Application of the Expectation-Maximization Clustering Method for Identifying Li Geochemical Anomalies in Stream Sediments in Southeastern Hunan Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Study Area and Samples
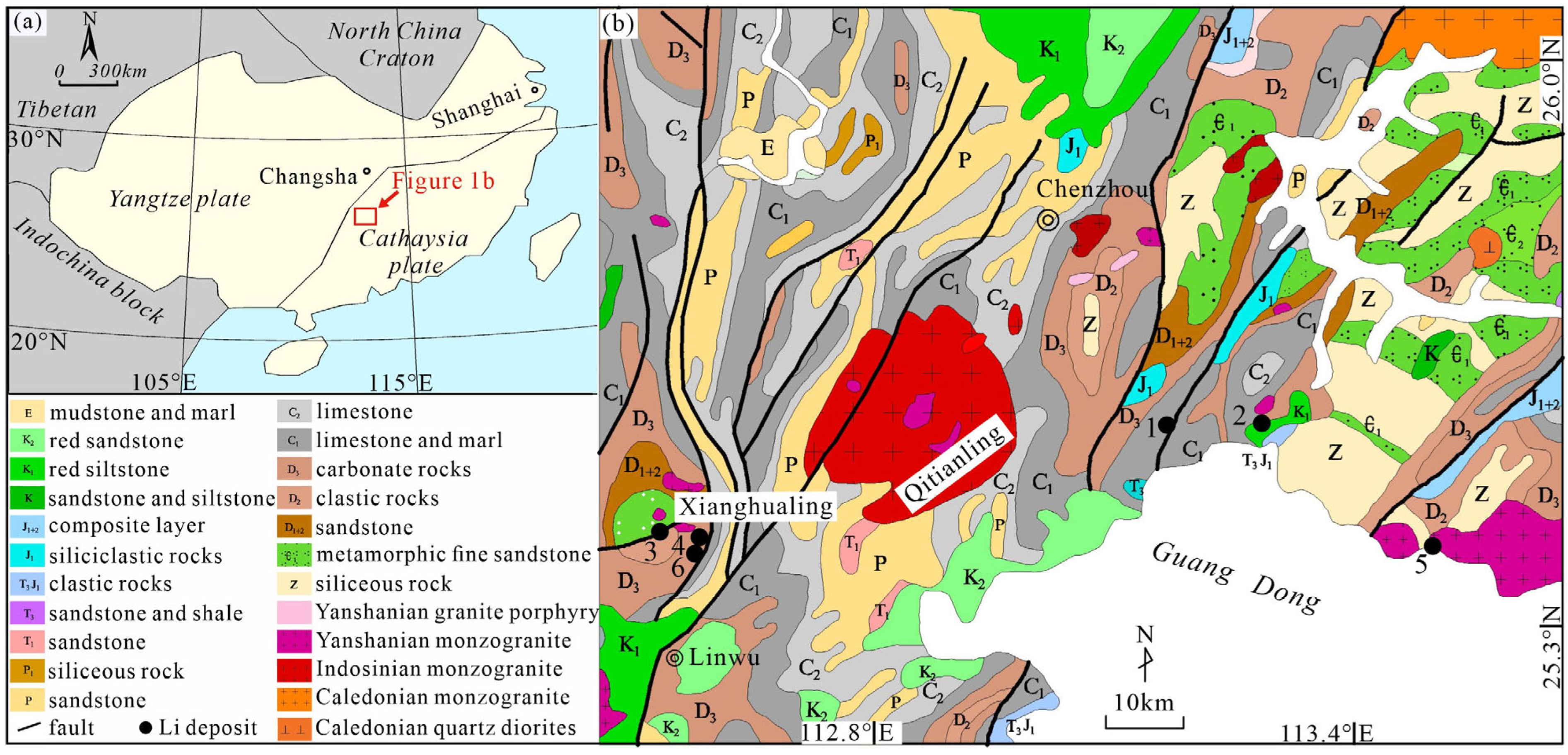
2.1. Geological Setting of the Study Area
2.2. Samples and Analysis
3. Methods
3.1. The EM Clustering Algorithm
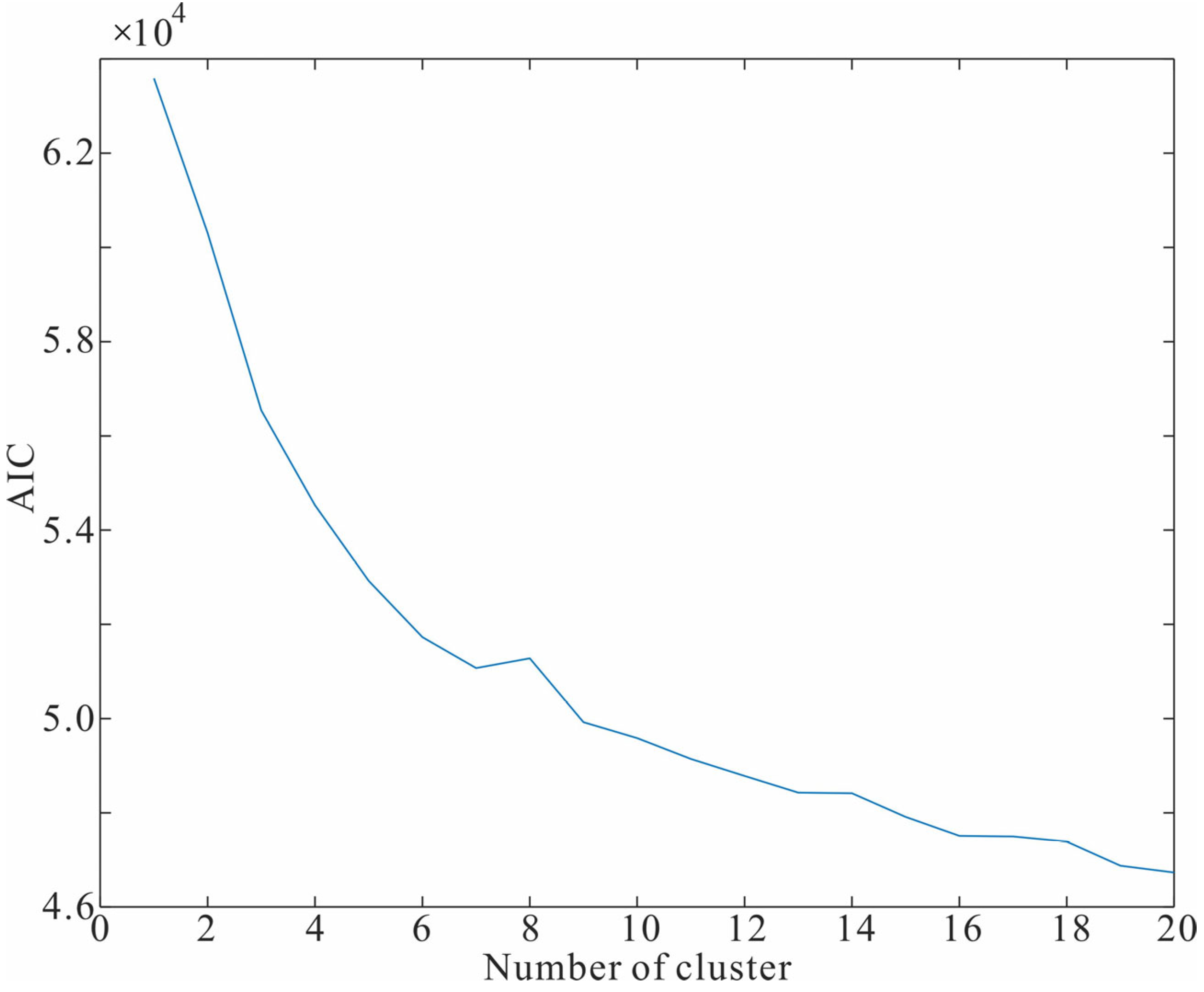
3.2. Data Processing Procedure
4. Results and Discussion
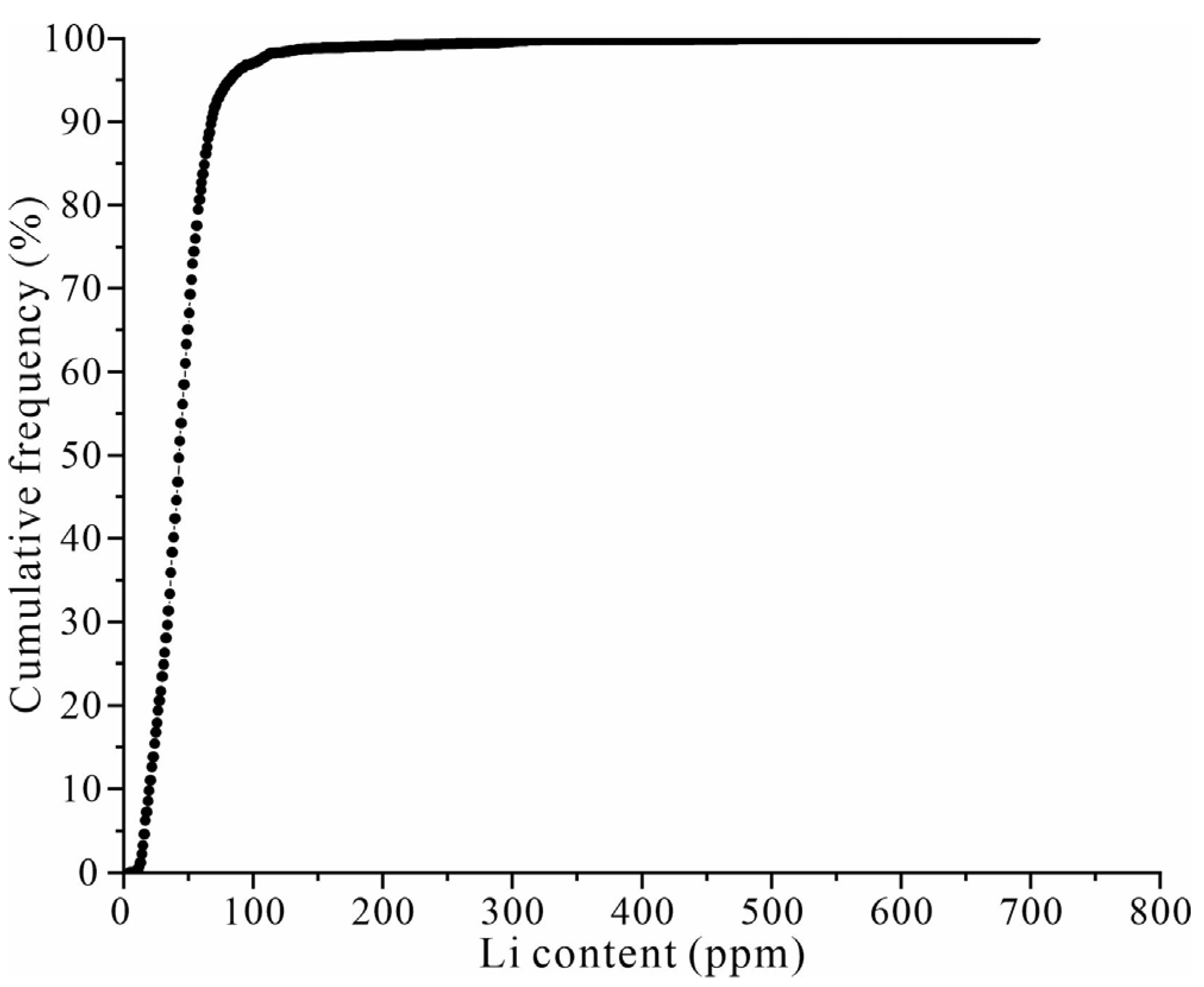
4.1. The Elimination of the Influence of Elemental Background Variations
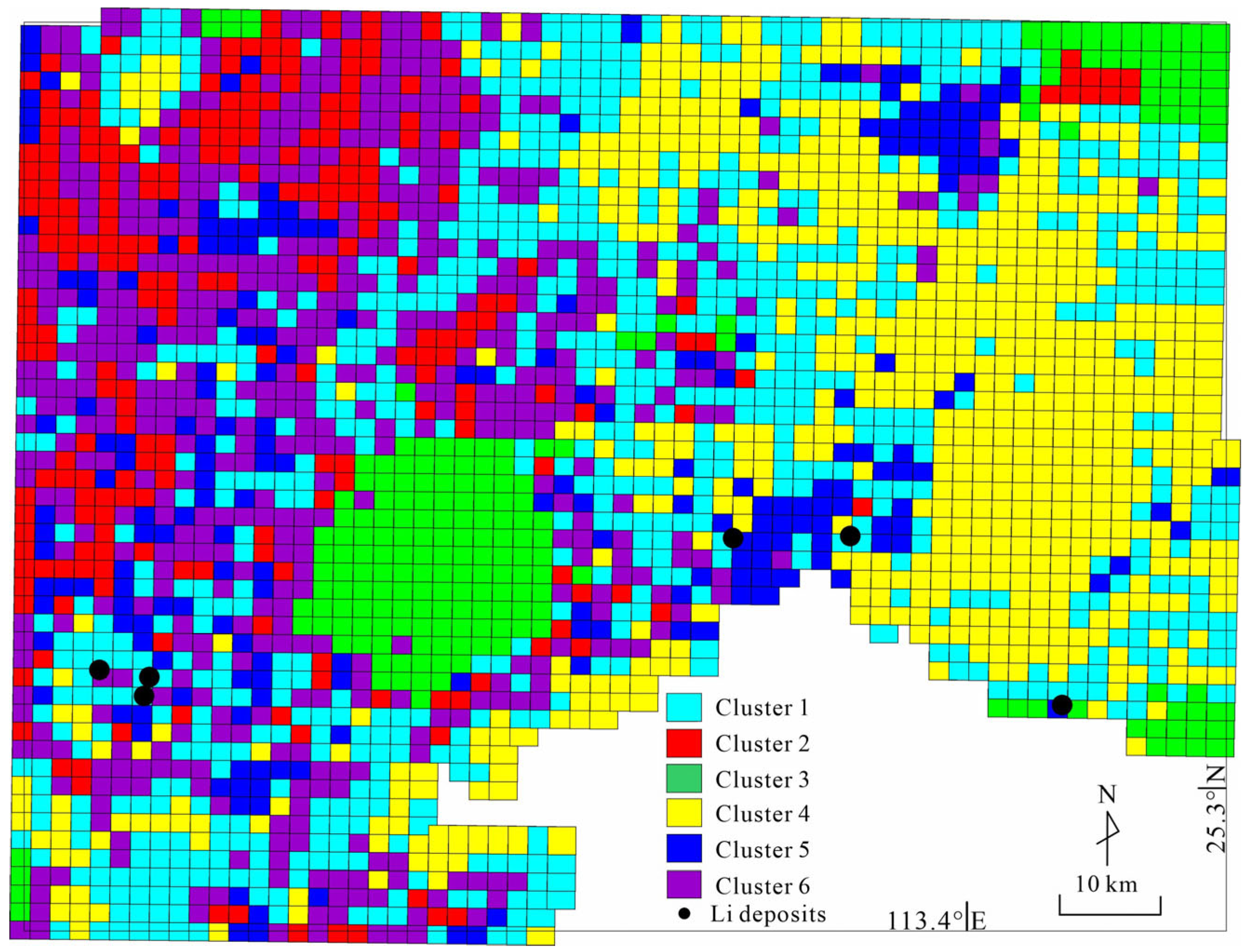
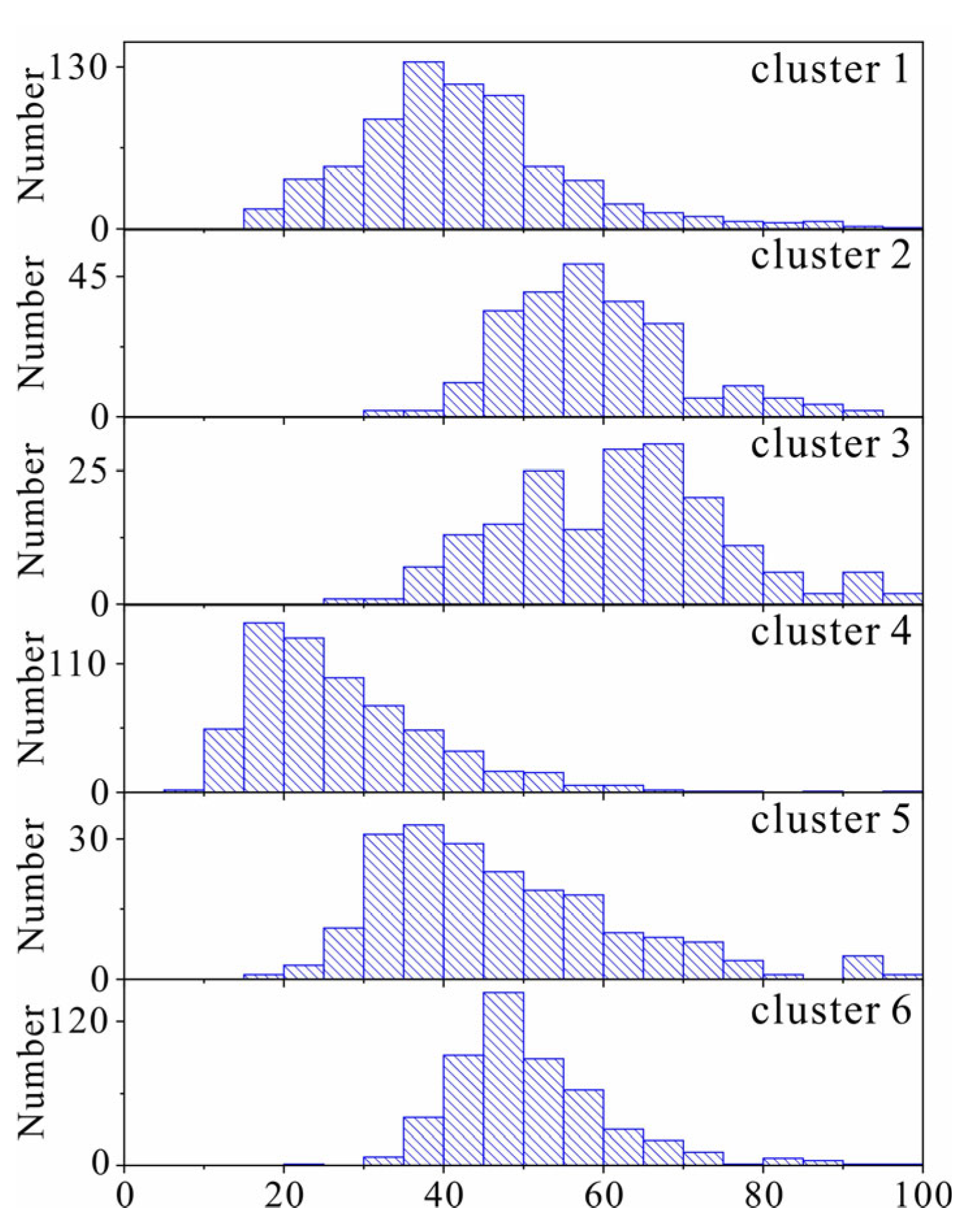
4.1.1. The Result of EM Clustering
4.1.2. The Effect of EM Clustering
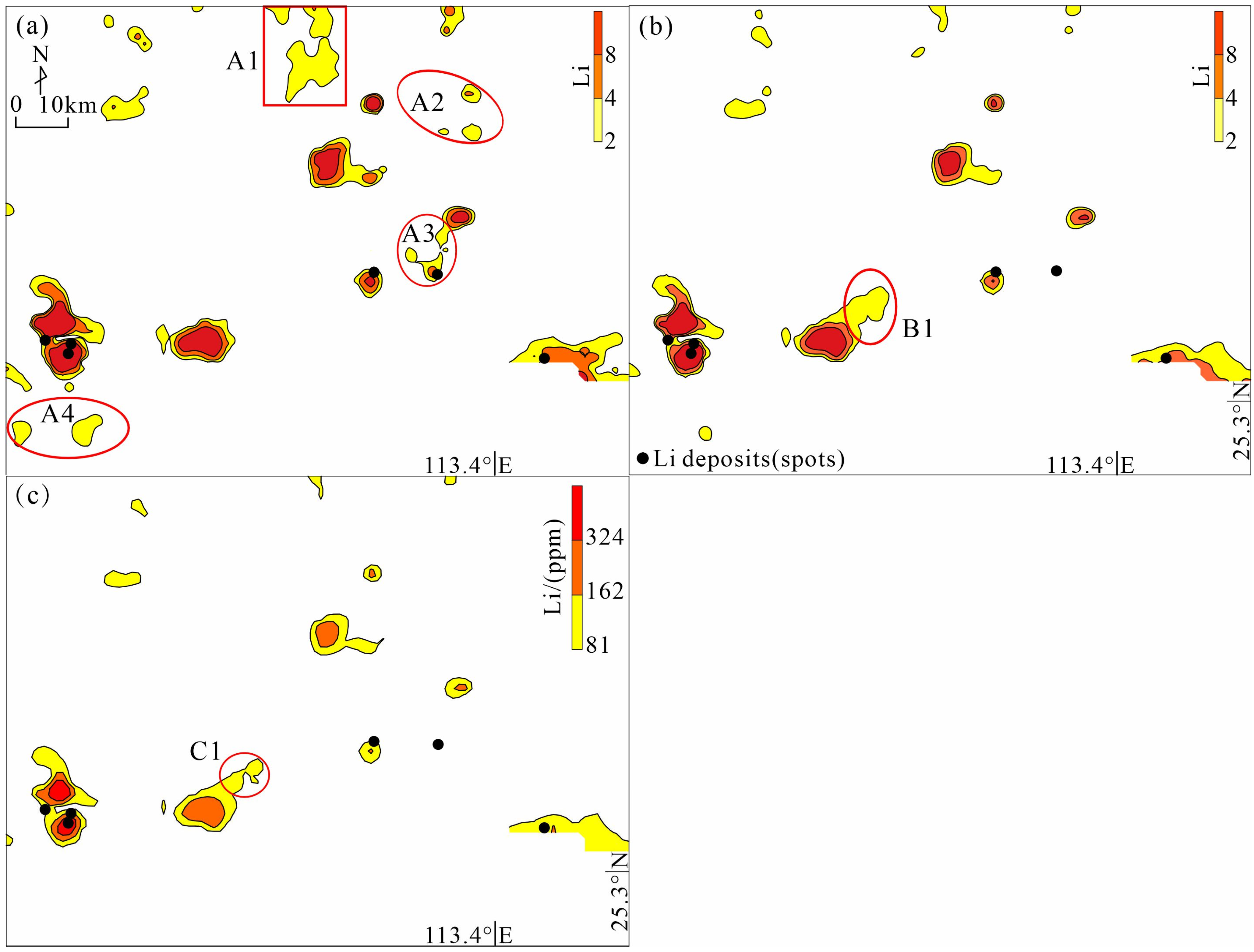
4.2. Li Geochemical Anomalies Based on the Classified Data
4.3. The Effect of EM Clustering on the Identification of Li Anomalies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dai, H.Z.; Wang, D.H.; Liu, S.B.; Li, X.; Wang, C.H.; Sun, Y. New progress in lithium prospecting abroad (2019~2021) and its significance to China’s strategic mining resources exploration. Acta Geol. Sin. 2023, 97, 583–595, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.H.; Dai, H.Z.; Liu, S.B.; Wang, C.H.; Yu, Y.; Zhao, Z. Progress in strategic critical minerals exploration and production and proposals for a new round of prospecting in China. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2024, 42, 7–25, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Balaram, V.; Santosh, M.; Satyanarayanan, M.; Srinivas, N.; Gupta, H. Lithium: A Review of Applications, Occurrence, Exploration, Extraction, Recycling, Analysis, and Environmental Impact. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Q.; Liu, H.L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B.M.; Xu, S.F. Geochemical Abundance and Spatial Distribution of Lithium in China: Implications for Potential Prospects. Acta Geosci. 2020, 41, 797–806. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Z.Z.; Xie, X.J. Influence of Variation in Element Background Values in Rocks on Metallogenic Prognosis in Geochemical Maps. Geol. China 2006, 33, 411–417, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Q.H.; Yan, M.C. Handbook of Elemental Abundance for Applied Geochemistry; Geological Publishing House: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Horstman, E.L.V.C. The Distribution of Lithium, Rubidium and Caesium in Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1957, 12, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Hao, L.B.; Lu, J.L.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Ma, C.Y.; Wei, Q.Q. Origin of skewed frequency distribution of regional geochemical data from stream sediments and a data processing method. J. Geochem. Explor. 2018, 194, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Hao, L.B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, J.L.; Shi, Y.X.; Ma, C.Y.; Li, Q.Q.; Wei, Q.Q. Identification of stream sediment geochemical anomalies in lithologically complex regions: Case study of Cu mineralization in Hunan province, SE China. Geochem. Explor. Environ. Anal. 2022, 22, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Hao, L.B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, J.L.; Shi, Y.X.; Ma, C.Y. Role of the EM clustering method in determining the geochemical background of As and Cr in soils: A case study in the north of Changchun, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2023, 45, 