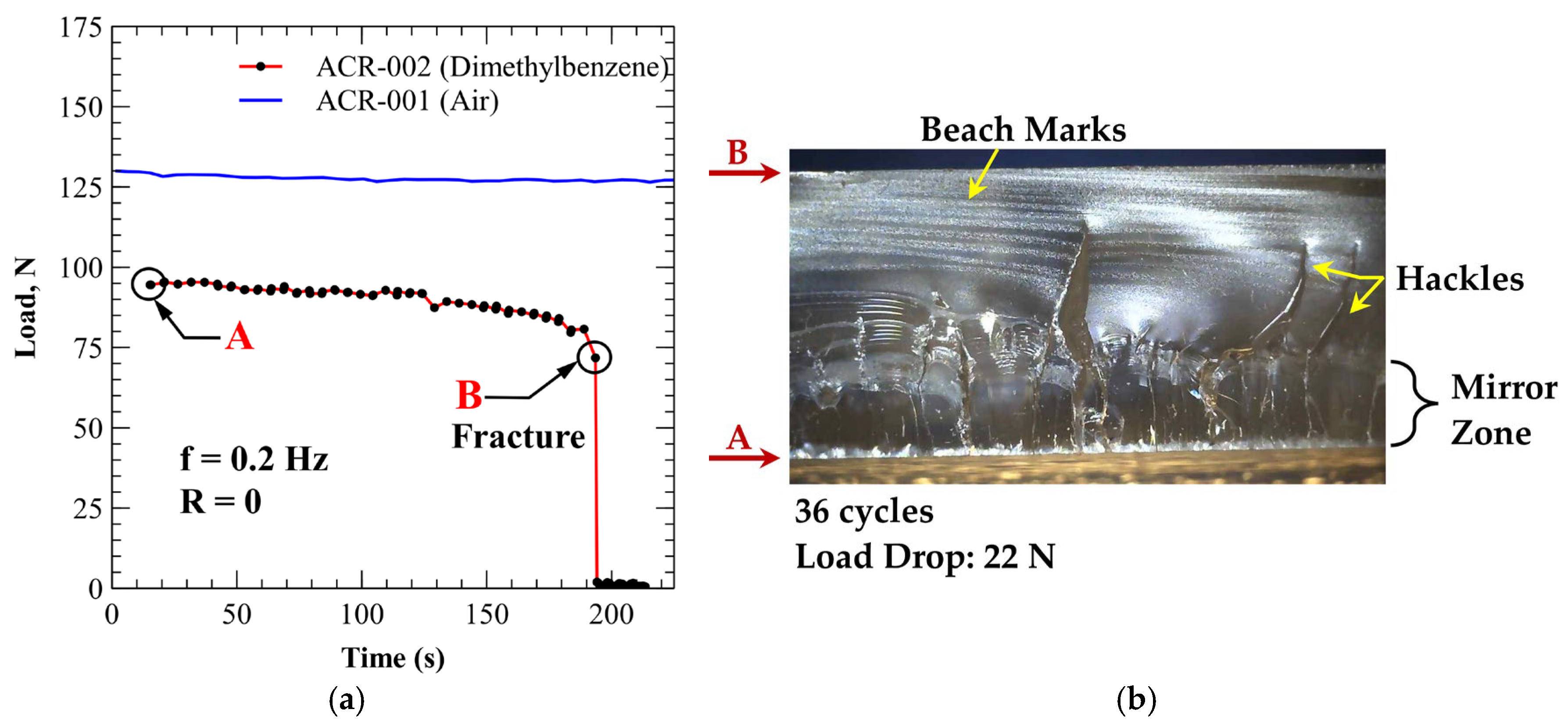
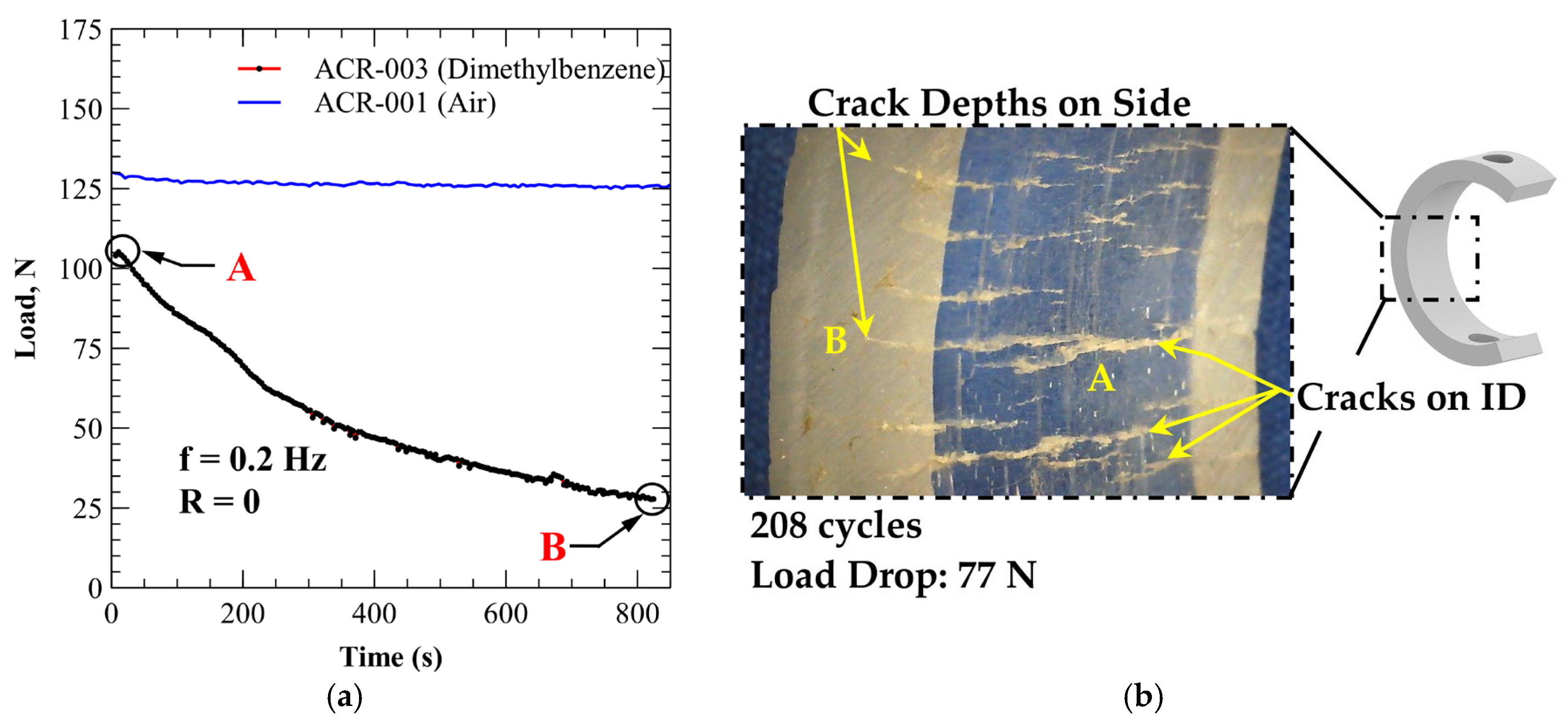
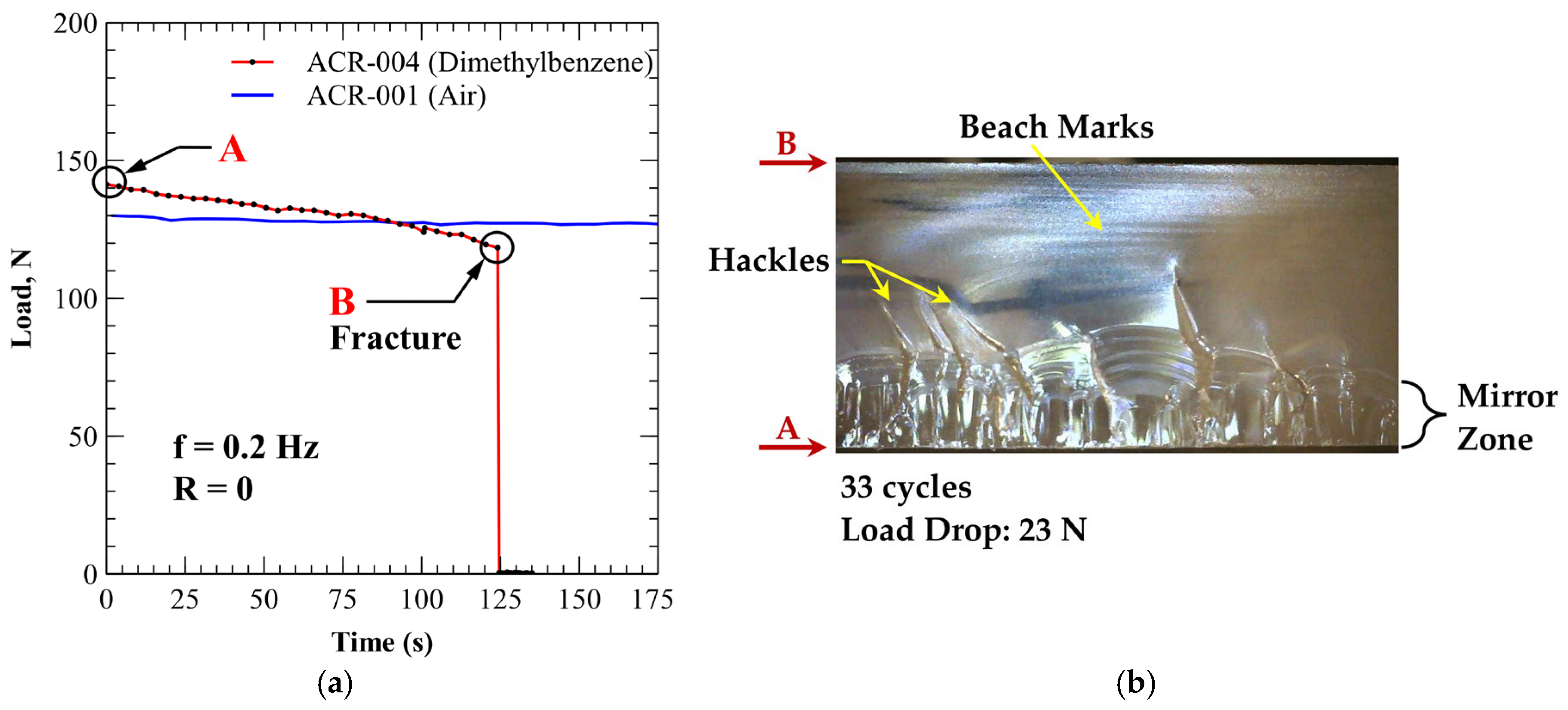
3.4.2. PMMA (Xylene Exposure)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, D. Principles and Prevention of Corrosion, 2nd ed.; Prentice-Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- API RP 571; Damage Mechanisms Affecting Fixed Equipment in the Refining Industry. 3rd ed. American Petroleum Institute: Washington, DC, USA, 2020.
- Stephens, R.; Fatemi, A.; Stephens, R.; Fuchs, H. Metal Fatigue in Engineering, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Shao, Y.; Gao, X.; Li, T.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, X. Corrosion Fatigue Crack Growth of Serviced API 5L X56 Submarine Pipeline. Ocean Eng. 2022, 256, 111502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, A.; Chen, N.-Z. An Extended Engineering Critical Assessment for Corrosion Fatigue of Subsea Pipeline Steels. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2018, 84, 262–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrosa, N.O.; Akid, R.; Ainsworth, R.A. Corrosion-Fatigue: A Review of Damage Tolerance Models. Int. Mater. Rev. 2018, 63, 283–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, J.; Wu, X.; Han, E.-H.; Yang, S.; Huang, P. Corrosion Fatigue Model of Austenitic Stainless Steels Used in Pressurized Water Reactor Nuclear Power Plants. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 541, 152407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Huang, M.; Wan, N.; Zhang, J. The Current Development of Structural Health Monitoring for Bridges: A Review. Buildings 2023, 13, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Kong, J.; Wang, H.; Huang, K.; Zhao, T.; Li, L. Multi-Scale Electromechanical Impedance-Based Bolt Loosening Identification Using Attention-Enhanced Parallel CNN. