Featured Application
This research emphasizes the antiviral prospects of turkey-originated Ligilactobacillus salivarius UMNPBX2 cell-free extract (CFE) as an effective postbiotic strategy for the management of H4N6 avian influenza virus in poultry production. The dose-dependent antiviral activity of CFE in cell culture and embryonated chicken eggs supports its potential use in managing poultry health.
Abstract
Avian influenza (AI) is a highly infectious disease affecting birds. Some strains of AI virus (AIV) have zoonotic potential, posing a threat to humans. The H4N6 subtype is a low-pathogenic virus and causes mild infection in poultry. However, it has raised increasing concern due to its capability to infect pigs and its high potential for reassortment when co-infected with other strains. This study investigated the antiviral properties of turkey-derived Ligilactobacillus salivarius UMNPBX2 (L. salivarius UMNPBX2) cell-free extract (CFE) using both cell culture and in ovo methods. We assessed the growth kinetics of the H4N6 virus and the cytotoxicity of L. salivarius UMNPBX2 CFE in Madin–Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) cells. The results revealed that the CFE from the 109 CFU/mL L. salivarius UMNPBX2 overnight culture had strong antiviral activities (p < 0.05). The CFE obtained from 107 to 105 CFU/mL of overnight culture also significantly reduced viral replication (p < 0.05), demonstrating dose-dependent inhibition of viral replication. Additionally, CFEs did not increase pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression of IL-1β and IL-6 but rather tended to decrease it (IL-6). The embryo survivability experiments revealed a significant dose-dependent increase in survival rate (p < 0.05). The findings of this study highlight the antiviral properties of L. salivarius UMNPBX2 CFE, which contain potential postbiotics against the H4N6 virus, warranting in vivo studies.
1. Introduction
Avian influenza (AI), also known as bird flu, is caused by the Influenza A virus, a member of the Orthomyxoviridae family. Every year, AI outbreaks occur worldwide, caused by both high- and low-pathogenic strains, posing a serious threat to avian and human populations. The segmented, single-stranded viral genome of the AI virus enables frequent genetic mutation and virus reassortment, resulting in diverse strains and subtypes. These genetic reassortments result in the development of AI virus strains with zoonotic potential. The zoonotic nature of the AI virus (AIV) amplifies its potential impact on human health. When the virus spreads from birds to humans, it can cause respiratory infections and, in rare cases, lead to mortality. The likelihood of human-to-human transmission is low; however, the possibility of disease transmission through close contact between farm workers and infected animals, combined with recent findings of disease transmission to mammals and humans, raises the threat of potential pandemics [1,2].
The latest AI outbreak caused by the HPAI H5N1 strain in dairy cattle, followed by human cases, has drawn more attention to the zoonotic nature of the virus. This outbreak is the first reported case of this strain infecting cattle and the first instance of mammal-to-human transmission caused by the H5N1 strain in the USA [1]. During the H5N1 outbreak, one death was reported; however, most infected individuals experienced moderate symptoms, and all recovered, with no persistent human-to-human transmission observed to date. However, we cannot rule out the possibility of reassortment between various viral strains, which may lead to the emergence of a highly virulent virus capable of causing a pandemic. The vaccination available for humans against the influenza virus includes seasonal flu vaccination, which does not protect against H5N1 avian flu. Still, it might reduce the risk of coinfection with seasonal and bird flu, lowering the likelihood of viral reassortment [1].
During an AI virus infection, affected birds and those in contact with them will be culled to control the spread of the disease. The economic burden associated with AI is so substantial that preventive measures should be taken before the disease becomes widespread. Biosecurity, disease surveillance, quarantine of infected poultry, and depopulation are measures to control the AI virus. However, recent outbreaks and their effect on industry demand novel approaches alongside the existing responses.
A critical intervention that can induce a protective immune response in the host is vaccination. Vaccines against AI are under development in some countries, including HA-expressing viral vectors, reverse genetics platforms, and inactivated whole-virus formulations [3]. In the USA, an RNA particle vaccine reduced cloacal shedding of the 2015 H5N2 outbreak strain [4]. However, the rapid mutation of viral surface proteins, variability in immunogenicity, lengthy production timelines, and the difficulty in distinguishing between vaccinated and infected birds pose significant challenges to vaccine development and deployment [3].
A few non-vaccine alternatives have shown promise against AI. Probiotics are widely recognized for their safety in poultry and their ability to modulate the immune response, provided the selected strains can colonize the gut and nasal passages [5]. The probiotic efficacy against AI depends on their ability to colonize and produce the desired outcomes. Recently, probiotic metabolites (postbiotics) have gained attention as a promising method against different AI viruses. Many probiotic bacteria and their fermentation byproducts have been studied for their antiviral properties against low-pathogenic and high-pathogenic AI viruses [5,6,7]. In addition to probiotics and their metabolites, prebiotics like mannan oligosaccharides and a combination of prebiotics and probiotics (synbiotics) have also been found to have antiviral properties against the AIV [8,9]. A few plant-derived compounds and essential oils were also found to be potentially effective against influenza viruses [10,11]. In addition to these approaches, various immune modulators like Toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands are known to enhance the host immunity against AIV, which is also at its exploratory stages [12].
The current antiviral drugs in humans include neuraminidase inhibitors, such as oseltamivir and zanamivir, and M2 blockers such as amantadine and rimantadine [13]. The Influenza A virus rapidly resists various medications due to mutations in its viral elements [14]. Compared to all these approaches, probiotics and postbiotics offer several advantages. Multiple comparative studies have shown their ability to promote growth, enhancing the immune response, antiviral property, and safety to use in poultry [7,15].
Exploring the potential of postbiotics, the fermentation metabolites of probiotics, has been an area of emerging interest in discovering novel antivirals with potential against AI viruses. This approach eliminates the need for bacterial attachment to the gut, as their effects on viruses can be standardized through their products. This study aims to investigate the effects of Ligilactobacillus salivarius UMNPBX2 (hereafter referred to as L. salivarius UMNPBX2) cell-free extract (CFE), which contains postbiotics, on the H4N6 subtype of low-pathogenic avian influenza (LPAI) virus using cell culture and in ovo methods. The results from these experiments will inform our ongoing bird studies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture and CFE Preparation
2.1.1. L. salivarius UMNPBX2
L. salivarius UMNPBX2 was cultivated in de Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe broth (MRS; NCM0079B, Neogen Culture Media, Lansing, MI, USA). A 100 µL aliquot of the stock culture, maintained at −80 °C, was added to 10 mL MRS broth. To ensure adequate bacterial growth, the culture was incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Post-incubation, the culture was centrifuged at 3600 rpm for 15 min at 4 °C using an Allegra X-14R centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, Inc., 250 S. Kraemer Blvd., Brea, CA, USA). A 10 mL aliquot of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS, pH 7.1) was used to rinse the pellet twice to remove residual components of MRS broth. The pellet was resuspended in PBS and used as the inoculum for further experiments. The inoculum was serially diluted for bacterial enumeration. A 100 µL of the diluted solution was then dispersed over MRS agar plates and incubated at 37 °C for 24 h to promote colony formation. As described previously, colony counts were performed following the incubation period [16,17]. After 24 h, the bacterial count was 109 CFU/mL. It was then diluted to 107 and 105 CFU/mL in broth for our studies. The bacterial populations in these dilutions were determined.
2.1.2. CFE Preparation
L. salivarius UMNPBX2 was grown in sterile MRS broth by incubating at 37 °C overnight for 24 h with continuous shaking at 100 rpm. After 24 h, the culture was centrifuged for 15 min (3600 rpm at 4 °C) to pellet the bacterial cells. The supernatant was carefully pipetted and filtered using a syringe filter (0.22 µm, Catalog # SLGS033, Millipore Sigma, 400 Summit Drive, Burlington, MA, USA) to obtain CFE. The pH of CFE was determined.
