Abstract
Clear aligners are increasingly used as an alternative to fixed appliances in orthognathic surgery, particularly for skeletal Class III malocclusions. This scoping review aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of clear aligners in the pre- and postoperative phases of surgical treatment and was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR) guidelines. Electronic searches were conducted in PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and OpenGrey. Data extraction considered study design, country, sample characteristics, surgical protocol, orthodontic biomechanics, use of auxiliaries, and cephalometric outcomes. Seven studies published between 2020 and 2024 were included. They involved 120 adult patients treated with Invisalign® combined with Le Fort I osteotomy and bilateral sagittal split osteotomy. All studies reported skeletal improvements, particularly in ANB angle and Wits appraisal, with maintenance of vertical dimensions. Clear aligners facilitated presurgical dental decompensation, torque control, and postsurgical occlusal refinement, with auxiliaries and digital tools enhancing predictability. Despite variability in protocols and limited long-term follow-up, outcomes were comparable to those achieved with fixed appliances. Current evidence supports the clinical viability of integrating clear aligners into orthognathic surgery, although standardized protocols and further high-quality prospective studies are needed to confirm long-term stability.
1. Introduction
Orthognathic surgery represents a foundational element in the correction of dentofacial skeletal discrepancies, having evolved into a reliable solution for restoring functional occlusion, facial aesthetics, and in some cases, airway management. The functional, aesthetic, and psychosocial impact of skeletal Class III malocclusion is well documented, with significant consequences on quality of life and social interactions [1]. Historically, its development followed parallel lines with facial trauma management, with osteotomies emerging as elective procedures based on fracture patterns described by Le Fort and refined by surgeons such as Obwegeser and Bell [2,3]. The incorporation of rigid fixation techniques in the 1980s and distraction osteogenesis in the 1990s significantly enhanced surgical predictability, while the 21st century has ushered in the digital era, characterized by three-dimensional planning and patient-specific devices [2]. Principles of craniofacial growth and surgical-orthodontic timing remain essential to understanding treatment planning, as outlined in classical orthodontic literature [3,4]
The therapeutic decision to recommend orthognathic surgery is based not only on the severity of skeletal imbalance but also on patient-specific considerations such as facial asymmetry, psychosocial factors, and the limitations of orthodontic camouflage. Class III skeletal patterns, significant Class II discrepancies, anterior open bite with vertical maxillary excess, and transversal discrepancies are among the most common indications [3]. Surgical intervention is typically delayed until after skeletal maturation, and its effectiveness relies heavily on interdisciplinary planning.
Traditionally, orthodontic preparation for surgery has relied on fixed appliances. This classic three-phase protocol—presurgical orthodontics, surgery, and postsurgical refinement—remains widely adopted and involves preoperative dental decompensation to unmask the true skeletal discrepancy [5]. Brackets and wires allow for precise control of root positioning and torque, and their use during and after surgery facilitates the application of intermaxillary fixation and occlusal settling. Despite their efficacy, fixed appliances are associated with prolonged treatment time, aesthetic concerns, and challenges in oral hygiene, which can negatively affect patient compliance [2,6].
In response to these limitations, clear aligner therapy (CAT) has gained increasing popularity, initially as an aesthetic alternative for mild malocclusions and more recently as part of comprehensive treatment protocols including orthognathic surgery. Introduced in 1997 by Align Technology, Invisalign® was the first commercially available aligner system that incorporated CAD/CAM technology. Recent evidence has demonstrated that clear aligners are effective in controlling certain types of tooth movement such as intrusion, distalization, and mild rotations, while showing lower accuracy in extrusion and complex root translation [2,5,7].
The use of aligners in presurgical orthodontics is now supported by digital planning tools, including virtual surgical planning (VSP), which allow for the integration of orthodontic objectives with osteotomy simulations [6,8]. Aligners provide improved patient comfort and aesthetics, and they can facilitate precise movements when properly staged. However, limitations in force application and reliance on patient compliance remain critical considerations. Moreover, in the postsurgical phase, aligners have been proposed as a valuable option for occlusal finishing, particularly when combined with CBCT-based superimpositions and guided planning [5,7].