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Moutaouakil, H.; Heimann, J.; Lozano, D.; Memmolo, V.; Schütze, A. Feature Extractor for Damage Localization on Composite-Overwrapped Pressure Vessel Based on Signal Similarity Using Ultrasonic Guided Waves. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethichandra, D.M.G.; Suntharavadivel, T.G.; Kalutara, P.; Piyathilaka, L.; Izhar, U. Influence of Smart Sensors on Structural Health Monitoring Systems and Future Asset Management Practices. Sensors 2023, 23, 8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G38-01; Standard Practice for Making and Using c-Ring Stress-Corrosion Test Specimens. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Wheeler, R.W.; Ronevich, J.; San Marchi, C.; Grimmer, P.; Emery, J.M. Development of C-Ring Geometry to Explore Fatigue Crack Extension and Verification in High-Pressure Vessels. In Proceedings of the ASME 2022 Pressure Vessels & Piping Conference, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 17–22 July 2022; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Elber, W. Fatigue Crack Closure under Cyclic Tension. Eng. Fract. Mech. 1970, 2, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh, S.; Zamiski, G.F.; Ritchie, D.R.O. Oxide-Induced Crack Closure: An Explanation for Near-Threshold Corrosion Fatigue Crack Growth Behavior. Metall. Trans. A 1981, 12, 1435–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliday, M.D.; Beevers, C.J. Non-Closure of Cracks and Fatigue Crack Growth in β Heat Treated Ti-6A1-4V. Int. J. Fract. 