Abstract
Background/Objectives: Herein, we investigated the effect of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) treatment combined with no-ozone cold plasma (NCP) on growth factor levels, rat bone-marrow stem cell (rBMSC) proliferation, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in the early stage of differentiation into osteoblasts. Methods: The PRF used in the experiment was prepared by collecting blood from the jugular vein of rats, followed by centrifugation. The obtained PRF was treated with NCP, and the cell culture media were conditioned with the PRF extracts alone or with NCP-treated PRF extracts. Three different experimental groups were defined: no treatment (NT); cell culture media extracted from PRF (PRF); and cell culture media extracted from PRF treated with NCP (PRF + NCP). Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were performed to determine the levels of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) AB. Water-soluble Tetrazolium-1 assay was performed to measure cell proliferation in rBMSCs. To analyze cell differentiation into osteoblasts, ALP staining and real-time PCR were performed. Results: Growth factor levels increased in response to treatment (TGF-β: p < 0.001, PDGF AB: p < 0.05), and the cell proliferation rate increased with treatment (145.29% and 150.05% for PRF and the PRF + NCP groups, respectively, relative to the NT group, p < 0.001). Evaluation of the ALP staining intensity and mRNA expression levels showed that the ALP activity was highest in the PRF + NCP group (p < 0.001). Conclusions: Our results confirmed that NCP treatment enhanced the release of several different growth factors contained in PRF to the culture media and that treatment with PRF and NCP increased the proliferation of rBMSCs and their differentiation into osteoblasts.
1. Introduction
Platelets are anucleated blood cells containing a range of proteins that include growth and coagulation factors, and whose activation leads to aggregation and blood clot formation [1]. Activated platelets migrate to infected tissues where immune cells are recruited and aggregate around bacteria [2]. The ability of platelets to promote regeneration was initially identified in the 1970s, revealing that they possess growth factors that enhance collagen production and stimulate cell differentiation [3]. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has been demonstrated to promote osteo-progenitor cell proliferation in the bone since its introduction in 1997 [4] in the context of oral surgical procedures. However, some risks associated with PRP application have been described, ranging from postoperative infections to inflammatory adverse reactions [5], thus necessitating the careful consideration of its use for dental treatments.
Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) is considered a next-generation platelet concentrate that contains an autologous fibrin matrix. PRF acts as a carrier for the transport of cells involved in tissue regeneration and is characterized by the sustained release of growth factors that promote wound healing [6,7,8]. Unlike PRP preparation, PRF preparation does not require the addition of an anticoagulant because the process of polymerization occurs naturally [9]. Coagulation and fibrin clot formation are inhibited by anticoagulants, and reactions to bovine thrombin and antibodies to bovine components can result in bleeding disorders or coagulopathies [10].
PRF can serve as a resorbable membrane for guided bone regeneration after surgical procedures, promoting bone regeneration and stabilization [11]. PRF contains platelets and leukocytes and releases cytokines capable of enhancing bone regeneration. In addition, macrophages have been reported to be present among the bone marrow leukocytes, which can promote bone formation via the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) [12,13]. In particular, alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, an indicator of osteoblastic differentiation, was higher when PRF membranes were used [14].
A comparative study in rat calvaria osteoblasts with exudates of PRP and PRF showed that PRF had a more pronounced and durable effect in terms of ALP expression and induction of mineralization [15]. However, despite the wide range of benefits of PRF reported in the literature, a comparative study showed that morphological characteristics after 6 months of sinus augmentation were similar regardless of whether PRF had been used or not, and the percentage of new bone formation showed no statistically significant differences. Although there were no adverse effects associated with the use of PRF, this study failed to provide any evidence supporting the use of PRF to promote bone regeneration [16].
The efficacy of cold plasma has been reported in several previous studies, following the development of medical devices and equipment in different fields of the life sciences and medicine. The reported effects of cold plasma include anti-inflammation [17], bacterial inhibition [18], tooth bleaching [19], wound healing [20], anticancer activity [21], and neuroregeneration [22]. Its effectiveness has also been confirmed in agricultural applications such as seed germination and seedling growth [23]. Cold plasma is produced by ionization of a gas mixture containing argon or helium and serves as an effective source of active species with high oxidation potential, such as hydroxyl radicals (OH) or hydrogen peroxide [24]. The bactericidal effect of cold plasma is the result of the combination of many different elements, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS). Recent studies have described the role of charged particles or electric fields in cold plasma applications [25]. The no-ozone cold plasma (NCP) device used in this experiment generates ozone at a level of 0.05 ppm or less as recommended by the WHO at a low temperature; its anti-inflammation [26] and prevention of tooth hypersensitivity [27] as well as its effect in increasing differentiation into osteoblasts [28] have been proven.
