Changes in Bilabial Contact Pressure as a Function of Vocal Loudness in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Speech Stimuli
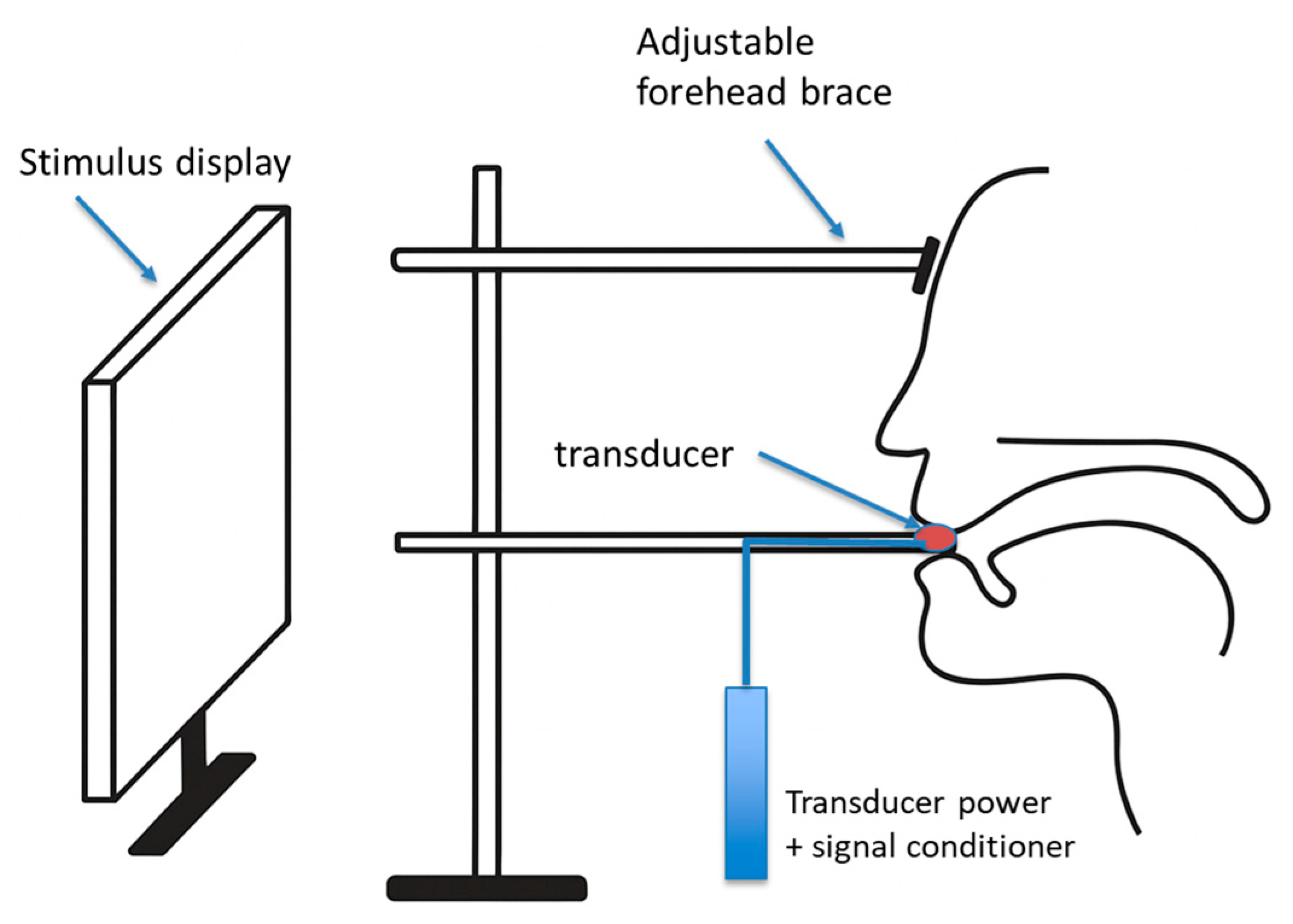
2.3. Instrumentation
2.4. Procedures
2.5. Analysis
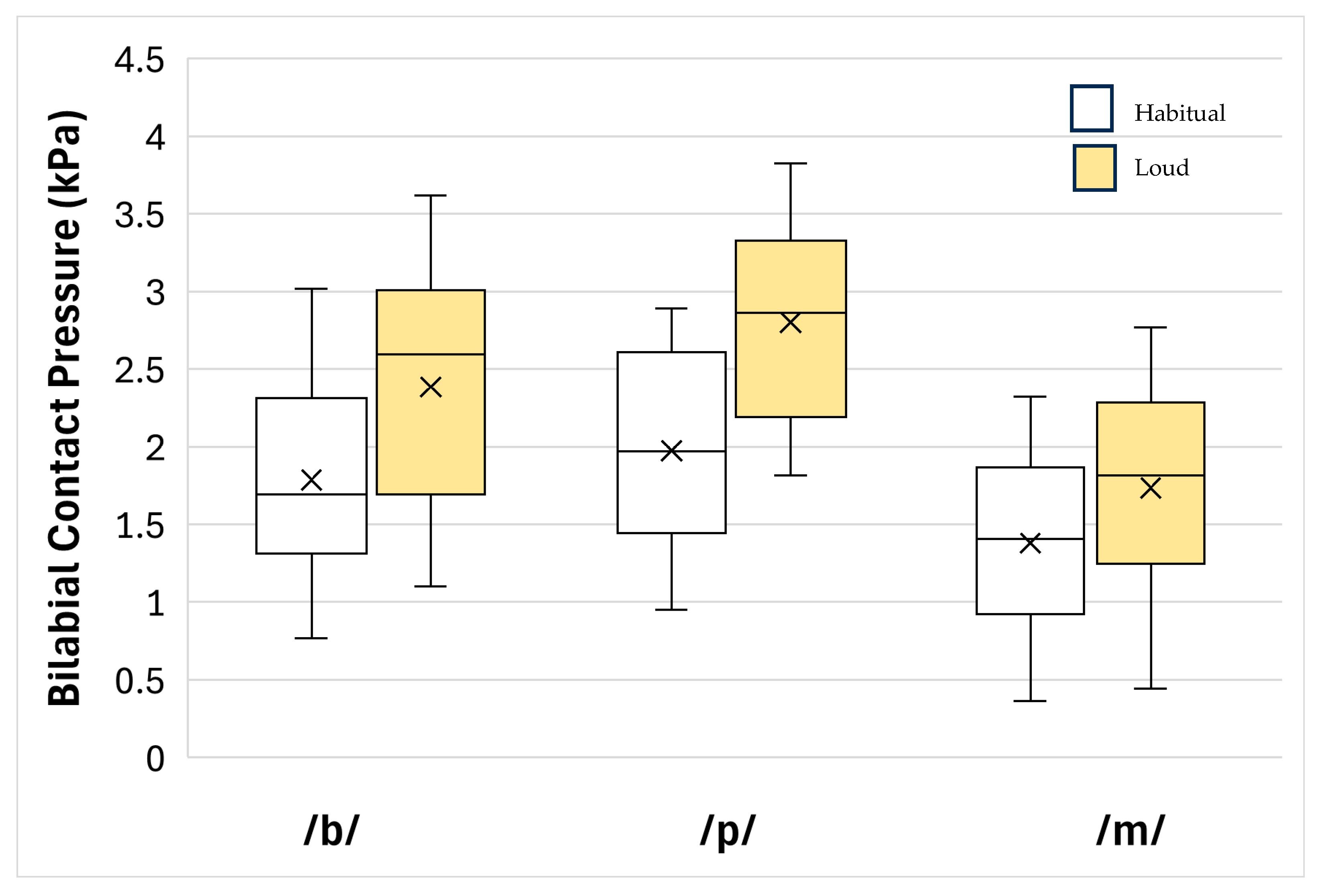
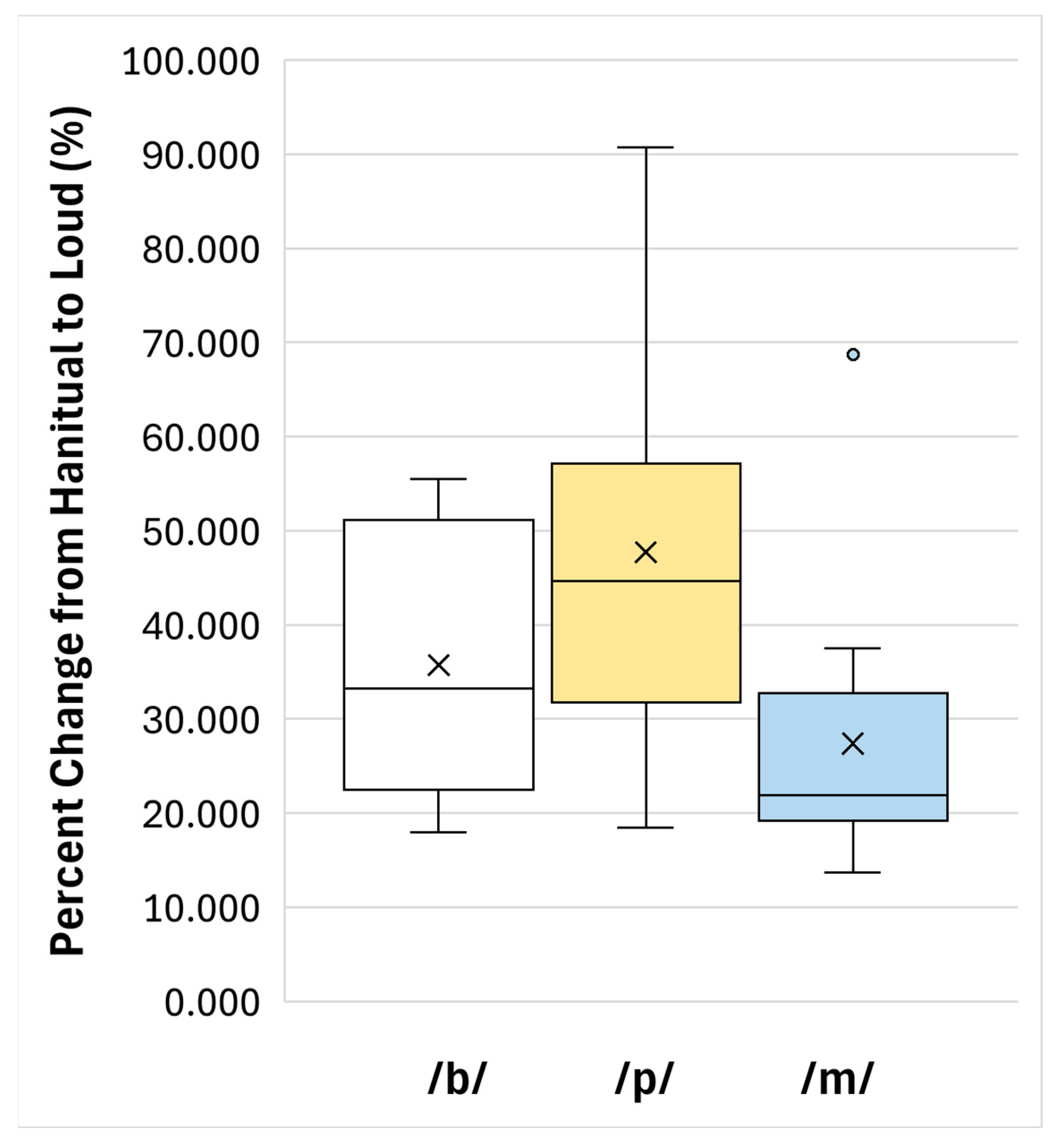
3. Results
4. Discussion
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, K.M.; Caplan, D.N. Communication impairment in Parkinson’s disease: Impact of motor and cognitive symptoms on speech and language. Brain Lang. 2018, 185, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schapira, A.H.V.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Jenner, P. Non-motor features of Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffy, J.R. Motor Speech Disorders: Substrates, Differential Diagnosis, and Management, 4th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Atalar, M.S.; Oguz, O.; Genc, G. Hypokinetic Dysarthria in Parkinson’s Disease: A Narrative Review. Sisli Etfal Hast. Tıp Bul. 2023, 57, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorsey, E.R.; Constantinescu, R.; Thompson, J.P.; Biglan, K.M.; Holloway, R.G.; Kieburtz, K.; Marshall, F.J.; Ravina, B.M.; Schifitto, G.; Siderowf, A.; et al. Projected number of people with Parkinson disease in the most populous nations, 2005 through 2030. Neurology 2007, 68, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global incidence, prevalence, years lived with disability (YLDs), disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs), and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 371 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2133–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAuliffe, M.J.; Baylor, C.R.; Yorkston, K.M. Variables associated with communicative participation in Parkinson’s disease and its relationship to measures of health-related quality-of-life. Int. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2017, 19, 407–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yorkston, K.; Baylor, C.; Britton, D. Speech Versus Speaking: The Experiences of People With Parkinson’s Disease and Implications for Intervention. Am. J. Speech-Lang. Pathol. 