Micro-Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Zr-Based Metallic Glass Matrix Composite Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
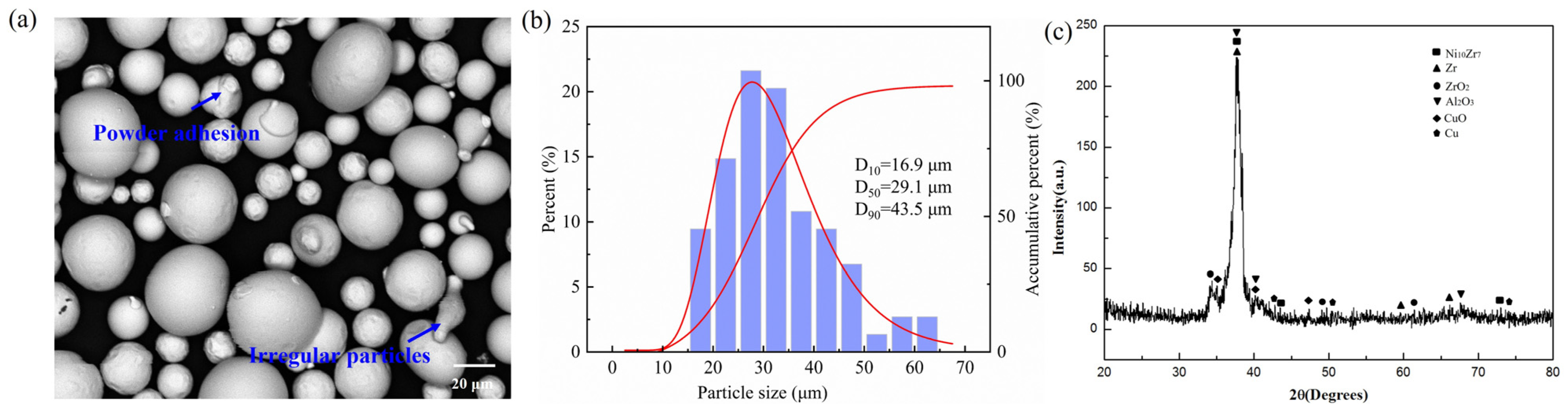
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Manufacturing Process and Parameters
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