There have been studies on the effects of PRF with diode laser treatment on early bone healing of extraction socket [29], and PRF derived from human venous blood has been used to create bioabsorbable fibrin scaffolds. Sheets derived from periodontal ligament stem cells and jaw bone mesenchymal stem cells were placed in a nude mouse model, where the production of predominantly bone-like tissues was verified [30]. However, no studies to date have explored the effect of the combined use of PRF and cold plasma.
Therefore, in this study, no-ozone cold plasma (NCP) with almost no ozone was used in combination with PRF treatment, and its effect on the proliferation of rat-derived bone marrow stem cells and in stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts were investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PRF Preparation
All procedures were approved by the Animal Lab of Pusan National University (PNU-2024-0448).
For PRF preparation, blood was collected from the jugular vein of 8-week-old male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats weighing approximately 250 g. The skin covering the jugular vein was disinfected with 70% ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA), and 1 mL of blood was collected from each animal. Immediately after blood collection, the tip of the syringe was removed; blood was slowly poured into a 1.5 mL tube and centrifuged at 800× g for 10 min. After centrifugation, only the PRF layer excluding the red blood cell layer was cut out and used in the experiment (Figure 1a).
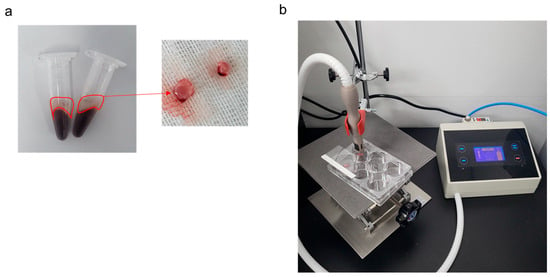
Figure 1.
Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and no-ozone cold plasma (NCP). (a) PRF clot obtained after centrifugation at 800× g for 10 min after rat blood collection. (b) NCP during PRF treatment.
2.2. Treatment with NCP
The cold plasma used in this study corresponded to NCP with minimal generation of ozone, developed by FEAGLE Corporation (Yangsan, Republic of Korea) (Figure 1b) [21,22,25,31]. PRF was washed with Dulbecco’s Phosphate Buffered Saline (DPBS; Gibco, Gaithersburg, MD, USA), and 100 µL of Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM; Gibco) was added to a 6-well plate, followed by NCP treatment for 5 min. Next, 5 mL of DMEM medium was added, followed by incubation in a 37 °C incubator for 48 h [32]. Then, each medium in the plate was collected, filtered through a 0.2 µm filter (ADVANTEC, Taipei, Taiwan), and diluted 1:10 to be used for all experiments [33]. Three different experimental groups were defined for this study: (1) NT, the no-treatment group; (2) PRF, a group treated with cell culture media that included PRF extracts, and (3) PRF + NCP, a group treated with PRF and with NCP.
2.3. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique was used to determine the concentrations of the following growth factors in the cell culture media containing PRF extracts: TGF-β (Human/Mouse/Rat/Porcine/Canine TGF-beta 1 ELISA—Quantikine, R & D Systems, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and PDGF-AB (Mouse/Rat PDGF-AB Quantikine ELISA Kit, R&D). Experiments were carried out with the three different types of cell culture medium: medium with no treatment, medium treated with PRF, and medium treated with PRF + NCP. Concentrations were measured in cell-free culture medium according to the protocol provided by the manufacturer.
2.4. Isolation and Culture of Rat Stem Cells
We obtained bone marrow cells from 10-week-old male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats weighing approximately 350 g. The experimental rats were euthanized, and their femurs and tibiae were carefully extracted from the articular cavity side and cut in half. Thereafter, the structures were repeatedly flushed with 1 mL of DMEM (Gibco) containing 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (Gibco) and 1% antibiotic-antimycotic (Gibco) to collect the bone marrow cells, followed by filtration with a 40 µm cell strainer (SPL, Seoul, Republic of Korea). The cells collected in the filtration step were suspended in red blood cell (RBC) Lysis Buffer (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, MA, USA) for 5 min, followed by centrifugation for cell harvesting. The collected cells were diluted in DMEM and incubated in a 37 °C incubator (Thermo Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA). After 4 days, unattached cells were aspirated, and those that adhered to the culture surface after 11 days were examined under a microscope and subjected to subculturing. All the cells used in the experiments were subjected to a maximum of 6 passages [34].
2.5. Stem Cell Marker
Bone marrow cells extracted from the rats were characterized using stem cell surface markers by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis. Passage-2 cells were collected and stained for 30 min at room temperature using a 1:100 dilution of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-conjugated CD 44 and FITC-conjugated CD 45 antibodies (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Then, flow cytometry analysis was performed using BD cytometry (FACSAriaIII; BD Biosciences, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) at a rate of up to 1 × 104 per second. The mouse IgG2a kappa isotype control FITC (Invitrogen) was used as a negative control [35].