1979, 15, R27–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbogen, E. Martensitic Transformation at a Propagating Crack. Acta Metall. 1978, 26, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.K.; Clayton, J.Q.; Clark, G. Retardation and Repair of Fatigue Cracks by Adhesive Infiltration. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 1997, 20, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Cardenas, H. Fatigue Crack Arrest in Mild Steel via Iron Electroplating. Mater. Sci. Appl. 2021, 12, 484–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur-Rehman, A.; Thomason, P.F. The Effect of Artificial Fatigue-Crack Closure on Fatigue-Crack Growth. Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 1993, 16, 1081–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.S.; Sheu, B.C.; Chou, H.H. Deposition of Plating Metals to Improve Crack Growth Life. Int. J. Fatigue 2001, 23, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z. Principles of Corrosion Engineering and Corrosion Control; Elsevier: Burlington, MA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Schlick, S.; Kruczała, K. ESR and ESR Imaging Methods for the Study of Oxidative Polymer Degradation. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2008, 53, 499–524. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, J.A.; Cardenas, H.E. Corrosion Behavior of Fe-Ni Electrodeposited Coatings in Weak Ammonium Hydroxide Solution. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2025, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5436-15R20; Standard Specification for Cast Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Plastic Rods, Tubes, and Shapes. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2020.