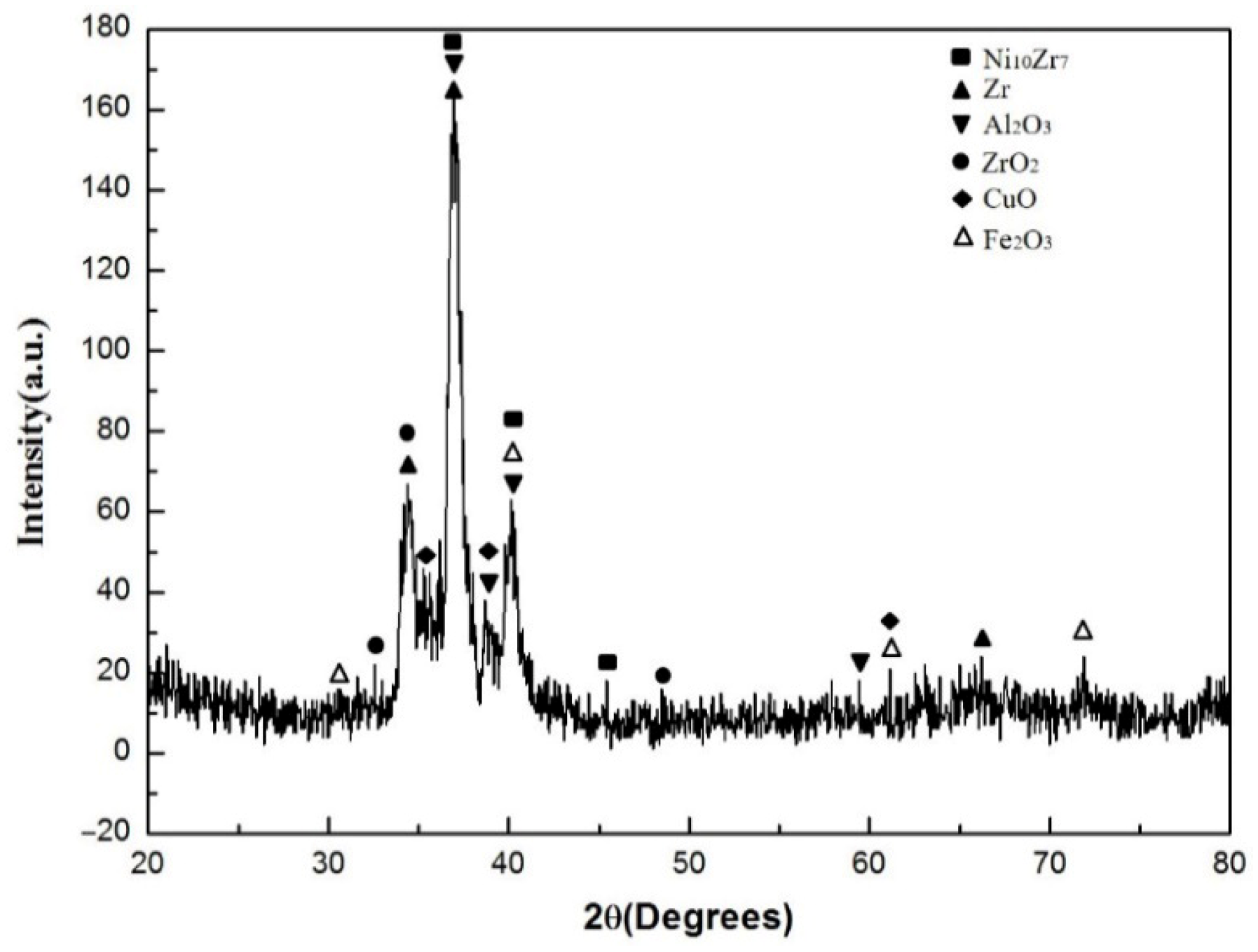
3.1. Phase Composition
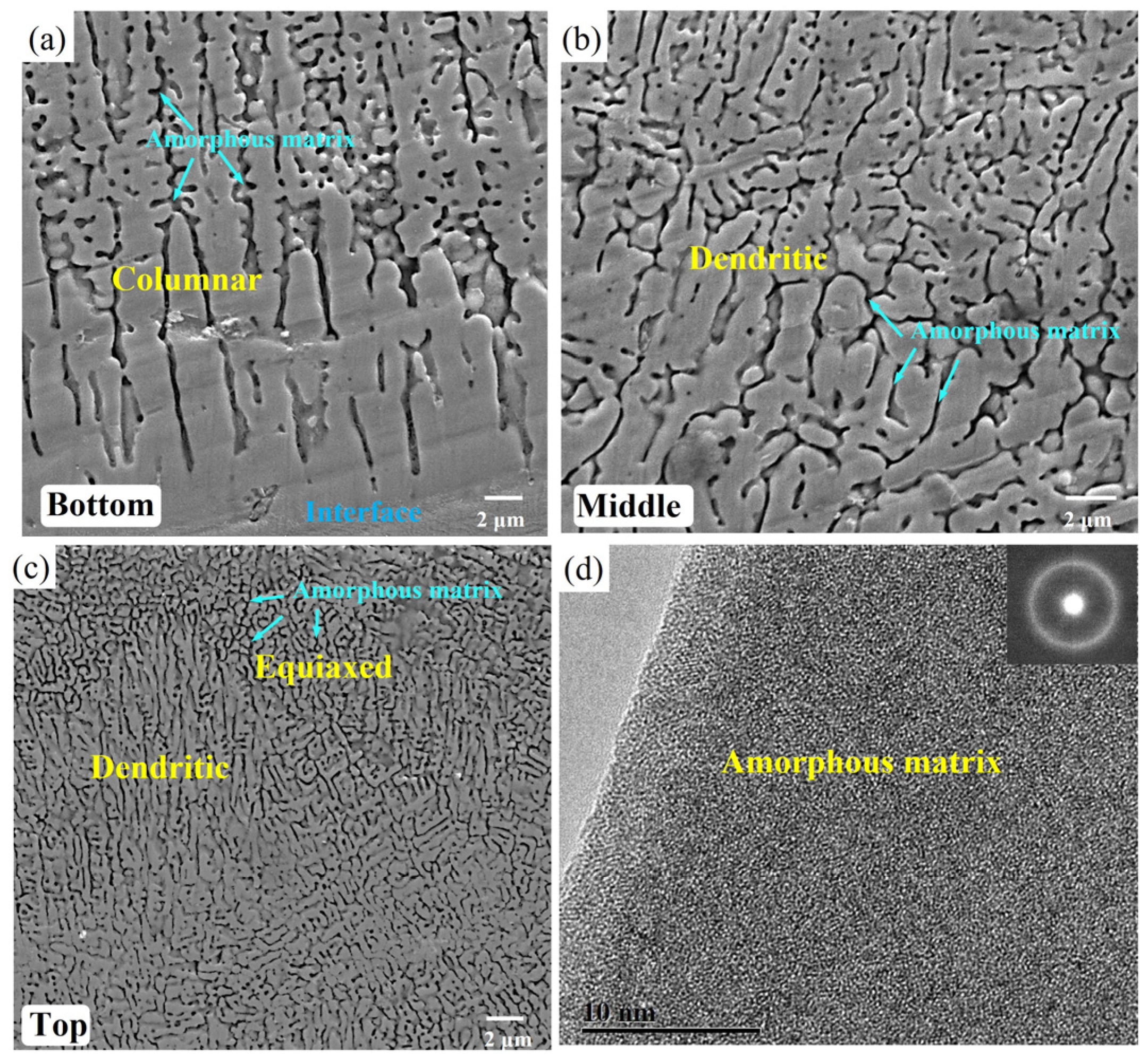
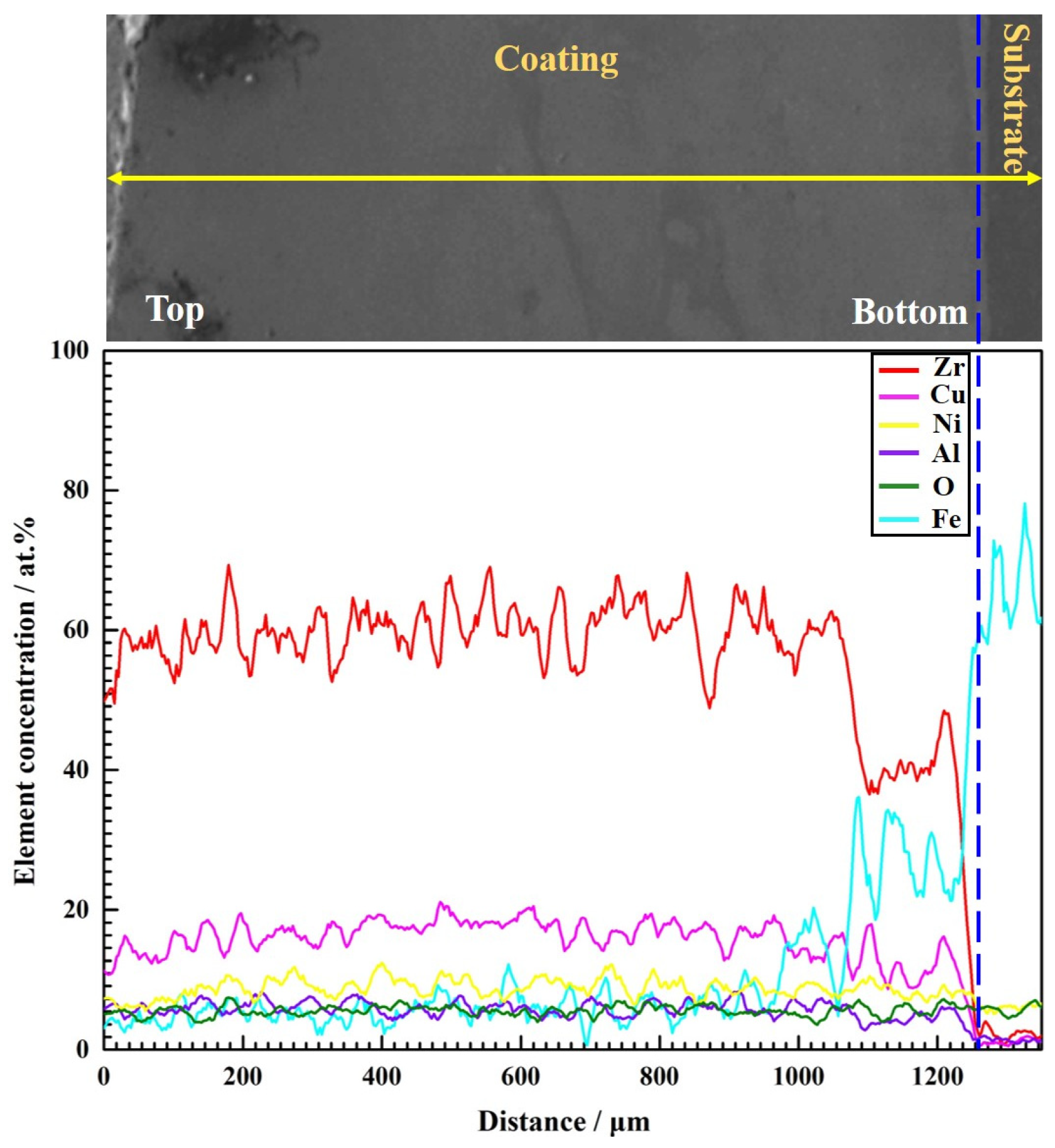