2017, 26, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalling, E.; Johansson, K.; Hartelius, L. Speech and Communication Changes Reported by People with Parkinson’s Disease. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2018, 69, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.K.; Bradshaw, J.L.; Iansek, R.; Alfredson, R. Speech volume regulation in Parkinson’s disease: Effects of implicit cues and explicit instructions. Neuropsychologia 1999, 37, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logemann, J.A.; Fisher, H.B.; Boshes, B.; Blonsky, E.R. Frequency and cooccurrence of vocal tract dysfunctions in the speech of a large sample of Parkinson patients. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1978, 43, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darley, F.L.; Aronson, A.E.; Brown, J.R. Differential diagnostic patterns of dysarthria. J. Speech Hear. Res. 1969, 12, 246–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, G.; Halpern, A.; Spielman, J.; Ramig, L.; Panzer, I.; Sharpley, A.; Freeman, K. Single word intelligibility of individuals with Parkinson’s disease in noise: Pre-specified secondary outcome variables from a randomized control trial (RCT) comparing two intensive speech treatments (LSVT LOUD vs. LSVT ARTIC). Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, R.; Read, C. The Acoustic Analysis of Speech; Singular Publishing Group, Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Logemann, J.A.; Fisher, H.B. Vocal tract control in Parkinson’s disease: Phonetic feature analysis of misarticulations. J. Speech Hear. Disord. 1981, 46, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.M.; Raming, L.O.; Ciucci, M.R.; Sapir, S.; McFarland, D.H.; Farley, B.G. The science and practice of LSVT/LOUD: Neural plasticity—Principled approach to treating individuals with parkinson disease and other nuerological disorders. Semin. Speech Lang. 2006, 27, 283–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramig, L.; Halpern, A.; Spielman, J.; Fox, C.; Freeman, K. Speech treatment in Parkinson’s disease: Randomized controlled trial (RCT). Mov. Disord. 