2.2. AIV Propagation in Madin–Darby Canine Kidney (MDCK) Cell Line
MDCK (NBL-2, CCL-34) was obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, 10801 University Boulevard, Manassas, VA, USA). This cell line has been used to propagate and isolate AI viruses [18,19,20]. Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Catalog #11965092, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS; Catalog #16140071, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA) and 1% penicillin–streptomycin (100 U/mL penicillin G and 100 µg/mL streptomycin, 5000 U/mL stock; Catalog #15070063, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA) was used as cell culture media. Once the cells reached confluence (>80%), they were subcultured by seeding them into 96-well plates at a concentration of 1 × 104 cells/well in 100 µL of tissue culture medium. The incubation conditions were maintained at 37 °C under a 5% CO2 environment.
The LPAI (H4N6; A/Mallard/Minnesota/AI09-2495/2009) strain (source: Dr. Carol Cardona, Minnesota Poultry Testing Laboratory, Willmar, Minnesota) was used in this study. The use of HPAI strain in this study has been approved by the Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) at the University of Minnesota, protocol #2310-41472H (19 December 2023–24 February 2026). The virus was propagated in the MDCK cell line cultured in a 75 cm2 flask. The media used was complete DMEM (cDMEM) prepared using DMEM with penicillin–streptomycin stock (100 U/mL penicillin G and 100 µg/mL streptomycin), 20 mM L-glutamine (L-glutamine 200 mM; Catalog #25030081, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA), 0.2% bovine serum albumin solution (BSA 7.5% solution; Catalog # 15260037, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA), and 25 mM HEPES buffer (1M; Catalog #15630130, Gibco, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA). The AIV growth medium was prepared by adding L-1-Tosylamide-2-phenylethyl chloromethyl ketone (TPCK)-treated trypsin (Catalogue #20233, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA) to cDMEM at a concentration of 1 µg/mL. The multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.01 was used to calculate the required viral volume. A TCID50 (50% Tissue Culture Infectivity Dose) assay was performed to determine the viral concentration, a standard method for evaluating viral inhibition in cell culture [19,21].
2.3. Determining the Cytotoxicity of CFE on MDCK Cells
The MTT assay [3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] was conducted to evaluate the cytotoxicity of L. salivarius UMNPBX2 CFE on MDCK cells (CyQUANT™ MTT assay kit, Catalog # V13154, Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA). MDCK cells at 104 cells/well were seeded into 96-well plates in 100 µL of tissue culture medium and incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 overnight. After the MDCK cells reached >80% confluence, they were exposed to various concentrations of CFE obtained from overnight L. salivarius UMNPBX2 cultures at 109 CFU/mL or its 10-fold dilutions (108, 107, 106, 105, 104, and 103 CFU/mL). Control wells were treated with PBS. The cells were then incubated for 2 h. The experiment was repeated three times. We chose a two-hour incubation time to test any acute cytotoxicity of all tested CFE concentrations on the cell lines.
After the incubation period, the cells were washed with sterile water, and the medium was replaced with 100 µL of fresh medium. The MTT cell viability test was conducted using the MTT assay kit. Each well received 10 µL of MTT stock solution and was incubated at 37 °C in a CO2 incubator for 4 h. After incubation, 100 µL of SDS-HCl solution was added to each well, and the plate was incubated for an additional 4 h in a CO2 incubator. Following the last incubation, the samples were mixed thoroughly by pipetting up and down. A multi-well spectrophotometer (MRX microplate reader; 1CXD-5388) was used to detect absorbance at 600 nm [22].
2.4. Determining the Antiviral Effect of CFE on H4N6 in MDCK Cells
2.4.1. CFE and H4N6 Interactions In Vitro
These experiments were conducted to determine the dose-dependent effects of CFE on the potential interaction of the H4N6 strain with MDCK cells. In the first experiment, equal volumes (1:1) of the H4N6 virus (106.6 TCID50/mL) and CFE at 109, 107, and 105 CFU/mL were mixed and incubated for 1 h at 37 °C and 5% CO2. An MOI of 1 was used to calculate the viral inoculum. In the subsequent experiment, the antiviral effect of CFE (109 CFU/mL) was evaluated against four different concentrations of the H4N6 virus: 106.6, 105.6, 104.6, and 102.6 TCID50/mL. The virus suspensions were mixed with the CFE in equal volumes (1:1) and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h in MDCK cells.
2.4.2. Infection of MDCK Cells with Treatments
The MDCK cell line was propagated in a 96-well plate with a seeding density of 2 × 104 cells/well in 100 µL of tissue culture medium. Once the cells had attained >80% confluence, the media was removed carefully, and the cells were washed with sterile PBS. A combination of 100 µL of the H4N6 virus and CFE, prepared through a series of 10-fold serial dilutions, was added to each well, except for the last two wells, which were reserved as controls. The plates were then incubated for 1 h at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 incubator. After incubation, the cells were carefully rinsed with sterile PBS before being added to the AI virus infection medium (cDMEM + TPCK-trypsin) in each well. Plates were incubated for 3 days in a CO2 incubator. On the third day, the plates were examined for cytopathic effect (CPE) indicative of viral infection. To ensure accurate observation of CPE, the wells were stained with 0.1% crystal violet (2.3% solution; Catalogue # HT901; 3050 Spruce Street, St. Louis, MO, USA). The viral titer in the treatment and control plates was determined using a TCID50 assay [23,24]. Each dilution was added to multiple wells per concentration, and each experiment was repeated at least three times.
2.5. Determining the Growth of AI Virus in MDCK Cells
The MDCK cells were propagated in 6-well tissue culture plates (Catalog # CLS3516, Corning Costar, Millipore Sigma, 400 Summit Drive, Burlington, MA, USA) at a density of 1 × 105 cells per well, using tissue culture medium (DMEM + 10% HI FBS + 1% penicillin–streptomycin) until they reached >80% confluency. The LPAI H4N6 virus stock was diluted in infection media (cDMEM + TPCK-trypsin) to produce an MOI of 0.1 in MDCK cells. A 100 µL of culture media was taken from the wells at different time intervals (0-, 4-, 8-, 12-, 24-, 48-, 72-, and 96 h post-infection (h.p.i.) for viral titer measurement using the TCID50 test [25].
2.6. Determining the Immune Gene Expression in MDCK Cells Using Quantitative Reverse Transcription PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.6.1. Effect of CFE on Immune Genes in MDCK Cells
MDCK cells were plated in 24-well cell culture plates at a density of 104 cells per well. Each treatment had six biological replicates (n = 6). Plates were cultured in a CO2 incubator overnight. When the cells reached >80% confluence, the culture medium was removed, and the cells were carefully rinsed with sterile PBS. A 100 µL of CFE from an overnight culture (109 CFU/mL) was added to the wells. In the negative control group, PBS was added to the cells. After adding the cell culture medium (cDMEM), the wells were incubated at 37 °C with 5% CO2 for an h. After 1 h of incubation, the inoculum was removed, and the cells were rinsed twice with PBS. Then, 1 mL of fresh growth medium (cDMEM alone) was added to each well. At 6 h.p.i., the cells were harvested for RNA extraction.
2.6.2. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
Total RNA was extracted from MDCK cells treated or untreated with CFE using the RNeasy Plus Mini Kit (Qiagen, catalog #74134, Hilden, NRW, Germany). Cells were lysed by applying the required amount of buffer RLT directly to the culture dish. The gDNA eliminator spin column included with the kit was then used to efficiently remove genomic DNA (gDNA) contamination from the samples. The RNA quality obtained was determined using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (NanoPhotometer® N60/N50, Implen GmbH, Schatzbogen 52, 81829 München, Germany) by measuring the OD260/280 ratio (1.8–2.1). To derive cDNA, a total of 450 ng RNA was used for reverse transcription using Superscript™ IV Reverse Transcriptase (catalog # 18090010, Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA), 10 mM dNTP mix, and 50 µM Oligo dT primer, per the manufacturer’s instructions. The resultant cDNA was amplified with an RT-qPCR.
2.6.3. RT-qPCR
For RT-qPCR analysis, 10% of the extracted cDNA was used in the reaction, prepared with PowerTrack™ SYBR Green Master Mix (Catalog # A46012, Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA) and run on a QuantStudio 6 Flex Real-Time PCR system. The thermal cycling conditions were set as follows: an initial activation step at 95 °C for 2 min, then 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s, and annealing at 58 °C for 60 s. A melting curve analysis was then conducted using the following steps: heating at 95 °C for 15 s, cooling to 60 °C for 1 min, and then gradually increasing the temperature to 95 °C for 15 s. The data obtained from the qRT-PCR and melting curve analysis were used to evaluate the specificity of the PCR amplification [26]. Primers were obtained from Integrated DNA Technologies (IDT, Inc., 1710 Commercial Park, Coralville, IA, USA). The sequences of primers used are provided in Table 1.