- Yang, X.; Wang, X.; Tang, Y. The Chemical Recovery of PMMA into Monomer. Chem.–Eur. J. 2025, 31, e202404030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E399-12; Standard Test Method for Linear-Elastic Plane-Strain Fracture Toughness Kic of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- LabJack U6 Datasheet. Available online: https://support.labjack.com/docs/u6-datasheet (accessed on 24 May 2025).
- Ravikumar, A.; Rostron, P.; Vahdati, N.; Shiryayev, O. Parametric Study of the Corrosion of API-5L-X65 QT Steel Using Potentiostat Based Measurements in a Flow Loop. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, Z.; Xing, L.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, P.; Yu, Z.; Xu, D. Corrosion Monitoring Techniques in Subcritical and Supercritical Water Environments. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, T.L. Fracture Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Samide, A.; Tutunaru, B.; Negrila, C.; Trandafir, I.; Maxut, A. Effect of Sulfacetamide on the Composi-Tion of Corrosion Products Formed onto Carbon Steel Surface in Hydrochloric Acid. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2011, 6, 663–673. [Google Scholar]
- Refait, P.; Grolleau, A.-M.; Jeannin, M.; Rémazeilles, C.; Sabot, R. Corrosion of Carbon Steel in Marine Environments: Role of the Corrosion Product Layer. Corros. Mater. Degrad. 2020, 1, 198–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, C.; Abdelmoula, M.; Naille, S.; Renard, A.; Khare, V.; Ona-Nguema, G.; Morin, G.; Génin, J.-M.R. Oxidation Modes and Thermodynamics of FeII–III Oxyhydroxycarbonate Green Rust: Dissolution–Precipitation versus in Situ Deprotonation. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 953–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohmoto, H. Nonredox Transformations of Magnetite-Hematite in Hydrothermal Systems. Econ. Geol. 2003, 98, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Carter, E.A. Ab Initio DFT + U Predictions of Tensile Properties of Iron Oxides. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 6703–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidaka, Y.; Anraku, T.; Otsuka, N. Deformation of Iron Oxides upon Tensile Tests at 600–1250 °C. Oxid. Met. 2003, 59, 97–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balafas, I.; Burgoyne, C.J. Modeling the Structural Effects of Rust in Concrete Cover. J. Eng. Mech. 2011, 137, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittel, D. An Investigation of the Heat Generated during Cyclic Loading of Two Glassy Polymers. Part I: Experimental. Mech. Mater. 2000, 32, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, I.; Williams, J.G.; Burns, D.J. Fatigue and Cyclic Thermal Softening of Thermoplastics. J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 1970, 12, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.D.; Edwards, D.B.; Shah, A.R. Fractography Basics. In Fractography in Failure Analysis of Polymers; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2015; pp. 48–92. [Google Scholar]



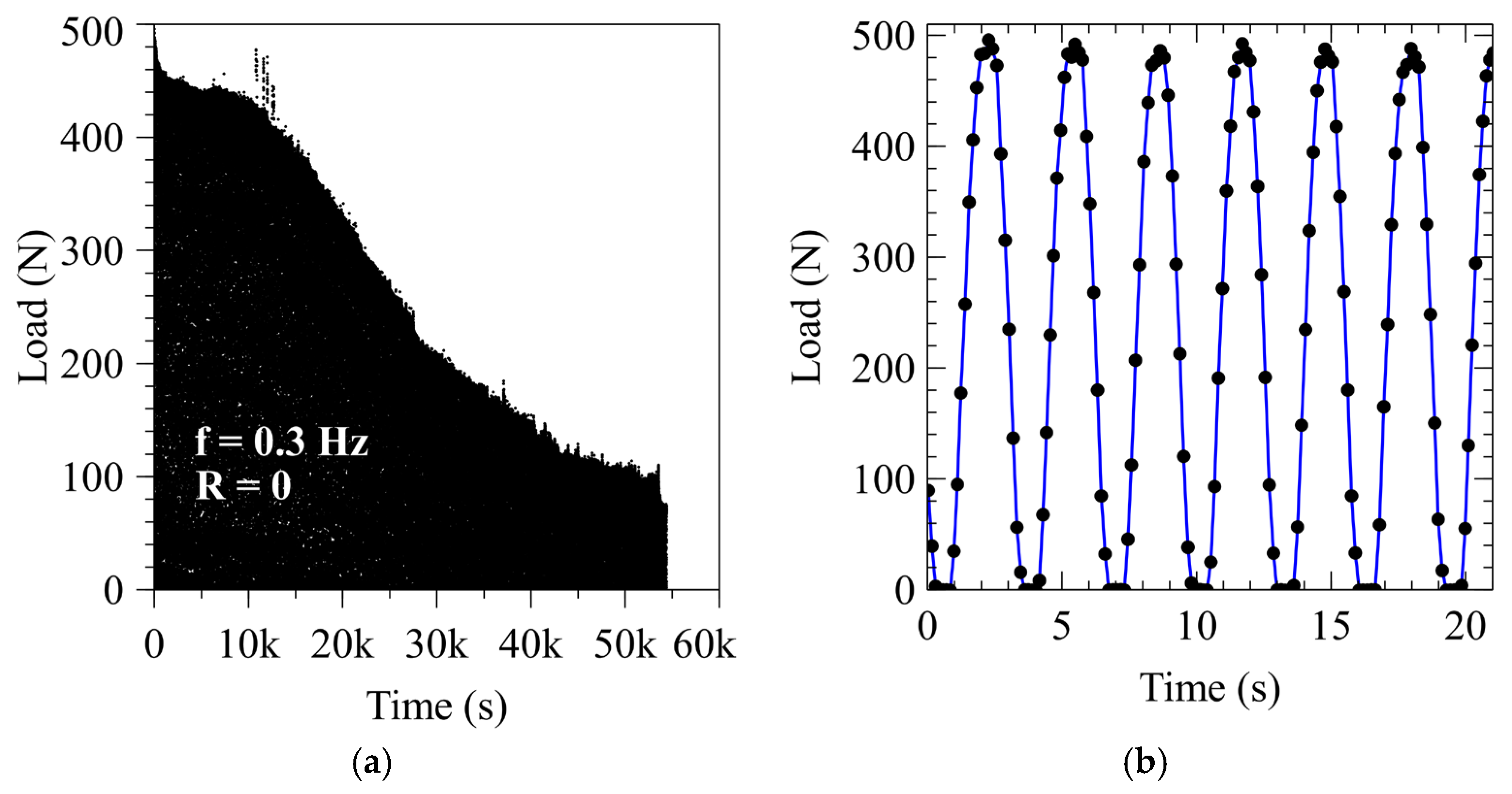
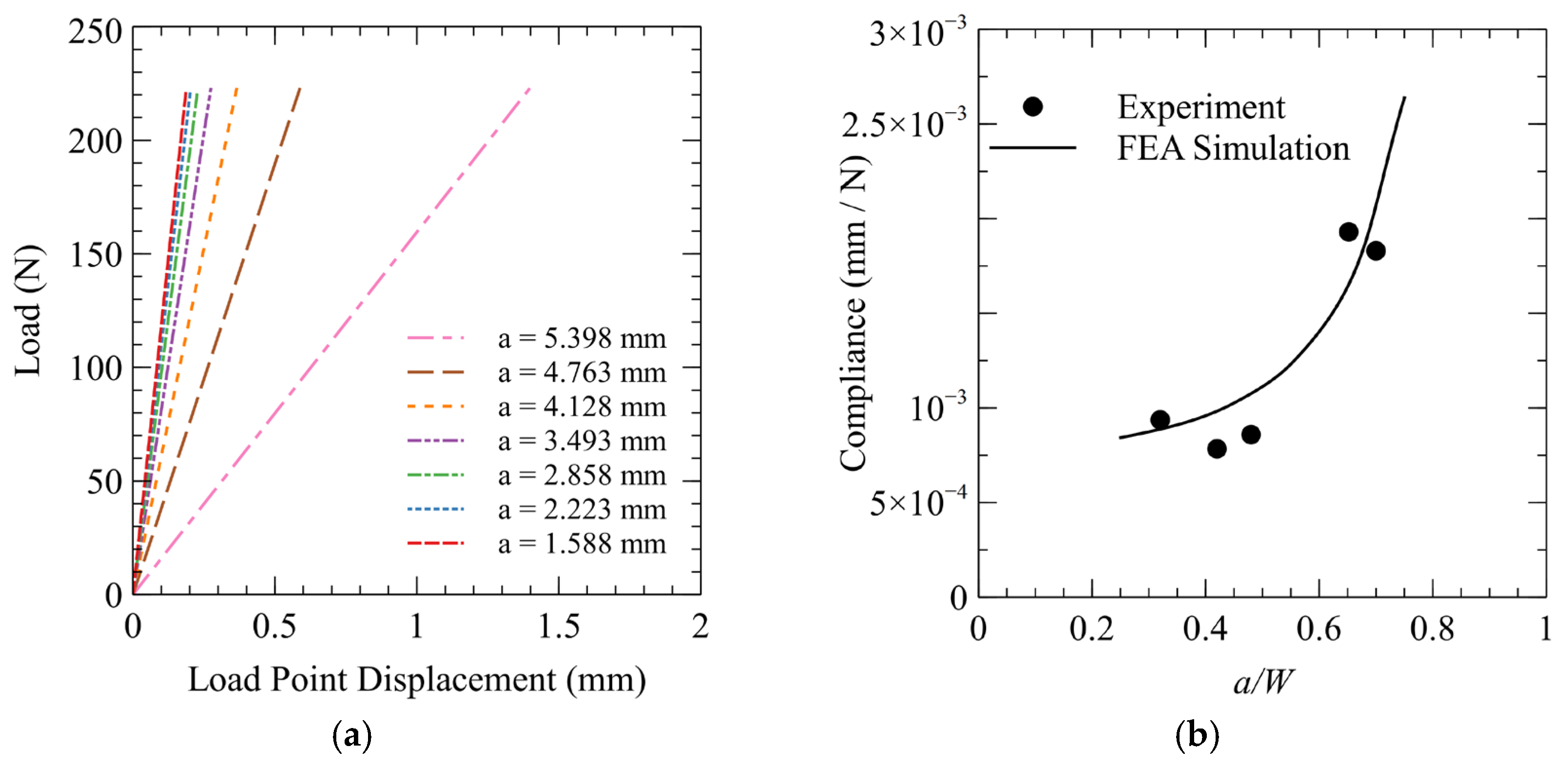
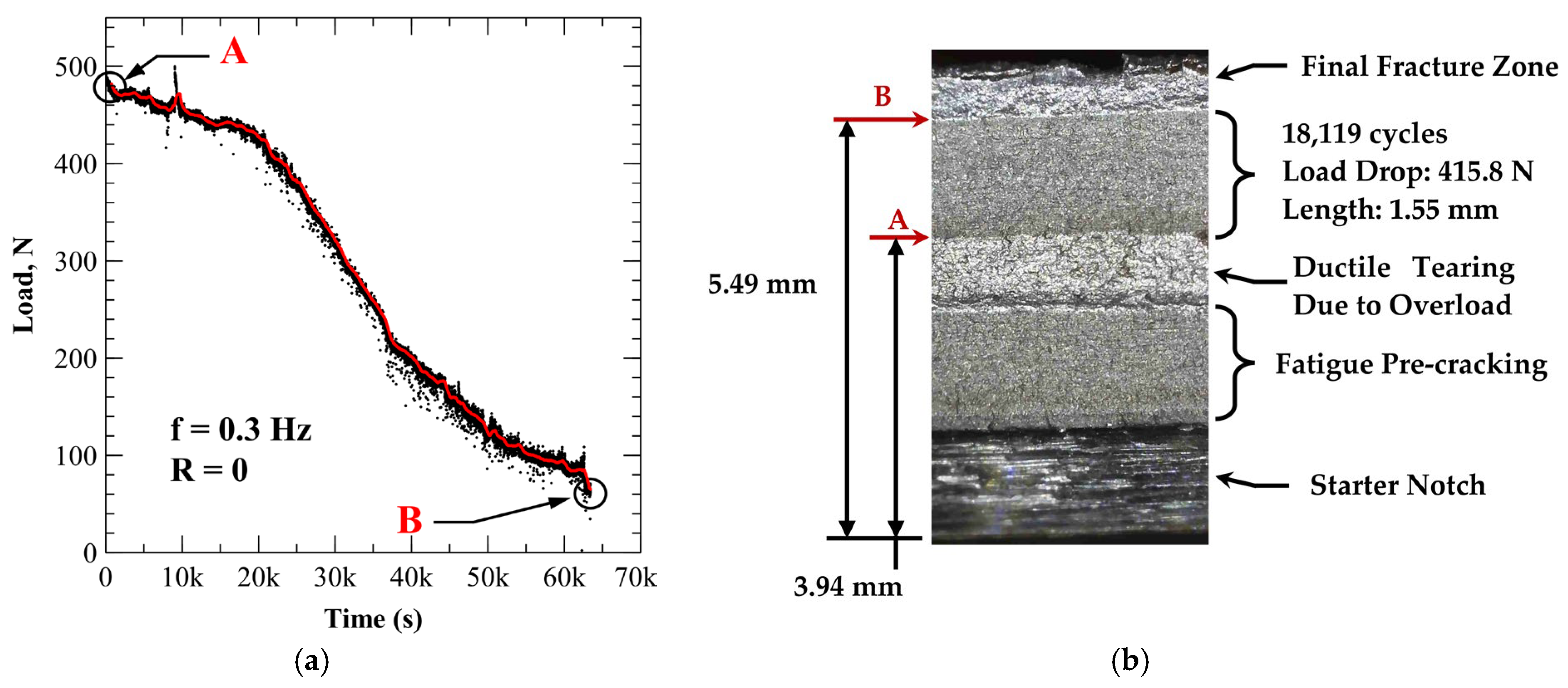
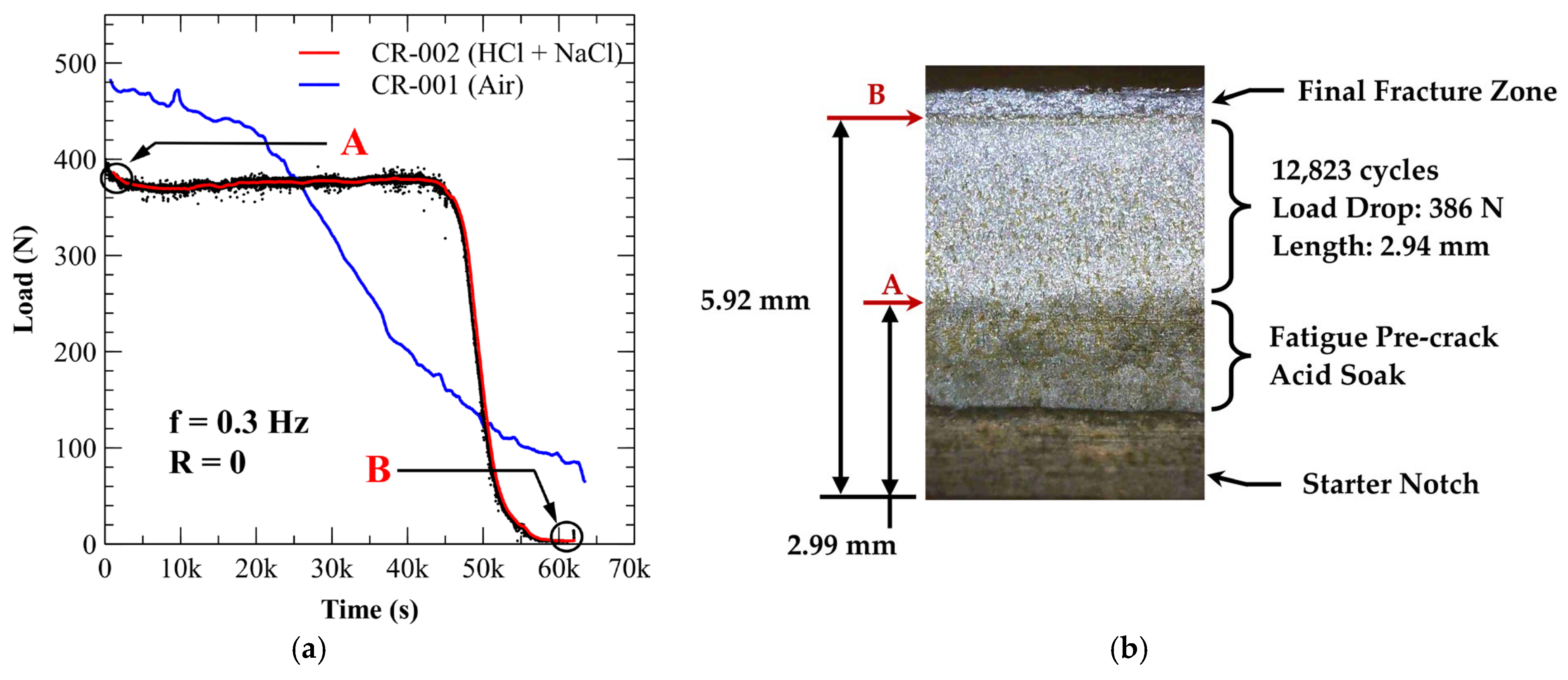
| Carbon (Max) | Manganese (Max) | Phosphorus (Max) | Sulfur (Max) | Silicon (Min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.27 | 0.93 | 0.035 | 0.035 | 0.10 |
| Property | PMMA | SA-210-A1 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength, min, MPa | 55 | 415 |
| Yield Strength, min, MPa | - | 255 |
| Elongation, min, % | 2 (at break) | 30 (in 50 mm) |
| Pin No. | Pin Name | Pin No. | Pin Name | Pin No. | Pin Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | GND 1 | 14 | AIN9 | 27 | Vs |
| 2 | 200 µA | 15 | AIN7 | 28 | Vm+ |
| 3 | FIO6 | 16 | AIN5 | 29 | DAC1 |
| 4 | FIO4 | 17 | AIN3 1 | 30 | GND |
| 5 | FIO2 | 18 | AIN1 1 | 31 | AIN12 |
| 6 | FIO0 1 | 19 | GND | 32 | AIN10 |
| 7 | MI01/CI01 | 20 | 10 µA | 33 | AIN8 |
| 8 | GND | 21 | FIO7 | 34 | AIN6 |
| 9 | Vm- | 22 | FIO5 | 35 | AIN4 1 |
| 10 | GND 1 | 23 | FIO3 | 36 | AIN2 1 |
| 11 | DAC0 1 | 24 | FIO1 1 | 37 | AIN0 1 |
| 12 | AIN13 | 25 | MIO0/CIO0 | ||
| 13 | AIN11 | 26 | MIO2/CIO2 |