2018, 33, 1777–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrman, A.; Cody, J.; Elandary, S.; Flom, P.; Chitnis, S. The Effect of SPEAK OUT! and The LOUD Crowd on Dysarthria Due to Parkinson’s Disease. Am. J. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2020, 29, 1448–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrman, A.; Cody, J.; Chitnis, S.; Elandary, S. Dysarthria treatment for Parkinson’s disease: One-year follow-up of SPEAK OUT!® with the LOUD Crowd®. Logop. Phoniatr. Vocol 2022, 47, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahler, L.A.; Ramig, L.O.; Fox, C. Evidence-based treatment of voice and speech disorders in Parkinson disease. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2015, 23, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.; Ebersbach, G.; Ramig, L.; Sapir, S. LSVT LOUD and LSVT BIG: Behavioral treatment programs for speech and body movement in Parkinson disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2012, 2012, 391946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutsen, F.; Park, E.; Dvorak, J.; Cid, C. Prosodic Improvement in Persons with Parkinson Disease Receiving SPEAK OUT!® Voice Therapy. Folia Phoniatr. Logop. 2018, 70, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, T.; Huang, M.; Kong, X.; Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Feng, X.; Wei, C.; Weng, X.; Xu, F. Lee Silverman Voice Treatment to Improve Speech in Parkinson’s Disease: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis. Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 2021, 3366870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neel, A.T. Effects of loud and amplified speech on sentence and word intelligibility in Parkinson disease. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2009, 52, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, E.; Giles, R.; Haworth, B.; Faloutsos, P.; Baljko, M.; Yunusova, Y. Sentence-Level Movements in Parkinson’s Disease: Loud, Clear, and Slow Speech. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 3426–3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searl, J.; Evitts, P. Changes in Articulatory Contact Pressure as a Function of Vocal Loudness. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jergas, H.; Petry-Schmelzer, J.N.; Hannemann, J.H.; Thies, T.; Strelow, J.N.; Rubi-Fessen, I.; Quinting, J.; Baldermann, J.C.; Mücke, D.; Fink, G.R.; et al. One side effect: Two networks? Lateral and posteromedial stimulation spreads induce dysarthria in subthalamic deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2025, 96, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searl, J. Bilabial contact pressure and oral air pressure during tracheoesophageal speech. Ann. Otol. Rhinol. Laryngol. 2007, 116, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weismer, G.; Yunusova, Y.; Bunton, K. Measures to evaluate the effects of DBS on speech production. J. Neurolinguist. 2012, 25, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, B.; Smith, A. Basic parameters of articulatory movements and acoustics in individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 843–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandini, A.; Orlandi, S.; Giovannelli, F.; Felici, A.; Cincotta, M.; Clemente, D.; Vanni, P.; Zaccara, G.; Manfredi, C. Markerless Analysis of Articulatory Movements in Patients with Parkinson’s Disease. J. Voice 2016, 30, 766.e1–766.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dromey, C. Articulatory kinematics in patients with Parkinson Disease using different speech treatment approaches. J. Med. Speech Lang. Pathol. 2000, 8, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Yunusova, Y.; Kearney, E.; Kulkarni, M.; Haworth, B.; Baljko, M.; Faloutsos, P. Game-based Augmented Visual Feedback for Enlarging Speech Movements in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Speech Lang. Hear. Res. 2017, 60, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thies, T.; Mücke, D.; Geerts, N.; Seger, A.; Fink, G.R.; Barbe, M.T.; Sommerauer, M. Compensatory articulatory mechanisms preserve intelligibility in prodromal Parkinson’s disease. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 112, 105487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konnai, R.; Van Harn, M.; Silbergleit, A. Conversational Vocal Intensity in Parkinson’s Disease: Treatment and Environmental Comparisons. J. Voice 2021, 37, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| S | Age | Sex | H&Y Score | Years Post PD Dx | Current PD Symptoms | PD Medication(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 56 | M | 2 | 6 | tremor, fatigue, depression | Sinemet, Mirapex, Selegiline |
| 2 | 48 | M | 1 | 2 | tremor, balance, shuffling gait, voice change | Sinemet, Rasagiline |
| 3 | 67 | M | 4 | 14 | bradykinesia, dysphagia, balance, | Parcopa, Amantadine |
| 4 | 70 | F | 1 | 5 | tremor, shuffling gait, fatigue | Sinemet, Ropinirole |
| 5 | 67 | M | 1 | 7 | tremor, bradykinesia | Sinemet, Parlodel, Mirapex |
| 6 | 63 | M | 2 | 1 | bradykinesia | Sinemet, Mirapex |
| 7 | 65 | M | 1 | 2 | tremor, bradykinesia, shuffling gait | Sinemet, Mirapex |
| 8 | 77 | M | 1 | 6 | tremor | Sinemet, Mirapex |
| 9 | 80 | F | 3 | 2 | tremor | Sinemet, Mirapex |
| 10 | 60 | F | 2 | 2 | tremor, rigidity | Sinemet, Requip |
| 11 | 64 | F | 1 | 5 | tremor, stooped posture | Sinemet, Mirapex |
| 12 | 47 | F | 2 | 2 | dystonia, tremor | Sinemet |
| S | Speech and Voice | Speech Treatment | Smelling and/or Swallowing Issues | Cognitive Difficulties |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | imprecise articulation, slow rate | none | coughing, aspiration | concentration, problem solving |
| 2 | reduced loudness | LSVT | Coughing, aspiration, drooling, anosmia | short-term memory, concentration, problem solving |
| 3 | reduced loudness, imprecise articulation | LSVT | Coughing, aspiration | self-monitoring, insight |
| 4 | imprecise articulation | none | other GI problems | general deterioration |
| 5 | reduced loudness, lower pitch | group | Coughing, aspiration, pills stuck in throat | none |
| 6 | vocal fatigue | none | none | -- |
| 7 | reduced loudness | group | none | general deterioration |