Table 1.
Sequence information of primers used in this study.
Two housekeeping genes, ACTB (beta-actin) and GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase), were used for normalizing the data. GAPDH was chosen for its expression stability as a normalization control. Ct values were normalized to the GAPDH reference gene to calculate ∆Ct values. No-template control (NTC) reactions were kept to identify PCR contamination [26]. Three technical replicates of each treatment were used in each experiment, and the experiment was repeated two times.
2.7. In Ovo Experiments
2.7.1. Virus Inoculation of Embryonated Chicken Eggs
Fertilized chicken eggs donated by a US commercial egg-layer operation were utilized for virus propagation. Upon arrival, the eggs were stored at a temperature of 10–15 °C with a relative humidity of 60% for a day. The next day, the eggs were cleaned and candled. Any broken or cracked eggs were discarded, while the intact eggs were placed in an incubator set to 100 °F with a humidity of 50–55%. On day 10, all eggs were candled, and those showing blood rings or dead embryos were discarded. Before moving the eggs to the biosafety cabinet for virus inoculation, their surfaces were disinfected with 70% ethanol.
Ten-day-old embryonated chicken eggs were arranged in a biosafety cabinet with the air sacs up. The egg surface was cleaned with 70% ethanol. A small hole was made in the shell over the air sac utilizing a needle (18 G x 1-1/2 in. BD Precision Glide™ Needle, Catalog #305196, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). A 0.2 mL H4N6 virus (HA titer = 8 log2) was aspirated in a 1 mL syringe with a 22 G, 1-1/2 in. The needle (1 mL BD® Tuberculin Syringe, catalog #309659, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) was inserted at a 45° angle into the allantoic cavity and inoculated. The syringe and needle were discarded. The hole was sealed using paraffin (Catalogue # 327212, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MA, USA), and the eggs were incubated at 100 °F and 50–55% humidity for three days without turning. After three days, the eggs were kept at 40 °C overnight, and allantoic fluid was harvested the next day. The fluid was then centrifuged at 500× g, 4 °C for 10 min to remove blood cells and tissue fragments, and was stored at −80 °C until use [22]. Each experiment included six eggs per treatment, and the experiment was repeated three times.
2.7.2. Evaluation of the Growth of AI Virus in Embryonated Chicken Eggs
The replication kinetics of the LPAI H4N6 virus were also conducted in embryonated chicken eggs. The eggs were incubated at 100 °F and 55% humidity for 10 days and used for the viral growth kinetics experiment. A 100 µL H4N6 virus stock containing (HA titer = 8 log2) was inoculated into 10-day-old embryonated chicken eggs. Eggs were sealed and kept for incubation at 100 °F, 55% humidity in an egg incubator (GQF Model 1502, Savannah, GA, USA). Allantoic fluid was collected at 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h.p.i. to calculate viral growth. The hemagglutination (HA) assay was performed at room temperature in two-fold serial dilution in a V-bottom 96-well plate [96 Well Conical (V) Bottom Plate, Catalog # 277143, Thermo Fisher Scientific, USA], using 0.5% chicken RBC (Chicken RBCs, 5%, catalog # 50-414-318, Fisher Scientific, 168 Third Avenue, Waltham, MA, USA) to test the HA property of the allantoic fluid. The titer was recorded and expressed in hemagglutination units per mL (HAU/mL). Each experiment included six eggs per treatment, and the experiment was repeated three times.
2.7.3. Determining the Antiviral Activity of CFE on H4N6 Virus in Embryonated Chicken Eggs
These experiments were conducted to determine the dose-dependent effects of CFE on the potential interaction of the H4N6 strain within the allantoic fluid. In the first experiment, an equal volume of CFE (109 CFU/mL) was mixed with different LPAI H4N6 virus concentrations (HA titer = 9 log2, 8 log2, 7 log2, 6 log2) and incubated at room temperature for 1 h. Sterile PBS was inoculated in the negative control groups. The H4N6 virus with the titer used for the respective experiment was inoculated in the positive control group for comparison with the treatment groups. After 1 h, the mixture was inoculated into the allantoic cavity of a 10-day-old embryonated chicken egg. The hole was sealed using paraffin and incubated for 72 h at 100 °F and 55% humidity. After three days, the allantoic fluid was harvested, and the viral titer was determined by HA assay, a well-established method for AIV studies [21]. The assay was conducted in a 96-well V-bottom using 0.5% SPF chicken RBC. Each experiment included six eggs per treatment, and the experiment was repeated three times (n = 18 eggs/treatment).
The second experiment investigated the dose-dependent antiviral activity of different concentrations of CFE on a set concentration of LPAI H4N6 virus. For this, CFE was obtained from an overnight culture of L. salivarius UMNPBX2 grown to 109 CFU/mL, diluted to 107 CFU/mL and 105 CFU/mL, and used. An HA assay was conducted using allantoic fluid to evaluate the viral titer [23]. Each experiment included six eggs per treatment, and the experiment was repeated three times (n = 18 eggs/treatment).
2.7.4. Effect of CFE on Embryo Survival in H4N6 Virus-Infected Eggs
The study evaluated the efficacy of CFE in preventing embryo death caused by experimental AI infection. The embryonated chicken eggs were divided into five treatment groups. Each group contained six eggs, and the experiment was repeated three times. In the first group, eggs inoculated with the H4N6 virus served as the positive control, while eggs inoculated with PBS served as the negative control. The eggs inoculated with CFE obtained from overnight L. salivarius UMNPBX2 growth at concentrations of 109, and diluent equivalent to 107 CFU/mL, and 105 CFU/mL, containing H4N6 (HA = 9 log2) virus were the treatment groups. After inoculation, eggs were incubated at 100 °F, 55% humidity in the incubator for 3 days. Eggs were candled to determine embryo viability. Live and dead embryos were recorded every day. Allantoic fluid was collected from a dead embryo to determine the viral titer.
2.8. Statistical Analysis
A completely randomized design (CRD) was utilized for all experiments. All experiments included duplicate samples for each treatment group, and each experiment was repeated at least three times. Significance was set at p < 0.05 for each test. Statistical analyses were conducted in R (version 4.3.1) using R Studio, with results reported as means ± SEM (n = 6). Differences between means were evaluated at a 95% confidence interval. The TCID50 assay and HA titer for each group were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and a pairwise t-test as a post hoc method. The percentage of live and dead embryos was calculated for each group for the embryo livability test. The Chi-square test was used for statistical analysis. Likewise, the cytotoxicity assay was performed using one-way ANOVA followed by a pair-wise t-test with Bonferroni adjustment for multiple comparisons. Gene expression data were analyzed relative to the housekeeping genes GAPDH and ACTB using QuantStudio Software v1.3 on the QuantStudio 6 Flex Real-Time PCR system, with data reported as mean ± SEM. The relative fold change of the housekeeping genes was computed using formula 2−∆∆Ct, where Ct is the cycle threshold for each gene and ∆Ct is the difference between the targeted and reference gene Ct values. ∆Ct values were determined as the mean of six replicates ± SD, while ∆∆Ct represented the difference between the ∆Ct of the negative control and treatment groups. For IL-6, a Welch t-test was performed, and a pooled t-test was employed for IL-1β, with significance set at p < 0.05. The results were visualized using bar and line graphs generated using the ggplot2 package in R [31].
3. Results and Discussion
The outcomes of H4N6 infection in MDCK cells, as determined in our study, are presented in Figure 1. The normal, uninfected MDCK cells (Figure 1A), change in response to H4N6 infection at 48 post-infection (h.p.i,) exhibiting plaque formation (Figure 1B) and CPE observed at 72 h.p.i. (Figure 1C). A detectable viral titer in MDCK was established after 12 h.p.i., peaking at 72 h.p.i. and remaining constant until 96 h.p.i.
