Research on a Task-Driven Classification and Evaluation Framework for Intelligent Massage Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Works
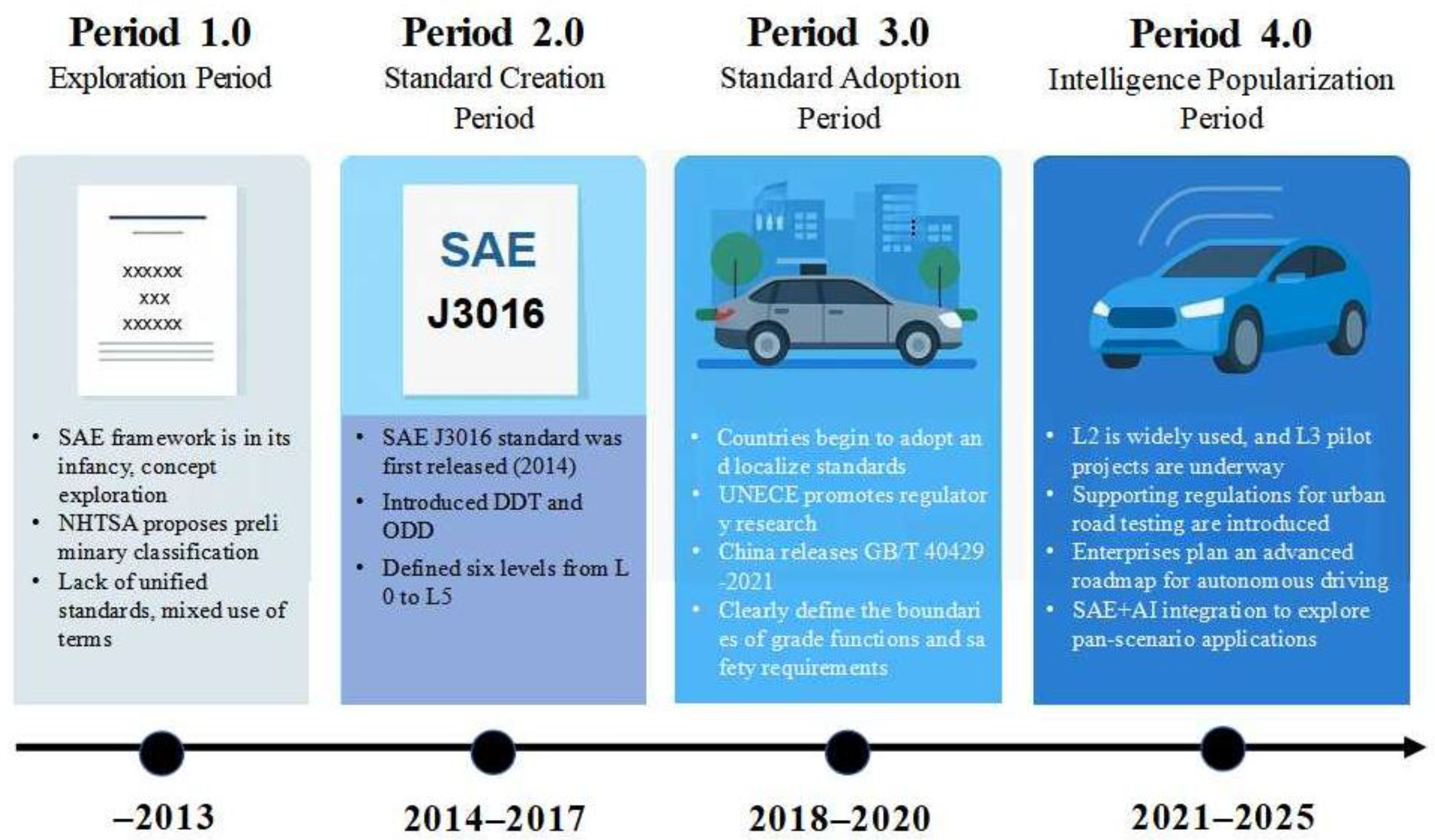
2.1. Current Status of Research on Vehicle Autonomous Driving Classification
2.2. Research Status of Intelligent Massage System
- Price gradient: Intelligence level is inferred based on product pricing. However, price does not have a linear correlation with functional capability, which can easily lead to misjudgment.
- Function stacking: Evaluation is conducted based on the number of massage programs, the variety of covered body regions, and the presence of additional modules (such as voice control, heating, or music). Nevertheless, this approach fails to reflect the structural nature of system intelligence.
- Subjective labels: Classification is based on marketing-oriented terms constructed from subjective expressions, such as “AI massage” or “automatic recognition”, which lack clear definitions and standardized criteria.
