Critical Appraisal of Coal Gangue and Activated Coal Gangue for Sustainable Engineering Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characterization of Coal Gangue
2.1. Chemical and Mineralogical Properties
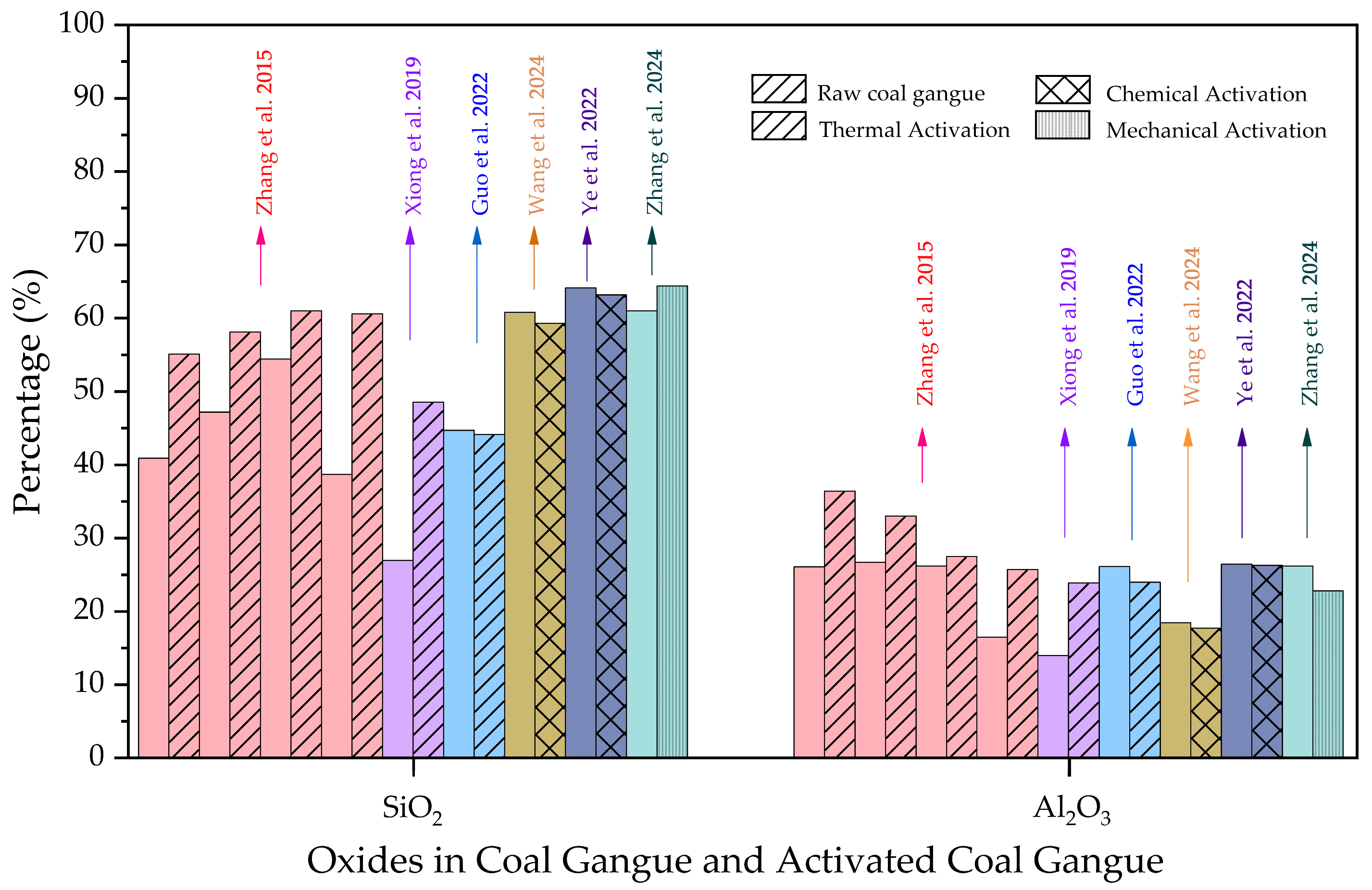
2.2. Physical Properties
2.2.1. Particle Size Distribution and Specific Gravity
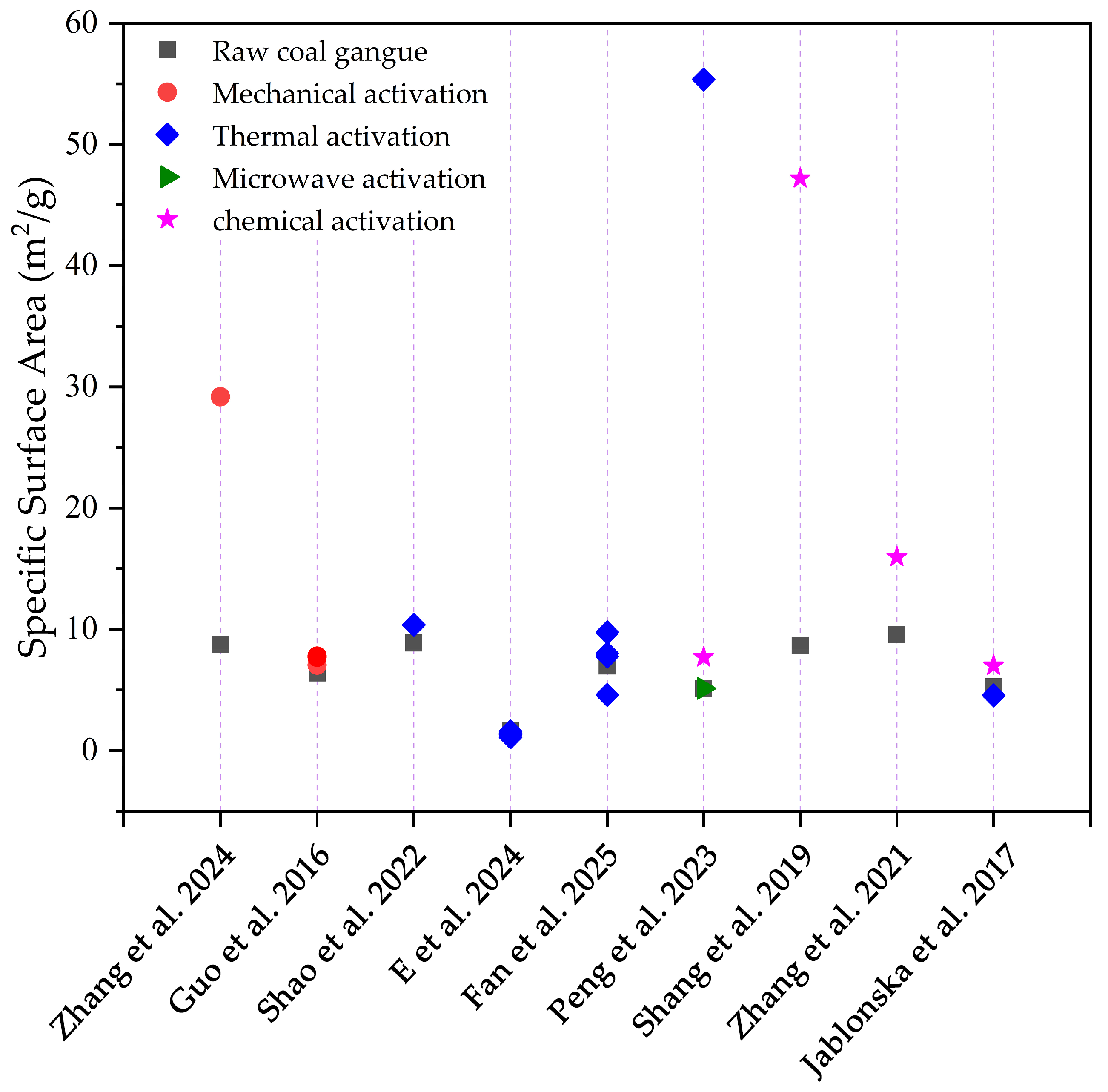
2.2.2. Specific Surface Area and Porosity
2.3. Geotechnical Properties
2.3.1. Atterberg Limits
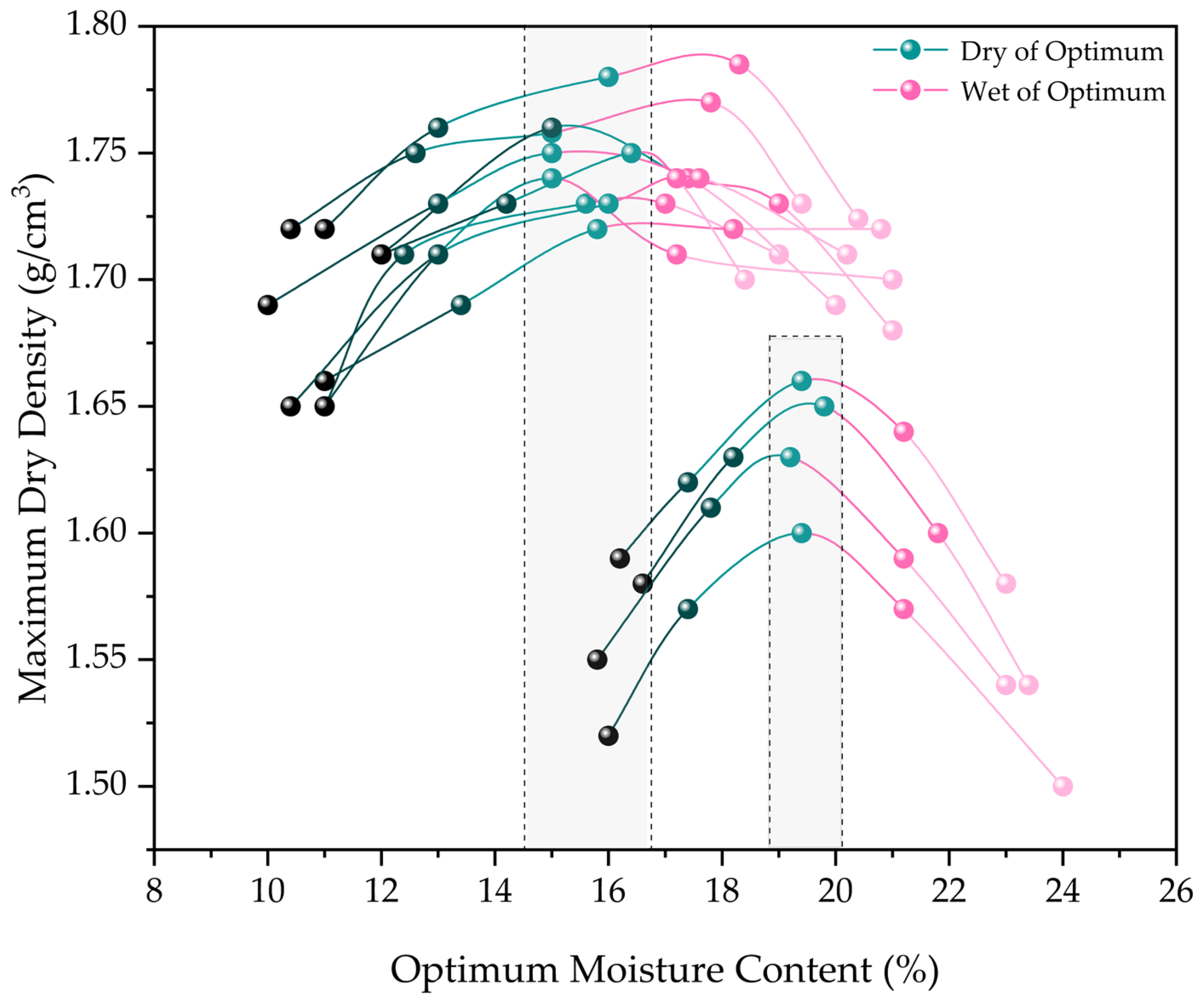
2.3.2. Compaction Properties