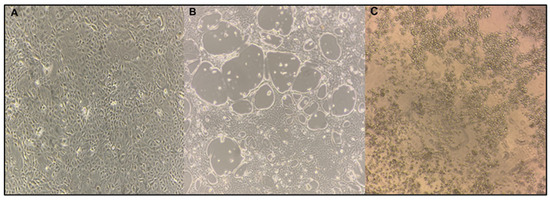
Figure 1.
Visualization of H4N6 virus infection in MDCK cells: (A) uninfected MDCK cell at 10× magnification; (B) MDCK cells infected with LPAI H4N6 displaying large plaques at 10× g magnification at 48 h.p.i.; (C) MDCK cells infected with LPAI H4N6 exhibited cytopathic effects (CPE) typical of AI, including cell rounding, degeneration, and detachment from the surface at 72 h.p.i.
The virus titer ranged from 2.8 to 6.5 log10 TCID50/mL (Figure 2A), indicating effective replication under the experimental conditions. No detectable viral titer was observed in PBS-treated (NC) groups, confirming the specificity of the viral infection observed. The results were consistent across three replicate experiments, demonstrating that H4N6 virus multiplication in MDCK cells was stable. Efficient viral replication is dependent on various parameters, including the MOI, the suitability of the culture medium, the use of trypsin-EDTA, the pathogenicity of the virus, and the presence of particular receptors on cell surfaces [18,32].
Figure 2.
(A) Growth kinetics of H4N6 virus grown in MDCK cells. MDCK cells were infected with the H4N6 virus at an MOI of 0.1 in the presence of trypsin. Extract was collected at various time points to assess viral growth kinetics using the TCID50 assay. A detectable viral titer was established after 12 h.p.i, peaking at 72 h.p.i, and remained the same until 96 h.p.i. (h.p.i—hours post-inoculation). (B) Growth kinetics of H4N6 virus in embryonated chicken eggs. The H4N6 virus stock, containing an HA titer of 8 log2, was inoculated into 11-day-old embryonated chicken eggs. The virus titer was measured at 4, 8, 12, 24, 48, 72, and 96 h. post-infection. The X-axis represents virus titer (Log10 TCID50/mL (for MDCK) & log HA units/50 µL for embryonated chicken eggs), and the Y-axis is time post-infection. The virus titer was observed after 8 h and reached maximum yield at 72 h.
In the current study, an MOI of 0.1 was utilized to investigate viral replication over time, allowing for several cycles of infection [32]. The MDCK cells possess both α-2,3 and α-2,6 sialic acid (SA) receptors. The AIV attaches to host cells primarily through the α-2,3 SA linkage [33,34,35]. Recent studies show that the duck-originated H4N6 AIV has an affinity for both α-2,3 and α-2,6 SA receptors, with higher affinity for α-2,3 receptors, indicating the potential to infect both humans and mammals [36,37].
Our study observed that viral replication peaked at 72 h.p.i., and then remained steady (Figure 2A), indicating the stage at which the virus produces the most infectious viral particles. After 72 h, the titer remained stable, indicating that most of the target MDCK cells had been infected and had either exhausted or achieved a steady state. The observed growth kinetics suggest that the virus is well-adapted to MDCK cells, and the dynamics may also reflect the cytotoxic effects of the virus on MDCK cells. As the virus replicates, it may cause cell death, which limits future viral production and contributes to the plateau observed after 72 h. Previously, it was found that the LPAI H9N2 virus replicated successfully in MDCK-II cells, reaching a titer of 4.9 log10 TCID50/mL, which is consistent with our observations [32]. Studies have shown that three strains (H1N1, H3N2, and H9N2) of AIV had a significant titer of 6.8 log10 ID50/mL at 72 h.p.i., compared to their replication potential in MDCK cells treated with 1 μg/mL of TPCK-trypsin [38]. Recent studies have shown that the H4N6 virus, isolated from wild birds, propagates well in MDCK cells, with peak titers achieved at 48 and 60 h.p.i. [37]. The replication kinetics studies in duck-origin H4N6 AIV revealed that these viruses replicate well in MDCK and avian Chicken Embryo Fibroblast (CEF) cells with a higher replication titer at 60 h.p.i. [36].
The replication kinetics results in embryonated chicken eggs showed that a virus titer was observed after 8 h and reached a maximum yield at 72 h.p.i. and then decreased afterward. The highest titer obtained was 9 log2 HAU (Figure 2B). The growth kinetics of AIV in embryonated chicken eggs depend on various factors, including the age of the embryo, route of inoculation, volume of inoculum, and external factors such as temperature and humidity. These studies are conducted to understand the phases of viral replication, including the lag, log, and plateau phases. Influenza viruses attach to the host through a receptor-mediated mechanism. For AIV, α2,3 sialic acid, and human influenza viruses, α2,6 sialic acid receptors are necessary for viral binding. The allantoic cells of embryonated chicken eggs contain α2,3 sialic acid receptors, so the allantoic cavity is a preferential site for AI virus inoculation [32,33].
The growth of the AIV in MDCK cells and embryonated chicken eggs indicated better virus multiplication (Figure 2). In a similar study, the highest yield was observed after 32 h. and remained the same virus titer until 72 h.p.i. in the embryonated chicken egg [32]. Another study [39] reported the optimal viral replication time of AI virus inoculated in embryonated chicken egg was 50–66 h.p.i. and the highest HA titer obtained from the allantoic fluid was 10 log2 HAU/50 µL. Wanasawaeng et al. [40] evaluated the replication kinetics and harvesting time for the H5N1 AIV and reported that the H5N1 virus multiplies better in embryonated chicken eggs than in MDCK cells, and the optimal harvesting time for the virus is 24 h.p.i. The earliest hour of viral detection by HA assay after inoculation in embryonated chicken eggs varied between 8 and 25 h. This depends on factors like the age of the embryo, the viral titer used for inoculation, and the method of allantoic fluid collection [41].
The LPAI virus multiplies at a higher rate in embryonated chicken eggs than in MDCK cells due to the presence of trypsin-like serine proteases in the allantoic and amniotic fluids. These enzymes are responsible for cleaving the HA protein, which is crucial for initiating viral multiplication and propagation [42,43]. An earlier study [42] showed that the LPAI virus strains such as H4N6 multiply effectively and reach detectable titers in the allantoic fluid as early as 24 h.p.i. and maximum titers by 48 h.p.i. under favorable conditions. Supporting our current findings, Moresco et al. [44] also reported that both MDCK cells and embryonated chicken eggs facilitate the growth of the AI virus. However, the viral isolation rate was higher in embryonated chicken eggs compared to MDCK cells.
The MDCK cell line is a widely used model for investigating influenza viruses’ responses to external agents [20,45]. However, before evaluating the antiviral properties of CFE, its cytotoxicity must be assessed to determine its potential to cause toxicity to the host cells [46]. The CFE includes byproducts of growth or fermentation in various substrates like short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), lactic acid, proteins, bacteriocins, and endotoxins [47,48]. These chemicals possess various properties, including antibacterial and immunomodulatory effects. However, higher doses and more extended exposure periods of these chemicals may cause cytotoxicity in epithelial cells, such as MDCK cells, by interacting with cellular pH or disrupting membrane integrity [49]. The cytotoxic effects of CFE on the MDCK cell line were determined using the MTT assay (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
MDCK cell viability at different concentrations of CFE after 2 h of incubation, as observed using the MTT assay. The X-axis represents groups, and the Y-axis represents cell viability in percentage. In the control group, 100% cell viability was observed. CFEs from 103 to 109 CFU/mL were used as treatments. ‘ns’ indicates no significant difference, (n = 6/treatment group).
The effects of different CFE dosages on MDCK cells were studied (Figure 3). The MTT test enables the measurement of the metabolic activity of MDCK cells after exposure to varying doses of CFE. The MTT assay operates on the principle that healthy cells with active metabolism can convert MTT, a tetrazolium salt, into formazan crystals, which can then be measured spectrophotometrically [45]. Our study showed 100% cell viability in the control group when treated with PBS. No decrease in cell viability was observed after 2 h incubation with CFEs (Figure 3).