Studies [5,6] have reported promising outcomes using clear aligners in the postsurgical setting, noting improvements in predictability and reduction in overall treatment duration when integrated within a digital workflow. Moreover, clear aligners have demonstrated high patient satisfaction and may contribute to improved long-term retention due to their removable nature and ability to serve as retainers [5,9].
Despite these advantages, concerns remain regarding the stability of outcomes, especially in skeletal Class III patients. Proffit [3] emphasized the risk of relapse due to mandibular growth or neuromuscular adaptation, highlighting the need for meticulous planning and long-term retention strategies. Zammit [2] further suggests that while digital planning and aligners offer unprecedented control and efficiency, they do not eliminate the biomechanical complexities of orthognathic cases. Therefore, the integration of clear aligners into orthognathic surgery represents a modern evolution of interdisciplinary care, enabled by technological advances but still anchored in fundamental biomechanical principles. As digital tools continue to evolve, clinicians must balance innovation with evidence-based practice, especially in cases requiring surgical intervention.
The aim of this scoping review is to evaluate the effectiveness of clear aligners in patients undergoing orthognathic surgery, focusing on their role in both presurgical and postsurgical orthodontic phases. Particular attention will be given to the predictability of tooth movements, long-term stability, and overall efficiency of treatment compared to conventional fixed appliances.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
This scoping review was conducted following the “Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyzes extension for conducting Scoping Reviews” PRISMA-ScR [10]. This scoping review was registered on the Open Science Framework platform and is available at the following link https://osf.io/jr6mf/.
2.2. Search Strategy
A comprehensive search strategy was designed, and the following online databases were recruited for the search: Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, PubMed, and the Cochrane Library. A search strategy was implemented on 16 June 2025. Additionally, a search was conducted with grey literature on OpenGrey. The search strategy designed for each database is shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Search Strategy.
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
Inclusion and exclusion criteria were established according to the PICO frame-work, defined in Table 2.

Table 2.
Pico framework.
Eligible studies comprised randomized clinical trials (RCTs) and observational designs (retrospective or prospective) that included adult patients with completed dentition and craniofacial growth, diagnosed with Class III malocclusion, and investigated orthodontic–surgical treatment with clear aligners.
Studies were excluded if they involved a surgery-first approach, included patients with craniofacial syndromes, or were review articles, case reports, or studies conducted on animals (including in vivo and in vitro experimental models). Additionally, studies focusing on treatment with fixed appliances combined with orthognathic surgery were excluded. No restrictions were applied regarding language and time.
2.4. Data Collection
The review process initially involved screening the titles and abstracts. Then, the full text of the selected papers was assessed. Two different reviewers (FL, RS) independently conducted the process, discordant evaluations were resolved through a discussion with a third researcher (FBD).
The final decision on inclusion or exclusion criteria in the review was reached through consensus between all the authors. The full text of each study was retrieved and independently evaluated by two authors. After through discussion, the studies were categorized into the following classes: diagnosis, clinical implications, treatment, and prevention.
Duplicates were removed using Zotero and then manually verified. To assess the level of agreement among the reviewers, Cohen’s kappa [11] coefficient (K: 0.66) was calculated, indicating substantial agreement. Authors showed a substantial agreement (Cohen’s kappa: 0.66). After reviewing the full texts, studies were chosen for inclusion in the review according to the established inclusion and exclusion criteria. The following data were extracted from the selected studies: first author and year of publication, Country of origin, study design, sample characteristics (sex and age) and outcomes.
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search and Screening Process
A total of 2804 studies were initially identified: 596 from PubMed, 605 from Embase, 802 from Web of Science, 716 from Scopus and 85 from Cochrane. By removing duplicates, 1735 publications were excluded. From the remaining 1044 records, after reviewing the title and abstract, 987 studies were excluded. Afterwards, the full text of the remaining 57 studies was thoroughly examined; one study could not be retrieved. After assessment of the full text, 47 reports were excluded. Ultimately, 7 records met the inclusion criteria. The flowchart of the screening process according to the PRISMA statement is shown in Figure 1.
