Collapse Behavior of Compacted Clay in a Water Content-Controlled Oedometer Apparatus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
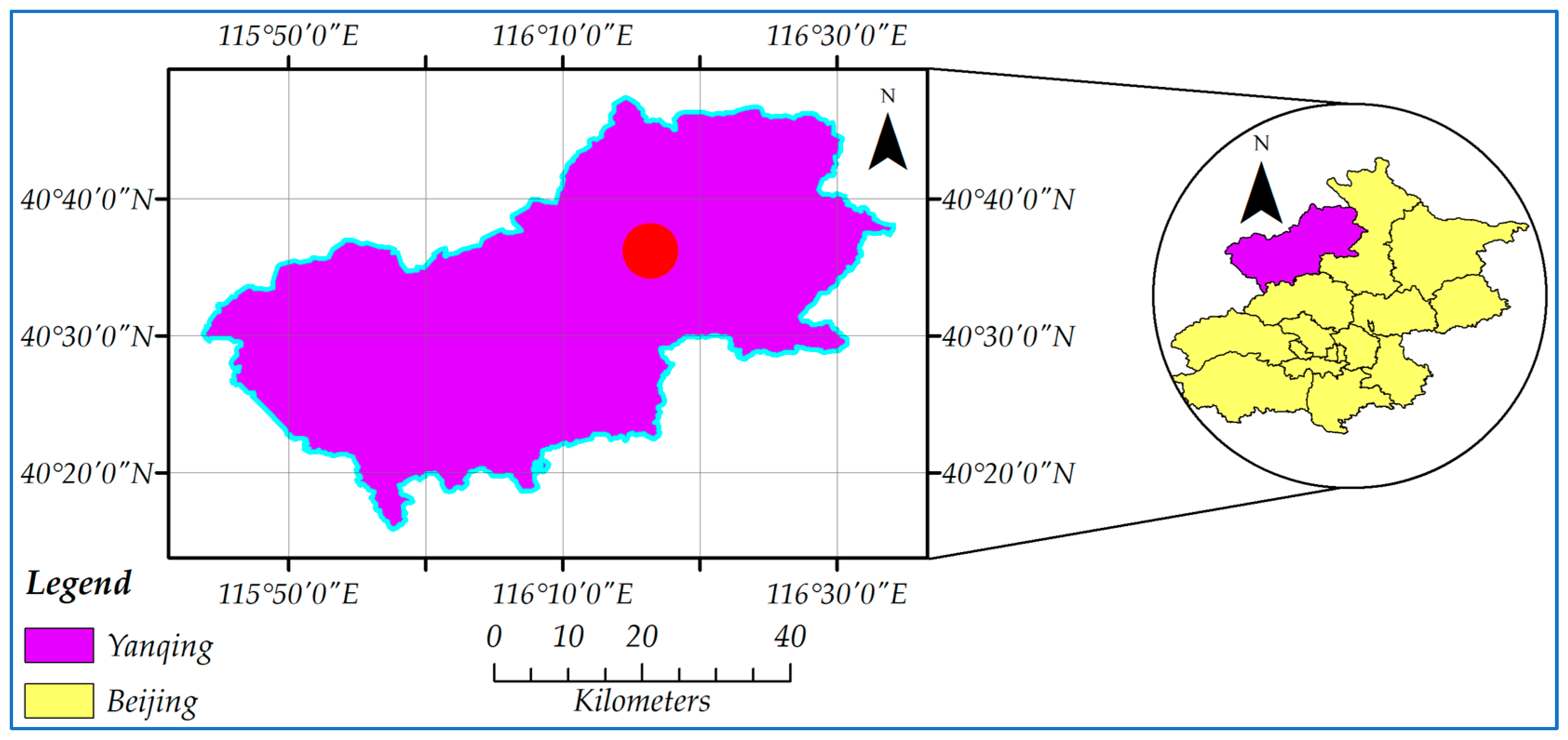
2.1. Study Area
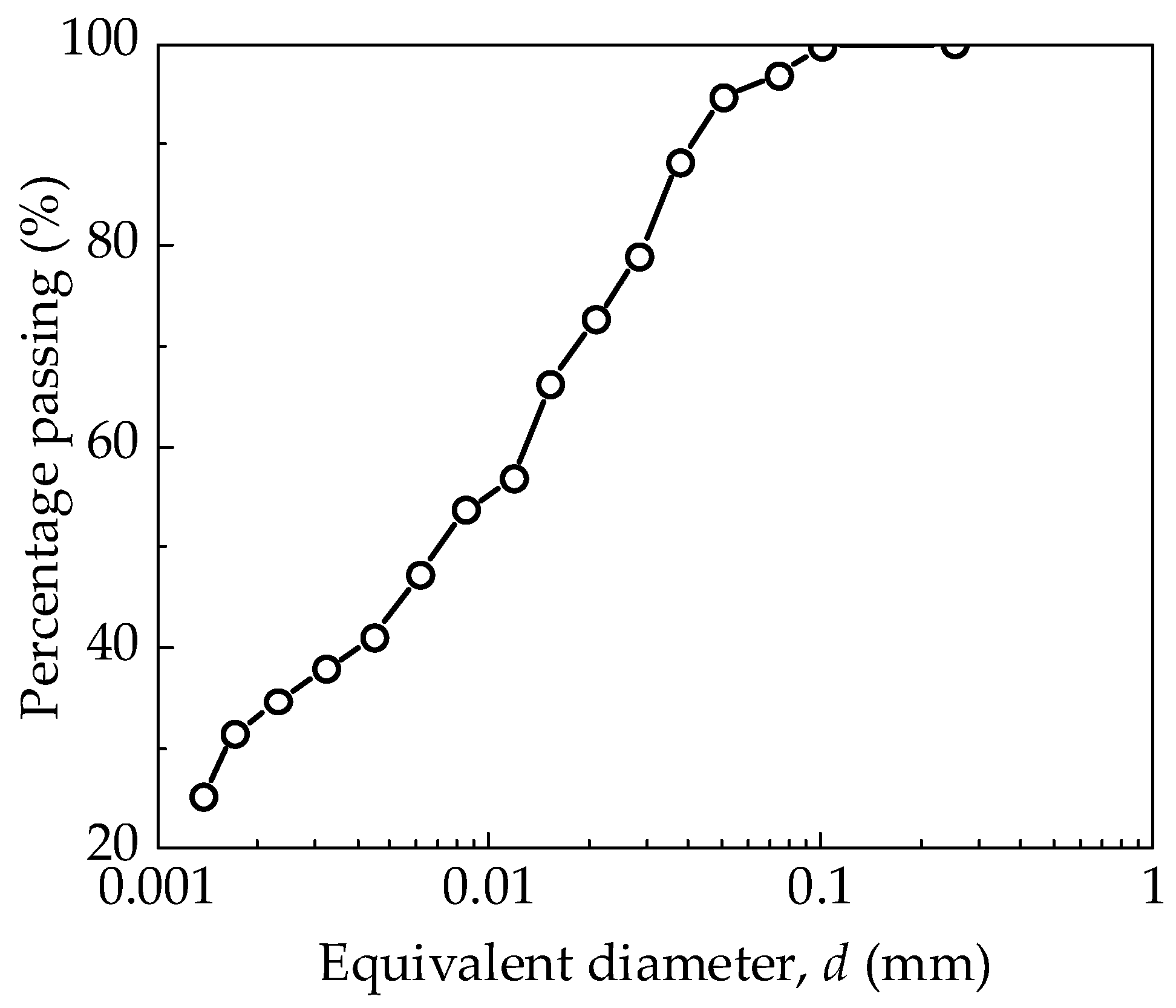
2.2. Material
2.3. Water Retention Tests
2.4. Compression Tests
2.5. Wetting Collapse Tests
3. Results and Discussions
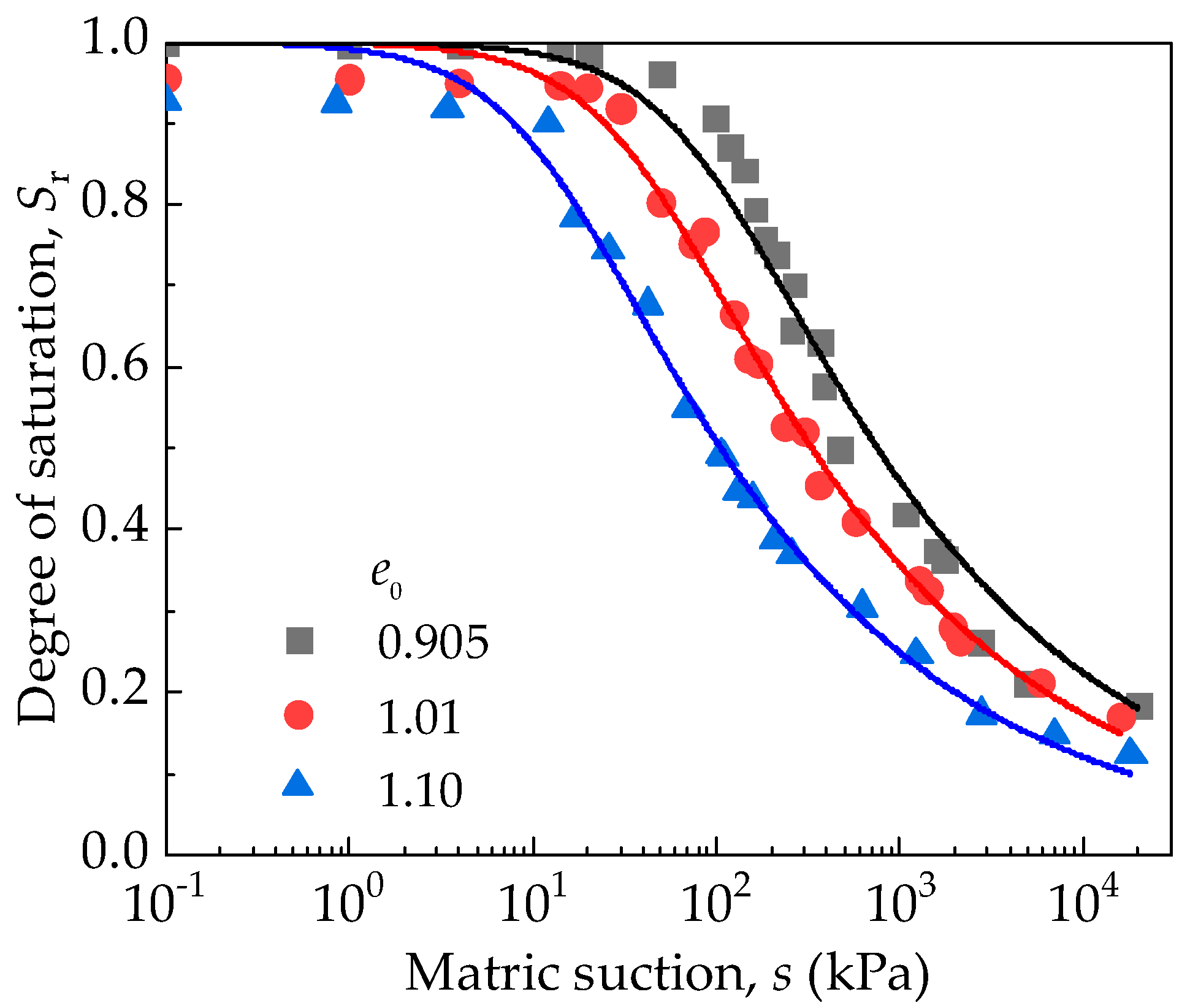
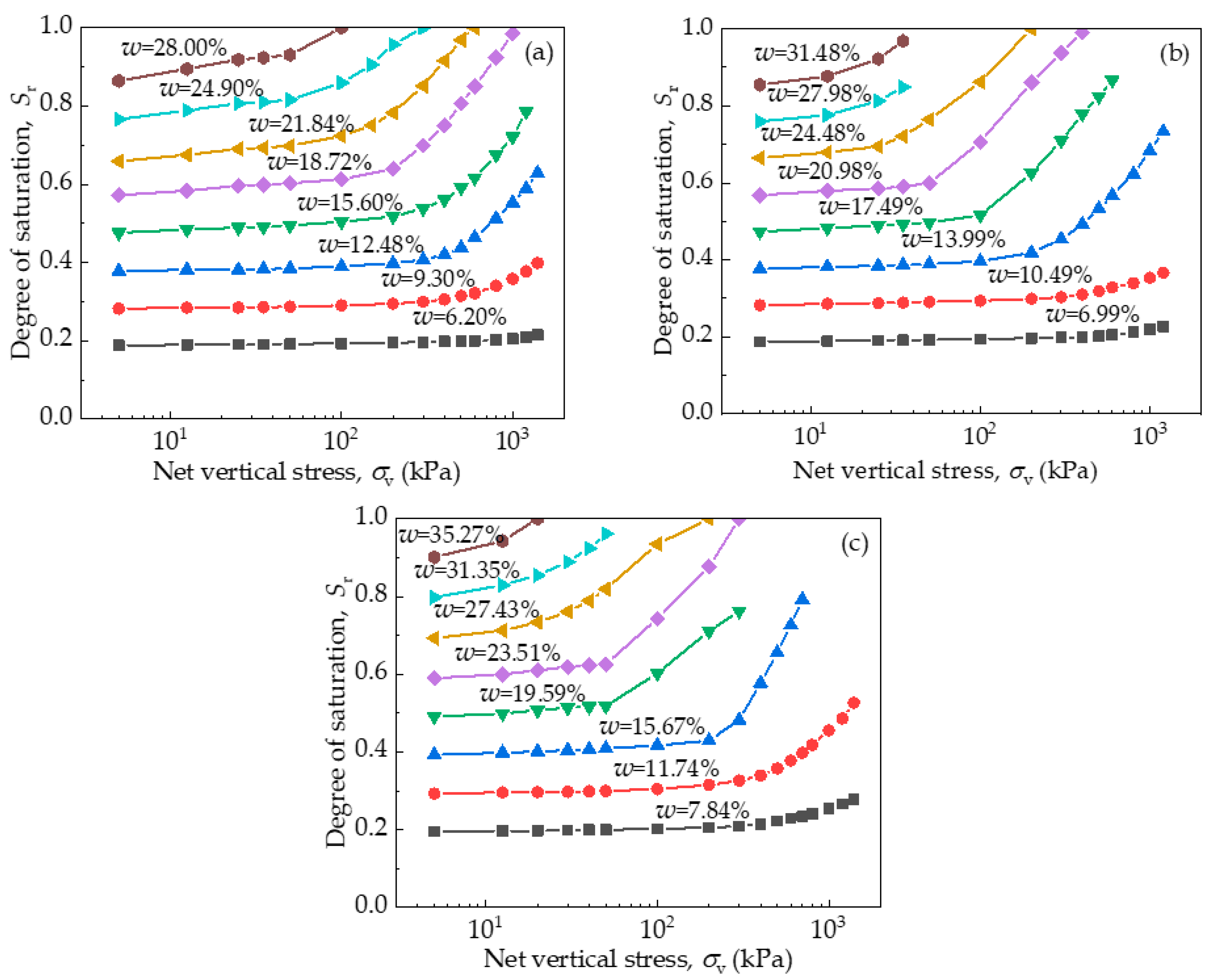
3.1. Water Retention Test Results and the Parameter Calibration
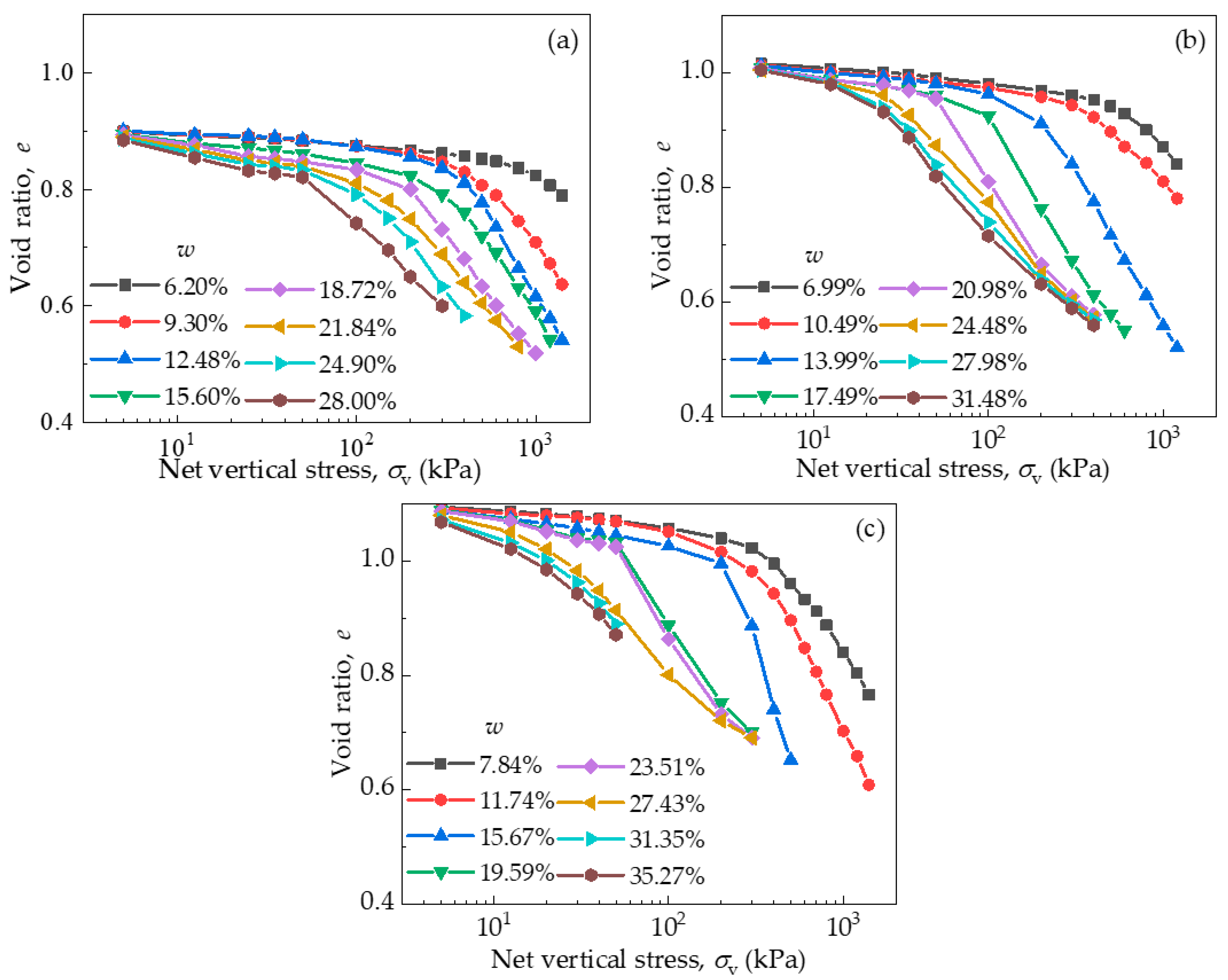
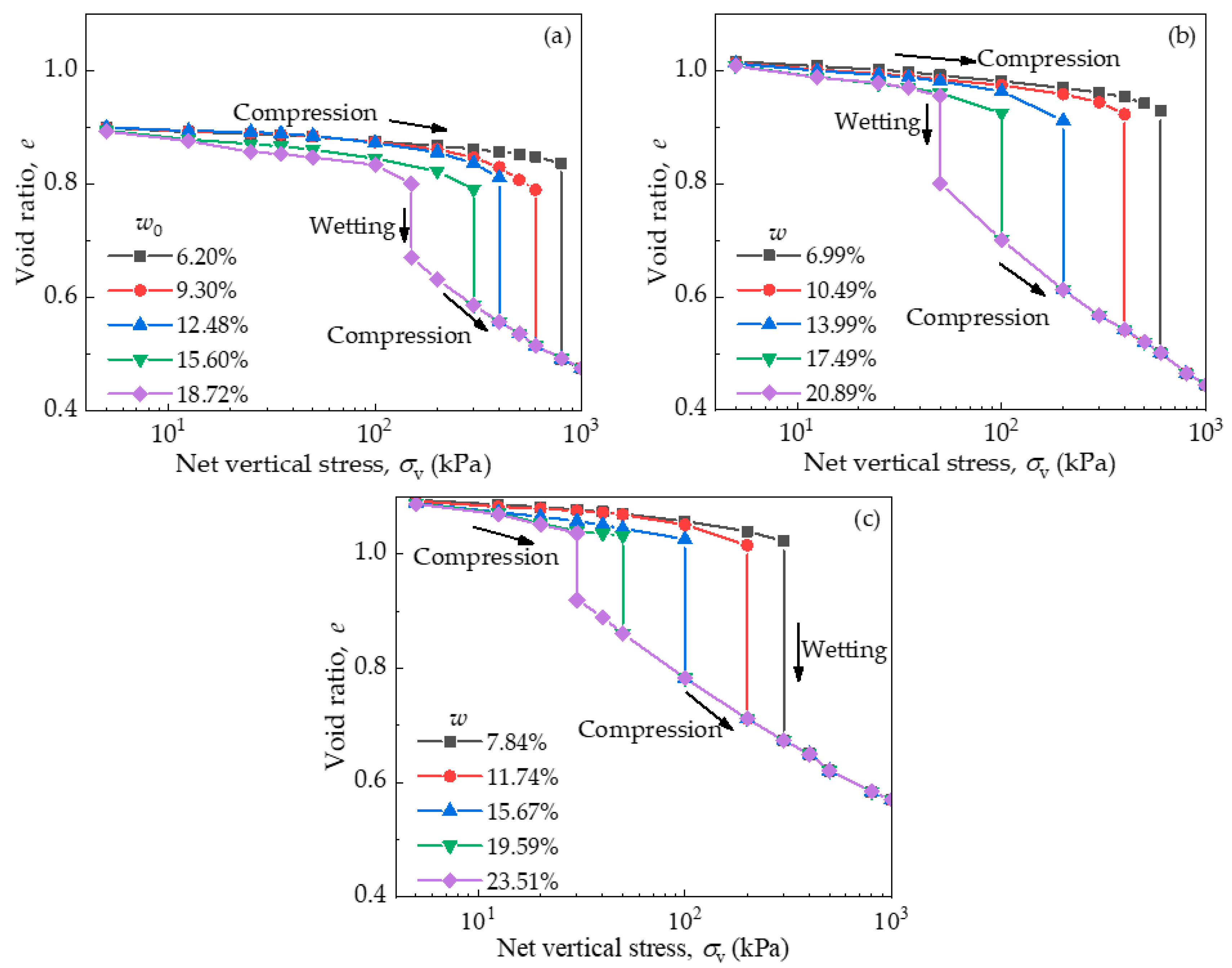
3.2. Compression Test Results
3.3. Compression–Wetting Collapse–Recompression Test Results
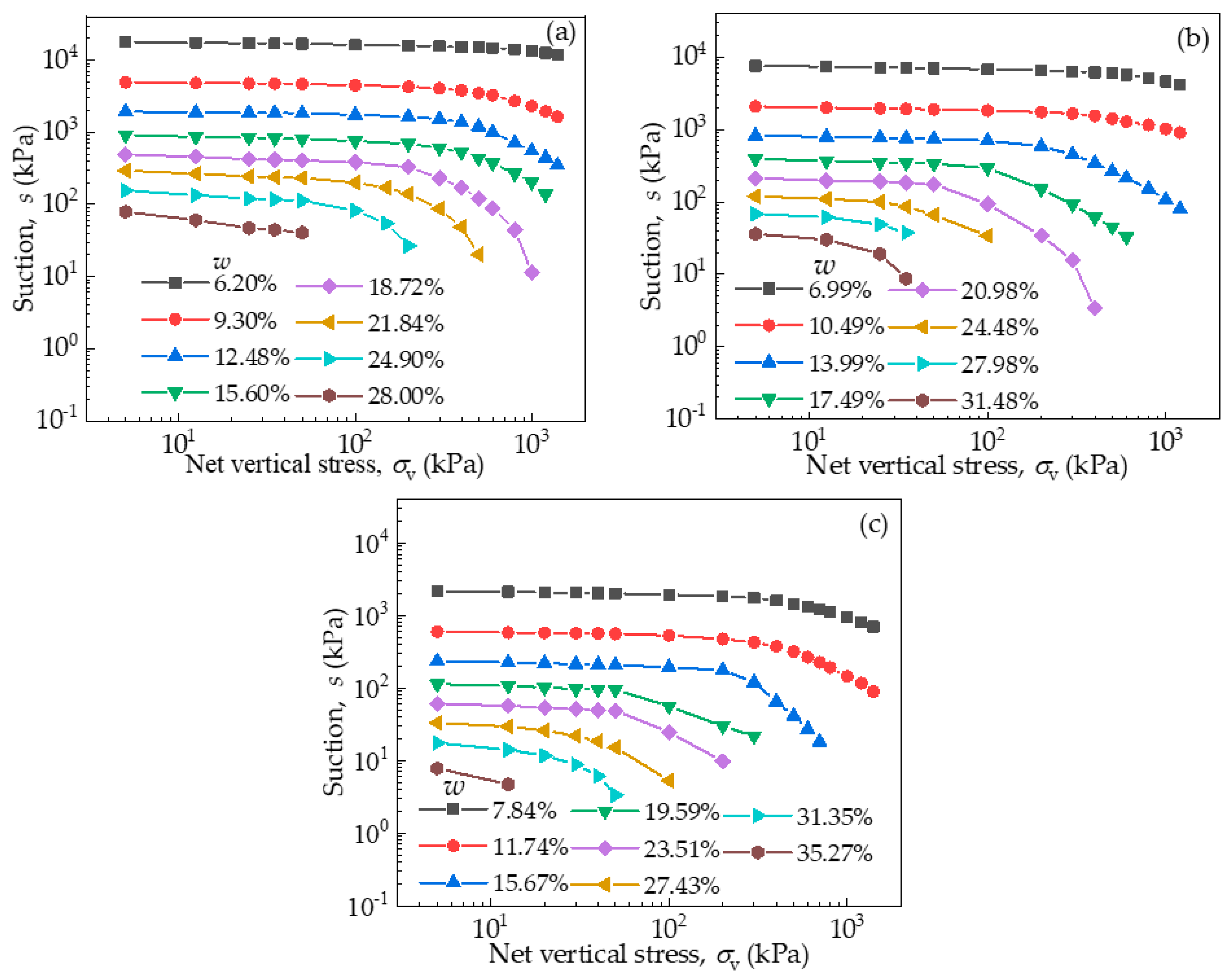
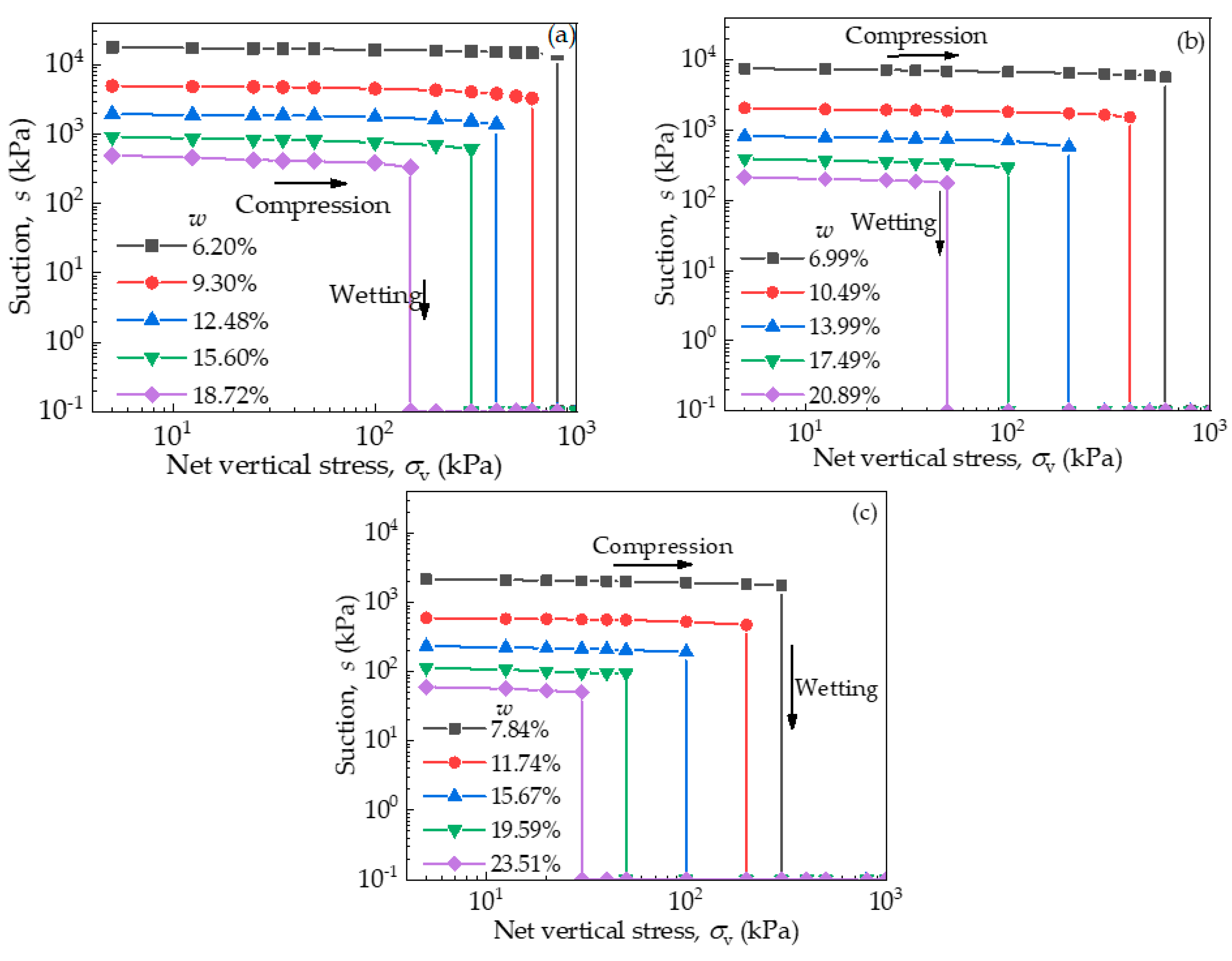
3.4. The Variation of Suction During Compression and Compression–Wetting–Recompression Tests
3.5. The Compression Lines at Constant Suctions
3.6. The Prediction of Wetting Collapse Deformation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fredlund, D.G.; Rahardjo, H. Soil Mechanics for Unsaturated Soils; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, J.E.; Knight, K. The Additional Settlement of Foundations Due to a Collapse of Sandy Subsoils on Wetting. In Proceedings of the 4th Regional Conference for Africa on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Cape Town, South Africa, 11–15 December 1967; pp. 99–105. [Google Scholar]