2.6. Cell Proliferation
Rat bone marrow cells were treated with media containing PRF extracts (PRF media) or NCP-treated PRF extracts (PRF + NCP media), and cell proliferation (%) was determined. Cells were seeded at a density of 1 × 104/well in a 96-well plate, followed by incubation in a 37 °C incubator for 24 h. Then, water-soluble Tetrazolium 1 (EX-Cytox, DoGenBio, Seoul, Republic of Korea), a reagent for cell proliferation assay, was added at a dilution ratio of 1:9, and cells were incubated for 2 h in an incubator. The absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 450 nm using a microplate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Darmstadt, Germany), and the recorded values were converted to a percentage relative to those recorded for the control group.
2.7. ALP Staining
Rat bone marrow cells were treated with the PRF or PRF +NCP media, and ALP activity was determined. The cells were seeded at a density of 1 × 105/well in a 24-well plate, followed by cell culture until they had reached 100% confluence. Next, no-treatment medium, PRF medium, and PRF + NCP medium were added at a ratio equivalent to 10% to the osteogenesis induction medium (10 nM dexamethasone, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate (Sigma-Aldrich), 50 μg/mL ascorbic acid) and used for treatment.
During cell culture, the medium was replaced every 2–3 days, and after 1 week, the cells were fixed for 1 min using a solution containing 3.7% formaldehyde and 90% ethanol, followed by two washes with tris-buffered saline. Staining was performed in dark conditions for 30 min using a fast 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate and nitro blue tetrazolium (BCIP/NBT) alkaline phosphatase substrate solution (Sigma-Aldrich). Finally, the cells stained in purple were photographed using a camera and microscope.
2.8. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
The cells were seeded at a density of 1 × 105/well in a 24-well plate, followed by cell culture until they reached 100% confluence. Next, osteogenesis induction medium containing PRF or PRF + NCP was added, and the medium was replaced every 2–3 days. After 1 week, the cells were rinsed with DPBS, followed by treatment with TRNzol Reagent (Invitrogen) for the extraction of total RNA. The extracted total RNA was used for complementary DNA (cDNA) synthesis using the One-step PreMix kit (nestep PreMix kit; iNtRON Biotechnology Inc., Seoul, Republic of Korea). Next, real-time PCR amplification was performed using a CFX 96 Real Time System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) with a SensiFAT SYBR No ROX kit (Bioline, Taunton, MA, USA). The following primers were used for the amplification: Alkaline phosphatase-1 Forward, 5′-AGGGTGGGTTTCTCTCTTGG-3′; Alkaline phosphatase-1 Reverse, 5′-AGAGAAGGGGTAGGGGAGAG-3′, GAPDH Forward 5′-CAAGTTCAACGGCACAGTCA-3′; GAPDH Reverse 5′-CCCCATTTGATGTTAGCGGG-3′. Relative qualification was performed using the comparative 2−ΔΔCt method.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The results are represented as mean ± standard deviation, and the SPSS statistical software package 20 version (IBM, Chicago, IL, USA) was used for testing statistical significance. Data analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), followed by Duncan’s post hoc analysis to determine significant differences between groups.
3. Results
3.1. Elevated Levels of Growth Factors
The results of the ELISA tests are shown in Figure 2. TGF-β levels were 836.5 pg/mL in the no-treatment group, 4141 pg/mL in the PRF group, and 4506.17 pg/mL in the PRF + NCP group, showing statistically significant increases in response to treatment. PDGF-AB levels were 7.67 pg/mL in the no-treatment group, 23 pg/mL in the PRF group, and 33 pg/mL in the PRF + NCP group. There were significant differences among the three groups, but in the post hoc test, only the no-treatment group and the PRF + NCP group were confirmed to have significant differences.
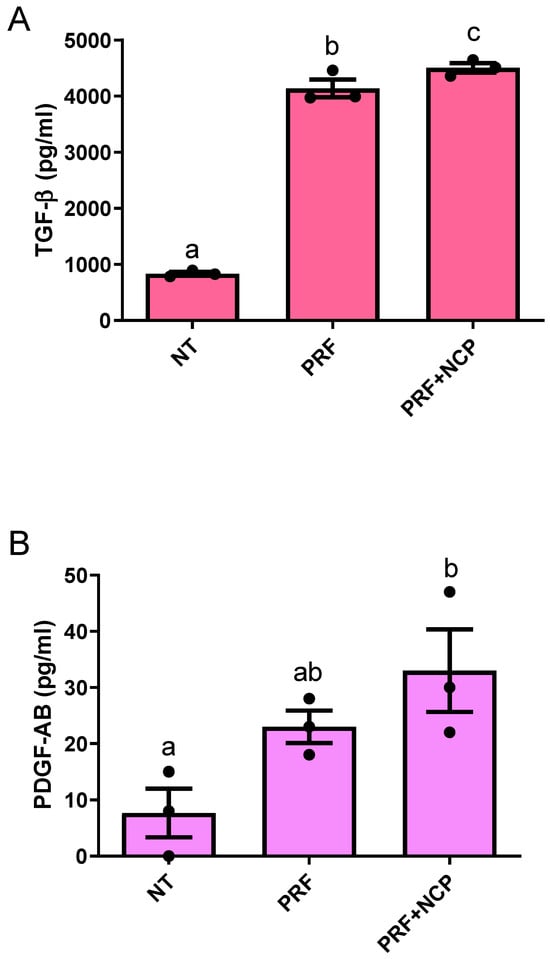
Figure 2.