| Channel | Description | Signal 1 | Type 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AIN0 | Solution temperature | AI | Single-ended |
| AIN1 | Load cell excitation voltage | AI | Single-ended |
| AIN2−AIN3 | Load cell bridge | AI | Differential |
| AIN4 | Solution pH | AI | Single-ended |
| AIN14 | Ambient temperature | AI | Single-ended |
| DAC0 | Metering pump for chem. injection | AO | Single-ended |
| FIO0 | Heater relay | DO | NA |
| FIO1 | Load cycle motor relay | DO | NA |
| Input (N) | Output (N) | % Error |
|---|---|---|
| 3.78 | 3.78 | 0.00 |
| 92.30 | 92.57 | 0.29 |
| 180.82 | 181.35 | 0.30 |
| 269.34 | 270.14 | 0.30 |
| Specimen * | Environment | Load Drop (N) | Crack Growth (mm) | Total Cycles | Delay Cycles | Avg. Crack Growth Rate (mm/cycle) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CR-001 | Open air | 416 | 1.55 | 18,119 | 0 | 8.55 × 10−5 |
| CR-002 | Acidic Chloride | 386 | 2.94 | 12,833 | 9475 | 8.76 × 10−4 |
| CR-004 | Acidic Chloride | 421 | 3.00 | 18,436 | 14,986 | 8.70 × 10−4 |
| CR-005 | Acidic Chloride | 481 | 3.30 | 19,265 | 15,042 | 7.81 × 10−4 |
| CR-006 | Acidic Chloride | 490 | 3.18 | 23,643 | 19,890 | 8.48 × 10−4 |
| CR-007 | Acidic Chloride | 178 | 1.73 | 2926 | 0 | 5.91 × 10−4 |
| Specimen | Environment | Load Drop (N) | Total Cycles | Avg. Load Drop Rate (N/cycle) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACR-001 | Open air | 9 | 855 | 0.01 |