| 8 | reduced loudness | none | none | short-term memory |
| 9 | low pitch, rough voice | group | pills stick in throat, anosmia | none |
| 10 | no issues | none | anosmia | general deterioration |
| 11 | reduced loudness | none | anosmia | short-term memory, concentration, problem solving |
| 12 | no issues | none | none | short-term memory, general deterioration |
| Fixed-Effect | Mean/Mean Difference | SD | 95% CI | t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Condition | |||||
| Habitual | 1.714 | 0.482 | 1.442–3.156 | -- | -- |
| Loud | 2.307 | 0.556 | 1.993–4.300 | -- | -- |
| Loud–Habitual | 0.593 | 0.148 | 0.509–0.676 | 16.211 | <0.001 |
| Phoneme | |||||
| /b/ | 2.086 | 0.730 | 1.673–3.759 | -- | -- |
| /p/ | 2.387 | 0.663 | 2.013–4.400 | -- | -- |
| /m/ | 1.558 | 0.615 | 1.210–2.769 | -- | -- |
| /p/–/b/ | 0.301 | 0.835 | −0.171–1.130 | 1.250 | 0.237 |
| /b/–/m/ | 0.528 | 0.450 | 0.273–0.801 | 4.067 | 0.002 |
| /p/–/m/ | 0.829 | 0.876 | 0.333–1.162 | 3.277 | 0.007 |
| Phoneme | Mean (%) | SD | Minimum | Maximum | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /b/ | 35.738 | 14.289 | 17.994 | 55.520 | 27.7–63.4 |
| /p/ | 47.744 | 21.646 | 18.430 | 90.755 | 35.5–83.2 |
| /m/ | 27.413 | 14.802 | 13.704 | 68.711 | 19.0–46.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Searl, J. Changes in Bilabial Contact Pressure as a Function of Vocal Loudness in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810165
Searl J. Changes in Bilabial Contact Pressure as a Function of Vocal Loudness in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(18):10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810165
Chicago/Turabian StyleSearl, Jeff. 2025. "Changes in Bilabial Contact Pressure as a Function of Vocal Loudness in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease" Applied Sciences 15, no. 18: 10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810165
APA StyleSearl, J. (2025). Changes in Bilabial Contact Pressure as a Function of Vocal Loudness in Individuals with Parkinson’s Disease. Applied Sciences, 15(18), 10165. https://doi.org/10.3390/app151810165