Concentrations of growth factors in NT, PRF, and PRF + NCP measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. (A) Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β, p < 0.001; n = 3. (B) Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) AB, p < 0.05; n = 3. NT, no-treatment group; PRF, cell culture media treated with PRF extracts; PRF + NCP, PRF treated with NCP, followed by cell culture media treatment. Different letters indicate significant differences.
3.2. Stem Cell Marker
To determine whether the cells extracted from the femurs and tibiae of the experimental rats corresponded to stem cells (Figure 3a), we evaluated the expression of the stem cell markers CD44 and CD45. The percentage of CD44-positive cells was 81.2%, and that of CD45-positive cells was 0% (Figure 3b). With confirmation of the stem cell marker results of CD44 positive, the extracted cells were identified to be the stem cells.
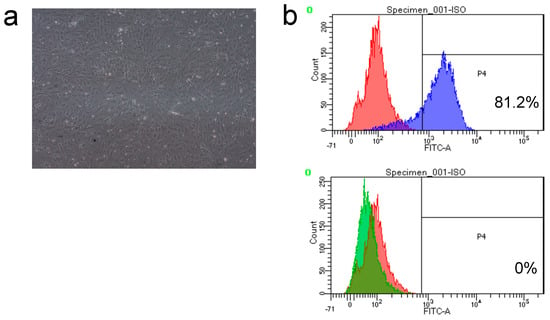
Figure 3.
Characterization and identification of rat bone marrow stem cells (rBMSCs). (a) Morphology of rBMSCs showing the characteristic spindle-shaped short fibroblasts at 11 days. (b) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) images showing the positive (CD44) and negative (CD45) rBMSCs. Red: mouse IgG2a kappa isotype control fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC); Blue: CD 44 FITC positive; Green: CD 45 FITC negative.
3.3. Cell Proliferation
The cell proliferation assay was performed to compare the cell proliferation rates (%) in rat bone marrow cells according to treatment. The corresponding proliferation rates were 100%, 145.29%, and 150.05% for the no-treatment group, PRF group, and PRF + NCP group, respectively (Figure 4). The difference between the no-treatment group and the PRF group and that between the no-treatment group and the PRF + NCP group were statistically significant, while that between the PRF group and the PRF + NCP group was not.
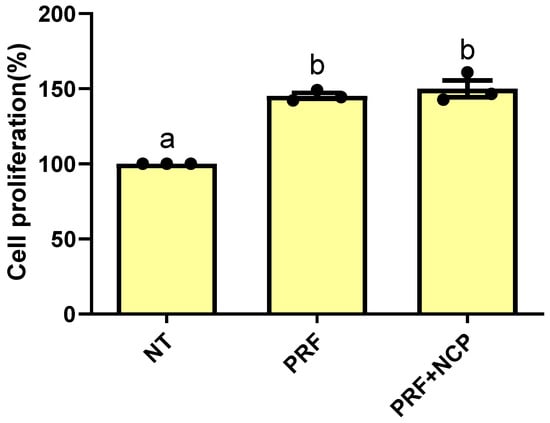
Figure 4.
Evaluation of the effects of NT, PRF, and PRF + NCP on rat bone marrow stem cell proliferation at 24 h. p < 0.001; n = 3. NT, no-treatment group; PRF, cell culture media treated with PRF extracts; PRF + NCP, PRF treated with NCP, followed by cell culture media treatment. Different letters indicate significant differences.
3.4. ALP Activity
Immunohistochemical staining for ALP and real-time PCR analysis were performed to evaluate ALP activity, a major marker of osteoblastic differentiation, in cultures in which osteoblastic differentiation had been induced. ALP staining intensity showed the most increased pattern in the PRF + NCP group (Figure 5A).
