An Accurate and Efficient Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis Method via Depthwise Separable Convolution and Multi-View Attention Mechanism
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Traditional Deep Learning-Based DR Diagnosis Methods
2.2. Multi-Modal Imaging and Advanced Feature Engineering
2.3. Lightweight Architectures and Edge Computing Optimization
3. Methodology
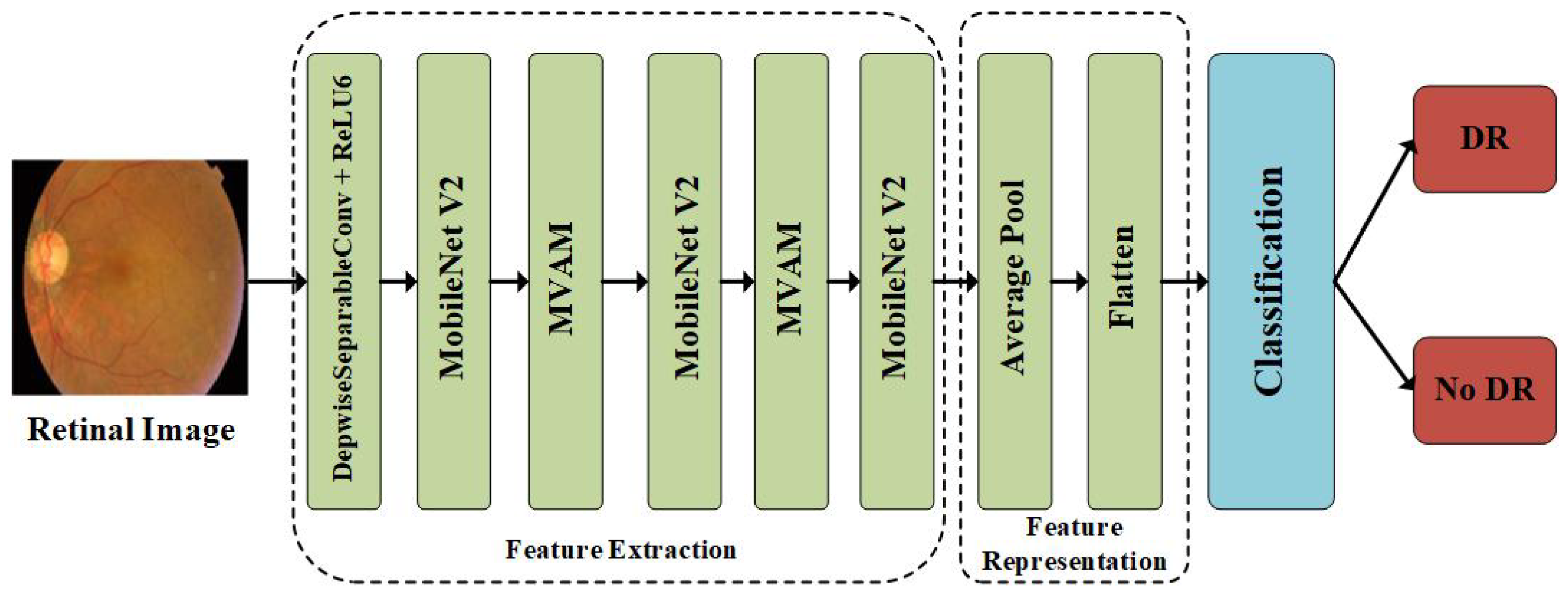
3.1. Overview of the Methodology
3.2. Feature Extraction
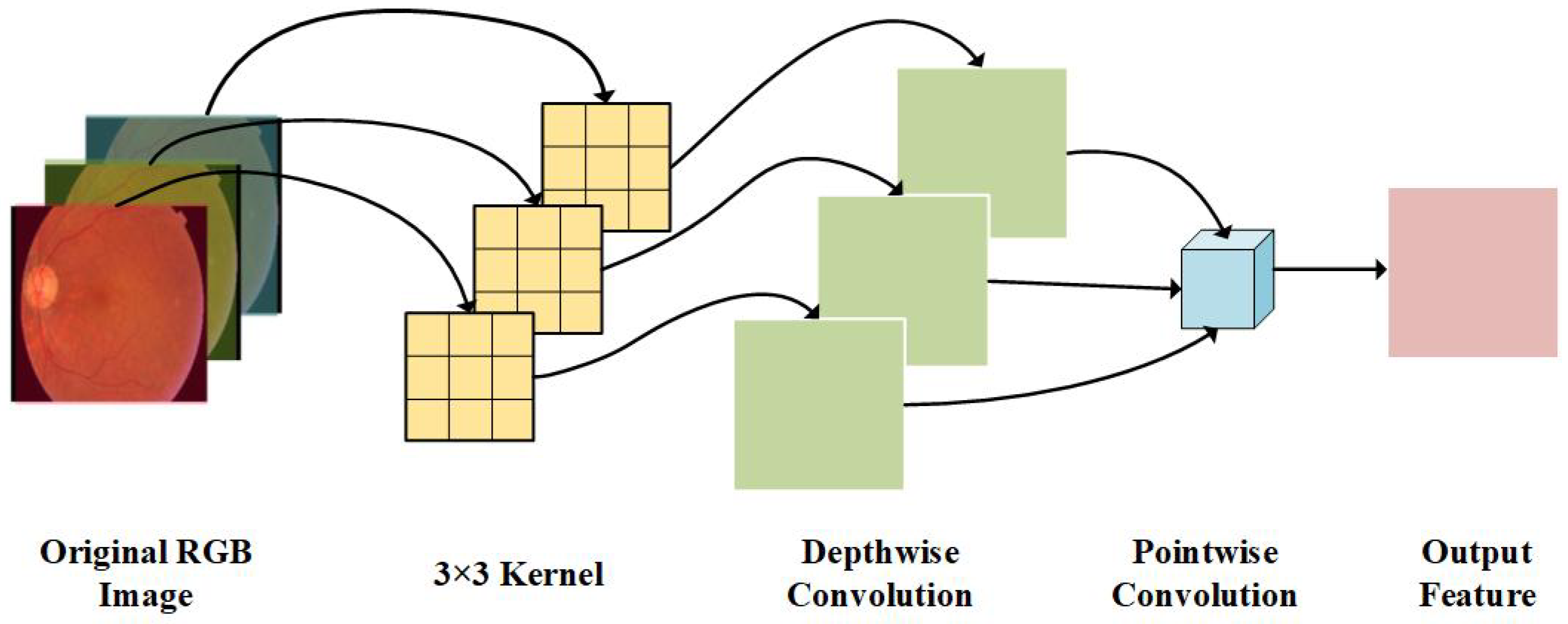
3.2.1. Depthwise Separable Convolution Layer
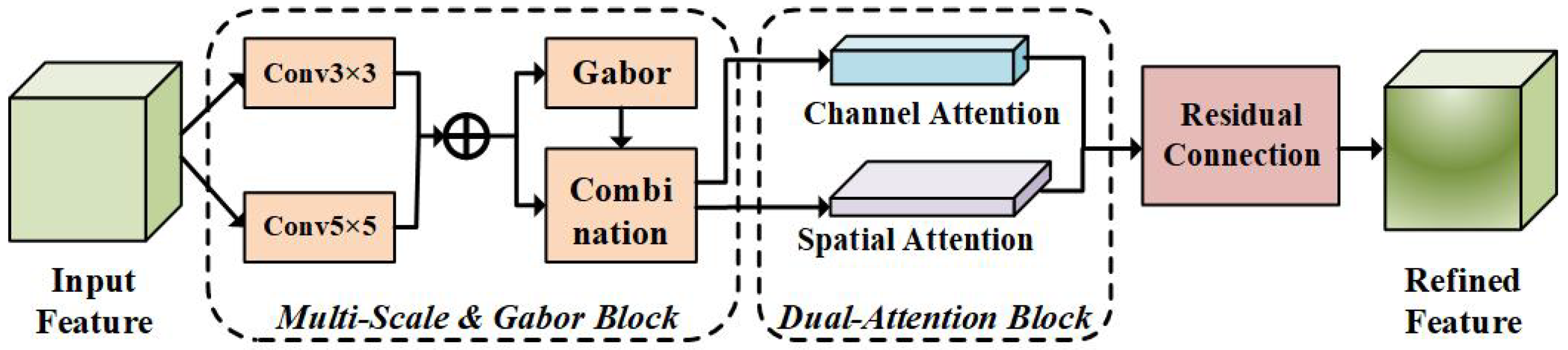
3.2.2. MVAM Layer for Feature Refinement
3.3. Feature Representation and Classification Layer
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Dataset and Preprocessing
4.2. Experimental Setup
4.3. Comparison of Experimental Results of Different Methods
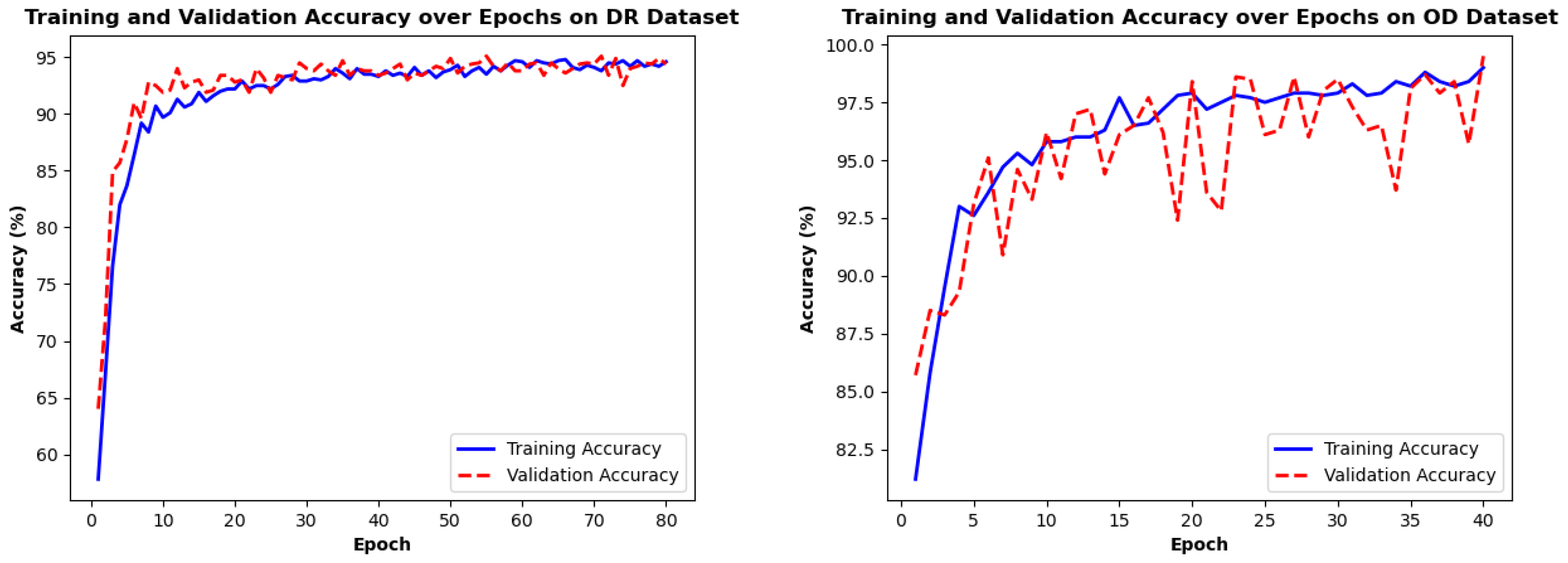
4.4. Training Loss/Accuracy Analysis
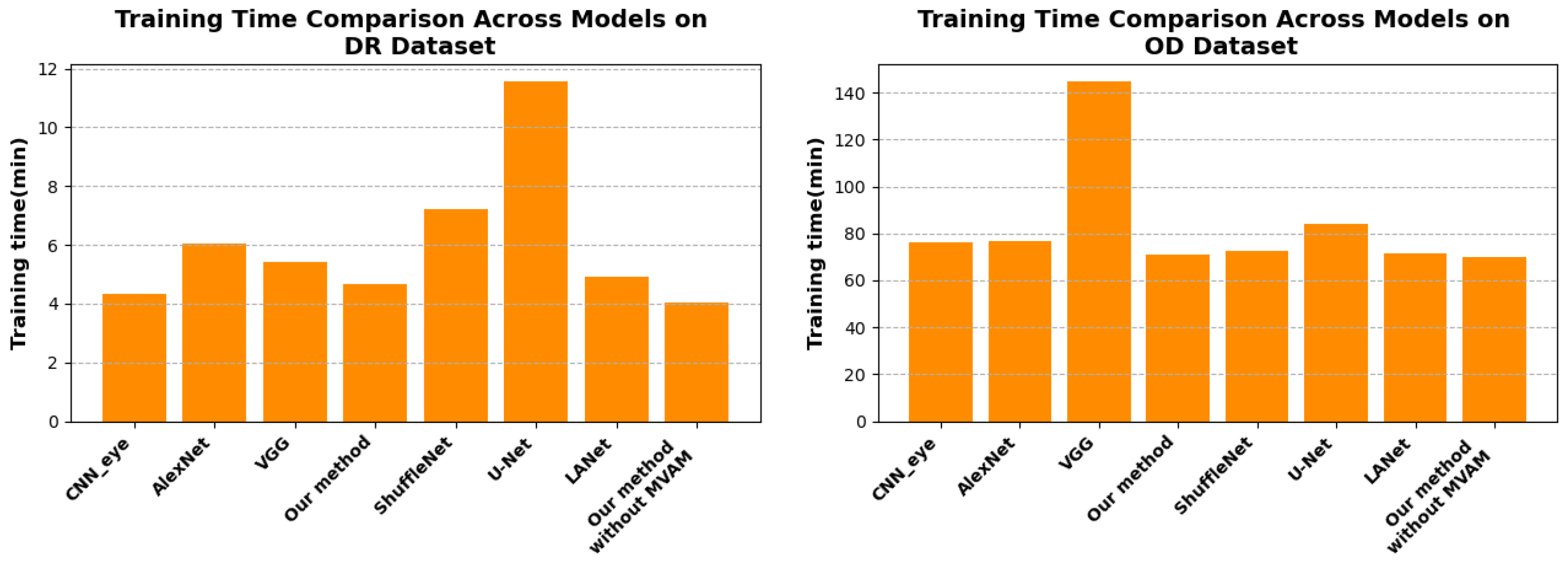
4.5. Training Time Efficiency Analysis
4.6. Ablation Experiments
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhang, N.; Cao, Y.; Liu, B. Mini Lesions Detection on Diabetic Retinopathy Images via Large Scale CNN Features. In Proceedings of the IEEE 31st International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 November 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tânia Melo, T.; Mendonça, A.M.; Campilho, A. Microaneurysm detection in color eye fundus images for diabetic retinopathy screening. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 126, 103995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Peng, K.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, X. MSFF-UNet: Image segmentation in colorectal glands using an encoder-decoder U-shaped architecture with multi-scale feature fusion. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2023, 83, 42681–42701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrera, E.; González, A.; Carrera, R. Automated detection of diabetic retinopathy using SVM. In Proceedings of the IEEE XXIV International Conference on Electronics, Electrical Engineering and Computing (INTERCON), Cusco, Peru, 15–18 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gulshan, V.; Peng, L.; Coram, M.; Stumpe, M.C.; Wu, D.; Narayanaswamy, A.; Venugopalan, S.; Widner, K.; Madams, T.; Cuadros, J.