- Delage, P.; Audiguier, M.; Cui, Y.J.; Howat, M.D. Microstructure of a Compacted Silt. Can. Geotech. J. 1996, 33, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallage, C.; Udukumburage, R.; Uchimura, T.; Abeykoon, T. Distribution of Expansive Soils in Australia. In Proceedings of the 13th Australia New Zealand Conference on Geomechanics, Sydney, Australia, 1–3 April 2019; pp. 1029–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.J.; Delage, P. Yielding and Plastic Behaviour of an Unsaturated Compacted Silt. Géotechnique 1996, 46, 291–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivakumar, V.; Wheeler, S.J. Influence of Compaction Procedure on the Mechanical Behaviour of an Unsaturated Compacted Clay. Part 1: Wetting and Isotropic Compression. Géotechnique 2000, 50, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estabragh, A.R.; Javadi, A.A.; Boot, J.C. Effect of Compaction Pressure on Consolidation Behaviour of Unsaturated Silty Soil. Can. Geotech. J. 2004, 41, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Onza, F.; Gallipoli, D.; Wheeler, S.J.; Casini, F.; Vaunat, J.; Khalili, N.; Laloui, L.; Mancuso, C.; Mašin, D.; Nuth, M.; et al. Benchmark of Constitutive Models for Unsaturated Soils. Géotechnique 2011, 61, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.; Sheng, D.; Aire, D. Experimental Study on the Volumetric Behaviour of Maryland Clay and the Role of Degree of Saturation. Can. Geotech. J. 2014, 51, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estabragh, A.R.; Javadi, A.A. Effect of Soil Density and Suction on the Elastic and Plastic Parameters of Unsaturated Silty Soil. Int. J. Geomech. 2015, 15, 04014079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.Q.; Han, B.W.; Asreazad, S.; Liu, C.; Zhou, A.N.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.G. Experimental Study on Critical State Behaviour of Unsaturated Silty Sand under Constant Matric Suctions. Géotechnique 2024, 74, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jotisankasa, A.; Ridley, A.; Coop, M. Collapse Behavior of Compacted Silty Clay in Suction-Monitored Oedometer Apparatus. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 867–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.A.; Sheng, D.C.; Xu, Y.F. Collapse Behaviour of Unsaturated Compacted Soil with Different Initial Densities. Can. Geotech. J. 2007, 44, 673–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilf, J.W. An Investigation of Pore Water Pressure in Compacted Cohesive Soils. Technical Memorandum