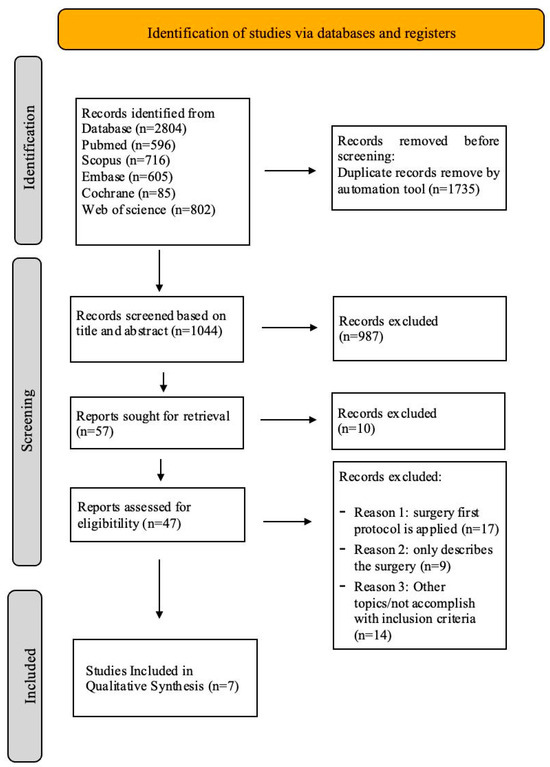
Figure 1.
PRISMA flowchart, flow diagram of the performed search.
3.2. Study Characteristics
A total of seven studies published between 2020 and 2024 were included in the review [12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. The studies involved patients with skeletal Class III malocclusion treated with a combination of clear aligners and orthognathic surgery. Five studies were retrospective [13,15,16,17,18] one prospective cohort study [12], and one randomized controlled trial [14].
The studies were conducted across various countries: two studies were from China [14,16], two were from Italy [12,13], one from France [17] and Vietnam [15] and one from Brazil [18], reflecting a diverse geographical representation.
Across the studies where patient demographics were specified, the total sample included 120 patients, with at least 30 males [13,14,17] and 22 females [13,14,17]. However, some studies did not specify sex distribution [12,15,16,18]. The average age of participants, where available, ranged from approximately 19 to 42 years, indicating that all patients were adults with completed craniofacial growth [14,17]. Five studies [12,13,15,16,18] did not provide information about the age range.
Overall, the included studies consistently reported positive clinical outcomes, emphasizing the effectiveness, predictability, and stability of clear aligner therapy in combination with orthognathic surgery for the correction of Class III malocclusions. The detailed description of results can be found in Table 3.

Table 3.
An overview of the included studies providing information on the experimental designs and settings.
3.3. Skeletal Class and Surgery
The surgical cephalometric values are detailed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Skeletal and Dental class, cephalometric changes and surgical approaches in the included studies.
All studies [12,13,14,15,16,17,18] included in this review involved patients with skeletal and dental Class III malocclusions, treated through a combination of clear aligners and orthognathic surgery. The most frequently performed surgical intervention was the Le Fort I osteotomy, often associated with bilateral sagittal split osteotomy (BSSO) for mandibular repositioning in more severe cases.
Cephalometric Values
Among the studies that reported cephalometric values, improvements in key sagittal parameters such as Wits appraisal and ANB angle were consistently observed following surgery. For instance, ref. [17] reported a substantial improvement in Wits from −12.85 mm pre-surgery to −5.25 mm post-surgery, and in ANB angle from −5.13° to 0.44°, indicating effective skeletal correction. Similarly, ref. [14] documented a Wits change from −8.62 mm to −0.47 mm and an ANB correction from −2.94° to 1.63°.
In [16], Wits improved from −6.5 mm to 0.39 mm, while the ANB angle shifted from −3.5° to 0.4°, with minimal change in the vertical dimension (FMA remained stable at ~27°). Study [15] also observed a comparable improvement, with Wits changing from −6.5 mm to 0.3 mm and ANB from −3.3° to +3.9° after surgery.
On the other hand, studies [12,13] did not report specific cephalometric values, although both confirmed the use of Le Fort I osteotomy as part of their surgical protocol. Study [16] provided ANB and MP–FH values but did not report Wits appraisal.
3.4. Summary of Clinical Studies on Clear Aligners
Table 5 presents a comparative overview of seven key studies investigating the use of clear aligners.

Table 5.
Orthodontic Protocols with clear aligners: Extractions, Attachments, and Auxiliaries.