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Detection of Diabetic Retinopathy in Retinal Fundus Photographs. JAMA 2016, 316, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gayathri, S.; Gopi, V.P.; Palanisamy, P. A lightweight CNN for Diabetic Retinopathy classification from fundus images. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2020, 62, 102115. [Google Scholar]
- Bilal, A.; Imran, A.; Baig, T.; Liu, X.; Long, H.; Alzahrani, A.; Shafiq, M. Improved Support Vector Machine based on CNN-SVD for vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy detection and classification. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0295951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, D.; Cheung, C.; Lim, G.; Tan, G.; Quang, N.; Gan, A.; Hamzah, H.; Garcia-Franco, R.; Yeo, I.; Lee, S.; et al. Development and Validation of a Deep Learning System for Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Eye Diseases Using Retinal Images from Multiethnic Populations with Diabetes. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2017, 318, 2211–2223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, N.; Jerome, S. Diabetic retinopathy detection using EADBSC and improved dilated ensemble CNN-based classification. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 33573–33595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, N.; Sengupta, S. A Hybrid CNN Model for Deep Feature Extraction for Diabetic Retinopathy Detection and Gradation. J. Circuits. Syst. Comput. 2023, 23, 2350036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sravya, V.S.; Srinivasu, P.N.; Shafi, J.; Hołubowski, W.; Zielonka, A. Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy Detection with the R–CNN: A Unified Visual Health Solution. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci. 2024, 34, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasashvini, R.; Vergin Raja Sarobin, M.; Panjanathan, R.; Graceline Jasmine, S.; Jani Anbarasi, L. Diabetic Retinopathy Classification Using CNN and Hybrid Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. Symmetry 2022, 14, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed Gani, V.K.U.; Shanmugasundaram, N. Cheetah optimized CNN: A bio-inspired neural network for automated diabetic retinopathy detection. AIP Adv. 2025, 15, 