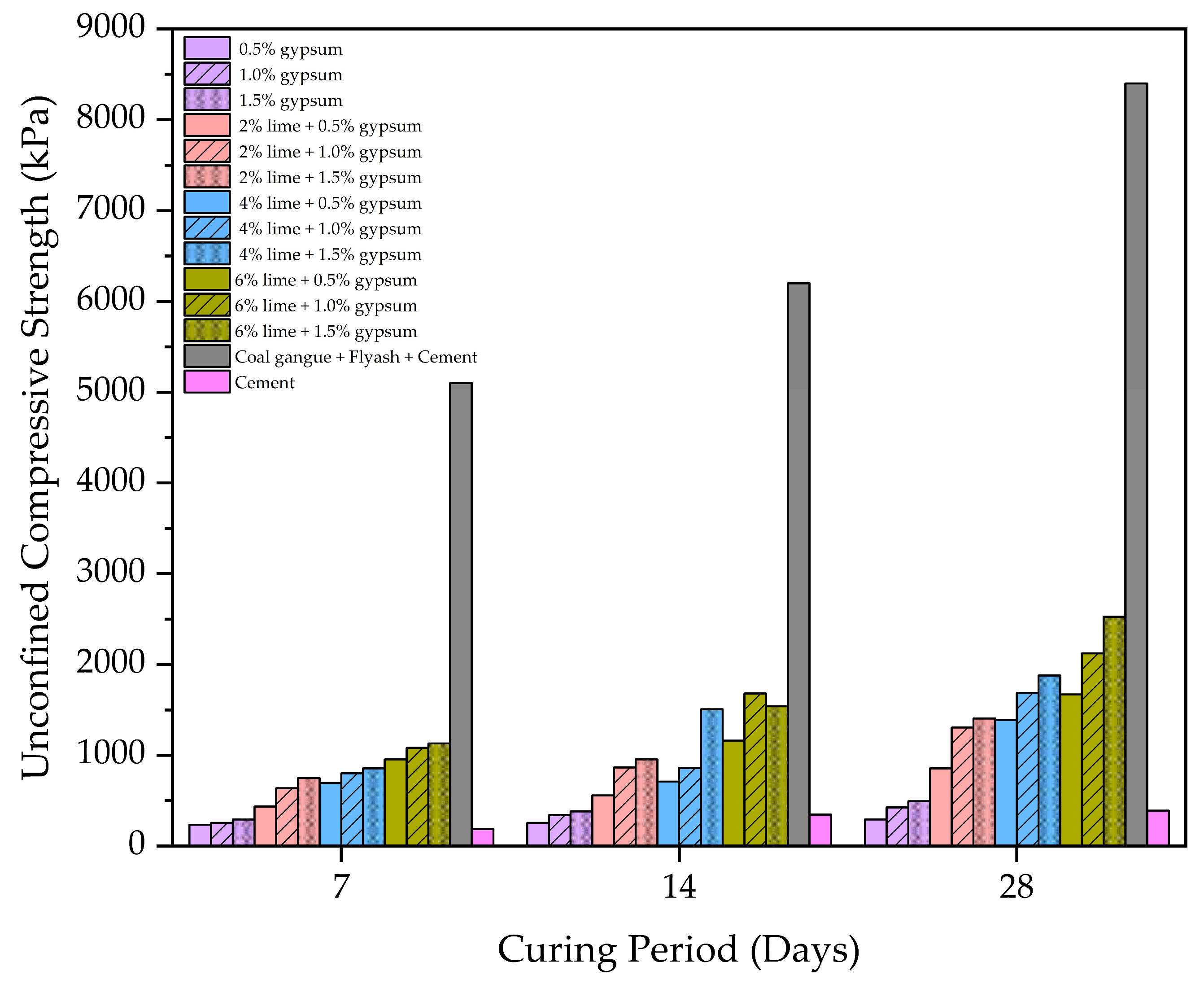
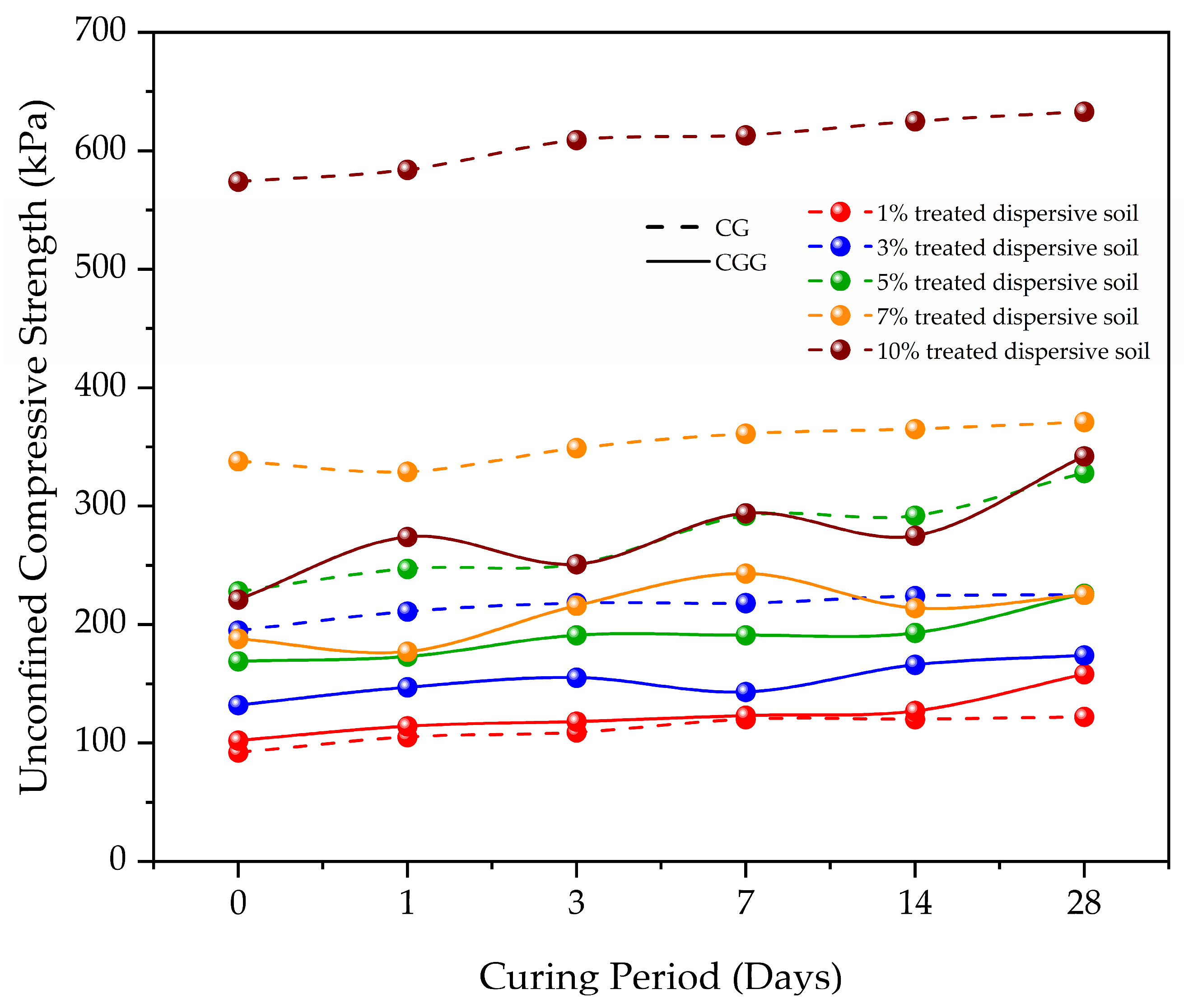
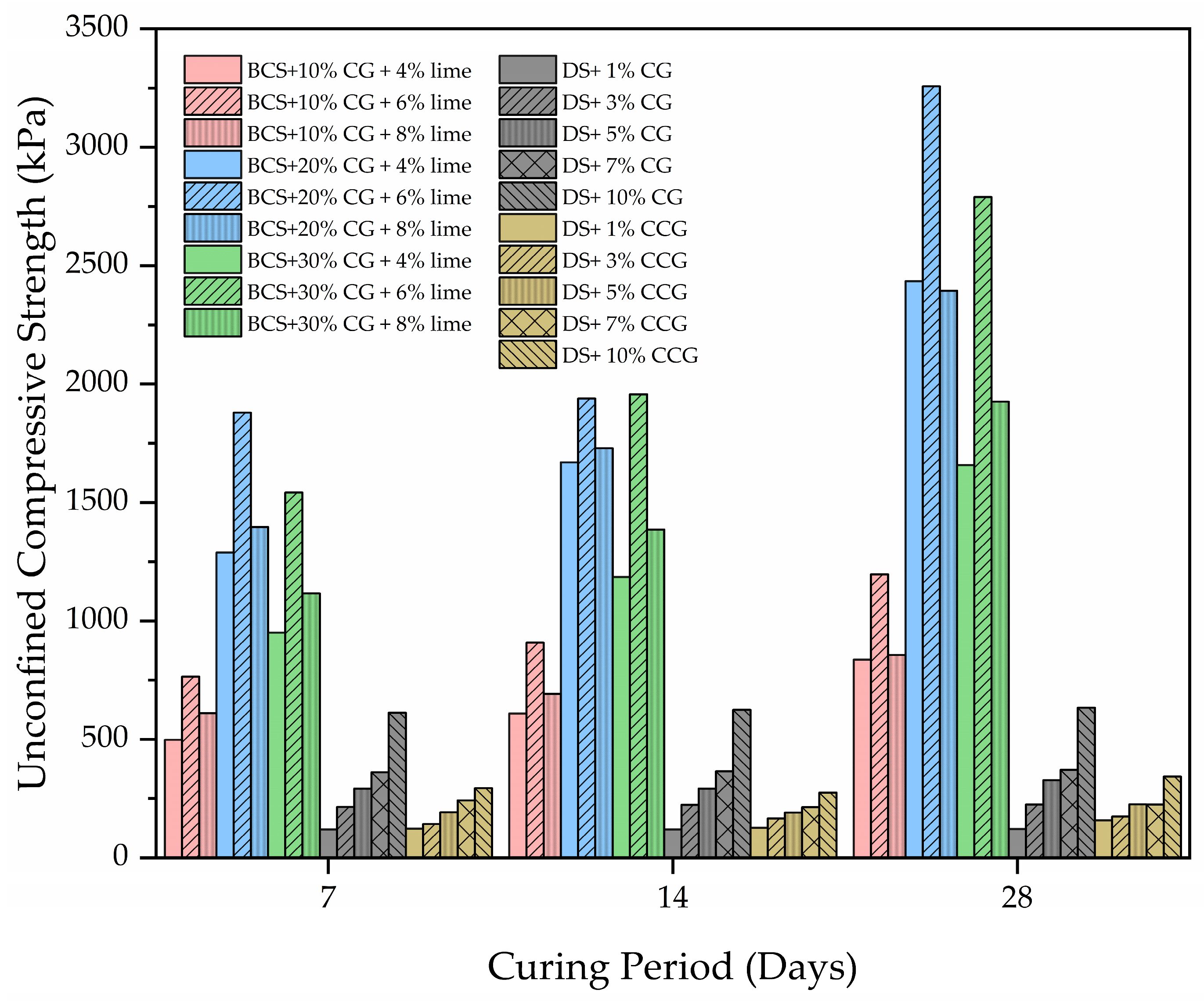
2.3.3. Unconfined Compressive Strength
3. Activation of Coal Gangue
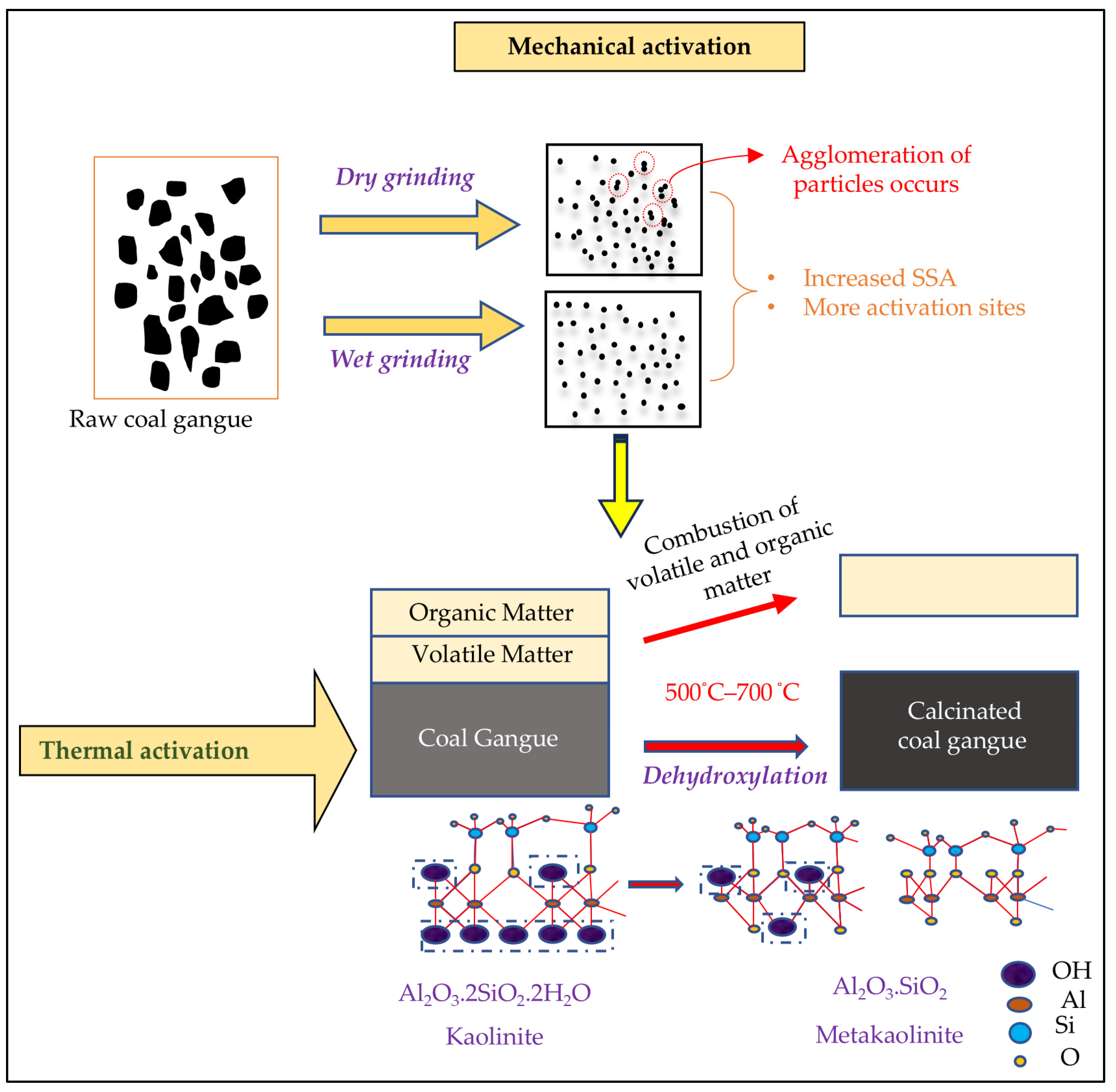
3.1. Mechanical Activation
3.2. Thermal Activation
3.3. Microwave Activation
3.4. Chemical Activation
4. Applications of Coal Gangue and Activated Coal Gangue
4.1. Construction Applications
4.1.1. Cement-Based Materials
4.1.2. Bricks
4.2. Geotechnical Applications
4.2.1. Backfill
4.2.2. Pavements
4.3. Geoenvironmental Applications
4.3.1. Phosphate Adsorption Performance of Coal Gangue
4.3.2. Removal of Dyes
4.3.3. Removal of Heavy Metals
4.3.4. Carbon Sequestration
4.4. Recovering Valuable Metals from the Coal Gangue
5. Secondary Pollution
6. Cost Analysis
7. Conclusions
- Activation induces significant physical and chemical modifications in coal gangue, including increased amorphous content, specific surface area, and availability of reactive components, which enhance its suitability for engineering applications.
- Hybrid activation methods, combining thermal, mechanical, chemical, or microwave techniques, are more effective than single-mode approaches in achieving desired material properties.
- Activated coal gangue demonstrates strong potential in construction materials and geoenvironmental applications, followed by geotechnical uses, due to the enhanced formation of reactive silica and alumina phases.
- Mechanical activation is environmentally safe but less effective in converting kaolinite fully; thermal activation ensures complete transformation into metakaolinite.