| ACR-002 | Xylene (100%) | 22 | 36 | 0.61 |
| ACR-003 | Xyl/ethanol (1:1) | 77 | 208 | 0.37 |
| ACR-004 | Xylene (100%) | 23 | 33 | 0.69 |
| ACR-005 | Xyl/ethanol (1:1) | 121 | 637 | 0.19 |
| ACR-006 | Xyl/ethanol (1:1) | 128 | 433 | 0.30 |
| ACR-007 | Xylene (100%) | 36 | 116 | 0.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hudson, J.A.; Alam, S.; Cardenas, H.E. Automated Testing System for Environmentally Assisted Fatigue Crack Propagation with Compliance-Based Crack Monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810252
Hudson JA, Alam S, Cardenas HE. Automated Testing System for Environmentally Assisted Fatigue Crack Propagation with Compliance-Based Crack Monitoring. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):10252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHudson, Joel Andrew, Shaurav Alam, and Henry E. Cardenas. 2025. "Automated Testing System for Environmentally Assisted Fatigue Crack Propagation with Compliance-Based Crack Monitoring" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 10252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810252
APA StyleHudson, J. A., Alam, S., & Cardenas, H. E. (2025). Automated Testing System for Environmentally Assisted Fatigue Crack Propagation with Compliance-Based Crack Monitoring. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 10252. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810252