6675–6692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Hao, L.B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, J.L.; Shi, Y.X.; Ma, C.Y.; Li, Q.Q. Application of the partial least square regression method in determining the natural background of soil heavy metals: A case study in the Songhua River basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 918, 170695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajihosseinlou, M.; Maghsoudi, A.; Ghezelbash, R. A comprehensive evaluation of OPTICS, GMM and K-means clus-tering methodologies for geochemical anomaly detection connected with sample catchment basins. Geochemistry 2024, 84, 126094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinclair, A.J. Selection of threshold values in geochemical data using probability graphs. J. Geochem. Explor. 1974, 3, 129–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krige, D.G.; Matheron, G. Two-dimensional weighted moving average trend surfaces for ore valuation. J. S. Afr. Inst. Min. Metall. 1967, 67, 12–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.Q.; Sun, Z.K. Study on the method of geochemical anomalies analysis. Northwest. Geol. 2004, 37, 102–108, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, D. Unit-wise adjustment of geochemical background data and its significance in geochemical anomaly delineation. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 1986, 10, 263–274, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Hao, L.B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Zhao, Y.Y.; Lu, J.L.; Sun, L.J. Determination of the geochemical background and anomalies in areas with variable lithologies. J. Geochem. Explor. 2014, 139, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.M.; Xu, Y.G.; Grunsky, E.C. Integrated spatial and spectrum method for geochemical anomaly separation. Nat. Resour. Res. 2000, 9, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.M.; Agterberg, F.P.; Ballantyne, S.B. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods. J. Geochem. Explor. 1994, 51, 109–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.M. A new model for quantifying anisotropic scale invariance and for decomposition of mixing patterns. Math. Geol. 2004, 36, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.Y.; Bao, Z.Y. Continuous Multifractal Model of Geochemical Fields. Geochimica 2002, 31, 191–200, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yan, G.S.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, M. The Principle of Moving Average with Zooming Windows. Geol. Rev. 2000, 46, 267–271, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, Y.Z.; Xiao, F. Identification of multi-element geochemical anomalies using unsupervised machine learning algorithms: A case study from Ag–Pb–Zn deposits in north-western Zhejiang, China. Appl. Geochem. 2020, 120, 104679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.Z.; Zuo, R.G.; Liu, G.; Yuan, F.; Mao, X.C.; Guo, Y.J.; Xiao, F.; Liao, J.; Liu, Y.P. The great-leap-forward development of mathematical geoscience during 2010–2019: Big data and artificial intelligence algorithm are changing mathematical geoscience. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2021, 40, 556–573+777. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, D.Z.; Zuo, R.G.; Wang, J. Geochemical anomaly identification and uncertainty quantification using a Bayesian convolutional neural network model. Appl. Geochem. 2022, 146, 105450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Harris, J.; Sherlock, R.; Behnia, P.; Grunsky, E.; Naghizadeh, M.; Rubingh, K.; Tuba, G.; Roots, E.; Hill, G. Mineral prospectivity mapping using machine learning techniques for gold exploration in the Larder Lake area, Ontario, Canada. J. Geochem. Explor. 