- Activation significantly improves surface area and porosity, making coal gangue suitable for geoenvironmental applications such as adsorbents, zeolites, and porous materials.
- When blended with problematic soils, activated coal gangue improves geotechnical properties to meet the requirements of IRC:37 (2012) and IRC:SP:72 (2007) for use in subgrade and subbase layers.
- Replacing clinker with activated coal gangue in cement production significantly reduces energy consumption. Producing one ton of activated coal gangue requires only 27.8 kg of coal equivalent, approximately 76% less than that needed for one ton of clinker, resulting in energy savings of up to 90.7 kg of coal equivalent per ton.
- Coal gangue, in its natural state, acts as a source of secondary pollutants. The leaching of heavy metals in coal gangue follows the order of Zn > Pb > Mn > Cu > Cr. Nevertheless, the effect of secondary pollutants can be mitigated by the activation techniques.
- The maximum decrease in leaching rate is observed when coal gauge is thermally activated at 800 °C; the leaching of Ni, Cd, Mn, Cu, Zn, and Pb is 99%, 67%, 86%, 40%, 99%, and 93%, respectively.
- CG-based composites allow for the high-value and bulk use of waste, lowering production costs by 44–55% while also providing notable environmental and economic advantages.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- IEA. Coal Mid-Year Update—July 2024. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/coal-mid-year-update-july-2024 (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Enerdata. World Energy & Climate Statistics-Yearbook. Available online: https://yearbook.enerdata.net/coal-lignite/coal-world-consumption-data.html (accessed on 7 August 2025).
- Cheng, F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, K.; Wu, J.; Zhang, D. Eliminating environmental impact of coal mining wastes and coal processing by-products by high temperature oxy-fuel CFB combustion for clean power Generation: A review. Fuel 2024, 373, 132341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haibin, L.; Zhenling, L. Recycling utilization patterns of coal mining waste in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 1331–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J. Comprehensive utilization and environmental risks of coal gangue: A review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 239, 117946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, W.; Feng, G.; Xiao, C. Green Synthesis of Coal Gangue-Derived NaX Zeolite for Enhanced Adsorption of Cu2+ and CO2. Materials 2015, 18, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yao, Q.; Xu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Experimental study on the purification mechanism of mine water by coal gangue. Water 2023, 15, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabłońska, B.; Kityk, A.V.; Busch, M.; Huber, P. The structural and surface properties of natural and modified coal gangue. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 190, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, Y.; Song, L.; Ma, M. Experimental research on improving activity of calcinated coal gangue via increasing calcium content. Materials 2023, 16, 2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, C.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Li, Z. Activity and structure of calcined coal gangue. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2007, 22, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y. Opportunities, challenges and modification methods of coal gangue as a sustainable soil conditioner—A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2007, 31, 58231–58251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, S.; Guo, L. Application of coal gangue as a coarse aggregate in green concrete production: A review. Materials 2021, 14, 6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Gu, Z.; Wang, J. Impacts of Thermal Activation on Physical Properties of Coal Gangue: Integration of Microstructural and Leaching Data. Buildings 2025, 15, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilikwazi, B.; Onyari, J.M.; Wanjohi, J.M. Determination of heavy metals concentrations in coal and coal gangue obtained from a mine, in Zambia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 20, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, C.; Zhou, G.; Yin, X.; Wang, C.; Chi, B.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Li, R. Assessment of heavy metal in coal gangue: Distribution, leaching characteristic and potential ecological risk. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 32321–32331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.Q.; Xiao, K.; Wang, X.D.; Lv, Z.H.; Mao, M. Evaluating the distribution and potential ecological risks of heavy metal in coal gangue. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18604–18615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, S.; Shao, H.; Liao, Q.; Fan, Y. Experimental study of the effects of stacking modes on the spontaneous combustion of coal gangue. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2019, 123, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, X.; Liu, S.; Shu, P.; Xia, S. Investigation of thermal behavior and hazards quantification in spontaneous combustion fires of coal and coal gangue. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 843, 157072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Wang, B.-F.; Yang, F.-L.; Cheng, F.-Q. Study on the environmental effects of heavy metals in coal gangue and coal combustion by ReCiPe2016 for life cycle impact assessment. J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 2020, 48, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Coal mine solid waste backfill process in China: Current status and challenges. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Shi, L.; Ma, D.; Chai, X.; Lin, C.; Zhang, F. Road performance evaluation of unburned coal gangue in cold regions. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Moghal, A.A.B.; Basha, B.M. The sustainable utilization of coal gangue in geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications. J. Hazard. Toxic Radioact. Waste 2022, 26, 03122003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Lal, M.H.; Moghal, A.A.B.; Murthy, V.R. Carbon footprint analysis of coal gangue in geotechnical engineering applications. Indian Geotech. J. 2020, 50, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Cheng, K.; Zhang, R.; Gao, Y.; Guan, X. Study on the influence mechanism of activated coal gangue powder on the properties of filling body. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 345, 128071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ling, T.C. Reactivity activation of waste coal gangue and its impact on the properties of cement-based materials–A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Tighe, S. Evaluation of mechanical properties and microscopic structure of coal gangue after aqueous solution treatment. Materials 2019, 12, 3207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.; Dong, J.; Yu, L.; Xu, C.; Jiao, X.; Wang, M. Effect of activated coal gangue in North China on the compressive strength and hydration process of cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, R.; Li, X.; Xu, P.; Liu, Q. Thermal activation and structural transformation mechanism of kaolinitic coal gangue from Jungar coalfield, Inner Mongolia, China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 223, 106508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Xue, H.; Wei, L.; Li, Y.; Dong, H. Comparison of performance, hydration behavior, and environmental benefits of coal gangue cementitious materials prepared by wet and dry grinding methods. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 471, 140665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, K.; Bai, L.; Guo, N.; Li, S. A short review of the sustainable utilization of coal gangue in environmental applications. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 39285–39296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Lu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, L. The metal ions release and microstructure of coal gangue corroded by acid-based chemical solution. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 3235–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Song, W.; Cao, W.; Shao, G.; Lu, H.; Yang, D.; Zhang, R. Utilization of coal gangue for the production of brick. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2017, 19, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, R.; Yan, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Jing, L. Microstructural characteristics of aluminosilicate minerals in cement clinker prepared from coal gangue, carbide slag, and desulfurization gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 451, 138861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Ma, H.; Zhu, H.; Li, W.; Xin, M.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y. Study on chloride binding capability of coal gangue based cementitious materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 167, 649–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Song, X.; Gong, C.; Pan, Z. Research on cementitious behavior and mechanism of pozzolanic cement with coal gangue. Cem Concr Res. 2006, 36, 1752–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wen, Q.; Hu, L.; Gong, M.; Tang, Z. Feasibility study on the application of coal gangue as landfill liner material. Waste Manag. 2017, 63, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, K.; Cui, L.; Cheng, F.; Lou, H.H. Effect of Na2CO3 additive on the activation of coal gangue for alumina extraction. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 131, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Yuan, S.; Gao, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Meng, X. Innovative utilization of red mud through co-roasting with coal gangue for separation of iron and aluminum minerals. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 98, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.; Zhou, Z.; Jiang, R.; Song, S.; Feng, S.; Lian, M. Extraction of aluminum and iron ions from coal gangue by acid leaching and kinetic analyses. Minerals 2022, 12, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhu, S.; Wang, D. Synthesis of coal-analcime composite from coal gangue and its adsorption performance on heavy metal ions. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 423, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Meng, X.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, F. Feasible synthesis of magnetic zeolite from red mud and coal gangue: Preparation, transformation and application. Powder Technol. 2023, 423, 118495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koshy, N.; Dondrob, K.; Hu, L.; Wen, Q.; Meegoda, J.N. Synthesis and characterization of geopolymers derived from coal gangue, fly ash and red mud. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 206, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Han, Y.; Wan, S.; Hou, H. Comparison of red mud and coal gangue blended geopolymers synthesized through thermal activation and mechanical grinding preactivation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 153, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z. Embankment displacement PLAXIS simulation and microstructural behavior of treated-coal gangue. Minerals 2020, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Song, J.; Bai, X.; Song, B.; Wang, R.; Zhou, T.; Pu, H. Leaching behavior and potential environmental effects of trace elements in coal gangue of an open-cast coal mine area, Inner Mongolia, China. Minerals 2016, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Hu, Z. Environmental impact assessment of acidic coal gangue leaching solution on groundwater: A coal gangue pile in Shanxi, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Ji, J.; Liu, Q.; He, Z.; Wang, H.; You, Z. Coal gangue applied to low-volume roads in China. Transp. Res. Rec. 2011, 2204, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Heeralal, M.; Moghal, A.A.B. Characterization studies on coal gangue for sustainable geotechnics. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhao, M.; Ma, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, T. Performance of ball-milling-modified coal gangue on Pb2+, Zn2+, and NH4+–N adsorption. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2024, 26, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, L.; Yang, F.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; An, J. Thermal activation and mechanical properties of high alumina coal gangue as auxiliary cementitious admixture. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 025201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussadik, A.; Ouzoun, F.; Agourrame, H.; Ez-zaki, H.; Saadi, M. Effect of Alkali-activation on Elaboration of a Binder Based on Ground Coal Gangue. Nano World J. 2023, 9, S12–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Q.; Liu, C.; Wan, Y.; Ren, C. Study of Road Performance and Curing Mechanism of Coal Gangue by Curing Agent. Lithosphere 2024, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, F.; Pan, Z.; Chen, W.; Muhammad, F.; Zhang, B.; Li, L. Geopolymerization of coal gangue via alkali-activation: Dependence of mechanical properties on alkali activators. Buildings 2024, 14, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Dong, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhai, H. Study on preparation of calcium-based modified coal gangue and its adsorption dye characteristics. Molecules 2024, 29, 2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Wu, T.; Ren, G.; Zhu, Z.; Gao, Y.; Shi, M.; Fan, H. Reusing waste coal gangue to improve the dispersivity and mechanical properties of dispersive soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 404, 136993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y. Environmentally friendly utilization of coal gangue as aggregates for shotcrete used in the construction of coal mine tunnel. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2021, 15, e00751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xia, J.; Xia, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. Study on the mechanical behavior and micro-mechanism of concrete with coal gangue fine and coarse aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 338, 127626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Liu, P.; Mo, L.; Liu, K.; Ma, R.; Guan, Y.; Sun, D. Mechanism of thermal activation on granular coal gangue and its impact on the performance of cement mortars. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 45, 103616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Pan, J.; Yang, F.; Liu, H.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, N. Extraction of lithium from coal gangue by a roasting-leaching process. Int. J. Coal Prep. Util. 2023, 43, 863–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qiu, J.; Ma, Z.; Sun, X. Eco-friendly treatment of coal gangue for its utilization as supplementary cementitious materials. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 285, 124834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Seetharaman, S.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Effects of chemistry and mineral on structural evolution and chemical reactivity of coal gangue during calcination: Towards efficient utilization. Mater. Struct. 2015, 48, 2779–2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, X.M. Performance of cemented coal gangue backfill. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2007, 14, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zang, L.; Zha, J.; Mahmood, Q.; He, Z. Phosphate removal from secondary effluents using coal gangue loaded with zirconium oxide. Sustainability 2019, 11, 2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, B.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Guo, Q. Insight into the Micro Evolution of Backfill Paste Prepared with Modified Gangue as Supplementary Cementitious Material: Dissolution and Hydration Mechanisms. Materials 2023, 16, 6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, E.; Zhang, X.; Su, L.; Liu, B.; Li, B.; Li, W. Analysis of calcination activation modified coal gangue and its acid activation mechanism. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 95, 109916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Xu, J.; Xu, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhu, X. Performance of cement-based materials containing calcined coal gangue with different calcination regimes. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 56, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Min, X.; Jiang, X.; Sun, M.; Li, X. Adsorption and Desorption of Coal Gangue Toward Available Phosphorus Through Calcium-Modification with Different pH. Minerals 2022, 12, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.N.; Iqbal, M.; Ashfaq, M.; Salami, B.A.; Khan, K.; Faraz, M.I.; Alabdullah, A.A.; Jalal, F.E. Prediction of Strength and CBR Characteristics of Chemically Stabilized Coal Gangue: ANN and Random Forest Tree Approach. Materials 2022, 15, 4330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frías, M.; Vigil de la Villa, R.; Sánchez De Rojas, M.I.; Medina, C.; Juan, A. Scientific aspects of kaolinite based coal mining wastes in pozzolan/Ca(OH)2 system. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 95, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Yang, Y.; Li, H. Cementitious properties of coal-based metakaolin prepared from coal gangue via Fe3O4-Assisted microwave activation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 448, 141277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guan, X.; Zhu, M.; Gao, J. Mechanism on activation of coal gangue admixture. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5436482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Cao, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C. Effect of calcination condition on the microstructure and pozzolanic activity of calcined coal gangue. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2016, 146, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, A.G.; Amulya, G.; Bind, A.; Yamsani, S.K. Effective Utilization of Coal Gangue for Stabilizing Black Cotton Soil: Geotechnical Performance and Microstructural Insights. Transp. Infrastruct. Geotechnol. 2025, 12, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yan, K.; Cui, L.; Cheng, F. Improved extraction of alumina from coal gangue by surface mechanically grinding modification. Powder Technol. 2016, 302, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, S.; Ma, B.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y. Extraction of valuable components from coal gangue through thermal activation and HNO3 leaching. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 113, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Wang, R.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, L.; He, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhang, X. Investigation on the adsorption performance of modified coal gangues to p-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2023, 40, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, X.; Liu, S.; Li, D. Removal of Pb (II), Cd (II) and Hg (II) from aqueous solution by mercapto-modified coal gangue. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 231, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Su, Y.; Du, C. A novel and green strategy for efficient removing Cr (VI) by modified kaolinite-rich coal gangue. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 211, 106208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okagbue, C.O.; Ochulor, O.H. The potential of cement-stabilized coal-reject as a construction material. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2007, 66, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Cai, K.; Zeng, X.; Li, Z.