055314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.; Sumathy, S. Classification of Diabetic Retinopathy Disease Levels by Extracting Topological Features Using Graph Neural Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 51435–51444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhan, M.H.; Albarqouni, S.; Yigitsoy, M.; Navab, N.; Eslami, A. Multi-scale Microaneurysms Segmentation Using Embedding Triplet Loss. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. 2019, 11764, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madarapu, S.; Ari, S.; Mahapatra, K. A multi-resolution convolutional attention network for efficient diabetic retinopathy classification. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2024, 117, 109243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zuo, W.; Chen, Y.; Meng, D.; Zhang, L. Beyond a Gaussian Denoiser: Residual Learning of Deep CNN for Image Denoising. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 3142–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, U.; Fujita, H.; Bhandary, S.; Gudigar, A.; Hong, T.; Acharya, U. Deep convolution neural network for accurate diagnosis of glaucoma using digital fundus images. Inf. Sci. 2018, 441, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, C.; Li, R.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wen, D.; Zhang, L.; Wei, W.; Zhang, Y. Multiple Multi-Scale Neural Networks Knowledge Transfer and Integration for Accurate Pixel-Level Retinal Blood Vessel Segmentation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 11907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ni, W.; Luo, Y.; Feng, Y.; Song, R.; Wang, X. TUnet-LBF: Retinal fundus image fine segmentation model based on transformer Unet network and LBF. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 159, 106937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, E.S.; Moult, E.M.; Greig, E.C.; Zhao, Y.; Pramil, V.; Gendelman, I.; Alibhai, A.Y.; Baumal, C.R.; Witkin, A.J.; Duker, J.S.; et al. Multiscale Correlation of Microvascular Changes on Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography With Retinal Sensitivity in Diabetic Retinopathy. Retina 2022, 42, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhini Selvaganapathy, N.; Siddhan, S.; Sundararajan, P.; Balasundaram, S. Automatic screening of retinal lesions for detecting diabetic retinopathy