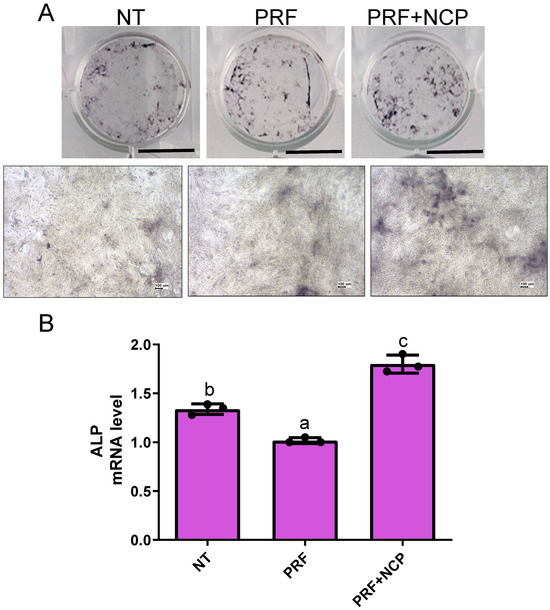
Figure 5.
Evaluation of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) staining and mRNA expression levels in rat bone marrow stem cells (rBMSCs). (A) ALP expression on day 7 in rBMSCs. Scale bar: 7.5 mm and 100 µm. (B) ALP mRNA expression on day 7 in rBMSCs using real-time PCR. p < 0.001; n = 3. NT, no-treatment group; PRF, cell culture media treated with PRF extracts; PRF + NCP, PRF treated with NCP, followed by cell culture media treatment. Different letters indicate significant differences.
The relative values for mRNA levels were 1.34, 1.02, and 1.80, for the no-treatment group, PRF group, and PRF + NCP group, respectively (Figure 5B), with the differences between the experimental groups being statistically significant. The PRF + NCP group showed a statistically significant increase of 1.34–1.76 times compared to the other groups. These results showed that the PRF + NCP group was capable of earlier differentiation into osteoblasts compared to the PRF group.
4. Discussion
Bone remodeling or regeneration involves the proliferation and differentiation of cells and the calcification of the bone extracellular matrix (ECM), and bone homeostasis is maintained by osteoblast–osteoclast communication [36]. In the case of bone healing following bone loss, the process begins with the formation of a hematoma by the bleeding in the wound area. Then, fibroblasts migrate to the area, and growth factors that are enriched in platelets (e.g., EGF, TGF, or PDGF) promote angiogenesis and granulation tissue formation. In the final step of this process, new bone is created by osteoblasts [37].
The differentiation of osteoblasts is intricately regulated by various growth factors, cytokines, and alterations in gene expression. During the differentiation process, mature osteoblasts express genes such as alkaline phosphatase (ALP), collagen, and osteopontin (OCN) [38]. Notably, ALP, which is produced during osteoblast differentiation, plays a crucial role in biomineralization. The formation of hydroxyapatite crystals depends on the local concentration of inorganic phosphate, which can be increased by ALP’s capacity to hydrolyze extracellular inorganic pyrophosphate that is in turn produced when adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is hydrolyzed [39]. ALP is expressed early in the osteoblast differentiation process. Later in the process, osteocalcin (OC), a later indicator of fully differentiated osteoblasts, is expressed more frequently [40]. Considering this, stem cells isolated from the bone of rats were treated with PRF, which is rich in growth factors, and with NCP, which induces the differentiation of stem cells into osteoblasts; the effects of these treatments was then experimentally assessed. TGF-β is one of the most abundant growth factors in skeletal tissues and has been reported to increase bone formation and promote fracture healing [41].
TGF-β is a critical regulator in bone metabolism, playing multiple functions. TGF-β knock-out mice have been reported to exhibit a decrease of approximately 30% in tibial length and a reduction in the mineral content of their bones [42]. In addition, TGF-β induces activation of Erk1/2 and p38 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase and regulates the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) [43].
PDGF, another growth factor, is synthesized in osteoblasts undergoing differentiation, and it has been reported to promote cell division in the early and late stages of osteoblast differentiation, stimulating the synthesis of collagen fibers during the process of wound healing [44]. Lepistö et al. [45] reported that in in vitro experiments, PDGF-AB increased the number of rat granulation tissue-derived fibroblasts and collagen accumulation at doses of 10 and 30 ng/mL, whereas Mitlak et al. [46] reported that systemically administered PDGF-BB (by tail vein injection) increased bone density and strength in SD rats throughout the entire skeleton. In this study, blood was collected from the rats, first, followed by PRF preparation and NCP treatment, and the conditioned cell culture media were used to perform ELISA. The TGF-β level increased in the PRF group by 5.3 times compared to the NT group and by 1.01 times in the PRF + NCP group compared to the PRF group. In addition, the PDGF-AB level was higher in the PRF group and the PRF + NCP group than that in the NT group. As in the result of TGF-β level, the PRF + NCP group showed a 1.43-fold increase compared to the PRF group, indicating that overall, NCP has a significant effect on the PRF releasing the growth factors.