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Huang, X. Experimental study on physical-mechanical properties of expansive soil improved by multiple admixtures. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2021, 2021, 5567753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashfaq, M.; Moghal, A.A.B.; Munwar Basha, B. Reliability-based design optimization of chemically stabilized coal gangue. J. Test. Eval. 2022, 50, 3116–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Ma, Z.; Li, H.; Gong, P.; Xu, M.; Chen, T. Laboratory tests, field application and carbon footprint assessment of cement-stabilized pure coal solid wastes as pavement base materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Yan, P.; Yan, C.; Tong, Y. Mechanical properties of furnace slag and coal gangue mixtures stabilized by cement and fly ash. Materials 2021, 14, 7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, J.; Lu, M.; Yao, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, D.; Yang, B.; Liu, H. An experimental study of the road performance of cement stabilized coal gangue. Crystals 2021, 11, 993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghal, A.A.B.; Rehman, A.U.; Vydehi, K.V.; Umer, U. Sustainable perspective of low-lime stabilized fly ashes for geotechnical applications: Promethee-based optimization approach. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z. Utilization of red mud and coal gangue for underground backfill material: Hydration and environmental characteristics. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2025, 32, 1358–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Meng, W.; Deng, B.; Liu, X.; Cui, H.; Feng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y. Mechanical Properties and Durability of Steel Slag-mineral Powder-coal Gangue Mixture by Uniform Design for Pavement Base. Mater. Sci. 2024, 30, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guo, T.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, J. Road performance analysis of cement stabilized coal gangue mixture. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 125502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, T.; Ren, G.; Zhao, G. A potential way for improving the dispersivity and mechanical properties of dispersive soil using calcined coal gangue. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 29, 3049–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, C.; Song, W.; Hou, W. High-capacity utilization of coal gangue as supplementary cementitious material, geopolymer, and aggregate: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 435, 136857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Wang, H.; Xue, S.; Cheng, Y. Study on the Activation Effect of Mechanical Force in the Process of Ultrafine Grinding of Coal Gangue. Min. Metall. Explor. 2025, 42, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Chen, J.; Zhu, M.; Gao, J. Performance of microwave-activated coal gangue powder as auxiliary cementitious material. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2799–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, Y.; Han, Y.; Gao, P.; Gong, G. Investigation on calcination behaviors of coal gangue by fluidized calcination in comparison with static calcination. Minerals 2017, 7, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, G.; Jiang, H.; Li, Z. Study on the calorific value and cementitious properties of coal gangue with 0–1 mm particle size. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 135061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Han, X.; Sun, Z.; Jin, P.; Li, K.; Wang, F.; Gong, J. Study on the Reactivity Activation of Coal Gangue for Efficient Utilization. Materials 2023, 16, 6321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, J.; Hao, Z. The thermal activation process of coal gangue selected from Zhungeer in China. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 126, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.L.; Ni, W.; Zhang, S.Q.; Wang, S.; Gai, G.S.; Wang, W.K. Preparation and properties of autoclaved aerated concrete using coal gangue and iron ore tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 104, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, Z.; Cheng, L.; Wang, G.; Qin, Y. Medium-temperature calcination and acid pressure leaching extract the Al2O3 from coal gangue: Activation mechanism and kinetic analysis. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11266–11275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiu, S.; Wang, M.; Chen, Y.; Chen, J.; Gao, Q. Synthesis and characterization of low-carbon cementitious materials from suspended calcined coal gangue. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 982861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Fu, Y.; Pan, S. The use of modified coal gangue for the remediation and removal of phosphorus in an enclosed water area. Clean Technol. Environ. 2019, 23, 1327–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gu, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, B.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y. Exploring microwave activation as a novel method for activating coal gangue: Focus on microwave activation mechanisms and hydration characteristics of cementitious supplementary materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Mi, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H. Synergistic performance of microwave-activated coal gangue with limestone in low-carbon cement. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 96, 110622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhai, H.; Gao, Z.; Gong, G.; Li, F. Study on the preparation of calcium modified coal gangue and its adsorption performance of phosphate. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischinenko, V.; Vasilchenko, A.; Lazorenko, G. Effect of waste concrete powder content and microwave heating parameters on the properties of porous alkali-activated materials from coal gangue. Materials 2024, 17, 5670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM C618-22; Standard Specification for Coal Fly Ash and Raw or Calcined Natural Pozzolan for Use in Concrete. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2003.
- Li, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Ni, W. Improvement on pozzolanic reactivity of coal gangue by integrated thermal and chemical activation. Fuel 2013, 109, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Luo, Z.; Shi, Z.; Ni, M. Utilization of coal gangue and copper tailings as clay for cement clinker calcinations. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2011, 26, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C.; Bold, T.; Wang, J.; Cui, K. Effect of activated coal gangue on the hydration and hardening of Portland cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 422, 135740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q. Influence of thermally activated coal gangue powder on the structure of the interfacial transition zone in concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 363, 132408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Hao, F.; Liu, P.; Mo, L.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Sun, D. Separation of calcined coal gangue and its influence on the performance of cement-based materials. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 51, 104293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhu, J.; Li, D.; Chen, J.; Yang, N. Early hydration of composite cement with thermal activated coal gangue. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2010, 25, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Sun, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. Early-age characteristics of red mud–coal gangue cementitious material. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 167, 927–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.H.; Pan, J.; Zhu, D.Q.; Guo, Z.Q.; Li, S.W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.J. Investigation on activation technology of self-heating decarbonization of coal gangue by a sintering process. J. Cent. South Univ. 2023, 30, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, K.; Fu, W.; Liu, C.; Yang, S. Preparation, characteristics and mechanisms of the composite sintered bricks produced from shale, sewage sludge, coal gangue powder and iron ore tailings. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 232, 117250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad Howladar, M.; Mostafijul Karim, M. The selection of backfill materials for Barapukuria underground coal mine, Dinajpur, Bangladesh: Insight from the assessments of engineering properties of some selective materials. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 73, 6153–6165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Li, A.; Zhou, N. Reutilisation of coal gangue and fly ash as underground backfill materials for surface subsidence control. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 254, 120113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Kang, S.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Q.; Shen, R.; Shu, Z. Research of the workability, mechanical and hydration mechanism of coal gangue-construction solid waste backfilling materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 408, 133833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yue, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Wang, J. Study on mechanical properties of coal gangue and fly ash mixture as backfill material based on fractal characteristics. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 111936–111946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, N. Effects of particle size of crushed gangue backfill materials on surface subsidence and its application under buildings. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amulya, G.; Moghal, A.A.B.; Almajed, A. Sustainable binary blending for low-volume roads—Reliability-based design approach and carbon footprint analysis. Materials 2023, 16, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Yin, H.; Dong, F.; Li, Y.