3.2. Microstructure
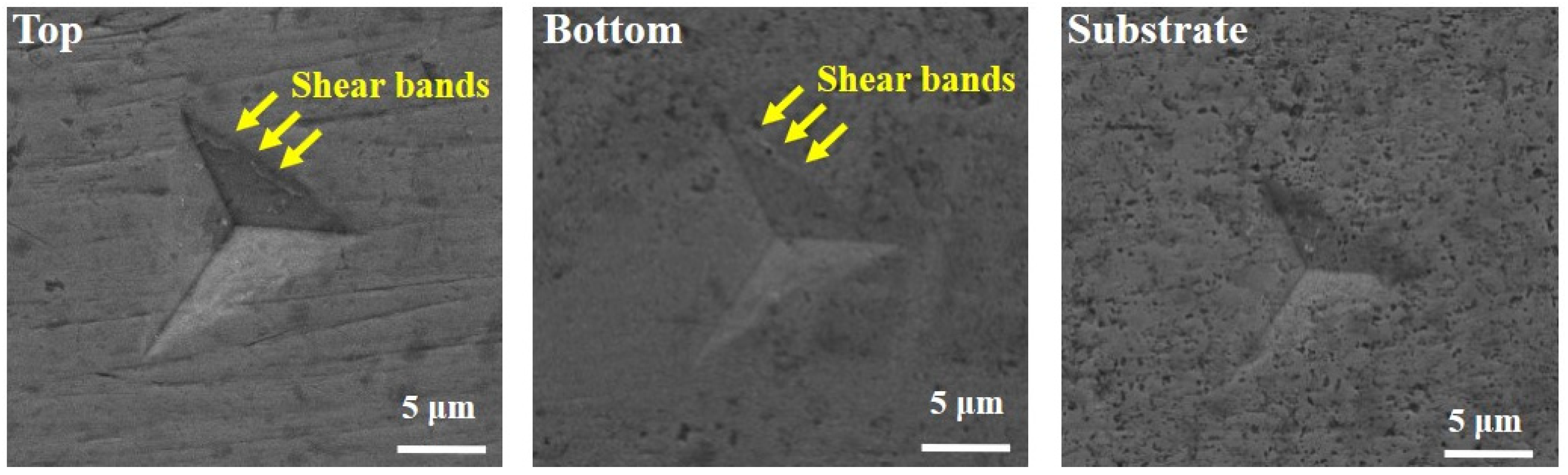
3.3. Nanoindentation Response
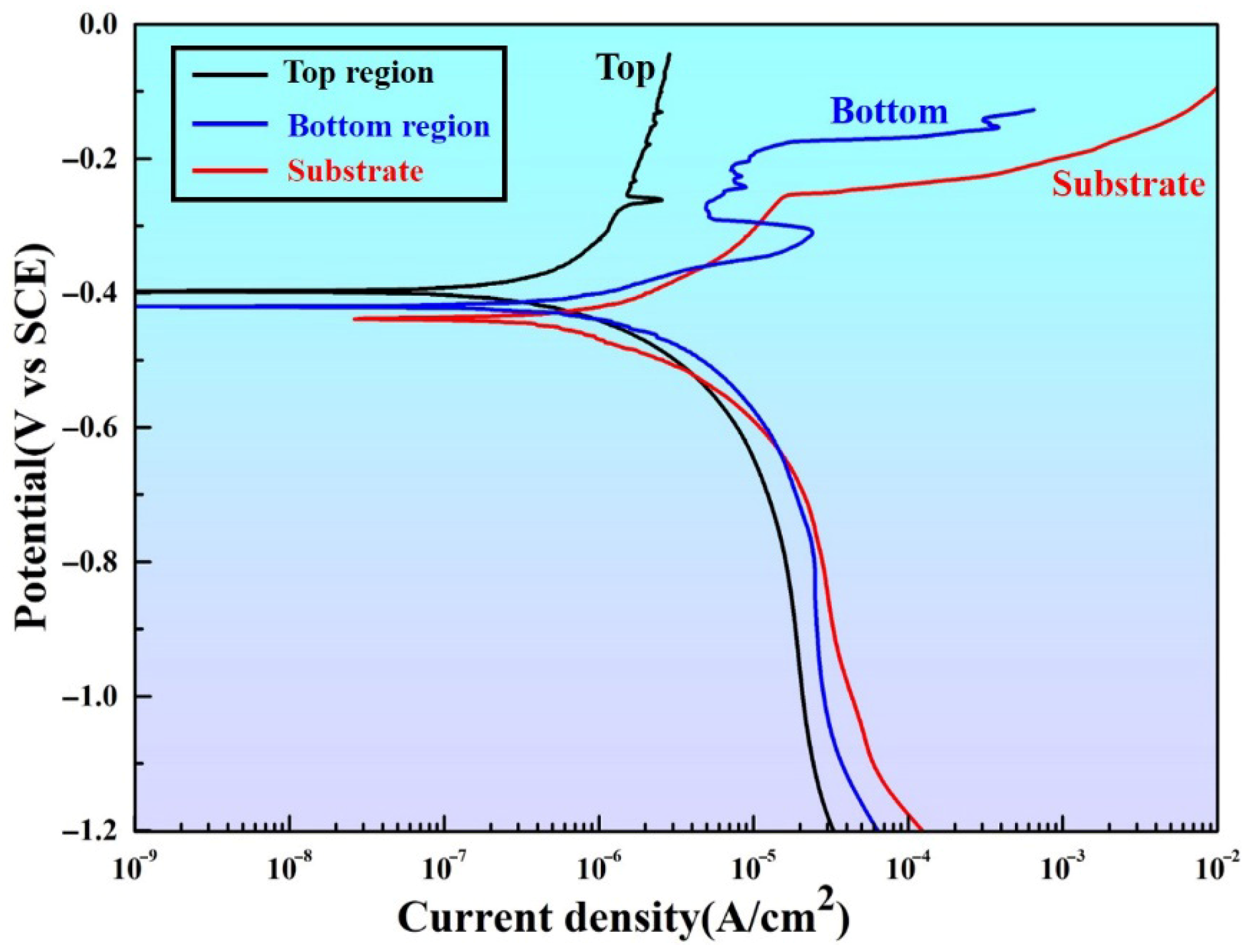
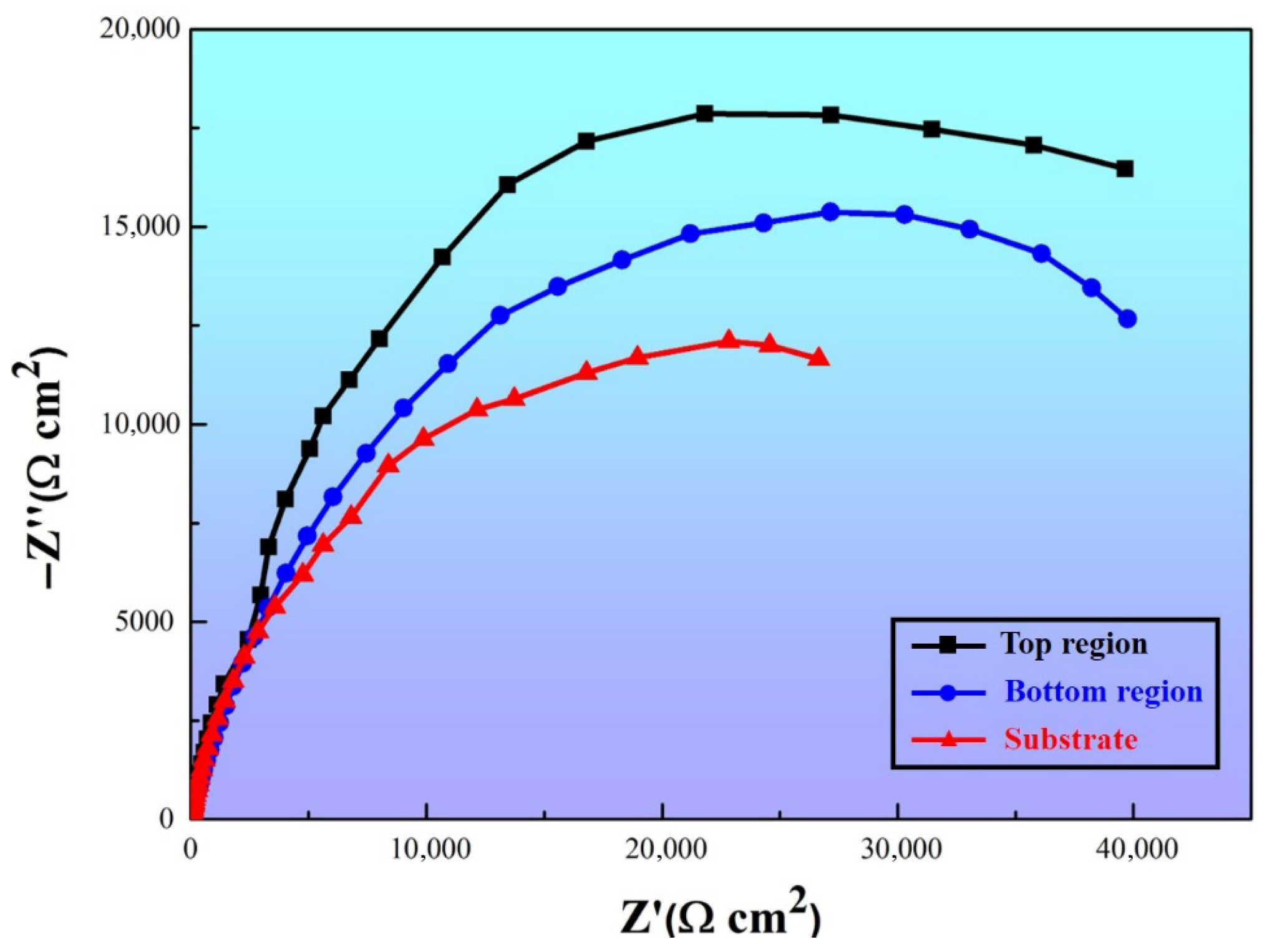
3.4. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The composite coating formed a metallurgical bond with the substrate and exhibited negligible porosity without crack formation. However, the high impurity content of the raw powder promoted the crystallization of the coating during laser cladding.