using adaptive multiscale MobileNet with abnormality segmentation from public dataset. Network 2024, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, T.S.; Gao, S.S.; Liu, L.; Lauer, A.K.; Bailey, S.T.; Flaxel, C.J.; Wilson, D.J.; Huang, D.; Jia, Y. Automated Quantification of Capillary Nonperfusion Using Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Diabetic Retinopathy. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bidwai, P.; Gite, S.; Pahuja, N.; Pahuja, K.; Kotecha, K.; Jain, N.; Ramanna, S. Multimodal image fusion for the detection of diabetic retinopathy using optimized explainable AI-based Light GBM classifier. Inf. Fusion 2024, 111, 102526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidwai, P.; Gite, S.; Gupta, A.; Pahuja, K.; Kotecha, K. Multimodal dataset using OCTA and fundus images for the study of diabetic retinopathy. Data Brief 2024, 52, 110033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Habib Daho, M.; Li, Y.; Zeghlache, R.; Atse, Y.C.; Le Boité, H.; Bonnin, S.; Cosette, D.; Deman, P.; Borderie, L.; Lepicard, C.; et al. Improved Automatic Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Classification Using Deep Multimodal Fusion of UWF-CFP and OCTA Images. In Proceedings of the Ophthalmic Medical Image Analysis (OMIA 2023), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 12 October 2023; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corso, R.; Khan, F.; Yezzi, A.; Comelli, A. Features for Active Contour and Surface Segmentation: A Review. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2025; Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, B.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, S.; Wang, H. Object Recognition Using Shape and Texture Tactile Information: A Fusion Network Based on Data Augmentation and Attention Mechanism. IEEE Trans. Haptics 2024, 18, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervella, A.S.; Rouco, J.; Novo, J.; Ortega, M. Multimodal image encoding pre-training for diabetic retinopathy grading. Comput. Biol. Med. 2022, 143, 105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Gao, Y.; Liu, F. TransMed: Transformers Advance Multi-Modal Medical Image Classification. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Qiu, X.; Tan, X. DMFusion: A dual-branch multi-scale feature fusion network for medical multi-modal image fusion. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2025, 105, 107572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, Q.; Ai, M. RIFT: Multi-Modal Image Matching Based on Radiation-Variation Insensitive Feature Transform. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 3296–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Fu, H.; Chen, G.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Hi-Net: Hybrid-Fusion Network for Multi-Modal MR Image Synthesis. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2772–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couturier, A.; Mané, V.; Bonnin, S.; Erginay, A.; Massin, P.; Gaudric, A.; Tadayoni, R. Capillary Plexus Anomalies in Diabetic Retinopathy on Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Retina 2015, 35, 2384–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akram, M.U.; Khalid, S.; Tariq, A.; Khan, S.A.; Azam, F. Detection and classification of retinal lesions for grading of diabetic retinopathy. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 45, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanthi, T.; Sabeenian, R.S. Modified Alexnet architecture for classification of diabetic retinopathy images. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2019, 76, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychowdhury, S.; Koozekanani, D.D.; Parhi, K.K. DREAM: Diabetic Retinopathy Analysis Using Machine Learning. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2014, 18, 1717–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Sui, L.; Qiu, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, S. Angel-Eye: A Complete Design Flow for Mapping CNN Onto Embedded FPGA. IEEE Trans. Comput.-Aided Des. Integr. Circuits Syst. 2018, 37, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Meng, Y.; Yu, X.; Bi, H.; Chen, Z.; Li, H. MBAB-YOLO: A Modified Lightweight Architecture for Real-Time Small Target Detection. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 78384–78401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-neck by GSConv: A lightweight-design for real-time detector architectures. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2024, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, M.; Burrello, A.; Conti, F.; Lamberti, L.; Chen, Y.; Benini, L. Lightweight Neural Architecture Search for Temporal Convolutional Networks at the Edge. IEEE Trans. Comput. 