A previous study aligned with the concentrations of L. salivarius UMNPBX2 used in our study [50]. They observed no toxic effect of probiotics at concentrations ranging from 107 to 109 CFU/mL in MDCK cells. It is essential to differentiate between cytotoxicity and antiviral activity, thereby determining the CFE inclusion limit that enables the selection of the working doses that are both effective against the virus and safe for host cells [51]. Cell viability above 85% has been reported as the threshold for selecting the CFE concentration in antiviral studies [6]. The bacteriocin enterocin B, derived from the probiotic bacterial strain Enterococcus faecium L3, exhibited no cytotoxicity in MDCK cells at 10 μg/mL concentrations. However, a 25% reduction in cell viability was detected when used at the undiluted starting concentration [52]. Cell-free supernatants from Lactobacillus species were tested for cytotoxicity in Vero and MDCK cells. The results showed no cytotoxic effects at a concentration of 3 × 105 CFU/mL [53]. Our studies examined the cytotoxicity of CFE concentrations in MDCK cells and identified optimal concentrations against the LPAI virus.
To follow, the effect of CFE at 109 CFU/mL against varying concentrations of H4N6 (102.6, 104.6, 105.6, and 106.6 ID50/mL) was determined (Figure 4A). This step determined the different viral concentrations that the highest concentration of CFE could inhibit. Although it is challenging to produce CFEs from L. salivarius UMNPBX2 at concentrations exceeding 109 CFU/mL in low volumes, we have standardized the probiotic growth to as high as 1011–12 CFU/bacterial button in large volume flasks. Even after 72 h of incubation, no CPE was observed in the MDCK cells exposed to CFE and viral concentrations up to 106.6 ID50/mL (p < 0.05; Figure 4A).
Figure 4.
(A) Effect of CFE on varying concentrations of LPAI H4N6 virus. MDCK cells were exposed to 100 µL of varying levels of H4N6 and the highest concentration of CFE and incubated at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 environment. Control groups: C1—102.6, C2—104.6, C3—105.6, and C4—106.6 ID50/mL of H4N6. Treatment groups: T1, T2, T3, and T4. Bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). After 72 h, MDCK cells treated with 109 CFU/mL CFE displayed no CPE, suggesting potential inhibition of AIV replication. a–e: Bars with different letters significantly differ at p < 0.05 (n = 6/treatment group). (B) Effect of CFE against LPAI H4N6 virus. Control groups: C1, C2, C3 (H4N6 virus-infected groups). Treatment groups: H4N6 + CFE at concentrations obtained from 105 (T1), 107 (T2), and 109 (T3) CFU/mL overnight growth of L. salivarius UMNPBX2. The experiment was repeated three times. Bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). MDCK cells treated with 109 CFU/mL CFE showed no CPE, suggesting potential inhibition of AIV replication. A significant 1.5 log reduction in viral infectivity was observed at 107 CFU/mL (p = 0.01), whereas 105 CFU/mL L. salivarius UMNPBX2 CFE did not affect viral titers, which remained similar to control levels (p > 0.05). a–c: Bars with different letters significantly differ at p < 0.05 (n = 6/treatment group).
Next, we assessed the range of CFE concentrations (109, 107, and 105 CFU/mL) against the highest concentration of virus tested in the previous experiment (106.6 TCID50/mL) in MDCK cells (Figure 4B). As observed in the last experiment, MDCK cells treated with 109 CFU/mL of CFE exhibited no CPE, suggesting a potential inhibitory effect of CFE on AI virus replication without any deleterious effects on the host cells (p < 0.05; p = 3 × 10−10). The group treated with CFE from 107 CFU/mL L. salivarius UMNPBX2 culture demonstrated a significant reduction of 1.8 log in viral infectivity (p < 0.05; p = 0.013). However, there was no reduction in viral titer at the lower concentration of CFE (105 CFU/mL), which remained comparable to the controls (p > 0.05, Figure 4B; Supplementary Figure S1). These findings underscore the dose-dependent antiviral activity of CFE against AI viruses in MDCK cells.
This study also analyzed immune gene expression in MDCK epithelial cells exposed to CFEs (Figure 5). Although a significantly lower expression was observed with IL-6, compared to the control, the difference in fold-change was less in magnitude [Figure 5 (left panel); p = 0.00004]. Additionally, no significant difference was observed in IL-1β expression between the CFE-treated and control groups [Figure 5 (right panel); p > 0.05].
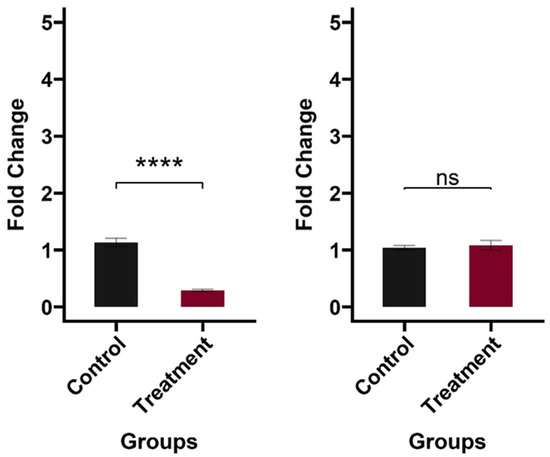
Figure 5.
Cytokine gene expression in MDCK cells induced by CFE. Left panel: IL-6 expression in MDCK cells (p < 0.05); Right panel: IL-1β expression in MDCK cells (p > 0.05). MDCK cells were treated with 100 µL of CFE and incubated for 6 h. MDCK cells treated with PBS served as the negative control. After incubation, cells were lysed immediately in the culture dish using Buffer RLT to extract RNA. cDNA was extracted, and gene expression was evaluated using RT-qPCR, with GAPDH serving as a housekeeping gene for relative fold change estimates. Three biological replicates were used for each treatment, and each qPCR reaction was performed twice, resulting in six samples per group. The asterisks (****) represent significant differences among the treatment and control groups (p < 0.05), whereas ‘ns’ indicates no significant difference.
The MDCK lines have been previously used to investigate gene expression and basal protein release under various stress conditions [26]. The influenza virus uses a receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway for host entry. Once inside the host, viral components are recognized by pathogen recognition receptors (PRRs), including Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in endosomes and retinoic acid-inducible gene I-like receptors (RLRs) in the cytoplasm [54]. This recognition initiates signaling pathways that activate IFN-regulating factors and produce pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and IL-1β [54]. In a previous study, stimulation of macrophages with three heat-killed Lactobacillus sp. resulted in significantly higher production of IFN-γ, IFN-β, and IL-1β [5]. Although we found a comparable expression of IL-1β (p > 0.05) and a slightly reduced expression of IL-6 compared to the control (p < 0.05), our current immune response findings are limited to evaluating only the expression of two pro-inflammatory cytokines in MDCK cells. Our planned in vivo studies will have a broader profiling of the avian immunome in response to AI challenge and CFE treatments.
After the studies in MDCK cells, the potential of CFE on AIV in embryonated chicken eggs was examined. As we did in the MDCK cells, we first investigated the effect of CFE, obtained from a culture concentration of 109 CFU/mL, against varying concentrations of H4N6 (HA titer 6 log2, 7 log2, 8 log2, and 9 log2). We noticed a complete inhibition of HA activity in all treatment groups, indicating a total suppression of viral infection in embryonated eggs inoculated with a mixture of CFE and the virus (Figure 6A).
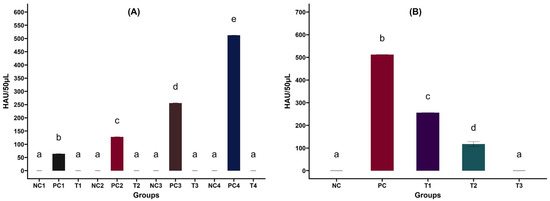
Figure 6.