3. Materials and Methods
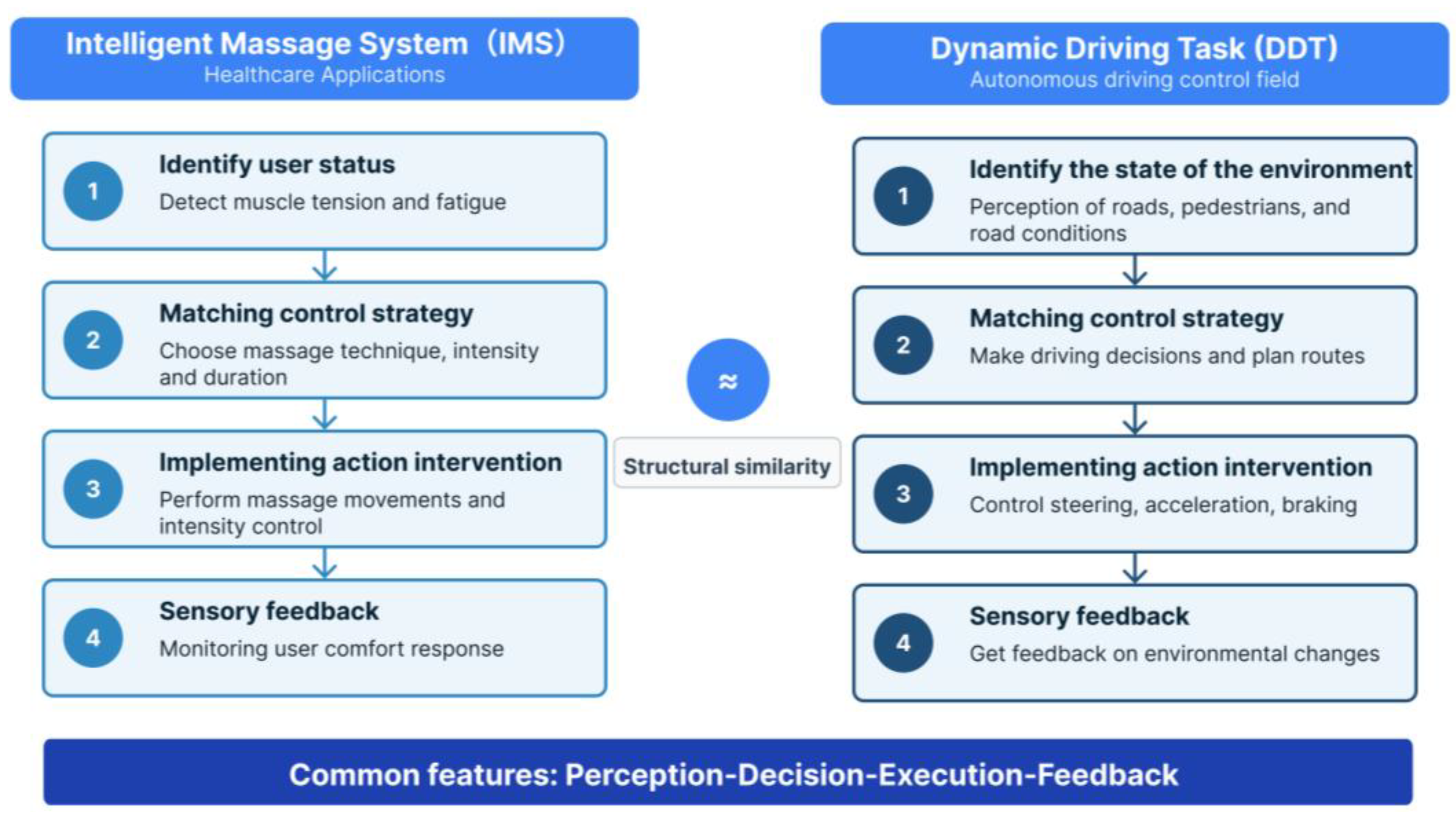
3.1. Definition of the Massage-Driven Task (MDT) Model
- 1.
- Perception stage (S1: Body State Recognition)
- 2.
- Decision stage (S2: Program Recommendation)
- 3.
- Execution stage (S3: Force and Rhythm Control; S4: Multi-Zone Coordination)
- 4.
- Feedback stage (S5: Abnormal Detection and Intervention; S6: User Modeling and Learning)
3.2. Design Logic of the Grading Structure
- Functional Delegation Structure (FDS): Measures the system’s autonomous task completion capability in the task execution dimension.
- Abnormal Perception Mechanism (APM): Evaluates the system’s ability to monitor and respond to operational anomalies.
- Human–Machine Interaction Bounds (HMIB): Reflects the system’s proactive service capability in the process of human–machine interaction.
- Task closed-loop capability: the degree to which the system autonomously undertakes each subtask in the MDT model (S1 to S6).
- Abnormal state handling capability: the system’s level of perception, judgment, and intervention in abnormal conditions during operation, reflecting its safety assurance capability.
- Interaction proactivity: the extent to which the system actively engages in user modeling, personalized learning, and service response.
3.2.1. Functional Delegation Structure (FDS)
- No Delegation (N): The system has no perception, judgment, or response capability in this task dimension, and all operations rely entirely on the user, representing a purely manual control stage.
- Limited Delegation (L): The system can perform part of the functions with the support of static rules or simple algorithms, such as executing programs based on fixed templates or adjusting feedback based on thresholds. However, in this state, the system lacks adaptability and closed-loop task capability and still requires user guidance or intervention.
- Full Delegation (F): The system possesses a complete capability chain from environmental perception and state judgment to action control and result feedback, enabling adaptive operation without user intervention and demonstrating strong task comprehension and system stability.
3.2.2. Abnormal Perception Mechanism (APM)
- No Perception: The system lacks any abnormal state monitoring functions. Unexpected conditions during operation cannot be detected, and all risk handling relies on the user to manually terminate the operation or restart the device, significantly compromising operational safety. (Corresponds to S5 “No Automation”)
- Rule-Based Perception: The system uses static threshold settings or predefined rule templates to identify and respond to certain typical abnormalities, for example, automatically reducing massage force when it exceeds a safety threshold or issuing a warning when a sensor fails. This mechanism has a single, fixed response path, lacks dynamic adaptability, and can only cover abnormal scenarios predefined in the rules. (Corresponds to S5 “Limited Automation”)
- Active Perception: The system integrates multi-source data (e.g., pressure, posture, time series) and builds dynamic behavior models, enabling it to predict, identify, and perform closed-loop regulation of irregular, complex, and evolving abnormalities. Typical capabilities include machine learning-based abnormal pattern recognition, dynamic strategy switching, process interruption control, and adaptive calibration, thereby establishing a fundamental safety assurance framework. (Corresponds to S5 “Full Automation”)
3.2.3. Human–Machine Interaction Bounds (HMIB)
- Fully Dependent Interaction: In subtasks such as S2 and S3, the system relies entirely on the user to issue start, adjustment, and termination commands. Interaction channels are primarily graphical user interfaces, voice commands, or mobile applications. The system lacks autonomous decision-making capabilities, resulting in a high operational workload for the user.
- Semi-Autonomous Interaction: In subtasks such as S1 and S2, the system can automatically execute certain processes based on predefined conditions (e.g., user posture, time markers). For example, it may automatically start a program upon detecting that the user is seated or transition to the next massage phase after completing a session. Although some processes run autonomously, critical points such as task switching and exception handling still require active user intervention.
- Passive–Aware Interaction: Based on its capabilities in subtasks S1 and S6, the system achieves continuous dynamic sensing and prediction of the user’s state. Without any explicit user commands, it can autonomously perform program recommendations, parameter adjustments, and process control. This mode, enabled by multimodal data fusion and behavioral modeling, significantly enhances task continuity, interaction immersion, and overall user experience.
3.3. Construction of the Grading Indicator System
3.3.1. Determination of Key Indicators
- 1.
- Task Recognition Accuracy (P1): Measures the system’s precision in identifying the user’s current physical state, corresponding to the classification performance of the S1 body state recognition module in FDS.
- 2.
- Abnormal Detection Sensitivity (P2): Evaluates the system’s capability to detect and respond to abnormal states in S5 (e.g., sensor failure, overload) in a timely manner, reflecting the coverage and emergency response capability of APM.
- 3.
- Recommendation Hit Rate (D1): Measures the degree to which program recommendations in S2 match the user’s actual needs, reflecting the decision-making accuracy of the FDS decision layer.