3.4.1. Tip and Torque Measurements
Only three studies reported detailed measurements: studies [16,17] provided specific angular changes in upper and lower incisor inclination (U1–PP from 106.3° to 106.8°; BL torque from 3.0° to 5.9°) relative to anatomical planes, showing slight improvements post-treatment. Study [12] included statistical ranges, confirming minimal yet consistent improvements after clear aligner use, reflecting controlled anterior dental positioning in support of skeletal corrections.
3.4.2. Tooth Extraction
To facilitate decompensation or alignment, five studies included premolar and third molar extractions as part of their treatment protocols. Studies [12,14] reported extractions of both upper and lower premolars (teeth 14, 24, 34, and 44), likely to assist in molar distalization. Studies [13,17] extracted upper and lower third molars (wisdom teeth). Study [18] also reported performing extractions, although the specific teeth were not specified.
3.4.3. Types of Attachments
Regarding attachments, studies [13,17] reported the use of horizontal and ellipsoid attachments. Studies [15,18] highlighted the use of optimized and conventional rectangular attachments. Some studies did not specify the types of attachments employed, including [12,14,16].
3.4.4. Auxiliary Devices
Various auxiliaries were used across the studies to support the planned orthodontic treatment. Study [17] reported the use of Power Ridges to aid in torque control, while [16] employed TADs (temporary anchorage devices). Study [13] relied on buttons.
Other studies, such as [12,14,15,18], either did not report the use of auxiliaries or indicated their use on a case-by-case basis.
3.4.5. Aligner System
All studies used the Invisalign® system, emphasizing the growing role of digital clear aligner therapy even in complex surgical cases.
3.4.6. Elastics Use
Studies [14,15,16,18] explicitly reported the use of intermaxillary elastics, likely for postoperative settling or occlusal guidance. In contrast, studies [13,17] did not use elastics, possibly due to their surgical sequencing or reliance on other auxiliary anchorage methods. For [12], the use of elastics was not specified.
4. Discussion
This scoping review has mapped the available evidence on the integration of clear aligners with orthognathic surgery for the correction of skeletal Class III malocclusions. The synthesis of the seven included studies [12,13,14,15,16,17,18] highlighted several recurring patterns. Consistent skeletal correction in the sagittal plane, moderate but stable vertical control, and generally favorable dental decompensation were observed when aligners were used in combination with surgical protocols. Despite variability in biomechanical strategies—such as the use of extractions, attachments, elastics, and auxiliaries—the overall treatment objectives were consistently achieved. These findings suggest that clear aligners, when properly integrated into surgical workflows, can produce outcomes comparable to those historically obtained with fixed appliances, while remaining consistent with the fundamental principles of orthognathic surgery [4].
When compared with the broader literature, these results support and extend previous reviews and clinical reports on the effectiveness of aligners [5,9,19,20]. Vertical stability, reported in several studies, is consistent with the evidence presented in the studies [3,7], who emphasized the importance of controlled biomechanics in avoiding undesirable vertical changes. Such considerations are also aligned with fundamental principles of surgical planning and dimensional control in orthognathic surgery [4]. Similarly, torque control and incisor inclination reported in selected studies [16,17] reflect Zhou’s [1] observations regarding the use of auxiliaries, such as temporary anchorage devices (TADs) and Power Ridges, to optimize aligner biomechanics and ensure predictable tooth movements.
Another recurring theme is the growing adoption of digital workflows in orthognathic treatment. Several studies have reported the use of virtual surgical planning, AI-assisted treatment simulations, and 3D-printed surgical splints, indicating a profound transformation of conventional protocols [21,22,23,24]. Recent evidence reinforces this trend, showing that digital planning can improve surgical accuracy, reduce intraoperative variability, and enhance interdisciplinary coordination [8,25,26,27,28,29]. Notably Aziz [30] emphasized how the overlap between digital workflows and aligner biomechanics facilitates the smooth incorporation of aligners into orthognathic protocols, while Papageorgiou et al. [31] pointed out that the standardization of these digital approaches remains an urgent research priority.