2023, 72, 744–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Liu, B.; Fu, P.; Chen, H. An efficient lightweight CNN acceleration architecture for edge computing based-on FPGA. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53, 13867–13881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhm, S.; Wirtz, G. PULCEO—A Novel Architecture for Universal and Lightweight Cloud-Edge Orchestration. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Service-Oriented System Engineering (SOSE), Athens, Greece, 17–20 July 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chang, X.; Guo, X. ESFCU-Net: A Lightweight Hybrid Architecture Incorporating Self-Attention and Edge Enhancement Mechanisms for Enhanced Polyp Image Segmentation. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2025, 35, e70026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, H.; Kong, Q.; Zhang, Y. Efficient On-Orbit Remote Sensing Imagery Processing via Satellite Edge Computing Resource Scheduling Optimization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2025, 63, 1000519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Xia, Y.; Kamruzzaman, J. Quantum Particle Swarm Optimization for Task Offloading in Mobile Edge Computing. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2023, 19, 9113–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Huang, Y. Joint Optimization of Computing Offload Strategy and Resource Allocation in Mobile Edge Computing. In Proceedings of the Computer Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (ChineseCSCW 2024), Hohhot, China, 11–13 July 2024; Volume 2344, pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, P.K. Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy Dataset. 2024. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/382264856_Diagnosis_of_Diabetic_Retinopathy (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Pkdarabi. Diagnosis of Diabetic Retinopathy. 2024. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/pkdarabi/diagnosis-of-diabetic-retinopathy (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Abhinav099802. Eye Disease Image Dataset—Mendeley. 2025. Available online: https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/abhinav099802/eye-disease-image-dataset (accessed on 16 August 2025).