- 4.
- Decision Response Latency (D2): Refers to the average delay from perception input to decision output, measuring the real-time performance of the system in converting information and initiating execution in S2–S3 subtasks.
- 5.
- Force Control Error (E1): Calculated as the average deviation between the actual applied force and the target force curve, indicating the execution accuracy in force control and rhythm coordination in S3.
- 6.
- Path Tracking Accuracy (E2): Measures the spatial deviation between the actual trajectory of the massage head and the preset path, assessing the spatial accuracy of multi-region coordinated control in S4.
- 7.
- Physiological Feedback Response Rate (F1): Measures the proportion of user physiological signals (e.g., EDA, HRV) effectively activated during the massage process, reflecting the effectiveness of the feedback loop between S5 and S6, and representing the HMIB’s capability for dynamic user state perception.
- 8.
- User Subjective Satisfaction (F2): Reflects the user’s subjective evaluation of the overall massage experience, typically collected via questionnaires or interviews, and provides a comprehensive view of HMIB’s service quality and user experience optimization at the perceptual level.
3.3.2. Indicator Quantification Method
3.3.3. Questionnaire Design and Implementation
3.3.4. Data Analysis and Quantification
- (1)
- Expert scoring aggregation and normalization calculation
- (2)
- Construction of the judgment matrix and consistency verification
- (3)
- Perturbation Analysis and Weight Robustness Testing
- (4)
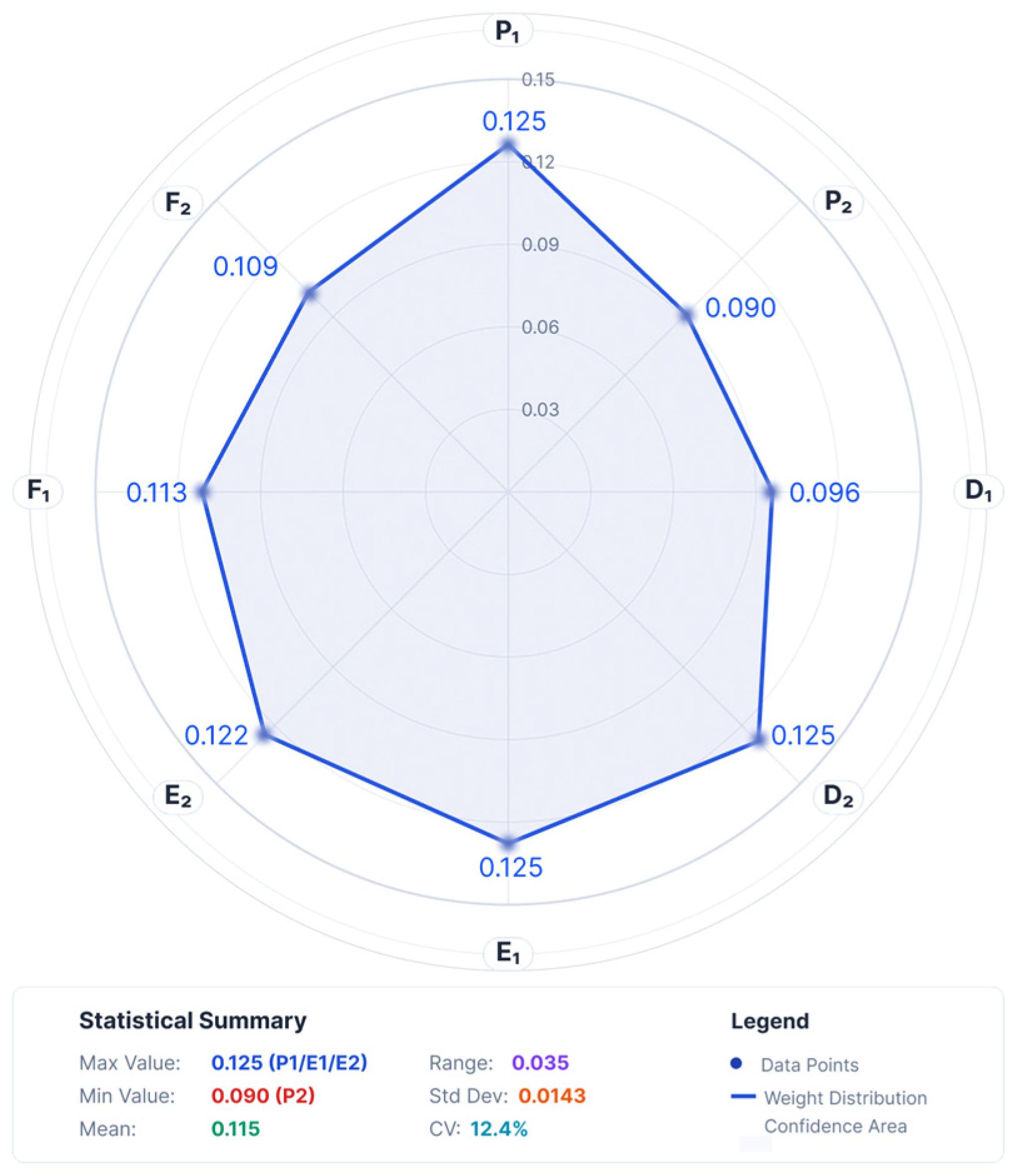
- Distribution of indicator weights and interpretation of system functions
3.3.5. Determination of the Grading Index System
4. Results
4.1. Intelligent Level Classification