Emerging clinical evidence also broadens the potential applications of aligners in particularly complex or high-risk populations. For instance, Meazzini et al. [32] demonstrated that clear aligners can be incorporated into multi-segmental maxillary surgery for patients with cleft lip and palate, achieving both functional and esthetic improvements. Similarly, Pagani et al. [33] reported favorable outcomes when using Invisalign® in combination with Class III surgical protocols, not only in the presurgical decompensation phase but also in postsurgical finishing, thereby emphasizing the dual role of aligners [34]. These findings are supported by preliminary clinical reports [35,36,37], suggesting that aligners may help reduce overall treatment duration, improve patient comfort, and increase compliance, especially in adult populations. Most recently, Chan et al. [29] published a scoping review consolidating these observations, confirming the growing role of aligner-assisted surgical protocols and identifying priority areas for future research. Interestingly, Muro et al. [38] arrived at similar conclusions regarding the general predictability of aligner therapy, highlighting consistent outcomes for sagittal corrections but more variability for vertical and torque-related movements.
In addition, Kwon et al. [39] proposed a structured multidisciplinary protocol for the management of orthognathic cases with clear aligners, reinforcing the importance of teamwork and highlighting that aligners can be fully integrated into interdisciplinary workflows. The question of long-term stability, however, remains critical: a systematic review by Inchingolo et al. [40] emphasized the risk of relapse after orthognathic surgery, underscoring the need for consistent biomechanical control and robust retention strategies when aligners are used in complex surgical cases. Similarly, the fast-track protocols discussed by Hwang and Cha [41] illustrate how surgical timing and sequencing can influence stability, providing useful parallels to aligner-assisted workflows where accelerated protocols may be increasingly adopted. Finally, the retrospective findings of Melsen and Allais [42] on the development of dehiscences during labial movement of mandibular incisors serve as an important reminder of the biological limits of tooth movement, which must be carefully respected in aligner-based surgical cases to avoid periodontal compromise. Simon et al. [43] reinforced this point by showing that movements such as premolar derotation and molar distalization often fall short of their digital setup predictions, which may exacerbate periodontal risks if overestimated.
The issue of predictability is particularly relevant: Castroflorio et al. [44] demonstrated that aligner design strongly impacts the expression of specific tooth movements, with significant discrepancies for angular corrections. These observations resonate with Kwon et al. [45], who analyzed occlusal outcomes in orthognathic cases and confirmed that although aligner-assisted treatments achieve excellent final results, intermediate discrepancies between digital setups and clinical reality remain common. Complementary evidence from Sabouni et al. [46] also indicates that skeletal and dentoalveolar changes induced with mandibular advancement appliances integrated into aligner systems can mirror those achieved with functional appliances, supporting their role in growing patients.
Patient-centered outcomes further strengthen the case for aligners in surgical contexts. De Leyva et al. [47] provided robust RCT evidence showing that patients treated with aligners post-surgically enjoyed better periodontal outcomes and higher quality of life than those managed with fixed appliances, a conclusion echoed by Weir [48], who contextualized the broader patient experience and compliance benefits of aligner therapy. Moreover, Muro et al. [41] and Chen et al. [48] both stress that beyond biomechanics, aligners offer substantial psychosocial and esthetic advantages, which are particularly relevant in adult surgical populations.
Taken together, the integration of references [30,31,32,39,45,46,47,48] underlines a coherent pattern: clear aligners are increasingly supported as a viable adjunct in orthognathic surgery, capable of producing skeletal, occlusal, and patient-centered outcomes comparable to those of fixed appliances. At the same time, variability in movement predictability [40,42], periodontal considerations [44], and long-term stability concerns [41,47,48] highlight the need for cautious implementation. As suggested by Papageorgiou et al. [31] and Aziz [30], standardized protocols and prospective multicenter trials will be essential to validate aligner-assisted surgical workflows and to clarify their role in future orthognathic treatment paradigms. This scoping review presents several limitations, which precluded the possibility of conducting a systematic review. Most of the included studies involved very small sample sizes, limiting statistical power and external validity. The predominance of retrospective designs increased the risk of selection and reporting bias. Moreover, there was substantial heterogeneity in treatment protocols—including variations in aligner systems, use of auxiliaries, and surgical techniques—that hindered direct comparison across studies. The majority of investigations reported only short-term outcomes, restricting conclusions about long-term stability and predictability. In addition, patient-reported outcomes such as satisfaction and quality of life were rarely assessed, leaving an important aspect of treatment evaluation underexplored. Nevertheless, the strength of the present review lies in its focus on a timely and underexplored topic. By synthesizing the available evidence on the integration of clear aligners with orthognathic surgery, this work contributes to the discussion of an emerging field and may support the development of more standardized protocols and validated methodologies for future research.