2023, 253, 107279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.H.; Lu, J.L.; Dai, W.M.; Wu, H.; Fan, Y.; Gou, Z.; Zhao, X. A novel method for the identification of geochemical anomalies with emphasis on addressing the problem of elemental background variation using Pb deposits in Shaoshan, central China, as a case study. Ore Geol. Rev. 2025, 181, 106615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govett, G.J.S.; Goodfellow, W.D.; Chapman, R.P. Exploration geochemistry—Distribution of elements and recognition of anomalies. Math. Geol. 1975, 7, 415–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vistelius, A.B. The skew frequency distributions and the fundamental law of the geochemical processes. J. Geol. 1960, 68, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dempster, A.P.; Laird, N.M.; Rubin, D.B. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via EM algorithm. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B-Methodol. 1977, 39, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, R.Z.; Zhou, S.; Chang, H.L.; Du, S.H.; Peng, S.B. The evolution of Li-bearing micas from Xianghualing granites and their ore prospecting significance in Hunan. J. Guilin Inst. Technol. 1998, 18, 49–57, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.X.; Rao, C.; Lin, X.Q.; Wu, R.Q.; Wang, Q. Constraints of lithium on the petrogenesis and mineralization of granite in Xianghualing area, Hunan Province. Geol. J. China Univ. 2021, 27, 149–162, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Song, Z.F.; Yang, Q.Z.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Cao, N.W. Prospecting potential of medium-fine-grained rock-type lithium resources in the Xianghualing orefield, Hunan Province, China. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2024, 48, 366–374, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, X.Q. Mineralogical Study on Metallogenic Processes of Rare (Earth) Metals from Jiepailing Porphyry Deposit, Hunan Province. Master’s Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2020. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.H. Ore-bearing potentian and metallogenic regularity about rare metal of Fengchuiluodai granite in the Changchengling, Hunan. Master’s Thesis, Kunming University of Science and Technology, Kunming, China, 2021. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Cawood, P.A.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, Y.J.; Zhao, G.C. Locating South China in Rodinia and Gondwana: A Fragment of Greater India Lithosphere? Geology 2013, 41, 903–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Jiang, S.Y.; Zhao, K.D.; Li, W.Q.; Liu, H.C. Origin of paleosubduction-modified mantle for Late Cretaceous (~100 Ma) diabase in northern Guangdong, South China: Geochronological and geochemical evidence. Lithos 2020, 370, 105603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.L.; Yuan, C.; Long, X.P.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Huang, Z.Y. Early Paleozoic intracontinental orogeny of the eastern South China block: Evidence from I-type granitic plutons in the SE Yangtze block. Geotecton. Metallog. 2013, 37, 698–720, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Bai, D.Y.; Tang, F.P.; Li, B.; Zeng, G.Q.; Li, Y.M.; Jiang, W. Summary of main mineralization events in Hunan Province. Geol. China 2022, 49, 151–180, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Hao, L.B.; Zhao, X.Y.; Lu, J.L.; Ma, C.Y.; Wei, Q.Q. The application of EM clustering method to the determination of stream sediment geochemical anomalies in areas with variable lithologies. Geophys. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 44, 1306–1312, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Tao, N.; Xie, Z.J.; Ren, T.X.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.P. Discovery of the intrusive rocks hydrothermal altered clay-type lithium mineralization in southern Anhui Province and its geological significance. Acta Petrol. Sin. 2024, 40, 2653–2663, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.P. The Occurrence Forms and Enrichment Mechanisms of Lithium in Carbonate-Hosted Clay-Type Lithium Deposit in the Yunnan-Guizhou Region, China. Master’s Thesis, Qinghai Institute of Salt Lakes, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xining, China, 2024. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Chen, L.; Wang, K.M.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.Q.; Nie, X.; Pang, X.Y. Metallogenic characteristics of sedimentary lithium resources. Miner. Depos. 2022, 41, 1073–1092, (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Reimann, C.; Filzmoser, P.; Garrett, R.G. Background and threshold: Critical comparison of methods of determination. Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 346, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Zhang, B.M.; Wang, W.; Han, Z.X.; Chi, Q.H.; Zhou, J.; Nie, L.S.; Xu, S.F.; Yao, W.S.; et al. Concentration and distribution of lithium in catchment sediments of China: Conclusions from the China Geochemical Baselines project. J. Geochem. Explor. 2020, 215, 106540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.F.; Li, W.Y.; Isokov, M.; Movlanov, J.; Mirkhamdamov, M.; Ma, Z.P.; Weng, K.; Cao, K.; Meng, G.L. Distribution, enrichment characteristics and prospecting potential of lithium in Uzbekistan: Insights from 1:1 million geochemical mapping. J. Geochem. Explor. 