4.1.1. Calculation of Three-Dimensional Ability Scores
4.1.2. Threshold Design and Grading
4.1.3. Comprehensive Intelligence Calculation
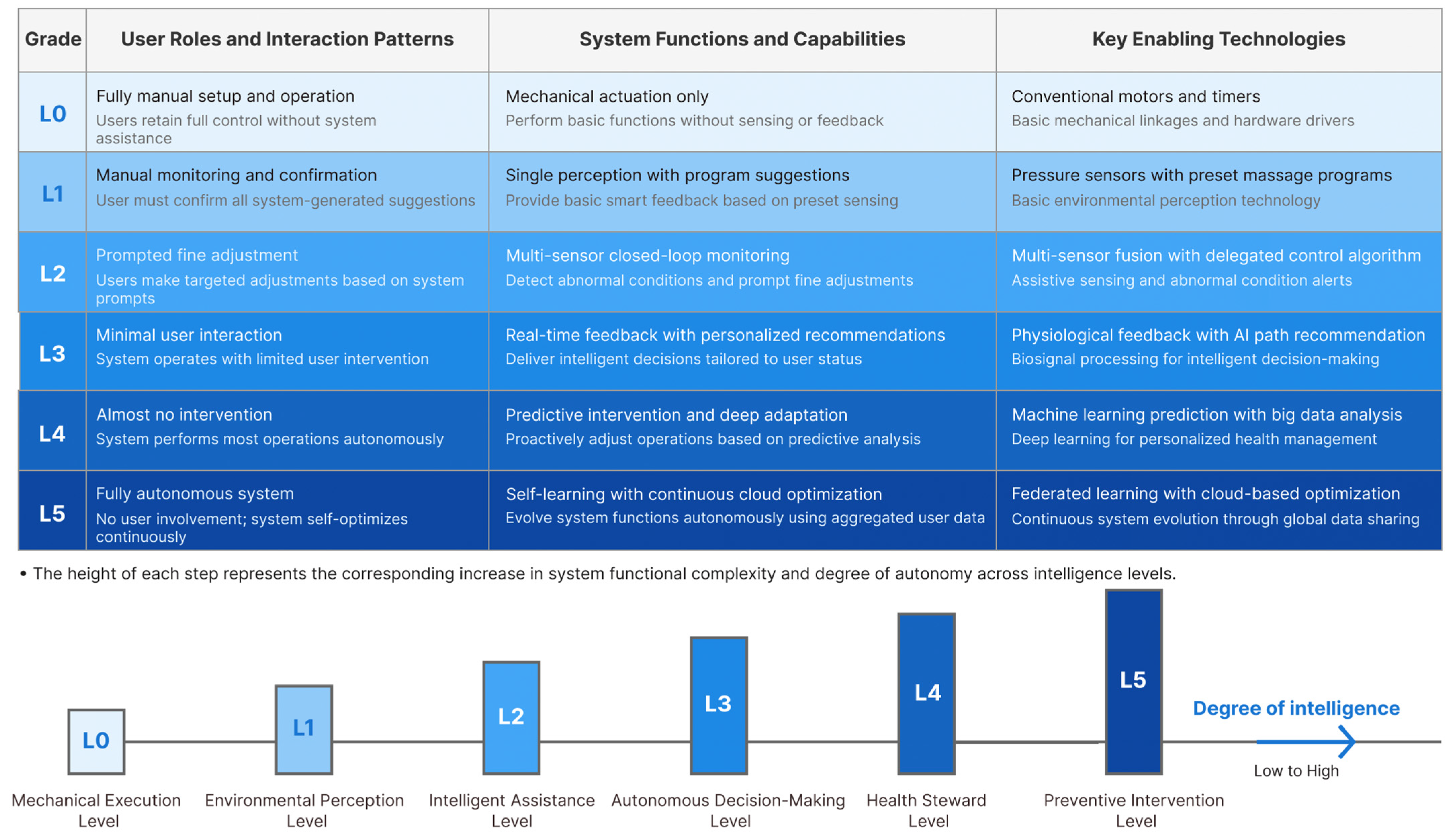
4.2. Definition of L0–L5 Levels
4.2.1. L0—Mechanical Execution Level
4.2.2. L1—Environmental Perception Level
4.2.3. L2—Intelligent Assistance Level
4.2.4. L3—Autonomous Decision-Making Level
4.2.5. L4—Health Steward Level
- Flexible electronic skin, millimeter-wave radar, and other multi-source sensors to enable non-intrusive monitoring of pressure, temperature, electromyography (EMG), electrodermal activity (EDA), electrocardiography (ECG), and vital signs.
- Digital modeling of traditional Chinese medicine acupoints and path optimization algorithms to enhance precise adaptation to individualized acupoints.
- Federated learning and cloud-based health profiling platforms to support multidevice data collaboration and secure sharing.
4.2.6. L5—Preventive Intervention Level
- Multiple types of non-invasive sensors for long-term physiological monitoring.
- Predictive algorithms such as machine learning and knowledge graphs to perform temporal prediction of health data and construct personalized user models.
- Integration of edge computing and cloud services to enable cross-scenario data sharing and privacy protection.
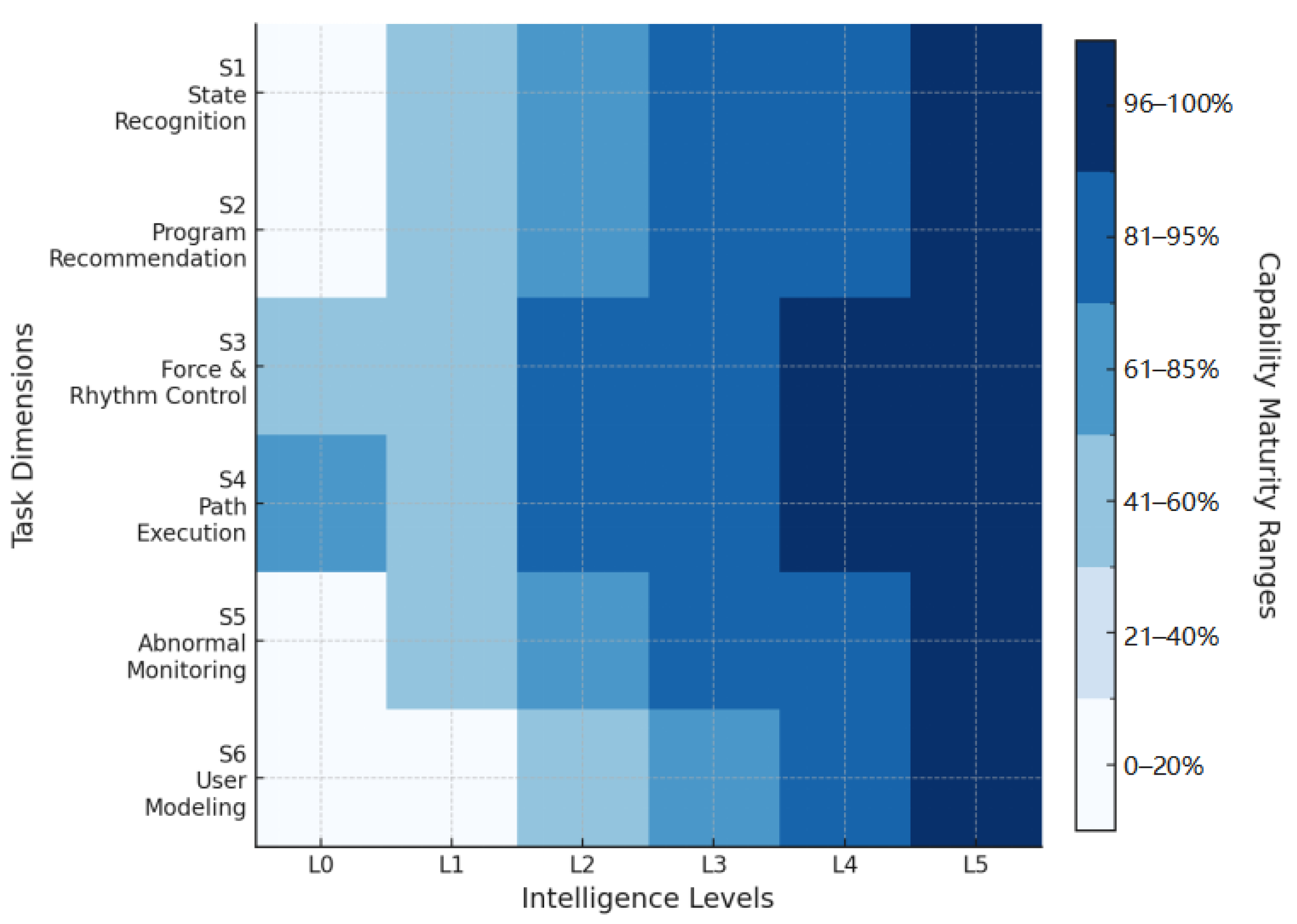
4.3. L0–L5 Level Capability Analysis
- L0–L1: The main task dimensions fall within the lowest (0–20%) or initial (21–40%) maturity intervals, with only localized responses observed in S3 and S4. This indicates that system functions rely heavily on external triggers or mechanical execution, resulting in a low level of intelligence. S1, S2, S5, and S6 remain largely undeveloped, showing the absence of critical capability support.