No. 654; U.S. Department of the Interior, Bureau of Reclamation: Denver, CO, USA, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, G.; Pineda, J.; Sheng, D.; Airey, D.; Zhang, F. Exploring One-Dimensional Compression of Compacted Clay under Constant Degree of Saturation Paths. Géotechnique 2016, 66, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, X.; Xiong, Y.L.; Tsunemoto, T.; Okino, S.; Qiu, X.Y.; Kurimoto, Y.; Zhang, F. Tests on Mechanical Behavior of Unsaturated Decomposed Granite and Its Modelling Considering Finite Deformation. Soils Found. 2019, 59, 253–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, E.E.; Gens, A.; Josa, A. A Constitutive Model for Partially Saturated Soils. Géotechnique 1990, 40, 405–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.F.; Ng, C.W.W. A State-Dependent Elasto-Plastic Model for Saturated and Unsaturated Soils. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 809–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, D.C.; Fredlund, D.G.; Gens, A. A New Modelling Approach for Unsaturated Soils Using Independent Stress Variables. Can. Geotech. J. 2008, 45, 511–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loret, B.; Khalili, N. An Effective Stress Elastic–Plastic Model for Unsaturated Porous Media. Mech. Mater. 2002, 34, 97–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, S.J.; Sharma, R.S.; Buisson, M.S.R. Coupling of Hydraulic Hysteresis and Stress–Strain Behaviour in Unsaturated Soils. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 41–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.A.; Sheng, D.C.; Sloan, S.W. Elastoplastic Modelling of Hydraulic and Stress–Strain Behaviour of Unsaturated Soils. Mech. Mater. 2007, 39, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ikariya, T. A New Model for Unsaturated Soil Using Skeleton Stress and Degree of Saturation as State Variables. Soils Found. 2011, 51, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.N.; Sheng, D.; Sloan, S.W.; Gens, A. Interpretation of Unsaturated Soil Behaviour in the Stress–Saturation Space, I: Volume Change and Water Retention Behaviour. Comput. Geotech. 2012, 43, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yin, Z.Y.; Cui, Y.J.; Liu, K.; Yin, J.H. An Elasto-Plastic Model of Unsaturated Soil with an Explicit Degree of Saturation-Dependent CSL. Eng. Geol. 2019, 260, 105240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Ma, T.T.; Cai, G.Q.; Liu, Y.; Wei, C.F. An effective stress-based approach to modeling the hydro-mechanical behavior of unsaturated soils. Can. Geotech. J. 2024, 61, 2235–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, D.; Gens, A.; Sharma, R.S.; Vaunat, J. An Elastoplastic Model for Unsaturated Soil Incorporating the Effects of Suction and Degree of Saturation on Mechanical Behaviour. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Liu, H.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Zhou, C.B.; Gallipoli, D. A Constitutive Model for Unsaturated Soils with Consideration of Interparticle Bonding. Computer. Geotech. 2014, 59, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, D.; Bruno, A.W. A Bounding Surface Compression Model with a Unified Virgin Line for Saturated and Unsaturated Soils. Géotechnique 2017, 67, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Genuchten, M.T. A Closed-Form Equation for Predicting the Hydraulic Conductivity of Unsaturated Soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1980, 44, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallipoli, D.; Wheeler, S.; Karstunen, M. Modelling the Variation of Degree of Saturation in a Deformable Unsaturated Soil. Géotechnique 2003, 53, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, A.Q.; Liu, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Y.K. A Rapid Method for Determining the Soil-Water Characteristic Curves in the Full Suction Range. Rock Soil Mech. 2022, 43, 299–306. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Gu, X.; Singh, V.P.; Kong, D.; Chen, X. Spatiotemporal Variability of Precipitation in Beijing during 1981–2017. Water 2020, 12, 716. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, P.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P.; Li, J. Spatiotemporal Trends of Extreme Precipitation in Beijing, China. Atmosphere 2019, 10, 16. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM D5298-94; Standard Test Method for the Measurement of Soil Potential (Suction) Using Filter Paper. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997.
- ASTM D3152-72; Test Method for Capillary-Moisture Relationships for Fine-Textured Soils by Pressure-Membrane Apparatus. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1997.
- Leong, E.C.; He, L.; Rahardjo, H. Factors Affecting the Filter Paper Method for Total and Matric Suction Measurements. Geotech. Test. J. 2002, 25, 322–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D4546-86; Standard Test Method for One-Dimensional Swell or Settlement Potential of Cohesive Soils. ASTM International: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1986.
- ASTM D5333-92; Standard Test Method for Measurement of Collapse Potential of Soils. ASTM International: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1993.