5. Conclusions
This scoping review highlights the current evidence on the use of clear aligners in combination with orthognathic surgery. The main findings can be summarized as follows:
- Clear aligners can provide consistent skeletal improvements, particularly in sagittal parameters, while maintaining vertical stability.
- Their effectiveness appears comparable to fixed appliances in presurgical decompensation, torque control, and postsurgical refinement.
- Additional advantages include improved aesthetics, patient comfort, and seamless integration into digital workflows.
- Current evidence is limited by small sample sizes, retrospective designs, and considerable heterogeneity in protocols.
- The absence of robust randomized controlled trials prevents definitive conclusions at this stage.
- Future prospective studies with standardized methodologies, longer follow-up, and patient-reported outcomes are required to confirm long-term effectiveness and stability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.V. and F.B.D.; methodology, F.L. and R.S.; software, F.B.D.; validation, A.V., E.S. and R.S.; formal analysis, A.V.; investigation, F.L.; resources, R.S.; data curation, A.V.; writing—original draft preparation, F.B.D.; writing—review and editing, A.V.; visualization, F.L. and R.S.; supervision, A.V. and E.S.; project administration, E.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The review protocol was registered in Open Science Framework platform and is available at the following link https://osf.io/jr6mf/.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| ABO-OGS | American Board of Orthodontics Objective Grading System: Objective scoring system for evaluating the quality of orthodontic treatment results. |
| ANB (°) | Angular measurement between Point A (maxilla) and Point B (mandible) with respect to Nasion |
| BL Torque | Posterior Buccal Inclination |
| BSSO | Bilateral Sagittal Split Osteotomy: Surgical procedure to reposition the maxilla (upper jaw). |
| CAT | Clear Aligner Therapy: orthodontic treatment using transparent plastic aligners instead of fixed braces. |
| CAD/CAM | Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing |
| FMA (°) | Frankfort Mandibular Angle—angle between the Frankfort horizontal plane and the mandibular plane |
| L1-MP | Lower incisor tip |
| MP-FH (°) | Angle between the mandibular plane (MP) and the Frankfort horizontal plane (FH). |
| PAR | Peer Assessment Rating Index: Orthodontic index used to assess the quality of occlusion and measure treatment outcomes. |
| RAP | Regional Acceleratory Phenomenon: temporary increase in bone remodeling and tooth movement following surgical trauma. |
| RCT | Randomized Controlled Trial |
| SFA | Surgery First Approach: orthognathic surgical protocol where the skeletal correction is performed before orthodontic alignment. |
| TADs | Temporary anchorage devices |
| U1-PP | Upper incisor Torque |
| Wits | A linear measurement (in mm) of the anteroposterior discrepancy between the maxilla and mandible |
| VSP | Virtual Surgical Planning |
References
- Leck, R.; Paul, N.; Rolland, S.; Birnie, D. The consequences of living with a severe malocclusion: A review of the literature. J. Orthod. 2022, 49, 228–239. [Google Scholar]
- Zammit, D.; Ettinger, R.E.; Sanati-Mehrizy, P.; Susarla, S.M. Current trends in orthognathic surgery. Medicina 2023, 59, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proffit, W.R.; Fields, H.W.; Larson, B.; Sarver, D.M. Contemporary Orthodontics, 6th ed.; Mosby Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 667–692. [Google Scholar]
- Benetti, M.; Montresor, L.; Trevisiol, L.; D’Agostino, A.; Zerman, N.; Verdecchia, A.; Spinas, E. Health and TMJ Function in Adult Patients Treated for Dentoskeletal Open Bite with Orthognathic Surgery—A Retrospective Cohort Study. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, G.; Parrini, S.; Castroflorio, T.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C.L. Efficacy of clear aligners in controlling orthodontic tooth movement: A systematic review. Angle Orthod. 2015, 85, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnagar, M.H.; Aronovich, S.; Kusnoto, B. Digital Workflow for Combined Orthodontics and Orthognathic Surgery. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 32, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deregibus, A.; Castroflorio, T.; Debernardi, C.L.; Rossini, G. Clear aligners: Evolution of orthodontic treatment and clinical evidence. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar]