- (2)
- Microstructural evolution across the coating exhibits significant regional heterogeneity. Coarse columnar crystals in the bottom region nucleate epitaxially at the coating/substrate interface and propagate along the thermal gradient parallel to the building direction, while dendritic structures dominate the middle region under moderate thermal gradients. Ultimately, fine dendritic and equiaxed crystals form within the amorphous matrix in the top region, attributable to the lowest thermal gradient and the highest cooling rate during laser processing.
- (3)
- The microstructure characteristics in the top region of the coating contribute to superior hardness, elastic modulus, and H/E ratio compared to both the bottom region and substrate. Enhanced micro-mechanical properties in the coating originate from the initiation and propagation of multiple shear bands.
- (4)
- The metallic glass matrix composite coating demonstrates significantly better corrosion resistance than the substrate due to its amorphous phase and protective passive film formation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, H.J.; Wang, M.S.W.; Liao, H.; Du, Y.L. Unraveling the interrelation between process parameters and defects to enhance the strength of laser additively manufactured CuZrAlTi bulk metallic glass. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1127–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.F. Ti-based metallic glass composites containing β-Ti dendrites. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2025, 152, 101472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.P.; Wang, D.S.; Wu, X.H.; Yang, Y.W. Laser-based additive manufacturing of bulk metallic glasses: A review on principle, microstructure and performance. Mater. Des. 2025, 252, 113750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.S.; Su, F.C.; Zhou, J.; Mao, Y.C.; Yang, J.M.; Xue, Z.Y.; Ke, H.B.; Sun, B.A.; Wang, W.H.; Bai, H.Y. Ductile Fe-based amorphous alloy with excellent soft magnetic properties induced by low-temperature stress annealing. Intermetallics 2024, 166, 108201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, S.; Fu, J.N.; Li, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, F.; Ma, J.; Wang, W.H. Manufacturing of metallic glass components: Processes, structures and properties. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 144, 101283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.Y.; Liu, Z.Y.; Zhang, P.L.; Ma, S.Y.; Sun, T.Z.; Li, R.F.; Lu, Q.H.; Yan, H.; Shi, H.C.; Li, M. Laser additive manufacturing CuZr based bulk metallic glasses: Simulations and experiments. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1011, 178467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.S.; Yakubov, V.; Nomoto, K.; Ringer, S.P.; Gludovatz, B.; Li, X.P.; Kruzic, J.J. Superior mechanical properties of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass via laser powder bed fusion process control. Acta Mater. 2024, 266, 119685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, P.L.; Liu, Z.Y.; Wu, D.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, T.Z.; Liu, C.H.; Yan, H.; Shi, H.C.; Ma, S.Y.; et al. Preparation of Zr-based metallic glasses gradient composites with designable amorphous fraction by laser powder bed fusion. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 120, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.L.; Hao, Q.H.; Yu, P.F.; Yang, Y.J.; Ma, M.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, R.P. Numerical simulation and experimental verification of large-sized Zr-based bulk metallic glass ring-shaped parts in casting process. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2022, 32, 581–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liverani, E.; Ascari, A.; Fortunato, A. Multilayered WC-Co coatings by Direct Energy Deposition-based cladding: Effect of laser remelting on interface defects. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 464, 129556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Guo, C.; Jiang, F.; Xiao, M.; Diao, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H. Adding high entropy alloys to improve microstructure and properties of laser cladding Fe-based amorphous coatings. J. Non Cryst. Solids. 2023, 619, 122559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liang, J.; Zhou, J. Evolution in microstructure features and properties of Mo-containing Fe-Cr-Ni-B-Si composite coatings by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2022, 619, 111926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhai, J.; Tian, L.; Lu, Y.; Li, X.; Kou, S. Fabrication of Fe-based amorphous composite coating by laser cladding. J. Non Cryst. Solids. 2022, 589, 121648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.W.; Zhao, L.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y.H.; Liu, X. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of laser-remelted Zr-based metallic glass matrix composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 178299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.L.; Guo, C.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Jiang, F.C.; Chen, L.; Xiao, M.Y.; Jiao, B.; Dong, T.; Wang, S.B.; Qiao, Z.H.; et al. Study on crystal and amorphous transformation of ultrasonic vibration assisted laser cladded Fe-based amorphous coatings. Ultrasonics 2025, 145, 107456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, N.; Panikar, R.S.; Jhabvala, J.; Buch, A.R.; Mischler, S.; Logé, R.E. Laser coating of a Zr-based metallic glass on an aluminum substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 400, 126223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Takeuchi, A. Recent development and application products of bulk glassy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2243–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrabi, N.; Ivas, T.; Jhabvala, J.; Schawe, E.K.J.; Löffler, F.J.; Ghasemi-Tabasi, H.; Logé, E.R. Quantitative prediction of crystallization in laser powder bed fusion of a Zr-based bulk metallic glass with high oxygen content. Mater. Des. 2024, 239, 112744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, T.; Elmer, J.W.; Wei, H.L.; Lienert, T.J.; Zhang, W.; Kou, S.; DebRoy, T. Control of grain structure, phases, and defects in additive manufacturing of high-performance metallic components. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2023, 138, 101153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, N.K.; Belger, A.; Paufler, P.; Kim, D.H. Nanoindentation studies on Cu-Ti-Zr-Ni-Si-Sn bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 449–451, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Nieh, T.G. A nanoindentation study of serrated flow in bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zuo, X.F.; Liu, R.; Pang, C.M.; Jin, F.; Zhu, W.W.; Yuan, C.C. Multi-scale defects activation in Gd18.33Tb18.33Dy18.34Co17.5Al27.5 high-entropy metallic glasses revealed by nanoindentation. Int. J. Plast. 2024, 174, 103893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Hu, L.W.; Lin, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Tang, J.L.; Qi, L.; Liu, X. Significant improvement of corrosion resistance in laser cladded Zr-based metallic glass matrix composite coatings by laser remelting. Corros. Sci. 2024, 238, 112360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liu, X.; Chen, T.; Le, G.; Li, J.; Qu, F.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, L.; Wang, D. Characterization of laser cladded Zr-Cu-Ni-Al in-situ metallic glass matrix composite coatings with enhanced corrosion-resistance. Vacuum 2020, 185, 109996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.W.; Xiao, M.Y.; Wang, Q.C. Corrosion Performance of Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings via Laser Cladding Assisted with Ultrasonic in a Simulated Marine Environment. Metals 2023, 13, 1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.N.; Cheng, Y.H.; Wan, Y.X.; Jeyaprakash, N.; Wang, Y.F.; Ma, K.; Yang, J.Y. Influence of scanning speed on microstructure and corrosion resistance of Fe-based amorphous coatings by high-speed laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 479, 130449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Region | Hardness, H (GPa) | Elastic Modulus, E (GPa) | H/E Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Top region | 7.6 ± 0.5 | 133 ± 5 | 0.057 ± 0.004 |
| Bottom region | 7.5 ± 0.5 | 132 ± 5 | 0.057 ± 0.005 |
| Substrate | 7.1 ± 0.5 | 162 ± 5 | 0.044 ± 0.005 |
| Ecorr (mV) | icorr (A/cm2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Top region | 395 | 1.1512 10−7 |
| Bottom region | 421 | 3.2878 10−7 |
| Substrate | 439 | 6.8217 10−7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Yan, Z. Micro-Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Zr-Based Metallic Glass Matrix Composite Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding Technology. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179698
Wang W, Yan Z. Micro-Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Zr-Based Metallic Glass Matrix Composite Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding Technology. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179698
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wenle, and Zhifeng Yan. 2025. "Micro-Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Zr-Based Metallic Glass Matrix Composite Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding Technology" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179698
APA StyleWang, W., & Yan, Z. (2025). Micro-Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance of Zr-Based Metallic Glass Matrix Composite Coatings Fabricated by Laser Cladding Technology. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9698. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179698