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y. Hydrochemical characteristics, cross-layer pollution and environmental health risk of groundwater system in coal mine area: A case study of Jiangzhuang coal mine. Environ. Geochem. Health. 2024, 46, 523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, R.; Azadmehr, A.; Maghsoudi, A. Fabrication of the alginate-combusted coal gangue composite for simultaneous and effective adsorption of Zn (II) and Mn (II). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 103494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, L.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Zhai, H. Preparation of Calcium-Based Coal Gangue Based on Response Surface Method and its Removal of Dyes. JOM 2024, 76, 5376–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Yan, S.; Yang, J. Adsorption removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions using ceramic adsorbents prepared from industrial waste coal gangue. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 234, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Feng, K.; Zhang, H.; Han, L.; He, Q.; Huang, F.; Wang, W. Sustainable green conversion of coal gangue waste into cost-effective porous multimetallic silicate adsorbent enables superefficient removal of Cd (II) and dye. Chemosphere 2023, 324, 138287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Feng, K.; Wang, L.; Yu, Q.; Du, F.; Guo, X. Characterization of coal gangue and coal gangue-based sodalite and their adsorption properties for Cd2+ ion and methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2023, 25, 1622–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Dong, B.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Deng, X.; Fang, C. Effective adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution by coal gangue-based zeolite granules in a fluidized bed: Fluidization characteristics and continuous adsorption. Powder Technol. 2022, 408, 117764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, N.; Moghal, A.A.B.; Rasheed, R.M.; Almajed, A. Critical review on the efficacy of electrokinetic techniques in geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Ouyang, S.; Fan, B.; Liu, Y. Study on dynamic adsorption characteristics of gangue to heavy metals in goaf and its water purification mechanism under leaching condition. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Pang, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, E.; Wu, D.; Ma, J. Coal gangue geopolymers as sustainable and cost-effective adsorbents for efficient removal of Cu (II). Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 32, 103416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruddin, M.; Moghal, A.A.B. State-of-the-art review on the geotechnical and geoenvironmental feasibility of select biochars. Indian Geotech. J. 2024, 54, 1073–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, C.; Chu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Su, S.; Su, R.; Gao, N. Amine-modified silica zeolite from coal gangue for CO2 capture. Fuel 2022, 322, 124184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Q.; Huo, B.; Zhou, N.; Zhou, Y.; Gu, W. Effect of carbonization pressure on CO2 sequestration and rheological properties of coal gangue-based backfilling slurry. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, D.; Du, H.; Li, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, S.; Xu, B.; Kang, L. Study on Green Controllable Preparation of Coal Gangue-Based 13-X Molecular Sieves and Its CO2 Capture Application. Coatings 2023, 13, 1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Du, H.; Gao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J. Syntheses of four novel silicate-based nanomaterials from coal gangue for the capture of CO2. Fuel 2019, 258, 116192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, X. Potentially useful elements (Al, Fe, Ga, Ge, U) in coal gangue: A case study in Weibei coal mining area, Shaanxi Province, northwestern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 11893–11904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Liu, F.; Zhao, H.; Ke, C.; Xu, Z. Mineral phase transformation in coal gangue by high temperature calcination and high-efficiency separation of alumina and silica minerals. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 2281–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Nie, T.; Zhou, C.; Yang, F.; Jia, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, H. The effect of calcination on the occurrence and leaching of rare earth elements in coal refuse. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Baaj, H.; Zhao, R. Evaluation for the leaching of Cr from coal gangue using expansive soils. Processes 2019, 7, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Lv, F.; Huang, P. Dynamic leaching behaviors of heavy metals from recycled coal gangue aggregate under loading conditions during solid backfill mining. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 125028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liu, L.; Yang, P.; Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Deng, S. Study on leaching and curing mechanism of heavy metals in magnesium coal based backfill materials. Process Saf. Environ. Protect. 2023, 177, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liao, H.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, F. A facile green and cost-effective manufacturing process from coal gangue-reinforced composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2023, 233, 109908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Dai, S.; Jian, S.; Huang, J.; Tan, H.; Li, B. Utilization of solid waste high-volume calcium coal gangue in autoclaved aerated concrete: Physico-mechanical properties, hydration products and economic costs. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 278, 123416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Y.; Li, T. Sustainable coal gangue–Based silicon fertilizer: Energy–Efficient preparation, performance optimization and conversion mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 505, 159205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | Activation Method | Optimum Temperature | Application | Compressive Strength (MPa) | Reference | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 Days | 7 Days | 28 Days | |||||
| Coal gangue, copper tailings, low calcium cement, and high calcium cement | Thermal | 1450 °C | Clinker production | 55 | 80 | Qiu et al. [107] | |
| Coal gangue | Thermal | 800 °C | Cementitious material | 28.4 | 38.5 | Guo et al. [66] | |
| Coal gangue blended with cement | Thermal | 700 °C | Cementitious material | 30 | 42 | Li et al. [108] | |
| Coal gangue | Thermal | 800 °C | Cementitious material | 15.51 | 22.43 | Su et al. [109] | |
| Coal gangue | Thermal | - | Cement mortar | 26 | 52 | Wang et al. [110] | |
| Clinker, gypsum, and coal gangue | Thermal | 700 °C | Clinker production | 25.2 | 52.8 | Guo et al. [111] | |
| Red mud and coal gangue | Thermal | 600 °C | Cementitious material | 24 | 28 | Zhang et al. [112] | |
| Cement and coal gangue | Thermal | - | Cementitious material | 3 | 22 | Zhao et al. [60] | |
| Coal gangue | Thermal | 750 °C | Cementitious material | 21.2 | 47.2 | Lu et al. [113] | |
| Coal gangue | Thermal | 700 °C | Admixture | 35 | 49 | Wang et al. [58] | |
| Activation | Applications | Limitations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cementitious Materials | Geotechnical | Geoenvironmental | ||||||
| Cement Mortar/Concrete | Bricks Production | Backfill | Pavements | Removal of Phosphorus | Removal of Dyes | Removal of Heavy Metals | ||
| Mechanical | Faster initial setting time, improves compressive strength, reduces porosity. | Improves the strength and uniformity of bricks | * | Enhances compaction and stability | Limited effectiveness in phosphorus removal | Moderate adsorption | Moderate adsorption efficiency | High energy consumption for fine grinding |
| Thermal | High setting time | Enhance water absorption and compressive strength | High compressive strength | Improves durability | Energy intensive | Good adsorption for cationic dyes | Highly effective for Pb2+, Cd2+, and Zn2+ | Requires high temperatures (500–900 °C), leading to significant energy demand |
| Chemical | Improves workability | Lower density, water absorption, and thermal conductivity | * | Enhances pozzolanic reaction when combined with lime | Efficient removal of phosphorus, risk of secondary pollution if the reagents are not recovered | High effective | Efficient removal of heavy metals, potential secondary pollution | Requires high temperatures (500–900 °C), leading to significant energy demand |
| Microwave | Increases the alkalinity of the cement slurry and secondary hydration of the coal gangue enhances the strength | * | * | * | * | * | Similar benefits as thermal activation; high adsorption potential, but scaling up remains challenging | Limited penetration depth for large particle sizes or bulk materials |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Snehasree, N.; Nuruddin, M.; Moghal, A.A.B. Critical Appraisal of Coal Gangue and Activated Coal Gangue for Sustainable Engineering Applications. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179649
Snehasree N, Nuruddin M, Moghal AAB. Critical Appraisal of Coal Gangue and Activated Coal Gangue for Sustainable Engineering Applications. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179649
Chicago/Turabian StyleSnehasree, Narlagiri, Mohammad Nuruddin, and Arif Ali Baig Moghal. 2025. "Critical Appraisal of Coal Gangue and Activated Coal Gangue for Sustainable Engineering Applications" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179649
APA StyleSnehasree, N., Nuruddin, M., & Moghal, A. A. B. (2025). Critical Appraisal of Coal Gangue and Activated Coal Gangue for Sustainable Engineering Applications. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9649. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179649