(A) Effect of CFE on varying concentrations of LPAI H4N6 virus in embryonated chicken eggs. Control groups: PC1—6 log2, PC2—7 log2, PC3—8 log2, PC4—9 log2 HAU/50 µL. Treatment groups (T1, T2, T3, T4): H4N6 + CFE at 109 CFU/mL. Negative control (NC1, NC2, NC3, NC4)-PBS inoculated groups. The experiment was repeated three times. a–e Bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). After 72 h, embryonated eggs inoculated with 109 CFU/mL CFE displayed no HA activity, suggesting potential inhibition of AIV replication. (B) Effect of CFE against LPAI H4N6 virus in embryonated chicken eggs. Positive Control groups (PC)—H4N6 (9 log2) inoculated groups. Treatment groups: H4N6 (9 log2) + L. salivarius UMNPBX2 CFE obtained from 105 (T1), 107 (T2), and 109 (T3) CFU/mL. Negative control (NC)—PBS inoculated groups. The experiment was repeated three times. a–d Bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). Embryonated eggs inoculated with 109 CFU/mL L. salivarius UMNPBX2 CFE showed no HA activity, suggesting potential inhibition of AIV replication. A significant reduction in HA activity was observed at 107 CFU/mL and 105 CFU/mL CFE-treated groups, indicating a dose-dependent inhibition of viral replication (p < 0.05).
To follow up, we investigated the application of varying CFE levels at a set virus concentration in embryonated chicken eggs. CFE prepared from L. salivarius UMNPBX2 at a 109 CFU/mL concentration completely suppressed viral replication in embryonated chicken eggs (Figure 6B). The CFE from lower concentrations (107 and 105 CFU/mL) also significantly reduced viral replication (p < 0.05; Figure 6B), but it was less effective than at higher concentrations. This is an evident dose-dependent viral inhibition by CFE. The results suggest that CFE possesses significant antiviral properties, as evidenced by its effect on embryonated eggs. The mechanism of action behind the antiviral property of CFE is unknown and has to be explored.
To validate our findings, we evaluated the potential of CFE on embryo survival in H4N6 virus-infected embryonated eggs. The CFE was prepared from an overnight culture of L. salivarius UMNPBX2 (105, 107, and 109 CFU/mL) and tested against the H4N6 virus at a 9 log2 HAU/50 µL concentration. The results revealed a significant dose-dependent increase in embryonic survival rate (p < 0.05, Figure 7).
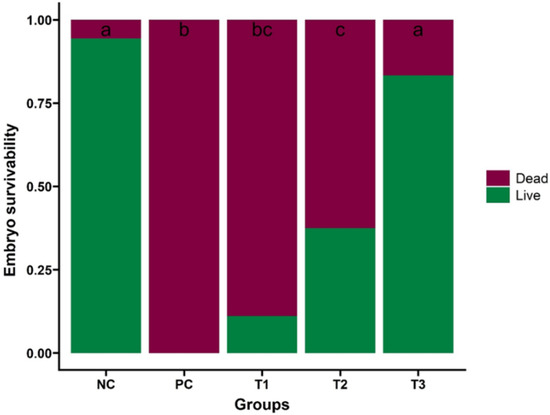
Figure 7.
Effect of CFE on embryo survival in H4N6 virus-infected eggs. The embryo survival percentage in the treatment groups was compared with that of the positive control (PC) and PBS-treated groups (NC). Treatment groups: H4N6 (9 log2 HAU/50 µL) + CFE at 105 (T1), 107 (T2), and 109 (T3) CFU/mL. Bars with different letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05). The study was performed three times, with six eggs per treatment group in each experiment (n = 18 eggs/treatment group), and the data are presented as mean ± SEM. a–c: Bars with different letters significantly differ at p < 0.05.
The highest concentration of CFE provided the best survivability of the embryos (15/18 embryos survived), and the lower survivability was observed at a lower concentration of CFE (105 CFU/mL) (2/18 embryos survived). The highest lethality was observed in the positive control group (inoculated with virus alone, without CFE; 18/18 embryos dead). One embryo was dead in the NC group. The observed embryonic survivability with CFEs may be attributed to the higher concentrations of bacteriocins, organic acids, and other bioactive compounds in CFE. These compounds could create an adverse environment for viral multiplication and enhance the immune response against the virus. Studies have reported enhanced immune responses following stimulation with probiotic-derived components [5,7,15]. These bioactive compounds may also help reduce oxidative stress, thereby improving the survival rate of infected cells [55]. The study by Rather and co-workers also revealed a similar pattern of embryo survivability compared to that of embryonated chicken eggs inoculated with a combination of H1N1 virus and L. plantarum probiotic supernatant [51]. Although these studies suggest excellent immunogenic potential of lactic acid bacteria-derived metabolites, further research is needed to elucidate the antiviral mechanisms and optimize their safety and efficacy in field conditions. More investigations on live poultry are required to determine whether the CFE application results in better survivability, resisting the infection without any adverse health conditions.
The antibacterial property of L. salivarius UMNPBX2 on multiple serotypes of Salmonella in turkeys has already been established previously by our group, indicating the potential of the probiotic strain to be friendly to the gut microbiome and metabolome [56,57,58]. L. salivarius UMNPBX2-derived CFEs could be rich in many metabolites like lactic acid, short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), antimicrobial peptides, and other small molecules. These metabolites create an unfavorable environment for microbes, including virus replication [59,60]. The SCFA metabolism, mainly butyrate metabolism, is negatively associated with Influenza A virus loads [61]. Lactic acid inhibits viral entry to the host cell either by directly binding to the virus or disrupting the viral envelope [62]. For example, the peptides isolated from Bacillus subtilis completely inhibited the influenza virus multiplication in MDCK cells [50]. Several other factors, like competitive exclusion for the receptors, physical barrier formation by probiotic CFEs, and immunomodulation, also contribute to the antiviral property of probiotics and their metabolites [53,63,64].
4. Conclusions
Overall, the study found that L. salivarius UMNPBX2-derived CFE exhibited significant antiviral activity against the LPAI H4N6 strain, with the highest levels of activity observed in the extract obtained from the highest culture concentration. CFEs did not increase the pro-inflammatory cytokine gene expression of the studied genes but rather tended to decrease it (IL-6). Postbiotics could potentially be utilized as an antiviral strategy in conjunction with vaccination or other biosecurity measures. Further studies are needed to validate the results in poultry and from an immunomics perspective. It will also be resourceful for producers and integrators to explore host-derived probiotic products for addressing pressing issues such as avian influenza.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/app151810075/s1, Figure S1: Effect of different concentrations of Lactobacillus salivarius cell-free extracts (CFEs; 105, 107, and 109 CFU/mL) on H4N6 at (106.6 ID50/mL) as determined by TCID50 (Tissue Culture Infectious Dose 50%) assay.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.K.J.; methodology, A.A. and D.M.P.; formal analysis, A.A. and D.M.P.; investigation, A.K.J., A.A. and D.M.P.; resources, A.K.J.; data curation, A.A.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.; writing—review and editing, A.K.J., D.M.P., V.D.K. and M.C.-J.C.; visualization, A.A.; supervision, A.K.J.; project administration, A.K.J.; funding acquisition, A.K.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station for Avian Influenza seed research funds and an equipment seed grant towards the AI Virology Laboratory. Support from the Minnesota Agricultural Experiment Station project (MIN-16-141; A.K.J.) is also acknowledged. The Authors would like to thank the Minnesota Discovery, Research, and InnoVation Economy—Global Food Venture Graduate Professional Development (MnDRIVE-GFV) Fellowship at the University of Minnesota, which was awarded to A.A. during this study period.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The use of the HPAI strain in this study was approved by the Institutional Biosafety Committee (IBC) at the University of Minnesota, protocol #2310-41472H (19 December 2023–24 February 2026).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article and Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our gratitude to Bernie Beckman and Jeremy Lies (Hy-Line NA) for donating embryonated eggs for this study. We want to extend our appreciation to Luna Akhtar, Hamza Javaid and Peter Bina for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the readability of the Figure 7. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- CDC Bird Flu. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/bird-flu/index.html (accessed on 13 September 2024).
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. 2024. Avian Influenza Weekly Update 2025. Available online: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/380024 (accessed on 1 September 2025).