Mao et al. [47] reported that PRF provides a sustained, steady release of growth factors, and in particular, an increase in each growth factor was observed on days 1, 3 and 7. However, in this study, the result obtained with NCP-treated PRF used a medium with 2 days of growth factor release. Thus, follow-up studies are required to investigate whether there is a difference in the release of growth factors over time. Stem cells can be isolated from bones, and in particular, mesenchymal stem cells are capable of self-renewal and have multi-lineage differential potential to osteoblasts, adipocytes, and chondrocytes in suitable culture environments [48].
Regarding stem cell markers, positive or negative expression of highly specific markers (CD 105, CD 90, CD 44 or CD 45, and CD 34, among others) can be used to identify stem cells [49]. In addition, the in vitro differentiation of stem cells is usually dependent on culture conditions, and osteogenic differentiation is induced by the addition of dexamethasone, ascorbic acid, and β-glycerophosphate [50]. In the present study, bone marrow cells extracted from rat bones were identified as stem cells capable of differentiation into osteoblasts through flow cytometry, and cell proliferation rates were evaluated before conducting a comparative experiment on differentiation into osteoblasts in response to PRF or PRF + NCP. Although the difference between the PRF group and PRF + NCP group was not statistically significant, the latter showed the highest value, which confirms that no cytotoxicity occurred as a consequence of the NCP treatment. The above result is consistent with those previously reported, confirming that PRF increased the proliferation of human alveolar bone marrow stem cells [51].
Another previous study in which osteoblasts harvested from iliac bone were treated with 3% PRF also reported a similar result, supporting that the application of PRF has the effect of enhancing bone regeneration [52]. Although the activity of ALP, which plays an essential role in the early stage of bone matrix mineralization, showed contradictory results in terms of BCIP/NBT staining and quantification of mRNA expression levels, the PRF + NCP group showed an elevated level of ALP activity compared to that of the no-treatment group or the PRF group.
These results confirmed that the initiation of osteogenic differentiation was substantially improved with the NCP-treated PRF medium that with the medium extracted from PRF alone, which is consistent with previous findings [28]; thus, this method is an alternative therapeutic approach to further elucidate the various effects of NCP. Furthermore, the study results showed that the PRF + NCP treatment was more effective in inducing early differentiation than the osteogenic differentiation protocol used in the existing method, suggesting its utility as an alternative to reduce the osteogenic differentiation induction time.
However, because the volume of blood that can be collected from rats is limited, and the PRF preparation was technically difficult, there were limitations in the measurement of several parameters. Thus, efficacy verification through large animal models or clinical trials will be necessary in the future. Other limitations of this study are the lack of experiments to confirm osteogenic activity and the absence of a group treated only with NCP, making it difficult to distinguish between the relatively observed effects of different groups.
It is expected that these limitations can be circumvented in the future through follow-up preclinical and clinical studies.
5. Conclusions
Considering all the study findings herein, NCP treatment promoted the elution of various growth factors included in PRF, which in turn enhanced stem cell differentiation into osteoblasts. These results provide useful insight into the proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts and suggest the potential of NCP treatment for the promotion of bone regeneration in vivo.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.B.R.C.; methodology, B.B.R.C.; validation, B.B.R.C.; formal analysis, B.B.R.C.; investigation, B.B.R.C.; writing—original draft preparation, B.B.R.C.; writing—review and editing, B.B.R.C. and G.C.K.; visualization, B.B.R.C.; supervision, G.C.K.; funding acquisition, B.B.R.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant from the Korean government (MSIT), grant number RS-2023-00249641.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All procedures were approved by the Animal Lab of Pusan National University (PNU-2024-0448, 26 March 2024).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
Byul Bo Ra Choi is an employee of Feagle Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Ferrer-Raventós, P.; Beyer, K. Alternative platelet activation pathways and their role in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 159, 105512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiter, O.; Walker, T.L. Platelets: The missing link between the blood and brain? Prog. Neurobiol. 2019, 183, 101695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, N.K.; Mukunda, K.S.; Tilak Raj, T.N. Platelet concentrates: A promising innovation in dentistry. J. Dent. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 50–61. [Google Scholar]