- L2–L3: Most task dimensions enter the medium maturity range (41–80%). Among them, the average maturity of five task dimensions (S1–S5) falls between 70% and 85%, while S6 rises sharply from about 10% at L1 to about 50% at L2. This reflects the system’s partial realization of closed-loop control and a significant enhancement in its ability to dynamically model user states.
- L4: Most task dimensions fall within the 81–95% deep-blue range, with S1–S6 capabilities highly coordinated. This indicates that the system has achieved a high-quality closed loop of perception, decision-making, execution, and feedback.
- L5: All task dimensions enter the 96–100% range, shown in the darkest blue in the figure, representing fully matured, end-to-end intelligent closed-loop capabilities.
4.4. Grading System Verification
- Very low group: FDS_score, APM_score, and HMIB_score are all set to 0.05, and the calculated score of falls in the interval [0.000, 0.167), corresponding to level L0.
- Midpoint group: The three-dimensional scores are all set to 0.425, and the score falls in the interval [0.350, 0.500), corresponding to the L2 level.
- Extremely high group: The three-dimensional scores were all set to 0.95, and the score fell in the interval [0.833, 1.000], corresponding to level L5.
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- To address the lack of evaluation for functional depth and proactiveness in the IMS operational process, an MDT model is proposed, which divides the system operation process into six subtasks (S1–S6). On this basis, a three-dimensional capability measurement framework, consisting of FDS, APM, and HMIB, is established to characterize the system’s agent capability and proactiveness level in each subtask.
- (2)
- In response to the current lack of reproducible quantitative methods, eight key performance indicators were selected to comprehensively reflect the intelligence level of the system. The Delphi method combined with the AHP was used to determine the weights of the indicators. The three-dimensional capability scores and the overall intelligence degree were then calculated through normalization and weighted summation. Subsequently, within the [0, 1] interval, the grading thresholds for L0–L5 were determined by combining equal-interval division with expert calibration, thereby achieving a quantitative mapping from the original performance indicators to the corresponding intelligence levels.
- (3)
- To address potential minor errors that may occur in the practical application of the grading system, experiments involving extreme-value and midpoint mapping of typical test vectors were designed, and a sensitivity analysis was conducted by introducing ±10% numerical perturbations to the midpoint group. The results indicate that the grading decisions remain stable within common error ranges, thereby verifying the stability and robustness of the grading system.
- (1)
- This study introduces the task-driven concept into the IMS capability grading framework for the first time. It integrates the three-dimensional capability framework, comprising FDS, APM, and HMIB, with the MDT model to establish a structured “Task-Capability-Level” mapping. This work fills the research gap in capability grading within the IMS domain and provides a quantifiable theoretical foundation for evaluating the capabilities of intelligent healthcare devices.
- (2)
- This study proposes a reproducible IMS grading method that combines the Delphi method and the AHP to determine indicator weights, followed by normalization and overall intelligence degree calculation. The resulting quantitative standard can be directly applied to product design, performance benchmarking and technical optimization.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Su, J. Promoting the steady and healthy development of China’s economy through the dual expansion of demand and supply. State-Own. Assets Rep. 2025, 90–93. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Lu, S. Behavioral decision-making of treatment plan of traditional Chinese medicine massage robot. J. Nat. Sci. Heilongjiang Univ. 2016, 33, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z. Design of Massage Manipulator and Research on Massage Effect Based on Surface Electromyography Signal. Ph.D. Thesis, Tianjin University, Tianjin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, C. Design and Analysis of Back Massage Robot Based on Traditional Chinese Medicine Massage Techniques. Ph.D. Thesis, Dongguan University of Technology, Dongguan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, Z. Research on Massage Manipulator Control Based on Vision and Force Feedback. Ph.D. Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, X.; Hu, L.; Xu, Y. Research on fatigue recovery effect of different massage modes of massage chair on shoulder trapezius muscle. Furnit. Inter. Decor. 2024, 31, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Zhai, J.; Chen, Y. Multimodal user comfort monitoring for massage robots. Mech. Des. Manuf. 2025, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Xu, B.; Xue, Y.; Li, J. Experimental study on the influence of EEG-based massage position on the comfort of wearable massager. Ergonomics 2023, 29, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, Y. Research on the design of integrated cervical massager based on emotional design strategy. Beauty Times 2024, 5, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Ji, Y. Research on the liability of autonomous driving car accidents from the perspective of SAE classification standards. Stand. Sci. 2019, 12, 50–54. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, H. Analysis of GB/T 40429-2021 “Automobile Driving Automation Classification”. China Automob. 2022, 5, 3–5+7. [Google Scholar]
- Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE). Taxonomy and Definitions for Terms Related to Driving Automation Systems for On-Road Motor Vehicles (J3016_201806); Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE): Warrendale, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Trypuz, R.; Kulicki, P.; Sopek, M. Ontology of autonomous driving based on the SAE J3016 standard. Semant. Web 2024, 15, 1837–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHTSA. Automated Driving Systems: A Vision for Safety 2.0. U.S. Department of Transportation. 2017. Available online: https://www.nhtsa.gov/technology-innovation/automated-vehicles-safety (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- UNECE. UN Regulation No. 157-Automated Lane Keeping Systems (ALKS). World Forum for Harmonization of Vehicle Regulations (WP.29). 2021. Available online: https://unece.org/transport/standards/transport/vehicle-regulations-wp29 (accessed on 25 June 2025).