- Alqazlan, N.; Astill, J.; Raj, S.; Sharif, S. Strategies for Enhancing Immunity against Avian Influenza Virus in Chickens: A Review. Avian Pathol. 2022, 51, 211–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladman, B.S.; Gelb, J.; Sauble, L.A.; Murphy, M.V.; Spackman, E. Protection Afforded by Avian Influenza Vaccination Programmes Consisting of a Novel RNA Particle and an Inactivated Avian Influenza Vaccine against a Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus Challenge in Layer Chickens up to 18 Weeks Post-Vaccination. Avian Pathol. 2019, 48, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojadoost, B.; Kulkarni, R.R.; Brisbin, J.T.; Quinteiro-Filho, W.; Alkie, T.N.; Sharif, S. Interactions between Lactobacilli and Chicken Macrophages Induce Antiviral Responses against Avian Influenza Virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 125, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, R.; Alam, M.B.; Paudel, K.R.; Ahmed, K.A.; Devkota, H.P.; Lee, S.-H.; Hansbro, P.M.; Park, Y.-H. Anti-Influenza Virus Potential of Probiotic Strain Lactoplantibacillus plantarum YML015 Isolated from Korean Fermented Vegetable. Fermentation 2022, 8, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqazlan, N.; Alizadeh, M.; Boodhoo, N.; Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Nagy, E.; Bridle, B.; Sharif, S. Probiotic Lactobacilli Limit Avian Influenza Virus Subtype H9N2 Replication in Chicken Cecal Tonsil Mononuclear Cells. Vaccines 2020, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talebi, A.; Amani, A.; Pourmahmod, M.; Saghaei, P.; Rezaie, R. Synbiotic Enhances Immune Responses against Infectious Bronchitis, Infectious Bursal Disease, Newcastle Disease and Avian Influenza in Broiler Chickens. Vet. Res. Forum 2015, 6, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, T.; Ara, G.; Ali, N.; ud Din Mufti, F.; Imran Khan, M. Effects of Dietary Supplementation of Mannan-Oligosaccharide on Virus Shedding in Avian Influenza (H9N2) Challenged Broilers. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 17, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbour, E.K.; Yaghi, R.H.; Jaber, L.S.; Shaib, H.A.; Harakeh, S. Safety and Antiviral Activity of Essential Oil Against Avian Influenza and NewCastle Disease Viruses. Int. J. Appl. Res. Vet. Med. 2010, 8, 60–64. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Baker, D.H.; Amarowicz, R.; Kandeil, A.; Ali, M.A.; Ibrahim, E.A. Antiviral Activity of Lavandula angustifolia L. and Salvia officinalis L. Essential Oils against Avian Influenza H5N1 Virus. J. Agric. Food Res. 2021, 4, 100135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, S.; Matsuyama-Kato, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Boodhoo, N.; Nagy, E.; Mubareka, S.; Karimi, K.; Behboudi, S.; Sharif, S. Treatment with Toll-like Receptor (TLR) Ligands 3 and 21 Prevents Fecal Contact Transmission of Low Pathogenic H9N2 Avian Influenza Virus (AIV) in Chickens. Viruses 2023, 15, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrukee, R.; Hurt, A.C. Antiviral Drugs for the Treatment and Prevention of Influenza. Curr. Treat. Options Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Galvin, H.D.; Haw, T.Y.; Nutsford, A.N.; Husain, M. Drug Resistance in Influenza A Virus: The Epidemiology and Management. Infect. Drug Resist. 2017, 10, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.J.; Rather, I.A.; Kumar, V.J.R.; Choi, U.H.; Moon, M.R.; Lim, J.H.; Park, Y.H. Evaluation of Leuconostoc mesenteroides YML003 as a Probiotic against Low-Pathogenic Avian Influenza (H9N2) Virus in Chickens: Probiotic against H9N2 Virus in Chickens. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 113, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tharmaraj, N.; Shah, N.P. Selective Enumeration of Lactobacillus Delbrueckii Ssp. Bulgaricus, Streptococcus Thermophilus, Lactobacillus Acidophilus, Bifidobacteria, Lactobacillus Casei, Lactobacillus Rhamnosus, and Propionibacteria. J. Dairy. Sci. 2003, 86, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, D.V.T.; Kollanoor-Johny, A. Effect of Propionibacterium Freudenreichii on Salmonella Multiplication, Motility, and Association with Avian Epithelial Cells1. Poult. Sci. 2017, 96, 1376–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youil, R.; Su, Q.; Toner, T.J.; Szymkowiak, C.; Kwan, W.-S.; Rubin, B.; Petrukhin, L.; Kiseleva, I.; Shaw, A.R.; DiStefano, D. Comparative Study of Influenza Virus Replication in Vero and MDCK Cell Lines. J. Virol. Methods 2004, 120, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balish, A.L.; Katz, J.M.; Klimov, A.I. Influenza: Propagation, Quantification, and Storage. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2013, 29, 15G.1.1–15G.1.24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugovtsev, V.Y.; Melnyk, D.; Weir, J.P. Heterogeneity of the MDCK Cell Line and Its Applicability for Influenza Virus Research. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Chambers, B.S.; Hensley, S.E.; López, C.B. Propagation and Characterization of Influenza Virus Stocks That Lack High Levels of Defective Viral Genomes and Hemagglutinin Mutations. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, I.A.; Kamli, M.R.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Ali, S. Evaluation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KAU007 against Low-Pathogenic Avian Influenza Virus (H9N2). Pathogens 2022, 11, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spackman, E. (Ed.) Animal Influenza Virus: Methods and Protocols; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 2123, ISBN 978-1-07-160345-1. [Google Scholar]
- Frias-De-Diego, A.; Crisci, E. Use of Crystal Violet to Improve Visual Cytopathic Effect-Based Reading for Viral Titration Using TCID50 Assays. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 180, e63063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, V.D.; Roach, E.; Zaidman, N.A.; Panoskaltsis-Mortari, A.; Rotschafer, J.H.; O’Grady, S.M.; Cheeran, M.C.-J. Differential Induction of Type I and Type III Interferons by Swine and Human Origin H1N1 Influenza A Viruses in Porcine Airway Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capellini, F.M.; Vencia, W.; Amadori, M.; Mignone, G.; Parisi, E.; Masiello, L.; Vivaldi, B.; Ferrari, A.; Razzuoli, E. Characterization of MDCK Cells and Evaluation of Their Ability to Respond to Infectious and Non-Infectious Stressors. Cytotechnology 2020, 72, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauter, S.N.; Allenspach, K.; Gaschen, F.; Gröne, A.; Ontsouka, E.; Blum, J.W. Cytokine Expression in an Ex Vivo Culture System of Duodenal Samples from Dogs with Chronic Enteropathies: Modulation by Probiotic Bacteria. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2005, 29, 605–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menezes-Souza, D.; Corrêa-Oliveira, R.; Guerra-Sá, R.; Giunchetti, R.C.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Oliveira, G.C.; Reis, A.B. Cytokine and Transcription Factor Profiles in the Skin of Dogs Naturally Infected by Leishmania (Leishmania) Chagasi Presenting Distinct Cutaneous Parasite Density and Clinical Status. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 177, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalilian, I.; Peranec, M.; Curtis, B.L.; Seavers, A.; Spildrejorde, M.; Sluyter, V.; Sluyter, R. Activation of the Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern Receptor P2X7 Induces Interleukin-1β Release from Canine Monocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2012, 149, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalcanti, A.S.; Ribeiro-Alves, M.; de Pereira, L.O.R.; Mestre, G.L.; Ferreira, A.B.R.; Morgado, F.N.; Boité, M.C.; Cupolillo, E.; Moraes, M.O.; Porrozzi, R. Parasite Load Induces Progressive Spleen Architecture Breakage and Impairs Cytokine mRNA Expression in Leishmania infantum-Naturally Infected Dogs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0123009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2. WIREs Comput. Stat. 2011, 3, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvin, R.; Shehata, A.A.; Heenemann, K.; Gac, M.; Rueckner, A.; Halami, M.Y.; Vahlenkamp, T.W. Differential Replication Properties among H9N2 Avian Influenza Viruses of Eurasian Origin. Vet. Res. 2015, 46, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Suzuki, Y.; Takada, A.; Kawamoto, A.; Otsuki, K.; Masuda, H.; Yamada, M.; Suzuki, T.; Kida, H.; Kawaoka, Y. Differences in Sialic Acid-Galactose Linkages in the Chicken Egg Amnion and Allantois Influence Human Influenza Virus Receptor Specificity and Variant Selection. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 3357–3362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrosovich, M.; Matrosovich, T.; Uhlendorff, J.; Garten, W.; Klenk, H.-D. Avian-Virus-like Receptor Specificity of the Hemagglutinin Impedes Influenza Virus Replication in Cultures of Human Airway Epithelium. Virology 2007, 361, 384–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisfeld, A.J.; Neumann, G.; Kawaoka, Y. Influenza A Virus Isolation, Culture and Identification. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2663–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhao, C.; Guo, Y.; Dong, J.; Du, F.; Zhou, Y.; Shu, S.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Cao, Z.; et al. Genetic and Biological Characteristics of Duck-Origin H4N6 Avian Influenza Virus Isolated in China in 2022. Viruses 2024, 16, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Tian, J.; Li, M.; Bai, X.; Zhao, Z.; Shi, J.; Zeng, X.; Tian, G.; Guan, Y.; Cui, P.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenicity of Influenza A (H4N6) Virus Isolated from Wild Birds in Jiangsu Province, China, 2023. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2024, 2024, 7421277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyushina, N.A.; Ikizler, M.R.; Kawaoka, Y.; Rudenko, L.G.; Treanor, J.J.; Subbarao, K.; Wright, P.F. Comparative Study of Influenza Virus Replication in MDCK Cells and in Primary Cells Derived from Adenoids and Airway Epithelium. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 11725–11734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadimipour, R.; Ghadimipour, I.; Ameghi, A.; Masoudi, S.; Sedigh-Eteghad, S.; Ebrahimi, M.M. Monitoring Virus Harvesting Time in Embryonated Chicken Eggs Inoculated with Avian Influenza H9N2 Vaccine Strain. Arch. Razi Inst. 2014, 69, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanasawaeng, W.; Bunpapong, N.; Leelamanit, W.; Thanawongnuwech, R. Growth Characteristics of the H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus in Chicken Embryonic Eggs and MDCK Cells. Thai J. Vet. Med. 2009, 39, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freymann, M.W.; Tamm, I.; Green, R.H. Growth Curves of Influenza Virus Based on Hemagglutination Titers in Individual Embryonated Eggs. Yale J. Biol. Med. 1951, 23, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lang, V.; Marjuki, H.; Krauss, S.L.; Webby, R.J.; Webster, R.G. Different Incubation Temperatures Affect Viral Polymerase Activity and Yields of Low-Pathogenic Avian Influenza Viruses in Embryonated Chicken Eggs. Arch. Virol. 2011, 156, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandeil, A.; Bagato, O.; Zaraket, H.; Debeauchamp, J.; Krauss, S.; El-Shesheny, R.; Webby, R.J.; Ali, M.A.; Kayali, G. Proteolytic Enzymes in Embryonated Chicken Eggs Sustain the Replication of Egg-Grown Low-Pathogenicity Avian Influenza Viruses in Cells in the Absence of Exogenous Proteases. J. Virol. Methods 2014, 202, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moresco, K.A.; Stallknecht, D.E.; Swayne, D.E. Evaluation of Different Embryonating Bird Eggs and Cell Cultures for Isolation Efficiency of Avian Influenza A Virus and Avian Paramyxovirus Serotype 1 from Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction–Positive Wild Bird Surveillance Samples. J. VET Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, H.-C.; Lehman, C.W.; Lin, C.-C.; Tsai, S.-W.; Chen, C.-M. Functional Evaluation for Adequacy of MDCK-Lineage Cells in Influenza Research. BMC Res. Notes 2019, 12, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Meerloo, J.; Kaspers, G.J.L.; Cloos, J. Cell Sensitivity Assays: The MTT Assay. In Cancer Cell Culture: Methods and Protocols; Cree, I.A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 237–245. ISBN 978-1-61779-080-5. [Google Scholar]
- Franco-Robles, E. (Ed.) Prebiotics and Probiotics: From Food to Health; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tindjau, R.; Chua, J.-Y.; Liu, S.-Q. Co-Culturing Propionibacterium Freudenreichii and Bifidobacterium Animalis Subsp. Lactis Improves Short-Chain Fatty Acids and Vitamin B12 Contents in Soy Whey. Food Microbiol. 2024, 121, 104525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niamah, A.K.; Al-Sahlany, S.T.G.; Verma, D.K.; Shukla, R.M.; Patel, A.R.; Tripathy, S.; Singh, S.; Baranwal, D.; Singh, A.K.; Utama, G.L.; et al. Emerging Lactic Acid Bacteria Bacteriocins as Anti-Cancer and Anti-Tumor Agents for Human Health. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starosila, D.; Rybalko, S.; Varbanetz, L.; Ivanskaya, N.; Sorokulova, I. Anti-Influenza Activity of a Bacillus subtilis Probiotic Strain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e00539-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rather, I.A.; Kamli, M.R.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Paray, B.A. Potential Antiviral Activity of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum KAU007 against Influenza Virus H1N1. Vaccines 2022, 10, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermolenko, E.I.; Desheva, Y.A.; Kolobov, A.A.; Kotyleva, M.P.; Sychev, I.A.; Suvorov, A.N. Anti–Influenza Activity of Enterocin B In Vitro and Protective Effect of Bacteriocinogenic Enterococcal Probiotic Strain on Influenza Infection in Mouse Model. Probiotics Antimicro Prot. 2019, 11, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-J.; Song, J.-H.; Ahn, Y.-J.; Baek, S.-H.; Kwon, D.-H. Antiviral Activities of Cell-Free Supernatants of Yogurts Metabolites against Some RNA Viruses. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2009, 228, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, A.H.; Cardani, A.; Braciale, T.J. The Host Immune Response in Respiratory Virus Infection: Balancing Virus Clearance and Immunopathology. Semin Immunopathol 2016, 38, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Hack, M.E.; El-Saadony, M.T.; Alqhtani, A.H.; Swelum, A.A.; Salem, H.M.; Elbestawy, A.R.; Noreldin, A.E.; Babalghith, A.O.; Khafaga, A.F.; Hassan, M.I.; et al. The Relationship among Avian Influenza, Gut Microbiota and Chicken Immunity: An Updated Overview. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjankattil, S.; Dewi, G.; Peichel, C.; Creek, M.; Bina, P.; Lerohl, K.; Deniz, K.; Akhtar, L.; Porter, R., Jr.; Johnson, T.J.; et al. Dairy-origin Propionibacterium freudenreichii, Turkey-Origin Lactobacillus salivarius, and a Salmonella Typhimurium Vaccine Elicit Comparable Colonization Resistance on Drug-Resistant Salmonella serotypes (S. Reading, S. Agona, and S. Saintpaul) in Growing Turkeys After Oral Challenge. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2024, 33, 100428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muringattu Prabhakaran, D.; Kollanoor Johny, A.; Nair, D.V.T.; Manjankattil, S.; Johnson, T.J.; Noll, S.; Reed, K.M. Beneficial Cecal Microbiome Modulation in Turkeys Exposed to Probiotics and Vaccine After Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella Heidelberg Challenge. Microbiol. Res. 2025, 16, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, G.; Ramanathan, R.; Kollanoor Johny, A. Cecal Metabolome Profiles of Turkey Poults in Response to Salmonella Heidelberg Challenge with or Without Turkey-Derived Lactobacillus Probiotic and Trans-Cinnamaldehyde. Animals 2025, 15, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosmann, C.; Anahtar, M.N.; Handley, S.A.; Farcasanu, M.; Abu-Ali, G.; Bowman, B.A.; Padavattan, N.; Desai, C.; Droit, L.; Moodley, A.; et al. Lactobacillus-Deficient Cervicovaginal Bacterial Communities Are Associated with Increased HIV Acquisition in Young South African Women. Immunity 2017, 46, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Moon, A.; Huang, J.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.-J. Antiviral Effects and Underlying Mechanisms of Probiotics as Promising Antivirals. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 928050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Fang, Z.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. The Potential Role of Probiotics in Protection against Influenza a Virus Infection in Mice. Foods 2021, 10, 902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachedjian, G.; Aldunate, M.; Bradshaw, C.S.; Cone, R.A. The Role of Lactic Acid Production by Probiotic Lactobacillus Species in Vaginal Health. Res. Microbiol. 2017, 168, 782–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, R.; Shah, N.P. Immune System Stimulation by Probiotic Microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 54, 938–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karst, S.M. The Influence of Commensal Bacteria on Infection with Enteric Viruses. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).