- Whitman, D.H.; Berry, R.L.; Green, D.M. Platelet gel: An autologous alternative to fibrin glue with applications in oral and maxillofacial surgery. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 1997, 55, 1294–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arita, A.; Tobita, M. Adverse events related to platelet-rich plasma therapy and future issues to be resolved. Regen. Ther. 2024, 26, 496–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Simonpieri, A.; Girard, M.O.; Schoeffler, C.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Dohan, D.M. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: Clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, e56–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohan, D.M.; Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Gogly, B. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part II: Platelet-related biologic features. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, e45–e50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbon, S.; Stocco, E.; Macchi, V.; Contran, M.; Grandi, F.; Borean, A.; Parnigotto, P.P.; Porzionato, A.; De Caro, R. Platelet-rich fibrin scaffolds for cartilage and tendon regenerative medicine: From bench to bedside. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlovic, V.; Ciric, M.; Jovanovic, V.; Trandafilovic, M.; Stojanovic, P. Platelet-rich fibrin: Basics of biological actions and protocol modifications. Open Med. 2021, 16, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jameson, C.A. Autologous platelet concentrate for the production of platelet gel. Lab. Med. 2007, 38, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.C.; Zhao, J.H. Effects of platelet-rich fibrin on human periodontal ligament fibroblasts and application for periodontal infrabony defects. Aust. Dent. J. 2011, 56, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeimi Darestani, M.; Asl Roosta, H.; Mosaddad, S.A.; Yaghoubee, S. The effect of leukocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin on the bone loss and primary stability of implants placed in posterior maxilla: A randomized clinical trial. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2023, 9, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mise-Omata, S.; Alles, N.; Fukazawa, T.; Aoki, K.; Ohya, K.; Jimi, E.; Obata, Y.; Doi, T. NF-κB RELA-deficient bone marrow macrophages fail to support bone formation and to maintain the hematopoietic niche after lethal irradiation and stem cell transplantation. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gassling, V.; Hedderich, J.; Açil, Y.; Purcz, N.; Wiltfang, J.; Douglas, T. Comparison of platelet rich fibrin and collagen as osteoblast-seeded scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. Clin. Oral Implant Res. 2013, 24, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lin, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, H. A comparative study of platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) on the effect of proliferation and differentiation of rat osteoblasts in vitro. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2009, 108, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tangl, S.; Huber, C.D.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, L.; Rausch-Fan, X. Effects of Choukroun’s platelet-rich fibrin on bone regeneration in combination with deproteinized bovine bone mineral in maxillary sinus augmentation: A histological and histomorphometric study. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirasawa, I.; Odagiri, H.; Park, G.; Sanghavi, R.; Oshita, T.; Togi, A.; Yoshikawa, K.; Mizutani, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Kobayashi, H.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of cold atmospheric plasma irradiation on the THP-1 human acute monocytic leukemia cell line. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0292267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Han, Q. Mechanisms of bacterial inhibition and tolerance around cold atmospheric plasma. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 5301–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, K.; Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Pan, J. Time-dependent efficacy and safety of tooth bleaching with cold plasma and H2O2 gel. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolgeo, T.; Maconi, A.; Gardalini, M.; Gatti, D.; Di Matteo, R.; Lapidari, M.; Longhitano, Y.; Savioli, G.; Piccioni, A.; Zanza, C. The Role of cold atmospheric plasma in wound healing processes in critically ill patients. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Gu, H.J.; Park, K.H.; Hwang, D.S.; Kim, G.C. Anti-cancer activity of the combinational treatment of noozone cold plasma with p-FAK antibody-conjugated gold nanoparticles in OSCC xenograft mice. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.T.; Jang, Y.S.; Kim, U.K.; Kim, H.J.; Ryu, M.H.; Kim, G.C.; Hwang, D.S. Non-thermal plasma application enhances the recovery of transected sciatic nerves in rats. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 1287–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, L.; Jiafeng, J.; Jiangang, L.; Minchong, S.; Xin, H.; Hanliang, S.; Yuanhua, D. Effects of cold plasma treatment on seed germination and seedling growth of soybean. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. The regulatory mechanism of cold plasma in relation to cell activity and its application in biomedical and animal husbandry practices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.S.; Yun, S.E.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, J.H.; Kim, G.C. No-ozone cold plasma can kill oral pathogenic microbes in H2O2-dependent and independent manner. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-H.; Jang, Y.-S.; Joo, J.-Y.; Kim, G.-C.; Choi, J.-H. Anti-Inflammatory Activity of No-Ozone Cold Plasma in Porphyromonas gingivalis Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Periodontitis Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.-B.; Park, S.-A.; Choi, J.-H.; Park, S.-R.; Kim, G.-C. Evaluation of Dentin Tubule Occlusion Using Pre-Treatment with No-Ozone Cold Plasma: An In Vitro Study. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 11728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.B.; Choi, J.H.; Kang, T.H.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, G.C. Enhancement of osteoblast differentiation using no-ozone cold plasma on human periodontal ligament cells. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkaya, S.; Toptaş, O. Evaluation of the effects of platelet-rich fibrin and diode laser on gingival blood perfusion and early bone healing of the extraction socket: A randomized controlled clinical trial. Lasers Med. Sci. 2023, 39, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.S.; Feng, Z.H.; Wu, G.F.; Bai, S.Z.; Dong, Y.; Chen, F.M.; Zhao, Y.M. The use of platelet-rich fibrin combined with periodontal ligament and jaw bone mesenchymal stem cell sheets for periodontal tissue engineering. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.B.R.; Song, K.W.; Lee, H.J.; Park, S.R.; Kim, G.C. Effects of no-ozone cold plasma and mouse mesenchymal stem cell treatments on wound healing in a mouse skin model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 738, 150562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Sato, A.; Ikehata, M.; Hatori, A.; Chikazu, D.; Ghanaati, S.; Kawase-Koga, Y. Platelet-rich fibrin-conditioned medium promotes osteogenesis of dental pulp stem cells through TGF-β and PDGF signaling. Regen. Ther. 2025, 30, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachtel, N.; Weber, L.; Moellhoff, N.; Kuhlmann, C.; Giunta, R.E.; Alberton, P.; Ehrl, D.; Wiggenhauser, S. Platelet-rich fibrin mediates beneficial effects on adipose-derived stem cells via increased levels of key cytokines. Wound Repair Regen. 2025, 33, e70040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chan, C. Isolation and enrichment of rat mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and separation of single-colony derived MSCs. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 22, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.L.; Zheng, W.; Chen, W.; Qian, Y.; Ouyang, Y.M.; Fan, C.Y. Lentivirus-mediated microRNA-124 gene-modified bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes the repair of spinal cord injury in rats. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.M.; Lin, C.; Stavre, Z.; Greenblatt, M.B.; Shim, J.H. Osteoblast-osteoclast communication and bone homeostasis. Cells 2020, 9, 2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElHawary, H.; Baradaran, A.; Abi-Rafeh, J.; Vorstenbosch, J.; Xu, L.; Efanov, J.I. Bone healing and inflammation: Principles of fracture and Repair. Semin. Plast. Surg. 2021, 35, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Yang, S.; Shao, J.; Li, Y.P. Signaling and transcriptional regulation in osteoblast commitment and differentiation. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 3068–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, S.; Ito, K.; Hofmann, S. Alkaline phosphatase activity of serum affects osteogenic differentiation cultures. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 12724–12733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrobel, E.; Leszczynska, J.; Brzoska, E. The characteristics of human bone-derived cells (HBDCS) during osteogenesis in vitro. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2016, 21, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsdal, M.A.; Fjording, M.S.; Foged, N.T.; Delaissé, J.M.; Lochter, A. Transforming growth factor-beta-induced osteoblast elongation regulates osteoclastic bone resorption through a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase- and matrix metalloproteinase-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 39350–39358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiser, A.G.; Zeng, Q.Q.; Sato, M.; Helvering, L.M.; Hirano, T.; Turner, C.H. Decreased bone mass and bone elasticity in mice lacking the transforming growth factor-beta1 gene. Bone 1998, 23, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, E.; Hu, M.; Wu, L.; Pan, X.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y. TGF-β signaling regulates differentiation of MSCs in bone metabolism: Disputes among viewpoints. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2024, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.H.; Westermark, B. Mechanism of action and in vivo role of platelet-derived growth factor. Physiol. Rev. 1999, 79, 1283–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepistö, J.; Kujari, H.; Niinikoski, J.; Laato, M. Effects of heterodimeric isoform of platelet-derived growth factor PDGF-AB on wound healing in the rat. Eur. Surg. Res. 1994, 26, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitlak, B.H.; Finkelman, R.D.; Hill, E.L.; Li, J.; Martin, B.; Smith, T.; D’Andrea, M.; Antoniades, H.N.; Lynch, S.E. The effect of systemically administered PDGF-BB on the rodent skeleton. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1996, 11, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Yang, M.; Chen, X.; Cui, L.; Bai, W. Platelet-rich fibrin improves repair and regeneration of damaged endometrium in rats. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1154958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Qin, R.; Glowacki, J.; Zhou, S.; Shi, J.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; Cheng, L. Synergistic stimulation of osteoblast differentiation of rat mesenchymal stem cells by leptin and 25(OH)D3 is mediated by inhibition of chaperone-mediated autophagy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021, 12, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavathuparambil Abdul Manaph, N.; Sivanathan, K.N.; Nitschke, J.; Zhou, X.F.; Coates, P.T.; Drogemuller, C.J. An overview on small molecule-induced differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells into beta cells for diabetic therapy. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittenger, M.F.; Mackay, A.M.; Beck, S.C.; Jaiswal, R.K.; Douglas, R.; Mosca, J.D.; Moorman, M.A.; Simonetti, D.W.; Craig, S.; Marshak, D.R. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999, 284, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.H.; Jeon, S.H.; Park, J.Y.; Chung, J.H.; Choung, Y.H.; Choung, H.W.; Kim, E.S.; Choung, P.H. Platelet-rich fibrin is a Bioscaffold and reservoir of growth factors for tissue regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Ha, Y.; Kang, N.H. Effects of growth factors from platelet-rich fibrin on the bone regeneration. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).