2025, 268, 107606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Lithium | Cluster 1 (725) | Cluster 2 (241) | Cluster 3 (204) | Cluster 4 (648) | Cluster 5 (218) | Cluster 6 (523) | Original Dataset (2559) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background | 40.5 | 58.3 | 63.7 | 25.5 | 45.3 | 49.6 | 42.8 |
| Mean | 48.4 | 60.6 | 75.6 | 27.2 | 56.5 | 52.2 | 47.8 |
| Median | 40.6 | 58.4 | 64.3 | 23.7 | 44.5 | 49.5 | 43.5 |
| Standard deviation | 68.6 | 15.3 | 50.7 | 16.6 | 56.0 | 15.3 | 46.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, X. Application of the Expectation-Maximization Clustering Method for Identifying Li Geochemical Anomalies in Stream Sediments in Southeastern Hunan Province, China. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179827
Dai W, Zhang Q, Zhao X. Application of the Expectation-Maximization Clustering Method for Identifying Li Geochemical Anomalies in Stream Sediments in Southeastern Hunan Province, China. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179827
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Weiming, Qinghao Zhang, and Xinyun Zhao. 2025. "Application of the Expectation-Maximization Clustering Method for Identifying Li Geochemical Anomalies in Stream Sediments in Southeastern Hunan Province, China" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179827
APA StyleDai, W., Zhang, Q., & Zhao, X. (2025). Application of the Expectation-Maximization Clustering Method for Identifying Li Geochemical Anomalies in Stream Sediments in Southeastern Hunan Province, China. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9827. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179827