- GB/T 40429-2021; Automobile Driving Automation Classification. State Administration for Market Regulation & National Administration of Standardization: Beijing, China, 2021.
- Hu, J.; Deng, J. Analysis of the standard “Automobile Driving Automation Classification” (Draft for Approval). Environ. Technol. 2020, 38, 192–195. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, Z.; Tian, Y. The classification is clearer. The Chinese version of the autonomous driving classification standard is announced. Intell. Connect. Veh. 2020, 2, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, P. The dilemma of attribution of liability for traffic accidents caused by autonomous driving vehicles and the criminal law response. J. South China Univ. Technol. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2023, 25, 30–40. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhan, J.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Chen, J. The future of autonomous driving technology: Single-vehicle intelligence and intelligent vehicle-road collaboration. J. Automot. Saf. Energy Conserv. 2024, 15, 611–633. [Google Scholar]
- Bimbraw, K. Autonomous cars: Past, present and future a review of the developments in the last century, the present scenario and the expected future of autonomous vehicle technology. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO), Colmar, France, 21–23 July 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Current status and development trend of autonomous driving technology research. Energy Technol. Manag. 2021, 46, 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Xinhuanet. The Penetration Rate of L2 Autonomous Driving Functions in China’s Passenger Cars Has Reached 55.7% [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.news.cn/fortune/20250226/5f2e955579de42cfb51dde1eb46a4ff5/c.html (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- PDay Smart Car Network. L3 Autonomous Driving Pilot Projects Continue to Advance, and Road Tests are Launched in Beijing and Other Places [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.pday.com.cn/Htmls/Report/202502/24550682.html (accessed on 26 June 2025).
- Atakishiyev, S.; Salameh, M.; Yao, H.; Goebel, R. Explainable artificial intelligence for autonomous driving: An overview and guide for future research directions. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 101603–101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badue, C.; Guidolini, R.; Carneiro, R.V.; Azevedo, P.; Cardoso, V.B.; Forechi, A.; Jesus, L.; Berriel, R.; Paixão, T.M.; Mutz, F.; et al. Self-Driving Cars: A Survey. Expert Syst. Appl. 2021, 165, 113816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosuru, V.S.R.; Venkitaraman, A.K. Advancements and challenges in achieving fully autonomous self-driving vehicles. World J. Adv. Res. Rev. 2023, 18, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L. Autonomous Driving Driven by Artificial Intelligence: Development Status and Future Prospects. Comput. Artif. Intell. 2025, 2, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sever, T.; Contissa, G. Automated driving regulations—Where are we Now? Transp. Res. Interdiscip. Perspect. 2024, 24, 101033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.-S.; Huang, H.; Daim, T.; Chien, P.-W.; Peng, R.-L.; Akgul, A.K. Assessing the technological trajectory of 5G-V2X autonomous driving inventions: Use of patent Analysis. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2023, 196, 122817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gora, P.; Rüb, I. Traffic Models for Self-driving Connected Cars. Transp. Res. Procedia 2016, 14, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Z. The Current Development and Future Prospects of Autonomous Driving Driven by Artificial Intelligence. Comput. Artif. Intell. 2025, 2, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S. Review of Development Trends and Challenges in Autonomous Driving Technology. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2025, 140, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Gui, J.; Jiang, P.; Chen, X.; Zeng, F.; Wan, S. A review of 6G autonomous intelligent transportation systems: Mechanisms, applications and Challenges. J. Syst. Archit. 2023, 142, 102929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J. Application of autonomous driving technology in intelligent connected vehicles. Automob. Pict. 2024, 8, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, T. A multi-sensor post-fusion method for autonomous driving. Bus Technol. Res. 2025, 47, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J. Application of multi-sensor fusion in environmental perception of autonomous driving vehicles. Automob. Maint. Tech. 2025, 2, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, C. On the development status and safety considerations of autonomous driving technology of intelligent vehicles in my country. J. Hunan Police Coll. 2019, 31, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Hangzhou Auto Channel. Several Car Companies Have Clarified the Timetable for Mass Production of L3 Autonomous Driving [EB/OL]. Available online: https://auto.hangzhou.com.cn/reading/content/2025-04/24/content_8981898.html (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Sina Finance. BYD, Xiaopeng and Others Are Accelerating the Promotion of High-End Intelligent Driving [EB/OL]. Available online: https://finance.sina.com.cn/stock/zqgd/2025-02-21/doc-inemeuym3096446.shtml (accessed on 28 June 2025).
- Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Ministry of Civil Affairs, National Health Commission. Action Plan for the Development of Smart Health Care Industry (2021–2025); Ministry of Industry and Information Technology: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M. The classification of automobile driving automation has a basis. China Transp. News 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Industry Information Network. China’s Massage Chair Industry Chain Map, Industrial Environment, Market Status and Future Trend Analysis in 2025 [EB/OL]. Available online: https://www.chyxx.com/industry/1222032.html (accessed on 29 June 2025).
- Zhou, L.; Feng, Z.; Cai, Z.; Yang, X.; Ai, C.; Shao, H.; Hu, Z. A Massage Area Positioning Algorithm for Intelligent Massage System. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 7678516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Lei, J.; Chen, D. Recognition Method of Massage Techniques Based on Attention Mechanism and Convolutional Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network. Sensors 2022, 22, 5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.C.; Chen, S.Y.; Yeh, K.C. Human body trajectory generation using point cloud data for robotics massage applications. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Hong Kong, China, 31 May–7 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, Z.; Xu, X. Visual feedback system for traditional chinese medical massage robot. In Proceedings of the 2019 Chinese Control Conference (CCC), Guangzhou, China, 27–30 July 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 6379–6385. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Sheng, Q.; Sheng, X. A novel realtime vision-based acupoint estimation for TCM massage robot. In Proceedings of the 2021 27th International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice (M2VIP), Shanghai, China, 26–28 November 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 771–776. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C. Application of genetic algorithm optimized BP neural network in traditional Chinese medicine massage robot. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2017, 44, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Sun, S.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, X. Acupoint detection based on deep convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2020 39th Chinese control conference (CCC), Shenyang, China, 27–29 July 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 7418–7422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, J.; Zeng, X.; Su, Z. An intelligent control system for robot massaging with uncertain skin characteristics. Ind. Robot Int. J. Robot Res. Appl. 2022, 49, 634–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y. Research on the technical principles and applications of massage robots. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2024, 77, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sina Finance. Ogawa AI Massage Robot Debuts, 5D Sensing Technology Leads the Industry Upgrade [EB/OL]. Available online: https://finance.sina.com.cn/wm/2025-05-14/doc-inewpmqy1033029.shtml (accessed on 30 June 2025).
