Elastic Time-Lapse FWI for Anisotropic Media: A Pyrenees Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology of Source-Independent Full-Waveform Inversion
2.1. FWI Objective Functions
2.2. Source-Independent FWI
2.3. Forward Modeling and Model Updating for FWI
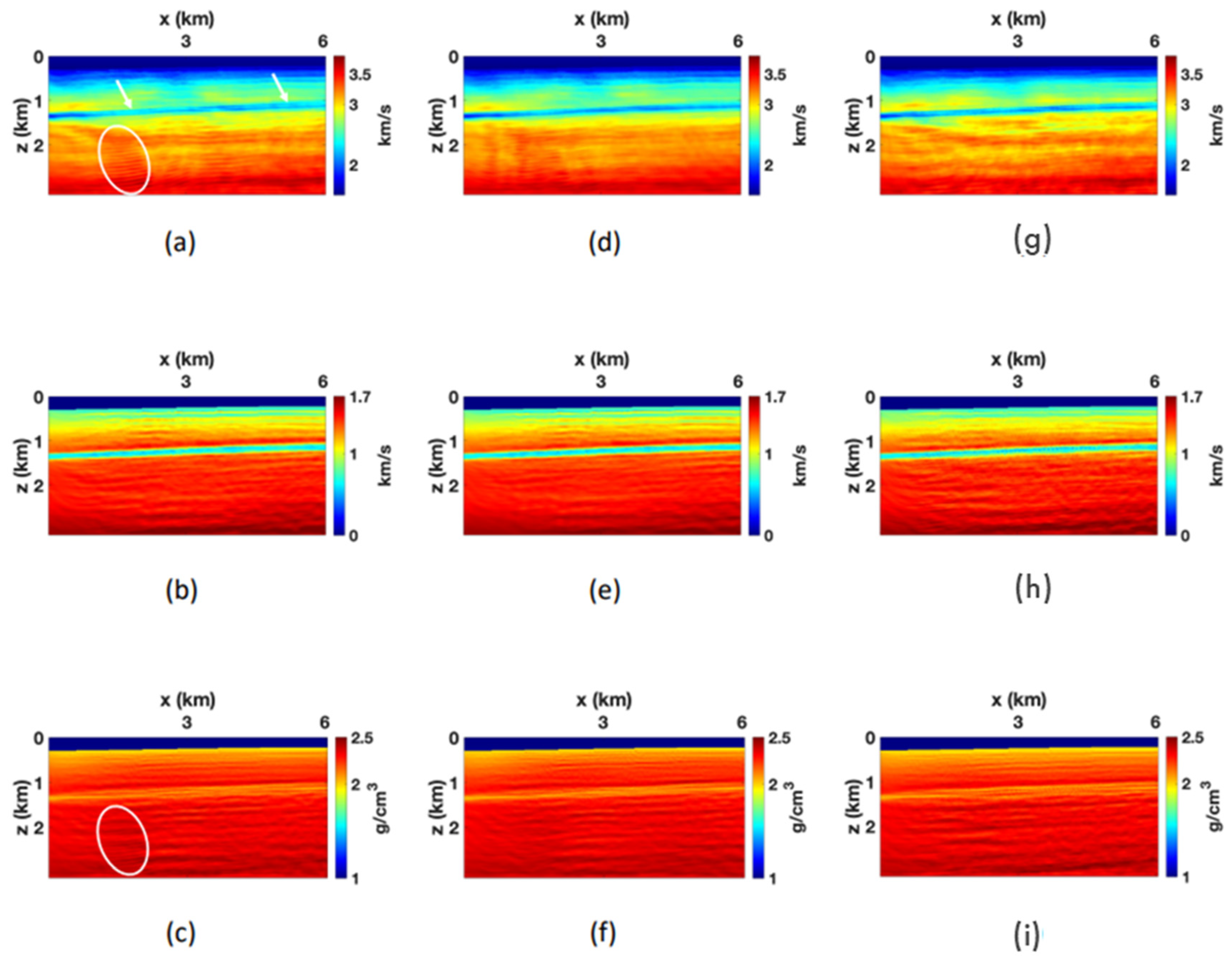
3. Field-Data Application
3.1. Location and Geology
3.2. Preprocessing
3.3. Initial Model
3.4. Wavelet Estimation
3.5. Inversion of the Baseline Data
3.5.1. Elastic Isotropic FWI
3.5.2. Elastic FWI for VTI Media
3.6. Inversion of the Monitor Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lumley, D. 4D seismic monitoring of CO2 sequestration. Lead. Edge 2010, 29, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.S.; Tsvankin, I. Sensitivity of compaction-induced multicomponent seismic time shifts to variations in reservoir properties. Geophysics 2013, 78, T151–T163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pevzner, R.M.; Urosevic, D.; Popik, V.; Shulakova, K.; Tertyshnikov, E.; Caspari, J.; Correa, T.; Dance, A.; Kepic, S.; Glubokovskikh, S.; et al. 4D surface seismic tracks small supercritical CO2 injection into the subsurface: CO2CRC Otway Project. Int. J. Greenh. Gas Control 2017, 63, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumley, D.E. Time-lapse seismic reservoir monitoring. Geophysics 2001, 66, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asnaashari, A.; Brossier, R.; Garambois, S.; Audebert, F.; Thore, P.; Virieux, J. Time-lapse seismic imaging using regularized full-waveform inversion with a prior model: Which strategy? Geophys. Prospect. 2015, 63, 78–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; To, R.; Wang, M.; Xie, Y.; Dickinson, D. 4D FWI using towed-streamer data: A case study near Laverda oil field. SEG Tech. Program Expand. Abstr. 2021, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plessix, R.-E.; Michelet, S.; Rynja, H.; Kuehl, H.; Perkins, C.; Maag, J.; Hatchell, P. Some 3D applications of full waveform inversion: EAGE Expanded Abstracts. In Proceedings of the 72nd EAGE Conference and Exhibition—Workshops and Fieldtrips, Barcelona, Spain, 14–17 June 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Routh, P.; Palacharla, G.; Chikichev, I.; Lazaratos, S. Full wavefield inversion of time—Lapse data for improved imaging and reservoir characterization. SEG Tech. Program Expand. Abstr. 2012, 4361–4366. [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe, T.; Shimizu, S.; Asakawa, E.; Matsuoka, T. Differential waveform tomography for time-lapse crosswell seismic data with application to gas hydrate production monitoring. SEG Tech. Program Expand. Abstr. 2004, 2323–2326. [Google Scholar]