- Sanati-Mehrizy, P.; Ettinger, R.E.; Zammit, D.; Susarla, S.M. Aligners in orthognathic surgery: A practical update. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 81, 834–843. [Google Scholar]
- Jaber, S.T.; Hajeer, M.Y.; Sultan, K. Treatment effectiveness of clear aligners in correcting complicated and severe malocclusion cases compared to fixed orthodontic appliances: A systematic review. Cureus 2023, 15, e38311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricco, A.C.; Lillie, E.; Zarin, W.; O’Brien, K.K.; Colquhoun, H.; Levac, D.; Moher, D.; Peters, M.D.; Horsley, T.; Weeks, L.; et al. PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR): Checklist and explanation. Ann. Intern. Med. 2018, 169, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meazzini, M.C.; Demonte, L.P.; Cohen, N.; Battista, V.M.A.; Rabbiosi, D.; Autelitano, L. The Use of Clear Aligners in Multi-Segmental Maxillary Surgery: A Case–Control Study in Cleft Lip and Palate and Skeletal Class III Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amodeo, G.; Meuli, S.; Carboni, A.; Dolci, A.; Farronato, G. Surgery first and Invisalign system: Combined digital approach. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2020, 31, 1681–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M. Invisible orthodontics combined with orthognathic surgery for Class III cases. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2023, 34, e390–e394. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.M. Clear aligners and skeletal repositioning: A Vietnam cohort. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 122, 614–621. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Surgery-first approach with clear aligners in Class III malocclusion: A randomized study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 53, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ghouli, Z. Presurgical orthodontics with aligners in skeletal Class III correction. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 125, 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Cong, A.; Rossi, M.; Li, P.; Chen, Y. Digital planning and aligners in orthognathic surgery. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2022, 25, 122–129. [Google Scholar]
- Hennessy, J.; Al-Awadhi, E.A. Clear Aligners Generations and Orthodontic Tooth Movement. J. Orthod. 2016, 43, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putrino, A.; Barbato, E.; Galluccio, G. Clear Aligners: Between Evolution and Efficiency—A Scoping Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G. Biomechanics in clear aligner-assisted orthognathic protocols. Chin. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 25, 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, H.J.; Choi, Y.K. Current trends in orthognathic surgery. Arch. Craniofac. Surg. 2021, 22, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, R.S. Orthognathic Surgery Past, Present, and Future. Clin. Investig. Orthod. 2022, 81, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Veldhuis, E.C.; Te Veldhuis, A.H.; Bramer, W.M.; Wolvius, E.B.; Koudstaal, M.J. The effect of orthognathic surgery on the temporomandibular joint and oral function: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2017, 46, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Susarla, S.M. Multidisciplinary planning of aligner-based orthognathic cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 81, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Sefidroodi, M.; Shino, I.L.; Vassis, S.; Hammer, K.E.; Kristensen, K.D.; Pedersen, T.K.; Nørholt, S.E.; Buhl, J. Surgery First and Aligners: A Case Report Combining In-House Surgical Guides and Pre-Adapted Titanium Plates. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankam, H.; Madari, S.; Sawh-Martinez, R.; Bruckman, K.C.; Steinbacher, D.M. Comparing Outcomes in Orthognathic Surgery Using Clear Aligners Versus Conventional Fixed Appliances. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2019, 30, 1488–1491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lou, T.; Caminiti, M. Orthognathic Surgery Combined with Clear Aligner Therapy. J. Clin. Orthod. 2021, 55, 44–58. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, A.S.; Jiang, L.; Ch’ng, J.; Delpachitra, S. Clear Aligner Therapy Combined with Orthognathic Surgery: A Scoping Review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofacial Orthop. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz, S.R. Clear aligner orthognathic surgery: An overview. Front. Oral Maxillofac. Med. 2022, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papageorgiou, S.N.; Keilig, L.; Alobeid, A.; Eliades, T. Clear aligner treatment with orthognathic surgery. Semin. Orthod. 2025, 31, 100–112. [Google Scholar]