- Lawton, E.C.; Fragaszy, R.J.; Hetherington, M.D. Review of wetting-induced collapse in compacted soil. J. Geotech. Eng. 1992, 118, 1376–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salager, S.; Nuth, M.; Ferrari, A.; Laloui, L. Investigation into water retention behaviour of deformable soils. Can. Geotech. J. 2013, 50, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Sun, D.A.; Zhu, Z.C.; Xu, X.F. Hydromechanical behavior of unsaturated soil with different initial densities over a wide suction range. Acta Geotech. 2019, 14, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.R.; Niu, G.; Li, X.C.; Sun, D.A. Hydro-mechanical behavior of expansive soils with different dry densities over a wide suction range. Acta Geotech. 2020, 15, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Du, X.L. A generalized water retention model in a wide suction range considering the initial void ratio and its verification. Computer. Geotech. 2024, 166, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.L.; Han, Z.; Vanapalli, S.K.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhao, G.T. Predicting volumetric behavior of compacted clays during compression. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 156, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampino, C.; Mancuso, C.; Vinale, F. Laboratory testing on an unsaturated soil: Equipment, procedures, and first experimental results. Can. Geotech. J. 1999, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, T.M.; Rahardjo, H.; Leong, E.C. Soil-water characteristic curve and consolidation behavior for a compacted silt. Can. Geotech. J. 2007, 44, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeri, S.M.; Khorshidi, M.; Garakani, A.A. Variation of the volume change and water content in undisturbed loessial samples in controlled matric suction tests. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Problematic Soils, Wuhan, China, 21–23 September 2012; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Raveendiraraj, A. Coupling of Mechanical Behaviour and Water Retention Behaviour in Unsaturated Soils. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow, Glasgow, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Jennings, J.E. The additional settlement of foundations due to a collapse of structure of sandy subsoils on wetting. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, London, UK, 12–24 August 1957; pp. 316–319. [Google Scholar]





| Specific Gravity, Gs | Liquid Limit, LL (%) | Plastic Limit, PL (%) | Plasticity Index, IP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.73 | 30.7 | 15.2 | 15.5 |
| Void Ratio | Water Content (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.905 | 6.24 | 9.30 | 12.48 | 15.60 | 18.72 | 21.84 | 24.90 | 28.00 |
| 1.01 | 6.99 | 10.49 | 13.99 | 17.49 | 20.98 | 24.48 | 27.98 | 31.48 |
| 1.10 | 7.84 | 11.74 | 15.67 | 19.59 | 23.51 | 27.43 | 31.35 | 35.27 |
| Test | Condition: w (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression | 0.905 | 6.24 | 9.30 | 12.48 | 15.60 | 18.72 | 21.84 | 24.90 | 28.00 |
| 1.01 | 6.99 | 10.49 | 13.99 | 17.49 | 20.98 | 24.48 | 27.98 | 31.48 | |
| 1.10 | 7.84 | 11.74 | 15.67 | 19.59 | 23.51 | 27.43 | 31.35 | 35.27 | |
| Test | Condition: (w, σv) (%, kPa) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Compression wetting | 0.905 | 6.24, 800 | 9.30, 600 | 12.48, 400 | 15.60, 300 | 18.72, 200 |
| 1.01 | 6.99, 600 | 10.49, 400 | 13.99, 200 | 17.49, 100 | 20.98, 50 | |
| 1.10 | 7.84, 300 | 11.74, 200 | 15.67, 100 | 19.59, 50 | 23.51, 30 | |
| e0 | w (%) | σv (kPa) | eb | Sr (%) | s (kPa) | Cp (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.905 | 6.20 | 800 | 0.84 | 20.22 | 14,135.33 | 41.34 |
| 9.30 | 600 | 0.79 | 32.14 | 3253.61 | 34.80 | |
| 12.48 | 400 | 0.81 | 41.99 | 1378.37 | 31.35 | |
| 15.60 | 300 | 0.79 | 53.82 | 605.25 | 25.94 | |
| 18.72 | 150 | 0.80 | 63.79 | 330.87 | 16.25 | |
| 1.01 | 6.99 | 600 | 0.93 | 20.54 | 5694.66 | 46.06 |
| 10.49 | 400 | 0.92 | 31.02 | 1540.44 | 41.37 | |
| 13.99 | 200 | 0.91 | 41.88 | 588.43 | 32.86 | |
| 17.49 | 100 | 0.93 | 51.61 | 295.26 | 24.20 | |
| 20.89 | 50 | 0.96 | 59.69 | 178.43 | 16.17 | |
| 1.10 | 7.84 | 300 | 1.02 | 20.91 | 1747.00 | 34.14 |
| 11.74 | 200 | 1.02 | 31.55 | 474.69 | 29.92 | |
| 15.67 | 100 | 1.03 | 41.67 | 194.28 | 23.72 | |
| 19.59 | 50 | 1.03 | 51.80 | 94.79 | 16.59 | |
| 23.51 | 30 | 1.04 | 61.89 | 50.87 | 11.29 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
K.C, M.S.; Li, X. Collapse Behavior of Compacted Clay in a Water Content-Controlled Oedometer Apparatus. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179530
K.C MS, Li X. Collapse Behavior of Compacted Clay in a Water Content-Controlled Oedometer Apparatus. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179530
Chicago/Turabian StyleK.C, Madhu Sudan, and Xu Li. 2025. "Collapse Behavior of Compacted Clay in a Water Content-Controlled Oedometer Apparatus" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179530
APA StyleK.C, M. S., & Li, X. (2025). Collapse Behavior of Compacted Clay in a Water Content-Controlled Oedometer Apparatus. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9530. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179530