- Denli, H.; Huang, L. Double-difference elastic waveform tomography in the time domain: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts. In Proceedings of the 2009 SEG Annual Meeting, Houston, TX, USA, 25–30 October 2009; pp. 2302–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Liu, F.; Morton, S.; Malcolm, A.; Fehler, M. Time-lapse full-waveform inversion with ocean-bottom-cable data: Application on Valhall field. Geophysics 2016, 81, R225–R235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks; Hoeber, H.; Houbiers, M.; Lescoffit, S.P.; Ratcliffe, A.; Vinje, V. Time-lapse full-waveform inversion as a reservoir-monitoring tool—A North Sea case study. Lead. Edge 2016, 35, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorov, A.; Pevzner, R.; Bόna, A.; Glubokovskikh, S.; Puzyrev, V.; Tertyshnikov, K.; Gurevich, B. Time-lapse full waveform inversion of vertical seismic profile data: Workflow and application to the CO2CRC Otway project. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 7211–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tsvankin, I. Methodology of time-lapse elastic full-waveform inversion for VTI media. J. Seism. Explor. 2021, 30, 257–270. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Tsvankin, I. Source-independent time-lapse full-waveform inversion for anisotropic media. Geophysics 2022, 87, R111–R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantola, A. Linearized inversion of seismic reflection data. Geophys. Prospect. 1984, 32, 998–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Alkhalifah, T. Application of multi-source waveform inversion to marine streamer data using the global correlation norm. Geophys. Prospect. 2012, 60, 748–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Tsvankin, I.; Naeini, E.Z. Facies-based full-waveform inversion for anisotropic media: A north sea case study. Geophys. Prospect. 2021, 69, 1650–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Alkhalifah, T. Source-independent time-domain waveform inversion using convolved wavefields: Application to the encoded multisource waveform inversion. Geophysics 2011, 76, R125–R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Wang, J. Robust source-independent elastic full-waveform inversion in the time domain. Geophysics 2016, 81, R29–R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, N.; Tsvankin, I. Elastic full-waveform inversion for VTI media: Methodology and sensitivity analysis. Geophysics 2016, 81, C53–C68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scibiorski, J.; Micenko, M.; Lockhart, D. Recent discovery in the Pyrenees member, Exmouth Sub-basin: A new oil play fairway. APPEA J. 2005, 45, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodall, M.; Stark, C. The Stratigraphy of the Pyrenees Member of the Ravensworth, Crosby and Stickle Fields, Exmouth Sub-Basin, Northwest Australia—A Wave- and Storm-Dominated Shelf-Margin Delta. Available online: https://archives.datapages.com/data/petroleum-exploration-society-of-australia/conferences/043/043001/pdfs/57.htm (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Cai, J.; Duncan, G.; Goody, A.; Kostas, K. Extract 4d signal from two streamer surveys with very different acquisition geometry by least-squares migration over pyrenees fields: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts. In Proceedings of the SEG International Exposition and Annual Meeting, San Antonio, TX, USA, 15–20 September 2019; pp. 5265–5269. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, G.H.F.; Gardner, L.W.; Gregory, A.R. Formation velocity and density-the diagnostic basics for stratigraphic traps. Geophysics 1974, 39, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, M.; Ratcliffe, A.; Nangoo, T.; Morgan, J.; Umpleby, A.; Shah, N.; Vinje, V.; Štekl, I.; Guasch, L.; Win, C.; et al. Anisotropic 3d full-waveform inversion. Anisotropic 2013, 78, R59–R80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.M.; Wang, S.X.; Yuan, S.Y. Effect of inaccurate wavelet phase on prestack waveform inversion. J. Appl. Geophys. 2014, 11, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Williamson, P.R.; Pratt, R.G. Frequency-domain acoustic-wave modeling and inversion of crosshole data: Part ii—Inversion method, synthetic experiments and real-data results. Geophysics 1995, 60, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, R.G. Seismic waveform inversion in the frequency domain, part 1: Theory and verification in a physical scale model. Geophysics 1999, 64, 888–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.A.; Treitel, S. Principles of digital wiener filtering. Geophys. Prospect. 1967, 15, 311–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asaka, M.; Sekine, T.; Furuya, K. Geologic cause of seismic anisotropy: A case study from offshore western australia. Lead. Edge 2016, 35, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, N.; Tsvankin, I.; Díaz, E. Elastic full-waveform inversion for VTI media: A synthetic parameterization study. Geophysics 2017, 82, C163–C174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, I. Weak elastic anisotropy. Geophysics 1986, 51, 1954–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsvankin, I. Seismic Signatures and Analysis of Reflection Data in Anisotropic Media, 3rd ed.; Society of Exploration Geophysicists: Houston, TX, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.; Tsvankin, I. Sensitivity analysis of elastic full-waveform inversion for orthorhombic media. J. Seism. Explor. 2022, 31, 105–130. [Google Scholar]
- Duncan, G.; Cai, J.; Kostas, K.; Perrett, T.; Florez, M.; Stewart, J.; Kuzmin, S. 4D Seismic over the Pyrenees Fields. ASEG Ext. Abstr. 2015, 2015, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Tsvankin, I.; Masaya, S.; Tani, M. Elastic Time-Lapse FWI for Anisotropic Media: A Pyrenees Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9553. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179553
Liu Y, Tsvankin I, Masaya S, Tani M. Elastic Time-Lapse FWI for Anisotropic Media: A Pyrenees Case Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9553. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179553
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yanhua, Ilya Tsvankin, Shogo Masaya, and Masanori Tani. 2025. "Elastic Time-Lapse FWI for Anisotropic Media: A Pyrenees Case Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9553. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179553
APA StyleLiu, Y., Tsvankin, I., Masaya, S., & Tani, M. (2025). Elastic Time-Lapse FWI for Anisotropic Media: A Pyrenees Case Study. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9553. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179553