- Meazzini, M.C.; Demonte, L.P.; Cohen, N.; Battista, V.M.A.; Rabbiosi, D.; Autelitano, L. The role of clear aligners in surgery-first orthognathic approach: Review and protocol. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 250. [Google Scholar]
- Pagani, R.; Signorino, F.; Poli, P.P.; Manzini, P.; Panisi, I. The Use of Invisalign® System in the Management of the Orthodontic Treatment before and after Class III Surgical Approach. Case Rep. Dent. 2016, 2016, 9231219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, S.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, B.; Yu, H. The Application of a Fully Digital Approach in the Treatment of Skeletal Class III Malocclusion: A Preliminary Study. BMC Oral Health 2023, 23, 625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Park, J. Postoperative Stability of Patients Undergoing Orthognathic Surgery with Orthodontic Treatment Using Clear Aligners: A Preliminary Study. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Steinbacher, D.M.; Nanda, R.; Uribe, F. “Surgery-First” Approach with Invisalign® Therapy to Correct a Class II Malocclusion and Severe Mandibular Retrognathism. J. Clin. Orthod. 2019, 53, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, A.D.; Patano, A.; Coloccia, G.; Ceci, S.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Marinelli, G.; Malcangi, G.; Pede, C.D.; Garibaldi, M.; Ciocia, A.M.; et al. Treatment of Class III Malocclusion and Anterior Crossbite with Aligners: A Case Report. Medicina 2022, 58, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muro, M.P.; Caracciolo, A.C.A.; Patel, M.P.; Feres, M.F.N.; Roscoe, M.G. Effectiveness and predictability of treatment with clear orthodontic aligners: A scoping review. Int. Orthod. 2023, 21, 100755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponduri, S.; Pringle, A.; Illing, H.; Brennan, P.A. Peer Assessment Rating (PAR) index outcomes for orthodontic and orthognathic surgery patients. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 49, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inchingolo, A.M.; Patano, A.; Piras, F.; Ruvo, E.D.; Ferrante, L.; Noia, A.D.; Dongiovanni, L.; Palermo, A.; Inchingolo, F.; Inchingolo, A.D.; et al. Orthognathic Surgery and Relapse: A Systematic Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, C.J.; Cha, J.Y. Fast-Track Orthognathic Surgery: An Evidence-Based Review. Korean J. Orthod. 2015, 45, 239–247. [Google Scholar]
- Melsen, B.; Allais, D. Factors of Importance for the Development of Dehiscences during Labial Movement of Mandibular Incisors: A Retrospective Study of Adult Orthodontic Patients. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2005, 127, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, M.; Keilig, L.; Schwarze, J.; Jung, B.A.; Bourauel, C. Treatment outcome and efficacy of an aligner technique—Regarding incisor torque, premolar derotation and molar distalization. BMC Oral Health 2014, 14, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castroflorio, T.; Sedran, A.; Parrini, S.; Garino, F.; Reverdito, M.; Capuozzo, R.; Mutinelli, S.; Grybauskas, S.; Vaitiekūnas, M.; Deregibus, A. Predictability of orthodontic tooth movement with aligners: Effect of treatment design. Prog. Orthod. 2023, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.; Alshehri, A.; Palo, L.; Kuo, C.-L.; Mu, J.; Blanck, N.; Nanda, R.; Abu Arqub, S.; Uribe, F. Assessment of the occlusal outcomes in patients treated with orthognathic surgery and clear aligners. Orthod. Craniofac. Res. 2023, 26, 371–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabouni, W.; Hansa, I.; Al Ali, S.M.; Adel, S.M.; Vaid, N. Invisalign treatment with mandibular advancement: A retrospective cohort cephalometric appraisal. J. Clin. Imaging Sci. 2022, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Leyva, P.; Eslava, J.M.; Hernández-Alfaro, F.; Acero, J. Orthognathic surgery and aligners. A comparative assessment of periodontal health and quality of life in postsurgical orthodontic treatment with aligners versus traditional fixed appliances: A randomized controlled trial. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2023, 28, e208–e216. [Google Scholar]
- Weir, T. Clear aligners in orthodontic treatment. Aust. Dent. J. 2017, 62 (Suppl. S1), 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).