- Gu, H.; Wang, D. Massage Robot Using Machine Vision. CN111343958A, 26 June 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, X. A Massage Robot Acupoint Tracking System Based on Visual Positioning. CN110882150A, 17 March 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L. Research on Expert System of Traditional Chinese Medicine Massage Robot. Ph.D. Thesis, Shandong Jianzhu University, Jinan, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Z. Intelligent Massage System Based on Big Data. Chinese Patent CN201910172730.2, 7 March 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, S.; Nakajima, R.; Nomura, J. A VR Relax/Refresh System Employing Physiological Feedback. IEEJ Trans. Electron. Inf. Syst. 1995, 115, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lin, C.; Chen, L.; Ren, Y.; Tang, B. Research on Intelligent Massage Chair Based on Fuzzy Control. Mech. Electr. Eng. 2011, 28, 201. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Jaafar, H.; Fariz, A.; Ahmad, S.A.; Yunus, N.A.M. Intelligent massage chair based on blood pressure and heart rate. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE-EMBS Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Sciences, Langkawi, Malaysia, 17–19 December 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Hiyamizu, K.; Fujiwara, Y.; Genno, H.; Yasuda, M.; Koma, T. Development of human sensory sensor and application to massaging chairs. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE International Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation. Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automation for the New Millennium (Cat. No. 03EX694), Kobe, Japan, 16–20 July 2003; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 140–144. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Alavandar, S.; Sundaram, K.A.; Nigam, M.J. Genetic algorithm based robot massage. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2007, 3, 102–109. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Shen, L.; Song, J. The influence of massage mode on the massage comfort of kneading massage chair. Ergonomics 2012, 2, 40–43. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Dai, F.; Yang, T. Research on robot constant force massage based on admittance control. Mech. Des. 2025, 42, 116–122. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Ma, L.; Yao, G.; Ni, Q.; Zhu, Z. Research on parallel-series hybrid robot for Chinese medicine massage with rolling method. Mech. Des. Res. 2005, 12, 43–46. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Yu, H.; Zhou, C.; Song, S. Based on ADAMS Design and analysis of bionic massage mechanical device. Robot. Appl. 2011, 44–46. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Q.; Deng, Z.; Zeng, C.; Li, Z.; He, B.; Zhang, J. Toward automatic robotic massage based on interactive trajectory planning and Control. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 4397–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerautret, Y. Caractérisation des Techniques de Massage et Validation des Bénéfices Physiologiques d’un Système de Massage Robotique, Autonome et Interactif. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lyon, Lyon, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, K. Research on Seated Electric Massage Chair. Ph.D. Thesis, China Jiliang University, Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, W. Research on the design of massage chair products for the elderly. Furniture 2022, 40–44. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, S.; Ma, L.; Guo, Z. Analysis of kinematic and dynamic characteristics of traditional Chinese medicine massage techniques. J. Shandong Univ. Technol. 2005, 19, 82–85. [Google Scholar]
- Su, D. Design and Research of Adaptive Massage Chair Control System. Ph.D. Thesis, Anhui University of Technology, Ma’anshan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Xu, P. Design of intelligent massage robot. Autom. Appl. 2024, 65, 74–76. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Shi, R.; Xu, L. Research on ESG evaluation system of Chinese automobile industry based on Delphi-AHP. Automob. Ind. Res. 2025, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ishizaka, A.; Nemery, P. Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis: Methods and Software; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, P. Remote Pulse Monitoring Using Millimeter Waves. 2021. Available online: https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1616868&dswid=4205 (accessed on 5 July 2025).
- Iyer, S.; Zhao, L.; Mohan, M.P.; Jimeno, J.; Siyal, M.Y.; Alphones, A.; Karim, M.F. mm-Wave radar-based vital signs monitoring and arrhythmia detection using machine learning. Sensors 2022, 22, 3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, W.; He, W.; Lin, X.; Miao, J. Non-contact monitoring of human vital signs using FMCW millimeter wave radar in the 120 GHz band. Sensors 2021, 21, 2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, D.; Choi, H. Vital Sign Monitoring System Using Millimeter Wave Radar. WO2015174879A1, 19 November 2015. [Google Scholar]



| Dimension/Aspect | Example Function | Technology Example | Core Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Massage Strategy | Adaptive adjustment driven by physiological signals | Heart-rate sensor, EMG detection + adaptive control algorithm | Real-time response to user state; high personalization |
| Massage Track | Dynamic path planning combining vision and algorithms | Depth camera/RGB camera + path-planning/optimization algorithms | Highly precise trajectories; adapts to varied postures and body shapes |
| Massage Mode | Traditional motions (kneading, tapping, rolling) + multimodal operations (heat therapy, electrical pulse, air-bag compression) | Multi-axis motor drive + heating elements + pneumatic control + pulse modules | Rich, composite actions; enhanced comfort and efficacy |
| Subtasks | N | L | F |
|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | Fully manual | Basic perception | Closed-loop intelligent identification |
| S2 | Manual selection by user | Preset programs | Intelligent dynamic recommendation |
| S3 | Manual adjustment | Step adjustment | Adaptive adjustment |
| S4 | No feedback | Simple instructions | Intelligent interaction |
| S5 | User-controlled | Basic safety | Smart protection |
| S6 | No continuous learning | Parameter memory | Deep learning and strategy optimization |
| Indicator Code | Indicator Name | Dimension | Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | Task recognition accuracy | FDS-Perception | % |
| P2 | Abnormal detection sensitivity | APM | % |
| D1 | Recommendation hit rate | FDS-Decision | % |
| D2 | Decision response delay | FDS-Decision | s |
| E1 | Force control error | FDS-Execution | N |
| E2 | Path tracking accuracy | FDS-Execution | mm |
| F1 | Physiological feedback response rate | HMIB-Feedback | % |
| F2 | User subjective satisfaction | HMIB-Feedback | point |
| Number | Question |
|---|---|