- Xia, X.; Zhan, K.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, W.; Shen, F. Lesion-aware network for diabetic retinopathy diagnosis. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2023, 33, 1914–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dataset | Total Samples | DR | No_DR |
|---|---|---|---|
| DR dataset | 2848 | 1411 | 1437 |
| OD dataset | 6112 | 3445 | 2667 |
| Param. Category | Param. Name | Value/Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Training Process | Epochs | 80 |
| Batch Size | 32 | |
| Optimizer | Adam (lr = 1 , wd = 1 ) | |
| LR Scheduler | Type | ReduceLROnPlateau |
| Factor/Patience | 0.5/20 | |
| Loss and Data | Loss Function | NLLLoss (reduction = “sum”) |
| Dataset Split | Train:Val:Test = 7:2:1 | |
| Device | Computing Device | MPS (Priority)/CPU |
| Param. Category | Param. Name | Value/Setting |
|---|---|---|
| Training Process | Epochs | 40 |
| Batch Size | 32 | |
| Optimizer | Adam (lr = 1 , wd = 1 ) | |
| LR Scheduler | Type | ReduceLROnPlateau |
| Factor/Patience | 0.5/20 | |
| Loss and Data | Loss Function | NLLLoss (reduction = “sum”) |
| Dataset Split | Train:Val:Test = 7:2:1 | |
| Device | Computing Device | MPS (Priority)/CPU |
| CNN_Eye | AlexNet | VGG | U-Net | ShuffleNet | LANet | Our Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | 0.9355 | 0.9442 | 0.9402 | 0.9576 | 0.9351 | 0.9652 | 0.9696 |
| Recall | 0.9348 | 0.9434 | 0.9390 | 0.9563 | 0.9349 | 0.9407 | 0.9698 |
| F1-score | 0.9350 | 0.9437 | 0.9393 | 0.9566 | 0.9350 | 0.9528 | 0.9697 |
| Accuracy | 0.9351 | 0.9477 | 0.9394 | 0.9567 | 0.9351 | 0.9524 | 0.9697 |
| CNN_Eye | AlexNet | VGG16 | U-Net | ShuffleNet | LANet | Our Method | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precision | 0.9426 | 0.9532 | 0.9524 | 0.9533 | 0.9418 | 0.9504 | 0.9662 |
| Recall | 0.9449 | 0.9523 | 0.9547 | 0.9549 | 0.9417 | 0.9907 | 0.9686 |
| F1-score | 0.9432 | 0.9527 | 0.9531 | 0.9539 | 0.9417 | 0.9543 | 0.9668 |
| Accuracy | 0.9434 | 0.9529 | 0.9533 | 0.9541 | 0.9419 | 0.9562 | 0.9669 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without MVAM | 0.9402 | 0.9390 | 0.9393 | 0.9394 |
| Without Depthwise Separable Convolution | 0.9445 | 0.9437 | 0.9436 | 0.9437 |
| Without MobileNet V2 | 0.9308 | 0.9307 | 0.9307 | 0.9307 |
| Our Method | 0.9696 | 0.9698 | 0.9697 | 0.9697 |
| Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without MVAM | 0.9356 | 0.9368 | 0.9353 | 0.9353 |
| Without Depthwise Separable Convolution | 0.9343 | 0.9356 | 0.9350 | 0.9352 |
| Without MobileNet V2 | 0.9226 | 0.9253 | 0.9214 | 0.9214 |
| Our Method | 0.9662 | 0.9686 | 0.9668 | 0.9669 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Q.; Wei, Y.; Liu, F.; Wu, Z. An Accurate and Efficient Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis Method via Depthwise Separable Convolution and Multi-View Attention Mechanism. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179298
Yang Q, Wei Y, Liu F, Wu Z. An Accurate and Efficient Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis Method via Depthwise Separable Convolution and Multi-View Attention Mechanism. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(17):9298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179298
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Qing, Ying Wei, Fei Liu, and Zhuang Wu. 2025. "An Accurate and Efficient Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis Method via Depthwise Separable Convolution and Multi-View Attention Mechanism" Applied Sciences 15, no. 17: 9298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179298
APA StyleYang, Q., Wei, Y., Liu, F., & Wu, Z. (2025). An Accurate and Efficient Diabetic Retinopathy Diagnosis Method via Depthwise Separable Convolution and Multi-View Attention Mechanism. Applied Sciences, 15(17), 9298. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15179298