| 1 | Is it important for the massage system to accurately identify your physical state? For example, it can distinguish whether you are “tired” or “relaxed”. |
| 2 | Is it important for the massage system to detect equipment failures in a timely manner? For example, problems such as sensor abnormalities and massage head jams can be detected quickly. |
| 3 | Is it important that the massage program recommended by the massage system meets your needs? |
| 4 | Is the speed at which the massage system makes decisions important? |
| 5 | Is the accuracy of the massage system’s force control important? |
| 6 | Is the accuracy of the massage system’s path tracking important? |
| 7 | Is it important for the massage system to adjust in real time based on your physiological signals? |
| 8 | Is your overall satisfaction with the massage experience important? |
| Indicator Code | ||
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 4.78 | 0.44 |
| P2 | 3.44 | 0.53 |
| D1 | 3.67 | 0.50 |
| D2 | 4.78 | 0.44 |
| E1 | 4.78 | 0.44 |
| E2 | 4.78 | 0.44 |
| F1 | 4.67 | 0.50 |
| F2 | 3.78 | 0.44 |
| Indicator Code | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.125 | 0.138 | 0.013 |
| P2 | 0.090 | 0.100 | 0.010 |
| D1 | 0.096 | 0.104 | 0.008 |
| D2 | 0.125 | 0.138 | 0.013 |
| E1 | 0.125 | 0.138 | 0.013 |
| E2 | 0.125 | 0.137 | 0.012 |
| F1 | 0.122 | 0.129 | 0.007 |
| F2 | 0.113 | 0.117 | 0.004 |
| Level | Threshold Interval |
|---|---|
| L0 | [0.000, 0.167) |
| L1 | [0.167, 0.350) |
| L2 | [0.350, 0.500) |
| L3 | [0.500, 0.650) |
| L4 | [0.650, 0.833) |
| L5 | [0.833, 1.000] |
| Expert ID | FDS vs. APM | FDS vs. HMIB | APM vs. HMIB |
|---|---|---|---|
| E1 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| E2 | 4 | 4 | 3 |
| E3 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| E4 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| E5 | 5 | 5 | 4 |
| E6 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| E7 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| E8 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Subtasks | Whether It Has | Ability to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | × | No automatic body shape/posture detection |
| S2 | × | No solution recommendation algorithm |
| S3 | √ | Supports fixed path/sequence execution, but lacks feedback correction mechanisms |
| S4 | √ | Can operate along fixed paths, but lacks online replanning capability |
| S5 | × | No anomaly detection or alerting capability |
| S6 | × | No user modeling or adaptive capability |
| Subtasks | Whether It Has | Ability to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | √ | Basic body shape/posture detection |
| S2 | √ | Program library scheme recommendation, slight improvement in D1 |
| S3 | √ | Execution of preset force/sequence (±20%), without adaptive correction |
| S4 | √ | Sequential execution of preset paths, without dynamic force allocation |
| S5 | √ | Fixed rule-based alarm triggering, longer D2 response delay |
| S6 | × | Only records basic usage parameters, no user modeling and adaptation |
| Subtasks | Whether It Has | Ability to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | √ | Multi-angle body scanning, P1 reaches the middle level |
| S2 | √ | Based on historical preference personalized recommendation, D1 significantly improved |
| S3 | √ | Strength/rhythm error ± 10%, limited fine-tuning possible based on real-time feedback |
| S4 | √ | Multi-area coordinated dynamic adjustment, key parts can be adjusted dynamically with simple strength |
| S5 | √ | Automatically identifies common faults and can quickly perform decompression or pause operations |
| S6 | √ | Preliminary adaptive learning of physiological signals |
| Subtasks | Whether It Has | Ability to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | √ | Multi-sensor dynamic body shape/posture recognition |
| S2 | √ | Online learning drives solution optimization |
| S3 | √ | Strength/rhythm error ± 10%, multiple fine-tuning can be performed based on real-time feedback |
| S4 | √ | Multi-area collaborative dynamic adjustment, continuous action switching between complex parts |
| S5 | √ | Multi-stage intelligent intervention for complex abnormalities |
| S6 | √ | Continuous closed-loop learning and precise recommendations |
| Subtasks | Whether It Has | Ability to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | √ | Real-time identification of multimodal health status |
| S2 | √ | Dynamic plan generation driven by health goals |
| S3 | √ | ±3% velocity/rhythm error before active pre-adjustment parameters |
| S4 | √ | Cross-site multi-stage continuous health intervention |
| S5 | √ | Predictive warning and intervention for subtle health fluctuations |
| S6 | √ | Long-term health record construction and personalized strategy promotion |
| Subtasks | Whether It Has | Ability to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| S1 | √ | Multi-source perception and physiological state prediction |
| S2 | √ | Big data-driven dynamic rehabilitation/massage program |
| S3 | √ | The force and rhythm error within ±1% can be automatically adjusted based on the prediction results |
| S4 | √ | Execute customized continuous actions to achieve preventive health interventions for the whole body |
| S5 | √ | Predictive warning and intervention for subtle health fluctuations |
| S6 | √ | Predict potential health risks and automatically implement intervention measures |
| S6 | √ | Online learning and real-time improvement of health profiles |
| Disturbance Amplitude | Calculated So Value | Corresponding Level |
|---|---|---|
| ±0% | 0.4253 | L2 |
| +10% | 0.4665 | L2 |
| −10% | 0.3831 | L2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, M.; Liu, G.; Fang, M.; Yan, X.; Wang, H.; Chen, B.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; et al. Research on a Task-Driven Classification and Evaluation Framework for Intelligent Massage Systems. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9327. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179327
Wang L, Wang J, Guo M, Liu G, Fang M, Yan X, Wang H, Chen B, Zhu Y, Hu J, et al. Research on a Task-Driven Classification and Evaluation Framework for Intelligent Massage Systems. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9327. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179327
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Lingyu, Junliang Wang, Meixing Guo, Guangtao Liu, Mingzhu Fang, Xingyun Yan, Hairui Wang, Bin Chen, Yuanyuan Zhu, Jie Hu, and et al. 2025. "Research on a Task-Driven Classification and Evaluation Framework for Intelligent Massage Systems" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9327. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179327
APA StyleWang, L., Wang, J., Guo, M., Liu, G., Fang, M., Yan, X., Wang, H., Chen, B., Zhu, Y., Hu, J., & Qi, J. (2025). Research on a Task-Driven Classification and Evaluation Framework for Intelligent Massage Systems. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9327. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179327






